Abstract
This study investigates the synthesis and characterization of Cu-(5 vol.%) Al2O3 nano-composites via a mechano-chemical process. CuO, Al, and Cu powders were mechanically alloyed for 12 h in an argon atmosphere, leading to the formation of Al2O3 nanoparticles within the Cu matrix. The composite powders were cold-compressed at pressures ranging from 200 to 400 MPa and sintered at temperatures between 700 °C and 900 °C for 1 to 3 h. X-ray diffraction and EDX analyses confirmed the disappearance of Al peaks, indicating the successful formation of Al2O3 in the Cu matrix. SEM images revealed Al2O3 particles (~10–20 nm) evenly distributed throughout the composite. The results demonstrated that increasing the compaction pressure from 200 MPa to 400 MPa reduced porosity by over 40%, enhancing microhardness by 30% and electrical conductivity by more than 32%, highlighting the significant influence of processing conditions, while lowering the effects in temperature and duration of sintering. These findings provide novel insights into optimizing Cu-Al2O3 composites via mechano-chemical routes.
1. Introduction
Copper (Cu) is widely recognized for its excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, making it one of the most commonly used materials in electrical applications, particularly for welding electrode spots [1] and electrical sliding contacts [2]. However, its practical applications are restricted due to inherent limitations, including low hardness, poor creep resistance, and limited yield strength. While grain refinement can improve Cu’s mechanical properties, elevated temperatures lead to grain growth, causing a reduction in strength [3]. Alloying Cu with metals such as Zr-Cr [4] and Nb [5] can enhance its strength, but this approach significantly reduces electrical conductivity.
Cu matrix composites have emerged as one of the most effective solutions to overcome these limitations, improving the strength of pure Cu while maintaining its excellent electrical, thermal conductivity, even under high-temperature conditions [6,7]. Previous studies have demonstrated that the properties of Cu matrix composites depend on the type, size of reinforcing particles and their content. While higher reinforcing particles improves mechanical properties, including strength, stiffness, and wear resistance [8,9], it also leads to a significant reduction in electrical conductivity [9,10].
The Cu matrix is reinforced by stable ceramic particles that maintain their integrity at high temperatures, such as Al2O3, TiC, TiB2, NbC, SiC, MgO, SiO2, ZrB2, and others [7]. Among ceramic reinforcement particles, Al2O3 is well-known for significantly enhancing the mechanical properties of the Cu matrix at both ambient and elevated temperatures. These improvements include increased tensile and compressive strength, microhardness, and wear resistance [11,12,13], along with high fracture toughness and low electrical resistance [14]. The nano-scale dispersion of Al2O3 particles imparts unique characteristics on the Cu-Al2O3 system, including high thermal and electrical conductivity and exceptional mechanical strength at elevated temperatures [1,11,15]. A fundamental requirement for dispersion-strengthened composite materials is the homogeneous distribution of ultra-fine ceramic particles (dispersoids) within the Cu matrix, ensuring optimal reinforcement and performance [16,17].
To fabricate Cu-based composite materials reinforced with Al2O3 particles, various methods have been investigated, such as mechanical milling [18], internal oxidation [19], mechano-chemical milling [11,16], and stir casting [20]. However, mechanical milling and stir casting methods struggle to ensure the uniform distribution of Al2O3 in the Cu matrix due to their differences in specific gravity. Additionally, impurities can easily be introduced during processing, reducing the electrical conductivity of Cu [18]. Internal oxidation is often a complex process due to the necessity of forming Al-Cu intermetallic phases before initiating oxidation. This requires high-temperature processing over an extended period, leading to significant energy consumption. The mechano-chemical synthesis method is an advanced technique for fabricating Cu-Al2O3 composite materials. This process combines mechanical activation and chemical reactions, enabling the direct formation of nano-scale Al2O3 particles within the Cu matrix without requiring external reinforcement. As a result, Al2O3 is more evenly dispersed, significantly enhancing the material’s hardness, thermal stability, and wear resistance. Additionally, precise control over parameters such as milling speed, duration, and ball-to-powder ratio allows for the optimization of microstructure, leading to superior mechanical and electrical properties.
Although the mechano-chemical synthesis method shows great potential for fabricating Cu-Al2O3 composite materials, experimental studies on this approach remain limited. Moreover, existing research has not identified the effects of key parameters such as compaction pressure, sintering temperature, and sintering time on the mechanical, electrical properties, and microstructure of the material. A deeper understanding of these factors is essential for optimizing the fabrication process and enhancing the quality and stability of Cu-Al2O3 composites, ensuring the best balance between mechanical strength, electrical conductivity, and thermal resistance.
In this study, Cu-Al2O3 nanocomposites containing 5 vol.% of Al2O3 nanoparticles—denoted as Cu-(5 vol.%) Al2O3—were fabricated via a mechano-chemical process. This work primarily focuses on evaluating phase formation, microstructure, porosity, microhardness, and electrical conductivity. Building upon earlier studies that typically investigated individual parameters or isolated responses, this study adopts a full factorial design to holistically analyze the interdependencies among key processing variables and their collective impact on composite performance.
2. Materials and Methods
Cu-Al2O3 nanocomposites were synthesized using high-purity powders of copper (II) oxide (CuO), copper (Cu), and aluminum (Al) as raw materials. The key properties of these powders are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Initial parameters of raw materials.
