Participation of the Cyanide Group in the Reaction Mechanism of Benzoxazole Formation: Monitoring by Continuous Flow Cell NMR †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
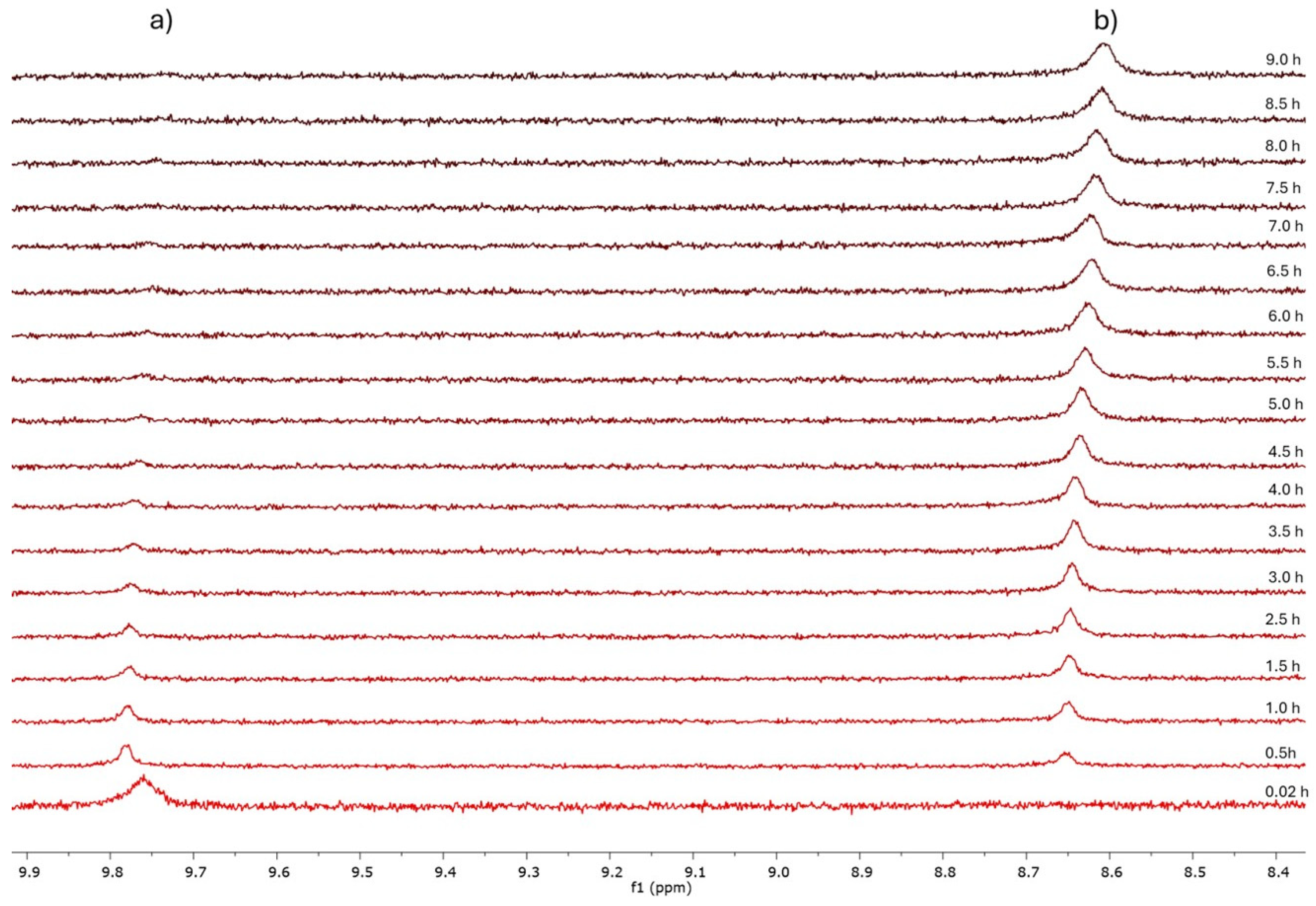
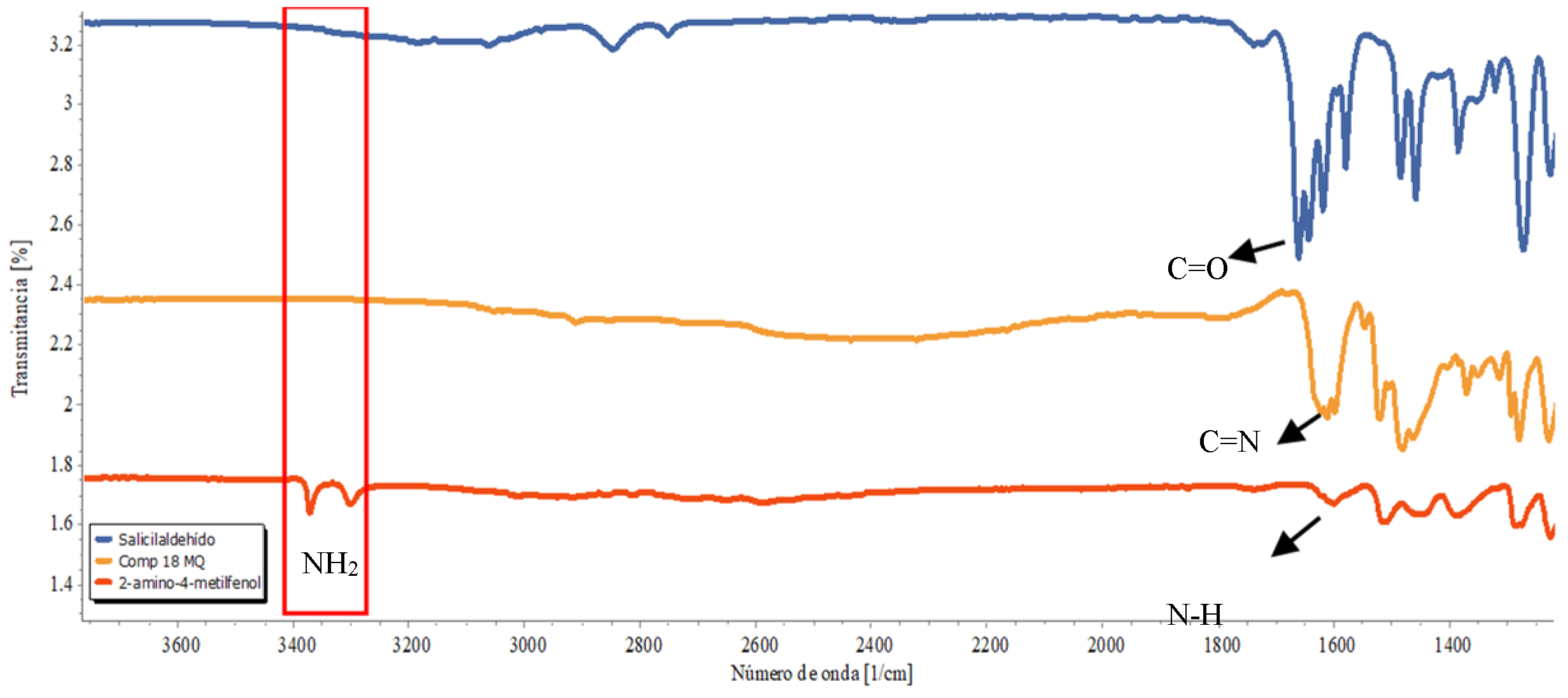
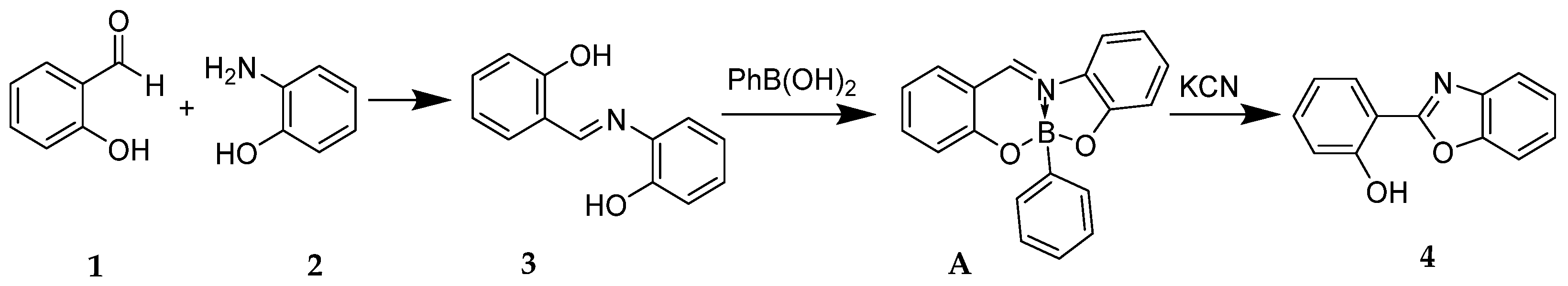
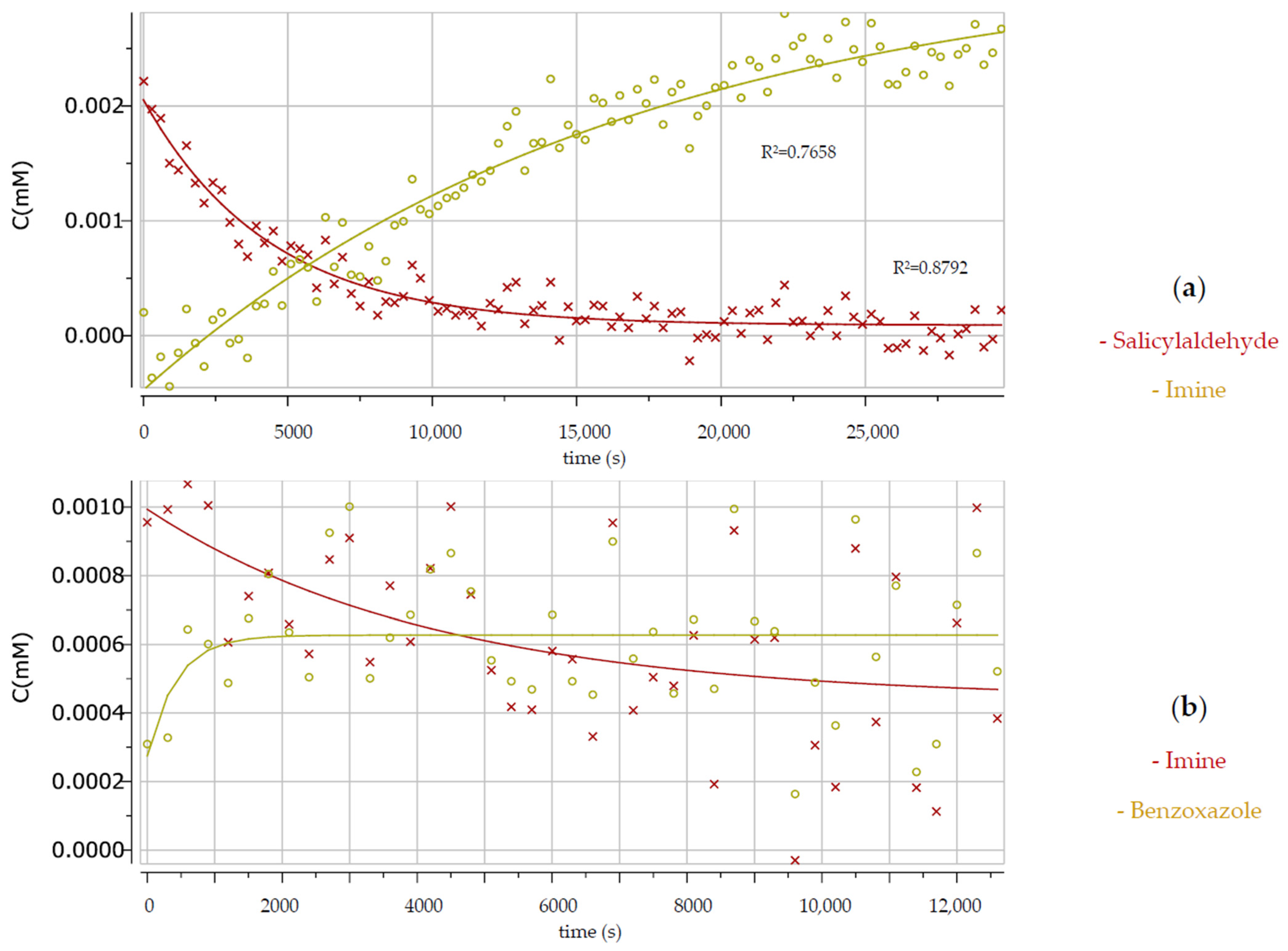
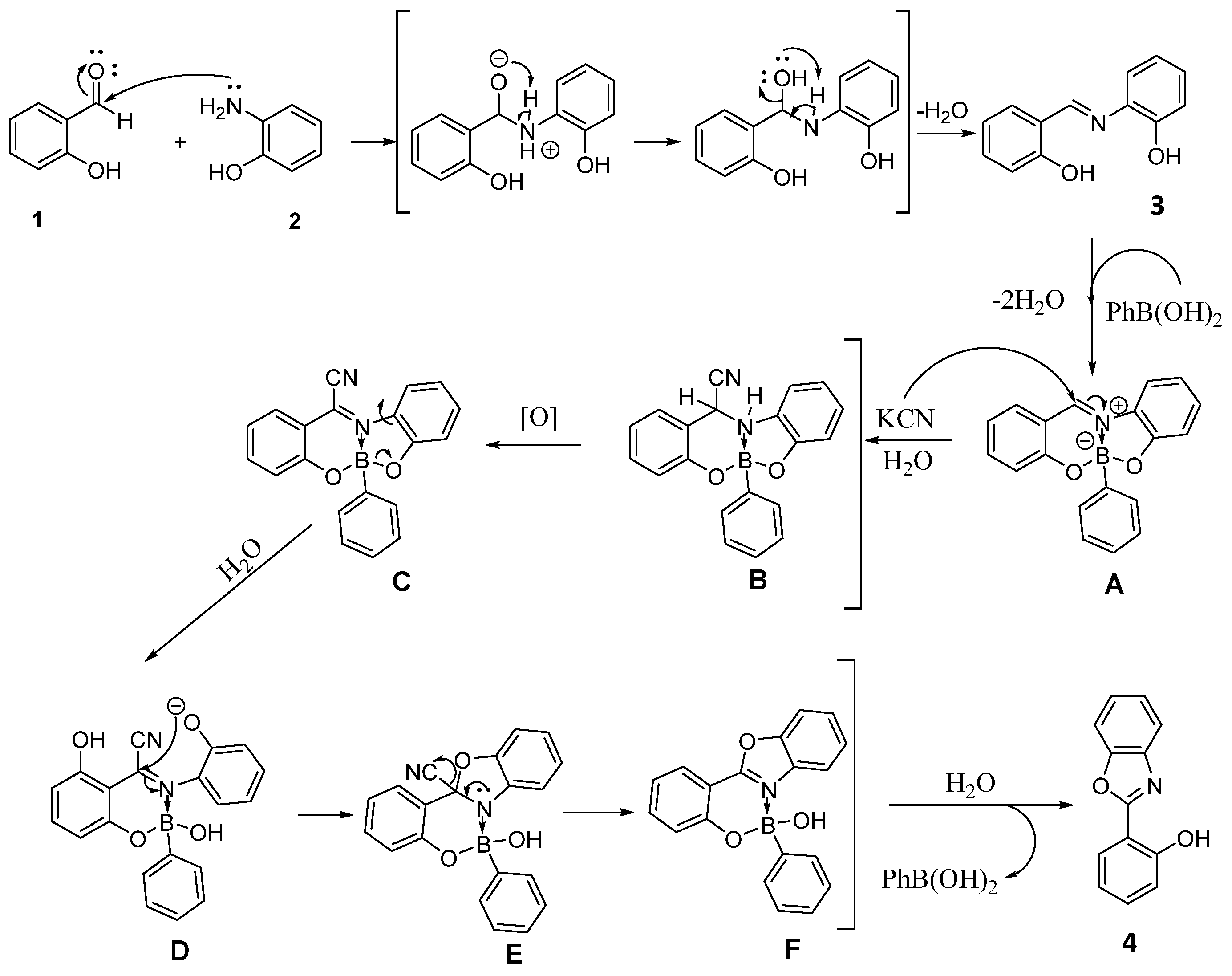
3. Results and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Horáček, J. Fischer–Tropsch synthesis, the effect of promoters, catalyst support, and reaction conditions selection. Monatsh. Chem. 2020, 151, 649–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meek, S.J.; Pitman, C.L.; Miller, A.J.M. Deducing reaction mechanism: A guide for students, researchers, and instructors. J. Chem. Educ. 2016, 93, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, X.; Fleurat-Lessard, P.; Gros, C.P.; Bolze, F.; Xu, H. Synthesis, photophysical properties and two-photon absorption of benzothiazole/benzoxazole π-expanded carbazole dyes. Dyes Pigment. 2022, 204, 110447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremond, E.; Leygue, N.; Saffon-Merceron, N.; Fery-Forgues, S. 2-Phenylbenzoxazole derivatives as solid-state fluorescence emitters: Influence of steric hindrance and hydrogen bonding on the optical properties. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 227, 117586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carayon, C.; Fery-Forgues, S. 2-Phenylbenzoxazole derivatives: A family of robust emitters of solid-state fluorescence. