Abstract
The evolution of Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents (HDESs) has expanded the applications of the new generation of solvents, known as Deep Eutectic Solvents (DES), to include water-based operations. How stable they are in aqueous media qualifies them to be categorised as hydrophobic. This also determines whether they are appropriate materials for water-based industrial processes or not or whether they end up constituting a greater pollution load than those processes due to the leaching of their precursors into the aqueous media when used. This work sought to prepare HDESs from a monoterpene (thymol), and three long-chain organic acids (octanoic acid, decanoic acid, and dodecanoic acid). The physicochemical characteristics of the prepared HDESs were investigated. Thereafter, their moisture absorption capacity and stability in an aqueous environment were determined to ascertain whether they are hydrophobic as predicted.
1. Introduction
Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs), also known as new-generation ionic liquids, are green solvents that are gradually taking over the roles of other conventional solvents. They are easy to prepare, release low volatile organic compounds, and have low costs [1,2]. This gives them an edge over ionic liquids. DESs are defined as solvents that are produced by the interaction of two or more components, Hydrogen Bond Donors (HBDs) and Hydrogen Bond Acceptors (HBAs), generally associated via hydrogen bonding, producing a liquid whose melting point is lower than that of the individual components. This hydrogen bond interaction produces a distinct chemical entity with a lower melting point than its precursors. So far, many DESs that have been researched are hydrophilic. This makes them unstable in aqueous environments, thereby limiting their applications [3,4]. Because of the increase in the applications of DESs, their synthesis is currently the subject of growing interest. This has resulted in a recent investigation into the synthesis of Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents (HDESs).
The synthesis of HDESs is achieved by using either water-insoluble or weakly water-soluble components. HBAs for HDES synthesis can be classified into two categories. The first is composed of ionic compounds (e.g., tetra-alkyl quaternary ammonium or phosphorous salts), while the second is composed of non-ionic compounds (e.g., monoterpenes). In the evolution of HDES synthesis, those synthesised from the combination of hydrophobic components alone were found to be more stable in aqueous environments than those synthesised from hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts. Hydrophilic components in HDESs were soluble in aqueous phases, which reduced their stability (due to the leaching of some portion of the hydrophilic DESs) in such environments [5].
Suitable application of HDESs can only be achieved through a thorough knowledge and interpretation of their mechanism of interaction and physicochemical properties. These properties are usually attributed to different HBA and HBD combinations, which create unique interactions [6]. Properties such as density, viscosity, surface tension, and the melting/freezing point depend on the HDES structure, while the moisture absorption capacity and thermal stability determine the appropriate application options. This paper sought to investigate the fundamental physicochemical properties of three (3) non-ionic HDESs prepared from thymol and long-chain saturated organic acids.
2. Method
Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvent Synthesis
Thymol (99.5% assay) was purchased from BDH chemicals, and Octanoic acid (99% assay), Decanoic acid (98% assay), and Dodecanoic acid (99% assay) were purchased from Loba Chemie. In this work, binary mixtures of thymol and carboxylic acids (octanoic acid, decanoic acid, and dodecanoic acid) were prepared by adding the components into glass vessels (at the molar ratios shown in Table 1), using a Mettler Toledo analytical weighing balance (ME 204E). The solid mixtures were melted under stirring on a magnetic stirrer hot plate at 80 °C until a homogeneous liquid mixture was obtained and cooled to room temperature.

Table 1.
Composition of different Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fourier Transform Infrared of HDESs
Hydrogen bonds are the primary intermolecular interaction between terpenes and organic acids in the formation of HDESs [7,8]. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectra of the different terpenes and organic acids and the resultant HDESs from their combinations were determined to investigate and ascertain this interaction. As represented in Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3, all thymol-based HDESs also reflected shifts in the initial OH stretching band of their HBA (thymol) from 3175.7 cm−1 to 3418 cm−1 in TC8, and TC10, while in TC12, the OH stretching band shifted to 3406.8 cm−1. Also, there were shifts from the initial C=O bands in C10 and C12 from 1692.2 cm−1 to 1707.1 cm−1 in TC10 and TC12, while TC8 maintained its original C=O band peak but had an increase in its intensity. The results obtained were compared with and validated by previous works, which showed similar shifts to higher wavelengths for the OH band of the monoterpene and the CO bands of the organic acid, thus depicting interactions between the components which resulted in the formation of DESs [9,10,11].
