Fe3O4 Magnetic Biochar Derived from Pecan Nutshell for Arsenic Removal Performance Analysis Based on Fuzzy Decision Network †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fe3O4-Pecan Biochar Synthesis via Co-Precipitation
2.2. Adsorption Process for as Removal
2.3. Analysis of Fuzzy Decision Network
3. Results and Discussion
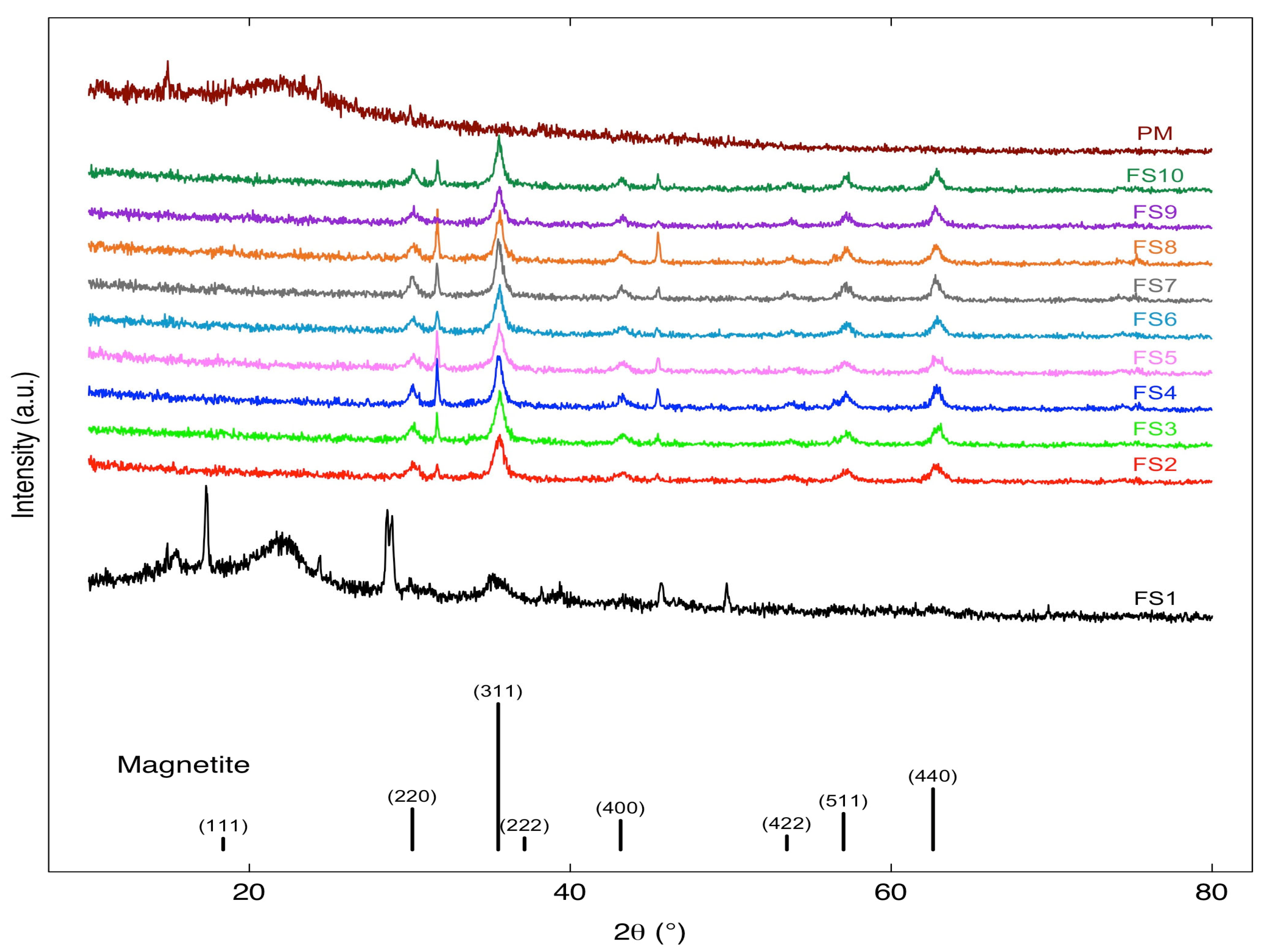
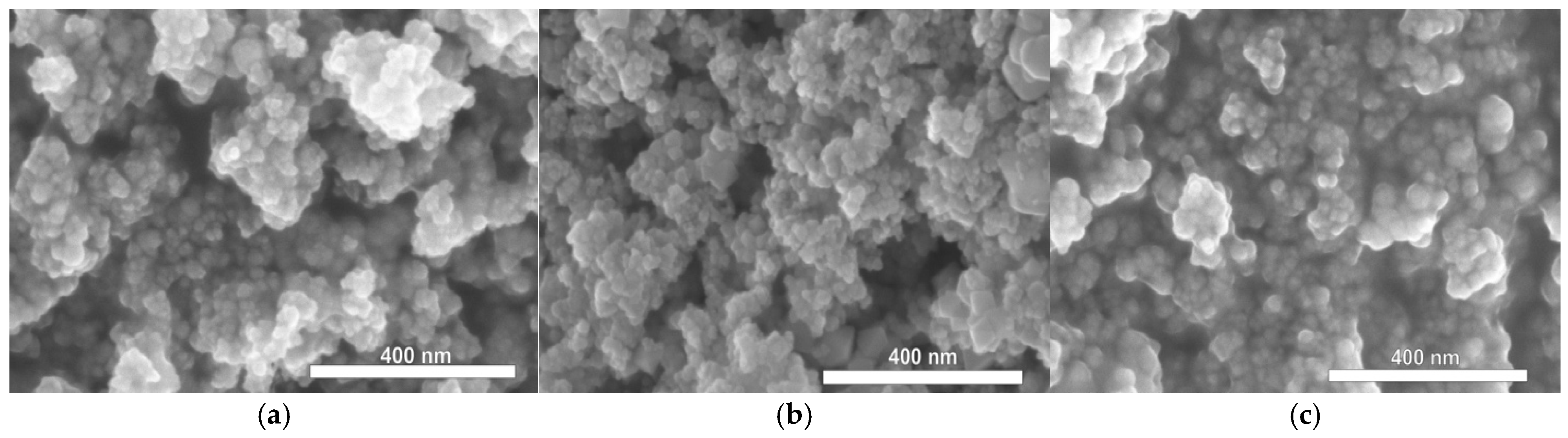
3.1. Characterization
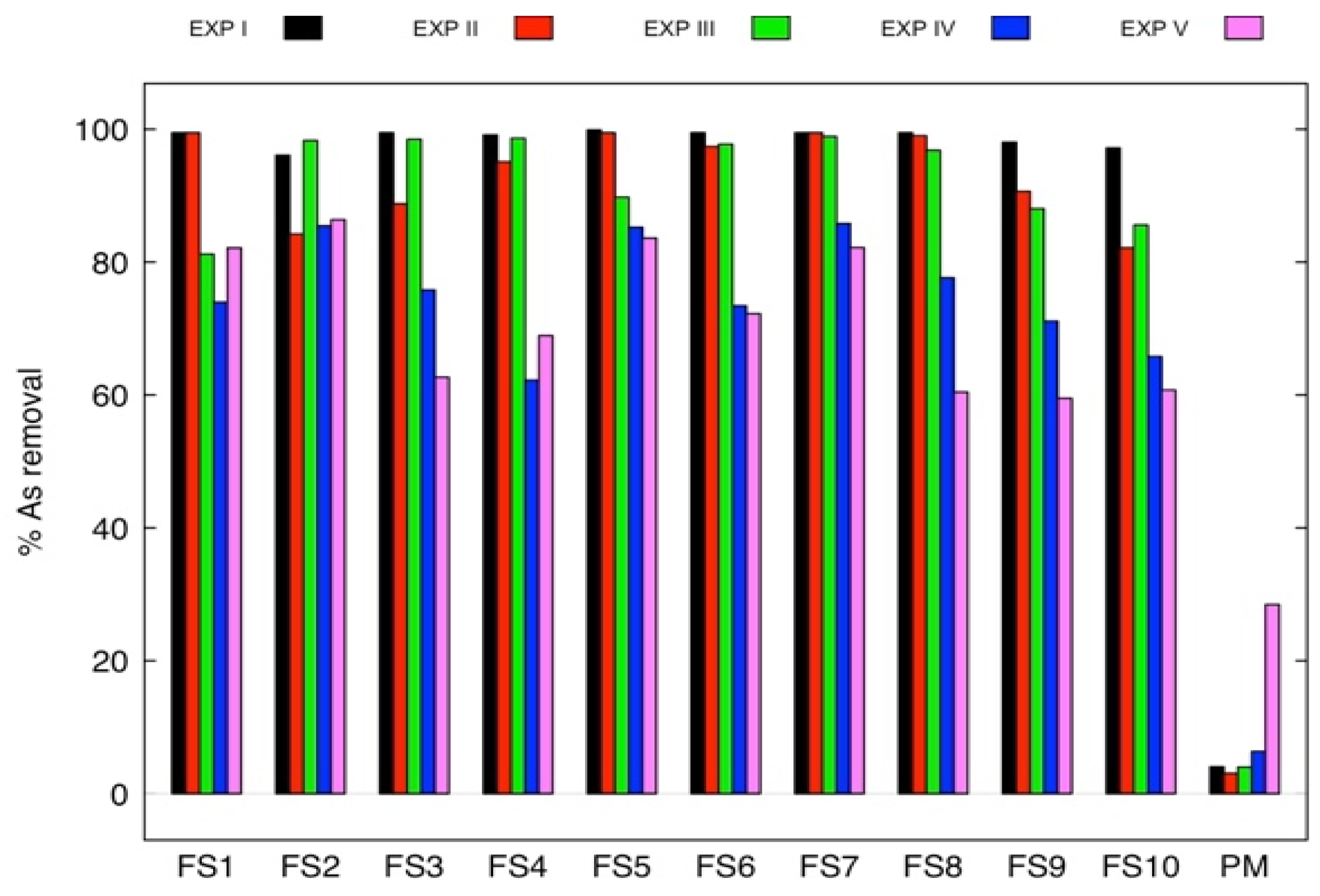
3.2. Arsenic Removal by Fe3O4-Pecan Magnetic Biochar
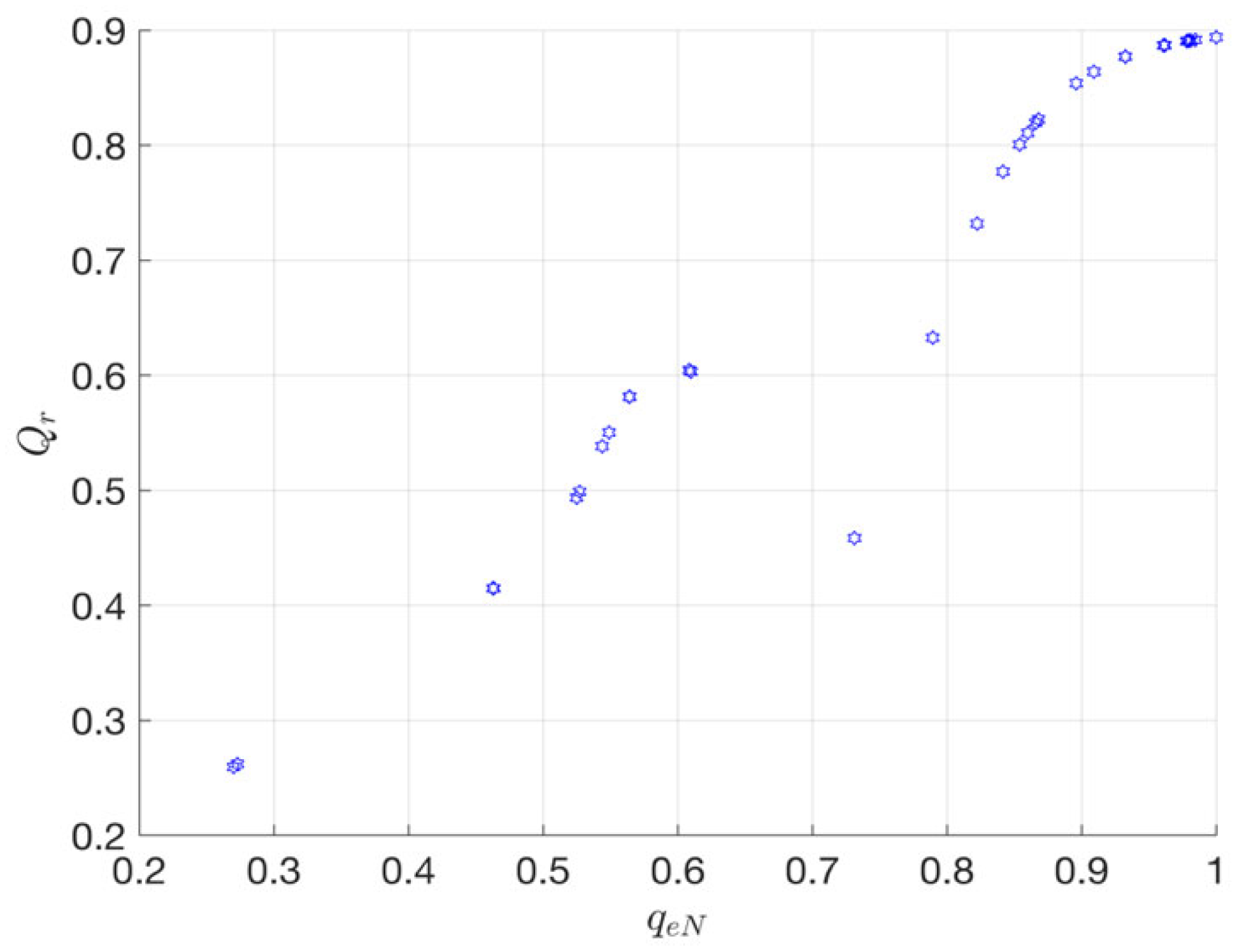
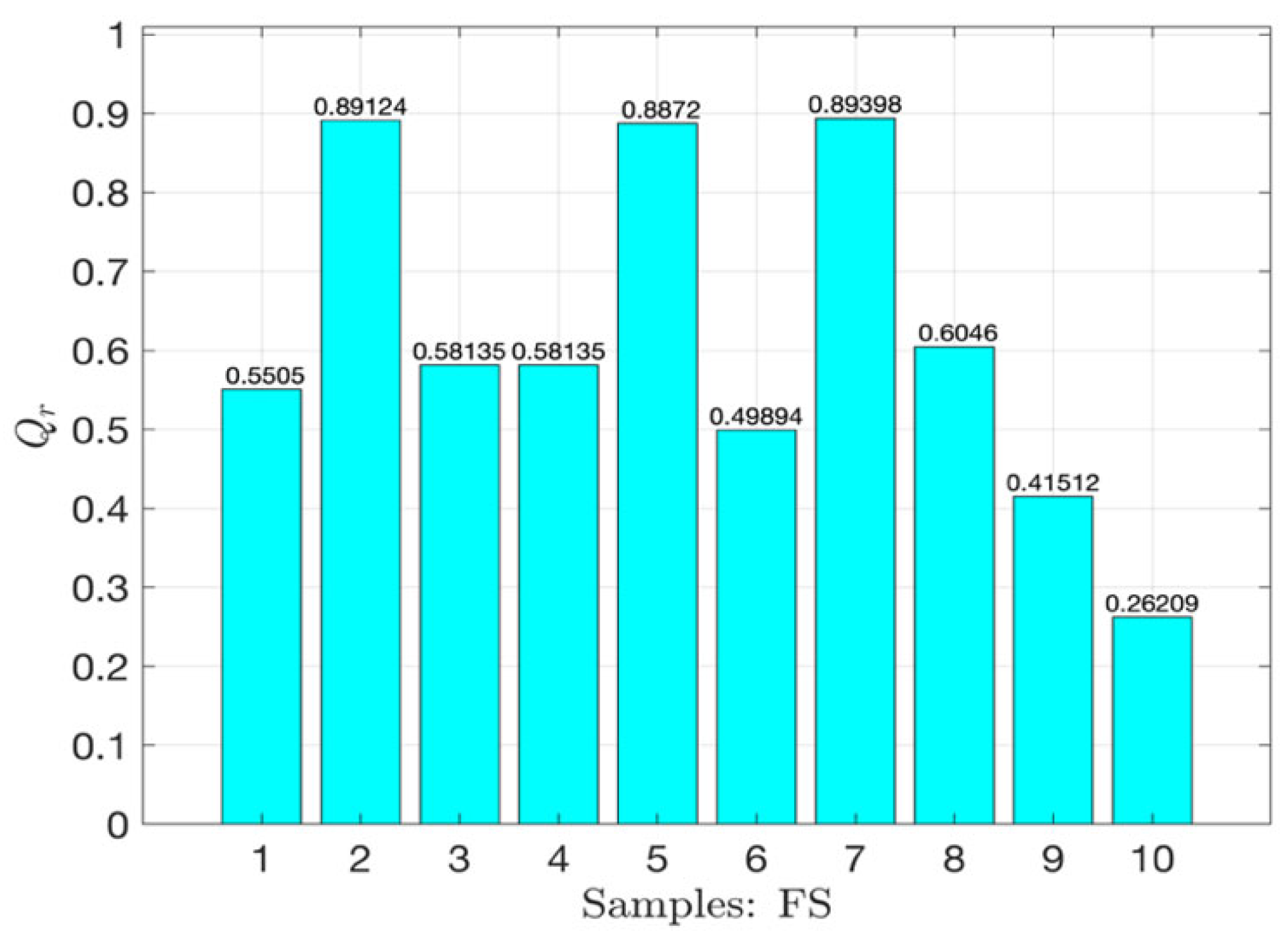
3.3. MiFREN Performance Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akintola, A.T.; Akinlabi, E.T.; Masebinu, S.O. Biochar as an Adsorbent: A Short Overview. In Green Energy and Technology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, B.; Tao, X.; Wang, H.; Li, W.; Ding, X.; Chu, H. Biochar as a Low-Cost Adsorbent for Aqueous Heavy Metal Removal: A Review. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2021, 155, 105081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fdez-Sanromán, A.; Pazos, M.; Rosales, E.; Sanromán, M.A. Unravelling the Environmental Application of Biochar as Low-Cost Biosorbent: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, B.; Chen, G. Preparation and Application of Magnetic Biochar in Water Treatment: A Critical Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Xu, T.; Song, X.; Nie, S.; Choi, S.E.; Si, C. Preparation and Application in Water Treatment of Magnetic Biochar. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 769667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khezri, A.; Schiller, V.; Goka, E.; Homri, L.; Etienne, A.; Stamer, F.; Dantan, J.Y.; Lanza, G. Evolutionary Cost-Tolerance Optimization for Complex Assembly Mechanisms via Simulation and Surrogate Modeling Approaches: Application on Micro Gears. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 126, 4101–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Wu, J.; Dong, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P. Performance Evaluation of Conductive Materials in Conductive Mortar Based on Machine Learning. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 92, 109695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munasir; Kusumawati, R.P. Synthesis and Characterization of Fe3O4@rGO Composite with Wet-Mixing (Ex-Situ) Process. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 2019, 1171, 012048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholia Lavasani, F.; Khalaj, Z.; Kabirifard, H.; Monajjemi, M. Fabrication and Characterization of the Fe3O4@SiO2-RGO Nanocomposite: A Catalyst for Multi-Component Reactions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2022, 25, 2821–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guel-Nájar, N.A.; Rios-Hurtado, J.C.; Muzquiz-Ramos, E.M.; Dávila-Pulido, G.I.; González-Ibarra, A.A.; Pat-Espadas, A.M. Magnetic Biochar Obtained by Chemical Coprecipitation and Pyrolysis of Corn Cob Residues: Characterization and Methylene Blue Adsorption. Materials 2023, 16, 3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Xing, Z.