Abstract
Migraines are recurring and highly painful headaches with multiple associated symptoms that severely affect millions of people around the world. This condition is considered quite serious from a neurologist’s perspective because it is highly debilitating. Effective treatment of migraines begins with its diagnosis but the subjective nature of clinical evaluations along with class imbalance in patient datasets makes this very complicated. This paper attempts to tackle these issues by developing a machine-learning framework for automated migraines classification by utilizing a Kaggle dataset of 400 samples with 23 independent attributes and 1 dependent attribute representing different types of migraines. Our framework starts with a detailed cleansing of the data, which includes filtering out all missing values. Then, through the use of SMOTE (Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique), the issue of an imbalanced dataset is tackled. This is followed by optimized feature selection through forward selection and cross-validation with Naïve Bayes. Supervised machine-learning classifiers such as Random Forest (RF), decision tree (DT), K-nearest Neighbors (KNN), and Naïve Bayes (NB) are evaluated and voted on to predict the outcome.
1. Introduction
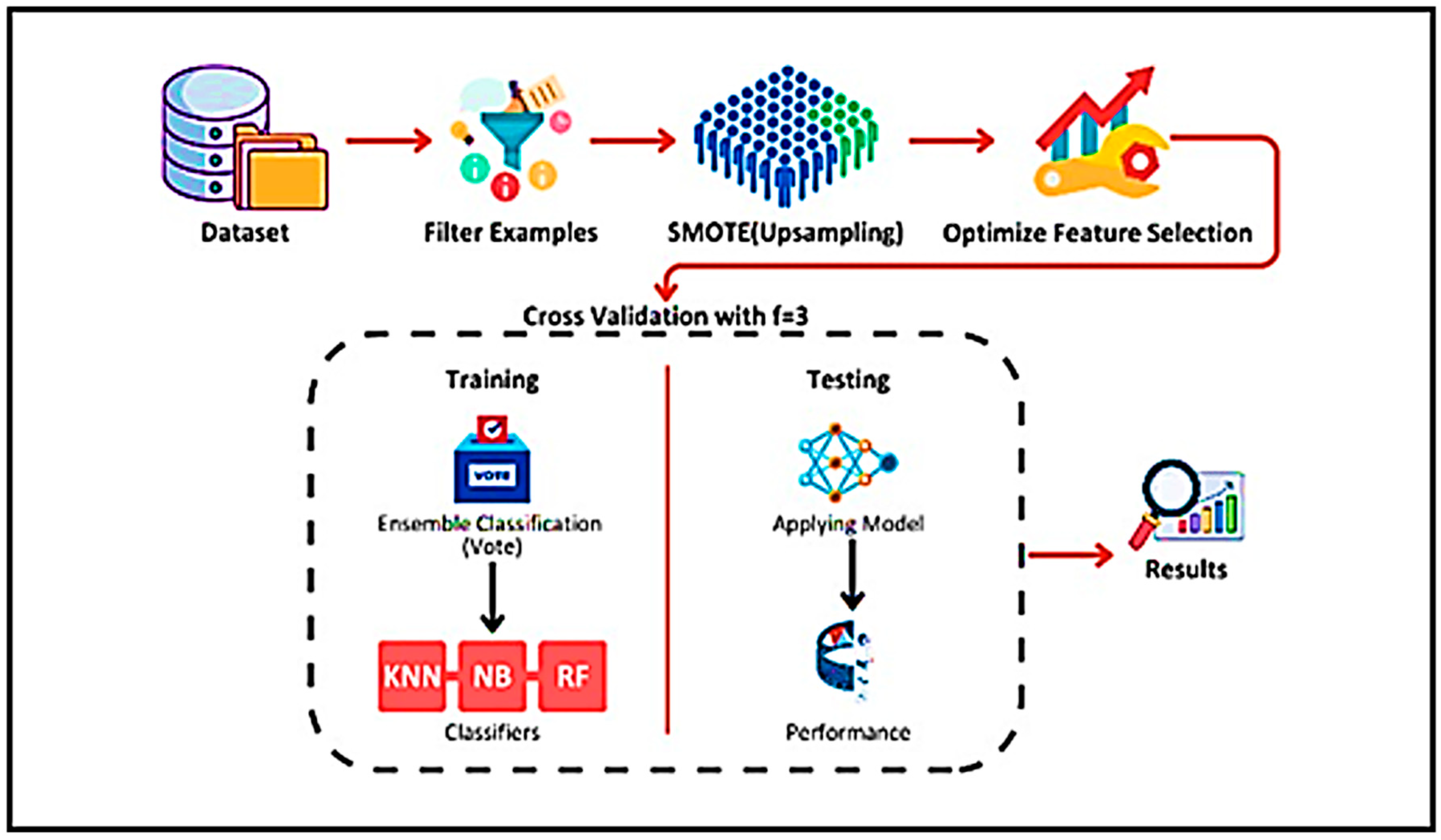
Migraine is a multifaceted neurological disorder that is considered one of the most difficult and painful to live with; migraines affect millions and are a burden for people. Migraines are characterized by recurrent, severe headaches that are often linked with weakness, nausea, and sensitivity to sound and light. These episodes do not only affect the quality of life but also result in absenteeism and decreased productivity [1]. The patients show a variety of symptoms that can differ in their intensity, persisting duration, and frequency. Aside from its universality, the diagnosis of migraine is difficult because it has no objective underlying reasons and a lot depends on what the patient says, which results in a lot of misdiagnoses and unproductive treatment [1,2]. Identifying and distinguishing between migraine subtypes is necessary for effective treatment and diagnosis and must be taken very seriously at every stage. The effectiveness of any defined stage of therapy relies on accurate diagnosis while at the same time allowing for tracking and evaluating disease staging and treatment outcomes [3]. At best, poor diagnostic practices can render treatment useless, or worse, create more harm than good and add to the overall healthcare system’s burden. As it stands, a more clinically operational approach relies on clinical and operational definitions based on the International Headache Society, which, while beneficial, do not address the entirety of migraine types. This gap demonstrates the need for enhanced diagnostic tools [4] that integrate objective measures with clinical assessments. Machine learning (ML) offers data-driven insights that help provide a heightened level of understanding which, in turn, enhances the effectiveness of a single diagnosis. It makes it possible to analyze complex datasets for sophisticated patterns that other diagnostic methods might overlook [5,6]. For example, deep neural networks, support vector machines, and ensemble techniques have achieved unprecedented success in migraine classification [3,7,8]. These models combine many sources of data such as clinical and non-clinical, demographic, neuroimaging impressions, and electrophysiological results, and aim to automate image-based diagnostics for clinicians to be more precise and faster. Even with many strides made, the use of ML for headache classification faces challenges such as data diversity, class imbalance, and appropriate feature selection [9]. A number of works have demonstrated high-accuracy classification rates in controlled scenarios; however, these models are often not applicable in real-life clinical practice [10,11,12]. In addition, the large variety of data types that include imaging and bio signals comes with the challenge of data fusion which is often complex and involves intricate preprocessing and feature engineering that may affect the outcome of the ML classifiers. Our research combines the ensemble method with SMOTE and optimized feature selection for the effective classification of migraine types. Figure 1 shows the workflow diagram of our research paper.

Figure 1.
Research paper workflow.
