Predicting Brain Stroke Risk Using Machine Learning: A Comprehensive Approach to Early Detection and Prevention †
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Headache without any reason;
- Numbness;
- Tingling in one part of the body;
- Weakness of one part of the body;
- Speech issue;
- Vitiligo;
- Walking issue;
- Dizziness;
- Temporary blindness, etc.
2. Literature Review
3. Methodology
3.1. Machine Learning (ML)
3.1.1. Naïve Bayes
3.1.2. Decision Tree
3.1.3. Random Forest
3.1.4. K-Nearest Neighbor
3.1.5. Gradient Boosting
3.2. Dataset and Attributes
3.2.1. About the Dataset
3.2.2. Context
3.2.3. Attributes with Description
| Attribute | Description | Type of Data |
|---|---|---|
| Age | Age of the person | Integer |
| Gender | Gender of the patient (male or female) | Binomial |
| Hypertension | Does the patient have hypertension | Binomial |
| Heart Disease | Is the patient suffering from any heart issue | Binomial |
| Marital Status | Single or married | Binomial |
| Work Type | The profession or job of the patient | Categorical |
| Residence Type | Residence of patients in rural or urban areas | Categorical |
| Avg Glucose Level | Average glucose level of the patient | Integer |
| BMI | Body mass index of the patient | Integer |
| ID | Unique identifier | Integer |
| Stroke | Prediction of stroke (0 means no, 1 means yes) | Binomial |
| Smoking Status | If the patient has smoking status | Categorical |
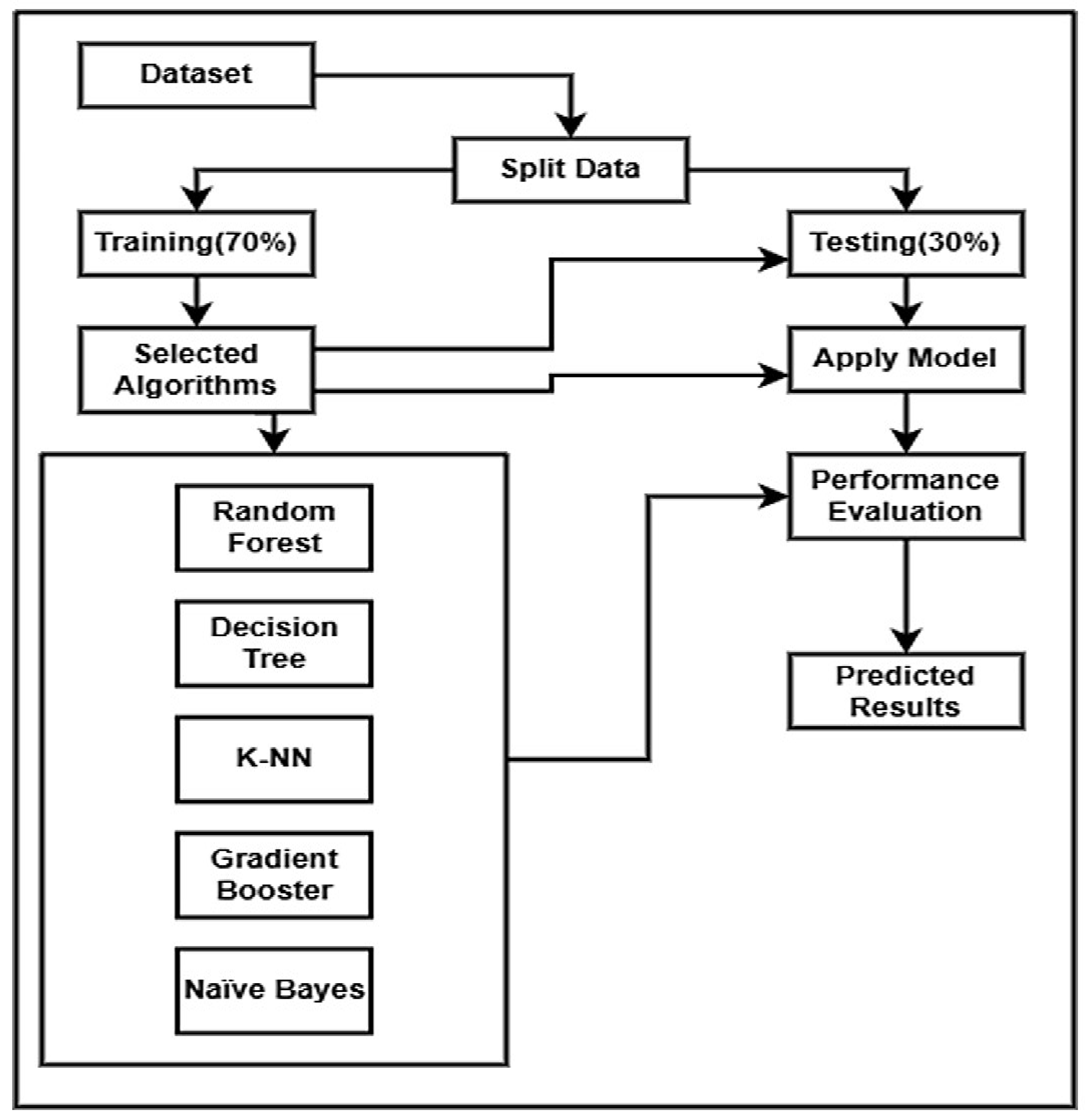
3.3. Framework
4. Results
4.1. Accuracy
4.2. Precision
4.3. Recall
4.4. Classification Error
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chawla, M.; Sharma, S.; Sivaswamy, J.; Kishore, L.T. A method for automatic detection and classification of stroke from brain CT images. In Proceedings of the 2009 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology society, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 3–6 September 2009; pp. 3581–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, S.L.; Buccino, G.; Solodkin, A. Brain Repair after Stroke—A Novel Neurological Model. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 698–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byna, A.; Lakulu, M.M.; Panessai, I.Y. Current critical review on prediction stroke using machine learning. Bull. Electr. Eng. Inform. 2024, 13, 3470–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, M.T.; Chua, Z.K.; Lee, M.; Yock-Corrales, A.; Churilov, L.; Monagle, P.; Donnan, G.A.; Babl, F.E. Stroke and Nonstroke Brain Attacks in Children. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Advances in Computing and Communication Engineering (ICACCE), Paris, France, 22–23 June 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Ghatak, S.; Dutta, S.; Chatterjee, B.; Gupta, M. A Survey on Comparison Analysis between EEG Signal and MRI for Brain Stroke Detection. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Emerging Technologies in Data Mining and Information Security, Kolkata, India, 23–25 July 2018; Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing. Springer: Singapore, 2019; Volume 814, pp. 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmento, R.M.; Vasconcelos, F.F.X.; Filho, P.P.R.; de Albuquerque, V.H.C. An IoT Platform for the Analysis of Brain CT Images Based on Parzen Analysis. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 105, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dourado, C.M.J.M.; da Silva, S.P.P.; da Nóbrega, R.V.M.; Antonio, A.C.; Filho, P.P.R.; de Albuquerque, V.H.C. Deep Learning IoT System for Online Stroke Detection in Skull Computed Tomography Images. Comput. Netw. 2019, 152, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoily, T.I.; Islam, T.; Jannat, S.; Tanna, S.A.; Alif, T.M.; Ema, R.R. Detection of Stroke Disease Using Machine Learning Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2019 10th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Kanpur, India, 6–8 July 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.; Gupta, N. Enhancing Stroke Prediction with Machine Learning in Smart Healthcare Systems. In Proceedings of the 2024 15th International Conference on Computing Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT 2024), Kamand, India, 24–28 June 2024; pp. 9616–9621. [Google Scholar]
- Sailasya, G.; Aruna Kumari, G.L. Analyzing the Performance of Stroke Prediction Using ML Classification Algorithms. Available online: http://www.ijacsa.thesai.org (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Emon, M.U.; Keya, M.S.; Meghla, T.I.; Rahman, M.M.; Al Mamun, M.S.; Kaiser, M.S. Performance Analysis of Machine Learning Approaches in Stroke Prediction. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Electronics, Communication and Aerospace Technology (ICECA), Coimbatore, India, 5–7 November 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1464–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.A.; Park, S.J.; Jun, J.A.; Pyo, C.S.; Cho, K.H.; Lee, H.S.; Yu, J.H. Deep Learning-Based Stroke Disease Prediction System Using Real-Time Bio Signals. Sensors 2021, 21, 4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobon Vasquez, J.A.; Scapaticci, R.; Turvani, G.; Bellizzi, G.; Rodriguez-Duarte, D.O.; Joachimowicz, N.; Duchêne, B.; Tedeschi, E.; Casu, M.R.; Crocco, L.; et al. A Prototype Microwave System for 3D Brain Stroke Imaging. Sensors 2020, 20, 2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Holanda, G.; Souza, L.F.D.F.; Silva, H.; Gomes, A.; Silva, I.; Ferreira, M.; Jia, C.; Han, T.; de Albuquerque, V.H.C.; et al. Deep Learning-Enhanced Internet of Medical Things to Analyze Brain CT Scans of Hemorrhagic Stroke Patients: A New Approach. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 24941–24951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mia, R.; Khanam, S.; Mahjabeen, A.; Ovy, N.H.; Ghimire, D.; Park, M.-J.; Begum, M.I.A.; Hosen, A.S.M.S. Exploring Machine Learning for Predicting Cerebral Stroke: A Study in Discovery. Electronics 2024, 13, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, E.N.; Pei, S.; Staibano, P.; van der Woerd, B. Clinical applications of large language models in medicine and surgery: A scoping review. J. Int. Med. Res. 2025, 53, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dev, S.; Wang, H.; Nwosu, C.S.; Jain, N.; Veeravalli, B.; John, D. A predictive analytics approach for stroke prediction using machine learning and neural networks. Healthc. Anal. 2022, 2, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diwaker, C.; Tomar, P.; Solanki, A.; Nayyar, A.; Jhanjhi, N.Z.; Abdullah, A.; Supramaniam, M. A New Model for Predicting Component-Based Software Reliability Using Soft Computing. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 147191–147203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, D.; Jhanjhi, N.Z.; Khan, N.A.; Ray, S.K.; Ashfaq, F.; Das, S.R. Diabetes detection framework for imbalanced data via explainable machine learning. In AIP Conference Proceedings, Proceeding of the International Conference on Cognitive Computing and Artificial Intelligence Chennai (ICCCAI—2024), Chennai, India, 7–8 March 2024; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2025; Volume 3257, p. 020040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashfaq, F.; Jhanjhi, N.Z.; Khan, N.A.; Javaid, D.; Masud, M.; Shorfuzzaman, M. Enhancing ECG Report Generation with Domain-Specific Tokenization for Improved Medical NLP Accuracy. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 85493–85506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
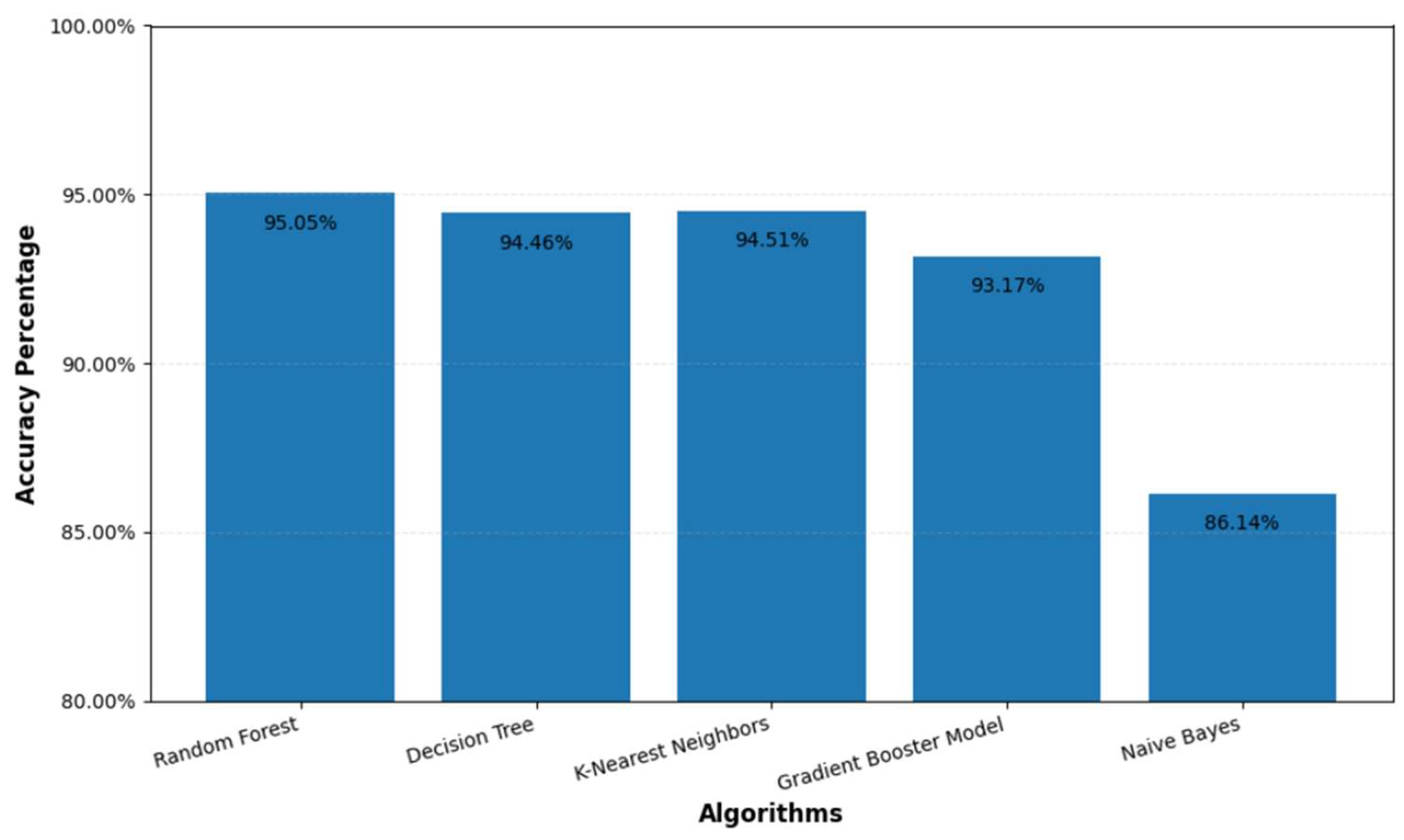
| Algorithm | Accuracy | Classification Error | Precision |
|---|---|---|---|
| Random Forest | 95.05% | 4.95% | 95.05% |
| Decision Tree | 94.44% | 5.56% | 95.26% |
| K-Nearest Neighbor | 94.51% | 5.49% | 95.20% |
