An ML Framework for the Early Detection and Prediction of Hypertension: Enhancing Diagnostic Accuracy †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Machine Learning Models
3.1. KKN
3.2. Naive Bayes
3.3. Decision Tree
3.4. Random Forest
3.5. Logistic Regression Model
3.6. Deep Learning Algorhythms
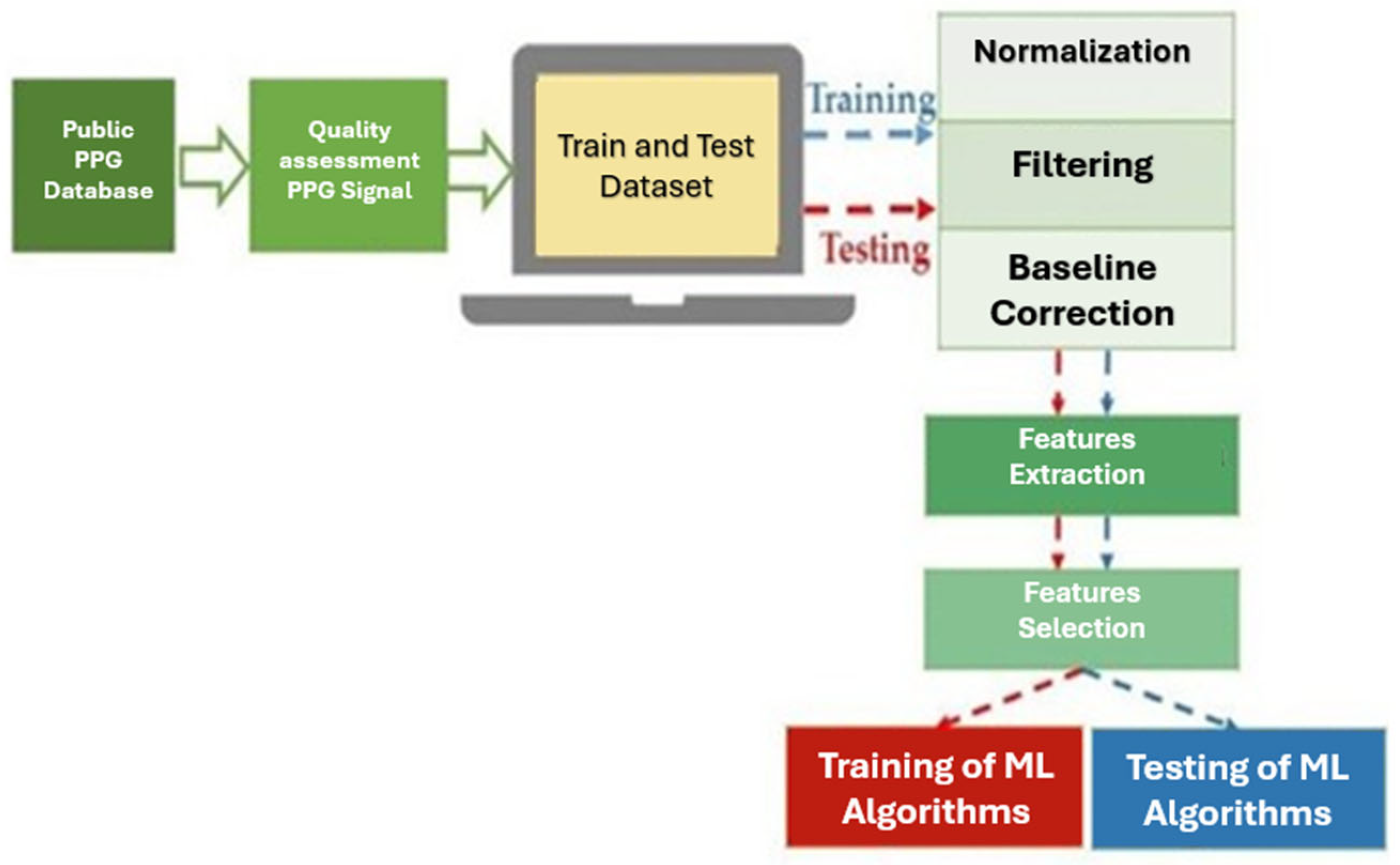
4. Proposed Framework
5. Results
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmed, S.; Hossain, M.A.; Bhuiyan, M.M.I.; Ray, S.K.A. A Comparative Study of Machine Learning Algorithms to Predict Road Accident Severity. In Proceedings of the 2021 20th International Conference on Ubiquitous Computing and Communications (IUCC/CIT/DSCI/SmartCNS), Virtual, 20–22 December 2021; pp. 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visco, V.; Izzo, C.; Mancusi, C.; Rispoli, A.; Tedeschi, M.; Virtuoso, N.; Giano, A.; Gioia, R.; Melfi, A.; Serio, B.; et al. Artificial Intelligence in Hypertension Management: An Ace up Your Sleeve. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2023, 10, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, X.; Huo, Y.; Yan, Z.; Wang, H.; Yuan, J.; Wang, Y.; Cai, J.; Zhao, W. An application of machine learning to etiological diagnosis of secondary hypertension: Retrospective study using electronic medical records. JMIR Med. Inform. 2021, 9, e19739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Effati, S.; Kamarzardi-Torghabe, A.; Azizi-Froutaghe, F.; Atighi, I.; Ghiasi-Hafez, S. Web application using machine learning to predict cardiovascular disease and hypertension in mine workers. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Ríos, E.; Montesinos, L.; Alfaro-Ponce, M.; Pecchia, L. A review of machine learning in hypertension detection and blood pressure estimation based on clinical and physiological data. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 70, 102813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, Y.; Yamamoto, A.; Jogo, A.; Kita, R.; Hirose, H.; Ikeda, K.; Terayama, E.; Ozaki, M.; Murai, K.; Kageyama, K.; et al. A Case of Successful Treatment of Gastric Varices Due to Left-sided Portal Hypertension with Multidisciplinary Treatment Including Transportal Coil-assisted Balloon-occluded Retrograde Transvenous Obliteration II and Partial Splenic Embolization. Interv. Radiol. 2025, 10, e2023-0025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nour, M.; Polat, K. Automatic Classification of Hypertension Types Based on Personal Features by Machine Learning Algorithms. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 2742781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pengo, M.; Montagna, S.; Ferretti, S.; Bilo, G.; Borghi, C.; Ferri, C.; Parati, G. Machine Learning in Hypertension Detection: A Study on World Hypertension Day Data. J. Med. Syst. 2023, 47, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mroz, T.; Griffin, M.; Cartabuke, R.; Laffin, L.; Russo-Alvarez, G.; Thomas, G.; Smedira, N.; Meese, T.; Shost, M.; Habboub, G.; et al. Predicting hypertension control using machine learning. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0299932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diwaker, C.; Tomar, P.; Solanki, A.; Nayyar, A.; Jhanjhi, N.Z.; Abdullah, A.; Supramaniam, M.A. A New Model for Predicting Component-Based Software Reliability Using Soft Computing. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 147191–147203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- du Toit, C.; Tran, T.Q.B.; Deo, N.; Aryal, S.; Lip, S.; Sykes, R.; Manandhar, I.; Sionakidis, A.; Stevenson, L.; Pattnaik, H.; et al. Survey and Evaluation of Hypertension Machine Learning Research. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2023, 12, e027896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kok, S.H.; Abdullah, A.; Jhanjhi, N.Z.; Supramaniam, M. A review of intrusion detection system using machine learning ap-proach. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2019, 12, 8–15. [Google Scholar]
- Hirata, Y.; Tsuji, T.; Kotoku, J.; Sata, M.; Kusunose, K. Echocardiographic artificial intelligence for pulmonary hypertension classification. Heart 2024, 110, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messerli, F.H.; Williams, B.; Ritz, E. Essential hypertension. Lancet 2007, 361, 1629–1641. Available online: https://www.thelancet.com (accessed on 1 January 2025). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Classifier | Accuracy |
|---|---|
| KNN | 99.87% |
| Naive Bayes | 82.74% |
| Decision Tree | 91.55% |
| Random Forest | 95.86% |
| Gradient Boosted Tree | 93.65% |
| Logistic Regression Model | 85.85% |
| Deep Learning Algorithms | 99.92% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Areeb, M.; Rehman, A.U.; Sujjada, A. An ML Framework for the Early Detection and Prediction of Hypertension: Enhancing Diagnostic Accuracy. Eng. Proc. 2025, 107, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025107018
Areeb M, Rehman AU, Sujjada A. An ML Framework for the Early Detection and Prediction of Hypertension: Enhancing Diagnostic Accuracy. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 107(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025107018
Chicago/Turabian StyleAreeb, Muhammad, Attique Ur Rehman, and Alun Sujjada. 2025. "An ML Framework for the Early Detection and Prediction of Hypertension: Enhancing Diagnostic Accuracy" Engineering Proceedings 107, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025107018
APA StyleAreeb, M., Rehman, A. U., & Sujjada, A. (2025). An ML Framework for the Early Detection and Prediction of Hypertension: Enhancing Diagnostic Accuracy. Engineering Proceedings, 107(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025107018






