Quantitative Evaluation and Comparison of Motion Discrepancy Analysis Methods for Enhanced Trajectory Tracking in Mechatronic Systems †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Vibrational Metrics
2.2. Similarity Metrics
2.3. Correlation Analysis
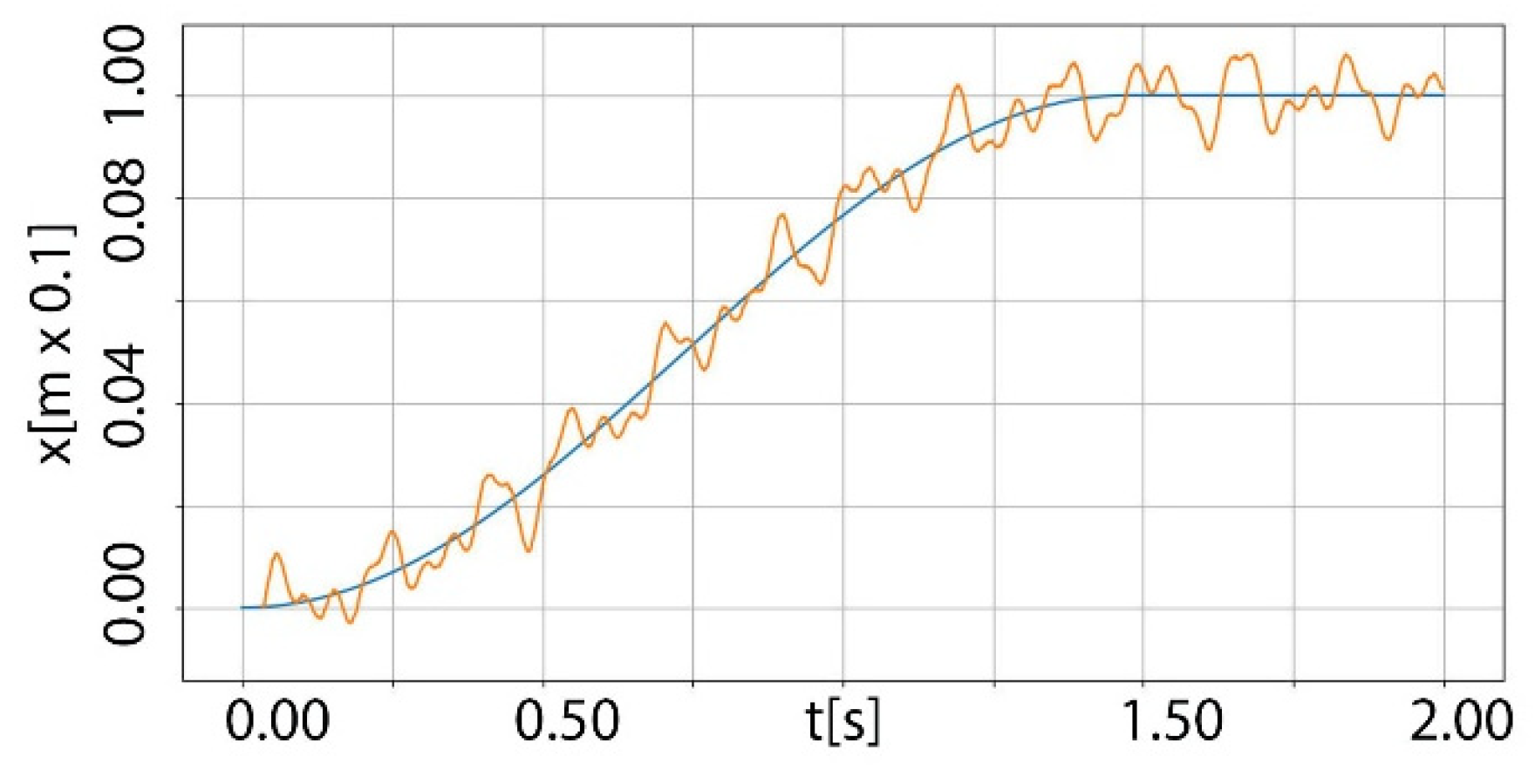
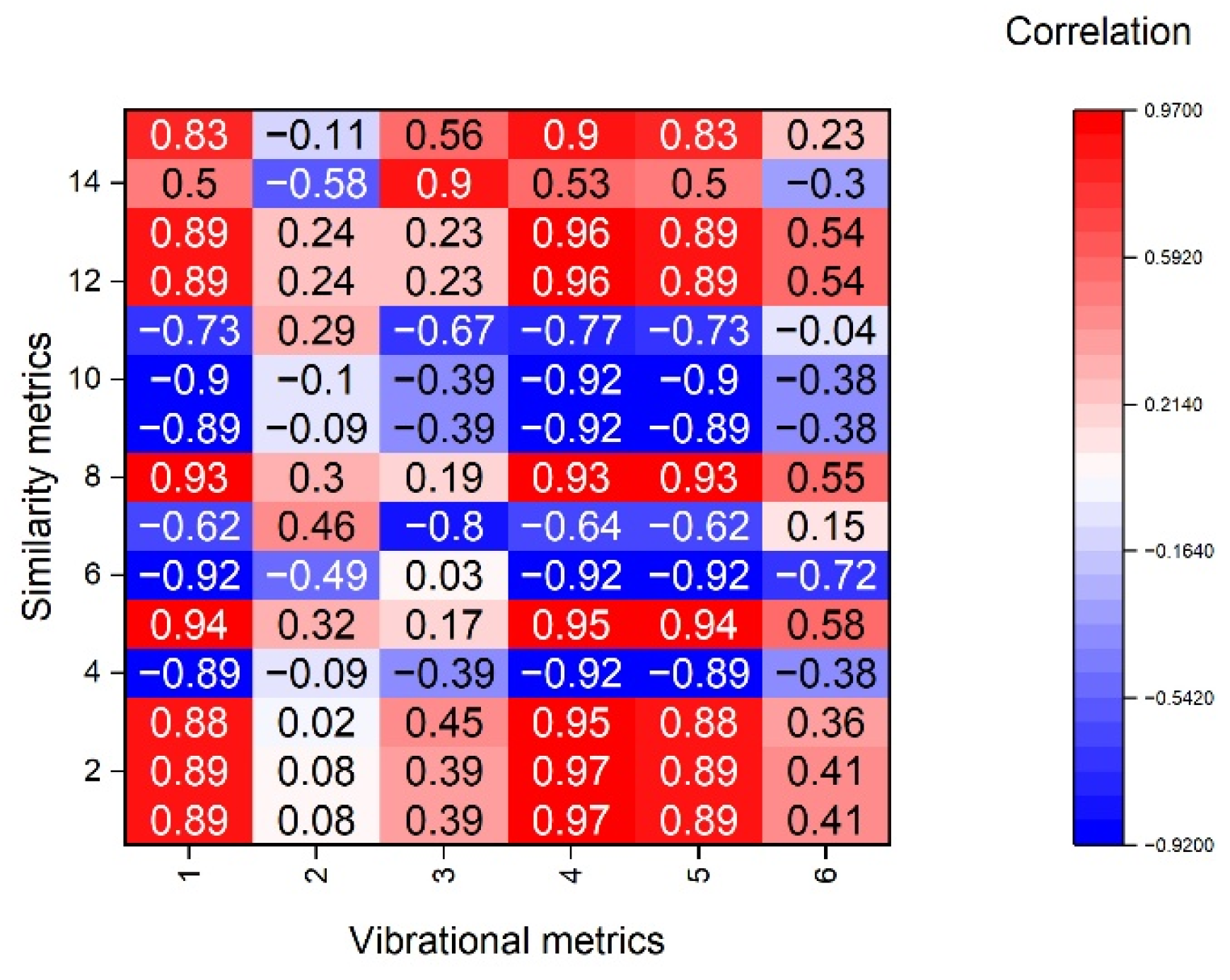
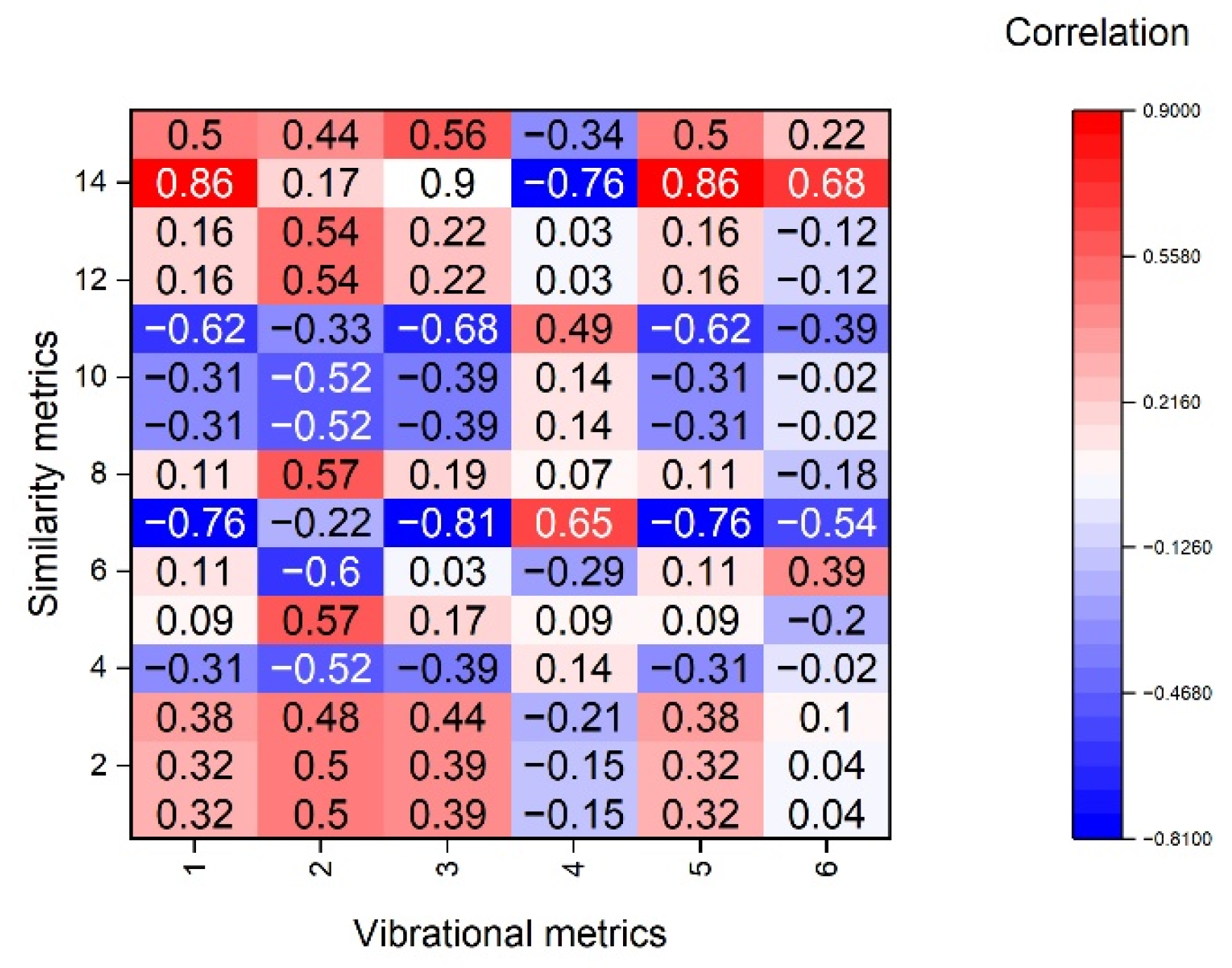
3. Results
- A random number of superimposed sine waves (3 to 7 oscillations),
- Frequency components ranging from 1 Hz to 50 Hz,
- Amplitude values between 0.01 and 0.15,
- Added white noise with an amplitude up to 0.02.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weiss, K.R. Vibration Problems in Engineering. Nature 1965, 208, 964–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, G.F.; Mendez, Y.A.D.; da Silva Lopes Alexandrino, P.; da Cunha, S.S.; Ancelotti, A.C. A Review of Vibration Based Inverse Methods for Damage Detection and Identification in Mechanical Structures Using Optimization Algorithms and ANN. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2019, 26, 883–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knezevic, B.Z.; Blanusa, B.; Marcetic, D.P. A synergistic method for vibration suppression of an elevator mechatronic system. J. Sound Vib. 2017, 406, 29–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amabili, M.; Païdoussis, M.P. Review of studies on geometrically nonlinear vibrations and dynamics of circular cylindrical shells and panels, with and without fluid-structure interaction. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2003, 56, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlaka, S. The influence of vibrations on the efficiency of the internal combustion engine. Vib. Eng. Technol. 2024, 112, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; You, L.; Hu, X. Performance degradation modeling and continuous worktime assessment of ultrasonic vibration systems. Processes 2024, 12, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazan State Energy University, Kazan, Russian Federation; Malyov, N.A. Analysis of vibrations and their influence on the operation of mechatronic systems. Ekon. I Upr. Probl. RESHENIYA 2024, 9, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Cárcel, C.; Jaramillo, V.H.; Mba, D.; Ottewill, J.R.; Cao, Y. Combination of process and vibration data for improved condition monitoring of industrial systems working under variable operating conditions. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 66–67, 699–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; Sun, L.; Jiang, Z. A high-performance multi-beam microaccelerometer for vibration monitoring in intelligent manufacturing equipment. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2013, 189, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saponi, M.; Borboni, A.; Adamini, R.; Faglia, R.; Amici, C. Embedded Payload Solutions in UAVs for Medium and Small Package Delivery. Machines 2022, 10, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrini, S.; Serpelloni, M.; Amici, C.; Gobbo, M.; Silvestro, C.; Buraschi, R.; Borboni, A.; Crovato, D.; Lopomo, N.F. Use of wearable inertial sensor in the assessment of Timed-Up-and-Go Test: Influence of device placement on temporal variable estimation. In Proceedings of the Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social-Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering, LNICST, Melbourne, Australia, 20–22 June 2017; pp. 310–317. [Google Scholar]