| Gradient Booster Model | 93.17% | 6.83% | 95.39% |
| Naïve Bayes | 86.14% | 13.86% | 96.62% |
| True 0 | True 1 | Precision | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pred 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.00% |
| Pred 1 | 74 | 1420 | 95.05% |
| Class Recall | 0.00% | 100.00% |
| Ref. | Year | Accuracy | Algorithms |
|---|---|---|---|
| [1] | 2009 | 90.00% | CT images |
| [2] | 2019 | 99.99% | Bayesian classifier, RF, KNN, SVMLinear, SVMBRF |
| [3] | 2019 | 98.41% | KNN-OLF-SVM |
| [4] | 2019 | 99.8% | Naive Bayes, J48, k-NN, RF in WEKA toolkit |
| [5] | 2020 | 86.42% | DT, RF, EM, GNB, and DNN |
| [6] | 2020 | 94.23% | DT, GNB, LR, L-SVM, P-SVM, RBG SVM, RF, AB, and AB with SGD |
| [7] | 2020 | 97% | LR, SGD, DT, AB, Gaussian, QDA, MLP, KNN, GB, and XGB |
| [8] | 2020 | 99.73% | DT, AB, RF, NB, KNN, SVM, MLP, and EM |
| [9] | 2020 | 95.97% | K-NN, NB, LR, DT, RF, MLP-NN, DL, and SVM |
| [10] | 2020 | 98% | ANN, AT Algorithms such as LM and SCG |
| [11] | 2021 | 82% | LR, DT, RF, K-NN, SVM, and NB |
| [12] | 2021 | 94.0% | LSTM, B-LSTM, CNN-LSTM, and CNN-B-LSTM |
| [13] | 2021 | 96% | NB, K-NN, LR, RF, AB, and DTC |
| [14] | 2022 | 97% | RF, K-NN, LR, SVM, NB, and MCC |
| [15] | 2023 | 97.17% | NB, SVM, RF, AB, and XGB |
| [16] | 2023 | 99% | XGB, AB, LGBM, RF, DT, LR, K-NN, SVM-LK, NB, and DNN |
| [17] | 2024 | 95.16% | NB, LR, SVM, K-NN, DT, RF, XGB, and NN |
| [18] | 2024 | 97% | NB, RF, etc. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Noor, I.; Aslam, A.; Mir, A.; Insany, G.P. Predicting Brain Stroke Risk Using Machine Learning: A Comprehensive Approach to Early Detection and Prevention. Eng. Proc. 2025, 107, 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025107123
Noor I, Aslam A, Mir A, Insany GP. Predicting Brain Stroke Risk Using Machine Learning: A Comprehensive Approach to Early Detection and Prevention. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 107(1):123. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025107123
Chicago/Turabian StyleNoor, Isha, Amara Aslam, Azka Mir, and Gina Purnama Insany. 2025. "Predicting Brain Stroke Risk Using Machine Learning: A Comprehensive Approach to Early Detection and Prevention" Engineering Proceedings 107, no. 1: 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025107123
APA StyleNoor, I., Aslam, A., Mir, A., & Insany, G. P. (2025). Predicting Brain Stroke Risk Using Machine Learning: A Comprehensive Approach to Early Detection and Prevention. Engineering Proceedings, 107(1), 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025107123






