Discovery and Biochemical Characterization of a Novel Polyesterase for the Degradation of Synthetic Plastics †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Cloning and Expression of MorEst Gene and Purification of Recombinant Enzyme
2.2. Biochemical Characterization of Recombinant MorEst
2.3. Hydrolysis of PET Oligomer, PET and Biodegradable Polymers
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Almeida, E.L.; Carrillo Rincón, A.F.; Jackson, S.A.; Dobson, A.D.W. In silico screening and heterologous expression of a polyethylene terephthalate hydrolase (PETase)-like enzyme (SM14est) with polycaprolactone (PCL)-degrading activity, From the marine sponge-derived strain Streptomyces sp. SM14. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, R.; Breite, D.; Song, C.; Gräsing, D.; Ploss, T.; Hille, P.; Schwerdtfeger, R.; Matysik, J.; Schulze, A.; Zimmermann, W. Biocatalytic degradation efficiency of postconsumer polyethylene terephthalate packaging determined by their polymer microstructures. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1900491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza MacHado, A.A.; Lau, C.W.; Till, J.; Kloas, W.; Lehmann, A.; Becker, R.; Rillig, M.C. Impacts of microplastics on the soil biophysical environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 9656–9665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narancic, T.; O’Connor, K.E. Plastic waste as a global challenge: Are biodegradable plastics the answer to the plastic waste problem? Microbiology 2019, 165, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvador, M.; Abdulmutalib, U.; Gonzalez, J.; Kim, J.; Smith, A.A.; Faulon, J.-L.; Wei, R.; Zimmermann, W.; Jimenez, J.I. Microbial genes for a circular and sustainable bio-PET economy. Genes 2019, 10, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, S.; Hiraga, K.; Takehana, T.; Taniguchi, I.; Yamaji, H.; Maeda, Y.; Toyohara, K.; Miyamoto, K.; Kimura, Y.; Oda, K. A bacterium that degrades and assimilates poly(ethylene terephthalate). Science 2016, 351, 1196–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinozaki, Y.; Kikkawa, Y.; Sato, S.; Fukuoka, T.; Watanabe, T.; Yoshida, S.; Nakajima-Kambe, T.; Kitamoto, H.K. Enzymatic degradation of polyester films by a cutinase-like enzyme from Pseudozyma antarctica: Surface plasmon resonance and atomic force microscopy study. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 8591–8598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Wu, Y.R.; Lin, B.K.; Maskaoui, K.; Zhuang, D.H.; Zheng, T.L. Isolation and characterization of two phenol-degrading yeast strains from marine sediment. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2006, 76, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Shi, K.; Su, T.; Wang, Z. Comparison of poly(butylene succinate) biodegradation by Fusarium solani cutinase and Candida antarctica lipase. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2019, 164, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, L.-F.; Chen, X.-Y.; Yuan, X.-L.; Zhang, M.; Chai, Y.-J.; Shan, S.-D. Application and comparison in biosynthesis and biodegradation by Fusarium solani and Aspergillus fumigatus cutinases. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimarogona, M.; Nikolaivits, E.; Kanelli, M.; Christakopoulos, P.; Sandgren, M.; Topakas, E. Structural and functional studies of a Fusarium oxysporum cutinase with polyethylene terephthalate modification potential. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2015, 1850, 2308–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolaivits, E.; Kokkinou, A.; Karpusas, M.; Topakas, E. Microbial host selection and periplasmic folding in Escherichia coli affect the biochemical characteristics of a cutinase from Fusarium oxysporum. Protein Expr. Purif. 2016, 127, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
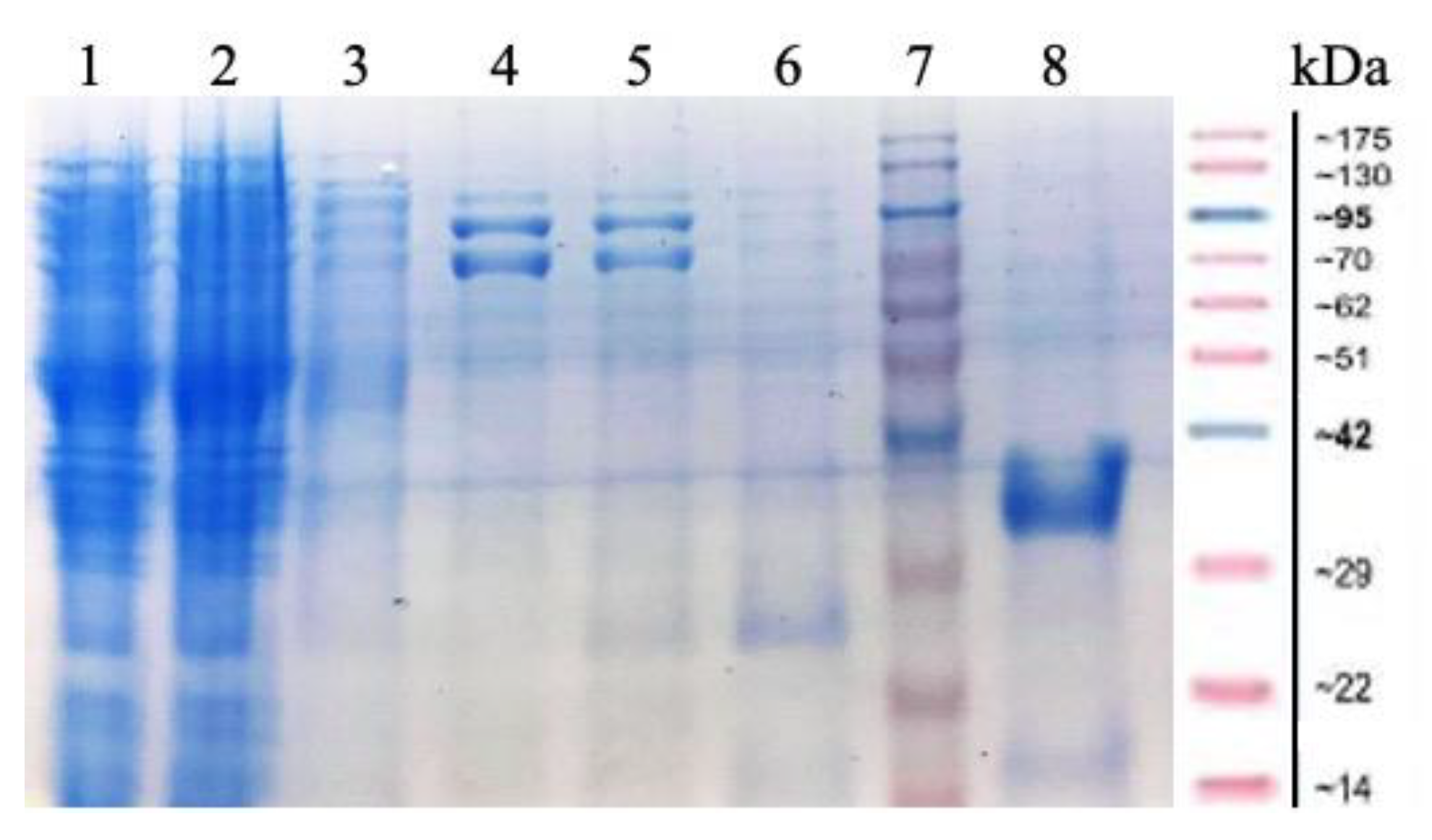
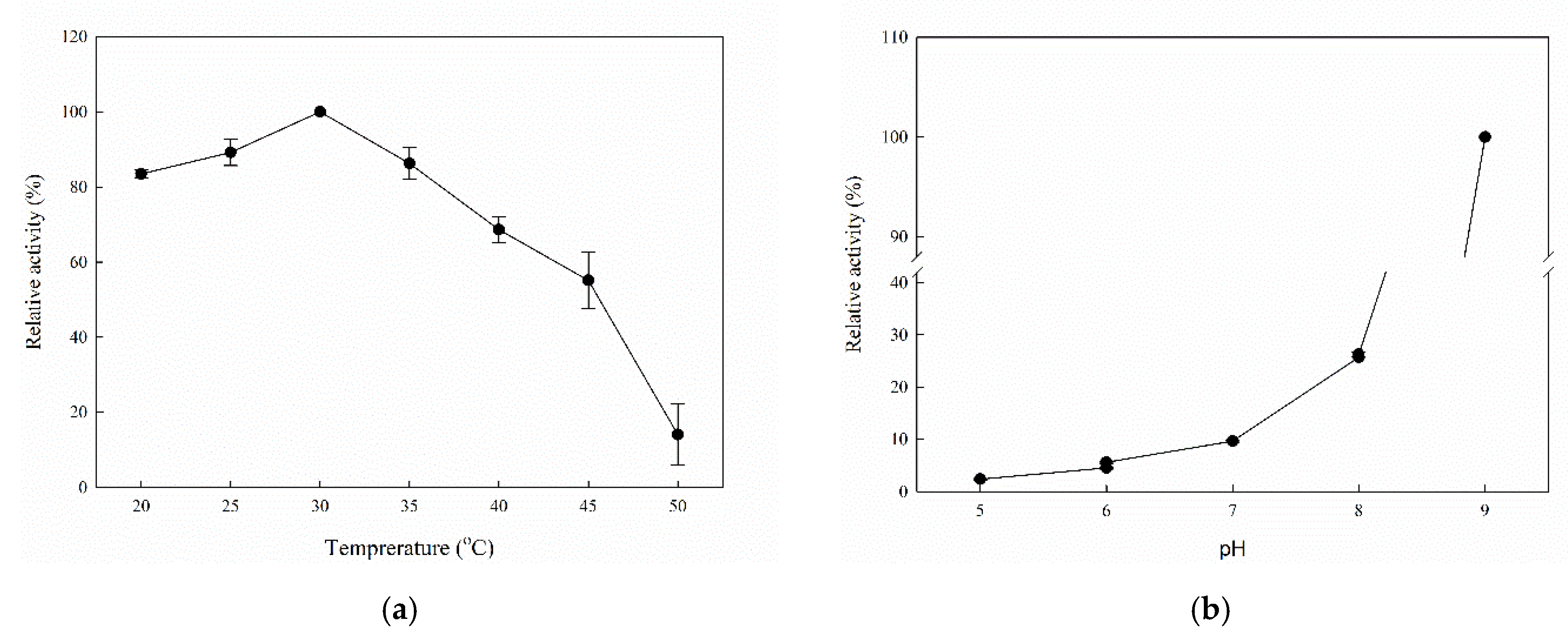
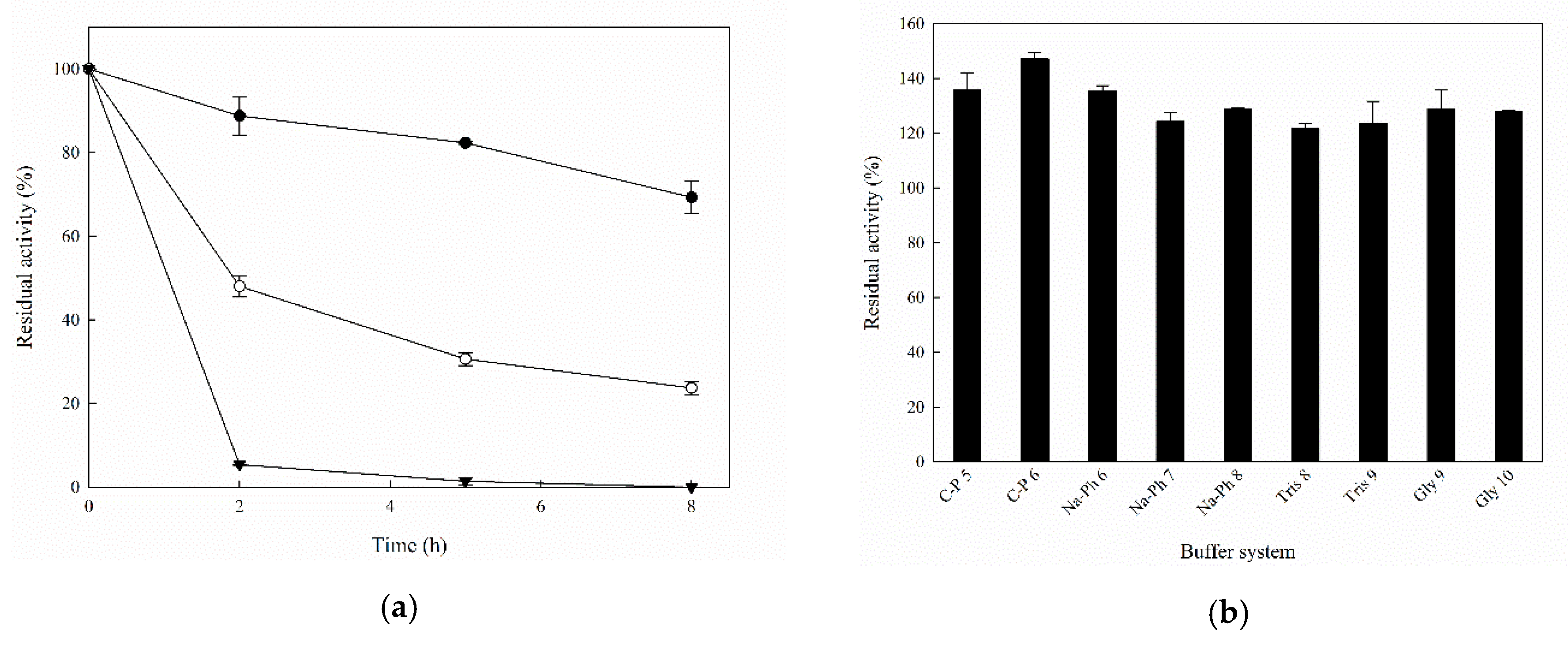
| Substrate | kcat (min−1) | KM (mM) | kcat/KM (min−1 mM−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| pNP-C2 | 69.6 ± 7.7 | 5.4 ± 1.0 | 12.8 ± 2.7 |