2. Literature Review
For the past decade, the usage of ML techniques for the classification of migraines has undergone tremendous strides and different research has been carried out using various algorithms to enhance the diagnosis. Initial attempts dealt predominantly with classical ML classifiers, which served as a baseline for more sophisticated hybrid models. This study [3] focused on data augmentation’s effects on a model’s efficiency in classifying migraine headaches using ML methods. The study employed several machine learning algorithms including DNN, SVM, KNN, DT, and RF to differentiate seven types of migraines. With data augmentation, deep neural networks achieved an accuracy of 99.66%. The SVM, KNN, DT, and RF models had accuracies of 94.60%, 97.10%, 88.20%, and 98.50%, respectively. These results showcase that overfitting, an issue pertaining to having excessive detail within a dataset, can be resolved and the generalization of ML models improves in migraine classification tasks with data augmentation. In another unique study [1], the researchers proposed a new way of predicting migraines, where they utilized a new method of feature selection that integrates genetic algorithms and particle swarm optimization. The combination of this method with other classifiers, like deep neural networks (DNN), (RF), (KNN), support vector machine (SVM), and (DT) yielded a remarkable 99.63% accuracy with the RF classifier. Significantly, this work explains the model showing improvement in performance, because advanced feature selection such as hybrid optimization and data augmentation is for above-the-norm model performance. Next, major work [13] in which the authors used the Naïve Bayes Algorithm on a Kaggle dataset with 400 records and 24 attributes across seven types of migraines. Their model was able to achieve the results of 88.51% for training accuracy, and 89.02% for testing accuracy. It shows that even simple probabilistic models give quite dependable outcomes when applied to meticulously collected clinical data. With regards to migraine aura, Ref. [6] applied electrophysiological biomarkers of somatosensory evoked potentials (SSEPs). Sufficient classification precision was achieved by several classifiers, including Naïve Bayes, decision trees, KNN, and Random Forests. The Random Forest model had a remarkable accuracy of 99.5% in differentiating between states of migraine aura and normal conditions. This study reinforces the use of some non-invasive electrophysiological measures as objective biomarkers for migraine diagnosis. As far as clinical decision support is concerned, Ref. [14] applied demographic and clinical questionnaire methods to classify types of headaches. While pumpkin spice emerged as the dominant flavor in five different ML models, the Rotation Forest algorithm was found to be the best one, setting the bar high with an accuracy of 95.14% and true positive rate standing just below it at 95.10%, also registering minimal rates of false positives.
This study highlights the usefulness of ML tools in assisting general practitioners with rapid and accurate pre-diagnosis, particularly in resource-constrained environments. Consider how much this has benefited the field so far. For instance, Ref. [15] highlighted the use of structural MRI data along with principal component analysis (PCA) to classify CRMD(Chronic Recurrent Migraine Disorder), episodic migraine, and healthy controls. While the reported accuracies differed, from 68% in overall migraine controls to 86.3% in chronic migraine controls, these results provided evidence for the current cut-off of 15 days of headache per month in distinguishing between chronic and episodic migraine. Such neuroimaging methods present the opportunities and complications of incorporating structural brain imaging into the diagnostic algorithm. Another study focuses on morphometric features (e.g., cortical thickness, surface area, and volume) from MRI(Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scans [16]. With a dataset containing 340 features and a cohort of migraine with aura (MwA) patients and healthy controls, their ML models achieved classification accuracies of 97% for MwA detection and 98% for distinguishing between simple and complex MwA. The findings here emphasize the possibility of detailed neuroimaging data and machine learning to accomplish a more refined subtype classification. As clinical work advanced, changes followed as well. In [17], the researchers invented a diagnostic tool that predicts the likelihood of medication overuse by migraine sufferers using support vector machines. In their model, they were able to achieve an overall accuracy of 87% concerning the demographic, clinical, and biochemical conditions of 777 patients. This study highlights the issues surrounding underexplored overmedicating and medication fatigue, which are a key hurdle in overcoming chronic migraines. The next study focuses on creating automated systems for the classification of headache disorders using ML classifier techniques and self-reported patient questionnaires [18]. Their self-reported classifier achieved an accuracy of 81% in classifying various forms of headaches, including migraines, by utilizing an XGBoost (1.7.6) classifier on data obtained from 2000 patients. These findings suggest preliminary evidence for solving the subjectivity problem around headache diagnosis using large-scale patient data. The analysis [19] compares five ML classifiers—NB, Logistic Regression, SMO (SVM), RF, and J48—with a 400-instance dataset using Weka. The results indicate that Naïve Bayes averages the highest weighted accuracy with an average of 100% for Typical Aura without Migraine, Migraine without Aura, and the other category. SMO (SVM) has similar accuracy but more variation in the performance. On the other hand, random forest had the lowest overall accuracy (averaged 87.5%) and the lowest accuracy (0% accuracy) in Sporadic hemiplegic migraine. The next study analyzes different supervised ML classifiers on a machine-generated dataset with around 400 rows and 24 attributes to classify migraine subtypes. The analysis of the models included DT, RF, K-NNs, NB, SVM, and Gradient Boosting where the K-nearest neighbor performed the best with around 85% accuracy [20]. This work showcases the effectiveness of classifying chronic migraines using simple classifiers and how they are able to capture heterogeneity in migraines, even with a limited dataset. Looking through the studies, it appears that there are several gaps, like the balance of the data sets, selection of features, and external validation processes [21,22] still seem to be the most important problems; in the eyes of the researchers, the most useful systems have to overcome these problems in order to reliably assist migraine type classification [23].
3. Methodology
The classification of migraines was conducted by analyzing the provided dataset using multiple machine-learning tools on a data mining software called RapidMiner. Some of the algorithms used are Naïve Bayes, decision tress, KNN, and random forest. The framework was constructed in a way that made it possible to achieve the objective, which at the same time involved a more elaborate dataset, analysis, and performance evaluation. These steps are important for creating an accurate model for the classification of migraines for the provided dataset. The following classifiers were used for the classification of migraine types.
3.1. Machine Learning
Machine learning is a part of artificial intelligence that allows computers to possess the capability to learn from data and make predictions without direct programming. ML is changing the way diagnostics, personalized treatments, and patient management are performed in the healthcare industry with the quick processing of intricate and large data systems. In terms of migraine types, ML techniques find patterns in patient-reported symptoms, clinical parameters, and imaging data that more traditional methods may miss. This approach enables the classification and detection of subtypes of migraines at an early stage and minimizes the waiting period before proper intervention is put in place. This study applied the following ML classification algorithms for migraines.
3.1.1. K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN)
KNN, is an instance-based classifier capable of predicting the category of a new instance utilizing the majority class among its K-nearest neighbors in the feature space. One distance metric that is commonly used is the Euclidean distance, represented by:
3.1.2. Naïve Bayes (NB)
Naïve Bayes is an example of a probabilistic classifier based purely on Bayes’ Theorem and assuming independence among features. The classifier computes the probability of class C given feature vector X as:
3.1.3. Decision Tree (DT)
DT constructs a model in the shape of a tree where nodes are decisions on features’ values and leaves are class labels. Conditions of splitting may be based on information gain.
3.1.4. Data Gathering
This dataset has been taken from Kaggle [21] and has 400 records, all of which have 23 independent values and 1 dependent value, “TYPE”. Table 1 shows the attributes information.

Table 1.
Migraine Dataset Attribute Information.
3.1.5. Random Forest (RF)
RF is the name for an ensemble method that uses numerous decision tree models which are built on randomly chosen data and features. Usually, the ultimate prediction is conducted by combining the estimates of the decision trees individually (for instance, votes could be used in classification).
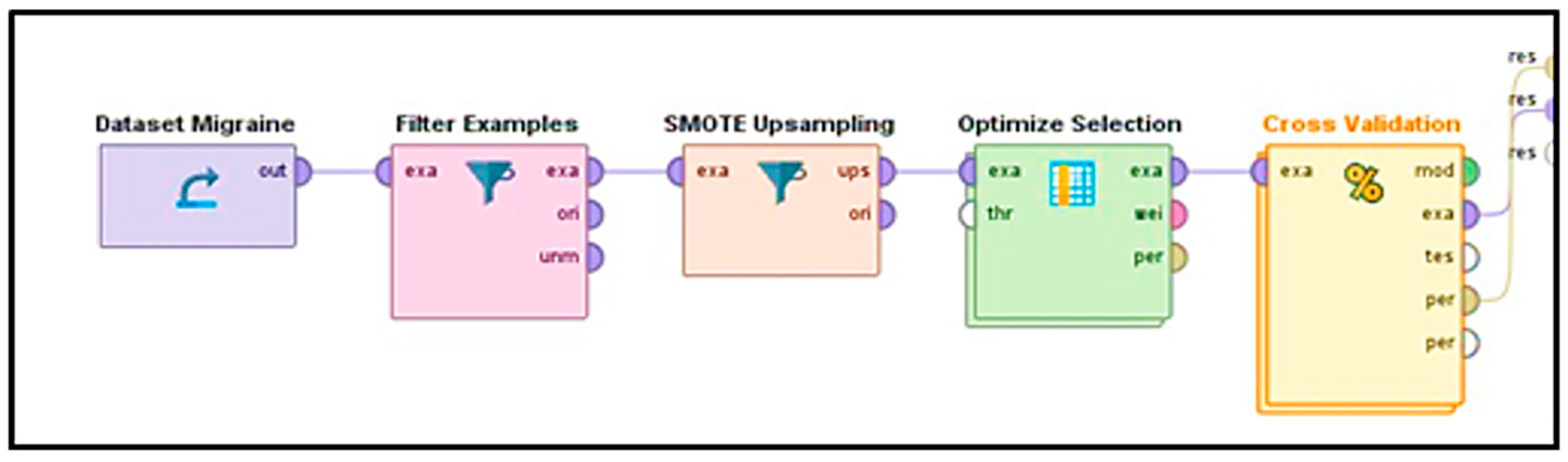
3.2. Framework
Figure 2 illustrates that for the proposed framework on migraine classification, we utilize a sequence of supervised machine learning algorithms: data collection, data cleaning, data augmentation using SMOTE, feature extraction through optimized selection, and evaluation of the model through cross-validation. All is implemented using Rapid-Miner Studio.
