Numerical and Experimental Modeling of Paper-Based Actuators †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Modeling
2.2.1. Concept of Design
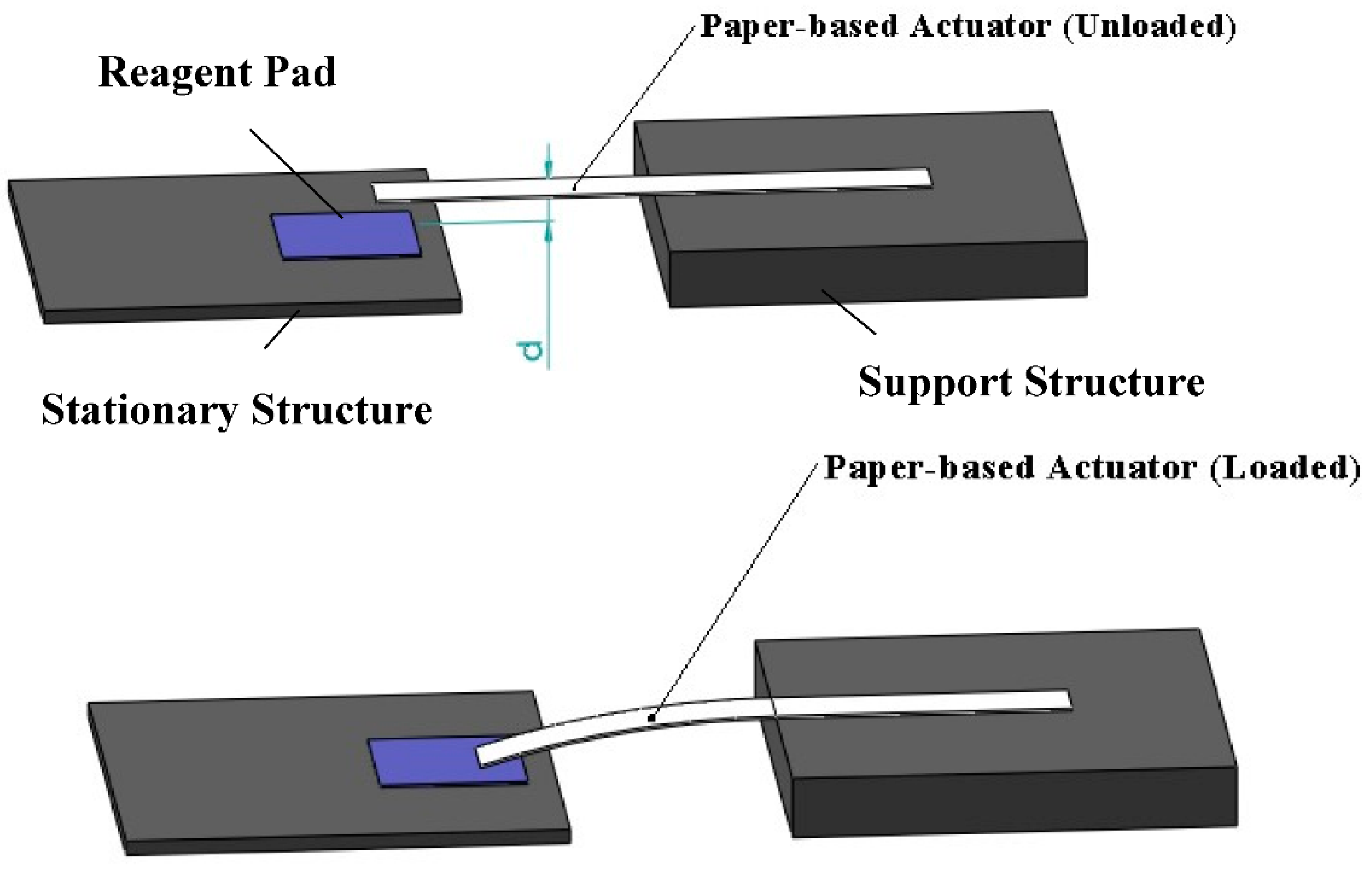
Single Cantilever Design