- Lundborg, G.; Lie-Stenström, A.K.; Sollerman, C.; Strömberg, T.; Pyykkö, I. Digital vibrogram: A new diagnostic tool for sensory testing in compression neuropathy. J. Hand Surg. 1986, 11, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özbek, O.; Saruhan, H. The effect of vibration and cutting zone temperature on surface roughness and tool wear in eco-friendly MQL turning of AISI D2. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 2762–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, S.; Li, T.; Jenkins, M.; Hughes, B. Novel concentric expandable stabilizer results in increased penetration rates and drilling efficiency with reduced vibration. In Proceedings of the SPE/IADC Drilling Conference, Proceedings, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 17–19 March 2009; pp. 768–780. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, D.J. Wheel-rail noise generation, part III: Rail vibration. J. Sound Vib. 1993, 161, 421–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, M.J. Minimum health and safety requirements for workers exposed to hand-transmitted vibration and whole-body vibration in the European Union; a review. Occup. Environ. Med. 2004, 61, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borboni, A.; Lancini, M. Commanded motion optimization to reduce residual vibration. J. Vib. Acoust. 2015, 137, 031016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Lee, J.S. Propagation and attenuation characteristics of various ground vibrations. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2000, 19, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borboni, A.; Aggogeri, F.; Pellegrini, N.; Faglia, R. Innovative modular SMA actuator. In Proceedings of the Advanced Materials Research, Chengdu, China, 7–8 January 2012; pp. 405–410. [Google Scholar]
- Borboni, A.; Faglia, R. Stochastic evaluation and analysis of free vibrations in simply supported piezoelectric bimorphs. J. Appl. Mech. Trans. ASME 2013, 80, 021003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakoshi, Y.; Sato, J.; Sato, T. Ultrasonic Imaging of Internal Vibration of Soft Tissue under Forced Vibration. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 1990, 37, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maul, G.P.; Thomas, M.B. A Systems Model and Simulation of the Vibratory Bowl Feeder. J. Manuf. Syst. 1997, 16, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y. Experimental modelling and amplitude-frequency response analysis of a piecewise linear vibration system. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 4279–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigaud, E.; Perret-Liaudet, J. Experiments and numerical results on non-linear vibrations of an impacting Hertzian contact. Part 1: Harmonic excitation. J. Sound Vib. 2003, 265, 289–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torvik, P.J. On estimating system damping from frequency response bandwidths. J. Sound Vib. 2011, 330, 6088–6097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bayoumy, L.E.; Srinivasan, A.V. Influence of mistuning on rotor-blade vibrations. AIAA J. 1975, 13, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, G.K.; da Costa, C.; da Silva Sousa, J.S. A smart experimental setup for vibration measurement and imbalance fault detection in rotating machinery. Case Stud. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 4, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhar, A.S.; Prabhu, B.S. Effects of coupling misalignment on vibrations of rotating machinery. J. Sound Vib. 1995, 185, 655–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, F.K.; Polyshchuk, V.; Zakrajsek, J.J.; Handschuh, R.F.; Townsend, D.P. Analysis of the effects of surface pitting and wear on the vibration of a gear transmission system. Tribol. Int. 1996, 29, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maru, M.M.; Castillo, R.S.; Padovese, L.R. Study of solid contamination in ball bearings through vibration and wear analyses. Tribol. Int. 2007, 40, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Klamecki, B.E. Milling Cutter Wear Monitoring Using Spindle Shaft Vibration. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. Trans. ASME 1997, 119, 118–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, N.J.; Parker, G.G.; Blough, J.R. Base Vibration Effects on Additive Manufactured Part Quality. Exp. Tech. 2024, 48, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salokyová, Š.; Krehel, R.; Pollák, M.; Koačiško, M. Research on impacts of mechanical vibrations on the production machine to its rate of change of technical state. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2016, 8, 1687814016655778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RaviKumar, S.; Pandian, C.K.A.; Hameed, S.S.; Muralidharan, V.; Syed Wahid Ali, M. Application of machine learning for fault diagnosis and operational efficiency in EV motor test benches using vibration analysis. Eng. Res. Express 2025, 7, 015355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggogeri, F.; Borboni, A.; Merlo, A.; Pellegrini, N. Machine tools thermostabilization using passive control strategies. In Proceedings of the Advanced Materials Research, Chengdu, China, 7–8 January 2012; pp. 252–257. [Google Scholar]