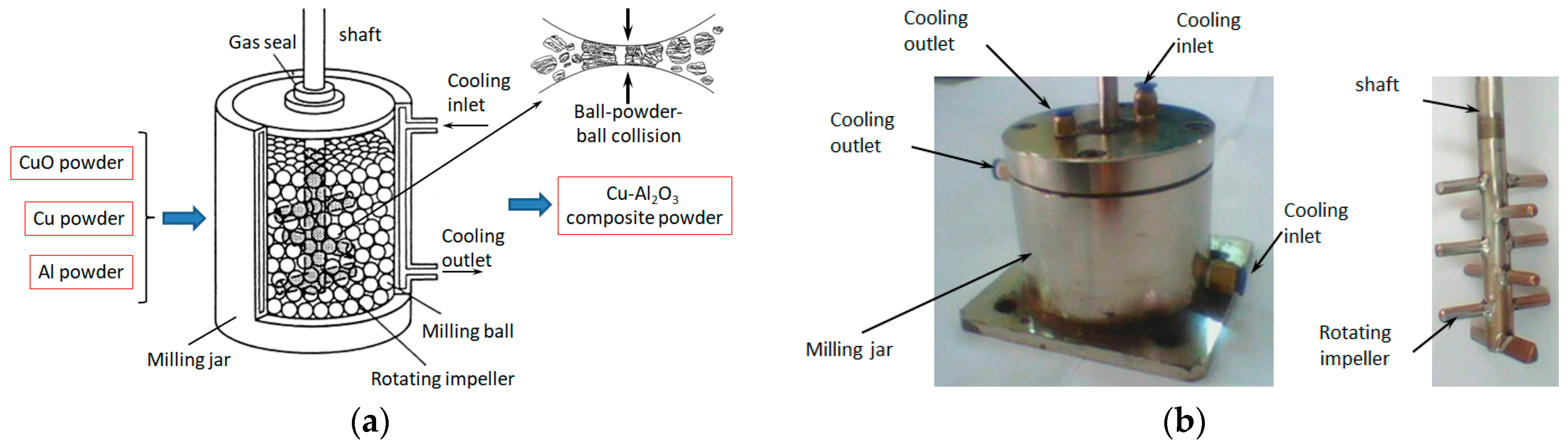
The fabrication of Cu-(5 vol.%) Al2O3 nanocomposite powder was prepared in two stages. The first step involved the synthesis of Cu-(20 vol.%) Al2O3 mixture powders, as illustrated in Figure 1a. In this step, a mixture of Cu, CuO, and Al powders was blended and mechanically alloyed for 12 h in an argon atmosphere using an attritor ball milling system operating at a constant rotational speed of 620 rpm. Tungsten carbide balls of two diameters (5 mm and 10 mm) were utilized in the milling process, with a fixed ball-to-powder weight ratio of 10:1. To maintain stability, the milling process was indirectly cooled using water. The photograph of the milling jar along with the milling shaft is shown in Figure 1b.
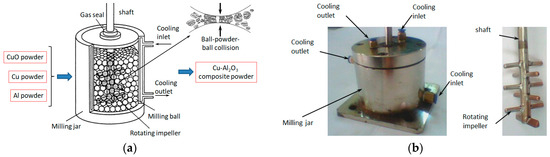
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the Cu-(20 vol.%) Al2O3 composite powder preparation process via the mechano-chemical method (a) and the experimental milling jar (b).
The composition of the raw powders was determined based on the following reaction equation:
3CuO + xCu + 2Al → (3 + x)Cu + Al2O3
In the second step, the Al2O3 content was adjusted by adding pure Cu powder to the Cu-(20 vol.%) Al2O3 mixture. This new mixture was then homogenized through drum ball milling for 3 h at a constant rotational speed of 300 rpm, forming Cu-(5 vol.%) Al2O3 composite powders.
This two-step powder processing method—synthesizing Cu-(20 vol.%) Al2O3 followed by dilution to 5%—was adopted to enhance reaction completeness and ensure uniform dispersion of Al2O3 nanoparticles. The higher content of oxidizable components promotes efficient phase transformation during the milling process.
The resulting nanocomposite powders were subsequently cold-compressed into cylindrical samples with a diameter of 10 mm and a height of 10 mm. These compacted specimens were conventionally sintered at various temperatures in a protective gas environment. The selected ranges of compressive pressure (p), sintering temperature (T), and sintering time (ts) are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
The input parameters of the cold compressing and sintering process.
Based on the ranges specified in Table 2, a full factorial experimental design (23) was implemented to systematically explore the individual and interactive effects of compaction pressure, sintering temperature, and sintering time. This structured design comprised eight experimental runs, covering all combinations of the three parameters at two levels. The run order, as shown in Table 3, was randomized to minimize potential bias and ensure statistical balance.

Table 3.
Experimental results.
