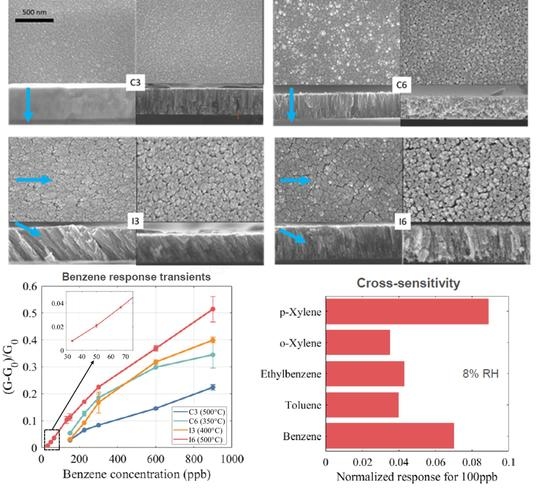
Detection of Indoor Air Pollutants Using Reactive Sputtering/GLAD of Tin Oxide Thin Films †
Abstract
:Supplementary Materials
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El Mohajir, A.; Sanchez, J.-B.; Arab Pour Yazdi, M.; Heintz, O.; Martin, N. Detection of Indoor Air Pollutants Using Reactive Sputtering/GLAD of Tin Oxide Thin Films. Chem. Proc. 2021, 5, 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/CSAC2021-10548
El Mohajir A, Sanchez J-B, Arab Pour Yazdi M, Heintz O, Martin N. Detection of Indoor Air Pollutants Using Reactive Sputtering/GLAD of Tin Oxide Thin Films. Chemistry Proceedings. 2021; 5(1):89. https://doi.org/10.3390/CSAC2021-10548
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl Mohajir, Achraf, Jean-Baptiste Sanchez, Mohammad Arab Pour Yazdi, Olivier Heintz, and Nicolas Martin. 2021. "Detection of Indoor Air Pollutants Using Reactive Sputtering/GLAD of Tin Oxide Thin Films" Chemistry Proceedings 5, no. 1: 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/CSAC2021-10548
APA StyleEl Mohajir, A., Sanchez, J.-B., Arab Pour Yazdi, M., Heintz, O., & Martin, N. (2021). Detection of Indoor Air Pollutants Using Reactive Sputtering/GLAD of Tin Oxide Thin Films. Chemistry Proceedings, 5(1), 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/CSAC2021-10548