Magnetic Nanoparticles for Toxic Wastewater Cleaning:Experimental Study on Phenol †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Synthesis
2.3. Stabilization and Silanization
2.4. Phenol Wastewater Model
2.5. Ultraviolet Radiation Exposure
2.6. Microstructural and Spectral Investigations
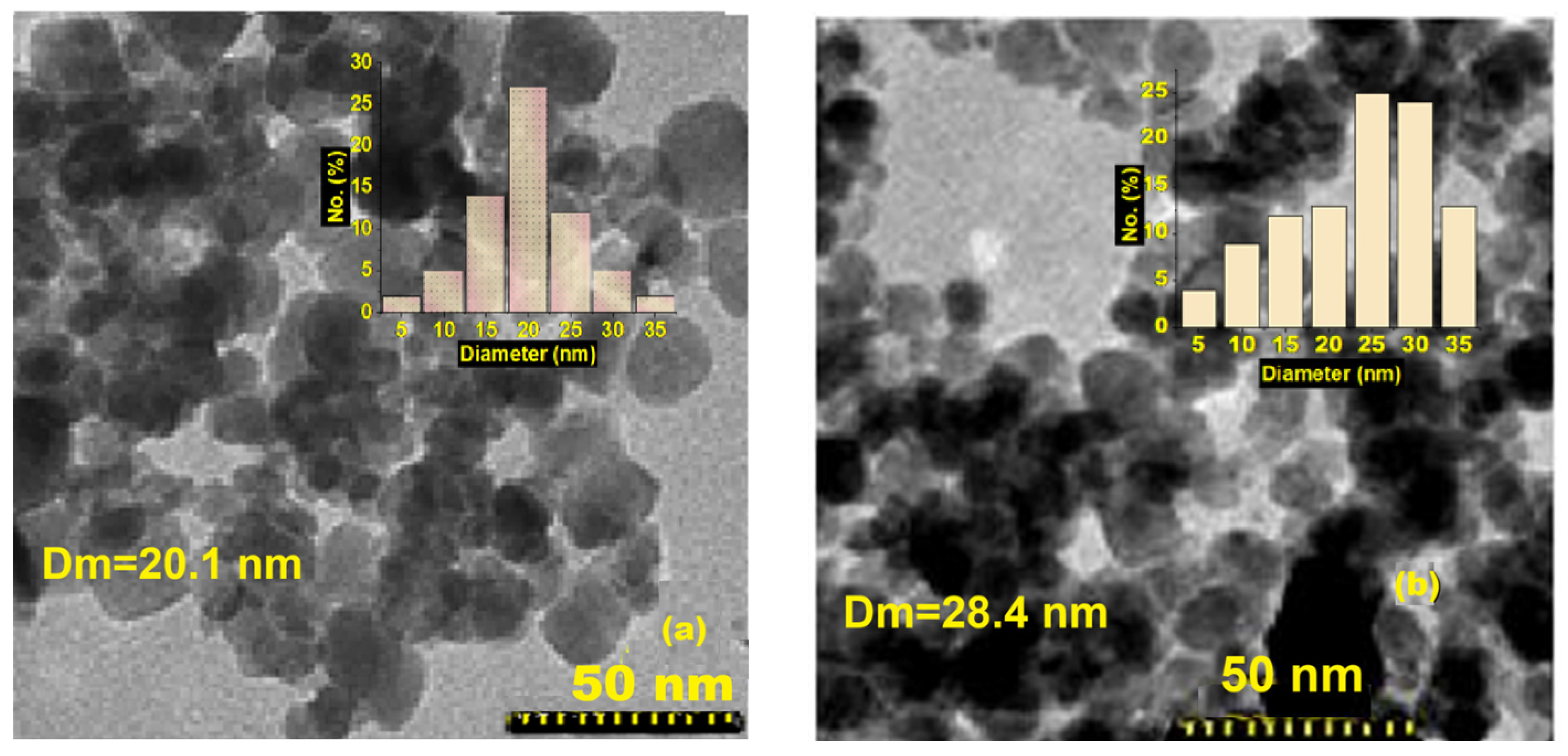
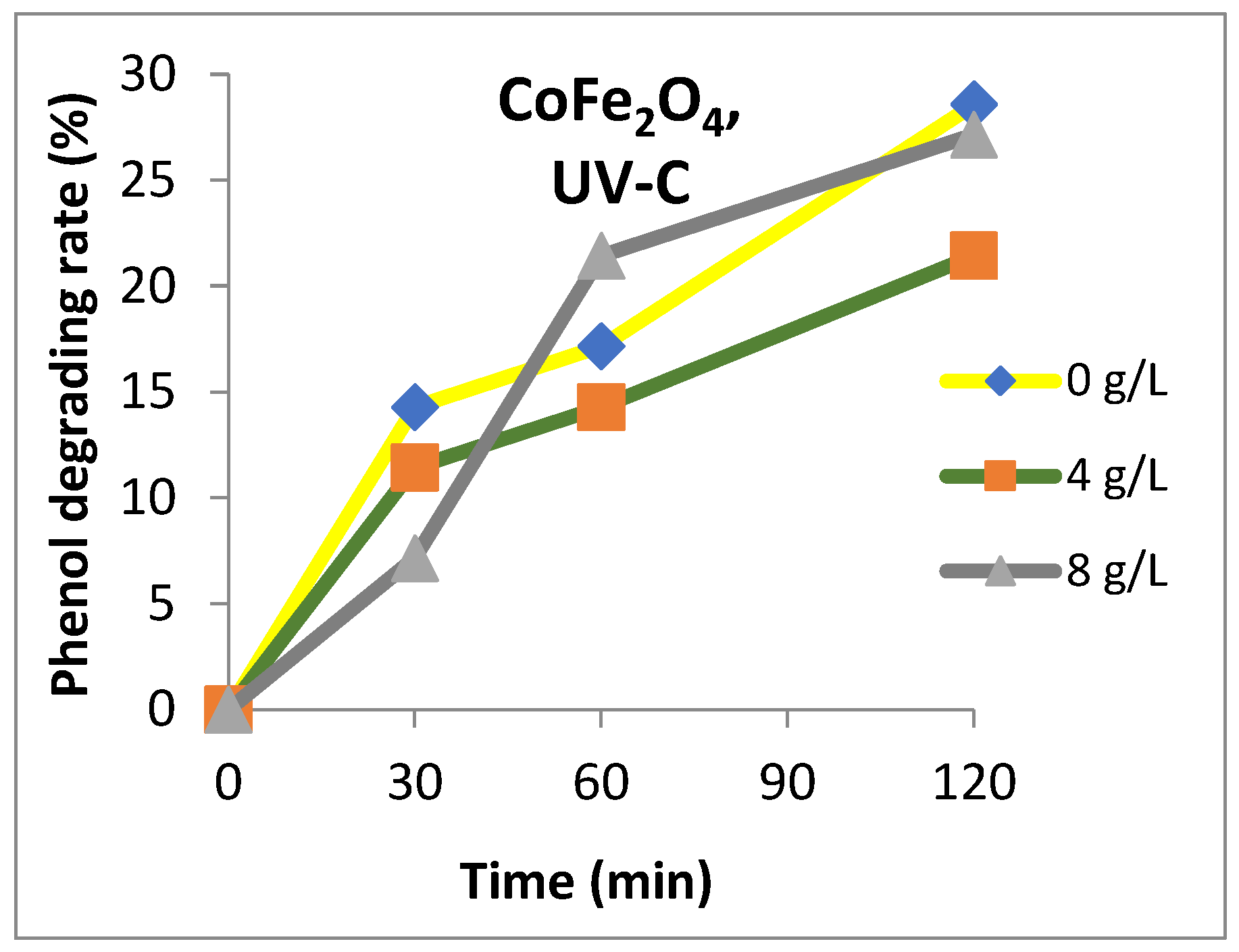
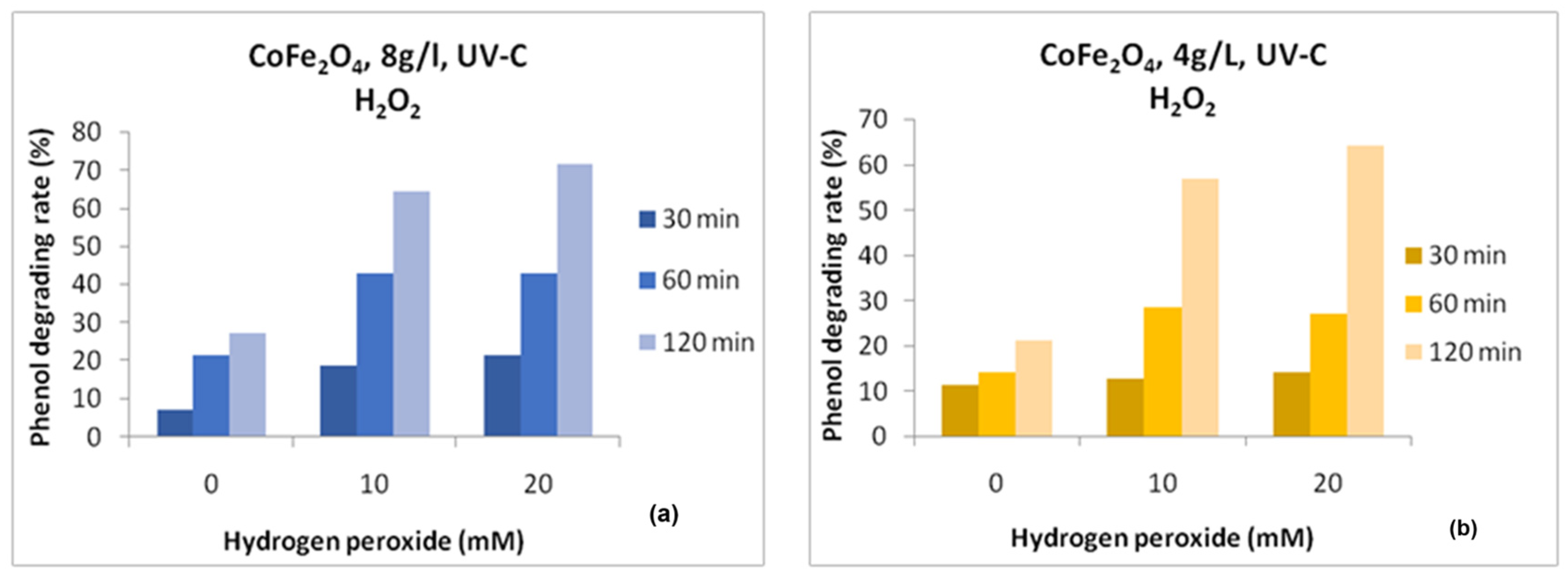
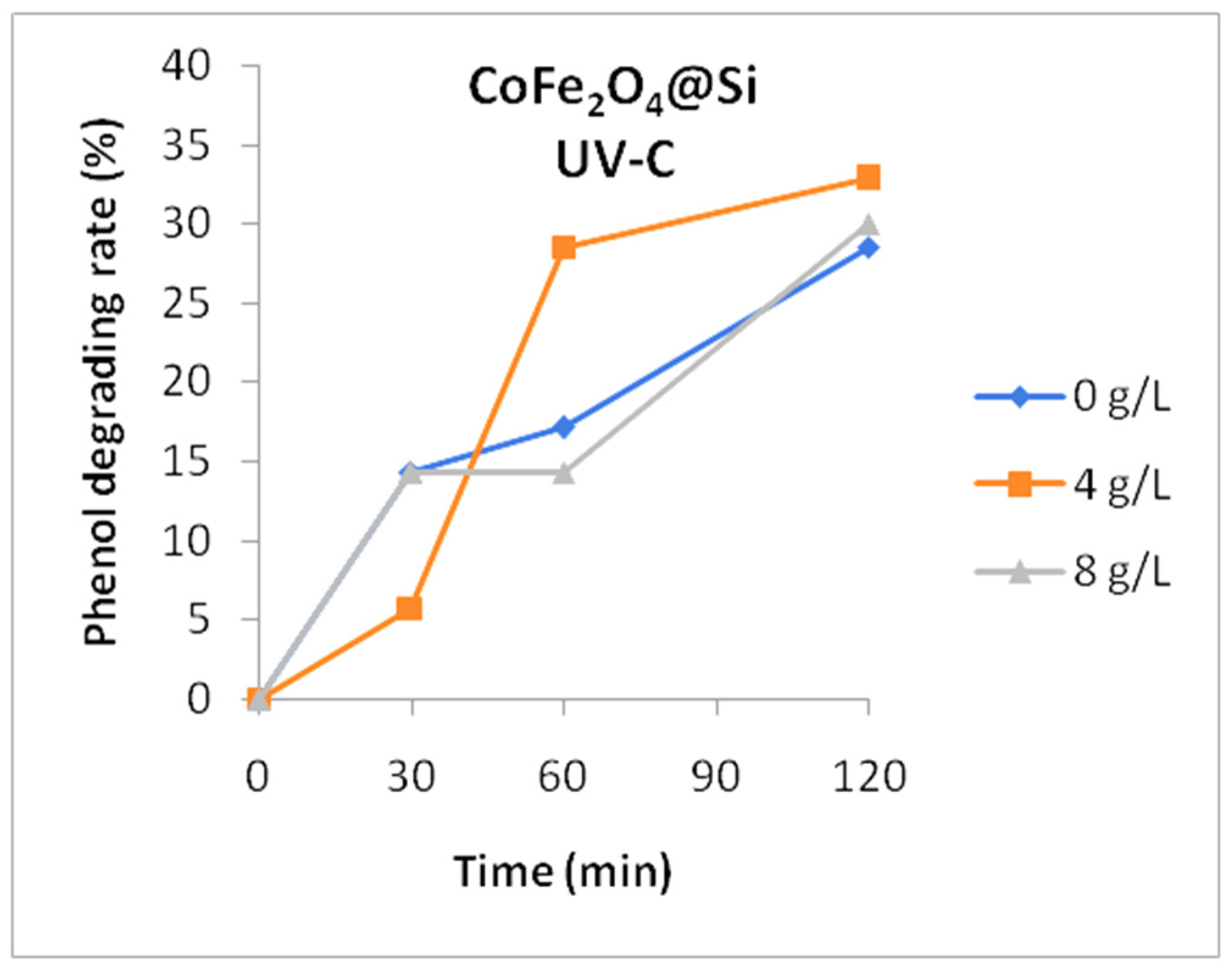
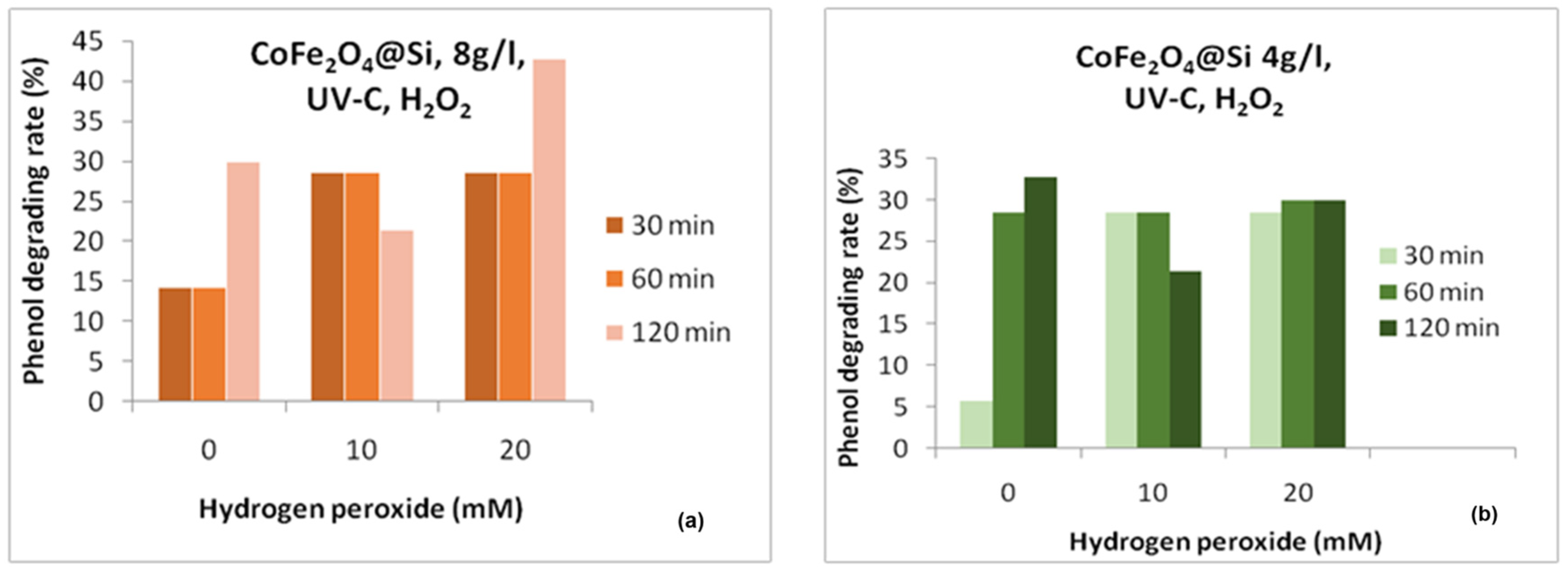
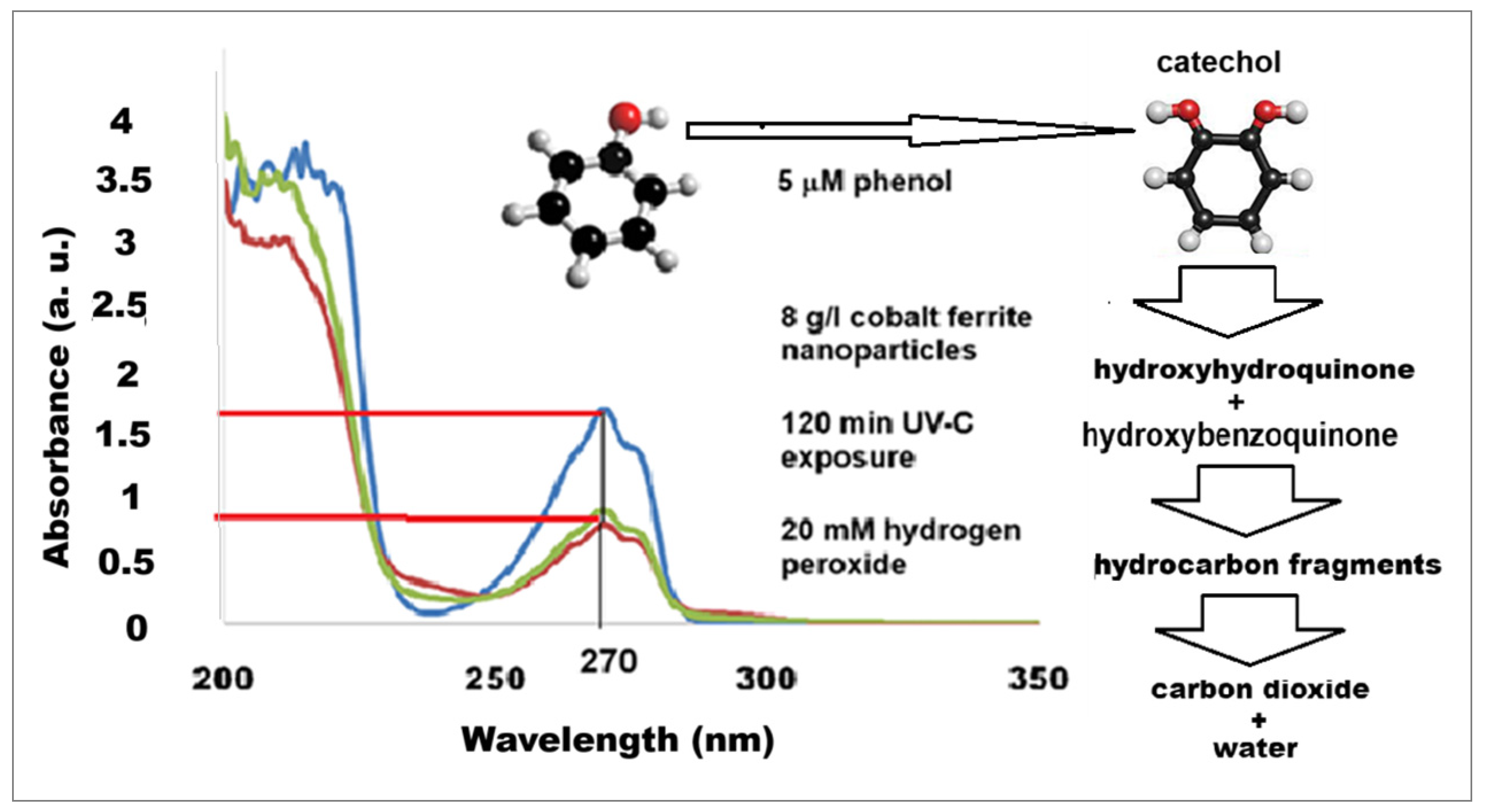
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UV | ultraviolet radiation |
| UV-C | ultraviolet radiation in the C subdomain |
| MNPs | magnetic nanoparticles |
| TEM | transmission electron microscopy |
| H2O2 | hydrogen peroxide |
| HO | hydroxyl |
| CoFe2O4 | cobalt ferrite |
References
- Yahya, M.D.; Obayomi, K.S.; Abdulkadir, M.B.; Iyaka, Y.A.; Olugbenga, A.G. Characterization of cobalt ferrite-supported activated carbon for removal of chromium and lead ions from tannery wastewater via adsorption equilibrium. Water Sci. Eng. 2020, 13, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, M.A.; El-Daly, A.A. Sm-substituted copper-cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: Preparation and assessment of structural, magnetic and photocatalytic properties for wastewater treatment applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 883, 160796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; You, J.