Using Large Language Models for Ontology Development †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Development of New Ontologies
2.2. Enhancing Existing Ontologies
2.3. Alignment of the Ontologies
2.4. Ontology Evaluation
3. Use Case
3.1. Define the Scope of the Ontology
3.2. Reuse of the Existing Ontologies
3.3. Enumeration of the Important Terms
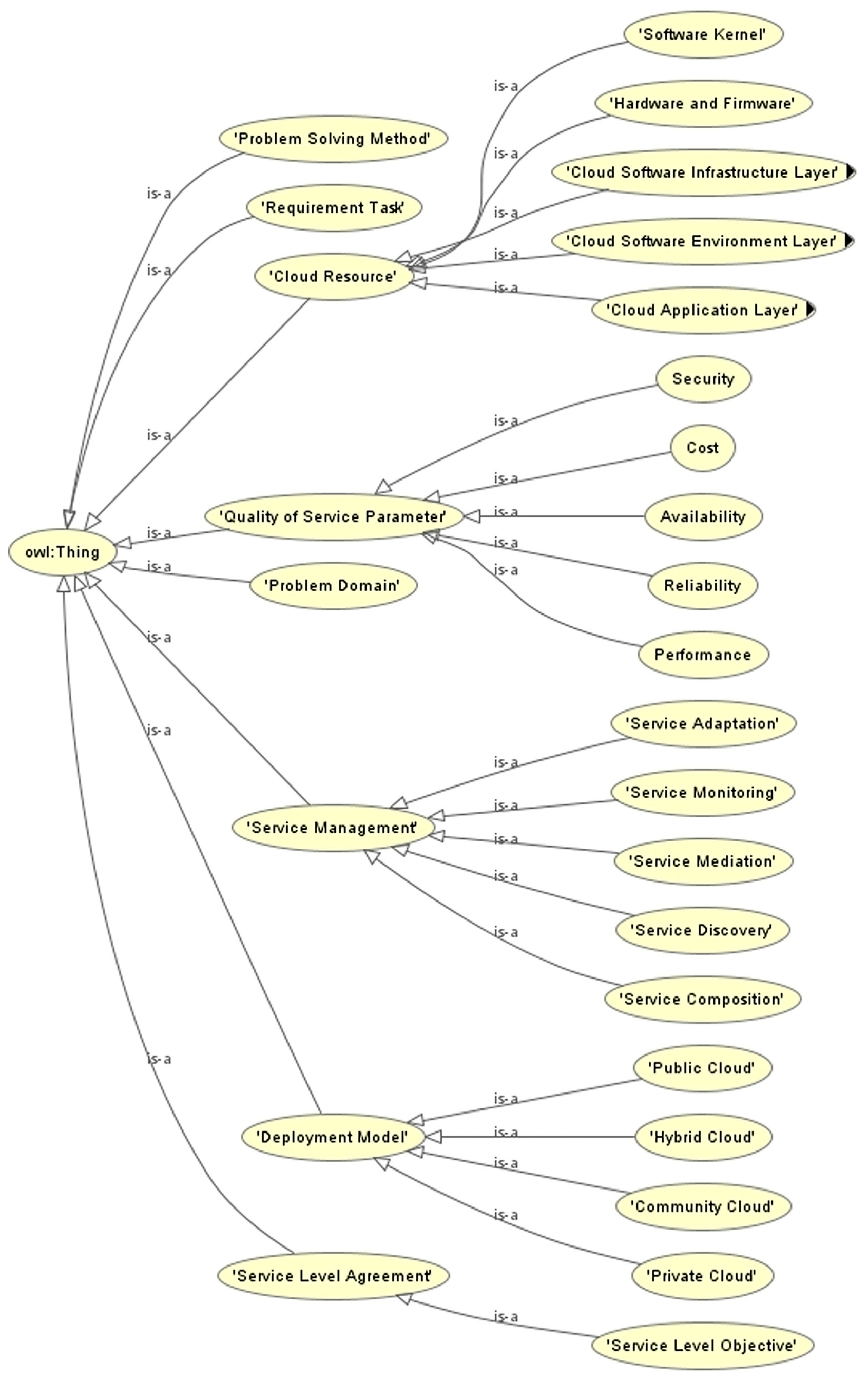
3.4. Definition of the Ontology’s Classes and Their Hierarchy
3.5. Definition of the Ontology’s Data and Object Properties
3.6. Creation of the Ontology’s Instances
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saeedizade, M.J.; Blomqvist, E. Navigating Ontology Development with Large Language Models. In The Semantic Web; Meroño Peñuela, A., Dimou, A., Troncy, R., Hartig, O., Acosta, M., Alam, M., Paulheim, H., Lisena, P., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 143–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei Giglou, H.; D’Souza, J.; Auer, S. LLMs4OL: Large Language Models for Ontology Learning. In The Semantic Web–ISWC 2023; Payne, T.R., Presutti, V., Qi, G., Poveda-Villalón, M., Stoilos, G., Hollink, L., Kaoudi, Z., Cheng, G., Li, J., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 408–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathallah, N.; Das, A.; Giorgis, S.D.; Poltronieri, A.; Haase, P.; Kovriguina, L. NeOn-GPT: A Large Language Model-Powered Pipeline for Ontology Learning. In The Semantic Web: ESWC 2024 Satellite Events; Meroño Peñuela, A., Corcho, O., Groth, P., Simperl, E., Tamma, V., Nuzzolese, A.G., Poveda-Villalón, M., Sabou, M., Presutti, V., Celino, I., et al., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; An, H.; Wang, K.; Liu, W. A Short Review for Ontology Learning: Stride to Large Language Models Trend. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.14991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Vetter, N.; Aryan, K. Using Large Language Models for OntoClean-based Ontology Refinement. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.15864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Ling, C.; Graetz, I.; Zhao, L. Ontology extension by online clustering with large language model agents. Front. Big Data 2024, 7, 1463543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini, R.; Norouzi, S.S.; Hitzler, P.; Amini, R. Towards Complex Ontology Alignment Using Large Language Models. In Knowledge Graphs and Semantic Web; Tiwari, S., Villazón-Terrazas, B., Ortiz-Rodríguez, F., Sahri, S., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei Giglou, H.; D’Souza, J.; Engel, F.; Auer, S. LLMs4OM: Matching Ontologies with Large Language Models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.10317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snijder, L.L.; Smit, Q.T.S.; de Boer, M.H.T. Advancing Ontology Alignment in the Labor Market: Combining Large Language Models with Domain Knowledge. Proc. AAAI Symp. Ser. 2024, 3, 31208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, G.; Lima, R.; Trojahn, C. Complex Ontology Matching with Large Language Model Embeddings. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.13619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaneva, S.; Vasic, S.; Sabou, M. LLM-driven Ontology Evaluation: Verifying Ontology Restrictions with ChatGPT. Semant. Web ESWC Satell. Events 2024, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, C.; Bender, E.M.; Zamani, H.; Bota, H.; Awadallah, A.H.; Diaz, F.; Lalmas, M. Using Large Language Models to Generate, Validate, and Apply User Intent Taxonomies. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2309.13063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zala, D. Perplexity AI Review: Research Tool That Doesn’t Hallucinate. Available online: https://dhruvirzala.com/perplexity-ai-review/ (accessed on 14 March 2025).