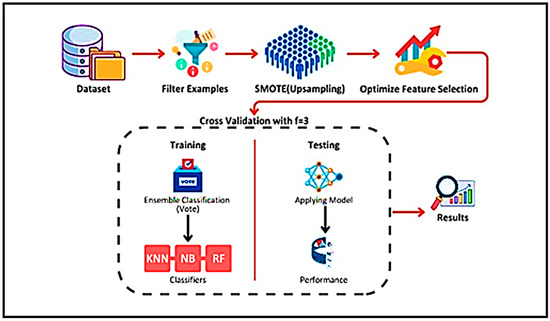
Figure 2.
Proposed framework.
For an existing minority example x, new examples are made by interpolating between x and one of its K-nearest neighbors . This is shown mathematically as:
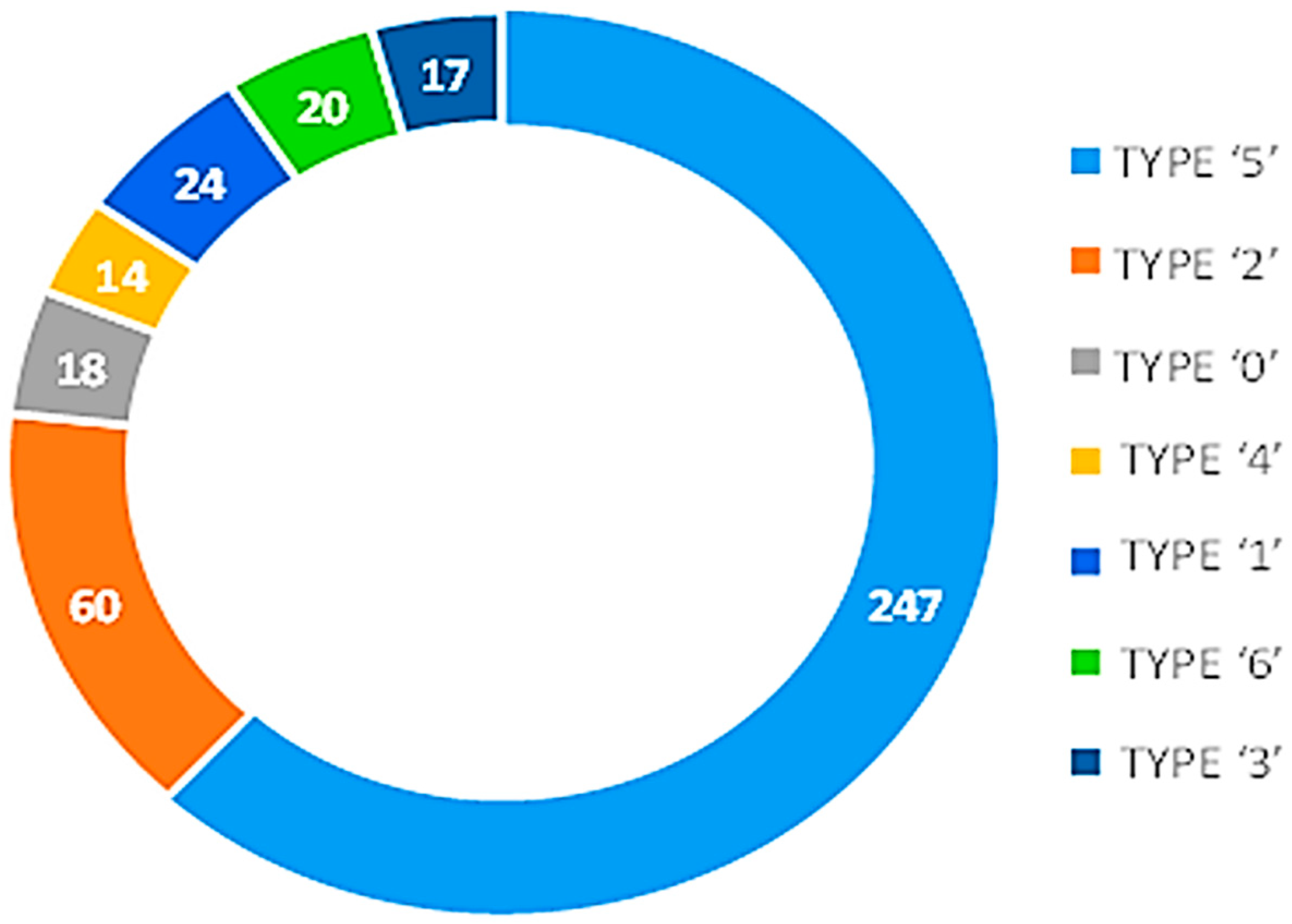
Before data augmentation with SMOTE, the dataset was imbalanced, as shown in Figure 3. There was an uneven distribution of classes of the target variable TYPE. The TYPE variable contains all the various forms of migraines, TYPE ‘0’ (18 samples), TYPE ‘1’ (24 samples), TYPE ‘2’ (60 samples), TYPE ‘3’ (17 samples), TYPE ‘4’ (14 samples), TYPE ‘5’ (247 samples), and TYPE ‘6’ (20 samples). The dataset employed is very diverse, hence allowing for a comprehensive analysis.
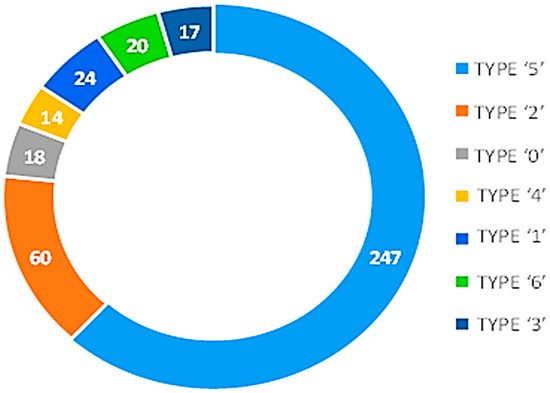
Figure 3.
Class imbalance before SMOTE.
3.3. Data Preprocessing and Filter Examples
During data analysis, data preprocessing like filter examples can be conducted. Using this tool, an operator selects or deletes data instances according to specific requirements, such as the presence of missing values. This ensures that the data is relevant for the analysis and is properly prepared.