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, H. Review on cobalt ferrite as photo-Fenton catalysts for degradation of organic waste water. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2023, 13, 274–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawi, A.K.; Hassan, R.; Alghamdi, A.M.; Ismail, B.; Osman, R.M.; Salama, R.S. Advancing cobalt ferrite-supported activated carbon from orange peels for real pulp and paper mill wastewater treatment. Desalin. Water Treat. 2024, 318, 100331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alia, A.E.; Salema, W.M.; Younes, S.M.; Elabdeen, A.Z. Ferrite nanocomposite (Rice Straw-CoFe2O4) as new chemical modified for treatment of heavy metal from waste water. Hydrol. Curr. Res. 2019, 10, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, J.C.; Cardoso, C.E.; Tavares, D.S.; Trindade, T.; Vale, C.; Freitas, R.; Pereira, E. Removal of chromium (III) from contaminated waters using cobalt ferrite: How safe is remediated water to aquatic wildlife? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 28789–28802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassar, M.Y.; Khatab, M. Cobalt ferrite nanoparticles via a template-free hydrothermal route as an efficient nano-adsorbent for potential textile dye removal. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 79688–79705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavari, S.; Mahmodi, N.M.; Teymouri, P.; Shahmoradi, B.; Maleki, A. Cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: Preparation, characterization and anionic dye removal capability. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 59, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Dosanjh, H.S.; Singh, H. Surface modified spinel cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for cationic dye removal: Kinetics and thermodynamics studies. J. Water Proc. Eng. 2016, 11, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.M.; Badawy, A.A.; Essawy, H.A. Improvement of dyes removal from aqueous solution by nanosized cobalt ferrite treated with humic acid during coprecipitation. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2019, 9, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayalakshmi, R.; Jeyanthi, J.; Sidhaarth, K.A. Versatile application of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for the removal of heavy metals and dyes from aqueous solution. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2022, 17, 100659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tan, L.; Tham, N.T.H.; Uyen, D.T.T.; Van Thinh, P. Statistical analysis of expanded graphite-decorated cobalt ferrite as adsorbent for removal of Congo Red dye using response surface methodology. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 38, 2737–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshanfekr Rad, L.; FarshiGhazani, B.; Irani, M.; Sadegh Sayyafan, M.; Haririan, I. Comparison study of phenol degradation using cobalt ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by hydrothermal and microwave methods. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 56, 3393–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, T.T.T.; Le, S.T.T.; Channei, D.; Khanitchaidecha, W.; Nakaruk, A. Photodegradation mechanisms of phenol in the photocatalytic process. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2016, 42, 5961–5974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cechinel, M.A.P.; Nicolini, J.L.; Tápia, P.M.; Miranda, E.A.C.; Eller, S.; de Oliveira, T.F.; Raupp-Pereira, F.; Montedo, O.R.K.; Wermuth, T.B.; Arcaro, S. Cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4) spinel as a new efficient magnetic heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst for wastewater treatment. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatarchuk, T.; Danyliuk, N.; Shyichuk, A.; Kotsyubynsky, V.; Lapchuk, I.; Mandzyuk, V. Green synthesis of cobalt ferrite using grape peroxide extract: The impact of cation distribution and inversion degree on the catalytic activity in the decomposition of hydrogen. Emergent Mater. 2022, 5, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massart, R. Preparation of aqueous magnetic liquids in alkaline and acidic media. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1981, 17, 1247–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Wu, G.; Gu, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Gao, H.; Ma, J. Magnetic and pH-sensitive nanoparticles for antitumor drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 103, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, D.; García, R.; Marín, R.; Barrera-Solano, C.; Blanco, E.; Domínguez, M.; Ramírez-del-Solar, M. Maghemite–silica nanocomposites: Sol–gel processing enhancement of the magneto-optical response. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 475706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabha, I.; Lathasree, S. Photodegradation of phenol by zinc oxide, titania and zinc oxide–titania composites: Nanoparticle synthesis, characterization and comparative photocatalytic efficiencies. Mat. Sci. Semicon. Proc. 2014, 26, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetteh, S.; Zugle, R.; Adotey, J.P.K.; Quashie, A. Electronic Spectra of ortho-Substituted Phenols: An Experimental and DFT Study. J. Spectrosc. 