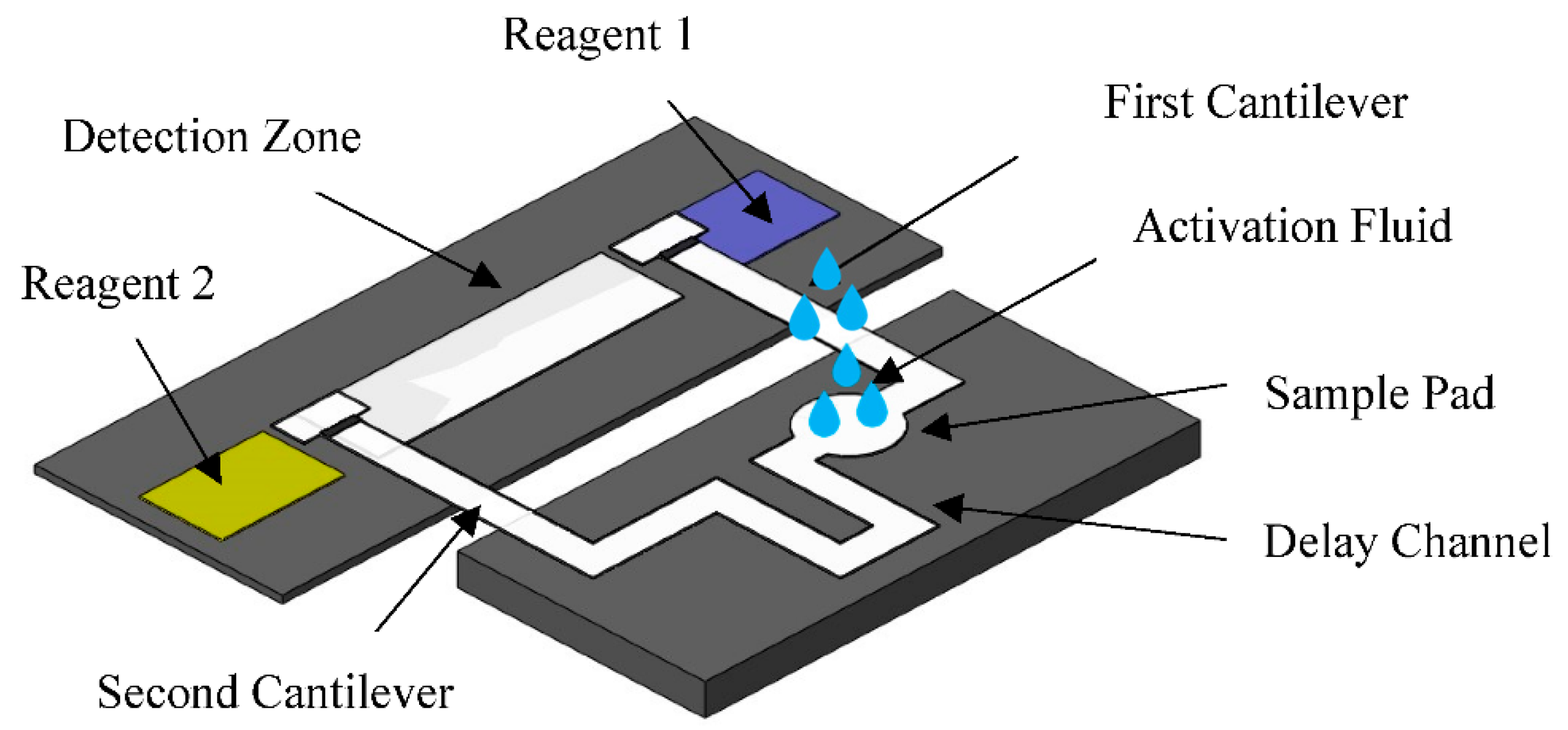
Double Cantilever Design
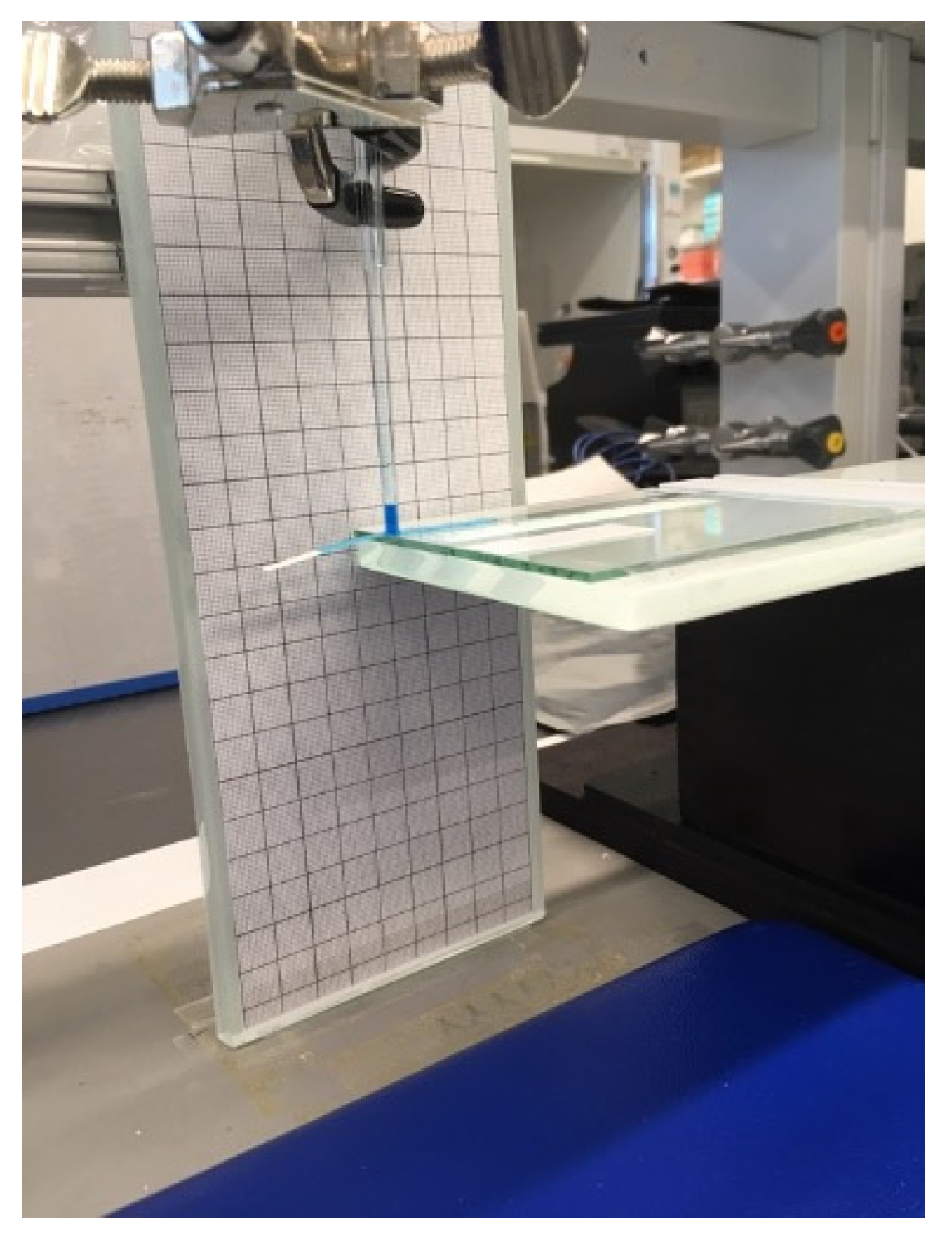
2.2.2. Experimental Model
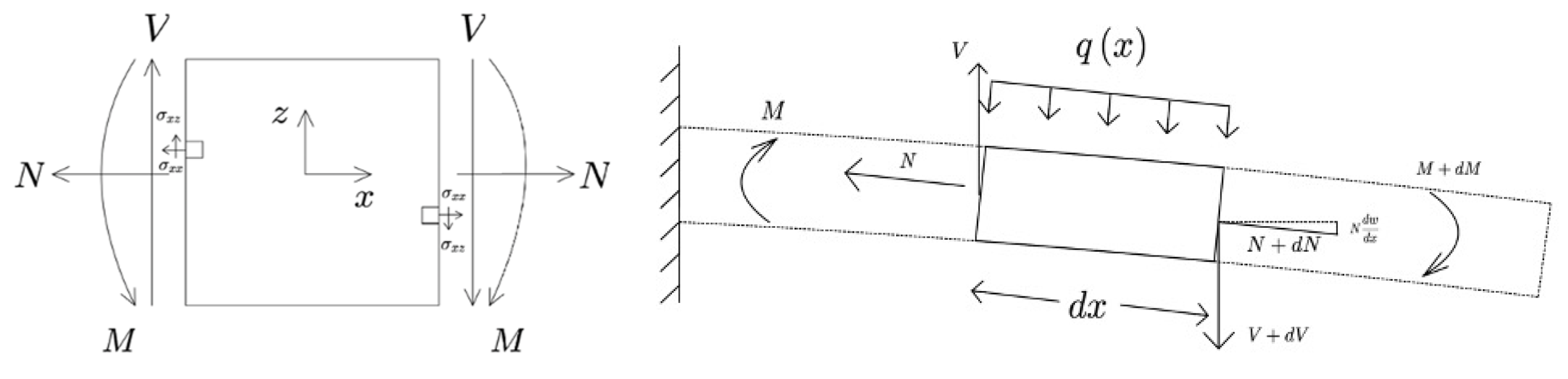
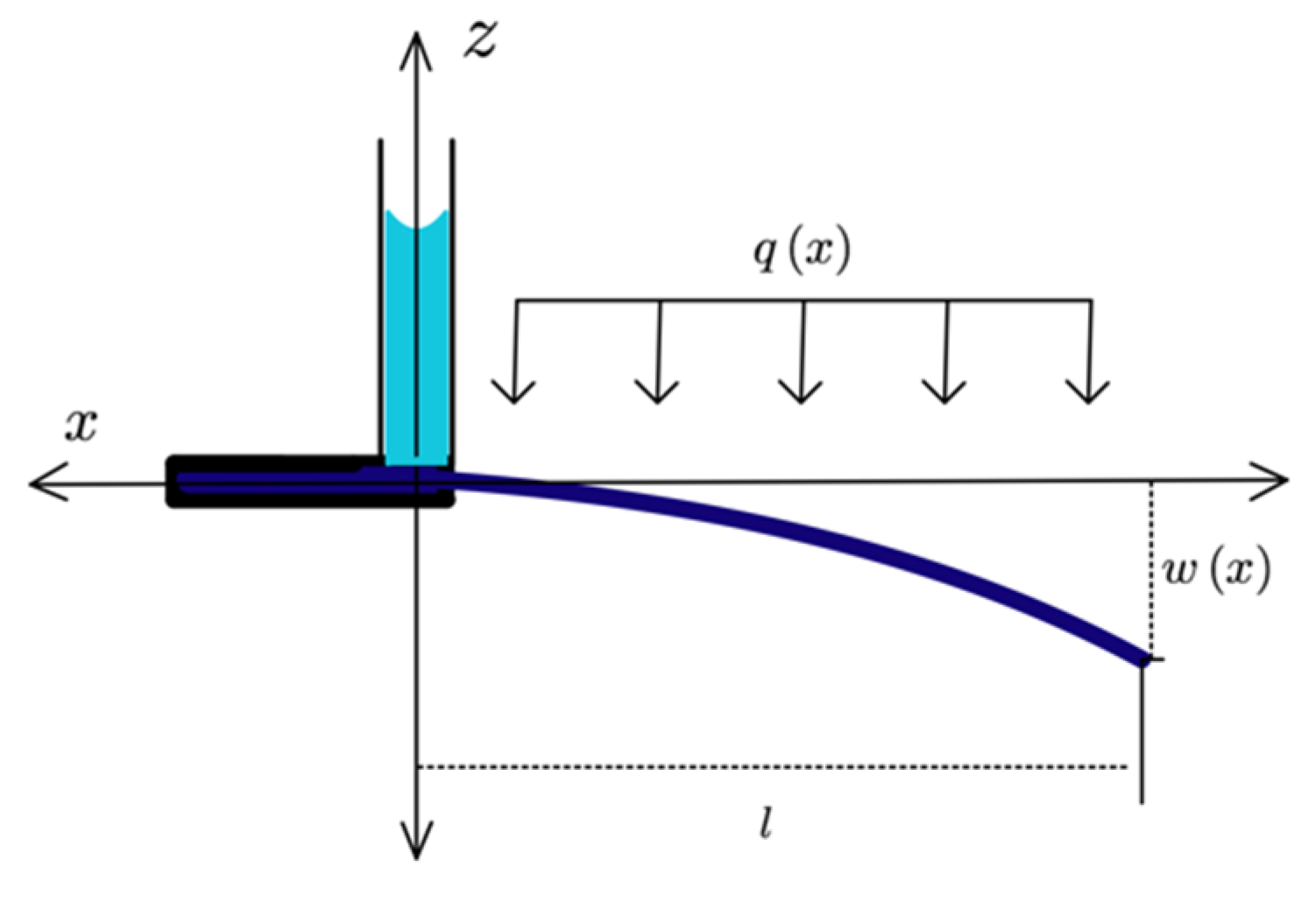
2.2.3. Mathematical Model
