Abstract
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a multifactorial neurological disease of unknown etiology that is associated with various risk factors. Various pharmacological approaches targeting distinct mechanisms have been investigated; however, they have not yet achieved disease-modifying effects. A series of nine trisubstituted 1,3,5-triazine-based derivatives was investigated as potential inhibitors of the β-secretase enzyme (beta-site amyloid precursor protein-cleaving enzyme 1, BACE1), one of the key enzymes in the pathogenesis of AD. Although the triazine-based derivatives are reported to be potent BACE1 inhibitors, the compounds discussed in this contribution, at a concentration of 10 µM, demonstrated completely insignificant activity. It is worth noting that methyl (4-{4-[(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)amino]-6-[(4-sulfamoylbenzyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}piperazin-1-yl)- acetate and 4-({4-chloro-6-[(3-hydroxypropyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}amino)benzenesulfonamide showed an approximately 9% and 2% inhibition of BACE1 activity, respectively.
1. Introduction
The triazine structure consists of a heterocyclic six-membered ring containing three nitrogen atoms; thus, three isomers can be found: 1,2,3-triazine, 1,2,4-triazine and 1,3,5-triazine. Triazine molecules are basic in nature but are weaker bases than pyridine. Although triazines are aromatic compounds, their resonance nature is much lower than that of benzene. Electrophilic substitution is difficult, but nucleophilic aromatic substitution is quite easy [1,2].
The best-known derivative of 1,3,5-triazine is melamine (2,4,6-triamino- 1,3,5-triazine), which has found industrial use in the production of resins. Other widely used 1,3,5-triazines are, e.g., cyanuric chloride (2,4,6-trichloro-1,3,5-triazine) and 6-alkyl/aryl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamines. Triazine-based agents such as atrazine, ametryn, prometryn, cyanazine, propazine, simazine, terbuthylazine and terbutryn are highly effective herbicides [3], unfortunately also with strong adverse impacts on humans and the environment [4,5,6,7,8,9]. On the other hand, 1,3,5-triazines represent a remarkable platform for the design of potential drugs, especially with anti-infective (antiviral, antibacterial, antimycobacterial, antifungal, antiprotozoal, anthelmintic) and anticancer effects, but also with anti-inflammatory, antidiabetic, antioxidant, antiulcer, anticonvulsant and cardioprotective activities, depending on the specific substitution of the 1,3,5-triazine scaffold [1,10,11,12,13,14].
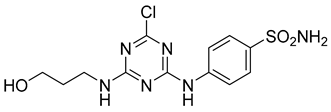
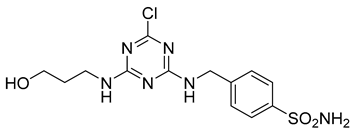
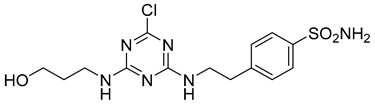
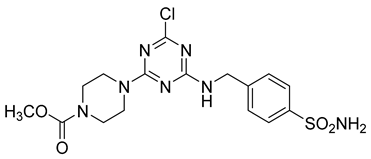
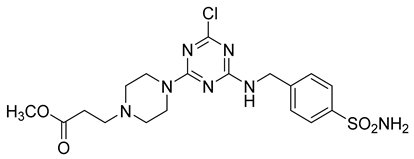
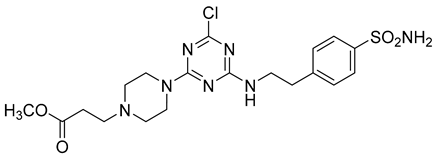
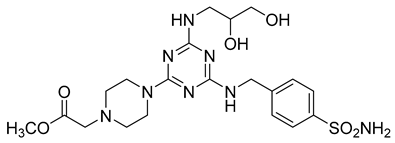
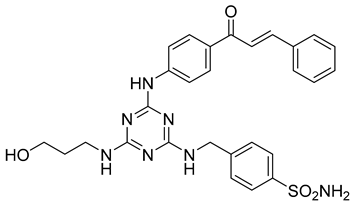
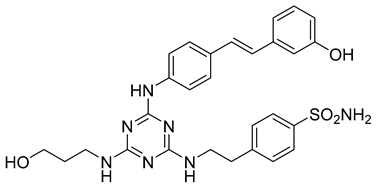
In addition to all these activities, triazines, both 1,2,4-isomers [15,16] and 1,3,5-isomers [17,18,19], were found to exhibit the ability to inhibit the beta-site amyloid precursor protein-cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1), see Figure 1.