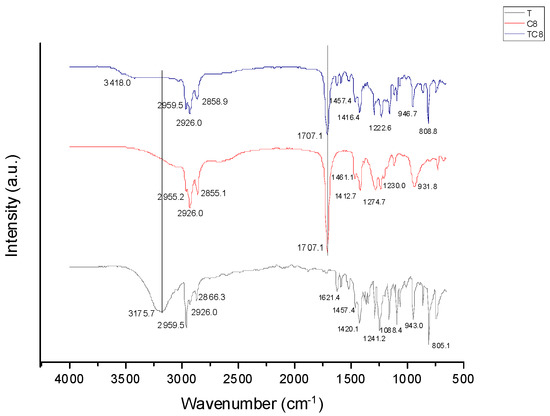
Figure 1.
FTIR spectra of thymol, Octanoic acid, and TC8 HDESs.
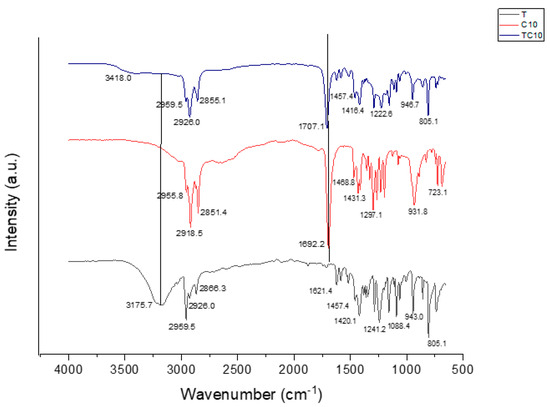
Figure 2.
FTIR spectra of thymol, Decanoic acid, and TC10 HDESs.
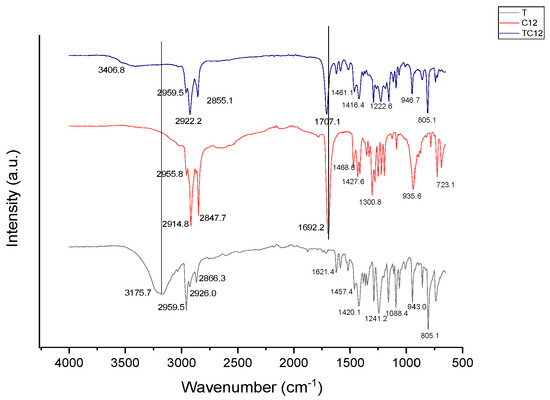
Figure 3.
FTIR spectra of thymol, Dodecanoic acid, and TC12 HDESs.
In FTIR, an increase in the peak intensity usually means an increase in the amount (per unit volume) of the functional group associated with the molecular bond. Therefore, the increase in peak intensity and the various peak shifts observed in the spectra of the HDESs can be attributed to the intermolecular hydrogen bonding between the HBDs and HBAs.
3.2. Physicochemical Properties
3.2.1. Density
Density is a crucial property of solvents that greatly influences dissolution, reaction, and separation processes, determining their viability. As seen in Figure 4, the density of all thymol-based HDESs ranged between 0.8820 and 0.9357 kg/L. All HDESs revealed a linear decrease in density with a consistent increase in temperature. Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents have been reported to possess lower densities than water [12]. The density of a Deep Eutectic Solvent reveals a temperature-dependent behaviour, which decreases linearly with increasing temperatures [13,14,15,16]. According to Florindo et al., the densities of thymol-based DESs were ≥0.925 kg/L at 30 °C [12]. Moreover, density depends on the choice of the hydrogen bond donor [13,14,16,17,18] and the molar ratio [19].
