Leveraging LSTM Neural Networks for Advanced Harassment Detection: Insights into Insults and Defamation in the U-Tapis Module †
Abstract
1. Introduction
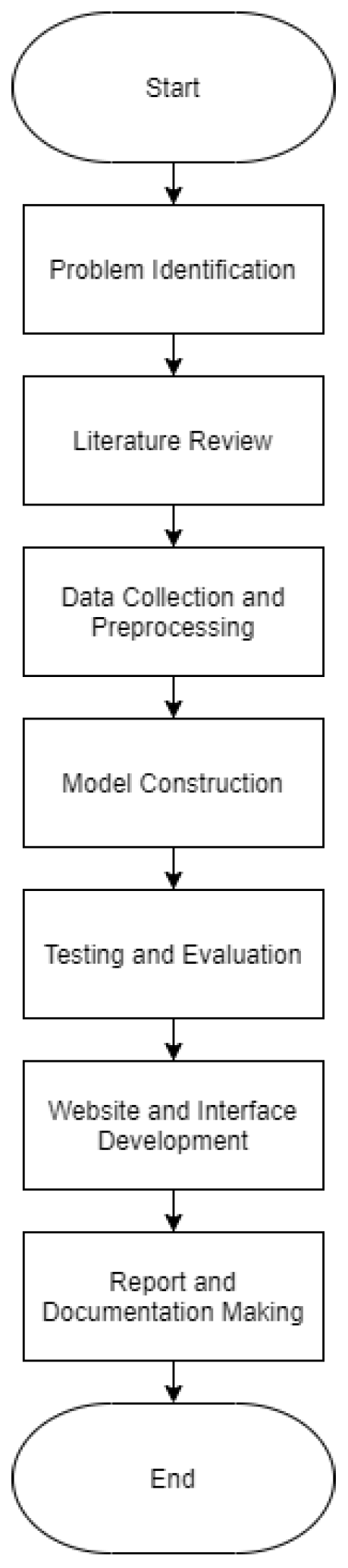
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Problem Identification
2.2. Literature Review
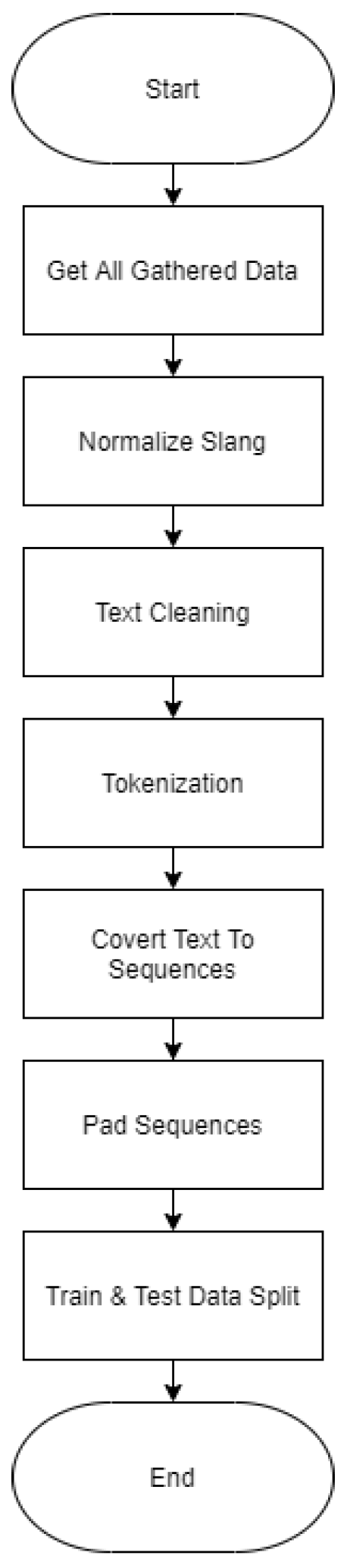
2.3. Data Collection and Preprocessing
2.3.1. Data Collection
2.3.2. Text Preprocessing
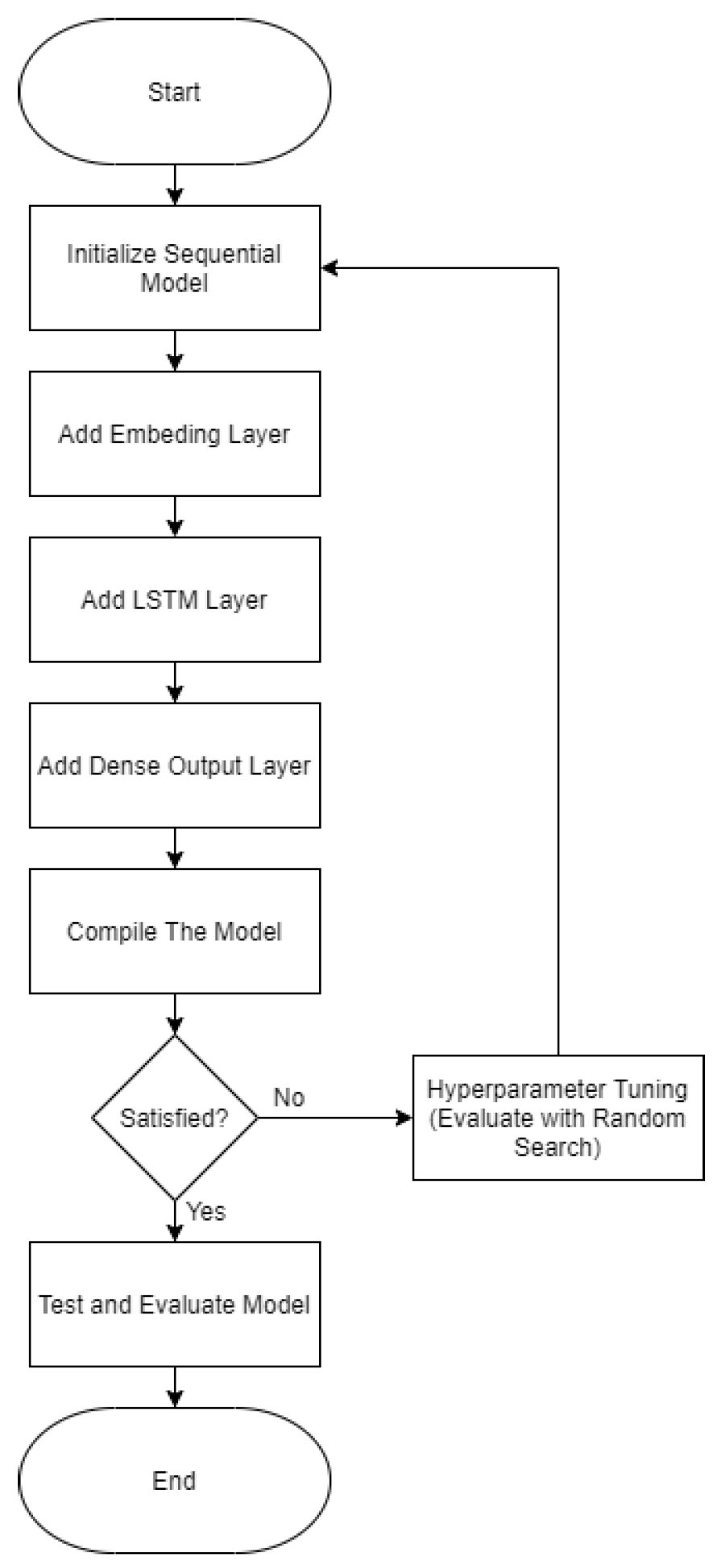
2.4. Model Construction
2.4.1. Model Construction
2.4.2. Hyperparameter Tuning
- The dimensionality of the embedding layer (embedding_dim), tested with values of 50, 100, and 200.
- The number of units in the first and second Bidirectional LSTM layers (lstm_units_1 and lstm_units_2), tested with values of 128 and 256 for each layer.
- Dropout rates for the first and second LSTM layers (dropout_1 and dropout_2), as well as the dense layer (dropout_dense), tested with values ranging from 0.2 to 0.5 in increments of 0.1.
- An embedding layer with a vocabulary size of 10,000 and sequence length of 100.
- Two Bidirectional LSTM layers, each followed by dropout layers to prevent overfitting.