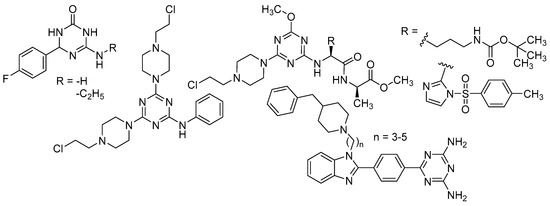
Figure 1.
Selected recently published structures of 1,3,5-triazine-based BACE1 inhibitors [17,18,19].
BACE1 (otherwise known as β-secretase) [20,21] is an enzyme that, in its subsequent interaction with γ-secretase, cleaves the amyloid precursor protein into the insoluble Aβ42 isoform of the amyloid-β (Aβ) protein (the so-called “amyloidogenic pathway”) [22]. This Aβ42 isoform, which was found in higher concentrations in patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD), is more prone to aggregation and deposition in the brain, leading to the development of Aβ plaques, the main feature of AD [23], formulated in the so-called “amyloid cascade hypothesis” [24]. This fact led to the suggestion that abnormal BACE1 activity is responsible for the pathogenesis of AD [25] and highlighted the potential of BACE1 as a promising target for drug development against AD progression [26,27].
It is needless to say that AD is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that is clinically manifested as memory loss, speech impairment and general disorientation in space and time [28,29]. AD is a multifactorial disease, in which both genetic and environmental factors contribute to its pathogenesis [30,31]. The disease is currently incurable; existing drugs from the group of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and the N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor blocker provide only symptomatic treatment for patients with AD without the possibility of affecting the progression of the disease in any way [28,32,33,34].
Recently, a series of trisubstituted derivatives based on 1,3,5-triazine were published [35,36,37,38]. The compounds were designed as inhibitors of eukaryotic and/or prokaryotic carbonic anhydrases [35,37]. However, the observation that triazines can inhibit BACE1 led to the selection of several compounds with different structural motifs on the 1,3,5-triazine scaffold and their retesting as potential compounds modulating BACE1 activity.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis
Starting 4-[(4,6-dichloro-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)amino]benzene-1-sulfonamide, 4-{[(4,6-dichloro-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)amino]methyl}benzene-1-sulfonamide and 4-{2-[(4,6-dichloro-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)amino]ethyl}benzene-1-sulfonamide were published by Garaj et al. [39]. Compound 1 was prepared according to the methodology published in [35]. Derivatives 2, 3 and 6 were prepared according to the methodology published in [36]. Compounds 4, 5 and 7 were prepared according to the methodology published in [37] and derivatives 8 and 9 were prepared according to the methodology published in [38]. All spectral data of the discussed investigated triazines were reported in [35,36,37,38].
2.2. Determination of Lipophilicity Using HPLC
The UHPLC separation system, Waters Acquity, equipped with a Xevo TQD (Waters Corp., Milford, MA, USA) was used. A chromatographic column, Acquity UPLC® HSS T3 1.8 μm, 2.1 × 100 mm (Waters Corp.), was applied. The UHPLC separation process was monitored via the MassLynx software (Waters Corp.). Isocratic elution using a mixture of LC-MS Grade ACN (40%) and H2O-HPLC Mili-Q grade (60%) as a mobile phase was used for the determination of the capacity factor k. The total flow of the column was 0.4 mL/min, injection 5 μL, column temperature 30 °C and sample temperature 10 °C. A thiourea methanolic solution was used for the determination of the dead time (td). Retention times (tR) were measured in minutes. The capacity factors k were calculated according to the formula k = (tR − td)/td, where tR is the retention time of the solute and td is the dead time obtained using an unretained analyte. Each experiment was repeated three times.
2.3. Determination of BACE1 Inhibitory Activity
The BACE inhibitory activity was determined via commercial assay according to manufacturer instructions (Merck Life Science, Bratislava, Slovakia) [40]. The principle of the assay is based on the fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) method, in which the fluorescence signal enhancement is observed after substrate cleavage by BACE1, meaning that the lower the percentage of BACE activity, the more BACE1 is inhibited by the test compounds.
