An Africa Lateral Flow Assay-Based Early Recognition Test for Tenofovir-Induced Acute Kidney Injury (ALERT-AKI) Development †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Equipment
2.2. Target Biomarker Selection
2.3. Conjugation of Antibodies to Gold Nanoparticles
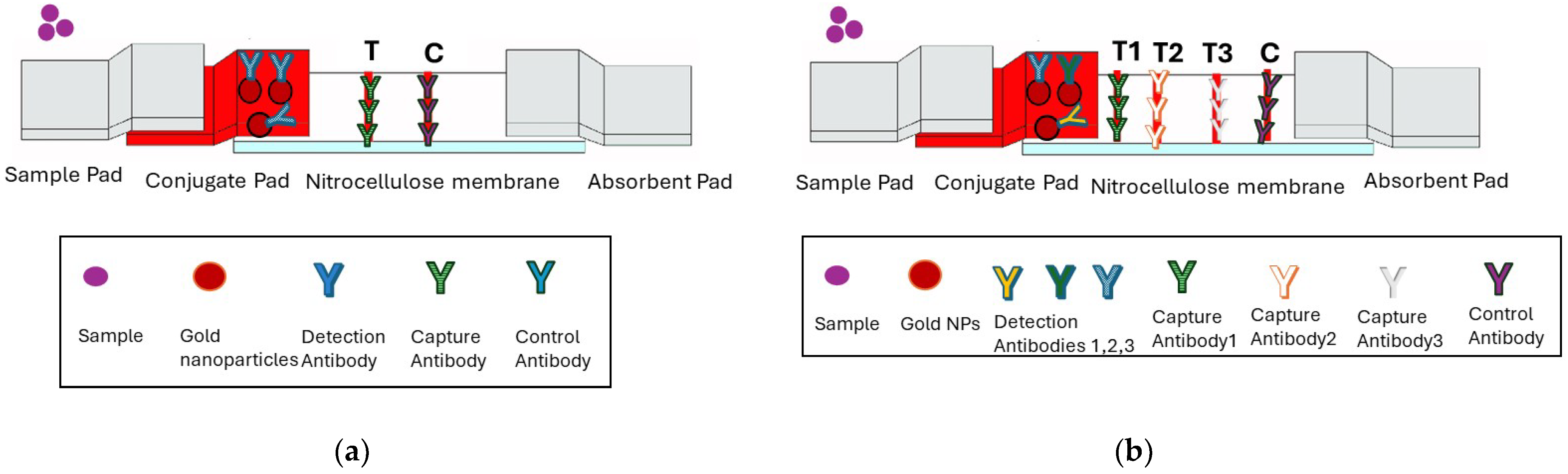
2.4. Singleplex and Multiplex Lateral Flow Test Developments
2.5. Limit of Detection (LOD)
3. Results
3.1. Optimization of the Monoplex Lateral Flow Test
3.2. Evaluation of Limit of Detection (LOD)
3.3. Development of a Multiplex Lateral Flow Test Strip
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Levey, A.S.; James, M.T. Acute kidney injury. Ann. Intern. Med. 2017, 167, ITC66–ITC80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venter, W.D.F.; Fabian, J.; Feldman, C. An overview of tenofovir and renal disease for the HIV-treating clinician. S. Afr. J. HIV Med. 2018, 19, a817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mwafongo, A.; Nkanaunena, K.; Zheng, Y.; Hogg, E.; Samaneka, W.; Mulenga, L.; Siika, A.; Currier, J.; Lockman, S.; Hughes, M.D.; et al. Renal events among women treated with tenofovir/emtricitabine in combination with either lopinavir/ritonavir or nevirapine. AIDS 2014, 28, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bygrave, H.; Kranzer, K.; Hilderbrand, K.; Jouquet, G.; Goemaere, E.; Vlahakis, N.; Triviño, L.; Makakole, L.; Ford, N.; Gray, C. Renal safety of a tenofovir-containing first-line regimen: Experience from an antiretroviral cohort in rural Lesotho. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Olowu, W.A.; Niang, A.; Osafo, C.; Ashuntantang, G.; Arogundade, F.A.; Porter, J.; Naicker, S.; Luyckx, V.A. Outcomes of acute kidney injury in children and adults in sub-Saharan Africa: A systematic review. Lancet Glob. Health 2016, 4, e242–e250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perazella, M.A. Drug-induced nephropathy: An update. Expert. Opin. Drug Saf. 2010, 9, 865–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lameire, N.; Van Biesen, W.; Vanholder, R. The changing epidemiology of acute renal failure. Nat. Clin. Pract. Nephrol. 2013, 2, 364–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyatt, C.M.; Schwartz, G.J.; Owino Ong’or, W.; Abuya, J.; Abraham, A.G.; Mboku, C.; M’mene, L.B.; Koima, W.J.; Hotta, M.; Maier, P.; et al. Estimating kidney function in HIV-infected adults in Kenya: Comparison to a direct measure of glomerular filtration rate by iohexol clearance. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e69601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glassock, R.J.; Christopher, W. An epidemic of chronic kidney disease: Fact or fiction? Nephrology Dialysis Transplantat. 2008, 23, 1117–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalim, S.; Szczech, L.A.; Wyatt, C.M. Acute kidney injury in HIV-infected patients. Semin Nephrol. 2008, 28, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.C.; Chen, C.P.; Wu, T.H.; Yang, C.H.; Lin, C.W.; Chen, C.Y. Gold Nanoparticle-Based Colorimetric Strategies for Chemical and Biological Sensing Applications. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, J.P.; Prado, A.R.; Keijok, W.J.; Antunes, P.W.P.; Yapuchura, E.R.; Guimarães, M.C.C. Impact of Conjugation Strategies for Targeting of Antibodies in Gold Nanoparticles for Ultrasensitive Detection of 17β-Estradiol. Sci. Rep. 2019, M9, 13859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murty, M.S.; Sharma, U.K.; Pandey, V.B.; Kankare, S.B. Serum cystatin C as a marker of renal function in detection of early acute kidney injury. Indian J. Nephrol. 2013, 23, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Taee, I.K.; Al-Safar, J.J.; Al-Falahi, Y.S.; Al-Shamma, I.A. The Clinical Significance of beta2-microglobulin in End-Stage Renal Disease. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transplant. 2003, 14, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Haase-Fielitz, A.; Haase, M.; Devarajan, P. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a biomarker of acute kidney injury: A critical evaluation of current status. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2014, 51 Pt 3, 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skepu, A.; Nxumalo, N.; Phiri, S. An Africa Lateral Flow Assay-Based Early Recognition Test for Tenofovir-Induced Acute Kidney Injury (ALERT-AKI) Development. Eng. Proc. 2025, 109, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025109009
Skepu A, Nxumalo N, Phiri S. An Africa Lateral Flow Assay-Based Early Recognition Test for Tenofovir-Induced Acute Kidney Injury (ALERT-AKI) Development. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 109(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025109009
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkepu, Amanda, Nolwandle Nxumalo, and Sibongile Phiri. 2025. "An Africa Lateral Flow Assay-Based Early Recognition Test for Tenofovir-Induced Acute Kidney Injury (ALERT-AKI) Development" Engineering Proceedings 109, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025109009
APA StyleSkepu, A., Nxumalo, N., & Phiri, S. (2025). An Africa Lateral Flow Assay-Based Early Recognition Test for Tenofovir-Induced Acute Kidney Injury (ALERT-AKI) Development. Engineering Proceedings, 109(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025109009





