Overlooked Ionic Phenomena Affecting the Electrical Conductivity of Liquid Crystals †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model
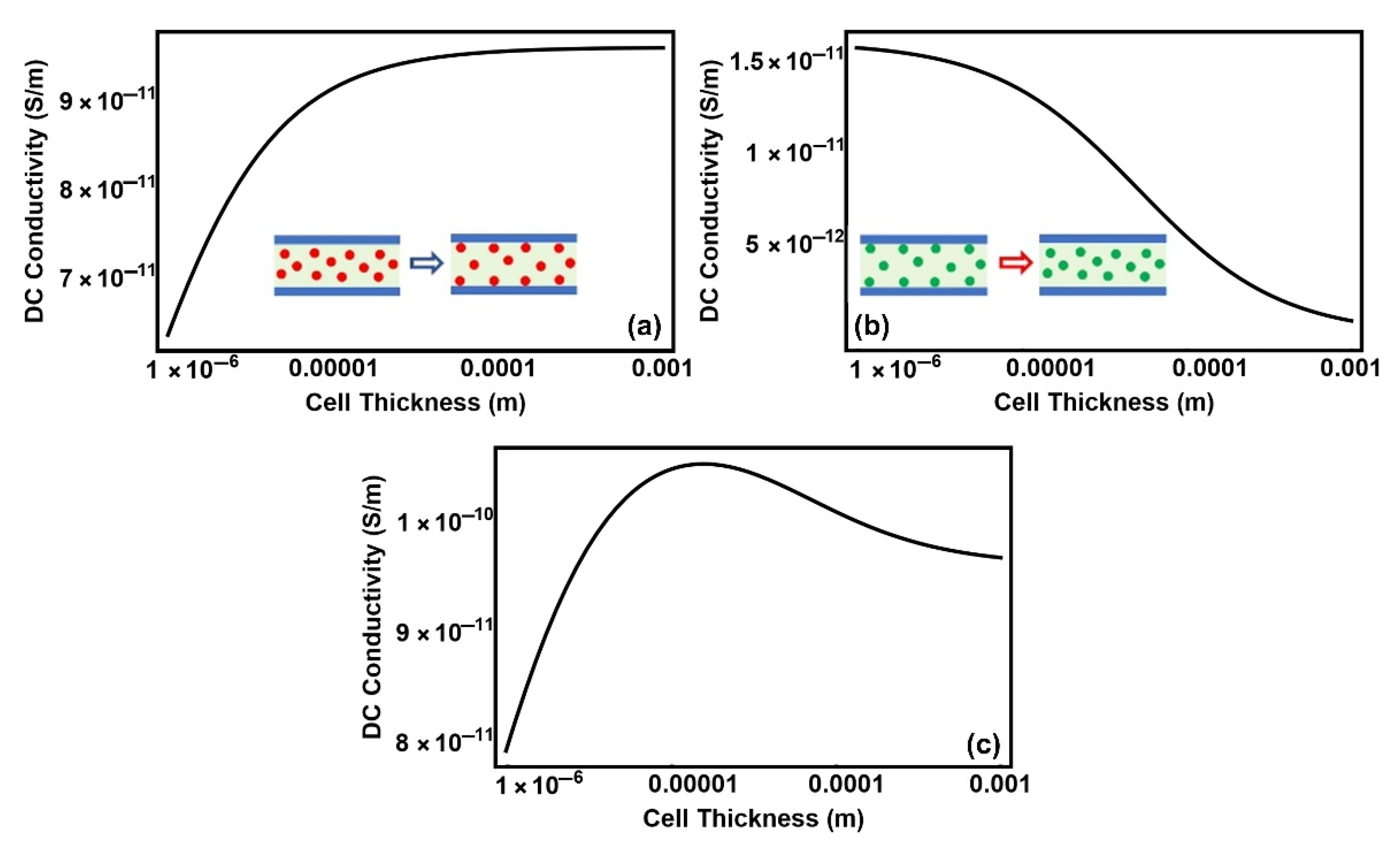
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, Y.; Liao, E.; Chen, R.; Wu, S.-T. Liquid-Crystal-on-Silicon for Augmented Reality Displays. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otón, J.M.; Otón, E.; Quintana, X.; Geday, M.A. Liquid-crystal phase-only devices. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 267, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarev, G.; Chen, P.-J.; Strauss, J.; Fontaine, N.; Forbes, A. Beyond the display: Phase-only liquid crystal on Silicon devices and their applications in photonics. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 16206–16249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulhalim, I. Non-display bio-optic applications of liquid crystals. Liq. Cryst. Today 2011, 20, 44–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Reshetnyak, V. Liquid crystal lenses with tunable focal length. Liq. Cryst. Rev. 2017, 5, 111–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sio, L.; Roberts, D.E.; Liao, Z.; Hwang, J.; Tabiryan, N.; Steeves, D.M.; Kimball, B.R. Beam shaping diffractive wave plates. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, A118–A121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chigrinov, V.G. Liquid Crystal Photonics; Nova Science Pub Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2014; 204p. [Google Scholar]
- Jeng, S.C. Applications of Tamm plasmon-liquid crystal devices. Liq. Cryst. 2020, 47, 1223–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lininger, A.; Zhu, A.Y.; Park, J.S.; Palermo, G.; Chatterjee, S.; Boyd, J.; Capasso, F.; Strangi, G. Optical properties of metasurfaces infiltrated with liquid crystals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 20390–20396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geis, M.W.; Bos, P.J.; Liberman, V.; Rothschild, M. Broadband optical switch based on liquid crystal dynamic scattering. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 13812–13823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konshina, E.A.; Shcherbinin, D.P. Study of dynamic light scattering in nematic liquid crystal and its optical, electrical and switching characteristics. Liq Cryst. 2018, 45, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaban, H.; Wu, P.-C.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, W. Dielectric and electro-optical responses of a dielectrically negative nematic liquid crystal doped with cationic surfactant. Opt. Mater. Express 2021, 11, 3208–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowski, R.; Dziaduszek, J.; Bozetka, J.; Piecek, W.; Mazur, R.; Chrunik, M.; Perkowski, P.; Mrukiewicz, M.; Żurowska, M.; Weglowska, D. Fluorinated smectics—New liquid crystalline medium for smart windows and memory displays. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 267, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; He, J.; Lv, P.; Yuan, D.; Hu, X.; Liu, D.; Broer, D.J.; et al. Electroconvection in zwitterion-doped nematic liquid crystals and application as smart windows. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2020, 27, 2001465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camley, R.; Celinski, Z.; Garbovskiy, Y.; Glushchenko, A. Liquid crystals for signal processing applications in the microwave and millimeter wave frequency ranges. Liq. Cryst. Rev. 2018, 6, 17–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinov, L.M. Structure and Properties of Liquid Crystals; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Neyts, K.; Beunis, F. Ion Transport in Liquid Crystals. In Handbook of Liquid Crystals: Physical Properties and Phase Behavior of Liquid Crystals; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2014; Volume 2, Chapter 11; pp. 357–382. [Google Scholar]