- Elias, S.; Matsagar, V. Research developments in vibration control of structures using passive tuned mass dampers. Annu. Rev. Control 2017, 44, 129–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; Ding, S.; Wang, X. Advances in machine learning-based active vibration control for automotive seat suspensions: A comprehensive review. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2025, 231, 112645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, J.; Su, W.; He, T. Vibration Suppression and Trajectory Tracking with Nonlinear Model Predictive Control for Urban Air Mobility Aircraft. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2025, 147, 041010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanou, K.; Gerodimos, V.; Karatrantou, K.; Jamurtas, A. Whole-body vibration and rehabilitation of chronic diseases: A review of the literature. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2012, 11, 187–200. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, H.; Zhang, P.; Lueth, T.C. Quantitative assessment of parkinsonian tremor based on an inertial measurement unit. Sensors 2015, 15, 25055–25071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.; Afsharfard, A.; Arasteh, R.; Safaie, J. Design of a noninvasive and smart hand tremor attenuation system with active control: A simulation study. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2018, 56, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggogeri, F.; Borboni, A.; Faglia, R. Reliability roadmap for mechatronic systems. In Proceedings of the Applied Mechanics and Materials, Wuhan, China, 24–25 August 2013; pp. 130–133. [Google Scholar]
- Jo, M.; Chung, M.; Kim, K.; Kim, H.Y. Improving Path Accuracy and Vibration Character of Industrial Robot Arms with Iterative Learning Control Method. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2024, 25, 1851–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, Z.; Keogh, P. H-infinity optimised control of external inertial actuators for higher precision robotic machining. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2022, 35, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keppler, M.; Lakatos, D.; Ott, C.; Albu-Schäffer, A. A passivity-based controller for motion tracking and damping assignment for compliantly actuated robots. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 55th Conference on Decision and Control, CDC 2016, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 12–14 December 2016; pp. 1521–1528. [Google Scholar]
- Aggogeri, F.; Borboni, A.; Merlo, A.; Pellegrini, N.; Ricatto, R. Real-time performance of mechatronic PZT module using active vibration feedback control. Sensors 2016, 16, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Futami, S.; Kyura, N.; Hara, S. Vibration Absorption Control of Industrial Robots by Acceleration Feedback. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1983, IE-30, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggogeri, F.; Borboni, A.; Faglia, R.; Merlo, A.; De Cristofaro, S. Precision Positioning Systems: An overview of the state of art. In Proceedings of the Applied Mechanics and Materials, Wuhan, China, 24–25 August 2013; pp. 1170–1173. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, S.T. Foundations of Ultra-Precision Mechanism Design; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Borboni, A.; Aggogeri, F.; Pellegrini, N.; Faglia, R. Precision point design of a cam indexing mechanism. In Proceedings of the Advanced Materials Research, Chengdu, China, 7–8 January 2012; pp. 399–404. [Google Scholar]