3. Results and Discussion
The synthesis of the discussed compounds is shown in Scheme 1. The starting 1,3,5-triazin-2-yl-aminoarylsulfonamides were synthesized according to Garaj et al. [39]. Subsequently, 4-[(4,6-dichloro-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)amino]benzene-1-sulfonamide, 4-{[(4,6- dichloro-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)amino]methyl}benzene-1-sulfonamide and 4-{2-[(4,6-dichloro- 1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)amino]ethyl}benzene-1-sulfonamide with appropriate reagents provided the final molecules as recently described [35,36,37,38]. The structures of the target compounds are shown in Table 1.
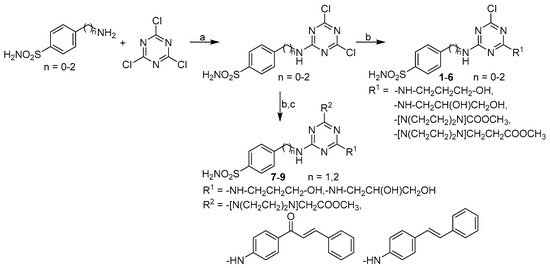
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of target compounds 1–9. Reagents and conditions: (a) acetone, 0–5 °C [39]; (b) suitable amine derivative (1 eq.), DMF, K2CO3, 35 °C; (c) suitable amine derivative (1 eq.), DMF, K2CO3, 100 °C [35,36,37,38].

Table 1.
Structures of discussed ring-substituted 1,3,5-triazine derivatives 1–9, experimentally determined lipophilicity (log k), predicted topological polar surface area (tPSA) of investigated compounds and in vitro reduction of BACE1 activity (%).
Although the discussed compounds were previously structurally fully characterized [35,36,37,38], their lipo-hydrophilic properties have only now been determined via reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) using an end-capped non-polar C18 stationary RP column and expressed as the logarithm of the capacity factor k. The retention times of the individual compounds were obtained under isocratic conditions with acetonitrile as an organic modifier in the mobile phase. The values of log k are given in Table 1.
Table 1 shows the structures of the tested compounds. The derivatives differ from each other in the length of the linker (n = 0–2) between the amino-triazine and benzenesulfonamide fragments. In addition, the compounds differ either by substitution of the second amino group of the triazine with 3-hydroxypropyl (compounds 1–3, 8, 9) or by the incorporation of the amino group into the substituted piperazine (compounds 4–7), and the last (third) substitution can be found on the triazine ring with either chlorine (compounds 1–6), 2,3-dihydroxypropylamino (compound 7), or a complex arylamine (compounds 8, 9).
Lipophilicity is one of the parameters that fundamentally influence not only the pharmacokinetics, but also the effect, of bioactive agents [41,42]. Even in this limited series of nine highly functionalized compounds, a wide range from −0.38 to 0.43 of log k values is evident, with 4-[({4-chloro-6-[(3-hydroxypropyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}- amino)methyl]benzenesulfonamide (2) showing the lowest experimental log k value, while methyl (4-{4-[(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)amino]-6-[(4-sulfamoylbenzyl)amino]- 1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}piperazin-1-yl)acetate (7) is the most lipophilic. However, in general, it can be stated that all derivatives are rather hydrophilic in nature, with five of them having a negative log k value, which indicates their problematic bioavailability due to limited transport through membranes.
In addition to lipophilicity, the topological polar surface area (tPSA), which is defined as the sum of the surfaces of the polar atoms (most often oxygens, nitrogens and attached hydrogens) in a molecule [43], has become a widely used molecular descriptor in the study of drug properties (to ensure so-called drug-likeness) [42]. This descriptor, showing a correlation with passive molecular transport through membranes, is also logically related to the magnitude of the drug–receptor interactions [44]. Therefore, the tPSA values for the individual studied compounds were calculated using the ChemBioDraw Ultra 13.0 program. The most common value is approx. 142 Å2 (compounds 1–6) and ca. 172 Å2 (compounds 8 and 9). The most lipophilic compound 7 also achieved the highest tPSA value, namely 194.54 Å2, which, similarly to its lipophilicity, is largely different from the values of the other derivatives.