- Noy, N.; Mcguinness, D. Ontology Development 101: A Guide to Creating Your First Ontology. Stanford Knowledge Systems Laboratory. 2001. Available online: http://protege.stanford.edu/publications/ontology_development/ontology101.pdf (accessed on 14 March 2025).
- Ali, A.; Shamsuddin, S.; Eassa, F. Ontology-based Cloud Services Representation. Res. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2014, 8, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscato, F.; Aversa, R.; Di Martino, B.; Fortis, T.-F.; Munteanu, V. An Analysis of mOSAIC ontology for Cloud Resources annotation. In Proceedings of the Federated Conference on Computer Science and Information Systems, Szczecin, Poland, 18–21 September 2011; pp. 973–980. [Google Scholar]
- Androcec, D.; Vrcek, N. Ontologies for Platform as Service APIs Interoperability. Cybern. Inf. Technol. 2016, 16, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banditwattanawong, T.; Masdisornchote, M. Infrastructure-as-a-Service Ontology for Consumer-Centric Assessment. Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 2023, 8, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekik, M.; Boukadi, K.; Ben-Abdallah, H. Cloud description ontology for service discovery and selection. In Proceedings of the 10th International Joint Conference on Software Technologies (ICSOFT), Colmar, France, 20–22 July 2015; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.B.; Jang, S.H.; Lee, J.S. Ontology-Based Resource Management for Cloud Computing. In Intelligent Information and Database Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Name of the Ontology | Brief Description of the Ontology |
|---|---|
| Cloud Computing Ontology (CoCoOn) [15] | An OWL-based ontology that defines functional and non-functional concepts, attributes, and relations of infrastructure services. |
| moSAIC Cloud Ontology [16] | This ontology aims to provide common access to cloud services and enable discovery in cloud federations. |
| PaaS API Ontology [17] | Focuses on remote operations of PaaS providers’ APIs and interoperability problems among different platform-as-a-service offers. |
| IaaS Ontology [18] | A consumer-centric ontology with 15 primary subclasses and 340 individual classes for IaaS assessment. |
| Cloud Description Ontology [19] | Designed for service discovery and selection in cloud federation environments. |
| Cloud Resource Ontology [20] | Developed by Y. Ma et al. for resource management in cloud environments. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andročec, D. Using Large Language Models for Ontology Development. Eng. Proc. 2025, 104, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025104009
Andročec D. Using Large Language Models for Ontology Development. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 104(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025104009
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndročec, Darko. 2025. "Using Large Language Models for Ontology Development" Engineering Proceedings 104, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025104009
APA StyleAndročec, D. (2025). Using Large Language Models for Ontology Development. Engineering Proceedings, 104(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025104009





