Abstract
Sodium lignosulphonate (NaLS) from spent sulfite liquor was purified by ultrafiltration, and the structure was confirmed by FTIR analysis. NaLS decreases water surface tension from 72.44 mN/m to 65.36 mN/m when its concentration increases from 0% to 1%. The critical aggregation concentration was determined using UV-Vis spectroscopy, and a value of 0.035% was obtained. NaLS (0.1%) was used as a cosurfactant in an oil-in-water emulsion prepared by a phase inversion method to encapsulate thyme essential oil. The formulation was stable for 24 h, with a droplet size of 154 nm and a polydispersity index value of 0.12.
1. Introduction
Biomass resulting as waste from different industries is becoming an important resource in the current scenario governed by economic and environmental challenges. Plant-derived by-products from the pulp and paper industry, such as lignin/lignin derivatives, macromolecules characterized by a profusion of functional groups (such as phenolic hydroxyl groups, carboxylic acid, methoxy, aromatic and aliphatic moieties), are a great prospect for the development of new value-added materials [1]. In the sulfite process, the sulphonation of lignin using Na, Ca, Mg or even ammonium sulfite salts, results in a class of water-soluble lignin derivatives called lignosulphonates (LS) [2]. Ultrafiltration is one of the most promising techniques for the separation of high purity lignosulphonates from spent sulfite liquor [3]. The chemical composition of the obtained LS depends mainly on the used raw materials, sulphonation reaction conditions and separation and purification procedures [4]. From a structural point of view, LS possesses ionizable (sulphonate, phenolic hydroxyl and carboxylic acid), hydrophilic (ketones, aldehydes, methoxy and aliphatic hydroxyl groups) and hydrophobic (aromatic and aliphatic units) functional groups. Its structure can be described as having a core made of hydrophobic groups surrounded by hydrophilic moieties, proving the amphiphilic nature of lignosulphonates [5]. One direct effect of having this kind of amphiphilic structure is its ability to reduce the surface tension of water and act as a (co)surfactant in emulsion stabilization following a combination of electrostatic repulsion, steric hindrance and the creation of a semi-rigid interface layer [6]. Sodium lignosulphonate was also used in microcapsules for encapsulating thymol and its derivatives [7,8].
This paper aims to prove the tensioactive properties and aggregation behavior of sodium lignosulphonate obtained by ultrafiltration from spent sulfite liquor and to use it as co-surfactant in an oil-in-water emulsion for the encapsulation of thyme essential oil that contains thymol [8] as the main ingredient.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The spent sulfite liquor was obtained from the Cellulose and Paper Enterprise—CCH (Drobeta Turnu-Severin, Mehedinți, Romania) and ethanol was from Chimreactiv (Bucharest, Romania). Anionic surfactant Tween 85 (polyoxyethylene sorbitan trioleate) was purchased from MP Biomedicals (Solon, OH, USA), fractionated coconut oil was obtained from Mayam (Elemental, Oradea, Romania) and thyme essential oil from Solaris (Bucharest, Romania). All experiments were performed using pure water. Spent sulfite liquor solutions were left to sit for 24 h to equilibrate and filtered before use. All other reagents were used as received, without any further purification.
2.2. Sodium Lignosulphonate Separation and Analysis
The spent sulfite liquor from CCH was pre-filtered under vacuum through two overlapping regular cloth filters. A sample from the filtrate was centrifuged at 2370× g for 20 min at 20 °C to assess the amount of insoluble residue. The test showed that this amount was negligible, confirming that the pre-filtration step was effective.
The pre-filtered stream was then poured into the feed tank of the XLab 5 crossflow filtration unit from Pall (New York, USA), which was fitted with a 5 μm pore-sized Membralox ceramic membrane. The operation was performed at the highest rate setting of a centrifugal pump which was fitted to the XLab 5 test to maximize transfer through the membrane. The temperature was fixed at 25 °C using a cooling jacket around the feed tank. Then, 10 L of feed was separated into 9 L of permeate and 1 L of retentate. A back pressure of 10 bars was applied every 30 s for 2 s from an N2 gas tank. The permeate was recovered. This step was necessary to minimize the long-term pore-blocking phenomena on the second ceramic membrane used, which had a mean pore size of 0.8 μm. Next, 2 L of the permeate from the previous step was mixed with 1 L of 96% EtOH. This induced a partial precipitation of the hemicellulose and the lignosulphonates of higher molecular weight. Upon crossflow filtration, the retentate was concentrated from 3 L to 1 L (volumetric concentration factor of 3) as 2 L of permeate was also collected. The retentate was lyophilized to obtain the sodium lignosulphonate powder.