- A dense layer with 64 units and ReLU activation, followed by a dropout layer.
- A softmax output layer for classifying sentences into neutral, insult, and defamation categories.
- EarlyStopping: Monitored the validation loss and stopped training after three consecutive epochs without improvement, restoring the best weights to prevent overfitting.
- ReduceLROnPlateau: Reduced the learning rate by a factor of 0.5 if the validation loss did not improve for two consecutive epochs, facilitating smoother convergence.
2.4.3. Test and Evaluate Model
2.5. Testing and Evaluation
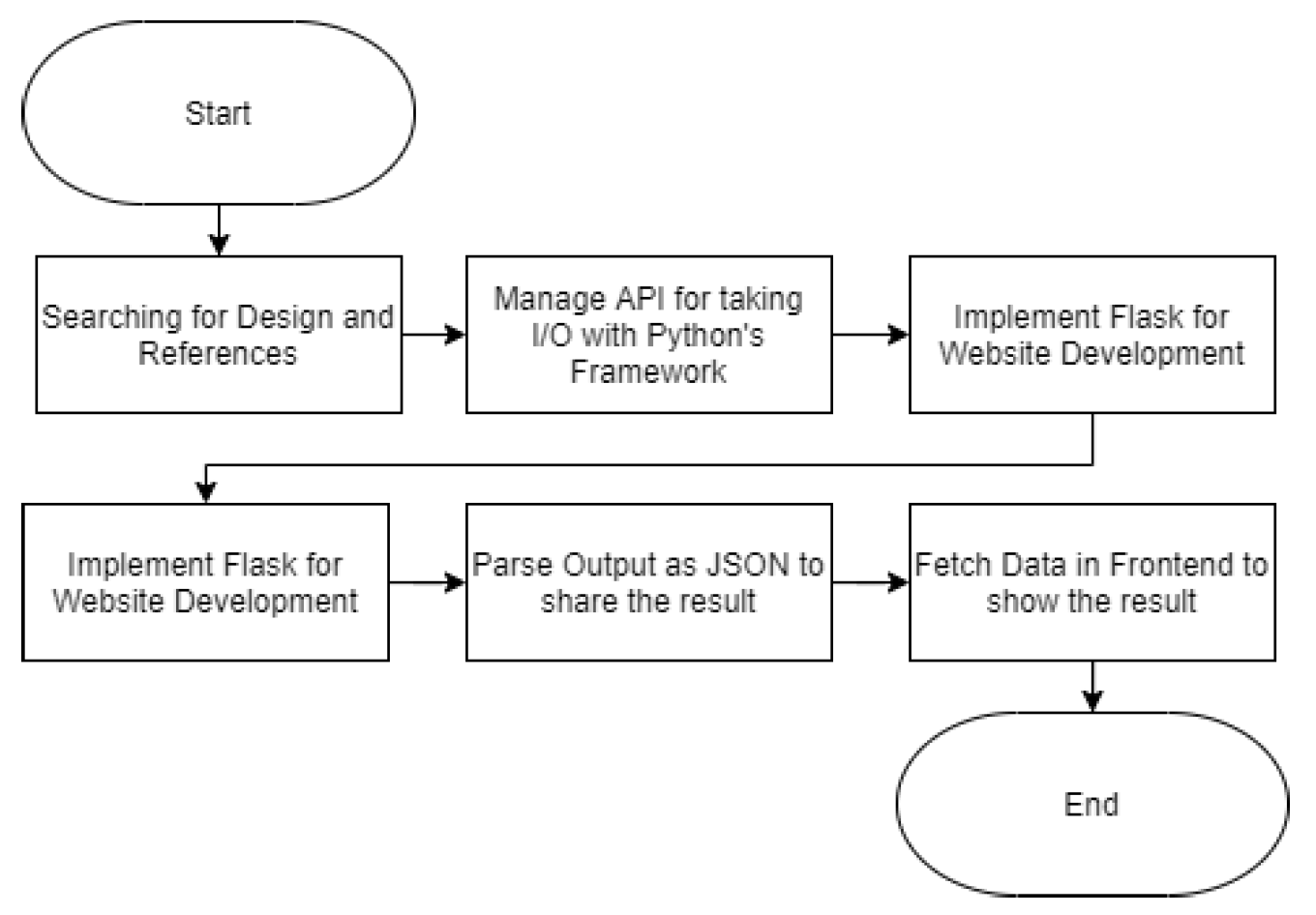
2.6. Website and Interface Development
2.7. Report and Documentation Making
3. Results
3.1. Dataset
3.2. Preprocessing
3.3. Website Implementation
3.4. Testing and Evaluation
3.4.1. Testing with 150 GPT Datasets
3.4.2. Testing with 1000 Internet-Sourced Datasets
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Exploring methods to enhance context understanding for borderline cases of insult or defamation.
