Adaptive Extended Kalman Filtering for Online Monitoring of Concrete Structures Subject to Impacts †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Modal Testing on CFST Specimens
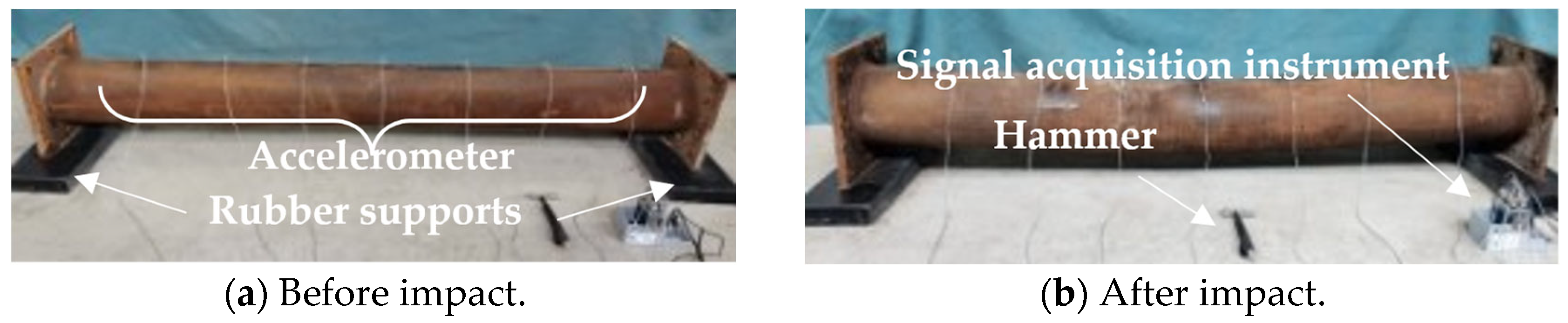
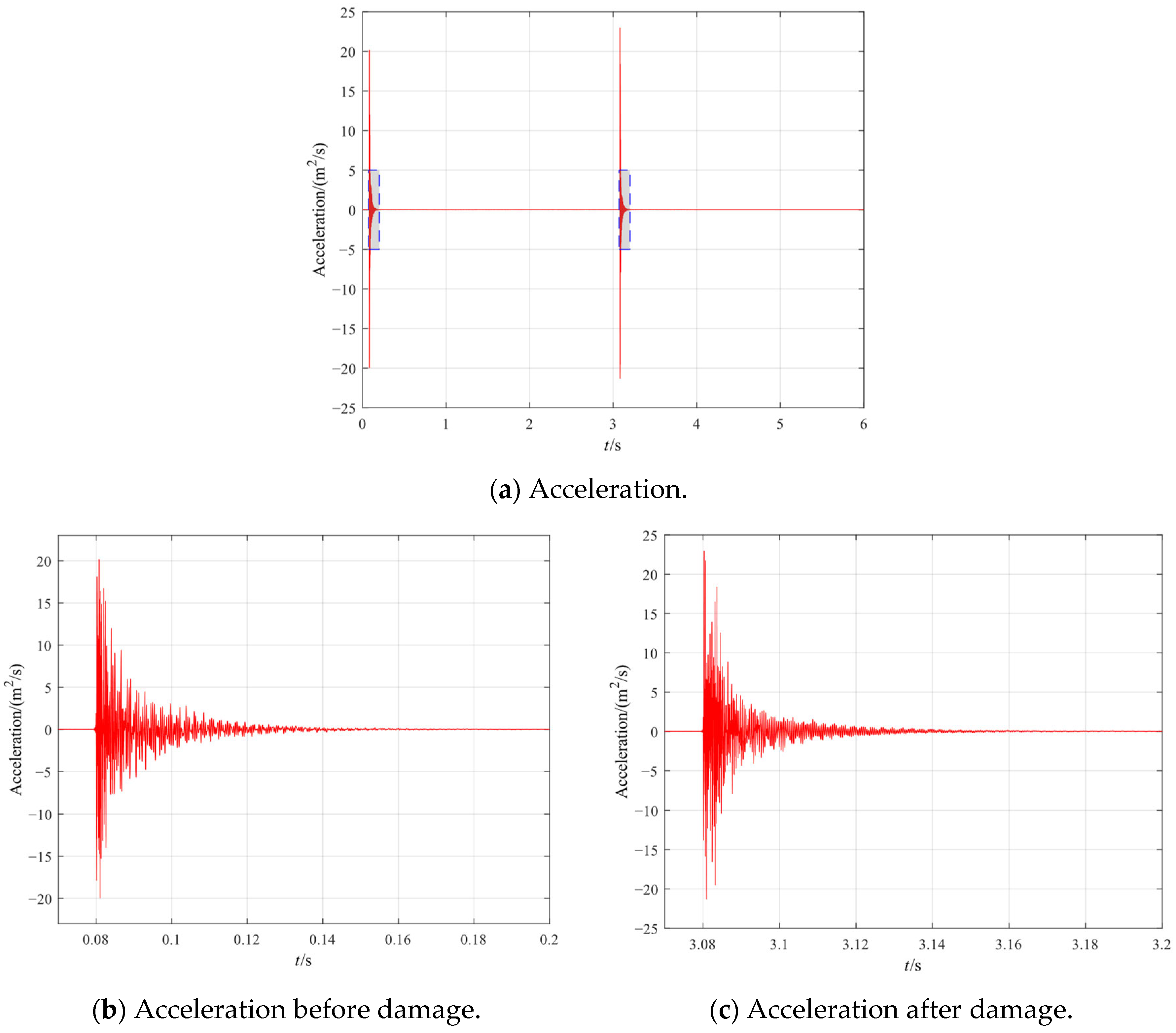
2.1. Modal Testing Setup and Data Splicing