2018, 1, 4193657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puscasu, E.; Sacarescu, L.; Popescu-Lipan, L.; Nica, V.; Grigoras, M.; Domocos, A.; Lupu, N.; Creanga, D. Study on the effect of some surface phenomena on the properties of citrate capped cobalt doped ferrites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 483, 1182–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świderska-Dąbrowska, R. Phenol oxidation in the photo-Fenton process catalyzed by clinoptylolite modified with Co. Environ. Protect. Ann. 2015, 17, 113–124. [Google Scholar]
- Berro, Y.; Gueddida, S.; Lebègue, S.; Pasc, A.; Canilho, N.; Kassir, M.; El Haj Hassan, F.; Badawi, M. Atomistic description of phenol, CO and H2O adsorption over crystalline and amorphous silica surfaces for hydrodeoxygenation applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 494, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalzone, A.; Bonifacio, M.A.; Cometa, S.; Cucinotta, F.; De Giglio, E.; Ferreira, A.M.; Gentile, P. pH-triggered adhesiveness and cohesiveness of chondroitin sulfate-catechol biopolymer for biomedical applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murillo-Acevedo, Y.S.; Giraldo, L.; Poon, P.S.; Matos, J.; Moreno-Piraján, J.C. The Cramer’s rule for the parametrization of phenol and its hydroxylated byproducts: UV spectroscopy vs. high performance liquid chromatography. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 6746–6757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oprica, L.; Popescu-Lipan, L.; Sacarescu, L.; Costache, M.; Hincu, C.; Creanga, D. Magnetic Nanoparticles for Toxic Wastewater Cleaning:Experimental Study on Phenol. Eng. Proc. 2025, 104, 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025104087
Oprica L, Popescu-Lipan L, Sacarescu L, Costache M, Hincu C, Creanga D. Magnetic Nanoparticles for Toxic Wastewater Cleaning:Experimental Study on Phenol. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 104(1):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025104087
Chicago/Turabian StyleOprica, Lacramioara, Larisa Popescu-Lipan, Liviu Sacarescu, Mihai Costache, Cosmin Hincu, and Dorina Creanga. 2025. "Magnetic Nanoparticles for Toxic Wastewater Cleaning:Experimental Study on Phenol" Engineering Proceedings 104, no. 1: 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025104087
APA StyleOprica, L., Popescu-Lipan, L., Sacarescu, L., Costache, M., Hincu, C., & Creanga, D. (2025). Magnetic Nanoparticles for Toxic Wastewater Cleaning:Experimental Study on Phenol. Engineering Proceedings, 104(1), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025104087