Phase composition was analyzed using X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) on a XRD D5005 (Siemens, Munich, Germany) and a HITACHI S-4800 (Hitachi, Ibaraki, Japan). Porosity was measured by Archimedes’ method with a Scientech electronic scale. Microhardness was evaluated using a Vickers-Brinell tester (HPO 250, Hegewald & Peschke, Saxony, Germany), and electrical conductivity was assessed with a Micro-Ohmmeter DO5000 (Seaward Electronic Ltd., Peterlee UK).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phase Formation
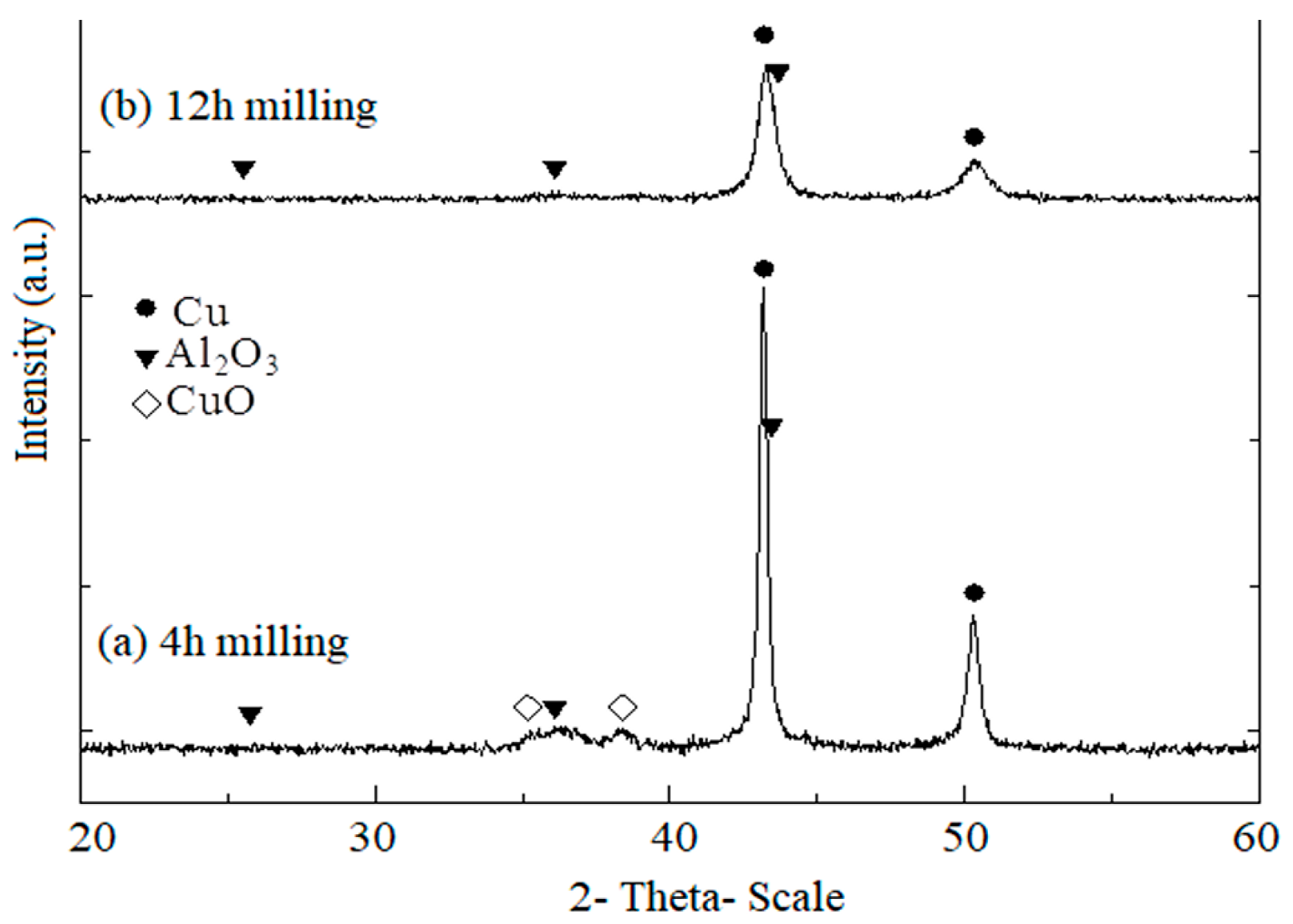
Figure 2 presents XRD patterns of CuO, Cu, and Al powder mixtures during the mechano-chemical process. The XRD patterns of Cu-(20 vol.%) Al2O3 mixture powders confirmed that a reaction between CuO, Cu, and Al powders had occurred. After 4 h of mechano-chemical milling, the formation of the Al2O3 phase began, as evidenced by the appearance of Al2O3 peaks in Figure 2a, following the reaction described in Equation (1). However, this process was incomplete, as the XRD pattern still exhibited CuO peaks.
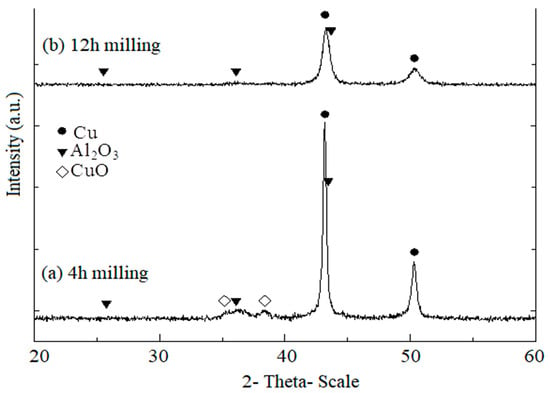
Figure 2.
XRD patterns of CuO, Cu, and Al powder mixtures during the mechano-chemical process at a constant rotation speed of 620 rpm: (a) after 4 h of milling; (b) after 12 h of milling.
After 12 h of milling, the peaks corresponding to Al and CuO phases disappeared entirely, indicating their full transformation (See Figure 2b). The Cu phase peaks remained present but showed a significant reduction in intensity with increasing milling time. Meanwhile, Al2O3 peaks appeared in the XRD patterns, though their low intensity made them difficult to distinguish. This result confirmed the formation of Al2O3 nanoparticles, which had an extremely fine size. Additionally, due to the mechanical energy imparted during milling, the particles underwent deformation, work hardening, and fragmentation, resulting in an exceptionally fine microstructure.
This phenomenon could be explained by the activation of Al atoms due to impact energy, making them more reactive and allowing easier diffusion into CuO particles, where they subsequently react with oxygen from CuO. The unexpected increase in the milling jar temperature during the experiment suggested that the reaction between Al and CuO was exothermic, with the released heat further facilitating Al atom diffusion into CuO particles. While the reaction between Al atoms and CuO molecules occurred, solid-state diffusion remained challenging, resulting in Al2O3 particles with an extremely fine size.