2.2. Adaptive Extended Kalman Filter
3. Results
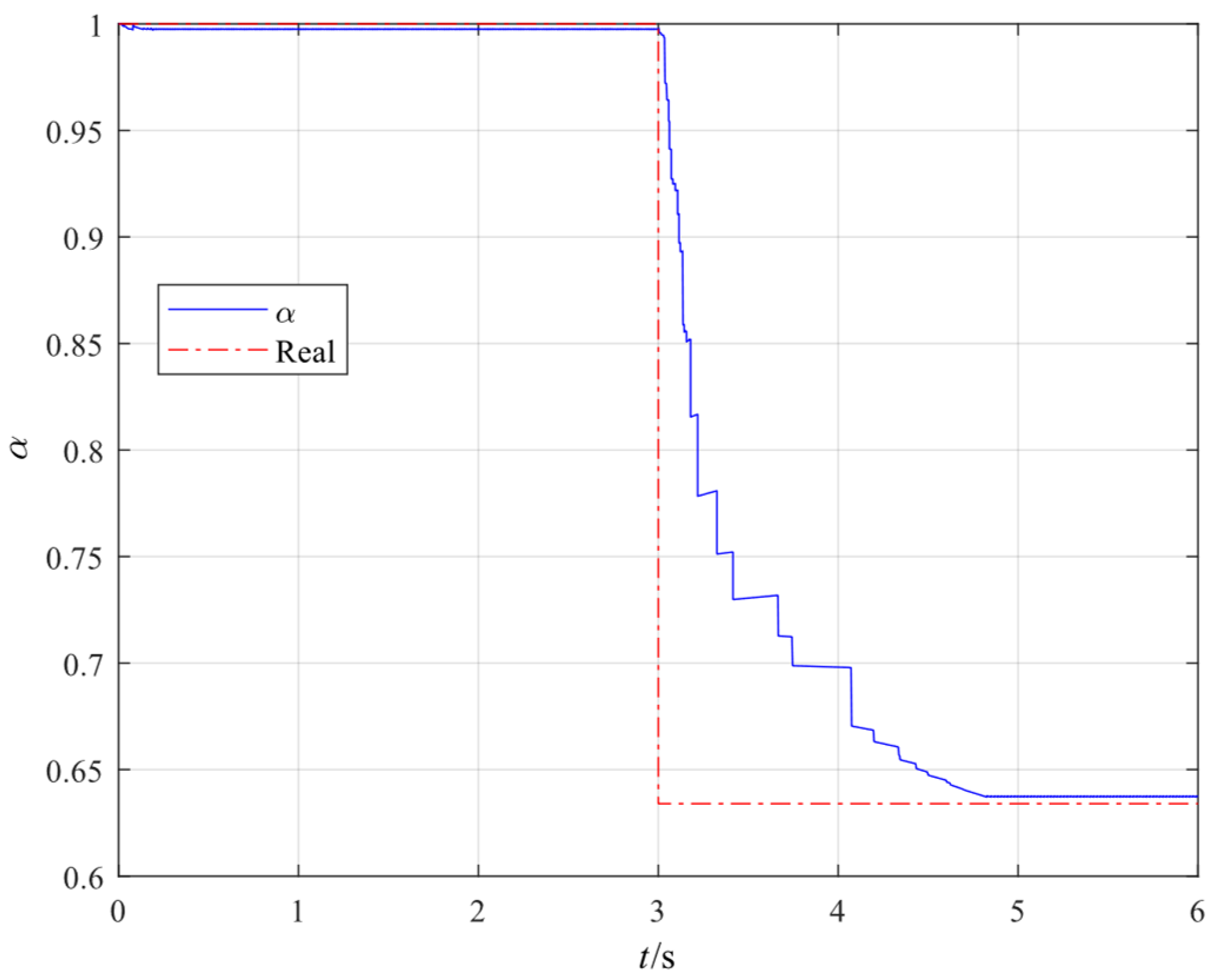
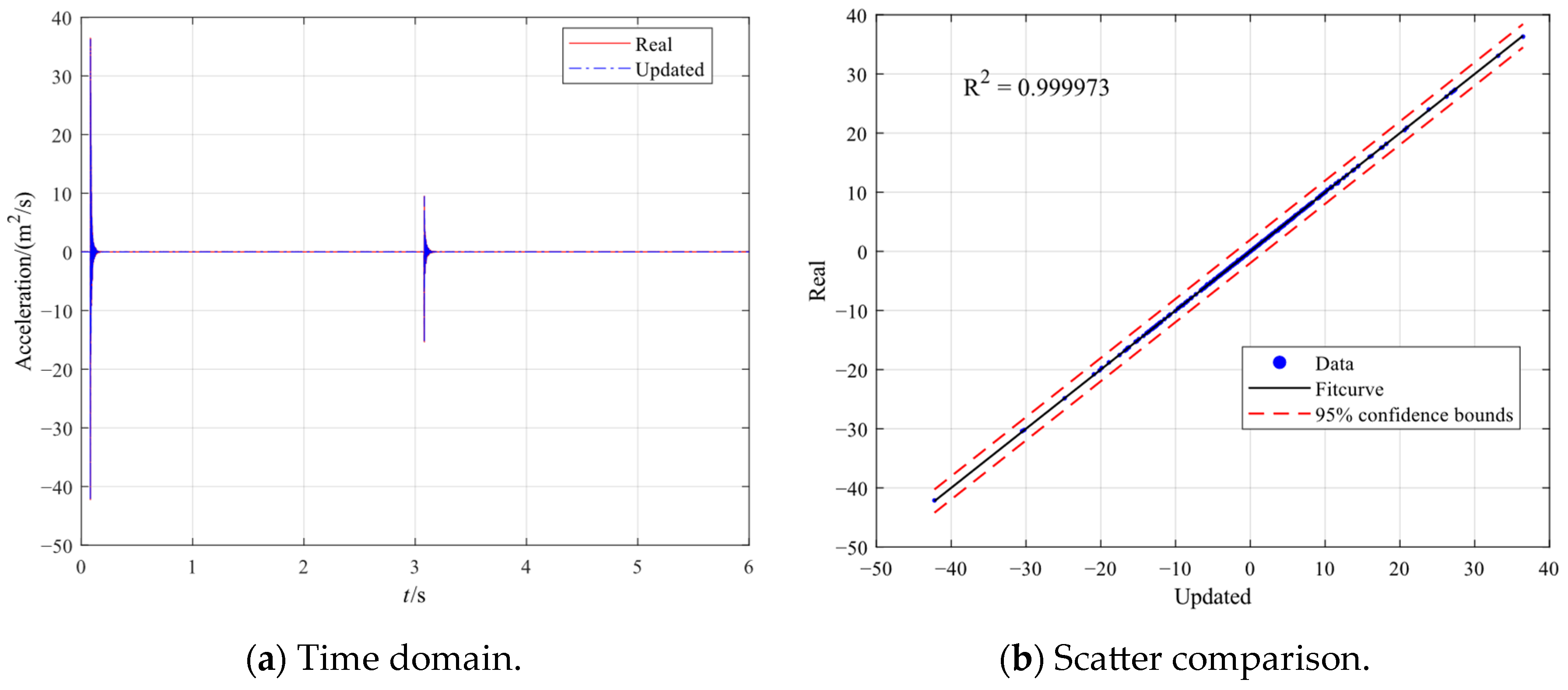