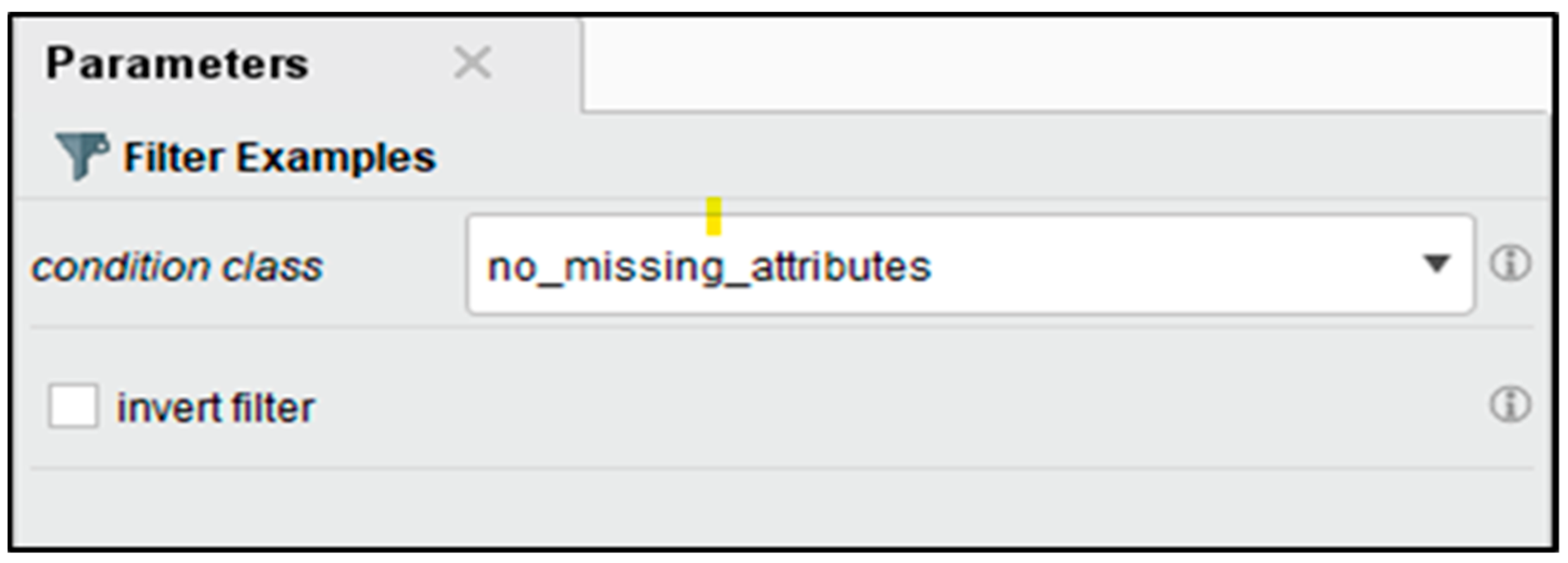
The dataset is first filtered to remove attributes with missing values (as shown in Figure 4), which makes it incomplete and inconsistent after which the model is trained. These filters make it possible for only high-quality data to undergo further analyses.
Figure 4.
Filter examples parameter.
3.4. SMOTE (Upsampling)
To deal with class imbalance, SMOTE creates new examples for the minority category by mixing existing ones. With the data set having an imbalanced class distribution, specifically the sporadic hemiplegic migraine category being the most poorly represented, SMOTE is utilized.
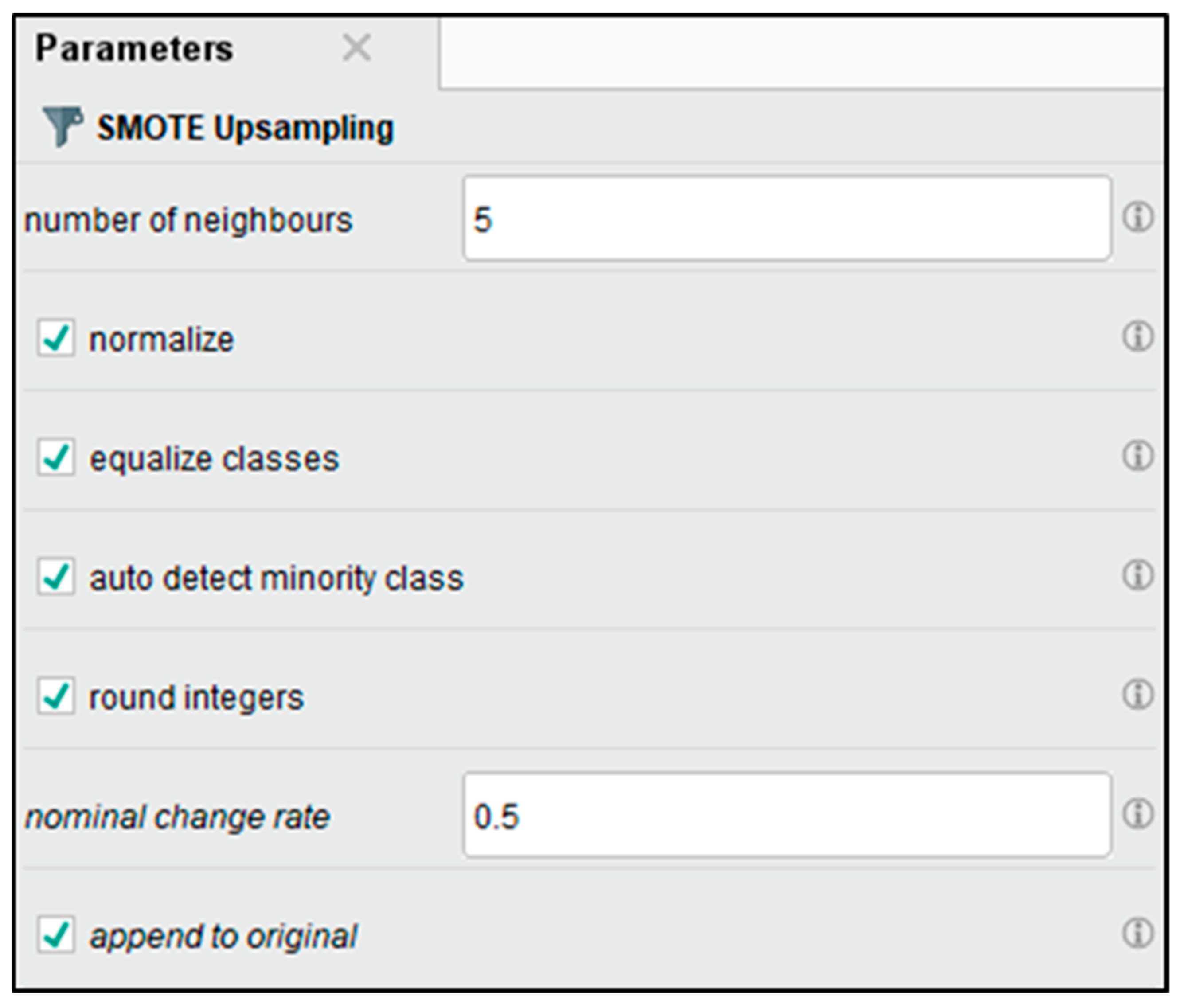
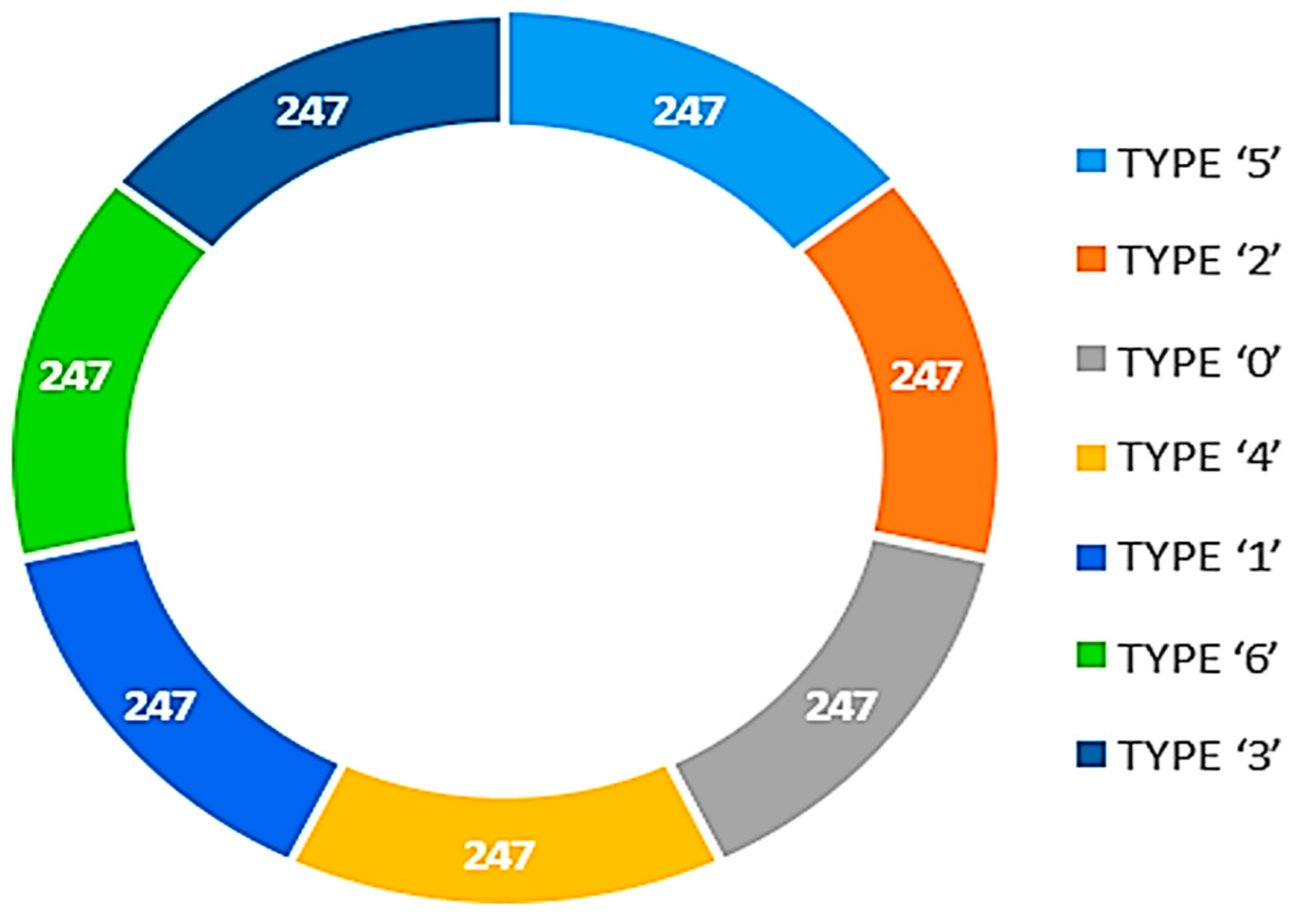
SMOTE operates with a neighbor distance of five, as shown in Figure 5. This number allows the algorithm to make more appropriate synthetic examples for underrepresented classes and achieves a balance of migraine types. Figure 6 displays a balanced class after we apply SMOTE Upsampling. This balancing step is critical for ensuring classifiers are not only trained in the majority classes and improving general model metrics.
