A Deep Convolutional Neural Network-Based Model for Aspect and Polarity Classification in Hausa Movie Reviews †
Abstract
1. Introduction
Background
2. Literature Review
3. Methodology
3.1. Dataset Description
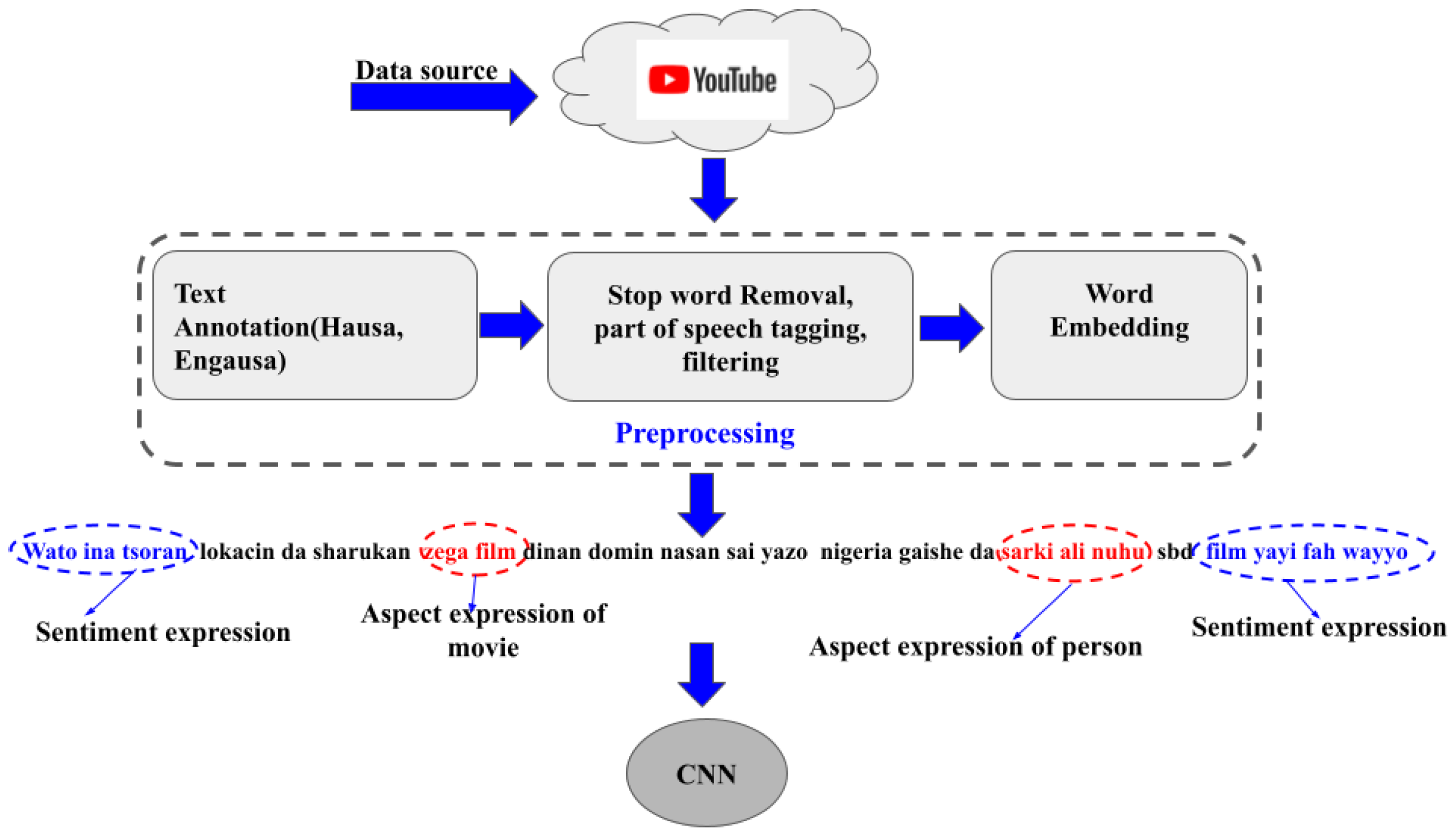
3.2. Dataset Collection and Preprocessing
3.3. Aspect Term Extraction Processing
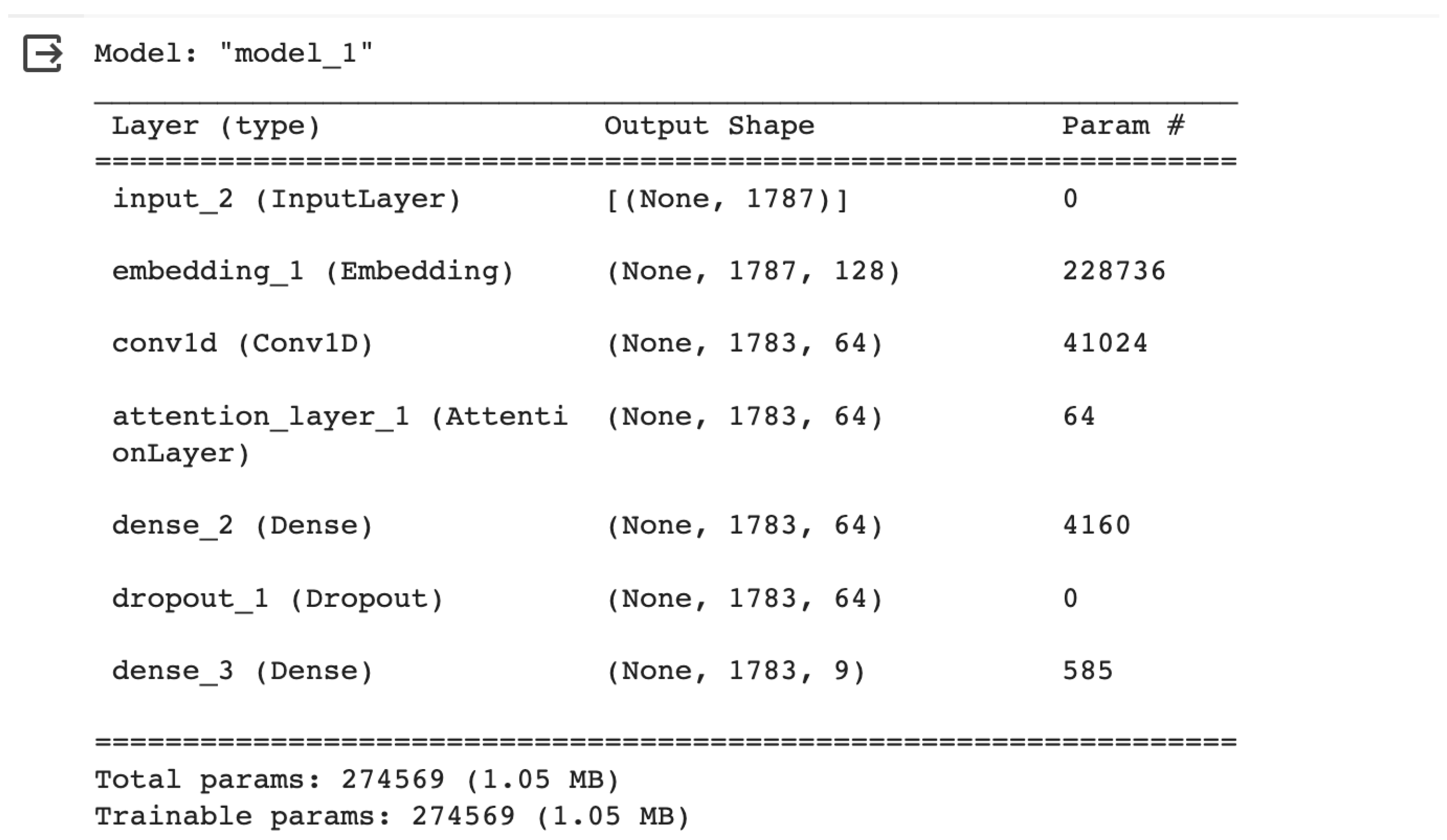
3.4. Model Building
3.5. Performance Metrics
- Accuracy is the number of successfully categorized instances (aspect-based sentiment) divided by the total number of cases (aspect-based sentiment instances). It can be calculated using the following formula:
- Precision is calculated as the proportion of true positive instances (positive sentiment polarity) correctly classified as positive. The formula for precision is as follows:
- Recall, also known as sensitivity, is the proportion of positive instances correctly classified as positive. The formula for recall is given by
- F1 Score: The F1 score is a metric that combines both precision and recall, striking a balance between them. It can be computed using the following formula:
4. Result and Discussion
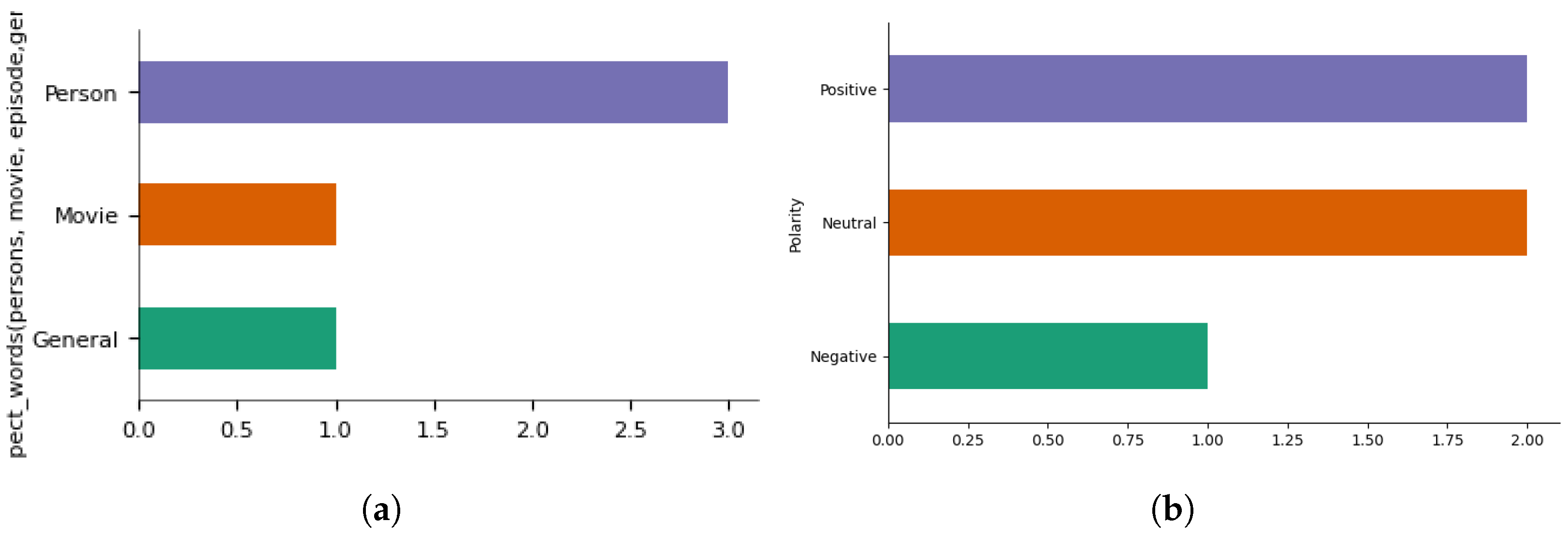
4.1. Preliminary Analysis
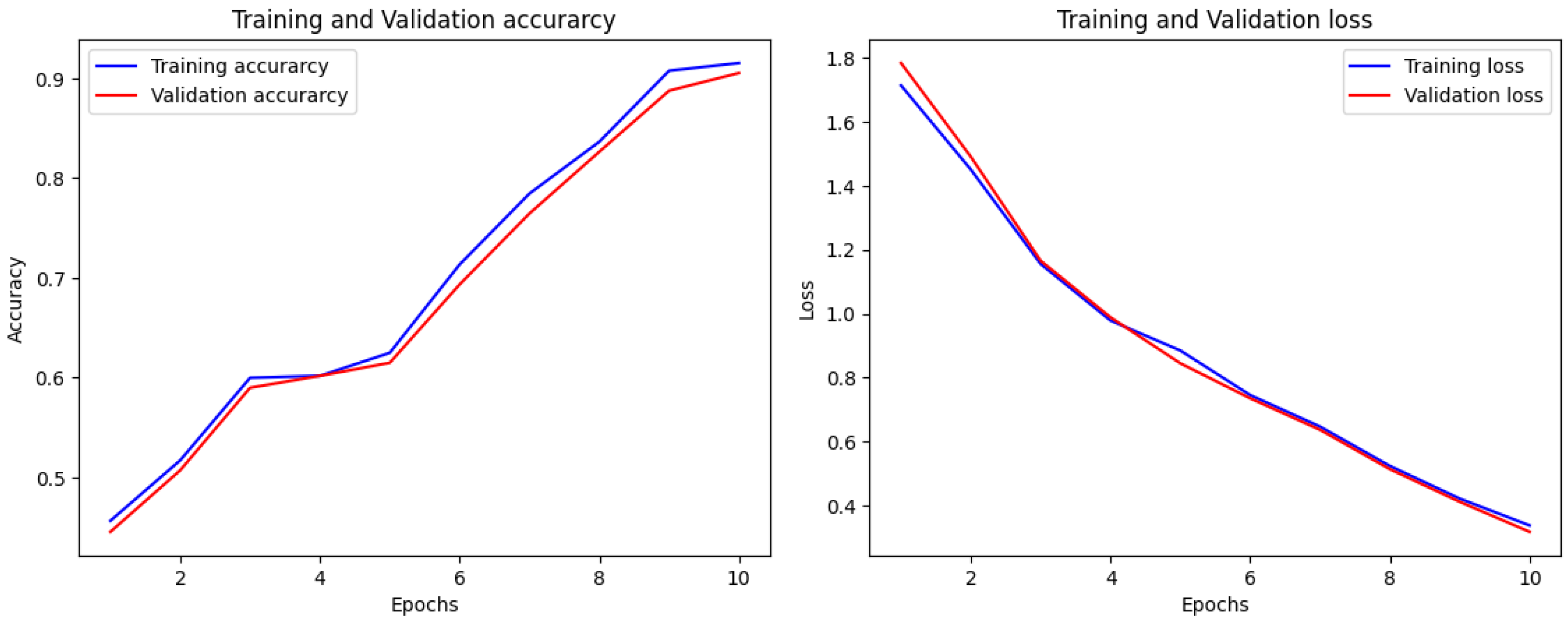
4.2. Performance of the Proposed Model
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hamada, M. Visual tools and examples to support active e-learning and motivation with performance evaluation. In International Conference on Technologies for E-Learning and Digital Entertainment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 147–155. [Google Scholar]
- Hamada, M.; Odu, N.B.; Hassan, M. A fuzzy-based approach for modelling preferences of users in multi-criteria recommender systems. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 12th International Symposium on Embedded Multicore/Many-core Systems-on-Chip (MCSoC), Hanoi, Vietnam, 12–14 September 2018; pp. 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Onalaja, S.; Romero, E.; Yun, B. Aspect-based sentiment analysis of movie reviews. SMU Data Sci. Rev. 2021, 5, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Sani, M.; Ahmad, A.; Abdulazeez, H.S. Sentiment analysis of Hausa language tweet using machine learning approach. J. Res. Appl. Math. 2022, 8, 