- Garbovskiy, Y. Conventional and unconventional ionic phenomena in tunable soft materials made of liquid crystals and nanoparticles. Nano Ex. 2021, 2, 012004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colpaert, C.; Maximus, B.; Meyere, D. Adequate measuring techniques for ions in liquid crystal layers. Liq. Cryst. 1996, 21, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbero, G.; Evangelista, L.R. Adsorption Phenomena and Anchoring Energy in Nematic Liquid Crystals; Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Khazimullin, M.V.; Lebedev, Y.A. Influence of dielectric layers on estimates of diffusion coefficients and concentrations of ions from impedance spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. E 2019, 100, 062601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karaawi, A.R.; Gavrilyak, M.V.; Boronin, V.A.; Gavrilyak, A.M.; Kazachonok, J.V.; Podgornov, F.V. Direct current electric conductivity of ferroelectric liquid crystals–gold nanoparticles dispersion measured with capacitive current technique. Liq. Cryst. 2020, 47, 1507–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbovskiy, Y. Evaluating the Concentration of Ions in Liquid Crystal Cells: Hidden Factors and Useful Techniques. Proceedings 2020, 62, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhara, S.; Madhusudana, N.V. Ionic contribution to the dielectric properties of a nematic liquid crystal in thin cells. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 90, 3483–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Varshney, D.; Prakash, J. Role of ionic contribution in dielectric behaviour of a nematic liquid crystal with variable cell thickness. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 303, 112520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbovskiy, Y. Ion capturing/ion releasing films and nanoparticles in liquid crystal devices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 110, 041103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbovskiy, Y. Ions and size effects in nanoparticle/liquid crystal colloids sandwiched between two substrates. The case of two types of fully ionized species. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2017, 679, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Physical Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| 10−21 m3 (Figure 1 and Figure 3a) | |
| 10−22 m3 (Figure 1 and Figure 3a) | |
| 10−23 m3 (Figure 2 and Figure 3b) | |
| 10−21 m3 (Figure 2 and Figure 3b) | |
| 5 × 1016 m−2 | |
| 10−10 m2/Vs | |
| 0 | |
| 10−3 (Figure 1 and Figure 2) 10−2 (Figure 3a) 10−4 (Figure 3b) | |
| 6 × 1018 m−3 | |
| 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Webb, D.; Garbovskiy, Y. Overlooked Ionic Phenomena Affecting the Electrical Conductivity of Liquid Crystals. Eng. Proc. 2021, 11, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/ASEC2021-11141
Webb D, Garbovskiy Y. Overlooked Ionic Phenomena Affecting the Electrical Conductivity of Liquid Crystals. Engineering Proceedings. 2021; 11(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/ASEC2021-11141
Chicago/Turabian StyleWebb, David, and Yuriy Garbovskiy. 2021. "Overlooked Ionic Phenomena Affecting the Electrical Conductivity of Liquid Crystals" Engineering Proceedings 11, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/ASEC2021-11141
APA StyleWebb, D., & Garbovskiy, Y. (2021). Overlooked Ionic Phenomena Affecting the Electrical Conductivity of Liquid Crystals. Engineering Proceedings, 11(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/ASEC2021-11141







