Advancing Lubrication Modeling: A Preliminary Study of Finite Element Solutions for Cavitation-Aware Reynolds Equation †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Governing Equations
3. Cavitation Model
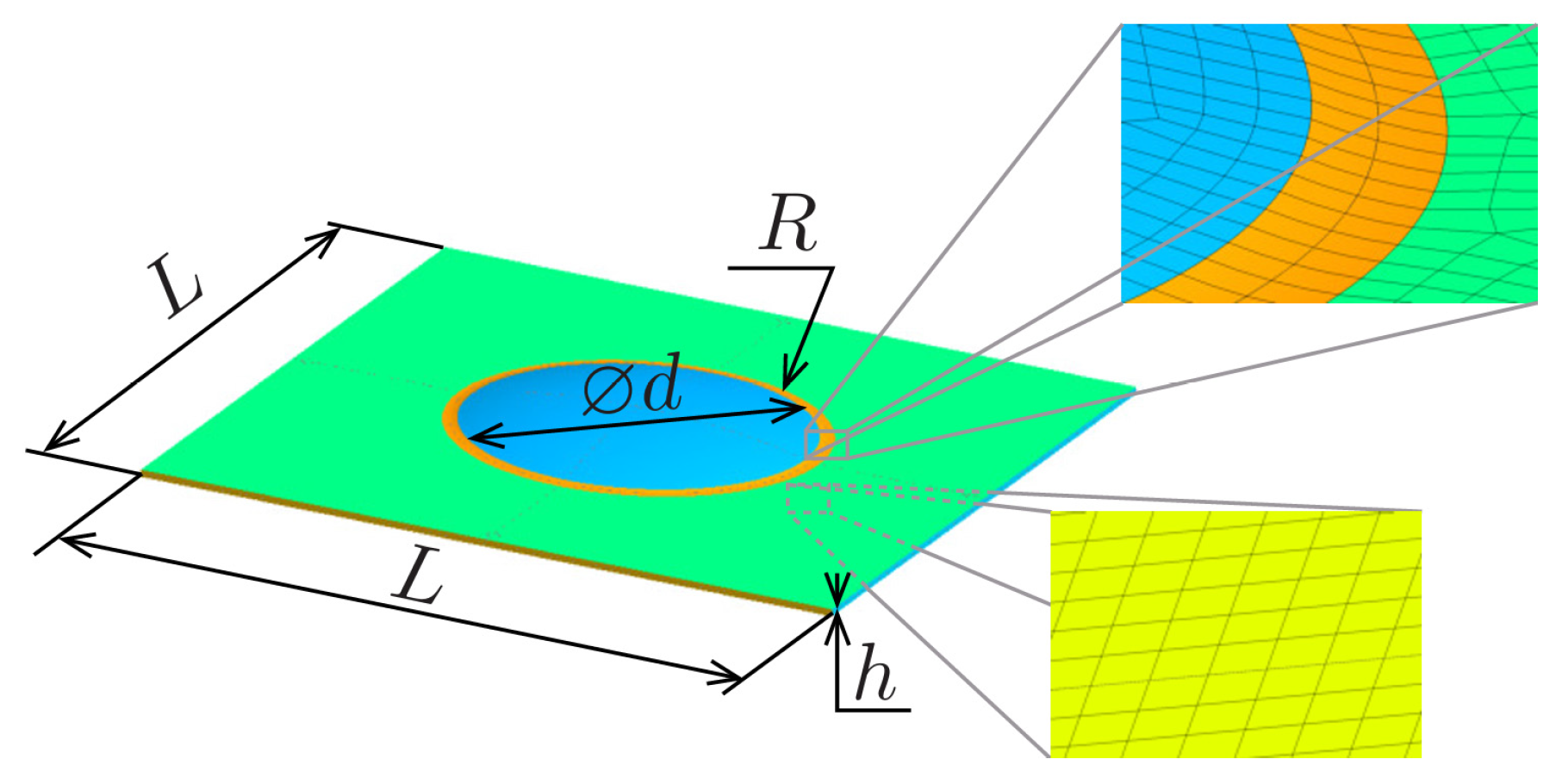
4. Parameter Study
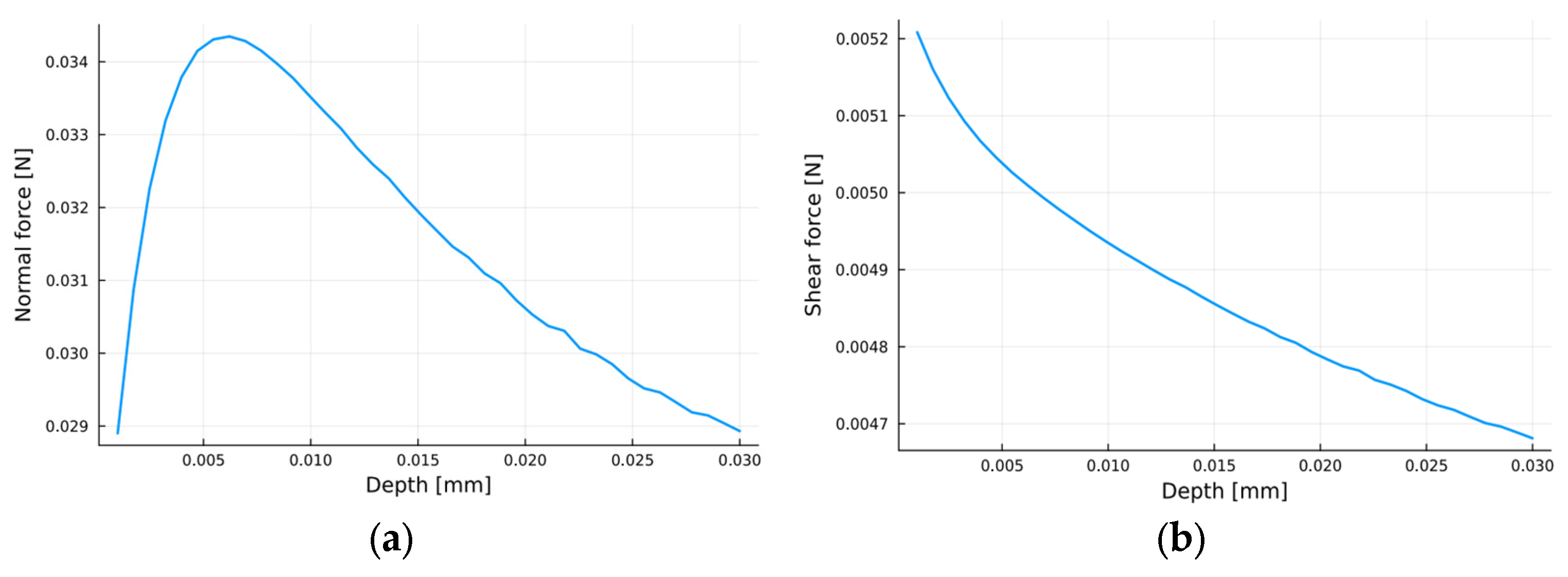
4.1. Depth Analysis
4.2. Fillet Radius Analysis
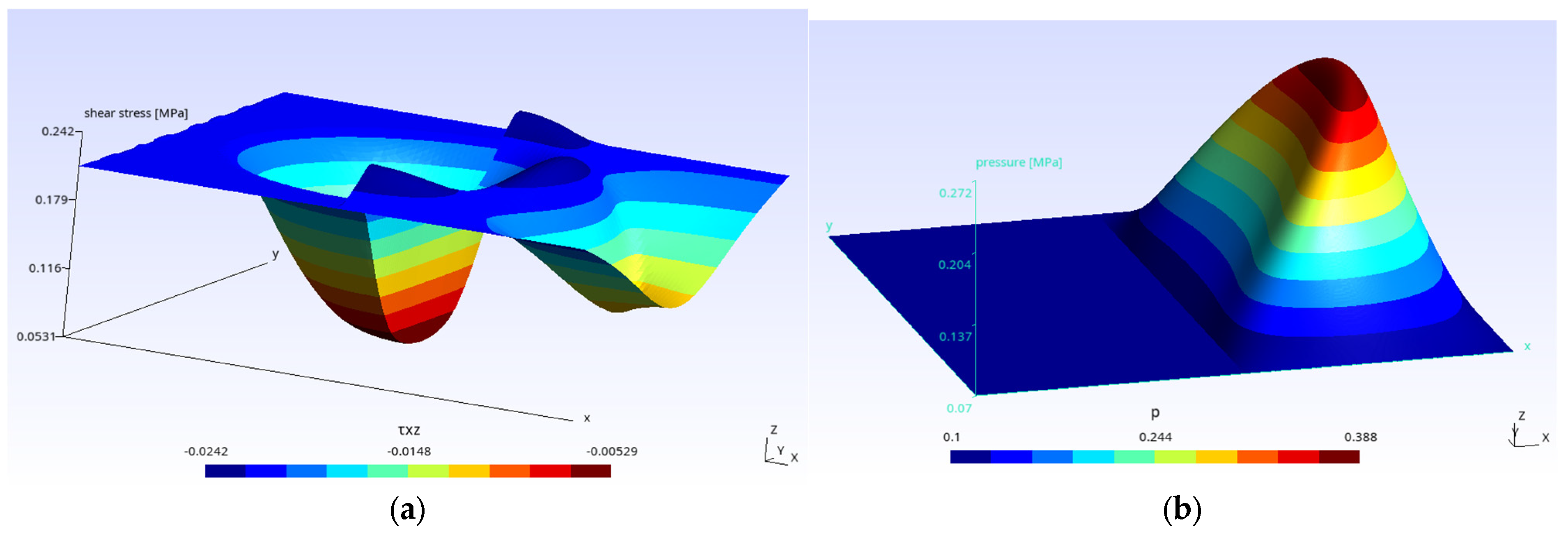
4.3. Comparison of Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Škurić, V.; Jasak, H.; Almqvist, A.; De Jaeger, P. Finite Area Algorithm for Thin Film Cavitation in OpenFOAM. Trans Motauto World 2019, 4, 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Profito, F.J.; Giacopini, M.; Zachariadis, D.C.; Dini, D. A General Finite Volume Method for the Solution of the Reynolds Lubrication Equation with a Mass-Conserving Cavitation Model. Tribol. Lett. 2015, 60, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravenkamp, H.; Pfeil, S.; Codina, R. Stabilized Finite Elements for the Solution of the Reynolds Equation Considering Cavitation. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2024, 418, 116488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarray, M.; Souchet, D.; Henry, Y.; Fatu, A. A Finite Element Solution of the Reynolds Equation of Lubrication with Film Discontinuities: Application to Helical Groove Seals. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 174, 012037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rom, M. Physics-Informed Neural Networks for the Reynolds Equation with Cavitation Modeling. Tribol. Int. 2023, 179, 108141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Deng, J.; Li, Y. A New Method to Solve the Reynolds Equation Including Mass-Conserving Cavitation by Physics Informed Neural Networks (PINNs) with Both Soft and Hard Constraints. Friction 2024, 12, 1165–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Song, Y.; Hao, Z.; Gu, C. Cavitation Mechanism of Oil-Film Bearing and Development of a New Gaseous Cavitation Model Based on Air Solubility. ASME J. Tribol. 2012, 134, 031701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulut, D.; Bader, N.; Poll, G. Cavitation and Film Formation in Hydrodynamically Lubricated Parallel Sliders. Tribol. Int. 2021, 162, 107113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Tian, Y.; Li, K.; Zhang, M.; Yang, J. Reynolds Boundary Condition Realization in Journal Bearings: Location of Oil Film Rupture Boundary with Layering-Sliding Mesh Method. Tribol. Int. 2022, 165, 107330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laki, G.; Boros, L.; Nagy, A.L. Topography Pre-Treatment of Laser-Textured Surfaces for Friction Simulation in AVL Excite. Eng. Proc. 2024, 79, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grützmacher, P.G.; Rosenkranz, A.; Szurdak, A.; König, F.; Jacobs, G.; Hirt, G.; Mücklich, F. From Lab to Application—Improved Frictional Performance of Journal Bearings Induced by Single- and Multi-Scale Surface Patterns. Tribol. Int. 2018, 127, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilhena, L.; Sedlaček, M.; Podgornik, B.; Rek, Z.; Žun, I. CFD Modeling of the Effect of Different Surface Texturing Geometries on the Frictional Behavior. Lubricants 2018, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Name | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| side length of rectangle | ||
| film thickness | ||
| ambient pressure | ||
| cavitation pressure | ||
| dynamic viscosity | ||
| velocity |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pere, B.; Lénárt, M. Advancing Lubrication Modeling: A Preliminary Study of Finite Element Solutions for Cavitation-Aware Reynolds Equation. Eng. Proc. 2025, 113, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025113002
Pere B, Lénárt M. Advancing Lubrication Modeling: A Preliminary Study of Finite Element Solutions for Cavitation-Aware Reynolds Equation. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 113(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025113002
Chicago/Turabian StylePere, Balázs, and Martin Lénárt. 2025. "Advancing Lubrication Modeling: A Preliminary Study of Finite Element Solutions for Cavitation-Aware Reynolds Equation" Engineering Proceedings 113, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025113002
APA StylePere, B., & Lénárt, M. (2025). Advancing Lubrication Modeling: A Preliminary Study of Finite Element Solutions for Cavitation-Aware Reynolds Equation. Engineering Proceedings, 113(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025113002