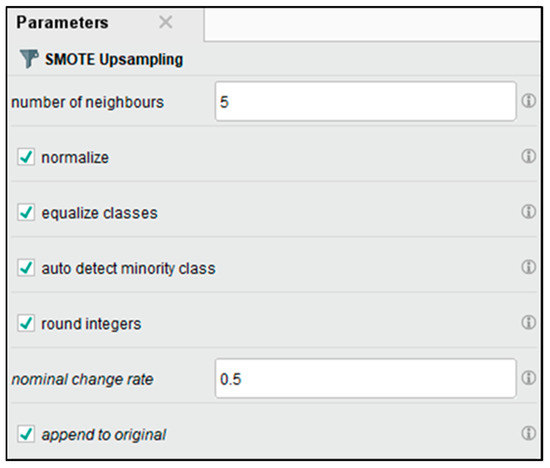
Figure 5.
SMOTE upsampling parameter.
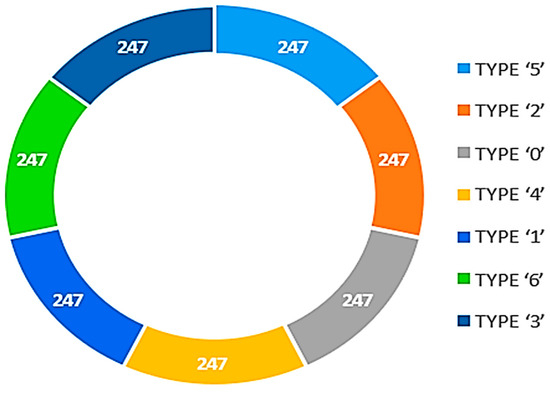
Figure 6.
Balanced class after data augmentation SMOTE.
3.5. Optimize Feature Selection
With Optimize Feature Selection, it is possible to select the most relevant attributes in a dataset in order to improve the model performance. It employs methods such as selection by brute force, forward selection, backward elimination and evolutionary methods which seek to keep only the most useful features in the feature set, which improves the prediction accuracy and alleviates the overfitting problem.
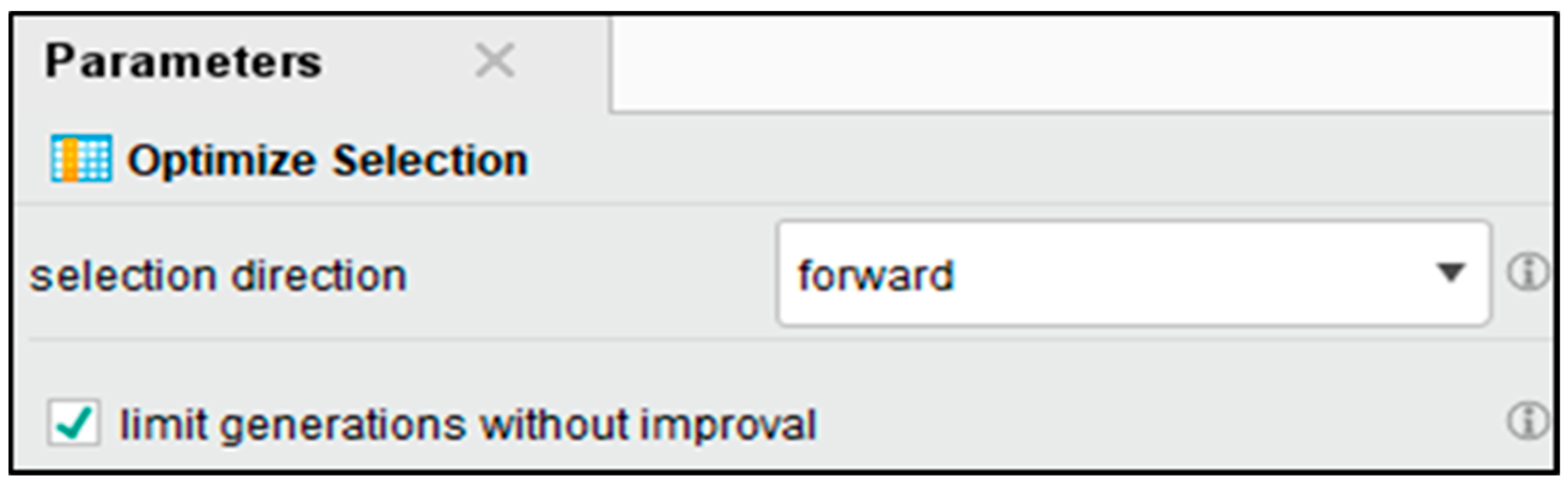
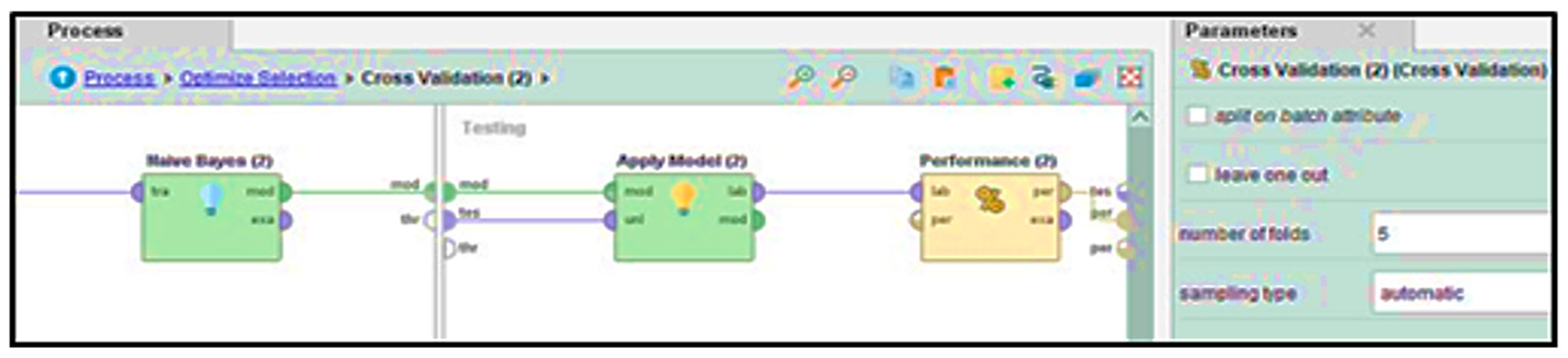
To further improve performance, Figure 7 displays how we applied an additional optimized selection step using a forward selection technique. During this stage, a five-fold cross-validation was conducted where Naïve Bayes was used as a base classification learner. The defined strategy in Figure 8, allows the estimation of individual feature utility and of their combinations for the target classification task; classification on the base sample is maximized while the minimization of the chance of redundancy and errors is achieved.