6–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, K.; Rashad, A.; Khan, M.; Ghadi, Y.; Aljuaid, H.; Nawaz, Z. A deep neural network-based approach for sentiment analysis of movie reviews. Complexity 2022, 2022, 5217491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, C.N.; Moreno-García, M.N.; De la Prieta, F. Hybrid deep learning models for sentiment analysis. Complexity 2021, 2021, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, H. Beyond anonymity, or future directions for internet identity research. New Media Soc. 2006, 8, 859–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, B.S.; Alhassan, M.A.; Inuwa-Dutse, I. #EndSARS protest: Discourse and mobilisation on Twitter. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.06176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhmanov, O.; Schlippe, T. Sentiment analysis for Hausa: Classifying students’ comments. In Proceedings of the 1st Annual Meeting of the ELRA/ISCA Special Interest Group on Under-Resourced Languages, Marseille, France, 24–25 June 2022; pp. 98–105. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, S.H.; Adelani, D.I.; Ruder, S.; Ahmad, I.S.; Abdulmumin, I.; Bello, B.S.; Choudhury, M.; Emezue, C.C.; Abdullahi, S.S.; Aremu, A.; et al. Naijasenti: A Nigerian Twitter sentiment corpus for multilingual sentiment analysis. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.08277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakar, A.I.; Roko, A.; Bui, A.M.; Saidu, I. An enhanced feature acquisition for sentiment analysis of English and Hausa tweets. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2021, 12, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandam, A.Y.; Muhammad, F.A.; Inuwa-Dutse, I. Online threats detection in Hausa language. In Proceedings of the 4th Workshop on African Natural Language Processing, Kigali, Rwanda, 1 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Salau, L.; Hamada, M.; Prasad, R.; Hassan, M.; Mahendran, A.; Watanobe, Y. State-of-the-art survey on deep learning-based recommender systems for e-learning. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Bing, L.; Li, P.; Lam, W.; Yang, Z. Aspect term extraction with history attention and selective transformation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.00760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellucci, G.; Filice, S.; Croce, D.; Basili, R. Unitor: Aspect based sentiment analysis with structured learning. In Proceedings of the 8th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval 2014), Dublin, Ireland, 23–24 August 2014; pp. 761–767. [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar, M.S.; Gupta, D.; Ekbal, A.; Bhattacharyya, P. Feature selection and ensemble construction: A two-step method for aspect based sentiment analysis. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2017, 125, 116–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, A.; Zhang, X.; Song, X. Unrestricted attention may not be all you need–masked attention mechanism focuses better on relevant parts in aspect-based sentiment analysis. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 8518–8528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, A.; Huang, L.; Bhayani, R. Twitter sentiment analysis. Entropy 2009, 17, 252. [Google Scholar]
- Saif, H.; He, Y.; Alani, H. Semantic sentiment analysis of Twitter. In The Semantic Web–ISWC 2012: 11th International Semantic Web Conference, Boston, MA, USA, 11–15 November 2012; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Proceedings, Part I; pp. 508–524. [Google Scholar]
- Krishna, A.; Akhilesh, V.; Aich, A.; Hegde, C. Sentiment analysis of restaurant reviews using machine learning techniques. In Emerging Research in Electronics, Computer Science and Technology: Proceedings of International Conference, ICERECT 2018; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 687–696. [Google Scholar]
- Rhanoui, M.; Mikram, M.; Yousfi, S.; Barzali, S. A CNN-BiLSTM model for document-level sentiment analysis. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 2019, 1, 832–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basiri, M.E.; Kabiri, A. Sentence-level sentiment analysis in Persian. In Proceedings of the 2017 3rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis (IPRIA), Shahrekord, Iran, 19 –20 April 2017; pp. 84–89. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, M.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, L. Attention-based LSTM for aspect-level sentiment classification. In Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Austin, TX, USA, 1–5 November 2016; pp. 606–615. [Google Scholar]