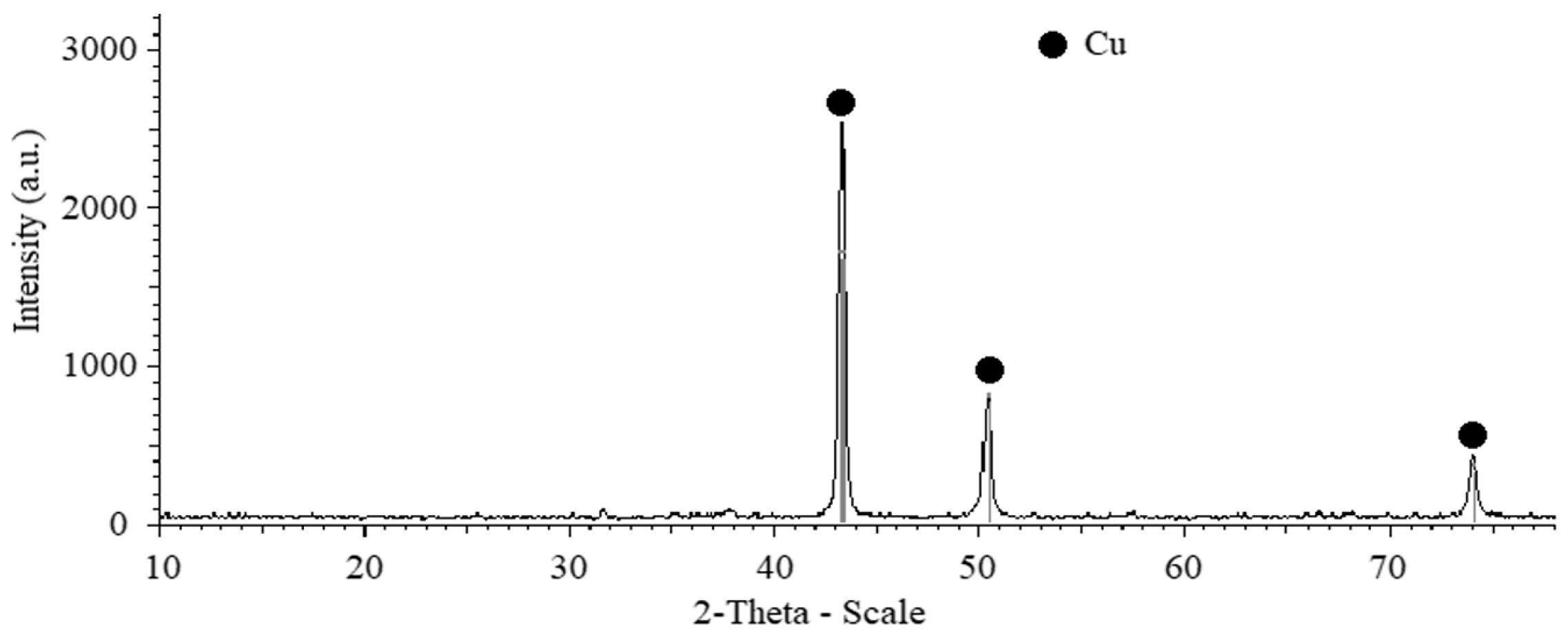
The XRD pattern of the composite powders Cu-(5 vol.%) Al2O3 after the second step (shown in Figure 3) reveals only peaks corresponding to the Cu phase, while peaks associated with the Al2O3 phase appear to be undetectable. This could be attributed to the low concentration and extremely fine particle size of the Al2O3 phase within the composite powder mixture.
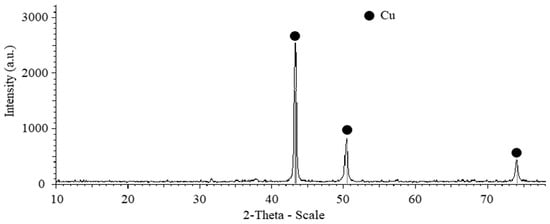
Figure 3.
XRD pattern of Cu-(5 vol.%) Al2O3 mixed powder after 3 h of mixing using drum ball milling at a constant rotation speed of 300 rpm.
3.2. Microstructures
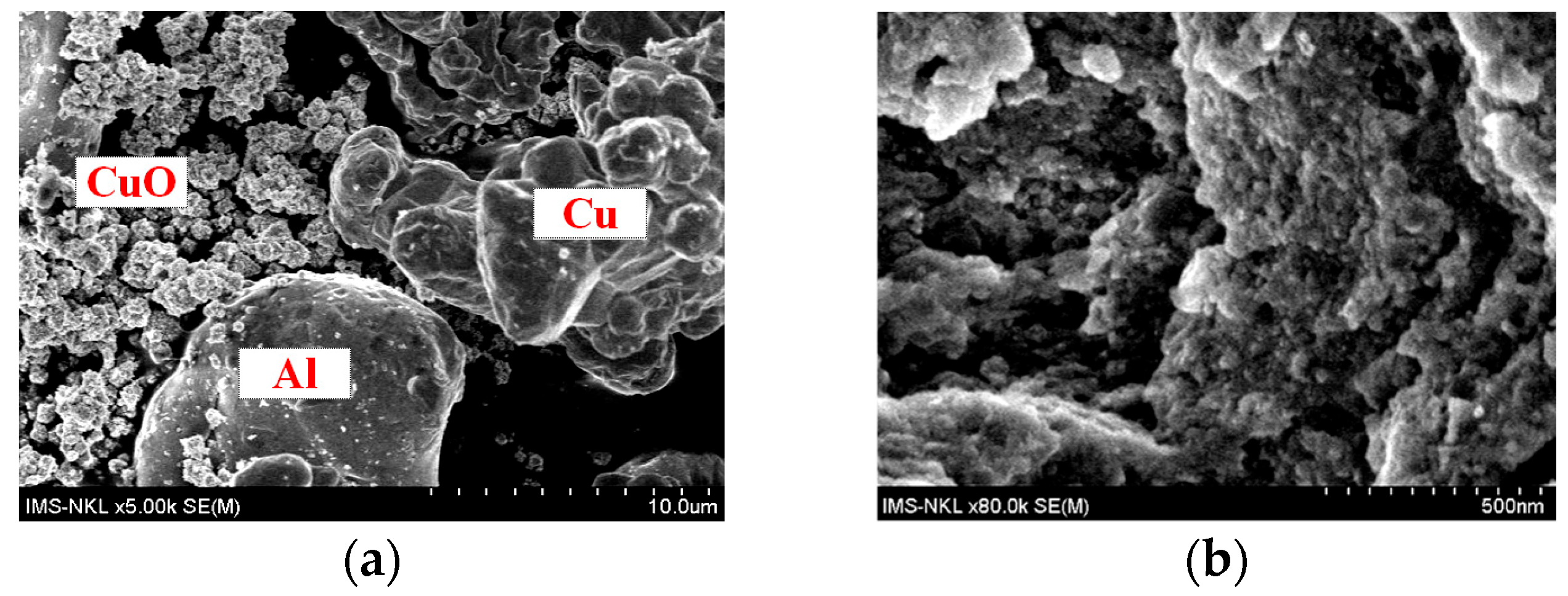
The SEM images in Figure 4 illustrated that after 12 h of mechano-chemical milling, the particle sizes of all powders significantly decreased.