All the investigated compounds (see Table 1) were tested for their ability to inhibit BACE1 using a commercially available kit [40]. Performance of the test is described in Section 2.3. As the IC50 values of known BACE1 inhibitors (including the kit reference standard [40]) are in the nanomolar range, all the evaluated compounds were tested at a concentration of 10 µM (see, e.g., [27]), as it is conceivable that if there is no activity at 10 µM, the compound most likely does not inhibit BACE1 [27]. As can be seen from the results in Table 1, the compounds showed no activity; only compound 7 demonstrated some ability to slightly inhibit the BACE1 enzyme (approx. 9% reduction in BACE1 activity). It should be noted that 4-({4-chloro-6-[(3-hydroxypropyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}- amino)benzenesulfonamide (1) also showed a 2% reduction in BACE1 activity. It can only be speculated whether the “significant” inhibition of BACE1 by derivative 7, compared to the zero activity of the other tested derivatives, is related to its highest log k and tPSA values within the series of the investigated compounds. Nevertheless, from the obtained data, it can be concluded that the mentioned trisubstituted triazines do not have the ability to interact with BACE1.
However, it must be admitted that, based on the latest studies and the situation with the early termination of all clinical trials of the main BACE1 inhibitors such as verubecestat atabecestat, elenbecestat lanabecestat umibecestat, LY2886721, RO5508887 or PF-06751979 by pharmaceutical companies (e.g., Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Merck, Eli Lilly, Roche, Novartis, Janssen, Biogen, Amgen) due to serious side effects or actual ineffectiveness, it is possible to speculate to what extent the development of BACE inhibitors (the β-secretase inhibition hypothesis) represents a dead end, or how long the development of these inhibitors for AD treatment will continue to be preferred by pharmaceutical companies [27,45,46]. On the other hand, natural BACE1 inhibitors with different structures are still being discovered [47] and the role of the Aβ peptide is being investigated in depth [48,49].
4. Conclusions
Recently, a series of trisubstituted 1,3,5-triazine derivatives was published and significant inhibitions of therapeutically important carbonic anhydrases were found. The finding that triazines are able to inhibit BACE1 led to an assay of their ability to inhibit BACE1. However, none of the evaluated compounds demonstrated a significant decrease in BACE1 activity.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.K. and J.J.; methodology, P.M. and A.K.; investigation, P.M., I.G., E.H. and T.J.; writing—original draft preparation, E.H., A.K. and J.J.; funding acquisition, A.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Slovak Research and Development Agency (projects APVV-21-0321, APVV-22-0133) and by VEGA 1/0116/22.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Verma, T.; Sinha, M.; Bansal, N. Heterocyclic compounds bearing triazine scaffold and their biological significance: A review. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 4–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, N.; Sharma, C.S. The chemistry of triazine isomers: Structures, reactions, synthesis and applications. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 2104–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmore, C.L.; Lange, A.H. The Triazine Herbicides; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Klementova, S.; Keltnerova, L. Triazine herbicides in the environment. In Herbicides, Physiology of Action, and Safety; Price, A., Kelton, J., Sarunaite, L., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2015; Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/48620 (accessed on 28 September 2023).