- Socher, R.; Perelygin, A.; Wu, J.; Chuang, J.; Manning, C.D.; Ng, A.Y.; Potts, C. Recursive deep models for semantic compositionality over a sentiment treebank. In Proceedings of the 2013 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Seattle, WA, USA, 18–21 October 2013; pp. 1631–1642. [Google Scholar]
- Sebastiani, F.; Esuli, A. Sentiwordnet: A publicly available lexical resource for opinion mining. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation, Genoa, Italy, 22–28 May 2006; pp. 417–422. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, D.; Qin, B.; Liu, T. Aspect level sentiment classification with deep memory network. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1605.08900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Liu, B.; Shu, L.; Yu, P.S. BERT post-training for review reading comprehension and aspect-based sentiment analysis. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.02232. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, W.; Li, T. Aspect-based sentiment analysis with gated convolutional networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.07043. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, D.; Qin, B.; Feng, X.; Liu, T. Effective LSTMs for target-dependent sentiment classification. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1512.01100. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulrashid, I.; Ahmad, I.S.; Musa, A.; Khalafalla, M. Impact of social media posts’ characteristics on movie performance prior to release: An explainable machine learning approach. In Electronic Commerce Research; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Cham, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Zhu, C.; Chen, W.; McAuley, J. Learning to attend on essential terms: An enhanced retriever-reader model for open-domain question answering. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1808.09492. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Ong, D.C. Context-guided BERT for targeted aspect-based sentiment analysis. Proc. Aaai Conf. Artif. Intell. 