To identify the functional groups of the lyophilized NaLS, FTIR spectroscopy was employed (IRTracer-100, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). Samples were deposited evenly on a diamond surface and fixed by the sample holder. Spectra were recorded between 400 and 4000 cm−1 with a resolution of 4 cm−1 and 45 scans per sample using LabSolutions IR version 2.30 software.
2.3. Tensioactive Behavior of Sodium Lignosulphonate
The tensioactive behavior of NaLS was determined by surface tension measurements using the pendant drop method. The surface tension of NaLS solution of different concentrations (0.01–1%) was measured using an optical tensiometer (OCA 50, DataPhysics Instruments, Filderstadt, Germany). Data were analyzed using SCA 20 version 4.5.13 software.
2.4. Critical Aggregation Concentration of Sodium Lignosulphonate
Critical aggregation concentration of NaLS was determined by UV-Vis spectroscopy following the protocol developed by Qiu et al. [9], using a UV-Vis spectrometer (UV-VIS-NIR USB 2000+, Ocean Optics, Dunedin, FL, USA). The absorbance of NaLS solution at concentrations between 0.01 and 1% was measured at 280 nm and plotted against the concentration of the sample. The curve inflection points represent the value of the critical aggregation concentration. Data were plotted and analyzed using Origin 2018.
2.5. Emulsion Preparation
Emulsions using NaLS solutions of different concentrations (0, 0.05, 0.1, 0.5 and 1%) as the aqueous phase were prepared using a phase inversion method adapted from [10]. An organic phase consisting of 10% (v/v) surfactant Tween 85, 23.81% (v/v) fractionated coconut oil and 1.19% (v/v) thyme essential oil was prepared by mixing all ingredients at 1000 rpm on a magnetic plate for 30 min. In the aqueous phase, 65% (v/v) was titrated against the organic phase and the resulting formulations were stirred at 1000 rpm for 60 min. The total volume of each emulsion was 7.5 mL.
2.6. Emulsion Characterization
The emulsion type (oil-in-water or water-in-oil) was established by adding one drop of emulsion (20 µL) to two mL of water or an oily component. If the emulsion is dispersible in water, it is of the oil-in-water type; if the emulsion is dispersible in oil, it is of the water-in-oil type.