- Yang, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Jiao, N. Environmental risk assessment of triazine herbicides in the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea and their toxicity to phytoplankton at environmental concentrations. Environ. Int. 2019, 133, 105175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abass, K.; Pelkonen, O.; Rautio, A. Chloro-s-triazines-toxicokinetic, toxicodynamic, human exposure, and regulatory considerations. Curr. Drug Metab. 2021, 22, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Lv, J.; Deng, H.; Liu, Q.; Liang, S. Occurrence and removal of triazine herbicides during wastewater treatment processes and their environmental impact on aquatic life. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Sun, P.; Zhao, W. Triazine herbicides risk management strategies on environmental and human health aspects using in-silico methods. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatib, I.; Horyn, O.; Bodnar, O.; Lushchak, O.; Rychter, P.; Falfushynska, H. Molecular and biochemical evidence of the toxic effects of terbuthylazine and malathion in zebrafish. Animals 2023, 13, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jameel, E.; Meena, P.; Maqbool, M.; Kumar, J.; Ahmed, W.; Mumtazuddin, S.; Tiwari, M.; Hoda, N.; Jayaram, B. Rational design, synthesis and biological screening of triazine-triazolopyrimidine hybrids as multitarget anti-Alzheimer agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 136, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singla, P.; Luxami, V.; Paul, K. Triazine as a promising scaffold for its versatile biological behavior. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 102, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Mandal, M.K.; Masih, A.; Saha, A.; Ghosh, S.K.; Bhat, H.R.; Singh, U.P. 1,3,5-Triazine: A versatile pharmacophore with diverse biological activities. Arch. Pharm. 2021, 354, e2000363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliszewski, D.; Drozdowska, D. Recent advances in the biological activity of s-triazine core compounds. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesarini, S.; Vicenti, I.; Poggialini, F.; Secchi, M.; Giammarino, F.; Varasi, I.; Lodola, C.; Zazzi, M.; Dreassi, E.; Maga, G.; et al. Privileged scaffold decoration for the identification of the first trisubstituted triazine with anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity. Molecules 2022, 27, 8829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iraji, A.; Firuzi, O.; Khoshneviszadeh, M.; Nadri, H.; Edraki, N.; Miri, R. Synthesis and structure-activity relationship study of multi-target triazine derivatives as innovative candidates for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 77, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, M.; Edraki, N.; Badri, R.; Khoshneviszadeh, M.; Iraji, A.; Firuzi, O. Multi-target inhibitors against Alzheimer disease derived from 3-hydrazinyl 1,2,4-triazine scaffold containing pendant phenoxy methyl-1,2,3-triazole: Design, synthesis and biological evaluation. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 84, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prati, F.; De Simone, A.; Bisignano, P.; Armirotti, A.; Summa, M.; Pizzirani, D.; Scarpelli, R.; Perez, D.I.; Andrisano, V.; Perez-Castillo, A.; et al. Multitarget drug discovery for Alzheimer’s disease: Triazinones as BACE-1 and GSK-3β inhibitors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2015, 54, 1578–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maliszewski, D.; Wrobel, A.; Kolesinska, B.; Fraczyk, J.; Drozdowska, D. 1,3,5-Triazine nitrogen mustards with different peptide group as innovative candidates for AChE and BACE1 inhibitors. Molecules 2021, 26, 3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimian, S.; Shekouhy, M.; Pirhadi, S.; Iraji, A.; Attarroshan, M.; Edraki, N.; Khoshneviszadeh, M. Synthesis and biological evaluation of benzimidazoles/1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine hybrid compounds: A new class of multifunctional Alzheimer targeting agents. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 15567–15584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, S.L.; Vassar, R. The Alzheimer’s disease β-secretase enzyme, BACE1. Mol. Neurodegener. 2007, 2, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R. Physiological functions of the β-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1 and 2. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; Hardy, J.; Blennow, K.; Chen, C.; Perry, G.; Kim, S.H.; Villemagne, V.L.; Aisen, P.; Vendruscolo, M.; Iwatsubo, T.; et al. The amyloid-β pathway in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 5481–5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Chen, W.D.; Wang, Y.D. β-Amyloid: The key peptide in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, J.A.; Higgins, G.A. Alzheimer’s disease: The amyloid cascade hypothesis. Science 1992, 256, 184–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampel, H.; Vassar, R.; De Strooper, B.; Hardy, J.; Willem, M.; Singh, N.; Zhou, J.; Yan, R.; Vanmechelen, E.; De Vos, A.; et al. The β-secretase BACE1 in Alzheimer’s disease. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 89, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathya, M.; Premkumar, P.; Karthick, C.; Moorthi, P.; Jayachandran, K.S.; Anusuyadevi, M. BACE1 in Alzheimer’s disease. Clin. Chim. Acta 2012, 414, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, B.; Yan, R. A close look at BACE1 inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease treatment. CNS Drugs 2019, 33, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jampilek, J.; Kralova, K.; Novak, P.; Novak, M. Nanobiotechnology in neurodegenerative diseases. In Nanobiotechnology in Neurodegenerative Diseases; Rai, M., Yadav, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 65–138. [Google Scholar]