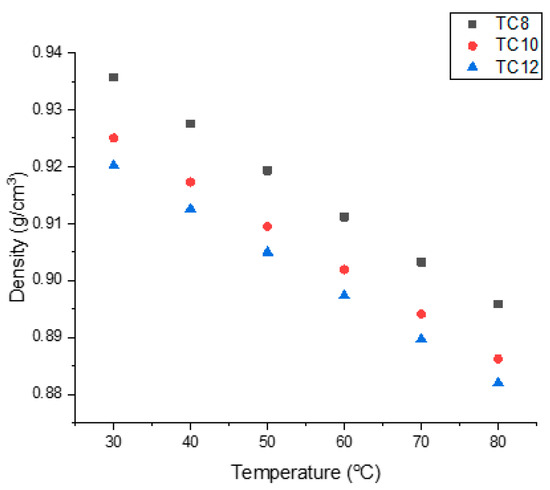
Figure 4.
Density–temperature graph for thymol-based HDESs.
3.2.2. Viscosity
The viscosities of the prepared HDESs were observed to be temperature-dependent. They decreased linearly with corresponding temperature increases. As seen in Figure 5, the viscosity of thymol-based HDESs increased from TC8 to TC12 (TC8 < TC10 < TC12) and was between 7 and 17 mPa.s. The results above align with the results obtained in previous work [12]. Also, from the results obtained, it was observed that an increase in the alkyl chain of the carboxylic acid (HBD) resulted in a corresponding rise in the viscosities of the HDESs. Noteworthy are the extraordinarily low viscosities (˂20 mPa.s) of HDESs based on fatty acids combined with menthol and thymol. These overcame one of the significant drawbacks of hydrophilic DESs, where, for example, a viscosity of 859.45 mPa.s was attained for ChCl/urea (1:2) [20].
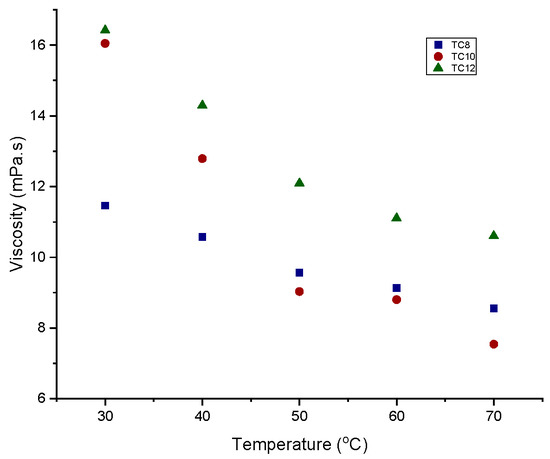
Figure 5.
Viscosity–temperature graph for thymol-based HDESs.
The viscosity of a eutectic mixture is affected by the nature of its components [16] their molar ratio [20], the temperature [21,22,23,24,25,26], and the water content [14,25,27,28,29].
3.2.3. Surface Tension
Surface tension is an essential property since it is highly dependent on the intensity of the intermolecular forces taking place between the hydrogen bond donor and the hydrogen bond acceptor. It also determines the suitability of HDESs in interfacial processes in which mass transfer occurs. In Figure 6, the surface tension of TC8, TC10, and TC12 falls between 26.0 and 28.5 mN/m. The surface tension of the HDESs was also temperature-dependent as it decreased with increasing temperatures. Studies have shown that surface tension decreases linearly with increasing temperature [18,30,31]. The surface tension of all HDESs was observed to be ˂30 mN/m, and, as exemplified in previous works, decreased with increasing temperatures.
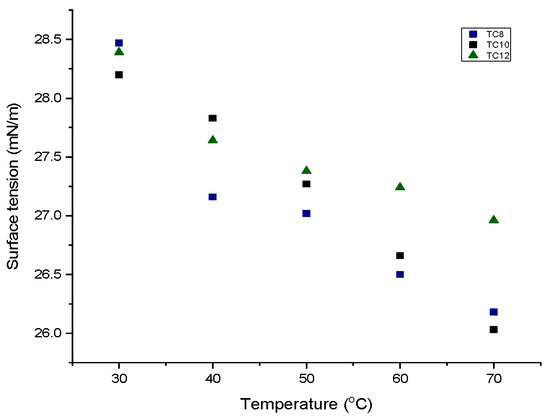
Figure 6.