| pNP-C4 | 29.2 ± 1.3 | 1.7 ± 0.2 | 17.6 ± 2.0 |
| pNP-C8 | 5.8 ± 0.7 | 7.2 ± 1.1 | 0.8 ± 0.2 |
| pNP-C10 | 2.7 ± 0.5 | 7.0 ± 1.8 | 0.4 ± 0.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nikolaivits, E.; Dimopoulou, P.; Maslak, V.; Nikodinovic-Runic, J.; Topakas, E. Discovery and Biochemical Characterization of a Novel Polyesterase for the Degradation of Synthetic Plastics. Chem. Proc. 2020, 2, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECCS2020-07572
Nikolaivits E, Dimopoulou P, Maslak V, Nikodinovic-Runic J, Topakas E. Discovery and Biochemical Characterization of a Novel Polyesterase for the Degradation of Synthetic Plastics. Chemistry Proceedings. 2020; 2(1):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECCS2020-07572
Chicago/Turabian StyleNikolaivits, Efstratios, Phaedra Dimopoulou, Veselin Maslak, Jasmina Nikodinovic-Runic, and Evangelos Topakas. 2020. "Discovery and Biochemical Characterization of a Novel Polyesterase for the Degradation of Synthetic Plastics" Chemistry Proceedings 2, no. 1: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECCS2020-07572
APA StyleNikolaivits, E., Dimopoulou, P., Maslak, V., Nikodinovic-Runic, J., & Topakas, E. (2020). Discovery and Biochemical Characterization of a Novel Polyesterase for the Degradation of Synthetic Plastics. Chemistry Proceedings, 2(1), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECCS2020-07572