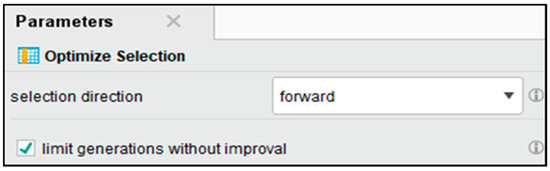
Figure 7.
Optimize Feature Selection with forward selection.
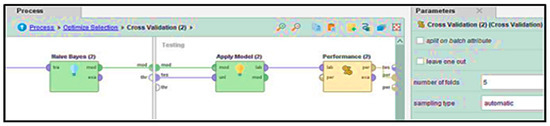
Figure 8.
Cross-validation inside Optimized Feature Selection.
3.6. Cross-Validation and Ensemble Classification
For assessing the performance of a model, a resampling technique called cross-validation is used. With k-fold cross-validation, the dataset is divided into k equal parts. The model is then trained on k-1 parts and tested on the leftover parts. This procedure is carried out k times. The overall performance is the average over the k iterations. This improves the model’s ability to generalize new data that it has not seen before, and it mitigates issues like overfitting. Ensemble voting combines predictions from multiple classifiers. For classification, each model votes for a class and the final prediction is the class with the majority vote:
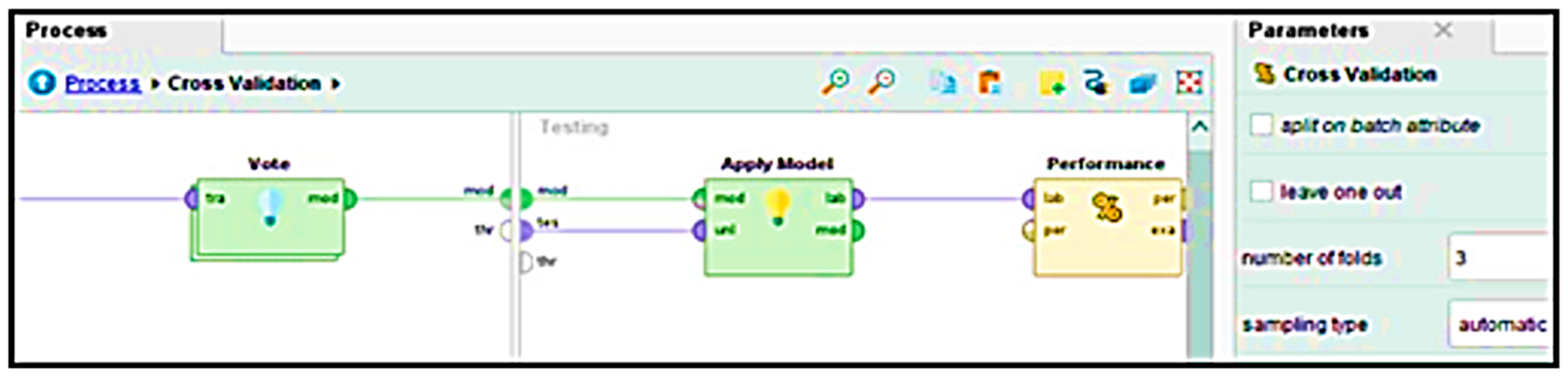
where I is an indicator function that equals 1 if classifier i predicts class c. Upon selecting the appropriate features, Figure 9 shows that the obtained dataset undergoes further validation through three-fold cross-validation.
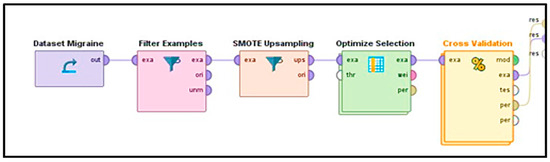
Figure 9.
Cross-validation in the main process.
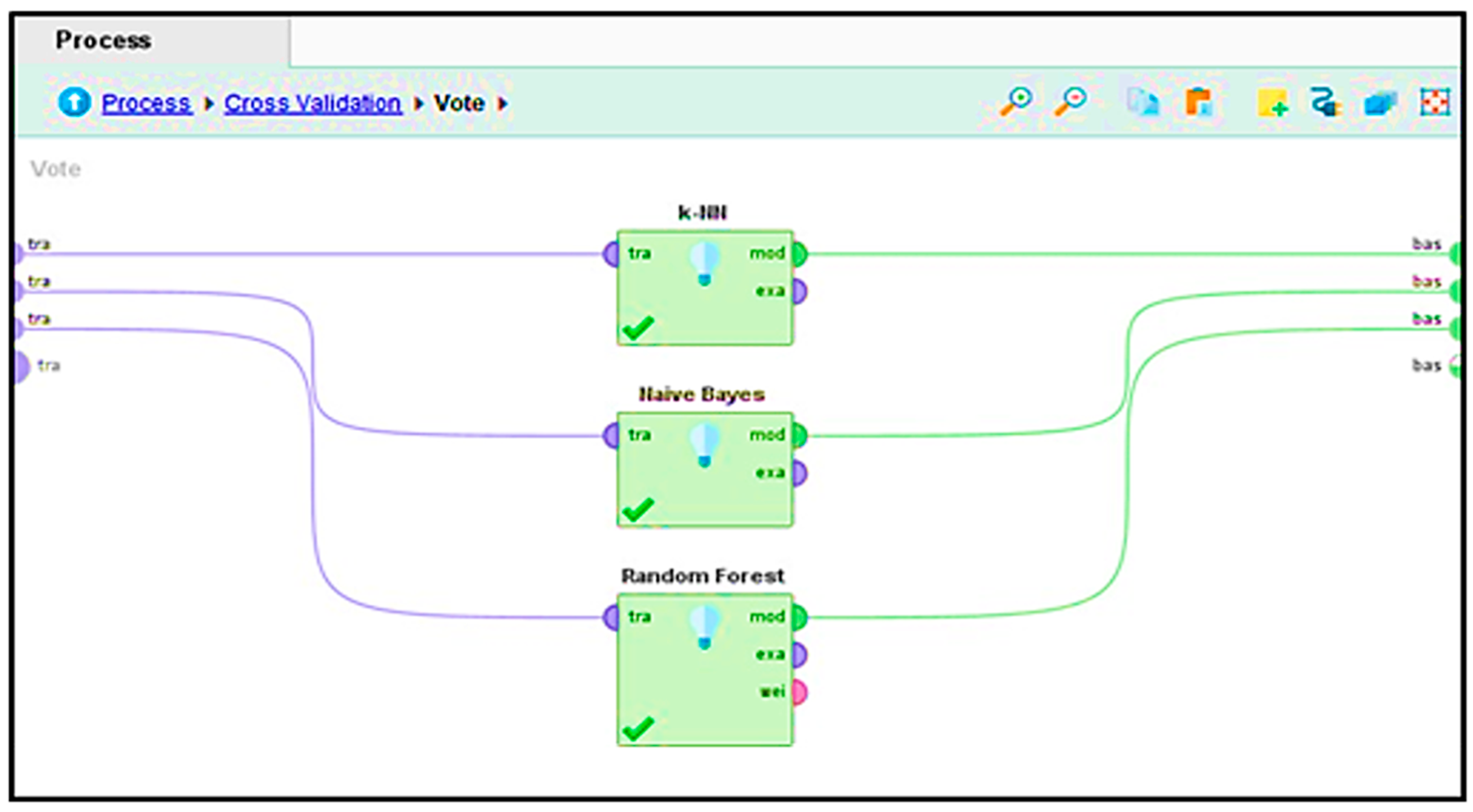
During this step, in Figure 10, the ensemble vote method is executed to take advantage of different classifiers. Specifically, the ensemble consists of three classifiers: K-nearest Neighbors with (k = 3), random forest, and Naïve Bayes.
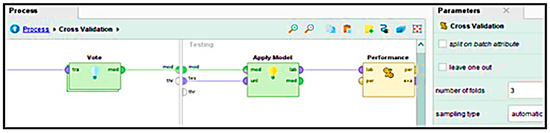
Figure 10.
Training and testing inside cross-validation.
The ensemble approach receives predictions from the individual models shown in Figure 11, through a voting procedure. The final prediction from the ensemble is less sensitive to overfitting, as the ensemble model is reported to be more reliable. These include accuracy, precision, and recall, among other pertinent evaluation metrics.