Modeling of Flow in Paper
Modeling of PBC
Non-Dimensional Model of PBC
Solution for PBC
3. Results
3.1. Analytical Solution
3.2. Numerical Solution
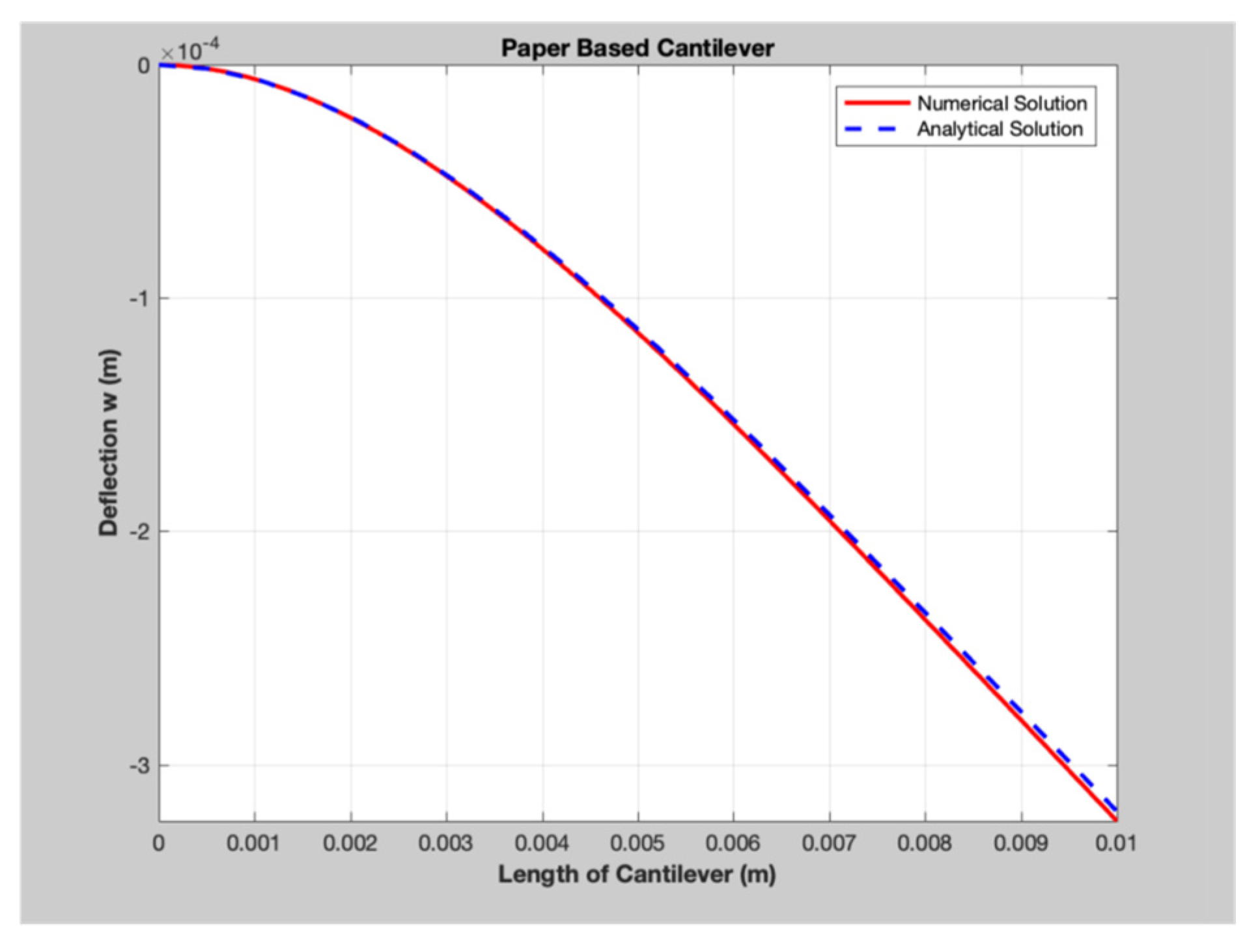
3.3. Comparison of Numerical and Analytical Solution