Surface tension–temperature graph for thymol-based HDESs.
3.3. Hydrophobicity Test
Figure 7 shows the image of the HDESs immediately after agitation. An oil-in-water emulsion-like mixture was observed. The samples were left for 24 h to see if the emulsion formed any phase separation. After 24 h, clear and distinctive phase separation was noticed with water (denser phase) seen at the bottom of the bottle and the HDESs (less dense phase) on top, as seen in Figure 8.
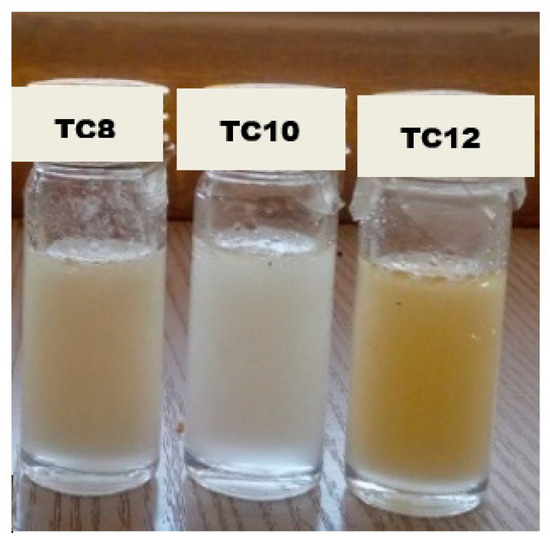
Figure 7.
HDESs in water immediately after agitation.
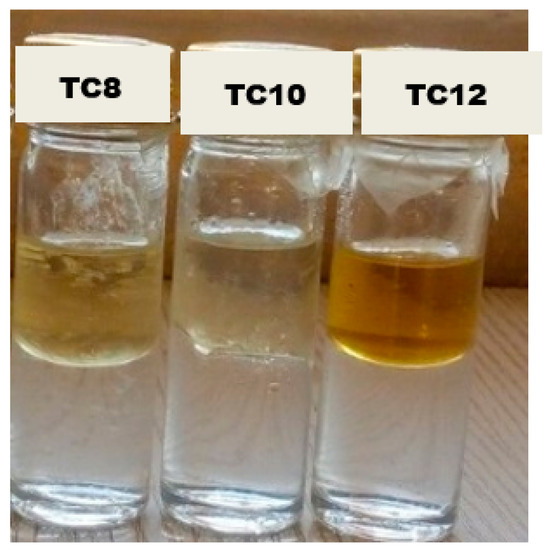

Figure 8.
HDESs in water 24 h after agitation.
Figure 9 is a chart indicating the moisture content determined in each HDES after its interaction with water for 24 h. The HDESs TC8, TC10, and TC12 had the following moisture content: 7.80%, 3.73%, and 3.10%, respectively. It can be seen that thymol-based HDESs had a lower moisture absorption capacity than their menthol-based counterparts. It was also reported by Florindo et al. that an increase in the alkyl chain of the HBDs resulted in the increased hydrophobicity of the HDESs [12].
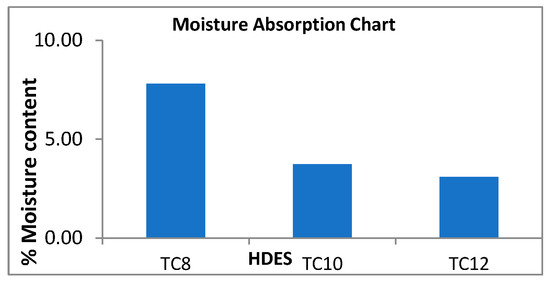
Figure 9.