3.1. AEKF Update Results Without Data Loss
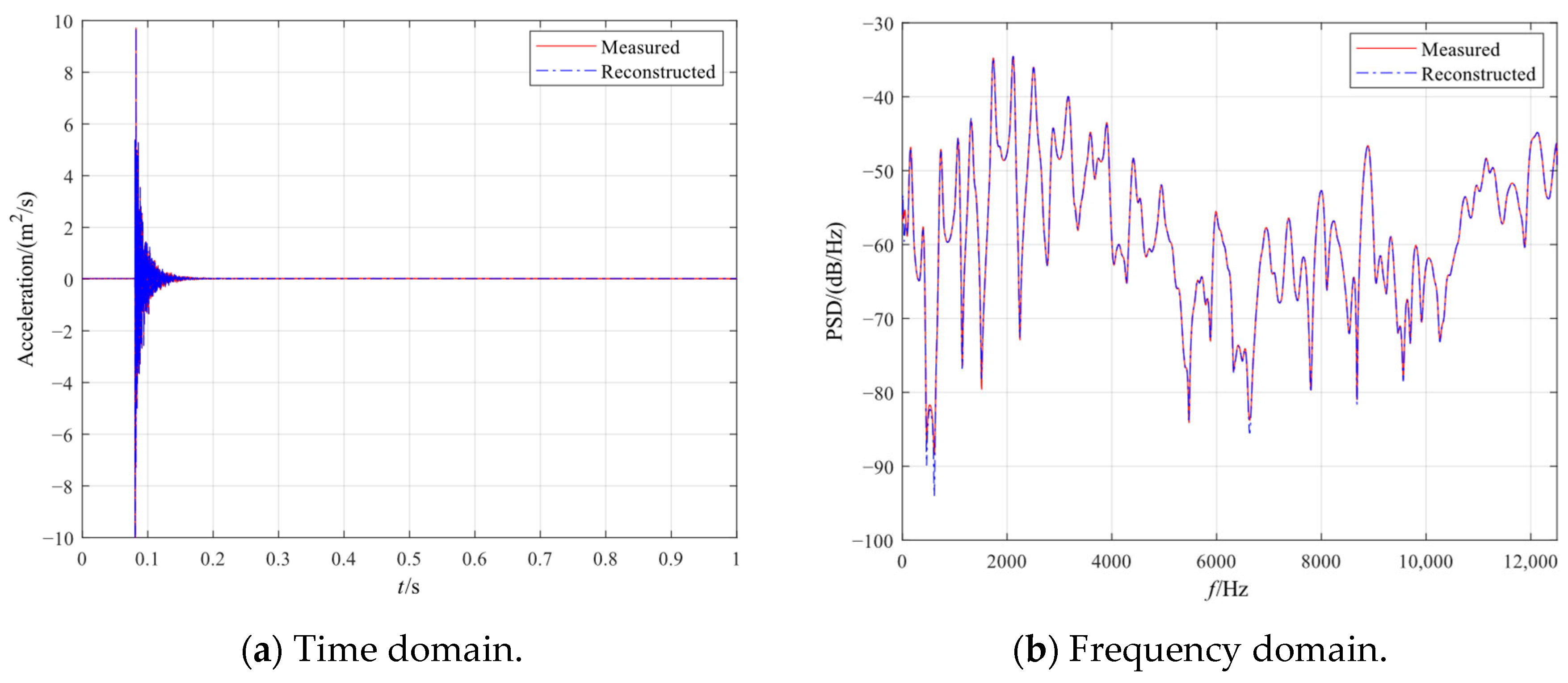
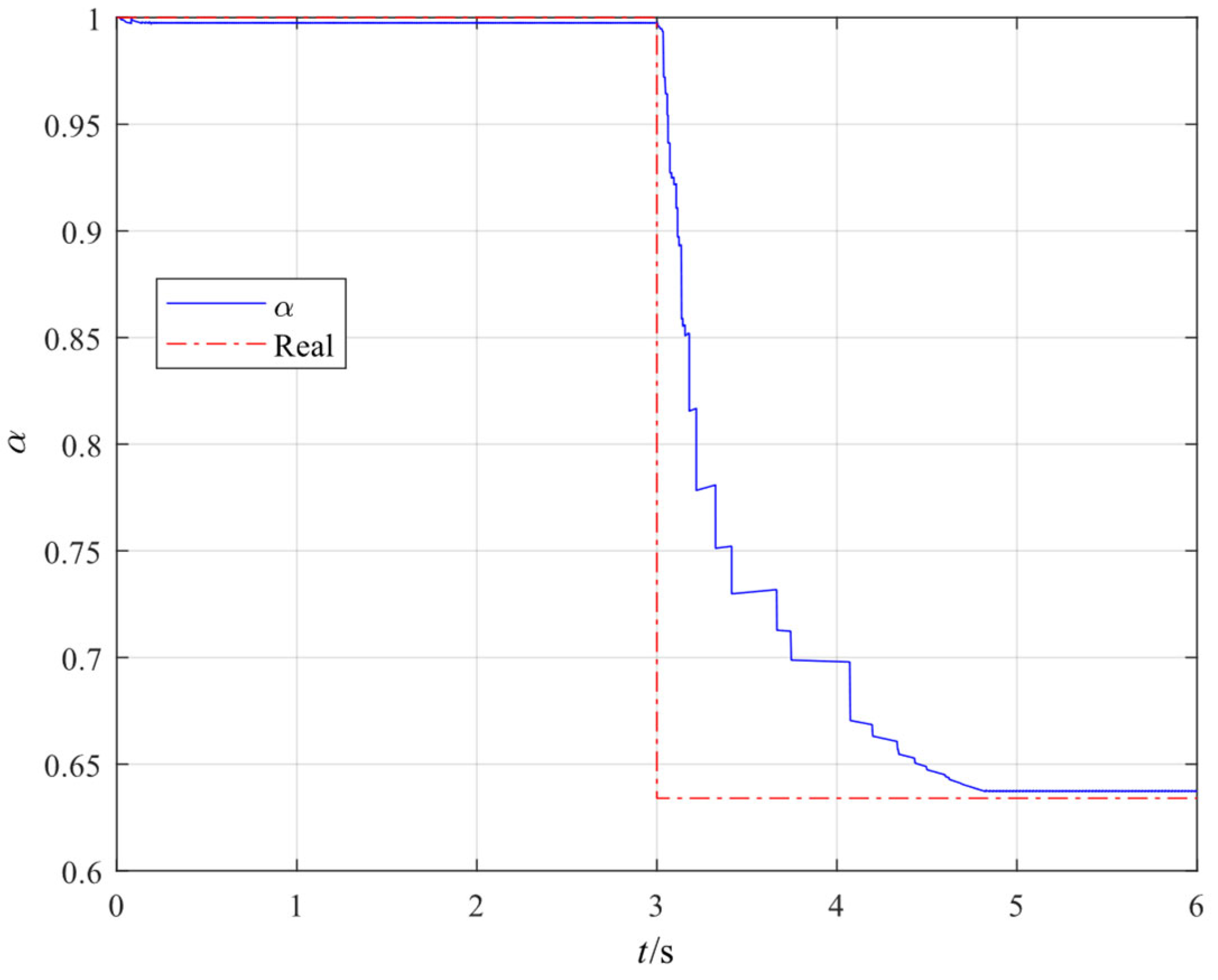
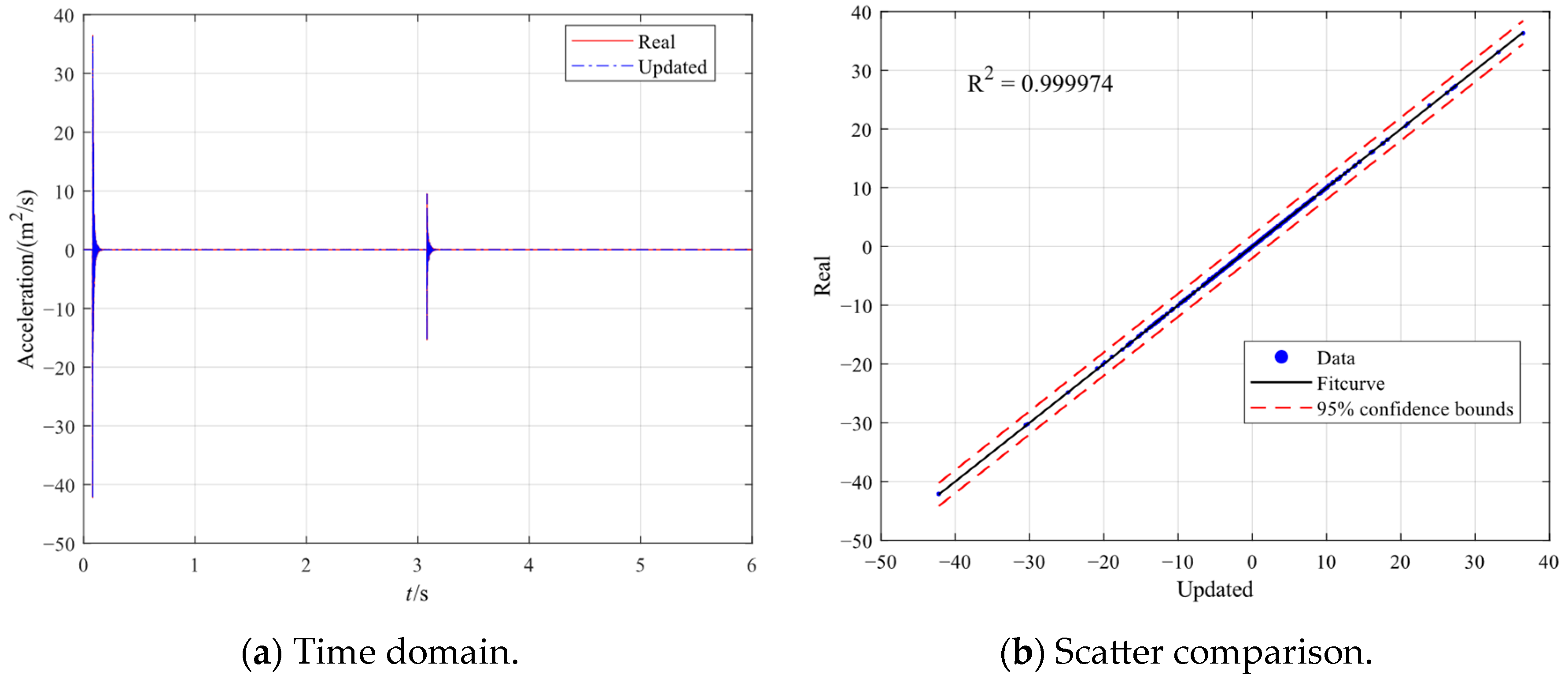
3.2. AEKF Update Results with Data Loss
4. Conclusions
- By adaptively updating Q and the scale factor βq, the proposed method avoids the estimation fluctuation problem caused by time-invariant Q, as in the traditional EKF, thereby maintaining stable, accurate filtering at varying damage states.