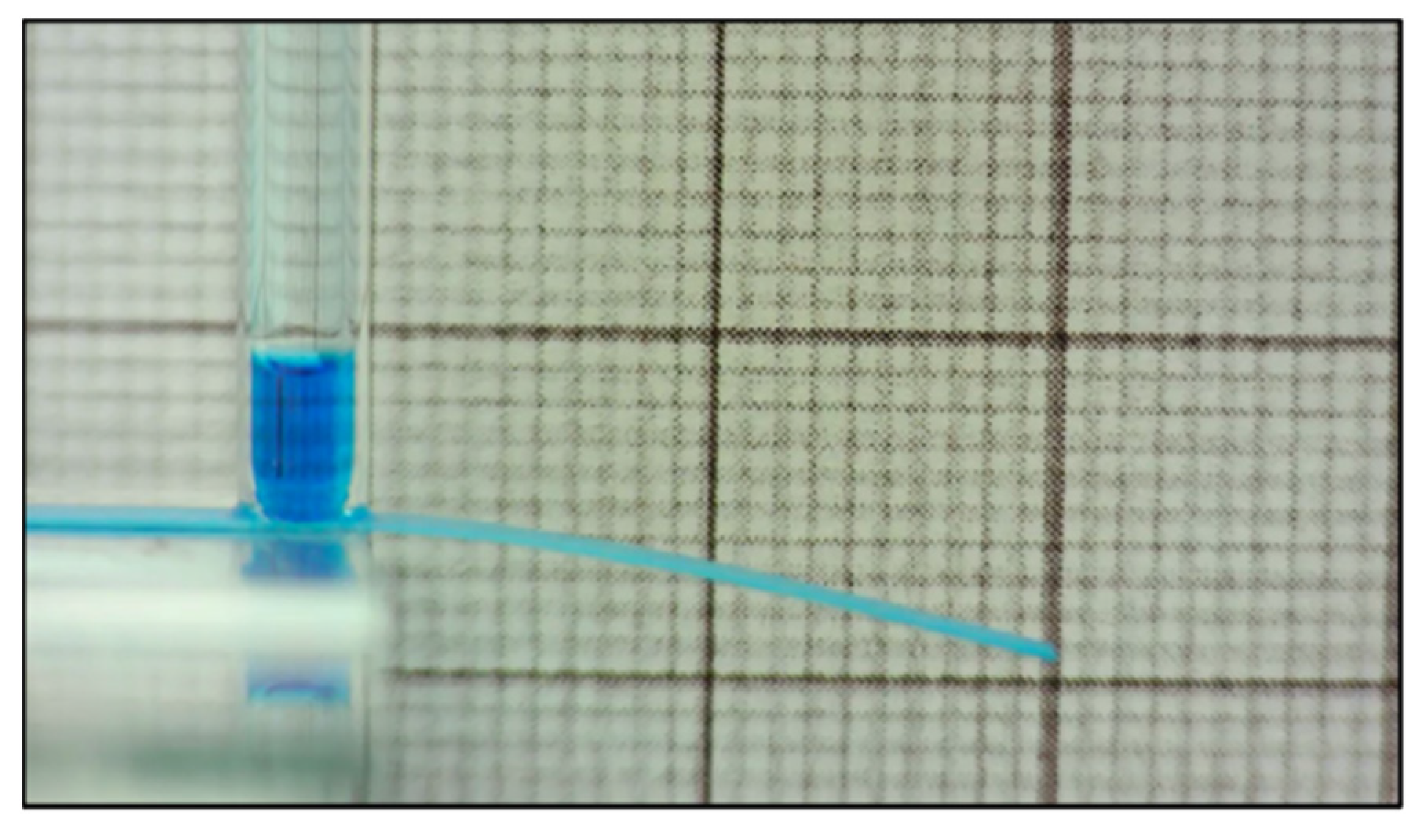
3.4. Experimental Results
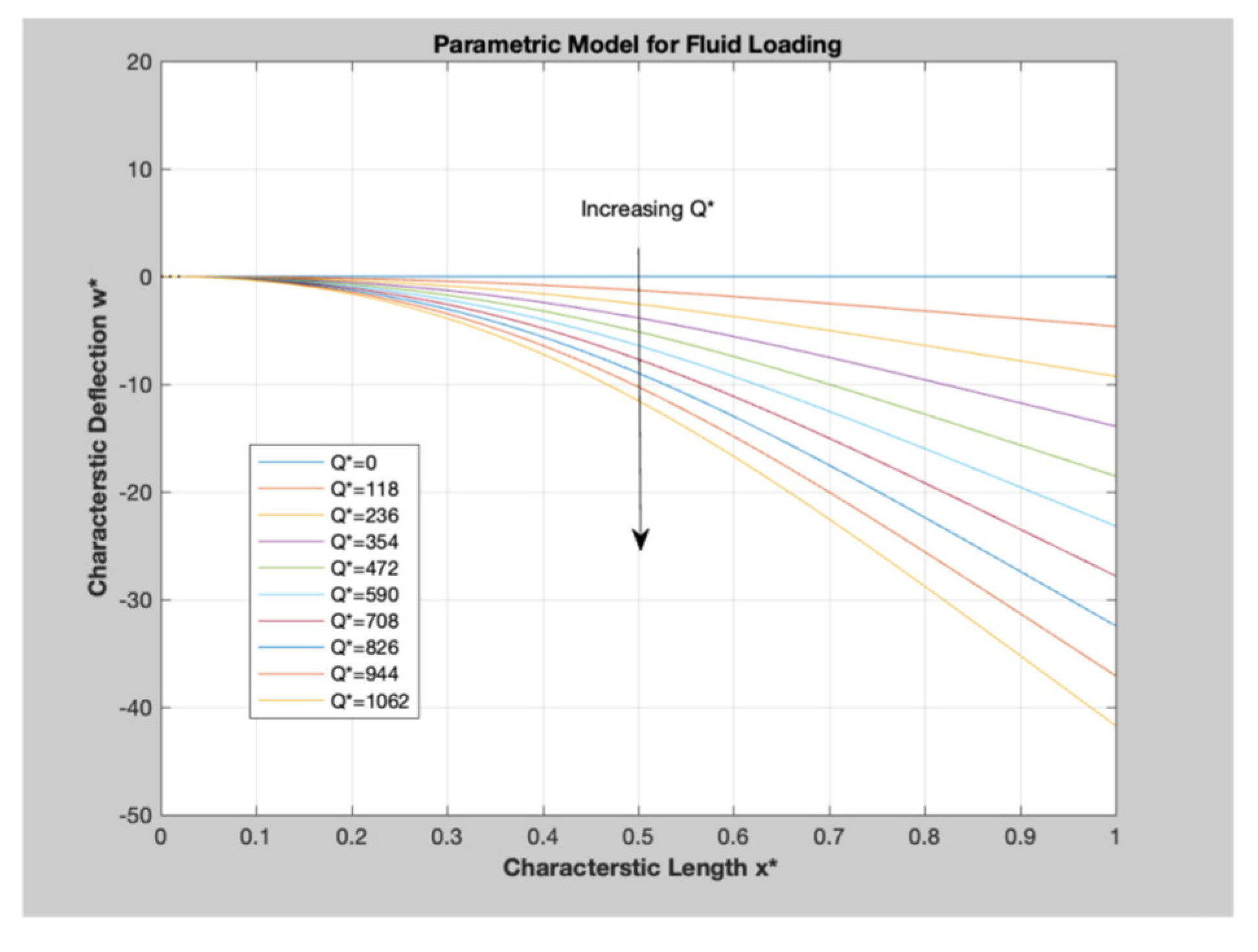
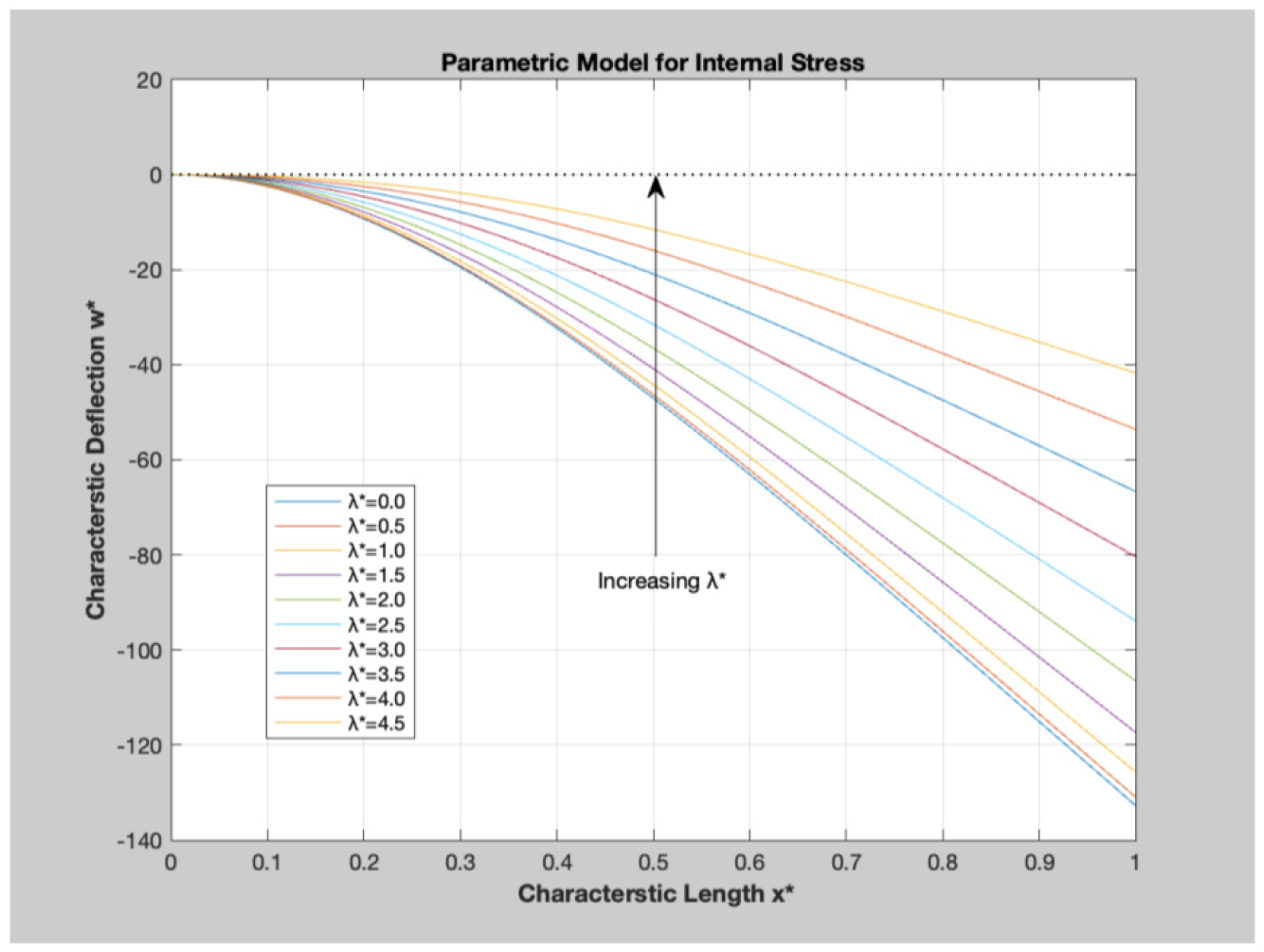
3.5. Parametric Model
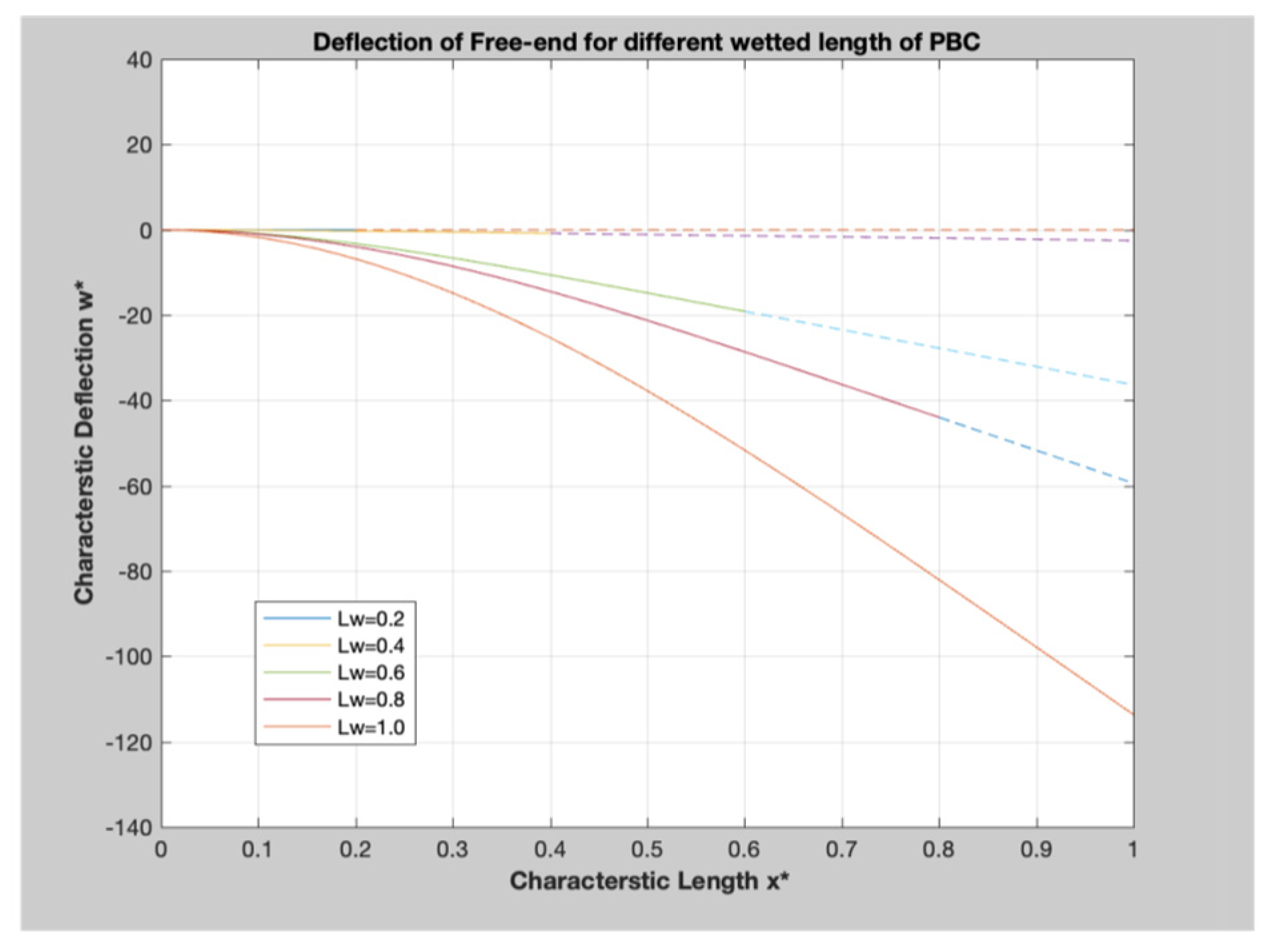
3.6. Transverse Displacement of the Free end of PBC
3.7. Model Summary
- The response deflection of PBC results in identical values both analytically and numerically. The analytical solution is obtained by the use of an experimental value for maximum deflection, whereas the numerical solution is obtained by the use of the material property of PBC, obtained from Table 3;
- Parametric model has been utilized to better understand the effect of fluid loading and internal stress on response deflection of PBC;
- The Washburn flow model is utilized to govern the imbibition of fluid into PBC, and the plots of the response deflection of the free end is demonstrated in Figure 11.