2021, 35, 14094–14102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, M.H.; Ogunbona, P.O. Modelling context and syntactical features for aspect-based sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Online, 5–10 July 2020; pp. 3211–3220. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Kang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Si, L.; Zhou, G. Aspect sentiment classification with both word-level and clause-level attention networks. IJCAI 2018, 2018, 4439–4445. [Google Scholar]
- He, R.; Lee, W.S.; Ng, H.T.; Dahlmeier, D. Exploiting document knowledge for aspect-level sentiment classification. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.04346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Hamada, M. Smart media-based context-aware recommender systems for learning: A conceptual framework. In Proceedings of the 2017 16th International Conference on Information Technology Based Higher Education and Training (ITHET), Ohrid, Macedonia, 10–12 July 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Musa, A.; Adam, F.M.; Ibrahim, U.; Zandam, A.Y. HauBERT: A Transformer Model for Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis of Hausa-Language Movie Reviews. Eng. Proc. 2025, 87, 43. [Google Scholar]
- Rosso, P.; Banchs, R.E.; Saggion, H. Exploiting SentiWordNet for sentiment analysis in Twitter. In Workshop on Sentiment Analysis Where AI Meets Psychology (SAAIP) in Conjunction, Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Computational Semantics (IWCS), Oxford, UK, 12–14 January 2011; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Thet, T.T.; Na, J.-C.; Khoo, C.S. Aspect-based sentiment analysis of movie reviews on discussion boards. J. Inf. Sci. 2010, 36, 823–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essebbar, A.; Kane, B.; Guinaudeau, O.; Chiesa, V.; Quénel, I.; Chau, S. Aspect Based Sentiment Analysis using French Pre-Trained Models. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2021), Online, 4–6 February 2021; Volume 1, pp. 519–525. [Google Scholar]
- Bensoltane, R.; Zaki, T. Towards Arabic aspect-based sentiment analysis: A transfer learning-based approach. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2022, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Hu, M.; Cheng, J. Opinion observer: Analyzing and comparing opinions on the web. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on World Wide Web, Chiba, Japan, 10–14 May 2005; pp. 342–351. [Google Scholar]

| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Naive Bayes | 0.70 | 0.71 | 0.70 | 0.67 |
| SVM | 0.7153 | 0.6900 | 0.7211 | 0.7021 |
| Random Forest | 0.7000 | 0.72 | 0.70 | 0.70 |
| Logistic Regression | 0.7624 | 0.7411 | 0.7602 | 0.7511 |
| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Naive Bayes | 0.64 | 0.60 | 0.64 | 0.52 |
| SVM | 0.64 | 0.60 | 0.64 | 0.52 |
| Random Forest | 0.64 | 0.60 | 0.64 | 0.52 |
| Logistic Regression | 0.64 | 0.60 | 0.64 | 0.52 |
| Model | Accuracy |
|---|---|
| Results on Aspects Extraction: | |
| Naive Bayes | 0.64 |
| SVM | 0.64 |
| Random Forest | 0.64 |
| Logistic Regression | 0.64 |
| Proposed DCNN model | 0.91 |
| Results on Polarity Classification: | |
| Naive Bayes | 0.64 |
| SVM | 0.64 |
| Random Forest | 0.64 |
| Logistic Regression | 0.64 |
| Proposed DCNN model | 0.92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ibrahim, U.; Zandam, A.Y.; Adam, F.M.; Musa, A.; Hassan, M.; Hamada, M.; Usman, M.S. A Deep Convolutional Neural Network-Based Model for Aspect and Polarity Classification in Hausa Movie Reviews. Eng. Proc. 2025, 107, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025107021
Ibrahim U, Zandam AY, Adam FM, Musa A, Hassan M, Hamada M, Usman MS. A Deep Convolutional Neural Network-Based Model for Aspect and Polarity Classification in Hausa Movie Reviews. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 107(1):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025107021
Chicago/Turabian StyleIbrahim, Umar, Abubakar Yakubu Zandam, Fatima Muhammad Adam, Aminu Musa, Mohamed Hassan, Mohamed Hamada, and Muhammad Shamsu Usman. 2025. "A Deep Convolutional Neural Network-Based Model for Aspect and Polarity Classification in Hausa Movie Reviews" Engineering Proceedings 107, no. 1: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025107021
APA StyleIbrahim, U., Zandam, A. Y., Adam, F. M., Musa, A., Hassan, M., Hamada, M., & Usman, M. S. (2025). A Deep Convolutional Neural Network-Based Model for Aspect and Polarity Classification in Hausa Movie Reviews. Engineering Proceedings, 107(1), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025107021