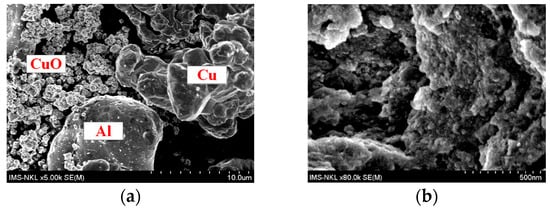
Figure 4.
SEM images of (a) raw powder mixture containing CuO, Cu, and Al; (b) powder mixture after 16 h of mechano-chemical milling.
The initial Al and Cu particles were relatively coarse (~10–20 µm, as shown in Figure 4a). However, after 12 h of milling, their sizes were reduced to below 500 nm (See Figure 4b). This significant reduction indicated the strong impact of mechanical energy during the milling process, which led to an increased surface area, enhanced diffusion, and improved reactivity between the components. The reduction in particle size may have also caused the decreased intensities of both Cu and Al2O3 peaks observed in Figure 2.
Figure 5a presents EDS results from two areas of the Cu-(20 vol.%) Al2O3 composite powder sample. The results indicated the presence of Al2O3 nanoparticles in the Cu matrix, formed during the mechano-chemical process.
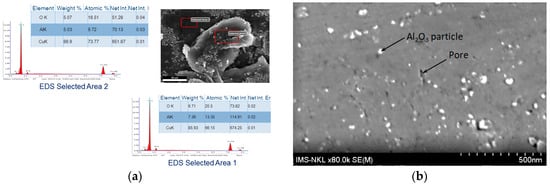
Figure 5.
(a) SEM image and EDS analysis of Cu-(20 vol.%) Al2O3 composite powders, and (b) SEM image of Cu-(5 vol.%) Al2O3 composites obtained under the conditions of 400 MPa compressive pressure, 3 h sintering time, and a sintering temperature of 900 °C.
Figure 5b shows the SEM image of the sample Cu-(5 vol.%) Al2O3 materials obtained under the conditions of 400 MPa compressive pressure and 3 h sintering at a temperature of 900 °C. Al2O3 particles, appearing as white regions, were clearly visible against the gray background of the Cu matrix. The SEM image shows that Al2O3 particles range in size from approximately 10 to 20 nm and are relatively well-dispersed throughout the Cu matrix. This result further confirms the formation of nano-sized particles within the Cu matrix through the mechano-chemical process. The simultaneous mechanical activation and chemical reaction contributed to particle size refinement and improved dispersion uniformity. This further validated the effectiveness of the processing method in achieving a well-integrated nanocomposite structure. In this study, the material properties of Cu-(5%vol.) Al2O3 nanocomposite including microhardness (HV), porosity, and relative electrical conductivity (AICS), were evaluated. The input parameters considered are compression pressure (p), sintering temperature (T), and sintering time (ts). The investigated parameter ranges are presented in Table 2 above. The experimental results are presented in Table 3. Each result represents the average of five independent repetitions to ensure experimental consistency.
3.3. Effects of Input Parameters on the Properties of Cu-(5 vol.%) Al2O3 Nanocomposite Materials
In this study, the material properties of Cu-(5 vol.%) Al2O3 nanocomposite, including microhardness (HV), porosity, and relative electrical conductivity (AICS), were evaluated. The input parameters considered were compression pressure (p), sintering temperature (T), and sintering time (ts). The parameter ranges investigated are presented in Table 2, and the experimental results are shown in Table 3. Each result represents the average of five independent repetitions to ensure experimental consistency.