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of Solutions
4.2. Non-Dimensional Model
4.3. Parametric Model
4.4. Transverse Displacement of Free End of PBC
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Davy, J.; Davy, H. LXVIII. On a gaseous compound of carbonic oxide and chlorine. Philos. Mag. 1812, 39, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Müller, R.H.; Clegg, D.L. Automatic Paper Chromatography. Anal. Chem. 1949, 21, 1123–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Butte, M.; Whitesides, G.M. Patterned Paper as a Platform for Inexpensive, Low-Volume, Portable Bioassays. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1318–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhm, A.; Carstens, F.; Trieb, C.; Schabel, S.; Biesalski, M. Engineering microfluidic papers: Effect of fiber source and paper sheet properties on capillary-driven fluid flow. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2014, 16, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carstens, F.; Gamelas, J.; Schabel, S. Engineering microfluidic papers: Determination of fibre source and paper sheet prop-erties and their influence on capillary-driven fluid flow. Cellulose 2017, 24, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tian, J.F.; Nguyen, T.; Shen, W. Paper-Based Microfluidic Devices by Plasma Treatment. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 9131–9134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanshahi-Anbuhi, S.; Chavan, P.; Sicard, C.; Leung, V.; Hossain, S.M.Z.; Pelton, R.; Brennan, J.D.; Filipe, C.D. Creating fast flow channels in paper fluidic devices to control timing of sequential reactions. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 5079–5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.N.; Choi, J.-S.; Kwon, J. Three-dimensional paper-based slip device for one-step point-of-care testing. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Nie, Z.; Cheng, C.-M.; Carrilho, E.; Wiley, B.; Whitesides, G.M. Programmable diagnostic devices made from paper and tape. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 2499–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, N.M.; Wong, W.S.; Liu, L.; Dewar, R.; Klapperich, C.M. A fully integrated paperfluidic molecular diagnostic chip for the extraction, amplification, and detection of nucleic acids from clinical samples. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayawardane, B.M.; Wei, S.; McKelvie, I.D.; Kolev, S. Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Device for the Determination of Nitrite and Nitrate. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 7274–7279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, H.; Phillips, S.T. Metering the Capillary-Driven Flow of Fluids in Paper-Based Microfluidic Devices. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 4181–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, B.; Liang, T.; Fu, E.; Ramachandran, S.; Kauffman, P.; Yager, P. Dissolvable fluidic time delays for programming mul-ti-step assays in instrument-free paper diagnostics. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 2840–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Cogswell, J.; Anagnostopoulos, C.; Faghri, M. A fluidic diode, valves, and a sequential-loading circuit fabricated on layered paper. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerbers, R.; Foellscher, W.; Chen, H.; Anagnostopoulos, C.; Faghri, M. A new paper-based platform technology for point-of-care diagnostics. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 4042–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.T.; Tsai, J.S.; Hsu, J.C.; Lu, Y.W. Automated paper-based devices by microfluidic timing-valve for competitive ELI-SA. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 30th International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 22–26 January 2017; pp. 1321–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, C.K.W.; He, F.; Nugen, S.R. An inkjet-printed electrowetting valve for paper-fluidic sensors. Analyst 2013, 138, 4998–5004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zwanenburg, P.; Liu, X. Magnetic timing valves for fluid control in paper-based microfluidics. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 2609–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, E.A.; Shen, R.; Zhao, S.; Linnes, J.C. Thermally actuated wax valves for paper-fluidic diagnostics. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 4230–4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, T.; Flanigan, S.; Weinstein, M.P.; Kalwa, U.; Legner, C.M.; Pandey, S. A fast, reconfigurable flow switch for paper microfluidics based on selective wetting of folded paper actuator strips. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 3621–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toley, B.J.; Wang, J.A.; Gupta, M.; Buser, J.R.; LaFleur, L.K.; Lutz, B.R.; Fu, E.; Yager, P. A versatile valving toolkit for automating fluidic operations in paper microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 1432–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Song, P.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, C.; Pan, P.; Li, X.; Li-Jessen, N.Y.K.; Liu, X. A paper-based microfluidic platform with shape-memory-polymer-actuated fluid valves for automated multi-step immunoassays. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2019, 5, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Cruz, A. Development of Paper-Based Hygro-Mechanical Systems for Liquid Characterization. Ph.D. Thesis, Concordia University, Montréal, QC, Canada, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Yuan, Y. Analytical Solution for an Infinite Euler-Bernoulli Beam on a Viscoelastic Foundation Subjected to Arbitrary Dynamic Loads. J. Eng. Mech. 2014, 140, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Kim, S.; Mahadevan, L. Bending and buckling of wet paper. Phys. Fluids 2016, 28, 042101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkelä, P.; Östlund, S. Orthotropic elastic–plastic material model for paper materials. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2003, 40, 5599–5620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qin, Q.-H. Methods of Fundamental Solutions in Solid Mechanics; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 53–90. [Google Scholar]



| Variables | Description | Dimension |
|---|---|---|
| x | Length coordinate | L |
| z | Height coordinate | L |
| t | Time | T |
| w | Deflection | L |
| q | Transverse loading | MT−2 |
| l | PBC length | L |
| b | PBC width | L |
| h | PBC height | L |
| ρ | Fluid density | ML−3 |
| E | Young’s modulus | ML−1T−2 |
| Variables | Expression | Description |
|---|---|---|
| x∗ | Characteristic Length | |
| w∗ | Characteristic Deflection | |
| t∗ | Characteristic Time | |
| λ∗ | Internal Stress Parameter | |
| Q∗ | Fluid Loading Parameter | |
| Rg | Radius of Gyration |
| Variables | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1000 kg/m3 | Density of water | |
| L | Volume of fluid moved into PBC | |
| m | Length of PBC | |
| b | m | Width of PBC |
| Height of PBC | ||
| N | N | Axial force |
| E | 20.5 MPa | Young’s modulus of wet paper [25] |
| Variables | Results (in mm) |
|---|---|
| Maximum Deflection of PBC | 3.04 |
| Change in Height of Capillary Tube | 8.96 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, A.; Heidari-Bafroui, H.; Charbaji, A.; Rahmani, N.; Anagnostopoulos, C.; Faghri, M. Numerical and Experimental Modeling of Paper-Based Actuators. Chem. Proc. 2021, 5, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/CSAC2021-10468
Kumar A, Heidari-Bafroui H, Charbaji A, Rahmani N, Anagnostopoulos C, Faghri M. Numerical and Experimental Modeling of Paper-Based Actuators. Chemistry Proceedings. 2021; 5(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/CSAC2021-10468
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Ashutosh, Hojat Heidari-Bafroui, Amer Charbaji, Nasim Rahmani, Constantine Anagnostopoulos, and Mohammad Faghri. 2021. "Numerical and Experimental Modeling of Paper-Based Actuators" Chemistry Proceedings 5, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/CSAC2021-10468
APA StyleKumar, A., Heidari-Bafroui, H., Charbaji, A., Rahmani, N., Anagnostopoulos, C., & Faghri, M. (2021). Numerical and Experimental Modeling of Paper-Based Actuators. Chemistry Proceedings, 5(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/CSAC2021-10468