- Integrating large language models specific to the Indonesian language to improve semantic representation and classification performance.
- Incorporating more real-world data from social media and other informal domains to address a broader range of linguistic styles.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| NLP | Natural Language Processing |
| Bareskrim | Badan Reserse Kriminal |
| BAP | Berita Acara Pemeriksaan |
| UU ITE | Undang-Undang Informasi dan Transaksi Elektronik |
| URL | Uniform Resource Locator |
| LLM | Large Language Model |
References
- Tenório, N.; Bjørn, P. Online Harassment in the Workplace: The Role of Technology in Labour Law Disputes. CSCW 2019, 28, 293–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niknik, M.; Wijaya, G.I.; (Universitas Multimedia Nusantara, Tangerang, Indonesia). Private communication, 2024.
- Niknik, M. Automation in Journalism: Challenges and Opportunities; Media Nusantara Press: Tangerang, Indonesia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mediyawati, N.; Young, J.C.; Nusantara, S.B. U-tapis: Automatic spelling filter as an effort to improve indonesian language competencies of journalistic students. Cakrawala Pendidikan 2021, 40, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutomo, R.; Mediyawati, N. UTAPIS Indonesian Word Error Detection Application: Design and Development. IJCS 2024, 13, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputra, A.K.B.; Overbeek, M.V. Harnessing long short-term memory algorithm for enhanced di-di word error detection and correction. In Proceedings of the International Conference Series on ICT, Entertainment Technologies, and Intelligent Information Management in Education and Industry ETLTC2024, Aizuwakamatsu, Japan, 23–26 January 2024; p. 040002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siswanto, V.G.A.; Overbeek, M.V. Development of “kata terikat” detection and writing errors correction using Rabin-Karp and random forest algorithm. In Proceedings of the International Conference Series on ICT, Entertainment Technologies, and Intelligent Information Management in Education and Industry ETLTC2024, Aizuwakamatsu, Japan, 23–26 January 2024; p. 040004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwitya, N.R.; Overbeek, M.V. Development of detection and correction of errors in spelling and compound words using long short-term memory. In Proceedings of the International Conference Series on ICT, Entertainment Technologies, and Intelligent Information Management in Education and Industry ETLTC2024, Aizuwakamatsu, Japan, 23–26 January 2024; p. 040005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, F.; Sani, A.K.; Moghadam, K. Forensic Linguistics in the Light of Crime Investigation. Pertanika J. Soc. Sci. & Hum. 2016, 24, 375–384. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, H.R. The Role of Forensic Linguistics in Crime Investigation: Uses in Legal Proceedings. IJLLIS 2021, 10, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulthard, M.; John, A. An Introduction to Forensic Linguistics: Language in Evidence; Routledge: Abingdon, ON, Canada, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Balakrishnan, V.; Khan, S.; Arabnia, H.R. Improving Cyberbullying Detection using Twitter Users’ Psychological Features and Machine Learning. Comput. Secur. 2020, 90, 101710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Luo, L. Hate Speech Detection: A Solved Problem? The Challenging Case of Long Tail on Twitter. arXiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widiyantoro, P.; Paradise, P.; Prasetyo, Y.D. Deteksi Cyberbullying pada Pemain Sepak Bola di Platform Media Sosial “X” Menggunakan Metode Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM). Repeater Publ. Tek. Inform. Dan Jar. 2025, 3, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qur’atul’Ain, N.; Pramono, B.; Wibowo, A.H. Penerapan Metode LSTM Pada Sistem Klasifikasi Komentar Publik Yang Termasuk Jenis Pelanggaran Undang-Undang ITE. J. Inform. Ilmu Komput. Dan Sist. Inf. 2024, 2, 10–17. [Google Scholar]