- Knopman, D.S.; Amieva, H.; Petersen, R.C.; Chetelat, G.; Holtzman, D.M.; Hyman, B.T.; Nixon, R.A.; Jones, D.T. Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abubakar, M.B.; Sanusi, K.O.; Ugusman, A.; Mohamed, W.; Kamal, H.; Ibrahim, N.H.; Khoo, C.S.; Kumar, J. Alzheimer’s disease: An update and insights into pathophysiology. Front. Aging. Neurosci. 2022, 14, 742408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madnani, R.S. Alzheimer’s disease: A mini-review for the clinician. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1178588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breijyeh, Z.; Karaman, R. Comprehensive review on Alzheimer’s disease: Causes and treatment. Molecules 2020, 25, 5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, M.; Silvestre, S. Alzheimer’s disease: Recent treatment strategies. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 887, 173554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Jin, H.; Xue, Y.H.; Chen, Q.; Yao, S.Y.; Du, M.Q.; Liu, S. Current and future therapeutic strategies for Alzheimer’s disease: An overview of drug development bottlenecks. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1206572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havrankova, E.; Garaj, V.; Mascaretti, S.; Angeli, A.; Soldanova, Z.; Kemka, M.; Motycka, J.; Brazdova, M.; Csollei, J.; Jampilek, J.; et al. Novel 1,3,5-triazinyl aminobenzenesulfonamides incorporating aminoalcohol, aminochalcone and aminostilbene structural motifs as potent anti-vre agents, and carbonic anhydrases I, II, VII, IX, and XII inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havrankova, E.; Csollei, J.; Pazdera, P. New approach for the one-pot synthesis of 1,3,5-triazine derivatives: Application of Cu(I) supported on a weakly acidic cation-exchanger resin in a comparative study. Molecules 2019, 24, 3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havrankova, E.; Csollei, J.; Vullo, D.; Garaj, V.; Pazdera, P.; Supuran, C.T. Novel sulfonamide incorporating piperazine, aminoalcohol and 1,3,5-triazine structural motifs with carbonic anhydrase I, II and IX inhibitory action. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 77, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havrankova, E.; Calkovska, N.; Padrtova, T.; Csollei, J.; Opatrilova, R.; Pazdera, P. Antioxidative activity of 1,3,5-triazine analogues incorporating aminobenzene sulfonamide, aminoalcohol/phenol, piperazine, chalcone, or stilbene motifs. Molecules 2020, 25, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garaj, V.; Puccetti, L.; Fasolis, G.; Winum, J.-Y.; Montero, J.L.; Scozzafava, A.; Vullo, D.; Innocenti, A.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: Synthesis and inhibition of cytosolic/tumor-associated carbonic anhydrase isozymes I, II, and IX with sulfonamides incorporating 1,2,4-triazine moieties. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 14, 5427–5433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- β-Secretase (BACE1) Activity Detection Kit (Fluorescent). Technical Bulletin. Sigma-Aldrich. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/documents/249/088/cs0010bul.pdf (accessed on 3 October 2023).
- Pliska, V.; Testa, B.; van der Waterbeemd, H. Lipophilicity in Drug Action and Toxicology; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Kerns, E.H.; Di, L. Drug-like Properties: Concepts. Structure Design and Methods: From ADME to Toxicity Optimization; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Molinspiration. Available online: https://www.molinspiration.com/services/psa.html (accessed on 5 October 2023).
- Prasanna, S.; Doerksen, R.J. Topological polar surface area: A useful descriptor in 2D-QSAR. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDade, E.; Voytyuk, I.; Aisen, P.; Bateman, R.J.; Carrillo, M.C.; De Strooper, B.; Haass, C.; Reiman, E.M.; Sperling, R.; Tariot, P.N.; et al. The case for low-level BACE1 inhibition for the prevention of Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 17, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzari, F.H.; Bazzari, A.H. BACE1 inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease: The past, present and any future? Molecules 2022, 27, 8823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Wang, S.L.; Nguyen, V.B. Microorganism-derived molecules as enzyme inhibitors to target Alzheimer’s diseases pathways. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiner, T.G.; Schreiner, O.D.; Adam, M.; Popescu, B.O. The roles of the amyloid beta monomers in physiological and pathological conditions. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, A. Conquering Alzheimer’s: A look at the therapies of the future. Nature 2023, 616, 26–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).