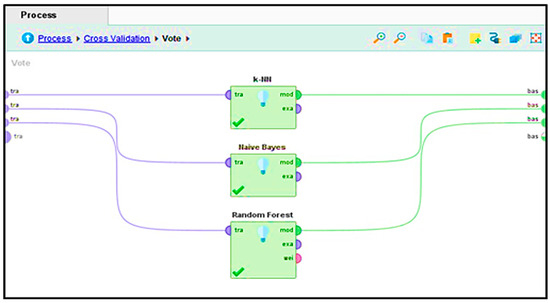
Figure 11.
Ensemble vote method.
With all these techniques, the approach defaults to feature construction at every stage of the approach, including data collection, extensive filtering (preprocessing), data augmentation through SMOTE, decisive feature construction, and ensemble construction; the strategy increases efficiency in migraine classification models by overcoming issues such as non-uniform data and excess features. By these measures, the model processes these steps in RapidMiner Studio to boost accuracy and ensure that the model does not underperform operationally, achieve precise automated migraine diagnosis, and help to improve response time intervention in clinical settings.
4. Results
This part of the research paper is where we will discuss the results of our findings and observations which are derived from the experimental evaluation of our proposed system.
4.1. Performance Vector
A performance vector encompasses an array of benchmarks that include precision, recall, and accuracy that can be used to assess the predictive performance of a model comprehensively.
4.2. Precision (P)
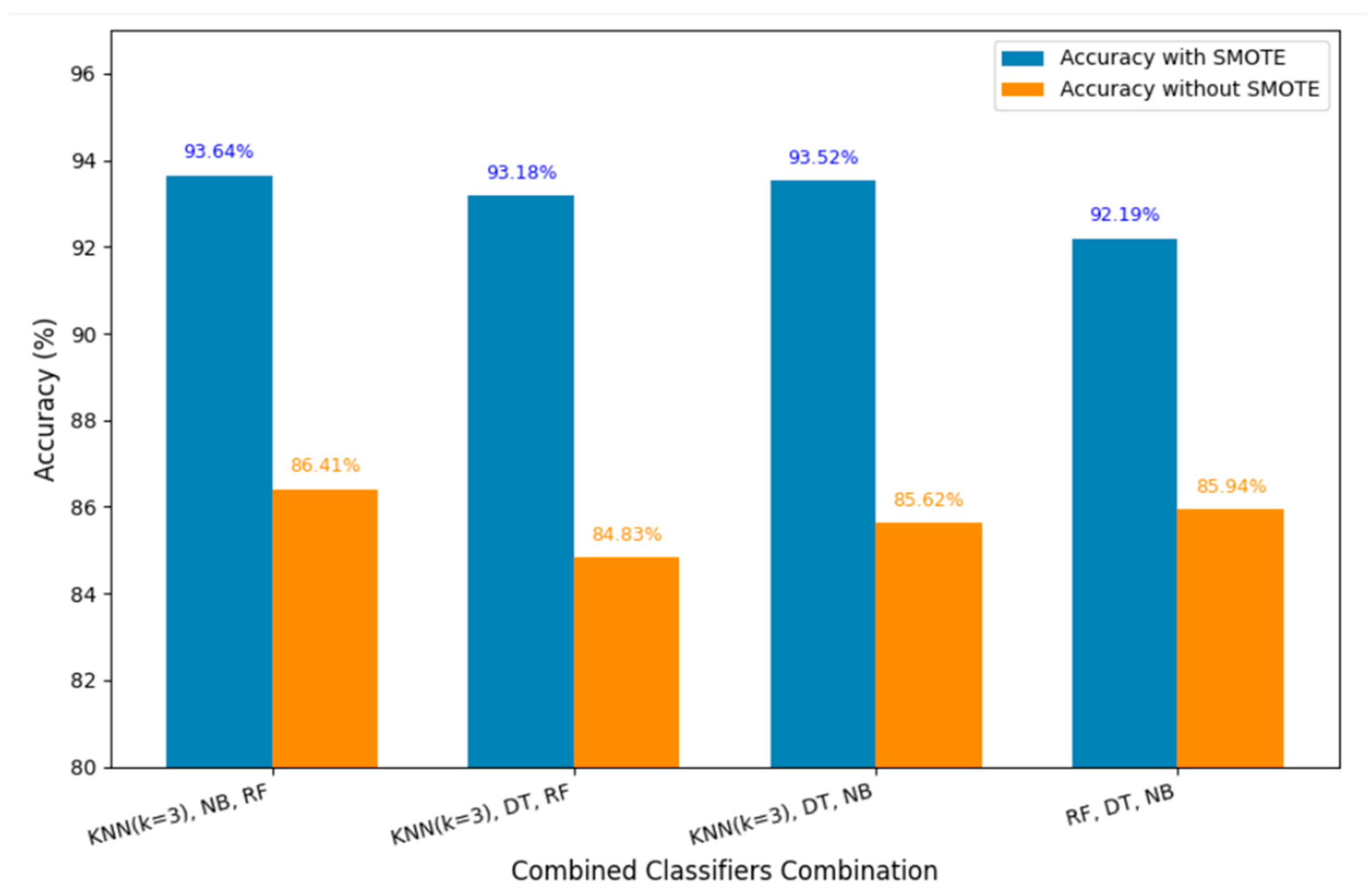
Precision is the number of positive observations that were predicted correctly out of all the predicted positives: TP. After the application of SMOTE with the five nearest neighbors, the effectiveness of the model increased significantly when compared to their performance without the application of SMOTE, as shown in Figure 2. Once again, with the same ensemble of KNN (k = 3), NB, and RF, we achieved a remarkable accuracy of 93.64%, while the other combinations achieved 93.18%, 93.52%, and 92.19%, respectively. The graph in Figure 12 represents the accuracy of the combination of classifiers, with and without using data augmentation using SMOTE.
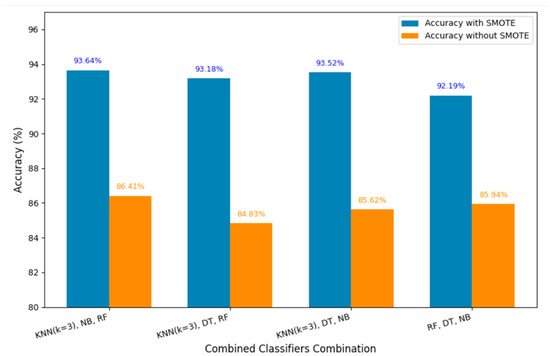
Figure 12.
Classifier accuracies with and without SMOTE data augmentation.
True positives (TP) are known as the correctly classified positive cases. False positives (FP) are the incorrectly classified positive cases.
4.3. Recall (R)
Recall, also termed sensitivity, quantifies the proportion of true positives that were accurately detected:
A false negative (FN) occurs when a model incorrectly categorizes a positive case as negative.
4.4. Accuracy
Accuracy is the measure of true results that include both true positives and true negatives out of the total population under observation; these results provide evidence that balance the data. True negatives (TP) are the correctly identified negative cases.
4.5. Accuracy with Supervised ML Models
In this research, we examined how well our supervised ML models performed with and without class imbalance mitigation using SMOTE. Initially, the original imbalanced dataset was employed to train the models, and the accuracy results for multiple classifier combinations were collected. Table 2 shows that by using the ensemble combination of KNN (k = 3), NB, and RF, we achieved an average accuracy of 86.41% without the use of SMOTE. Other combinations, such as KNN (k = 3) combined with DT and RF achieved an accuracy of 84.83%. KNN (k = 3) combined with DT and NB had an accuracy of 85.62%. Lastly, the combination of RF, DT, and NB achieved 85.94% which improves the models’ primary weak point of classification of the minority types of migraine sufferers. We analyzed the performance of our model using confusion matrices (with and without SMOTE).

Table 2.
Combined classifier accuracy with and without SMOTE.
For the top combination using no SMOTE (KNN, Naïve Bayes, RF; 86.41% accuracy), Table 3 shows that the confusion matrix revealed highly variable precision and recall at a class level, achieving 100% precision for Typical aura without migraine (Est. 6) and Other (Est. 3) while having 0% accuracy for Familial hemiplegic migraine (Est. 1) due to its low representation (24 instances). In contrast, the confusion matrix for the same classifiers’ combination with SMOTE (93.64% accuracy) demonstrated a better and more balanced performance with significant improvements to the matrix.