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2017, 16, 1020–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetrova, E.V.; Tupaeva, I.O.; Sayapin, Y.A.; Gusakov, E.A.; Nikolaevskii, S.A.; Demidov, O.P.; Minkin, V.I.; Metelitsa, A.V. Chromogenic properties of 2-(2-carbomethoxy-3,4-dichloro-6-hydroxyphenyl)benzoxazole and its Zn(II) and Cd(II) complexes. Dyes Pigment. 2020, 180, 108417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Baumann, H.; Bi, X.; Shriver, L.P.; Zhang, Z.; Pang, Y. Efficient synthesis of NIR emitting bis [2-(2′-hydroxylphenyl)benzoxazole] derivative and its potential for imaging applications. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 96, 103585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, P.-F.; Qi, M.-Z.; Wang, Z.-P.; Ding, S.-Y.; Yu, W.; Liu, Q.; Wang, L.-K.; Wang, H.-Z.; An, W.-K.; Wang, W. Benzoxazole-linked ultrastable covalent organic frameworks for photocatalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 4623–4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, A.; Thomas, K.R.J.; Singh, M.; Jou, J.H. Fine tuning of photophysical and electroluminescence properties of benzoxazole based dyes. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 12188–12200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashita, Y.; Nakamichi, N.; Kawabata, H.; Hayashi, M. Direct and practical synthesis of 2-arylbenzoxazoles promoted by activated carbon. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 3713–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Hu, X.; Liu, J.; Liao, Y.; Deng, G.J. Iron catalyzed 2-arylbenzoxazole formation from o-aminophenols and aldehydes. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 5306–5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, X.T.T.; Nguyen, T.T.; Nguyen, H.L.H.; Tran, P.H. Synthesis of benzoxazoles, benzimidazoles, and benzothiazoles Using a Brønsted acidic ionic liquid gel. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 21999–22008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, S.; Sahiba, N.; Teli, S.; Teli, P.; Agarwal, L.K.; Agarwal, S. Advances in the synthetic strategies of benzoxazoles using 2-aminophenol as a precursor: An up to up-to-date review. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 24358–24391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Mao, D.; Lou, S.; Qian, J.; Xu, Z. Facile and efficient one pot synthesis of 2-arylbenzoxazoles catalyzed by HAuCl4. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2009, 10, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeimi, H.; Rouzegar, Z.; Rahmatinejad, S. Catalyst-free microwave-promoted one pot synthesis of 2-aryl benzoxazoles using MnO2 nanoparticles as a convenient oxidant under mild condition. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2017, 43, 4745–4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Ruiz, H.; Briseño Ortega, H.; Rojas Lima, S.; Santillán, R.; Farfán, N. An efficient potassium cyanide promoted synthesis of 2 Arylbenzoxazoles from [4.3.0] boron heterobicycles. Tetrahedron Lett. 2010, 51, 2633–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, H.; Beltran, H.I.; Rivera Becerril, E. One pot synthesis of 2 phenylbenzoxazoles by potassium cyanide assisted reaction of o-aminophenols and benzaldehydes. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011, 52, 308–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Ruiz, H.; Briseño Ortega, H.; Rojas Lima, S.; Santillán, R.; Farfán, N. Phenylboronic acid catalyzed, cyanide promoted one pot synthesis of 2 (2 Hydroxyphenyl)benzoxazoles. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011, 52, 4308–4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Zarate, L. Mecanosíntesis de Benzoxazoles Funcionalizados con Potencial Aplicación en el Desarrollo de Diodos Orgánicos Emisores de luz. Bachelor’s Thesis, Universidad del Papaloapan, Oaxaca, Mexico, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Doan, S.H.; Tran, C.B.; Cao, A.L.N.; Le, N.T.H.; Phan, N.T.S. A new pathway to 2-arylbenzoxazoles and 2-arylbenzothiazoles via one-pot oxidative cyclization reactions under iron-organic framework catalysis. Catal. Lett. 2019, 149, 2053–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, M.C.; Abbinante, V.M.; Sutherland, A. Iron-catalyzed regioselective synthesis of 2-arylbenzoxazoles and 2-arylbenzothiazoles via alternative reaction pathways. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 19, 2819–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kircher, R.; Mross, S.; Hasse, H.; Münnemann, K. 1H Benchtop NMR Spectroscopy by paramagnetic shift reagents for process monitoring. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2023, 54, 1515–1532. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, Y.; Lin, Z.; Lawon, L.; Lévesque, F.; Foley, D.A.; Espina, R.; Robert, H. Coupling probe based autosampler with Benchtop NMR for automated sampling and online measurement. React. Chem. Eng. 2023, 8, 3323–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giberson, J.; Scicluna, J.; Legge, N.; Longstaffe, J. Developments in Benchtop NMR Spectroscopy 2015–2020. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2021, 124–125, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Kern, S.; Wander, L.; Meyer, K.; Guhl, S.; Mukkula, A.R.G.; Holtkamp, M.; Salge, M.; Fleischer, C.; Weber, N.; King, R.; et al. Flexible automation with compact NMR for process analytics. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 5129–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkhardtsmaier, P.; Pavlovskaja, K.; Maier, D.; Schäfer, S.; Salat, U.; Schmidt, M.S. Quantitative monitoring of fermentation by Benchtop NMR. Food Anal. Methods 2021, 14, 2369–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, D.A.; Bez, E.; Codina, A.; Colson, K.L.; Fey, M.; Krull, R.; Piroli, D.; Zell, M.T.; Marquez, B.L. NMR flow tube for Online NMR reaction monitoring. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 12008–12013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, Y.; Min, S.; Park, E.; Lim, C.; Cheon, C.H.; Jeong, K.; Kwak, K.; Cho, M. Real time reaction monitoring with in operando flow NMR and FTIR: Reaction mechanism of benzoxazole synthesis. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 2106–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, M.V.; de la Hoz, A. NMR reaction monitoring in flow synthesis (Review). Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2017, 13, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez-Galero, N.X.; Galindo, D.; Pérez-Picaso, L.; Peña-Zarate, L. Participation of the Cyanide Group in the Reaction Mechanism of Benzoxazole Formation: Monitoring by Continuous Flow Cell NMR. Chem. Proc. 2025, 18, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-29-26850
Martínez-Galero NX, Galindo D, Pérez-Picaso L, Peña-Zarate L. Participation of the Cyanide Group in the Reaction Mechanism of Benzoxazole Formation: Monitoring by Continuous Flow Cell NMR. Chemistry Proceedings. 2025; 18(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-29-26850
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez-Galero, Nelda Xanath, Daniel Galindo, Lemuel Pérez-Picaso, and Lucio Peña-Zarate. 2025. "Participation of the Cyanide Group in the Reaction Mechanism of Benzoxazole Formation: Monitoring by Continuous Flow Cell NMR" Chemistry Proceedings 18, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-29-26850
APA StyleMartínez-Galero, N. X., Galindo, D., Pérez-Picaso, L., & Peña-Zarate, L. (2025). Participation of the Cyanide Group in the Reaction Mechanism of Benzoxazole Formation: Monitoring by Continuous Flow Cell NMR. Chemistry Proceedings, 18(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-29-26850