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhai, J. Effect of Pyrolysis Temperature on the Carbon Sequestration Capacity of Spent Mushroom Substrate Biochar in the Presence of Mineral Iron. Molecules 2024, 29, 5712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, T.C.F.; Vergütz, L.; Pacheco, A.A.; Melo, L.F.; Renato, N.S.; Melo, L.C.A. Characterization and Application of Magnetic Biochar for the Removal of Phosphorus from Water. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2020, 92, e20190440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khamkure, S.; Treesatayapun, C.; Bustos-Terrones, V.; Díaz-Jimenéz, L.; Pacheco-Catalán, D.-E.; Reyes-Rosas, A.; Gamero-Melo, P.; Zermeño-González, A. Fe3O4 Magnetic Biochar Derived from Pecan Nutshell for Arsenic Removal Performance Analysis Based on Fuzzy Decision Network. Eng. Proc. 2025, 107, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025107047
Khamkure S, Treesatayapun C, Bustos-Terrones V, Díaz-Jimenéz L, Pacheco-Catalán D-E, Reyes-Rosas A, Gamero-Melo P, Zermeño-González A. Fe3O4 Magnetic Biochar Derived from Pecan Nutshell for Arsenic Removal Performance Analysis Based on Fuzzy Decision Network. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 107(1):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025107047
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhamkure, Sasirot, Chidentree Treesatayapun, Victoria Bustos-Terrones, Lourdes Díaz-Jimenéz, Daniella-Esperanza Pacheco-Catalán, Audberto Reyes-Rosas, Prócoro Gamero-Melo, and Alejandro Zermeño-González. 2025. "Fe3O4 Magnetic Biochar Derived from Pecan Nutshell for Arsenic Removal Performance Analysis Based on Fuzzy Decision Network" Engineering Proceedings 107, no. 1: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025107047
APA StyleKhamkure, S., Treesatayapun, C., Bustos-Terrones, V., Díaz-Jimenéz, L., Pacheco-Catalán, D.-E., Reyes-Rosas, A., Gamero-Melo, P., & Zermeño-González, A. (2025). Fe3O4 Magnetic Biochar Derived from Pecan Nutshell for Arsenic Removal Performance Analysis Based on Fuzzy Decision Network. Engineering Proceedings, 107(1), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025107047