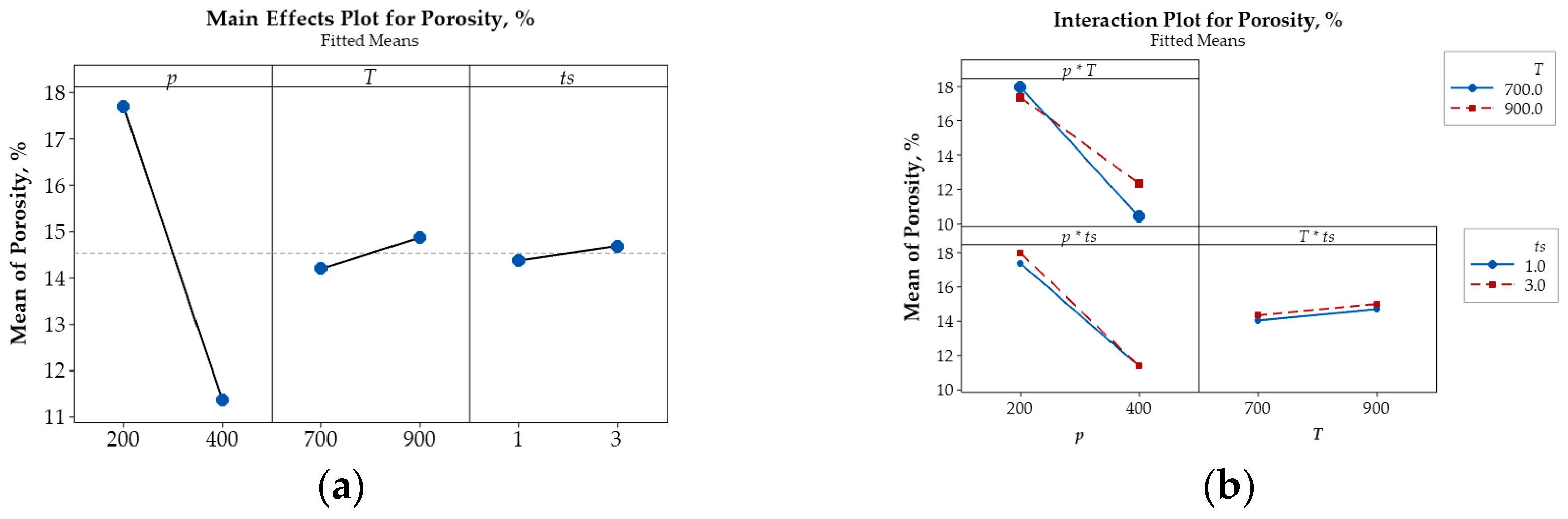
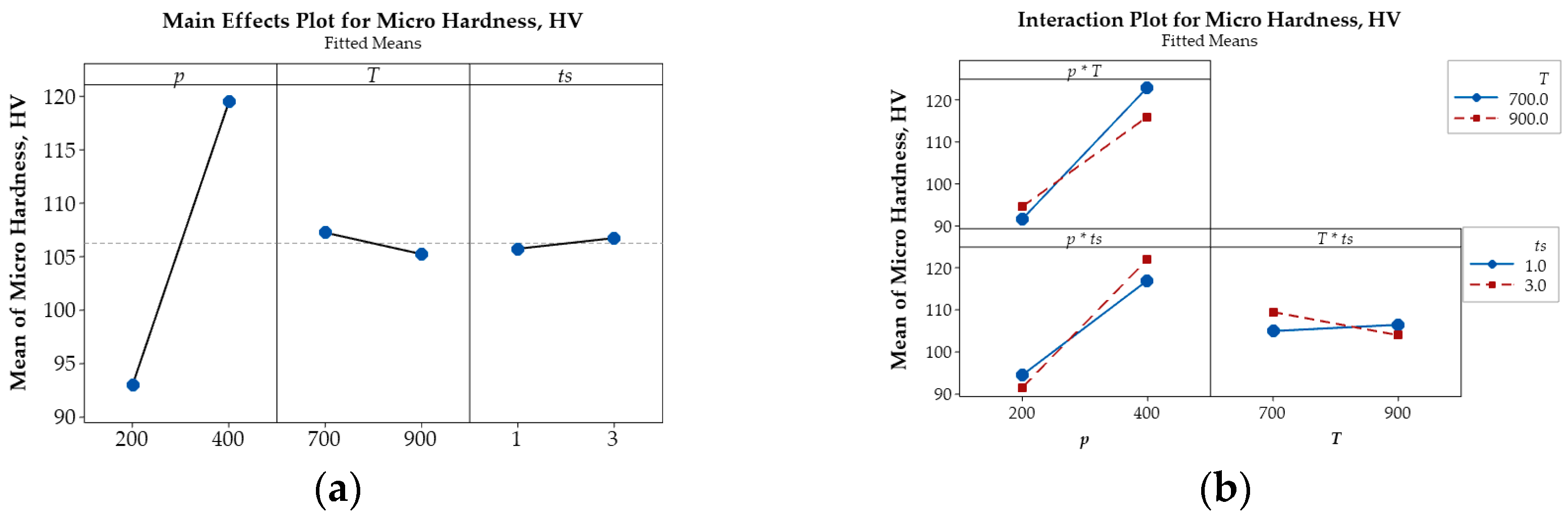
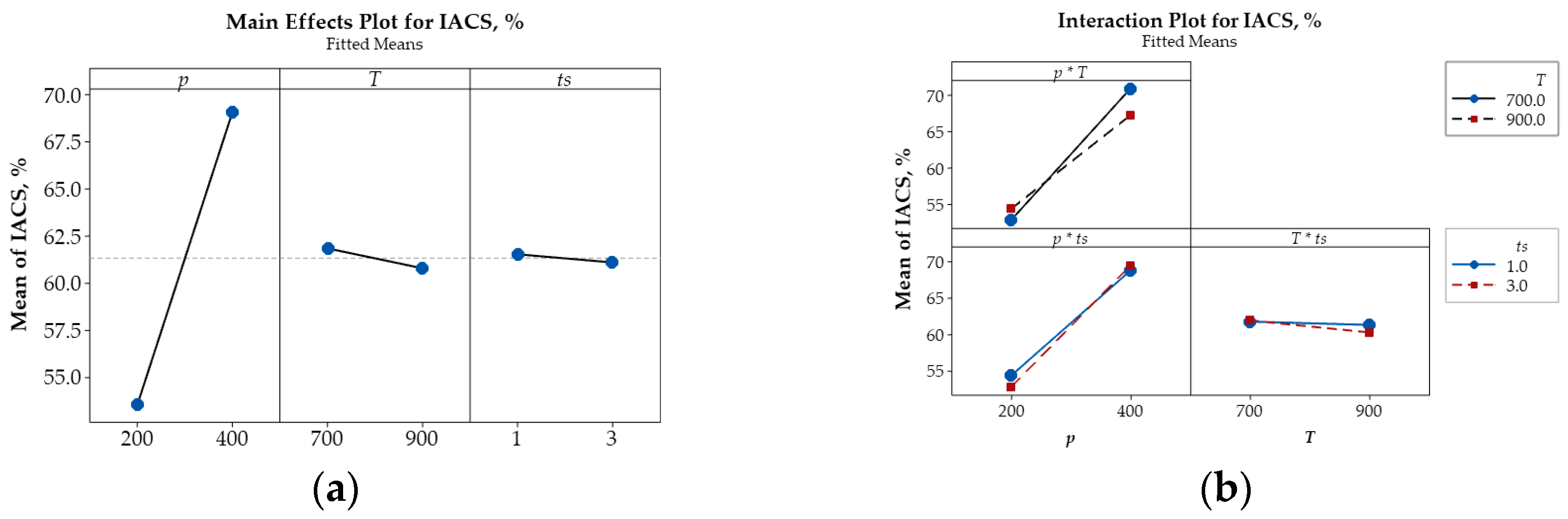
Sintering temperature exhibits a comparatively weaker influence than compaction pressure, as indicated by the shallower slopes in the corresponding plots. Nevertheless, unlike compaction pressure, increasing the sintering temperature leads to greater porosity, accompanied by reductions in both microhardness and electrical conductivity. This likely results from the expansion of air trapped between powder particles at elevated temperatures, thereby increasing pore volume. Additionally, higher sintering temperatures promote recovery and grain softening, rendering the material less compact. As a result, both microhardness and electrical conductivity decrease due to the reduced matrix density and increased pore content. SEM micrographs (Figure 5b) support these observations, revealing broader and less uniform pore structures, indicative of lower densification and weakened interparticle bonding.
Among the examined parameters, sintering time exerts the least influence on porosity, microhardness, and electrical conductivity of Cu-(5 vol.%) Al2O3 nanocomposites. Main effects plots indicate that prolonged sintering slightly increases porosity while reducing both microhardness and electrical conductivity. This trend may be attributed to gas expansion or pore coalescence during extended thermal exposure, which lowers packing efficiency. Although longer sintering durations promote atomic diffusion and facilitate interparticle bonding, grain boundary softening and pore growth appear to counteract potential gains in material density. As such, the mechanical and electrical properties slightly deteriorate, consistent with the broader pore structures observed in SEM images (Figure 5b).