- Salawu, O.S. Detection of structural damage through changes in frequency: A review. Eng. Struct. 1997, 19, 718–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrar, C.R.; Worden, K. Structural Health Monitoring: A Machine Learning Perspective; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Vakakis, A.F.; Gendelman, O.V.; Bergman, L.A.; McFarland, D.M.; Kerschen, G.; Lee, Y.S. Nonlinear Targeted Energy Transfer in Mechanical and Structural Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, L. Time-frequency analysis. In Englewood Cliffs; Prentice Hall: West Trenton, NJ, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Randall, R.B. Vibration-Based Condition Monitoring: Industrial, Aerospace and Automotive Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, T.K. Similarity methods in signal processing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1996, 44, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raschka, S.; Patterson, J.; Nolet, C. Machine learning in python: Main developments and technology trends in data science, machine learning, and artificial intelligence. Information 2020, 11, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, T.; Worden, K.; Sun, L.; Cross, E.J. Canonical-correlation-based fast feature selection for structural health monitoring. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2025, 223, 111895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagani, R.; Nuzzi, C.; Ghidelli, M.; Borboni, A.; Lancini, M.; Legnani, G. Cobot user frame calibration: Evaluation and comparison between positioning repeatability performances achieved by traditional and vision-based methods. Robotics 2021, 10, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Wang, W.; Ma, C.; Hartwig, M.; Narayanan, A. Vibro-Acoustic Analysis of Different Rotor Skewing Patterns on Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. In Proceedings of the SAE Technical Papers, Detroit, MI, USA, 8–10 April 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.L.; Liang, Y.; Wang, S.C. Review on dynamic time warping in time series data mining. Kongzhi Yu Juece/Control Decis. 2018, 33, 1345–1353. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benesty, J.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Cohen, I. Pearson correlation coefficient. In Springer Topics in Signal Processing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 2, pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Liberti, L.; Lavor, C.; Maculan, N.; Mucherino, A. Euclidean distance geometry and applications. SIAM Rev. 2014, 56, 3–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, P.; Zhang, L.; Li, F. Learning similarity with cosine similarity ensemble. Inf. Sci. 2015, 307, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaccard, P. New research on floral distribution (Nouvelles recherches sur la distribution florale). Bull. Soc. Vaud. Sci. Nat. 1908, 44, 223–270. (In French) [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, J.C.; Han, T.H. Fast normalized cross-correlation. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2009, 28, 819–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunet, D.; Vrscay, E.R.; Wang, Z. On the mathematical properties of the structural similarity index. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2012, 21, 1488–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttenlocher, D.P.; Klanderman, G.A.; Rucklidge, W.J. Comparing Images Using the Hausdorff Distance. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1993, 15, 850–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringmann, K. Why walking the dog takes time: Frechet distance has no strongly subquadratic algorithms unless SETH fails. In Proceedings of the Proceedings—Annual IEEE Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, FOCS, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 18–21 October 2014; pp. 661–670. [Google Scholar]
- Yujian, L.; Bo, L. A normalized Levenshtein distance metric. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2007, 29, 1091–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Maesschalck, R.; Jouan-Rimbaud, D.; Massart, D.L. The Mahalanobis distance. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2000, 50, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedgwick, P. Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient. BMJ 2014, 349, g7327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorston, C.; Chen, C.; Camelio, J. Advancing architectural frameworks for vibration signature classification in rotating machinery. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2025, 239, 711–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borboni, A.; Aggogeri, F.; Elamvazuthi, I.; Incerti, G.; Magnani, P.L. Effects of profile interpolation in cam mechanisms. Mech. Mach. Theory 2020, 144, 103652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borboni, A.; Pagani, R.; Amici, C. Quantitative Evaluation and Comparison of Motion Discrepancy Analysis Methods for Enhanced Trajectory Tracking in Mechatronic Systems. Eng. Proc. 2025, 118, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECSA-12-26574
Borboni A, Pagani R, Amici C. Quantitative Evaluation and Comparison of Motion Discrepancy Analysis Methods for Enhanced Trajectory Tracking in Mechatronic Systems. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 118(1):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECSA-12-26574
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorboni, Alberto, Roberto Pagani, and Cinzia Amici. 2025. "Quantitative Evaluation and Comparison of Motion Discrepancy Analysis Methods for Enhanced Trajectory Tracking in Mechatronic Systems" Engineering Proceedings 118, no. 1: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECSA-12-26574
APA StyleBorboni, A., Pagani, R., & Amici, C. (2025). Quantitative Evaluation and Comparison of Motion Discrepancy Analysis Methods for Enhanced Trajectory Tracking in Mechatronic Systems. Engineering Proceedings, 118(1), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECSA-12-26574