- Nikmah, T.L.; Ammar, M.Z.; Allatif, Y.R.; Mahjati, R.; Husna, P.; Kurniasari, P.A.; Bahri, A.S. Comparison of LSTM, SVM, and naive bayes for classifying sexual harassment tweets. J. Soft Comput. Explor. 2022, 3, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radjavani, A.; Sasongko, T.B. Analisa Perbandingan Algoritma CNN dan LSTM untuk Klasifikasi Pesan Cyberbullying pada Twitter. Indones. J. Comput. Sci. 2023, 12, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Moreau, T.; Jiang, Z.; Zheng, L.; Yan, E.; Cowan, M.; Shen, H.; Wang, L.; Hu, Y.; Ceze, L.; et al. TVM: An Automated End-to-End Optimizing Compiler for Deep Learning. arXiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yao, L.; Sun, A.; Tay, Y. Deep Learning Based Recommender System: A Survey and New Perspectives. ACM Computing Surveys 2019, 52, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long Short-Term Memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badjatiya, P.; Gupta, S.; Gupta, M.; Varma, V. Deep Learning for Hate Speech Detection in Tweets. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on World Wide Web Companion, Perth, Australia, 3–7 April 2017; pp. 759–760. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Lee, B.; Sohn, K.-A. Why Is It Hate Speech? Masked Rationale Prediction for Explainable Hate Speech Detection. arXiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, Y. Hate Speech Detection based on Sentiment Knowledge Sharing. In Proceedings of the Joint Conference of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (ACL-IJCNLP 2021), Online, 1–6 August 2021; pp. 7158–7166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.; Wiegand, M. A Survey on Hate Speech Detection using Natural Language Processing. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Workshop on Natural Language Processing for Social Media (SocialNLP), Valencia, Spain, 3–7 April 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Chen, Y. Generative AI for Synthetic Data Generation: Methods, Challenges and the Future. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.04190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanadian, H.; Nejadgholi, I.; Osman, H.A. Socially Aware Synthetic Data Generation for Suicidal Ideation Detection Using Large Language Models. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 14350–14363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| True Label | Neutral (0) | Insult (1) | Defamation (2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neutral (0) | 54 | 0 | 0 |
| Insult (1) | 15 | 32 | 2 |
| Defamation (2) | 5 | 0 | 42 |
| Label | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neutral (0) | 0.73 | 1.00 | 0.84 | 54 |
| Insult (1) | 1.00 | 0.65 | 0.79 | 49 |
| Defamation (2) | 0.95 | 0.89 | 0.92 | 47 |
| Accuracy: 0.85 (85%) | ||||
| True Label | Neutral (0) | Insult (1) | Defamation (2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neutral (0) | 356 | 24 | 32 |
| Insult (1) | 15 | 274 | 31 |
| Defamation (2) | 19 | 27 | 222 |
| Label | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neutral (0) | 0.91 | 0.86 | 0.89 | 412 |
| Insult (1) | 0.84 | 0.86 | 0.85 | 320 |
| Defamation (2) | 0.78 | 0.83 | 0.80 | 268 |
| Accuracy: 0.85 (85%) | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wijaya, G.I.; Overbeek, M.V. Leveraging LSTM Neural Networks for Advanced Harassment Detection: Insights into Insults and Defamation in the U-Tapis Module. Eng. Proc. 2025, 107, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025107011
Wijaya GI, Overbeek MV. Leveraging LSTM Neural Networks for Advanced Harassment Detection: Insights into Insults and Defamation in the U-Tapis Module. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 107(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025107011
Chicago/Turabian StyleWijaya, Gerald Imanuel, and Marlinda Vasty Overbeek. 2025. "Leveraging LSTM Neural Networks for Advanced Harassment Detection: Insights into Insults and Defamation in the U-Tapis Module" Engineering Proceedings 107, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025107011
APA StyleWijaya, G. I., & Overbeek, M. V. (2025). Leveraging LSTM Neural Networks for Advanced Harassment Detection: Insights into Insults and Defamation in the U-Tapis Module. Engineering Proceedings, 107(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025107011