Percentage moisture content graph for HDESs (test for hydrophobicity).
It is highly recommended to determine the chemical stability of Deep Eutectic Solvents that find applications in aqueous environments to ascertain that there is no contamination of the water phase with the DES and no loss of the DES structure due to water absorption. The ability of an HDES to maintain its structure and not lose its integrity in the presence of water is of enormous importance.
4. Conclusions
Three (3) Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents from thymol and long-chain organic acids were successfully prepared, all in ratios of 1:1. All were liquids at room temperature, with TC8 having a pale-yellow colour, TC10 being colourless, and TC12 having a golden yellow colour. The prepared HDESs were characterised using FTIR, and the spectra revealed remarkable shifts in the O-H stretching bands and C=O stretching bands of the HDESs compared with those of their precursors. The changes in the OH stretching bands and C=O stretching bands resulted from the intermolecular hydrogen bond formed between the starting materials to give HDESs.
Also, physicochemical analysis was carried out on the synthesised HDESs, which revealed their excellent characteristics. This better informs researchers on their best areas of application, potentially in the removal of recalcitrant aromatic contaminants in wastewater. The density of thymol-based HDESs was within 0.925–0.940 kg/L; all densities were found to decrease with an increase in temperature. The viscosity of the HDESs was found to be ˂20 mPa.s and decreased with an increase in temperature. Similar to viscosity, the surface tension of HDESs also reduced with an increase in temperature and was observed to be ˂30 mN/m. Finally, the extent of moisture absorption into the matrix of the HDESs was determined to be between 3.10 and 7.80%. It was observed that the degree of hydrophobicity increased with an increase in the alkyl chain of the organic acids (HBDs).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.O.A.; Methodology, D.O.A., Z.S.G. and A.Y.A.; validation, D.O.A., Z.S.G. and A.Y.A.; formal analysis, D.O.A. and Z.S.G.; investigation, D.O.A.; resources, D.O.A., Z.S.G. and A.Y.A.; data curation, D.O.A.; writing—original draft preparation, D.O.A.; writing—review and editing, D.O.A., Z.S.G., O.U.A., S.M.S., A.Y.A. and B.Y.J.; visualization, D.O.A.; supervision, Z.S.G. and A.Y.A.; project administration, A.Y.A. and B.Y.J.; funding acquisition, Z.S.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project was partly funded by National Research Institute for Chemical Technology under the project number FGN/AB2021/ERG30122610.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Supporting data available on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Francisco, M.; Van Den Bruinhorst, A.; Kroon, M.C. Low-transition-temperature mixtures (LTTMs): A new generation of designer solvents. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3074–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, A.; Craveiro, R.; Aroso, I.; Martins, M.; Reis, R.L.; Duarte AR, C. Natural deep eutectic solvents-Solvents for the 21st century. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos, H.; Tavares DJ, P.; Ferreira, A.M.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho JA, P. Are Aqueous Biphasic Systems Composed of Deep Eutectic Solvents Ternary or Quaternary Systems? ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2881–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, N.H.C.S.; Pinto, R.J.B.; Freire, C.S.R.; Marrucho, I.M. Production of lysozyme nanofibers using deep eutectic solvent aqueous solutions. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 147, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Branco, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M. Development of hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents for extraction of pesticides from aqueous environments. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2017, 448, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, M.; Wang, Q.; Du, H.; Zhang, L. Deep eutectic Solvent-Based Microwave-Assisted method for extraction of hydrophilic and hydrophobic components from radix salviae miltiorrhizae. Molecules 2016, 21, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.H.; Ghareeb, M.M.; Al-Remawi, M.; TAl-Akayleh, F. New insight into sin7gle phase formation of capric acid/menthol eutectic mixtures by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy and differential scanning calorimetry. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2020, 19, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; De Oliveira Vigier, K.; Royer, S.; Jérôme, F. Deep eutectic solvents: Syntheses, properties and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7108–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, R.K.; Hayyan, M.; AlSaadi, M.A.; Ibrahim, S.; Hayyan, A.; Hashim, M.A. Physical properties of ethylene glycol-based deep eutectic solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 276, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mjalli, F.S.; Murshid, G.; Al-Zakwani, S.; Hayyan, A. Monoethanolamine-based deep eutectic solvents, their synthesis and characterization. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2017, 448, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, A.P.R.; Mora-Vargas, J.A.; Guimarães TG, S.; Amaral CD, B.; Oliveira, A.; Gonzalez, M.H. Sustainable synthesis of natural deep eutectic solvents (NADES) by different methods. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 293, 111452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Branco, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M. Quest for Green-Solvent Design: From Hydrophilic to Hydrophobic (Deep) Eutectic Solvents. ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Li, C.; Yin, J.; Li, S.; Jia, Y.; Bao, M. Design, synthesis and properties of acidic deep eutectic solvents based on choline chloride. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 236, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Oliveira, F.S.; Rebelo LP, N.; Fernandes, A.M.; Marrucho, I.M. Insights into the synthesis and properties of deep eutectic solvents based on cholinium chloride and carboxylic acids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 2416–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, K.; Baroutian, S.; Mjalli, F.S.; Hashim, M.A.; Alnashef, I.M. Densities of ammonium and phosphonium based deep eutectic solvents: Prediction using artificial intelligence and group contribution techniques. Thermochim. Acta 2012, 527, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Barron, J.C.; Ryder, K.S.; Wilson, D. Eutectic-based ionic liquids with metal-containing anions and cations. Chem. -A Eur. J. 2007, 13, 6495–6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, A.P.; Harris, R.C.; Ryder, K.S. Application of hole theory to define ionic liquids by their transport properties. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 4910–4913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, G.; Aparicio, S.; Ullah, R.; Atilhan, M. Deep eutectic solvents: Physicochemical properties and gas separation applications. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 2616–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Harris, R.C.; Ryder, K.S.; Agostino, C.D.; Gladden, F.; Mantle, M.D. Green Chemistry Glycerol eutectics as sustainable solvent systems. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekaari, H.; Zafarani-Moattar, M.T.; Mohammadi, B. Thermophysical characterization of aqueous deep eutectic solvent (choline chloride/urea) solutions in full ranges of concentration at T = (293.15–323.15) K. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 243, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Boothby, D.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R. Deep Eutectic Solvents Formed Between Choline Chloride and Carboxylic Acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9142–9147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K. Ionic Liquid Analogues Formed from Hydrated Metal Salts. Chem.-A Eur. J. 2004, 10, 3769–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott Andrew, P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 1, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Gray, S. Design of improved deep eutectic solvents using hole theory. ChemPhysChem 2006, 7, 803–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Witkamp, G.J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Tailoring properties of natural deep eutectic solvents with water to facilitate their applications. Food Chem. 2015, 187, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kareem, M.A.; Mjalli, F.S.; Hashim, M.A.; Alnashef, I.M. Phosphonium-based ionic liquids analogues and their physical properties. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 4632–4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, C.; Harris, R.C.; Abbott, A.P.; Gladden, L.F.; Mantle, M.D. Molecular motion and ion diffusion in choline chloride based deep eutectic solvents studied by 1H pulsed field gradient NMR spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 21383–21391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, C.; Zhao, B.; Chen, X.B.; Birbilis, N.; Yang, H. Effect of water presence on choline chloride-2urea ionic liquid and coating platings from the hydrated ionic liquid. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, D.; Mjalli, F.S. Effect of water on the thermo-physical properties of Reline: An experimental and molecular simulation- based approach. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 23900–23907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapeña, D.; Lomba, L.; Artal, M.; Lafuente, C.; Giner, B. The NADES glyceline as a potential Green Solvent: A comprehensive study of its thermophysical properties and effect of water inclusion. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2019, 128, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, R.J.; Saramago, B.; Marrucho, I.M. Surface Tension of dl -Menthol:Octanoic Acid Eutectic Mixtures. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 4915–4923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).