The main effects plot illustrating the influence of key parameters on porosity (%), microhardness (HV), and relative electrical conductivity (IACS, %) are presented in Figure 6a, Figure 7a, and Figure 8a, respectively. These plots reveal that compaction pressure has the strongest influence on the porosity, microhardness (HV), and electrical conductivity (IACS, %) of Cu-(5 vol.%) Al2O3 nanocomposite materials. When compressive pressure increases, porosity decreases, both microhardness and electrical conductivity improve. This effect can be explained by the fact that higher pressure induces more intense plastic deformation in the powder particles, minimizing interparticle space and increasing packing density. Lower porosity resulted in a more tightly bonded Cu matrix, enhancing the material’s microhardness. Additionally, improved particle contact facilitated better bonding, thereby increasing the material’s electrical conductivity.
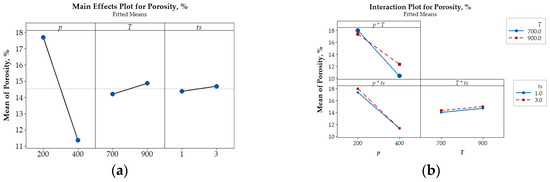
Figure 6.
Main effects plot (a) and interaction plot (b) illustrating the influence of p, T, and ts on the porosity (%) of Cu-(5 vol.%) Al2O3 nanocomposite materials.
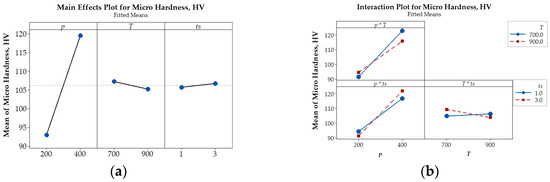
Figure 7.
Main effects plot (a) and interaction plot (b) illustrating the influence of p, T, and ts on the micro hardness (HV) of Cu-(5 vol.%) Al2O3 nanocomposite materials.
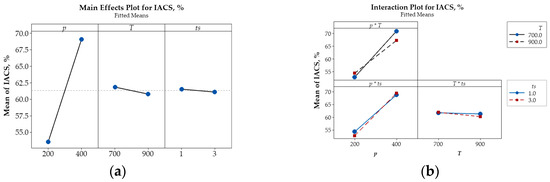
Figure 8.
Main effects plot (a) and interaction plot (b) illustrating the influence of p, T, and ts on the relative electrical conductivity IACS (%) of Cu-(5 vol.%) Al2O3 nanocomposite materials.
Beyond the main effects, the interactive influences among input parameters on porosity, microhardness, and electrical conductivity are also illustrated in Figure 6b, Figure 7b and Figure 8b.
