Perspectives on Synthetic Adducts (Salts) of NitroxolineTM and 2-Aminoquinolin-8-ol as Promising Antibacterial Agents †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lotus. Natural Products Online. Available online: https://lotus.naturalproducts.net/compound/lotus_id/LTS0213634 (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Pan, K. Base Addition Salts of Nitroxoline and Use Thereof. U.S. Patent 2016/0031819A1, 12 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Huigens, R.W.; Basak, A.; Abouelhassan, Y. Halogenated Quinoline Derivatives as Antimicrobial Agents. WO 2017/053696A2, 30 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, J.P. The reactions of 8-Quinolinol. Chem. Rev. 1956, 56, 271–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherdtrakulkiat, R.; Boonpangrak, S.; Sinthupoom, N.; Prachayasittikul, S.; Ruchirawat, S.; Prachayasittikul, V. Derivatives (halogen, nitro and amino) of 8-hydroxyquinoline with highly potent antimicrobial and antioxidant activities. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2016, 6, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, P. Chemoselective synthesis of 5-amino-7-bromoquinolin-8-yl sulfonate derivatives and their antimicrobial evaluation. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2018, 193, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, C.; Prognon, P.; Bourlioux, P. Roles of divalent cations and pH in mechanism of action of Nitroxoline against Escherichia coli strains. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1995, 39, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rbaa, M.; Jabli, S.; Lakhrissi, Y.; Ouhssine, M.; Almalki, F.; Hadda, T.B.; Messgo-Moumene, S.; Zarrouk, A.; Lakhrissi, B. Synthesis, antibacterial properties and bioinformatics computational analyses of novel 8-hydroxyquinoline derivatives. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobke, A.; Klinger, M.; Hermann, B.; Sachse, S.; Nietzsche, S.; Makarewicz, O.; Keller, P.M.; Pfister, W.; Straubea, E. The urinary antibiotic 5-nitro-8-hydroxyquinoline (Nitroxoline) reduces the formation and induces the dispersal of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms by chelation of iron and zinc. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 6021–6025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hof, H.; Juretschke, C. Nitroxoline: An option for the treatment of urinary tract infection with multi-resistant uropathogenic bacteria. Infection 2019, 47, 493–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, B.B.; Spiteller, M. Organic mandelates as promising materials with non-linear optical application. Struct. Chem. 2010, 21, 989–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Code | Compound | Structure |
|---|---|---|
| NQ | NitroxolineTM | 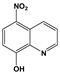 |
| NQs1 | NitroxolineTM, natrium salt | 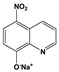 |
| NQs2 | NitroxolineTM salt with 4-benzylamine | 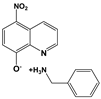 |
| NQs3 | NitroxolineTM salt with, 4-(aminomethyl)pyridine | 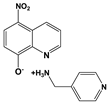 |
| 2A8OHQ | 2-Amino-8-hydroxyquinoline | 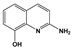 |
| 2A8OHQs1 | 2-Amino-8-hydroxyquinoline salt with oxalic acid | 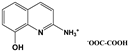 |
| 2A8OHQs2 | 2-Amino-8-hydroxyquinoline salt with 2,3-pyrazinedicarboxylic acid | 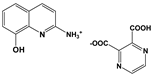 |
| 2A8OHQs3 | 2-Amino-8-hydroxyquinoline salt with chelidonic acid | 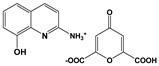 |
| 2A8OHQs4 | 2-Amino-8-hydroxyquinoline salt with quinalid acid | 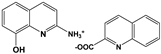 |
| 2A8OHQs5 | 2-Amino-8-hydroxyquinoline salt with 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid | 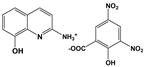 |
| 2A8OHQs6 | 2-Amino-8-hydroxyquinoline salt with quinoline-2-carboxylic acid | 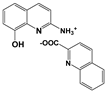 |
| 2A8OHQs7 | 2-Amino-8-hydroxyquinoline salt with quinoline-3-carboxylic acid | 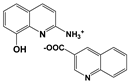 |
| 2A8OHQs8 | 2-Amino-8-hydroxyquinoline salt with xanthurenic acid | 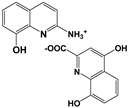 |
| 2A8OHQs9 | 2-Amino-8-hydroxyquinoline salt with kynurenic acid | 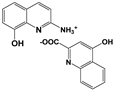 |
| Strain No./ Compound Code | MIC (mg/L) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4498 | 3541 | 500 | 3396 | 3333 | 636 | 1942 | 4352 | |
| NQ | 32 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 8 | 16 | 8 | 32 |
| NQs1 | 8 | 8 | 12 | 32 | 4 | 8 | 4 | 12 |
| NQs2 | 16 | 16 | 8 | 32 | 8 | 8 | 4 | 8 |
| NQs3 | 32 | 8 | 8 | 32 | 8 | 8 | 4 | 8 |
| 2A8OHQ | 64 | 64 | 32 | 64 | 32 | 16 | 64 | 64 |
| 2A8OHQs1 | 64 | 32 | 32 | 64 | 32 | 16 | 32 | 64 |
| 2A8OHQs2 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 64 | 32 | 16 | 32 | 64 |
| 2A8OHQs3 | 64 | 32 | 32 | 64 | 32 | 8 | 32 | 64 |
| 2A8OHQs4 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 64 | 32 | 8 | 32 | 64 |
| 2A8OHQs5 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 16 | 32 | 64 |
| 2A8OHQs6 | 64 | 32 | 32 | 64 | 32 | 16 | 32 | 64 |
| 2A8OHQs7 | 64 | 32 | 32 | 64 | 32 | 4 | 16 | 64 |
| 2A8OHQs8 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 64 | 32 | 16 | 32 | 64 |
| 2A8OHQs9 | 64 | 32 | 32 | 64 | 32 | 4 | 16 | 64 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maliar, T.; Gašparová, R.; Maliarová, M. Perspectives on Synthetic Adducts (Salts) of NitroxolineTM and 2-Aminoquinolin-8-ol as Promising Antibacterial Agents. Chem. Proc. 2024, 16, 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-28-20260
Maliar T, Gašparová R, Maliarová M. Perspectives on Synthetic Adducts (Salts) of NitroxolineTM and 2-Aminoquinolin-8-ol as Promising Antibacterial Agents. Chemistry Proceedings. 2024; 16(1):92. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-28-20260
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaliar, Tibor, Renata Gašparová, and Mária Maliarová. 2024. "Perspectives on Synthetic Adducts (Salts) of NitroxolineTM and 2-Aminoquinolin-8-ol as Promising Antibacterial Agents" Chemistry Proceedings 16, no. 1: 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-28-20260
APA StyleMaliar, T., Gašparová, R., & Maliarová, M. (2024). Perspectives on Synthetic Adducts (Salts) of NitroxolineTM and 2-Aminoquinolin-8-ol as Promising Antibacterial Agents. Chemistry Proceedings, 16(1), 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-28-20260