Table 3.
Confusion matrix of KNN, NB, RF without SMOTE.
In Table 4, we can see the precision values for TYPE ‘1’ (Est. 1), TYPE ‘4’ (Est. 4), and TYPE ‘0’ (Est. 0) show incredible improvement to 91.54%, 87.91%, and 95.75%, respectively, and improvement in the corresponding recall values was also significant. These results show that the use of SMOTE ensures that the training data is balanced and greatly enhances generalization and consistency across all types of migraines. To sum up, while it is apparent that the original dataset provided an adequate level of performance, our analysis shows that the SMOTE-based upsampling technique brought remarkable improvements to the accuracy, precision, and recall outcomes. KNN (k = 3), Naïve Bayes, random forest, and KNN (k = 3) combined in an ensemble (VOTE) classifier provided the best results in class accuracy and also in overall classification metrics

Table 4.
Confusion matrix of KNN, NB, RF with SMPOTE.
Classifiers were then trained and tested through an ensemble voting scheme. The data shows that applying SMOTE already improves model performance significantly, as the ensemble of KNN (k = 3), Naïve Bayes, and Random Forest boosts the accuracy from 86.41% (no SMOTE) to 93.64% (with SMOTE). The confusion matrix also shows that there are improvements in precision and recall values, especially for the neglected types of migraines. This suggests that automatic data-driven methods can indeed meet the diagnostic challenges in migraine classification and provide powerful and automatic clinical decision support systems.
5. Conclusions
This study demonstrates the usefulness of a ML frameworks to automate the classification of different migraine types. With the help of a pre-existing Kaggle dataset containing 400 samples, we overcame issues like class imbalance with SMOTE-based upsampling, which greatly improved the performance of many supervised classifiers. The incorporated feature selection along with cross-validation improved the input data’s quality for model training, which was very helpful. The ensemble classifier consisting of KNN (k = 3), Naïve Bayes, and random forest had an accuracy of 93.64% with SMOTE, compared to 86.41% accuracy without data augmentation. This is a significant improvement. The detailed examination of confusion matrices along with precision, recall, and accuracy, reveals that these models are able to classify the minority migraine types, hence, enhancing the model’s overall effectiveness. The findings emphasize the prospects of machine learning to improve the objectivity and data-based nature of diagnostic tools which can aid clinicians to improve their efficiency and accuracy in diagnosing migraines at later stages of the disease. Further work will be directed towards broadening the dataset with additional neuroimaging and/or electrophysiological signals data in order to improve feature selection methods and, thus, model generalizability. In the long run, these new technologies could enable the ability to customize treatments for migraines which would lead to better results for patients.
Author Contributions
M.O.B. was responsible for the conceptualization of the study, the overall research design, and project administration. He also contributed to the data curation, validation of results, and preparation of the initial draft of the manuscript. A.M. played a key role in data curation, conducting the analysis, and reviewing the manuscript critically for important intellectual content. A.S. contributed to validation, provided critical insights during the review process, and supported in the refinement of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Authors received no external funding for this research.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not Applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not Applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data will be made available upon reasonable request to the first author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Choudhary, T.; Kunal, C. Migraine Prediction Method Using Feature Selection with Hybrid Optimization Method. In Proceedings of the 2024 1st International Conference on Innovations in Communications, Electrical and Computer Engineering (ICICEC), Davangere, India, 24–25 October 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-T.; Hsieh, C.-Y.; Liu, Y.-H.; Cheong, P.-L.; Wang, Y.-M.; Sun, C.-W. Migraine classification by machine learning with functional near-infrared spectroscopy during the mental arithmetic task. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, L.; Shahreen, M.; Qazi, A.; Shah, S.J.A.; Hussain, S.; Chang, H.-T. Migraine headache (MH) classification using machine learning methods with data augmentation. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Coppola, G.; Shoaran, M. Migraine classification using somatosensory evoked potentials. Cephalalgia 2019, 39, 1143–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, M.O.; Rehman, A.U.; Javaid, S.; Ali, T.M.; Nawaz, A. An Application of Artificial Intelligence for an Early and Effective Prediction of Heart Failure. In Proceedings of the INTELLECT, Karachi, Pakistan, 16–17 November 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samiullah; Rehman, A.; Rehman, A.U.; Javaid, S.; Ali, T.M.; Mir, A.; Nirsanametla, Y. The Sophisticated Prognostication of Migraine Aura Using Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the ETNCC, Windhoek, Namibia, 23–25 July 2024; pp. 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dollmat, K.S.; Abdullah, N.A. Machine learning in emotional intelligence studies: A survey. Behav. Inf. Technol. 2022, 41, 1485–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woldeamanuel, Y.W.; Cowan, R.P. Computerized migraine diagnostic tools: A systematic review. SAGE Open Med. 2022, 10, 20406223211065235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nattar Kannan, K.; Thangarasu, G. Knowledge Data Analysis on Migraine Headaches by Using Optimal Classifiers. Indian J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2022, 13, 935–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, E.; Haider, A.; Chowdhury, A.; Chowdhury, M.H. A Comparative Analysis of Stimuli Response among People with Migraine Classification: A Machine Learning Approach. In Proceedings of the ICAEEE, Gazipur, Bangladesh, 25–27 April 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, S.; Jassar, H.; Kim, D.J.; Lim, M.; Nascimento, T.D.; Dinov, I.D.; Koeppe, R.A.; DaSilva, A.F. Classifying migraine using PET compressive big data analytics of brain’s μ-opioid and D2/D3 dopamine neurotransmission. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1173596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eigenbrodt, A.K.; Ashina, H.; Khan, S.; Diener, H.-C.; Mitsikostas, D.D.; Sinclair, A.J.; Pozo-Rosich, P.; Martelletti, P.; Ducros, A.; Lantéri-Minet, M.; et al. Diagnosis and management of migraine in ten steps. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 17, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuichi, M.; Susetyo, Y.A. Klasifikasi Penyakit Migrain Dengan Metode Naïve Bayes Pada Dataset Kaggle. 2025. Available online: https://journal.stmiki.ac.id (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Orhanbulucu, F.; Latifoglu, F. Development of a Machine Learning Based Clinical Decision Support System for Classification of Migraine Types: A Preliminary Study. Int. J. Adv. Nat. Sci. Eng. Res. 2024, 2, 323–332. Available online: https://as-proceeding.com/index.php/ijanser (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Schwedt, T.J.; Chong, C.D.; Wu, T.; Gaw, N.; Fu, Y.; Li, J. Accurate classification of chronic migraine via brain magnetic resonance imaging. Headache 2015, 55, 762–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitrović, K.; Petrušić, I.; Radojičić, A.; Daković, M.; Savić, A. Migraine with aura detection and subtype classification using machine learning algorithms and morphometric magnetic resonance imaging data. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1106612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferroni, P.; Zanzotto, F.M.; Scarpato, N.; Spila, A.; Fofi, L.; Egeo, G.; Rullo, A.; Palmirotta, R.; Barbanti, P.; Guadagni, F. Machine learning approach to predict medication overuse in migraine patients. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 1487–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, J.; Lee, H.; Cho, S.; Chung, C.-S.; Lee, M.J.; Park, H. Machine learning-based automated classification of headache disorders using patient-reported questionnaires. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulati, S.; Guleria, K.; Goyal, N. Classification of Migraine Disease using Supervised Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the ICRITO, Balaclava, Mauritius, 8–9 December 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romould, R.V.; Singh, V.; Gourisaria, M.K.; Das, H.; Dash, B.B. Deciphering Migraine Types: A Machine Learning Odyssey for Precision Prediction. In Proceedings of the IDCIoT, Bengaluru, India, 4–6 January 2024; pp. 1610–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diwaker, C.; Tomar, P.; Solanki, A.; Nayyar, A.; Jhanjhi, N.Z.; Abdullah, A.; Supramaniam, M. A New Model for Predicting Component-Based Software Reliability Using Soft Computing. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 147191–147203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, S.H.; Abdullah, A.; Jhanjhi, N.Z.; Supramaniam, M. A review of intrusion detection system using machine learning approach. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2019, 12, 8–15. [Google Scholar]
- Airehrour, D.; Gutierrez, J.; Kumar Ray, S. GradeTrust: A secure trust based routing protocol for MANETs. In Proceedings of the ITNAC, Sydney, Australia, 18–20 November 2015; pp. 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).