The intersecting lines in the porosity plot (Figure 6b) demonstrate strong interactions between p and T and between p and ts, while the parallel lines indicate the negligible interaction of T and ts confirm that their effect on porosity is negligible. In contrast, the interaction plots for microhardness (Figure 7b) and electrical conductivity (Figure 8b) reveal strong interactions among input parameters, as evidenced by their intersection.
4. Conclusions
Cu-(5 vol.%) Al2O3 composites were successfully synthesized via a mechano-chemical process using CuO, Cu, and Al powders. Milling for 12 h at 620 rpm with a 10:1 ball-to-powder ratio in an argon atmosphere enabled direct formation of Al2O3 nanoparticles within the Cu matrix. Analysis also revealed the uniform dispersion of Al2O3 particles (10–20 nm).
Porosity, microhardness, and electrical conductivity were found to be strongly influenced by compaction pressure, with higher pressure reducing porosity while improving hardness and conductivity. Although sintering temperature and time also affect these properties, their impact was weaker. Additionally, interactions among input parameters significantly influence all three characteristics.
This preliminary study identified key trends among processing parameters, though formal statistical validation was not performed. Future work will expand experimental runs, apply multi-objective optimization, and deepen microstructural analysis to clarify underlying mechanisms.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.-T.H.; methodology, K.-T.H.; formal analysis, D.-D.N.; investigation, D.-D.N. and K.-T.H.; data curation, D.-D.N.; writing—original draft preparation, K.-T.H.; writing—review and editing, K.-T.H.; visualization, D.-D.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their sincere gratitude to Thai Nguyen University of Technology for their invaluable support throughout this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lee, D.W.; Kim, B.K. Nanostructured Cu–Al2O3 composite produced by thermochemical process for electrode application. Mater. Lett. 2004, 58, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annaraj, J.P.; Bose, N.; Hynes, N.R.J. A review on mechanical and tribological properties of sintered copper matrix composites. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2142, 070027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Shen, Y.; Chen, X.; Qian, L.; Lu, K. Ultrahigh Strength and High Electrical Conductivity in Copper. Science 2004, 304, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, A.H.; Wang, Y.F.; Wang, M.S.; Song, L.Y.; Li, Y.S.; Gao, L.; Huang, C.X.; Zhu, Y.T. Optimizing the strength, ductility and electrical conductivity of a Cu–Cr–Zr alloy by rotary swaging and aging treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 746, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botcharova, E.; Freudenberger, J.; Schultz, L. Mechanical and electrical properties of mechanically alloyed nanocrystalline Cu–Nb alloys. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 3333–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motaman, A.; Salahi, E. Synthesis of Cu–Al2O3 metal matrix nanocomposite powder from CuO and Al powders by using high energy planetary fast milling. Int. J. Nanosci. 2011, 08, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, M.M.J.; Ravichandran, M.; Meignanamoorthy, M. Influence of different reinforcements on properties of copper matrix composites: A review. AIP Conf. Proc. 2020, 2283, 020129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaneme, K.K.; Odoni, B.U. Mechanical properties, wear and corrosion behavior of copper matrix composites reinforced with steel machining chips. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2016, 19, 1593–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Zheng, T.; Yao, G.; Chi, Y.; De Rosa, I.; Li, X. High-strength and high-conductivity in situ Cu–TiB2 nanocomposites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 831, 141952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulima, I.; Boczkal, G. Processing and Properties of ZrB2–Copper Matrix Composites Produced by Ball Milling and Spark Plasma Sintering. Materials 2023, 16, 7455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezayat, M.; Karamimoghadam, M.; Ashkani, O.; Bodaghi, M. Characterization and Optimization of Cu–Al2O3 Nanocomposites Synthesized via High Energy Planetary Milling: A Morphological and Structural Study. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Gao, P.; He, Y.; Gong, J.; Du, J. A Cu–Al2O3 Composite with Ultrahigh Tensile Strength Prepared by High-Pressure Torsion. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2022, 31, 9425–9430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, P.; Paswan, M.K.; Sadasivuni, K.K.; Gupta, P. Structural, wear and thermal behaviour of Cu–Al2O3–graphite hybrid metal matrix composites. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2020, 234, 1154–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha-Rangel, E.; Miranda-Hernández, J.G. Alumina-Copper Composites with High Fracture Toughness and Low Electrical Resistance. Mater. Sci. Forum 2010, 644, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koumoulos, E.P.; Kartsonakis, I.A.; Bakolas, A.; Charitidis, C.A. Nanomechanical properties and thermal decomposition of Cu–Al2O3 composites for FGM applications. Manuf. Rev. 2016, 3, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.J.; Lee, J.-H. Mechanochemical synthesis of Cu–Al2O3 nanocomposites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 405, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, P.K.; Brocchi, E.A.; Motta, M.S. In-situ formation of Cu–Al2O3 nano-scale composites by chemical routes and studies on their microstructures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 313, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.-F.; Kou, S.-Q.; Yang, H.-Y.; Shu, S.-L.; Qiu, F.; Jiang, Q.-C.; Zhang, L.-C. Ceramic particles reinforced copper matrix composites manufactured by advanced powder metallurgy: Preparation, performance, and mechanisms. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2023, 5, 032006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Zhang, D.; Feng, B.; Lin, Y.; Wang, J.; Zheng, K. Microstructure and Properties of Cu–0.4 wt.% Al2O3 Composites Fabricated by Hot Extrusion and Cold Drawing. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2022, 31, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, P.; Sengar, S.S.; Sorabh; Paswan, M.K.; Mehta, J.; Chawla, D.; Gupta, P. Challenges and Opportunities in Synthesis of Hybrid Cu–Al2O3–C and Cu–ZrO2–C Composites Through Stir Casting Route. In Advances in Engineering Materials: Select Proceedings of FLAME 2020; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).