- This study incorporated the lowest three natural frequencies and the damage parameter α into the state vector and updated them in the nonlinear state transfer and observation model. It can therefore automatically track a gradual degradation process of the structural flexural stiffness, if any.
- When acceleration data are missing, the weighted MP method can be used, and weights were applied to the time domain and the target mode to complete data reconstruction. The reconstructed data were found to be highly consistent with the real measurements in both time and frequency domains, and the subsequent AEKF process yielded an effective stiffness reduction in close agreement with the true value. The proposed methodology has been shown to achieve high accuracy and prompt response to changing states, as well as tolerance to sensor failures in actual operational conditions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, L.-H.; Li, W.; Bjorhovde, R. Developments and Advanced Applications of Concrete-Filled Steel Tubular (CFST) Structures: Members. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2014, 100, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Hu, F.; Shi, Y. Recent Research Advances of High Strength Steel Structures and Codification of Design Specification in China. Int. J. Steel Struct. 2014, 14, 873–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Andjelic, A.; Li, Z.; Lei, Z.; Bie, X. Residual Axial Bearing Capacity of Concrete-Filled Circular Steel Tubular Columns (CFCSTCs) after Transverse Impact. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Jang, S.; Sun, X. An Integrated Real-Time Structural Damage Detection Method Based on Extended Kalman Filter and Dynamic Statistical Process Control. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2017, 20, 549–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Jang, S.; Sun, X.; Li, J.; Christenson, R. Damage Detection of a Highway Bridge under Severe Temperature Changes Using Extended Kalman Filter Trained Neural Network. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 2016, 6, 545–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y. Adaptive Extended Kalman Filter Based State of Charge Determination for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 283, 1432–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.N.; Lin, S.; Huang, H.; Zhou, L. An Adaptive Extended Kalman Filter for Structural Damage Identification. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2006, 13, 849–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Rosafalco, L.; Ghisi, A.; Mariani, S. Structural Health-Monitoring Strategy Based on Adaptive Kalman Filtering. Eng. Proc. 2024, 82, 76. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.-J.; Hou, C.-C. Study on Dynamic Flexural Stiffness of CFST Members through Bayesian Model Updating. Steel Compos. Struct. 2024, 51, 697. [Google Scholar]
- Ewins, D.J. Modal Testing: Theory, Practice and Application; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-0-86380-218-8. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, Y.; Sarkar, T.K. Matrix Pencil Method for Estimating Parameters of Exponentially Damped/Undamped Sinusoids in Noise. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1990, 38, 814–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Overschee, P.; de Moor, B.L. Subspace Identification for Linear Systems: Theory—Implementation—Applications; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; ISBN 978-1-4613-0465-4. [Google Scholar]
- Zoltowski, M.D. Novel Techniques for Estimation of Array Signal Parameters Based on Matrix Pencils, Subspace Rotations, and Total Least Squares. In Proceedings of the ICASSP-88, International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, New York, NY, USA, 11–14 April 1988; IEEE Computer Society: New York, NJ, USA, 1988; pp. 2861–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichel, L.; Opfer, G. Chebyshev-Vandermonde Systems. Math. Comp. 1991, 57, 703–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demmel, J.; Koev, P. The Accurate and Efficient Solution of a Totally Positive Generalized Vandermonde Linear System. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 2005, 27, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golla, T.; Kennedy, G.J.; Riso, C. Sliding-Window Matrix Pencil Method for Design Optimization with Limit-Cycle Oscillation Constraints. AIAA J. 2024, 62, 4170–4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckermann, B. The Condition Number of Real Vandermonde, Krylov and Positive Definite Hankel Matrices. Numer. Math. 2000, 85, 553–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greś, S.; Tatsis, K.E.; Dertimanis, V.; Chatzi, E. Low-Rank Approximation of Hankel Matrices in Denoising Applications for Statistical Damage Diagnosis of Wind Turbine Blades. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 197, 110391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazzi, A.; Guglielmi, N.; Markovsky, I. A Gradient System Approach for Hankel Structured Low-Rank Approximation. Linear Algebra Its Appl. 2021, 623, 236–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Cai, J.-F.; You, J. Structured Gradient Descent for Fast Robust Low-Rank Hankel Matrix Completion. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 2023, 45, A1172–A1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.; Lei, Y.; Zhu, S.; Xu, Y.-L.; Zhang, X.-H.; Krishnaswamy, S. Moving-Window Extended Kalman Filter for Structural Damage Detection with Unknown Process and Measurement Noises. Measurement 2016, 88, 428–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, D. Kalman Filter Damage Detection in the Presence of Changing Process and Measurement Noise. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2013, 39, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Hu, G.; Li, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhong, Y. Maximum Likelihood-Based Measurement Noise Covariance Estimation Using Sequential Quadratic Programming for Cubature Kalman Filter Applied in INS/BDS Integration. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 9383678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Shmaliy, Y.S.; Shi, P.; Ahn, C.K. Fusion Kalman/UFIR Filter for State Estimation with Uncertain Parameters and Noise Statistics. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 3075–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Mu, D.; Zhong, Y.; Gu, C.; Ren, C. Adaptively Random Weighted Cubature Kalman Filter for Nonlinear Systems. Math. Probl. Eng. 2019, 2019, 4160847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Gao, S.; Zhong, Y.; Qi, X.; Li, G.; Liu, Y. Moving-Window-Based Adaptive Fitting H-Infinity Filter for the Nonlinear System Disturbance. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 76143–76157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Gao, S.; Hu, G.; Zhong, Y.; Gu, C. Maximum Likelihood Principle and Moving Horizon Estimation Based Adaptive Unscented Kalman Filter. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2018, 73, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julier, S.J.; Uhlmann, J.K. Unscented Filtering and Nonlinear Estimation. Proc. IEEE 2004, 92, 401–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arasaratnam, I.; Haykin, S. Cubature Kalman Filters. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2009, 54, 1254–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Astroza, R.; Ebrahimian, H.; Moaveni, B.; Papadimitriou, C. Adaptive Kalman Filters for Nonlinear Finite Element Model Updating. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 143, 106837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, S.-J.; Hou, C.-C.; Mariani, S. Adaptive Extended Kalman Filtering for Online Monitoring of Concrete Structures Subject to Impacts. Eng. Proc. 2025, 118, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECSA-12-26587
Chen S-J, Hou C-C, Mariani S. Adaptive Extended Kalman Filtering for Online Monitoring of Concrete Structures Subject to Impacts. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 118(1):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECSA-12-26587
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Shang-Jun, Chuan-Chuan Hou, and Stefano Mariani. 2025. "Adaptive Extended Kalman Filtering for Online Monitoring of Concrete Structures Subject to Impacts" Engineering Proceedings 118, no. 1: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECSA-12-26587
APA StyleChen, S.-J., Hou, C.-C., & Mariani, S. (2025). Adaptive Extended Kalman Filtering for Online Monitoring of Concrete Structures Subject to Impacts. Engineering Proceedings, 118(1), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECSA-12-26587