Emulsions were characterized through droplet size and polydispersity index (PDI) assay using the dynamic light scattering technique (Amerigo Particle Size & Zeta Potential Analyzer, Cordouan Technologies, Pessac-Bordeaux, France). Samples were 100 times diluted in water. Measurements were performed at room temperature at an angle of 135° using the DTC head. Data were analyzed by Amerigo Software version 3.2.3.0. using the cumulant algorithm.
The stability of the emulsions was determined by measuring the size and PDI 24 h after preparation, as previously described. Visual observations were also made.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sodium Lignosulphonate Separation and Analysis
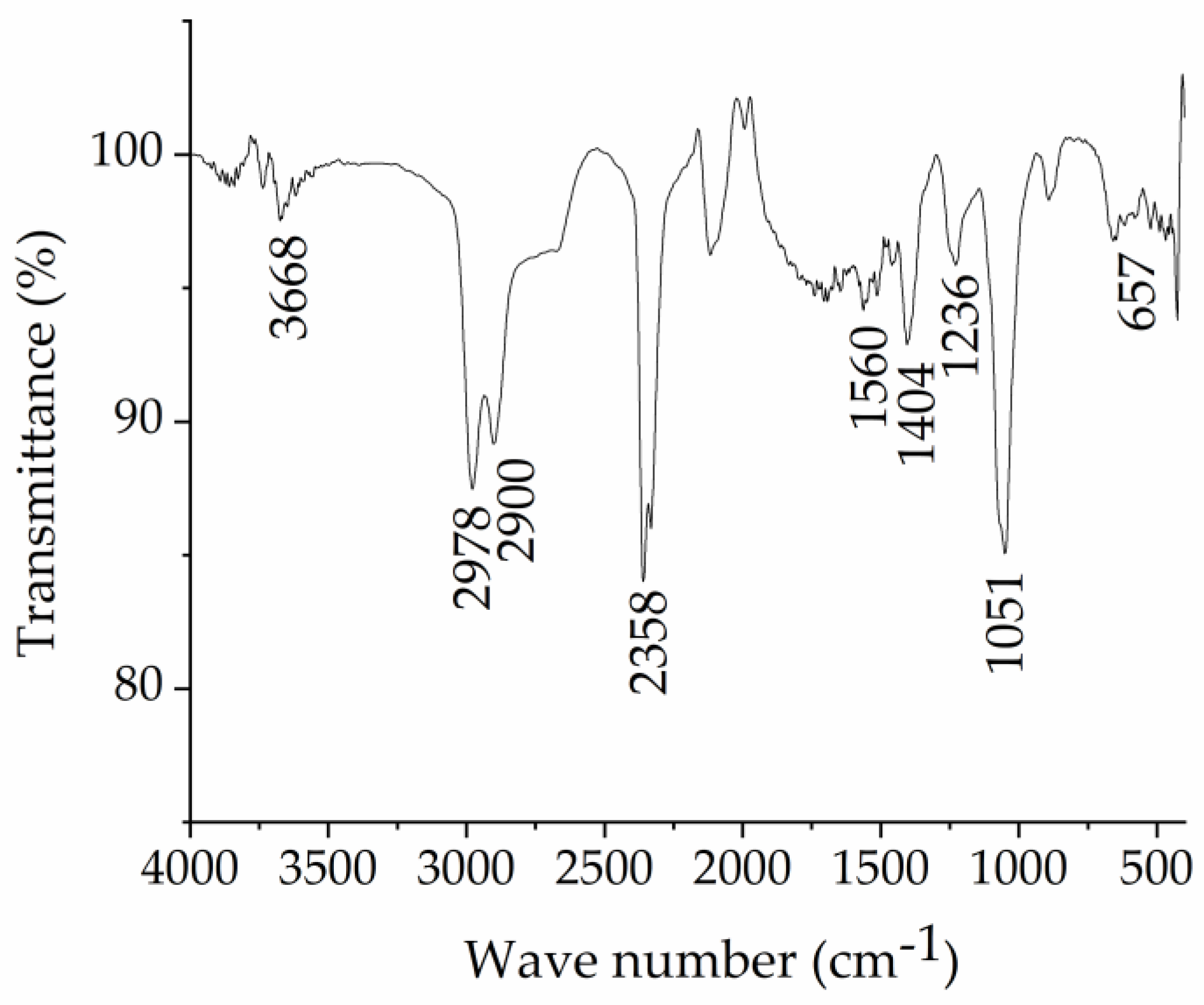
Sodium lignosulphonate was separated from the CCH stream using an ultrafiltration method, and its structure was confirmed by FT-IR spectroscopy. Figure 1 shows the functional groups of the separated lignosulphonate. The bands are attributed as follows: 3668 cm−1 (-OH stretching vibrations), 2978 cm−1 and 2900 cm−1 (-CH symmetric stretching vibrations), 1560 cm−1 and 1404 cm−1 (stretching vibrations of aromatic groups), 1236 cm−1 (-OCH3 group vibration), 1051 cm−1 (S=O symmetric stretching of the -SO3 groups) and 600–700 cm−1 (S-O group vibration). Data agree with those reported in the literature [11], confirming that sulphonate groups were added to lignin.
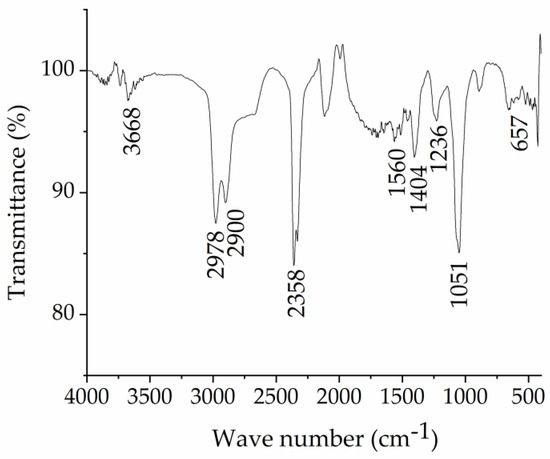
Figure 1.
FTIR spectra of sodium lignosulfonate NaLS.
3.2. Tensioactive Behavior of Sodium Lignosulphonate
The tensioactive behavior of the previously obtained NaLS was determined using surface tension measurements at the water–air interface. It was observed that the surface tension of water decreased from 72.44 mN/m to 65.36 mN/m when NaLS concentration increased from 0 to 1%. This behavior is owed to the amphiphilic nature of sodium lignosulphonate. Due to the irregular distribution of the SO3− groups present in the hydrophilic portion, the NaLS molecules orient so that the hydrophobic core adsorbs at the liquid–air interface to obtain a lower state of energy, resulting in reduction of the surface tension of water. This characteristic has been attributed by some authors [12] to the aggregation of NaLS molecules in aqueous environments.
3.3. Critical Aggregation Concentration of Sodium Lignosulphonate
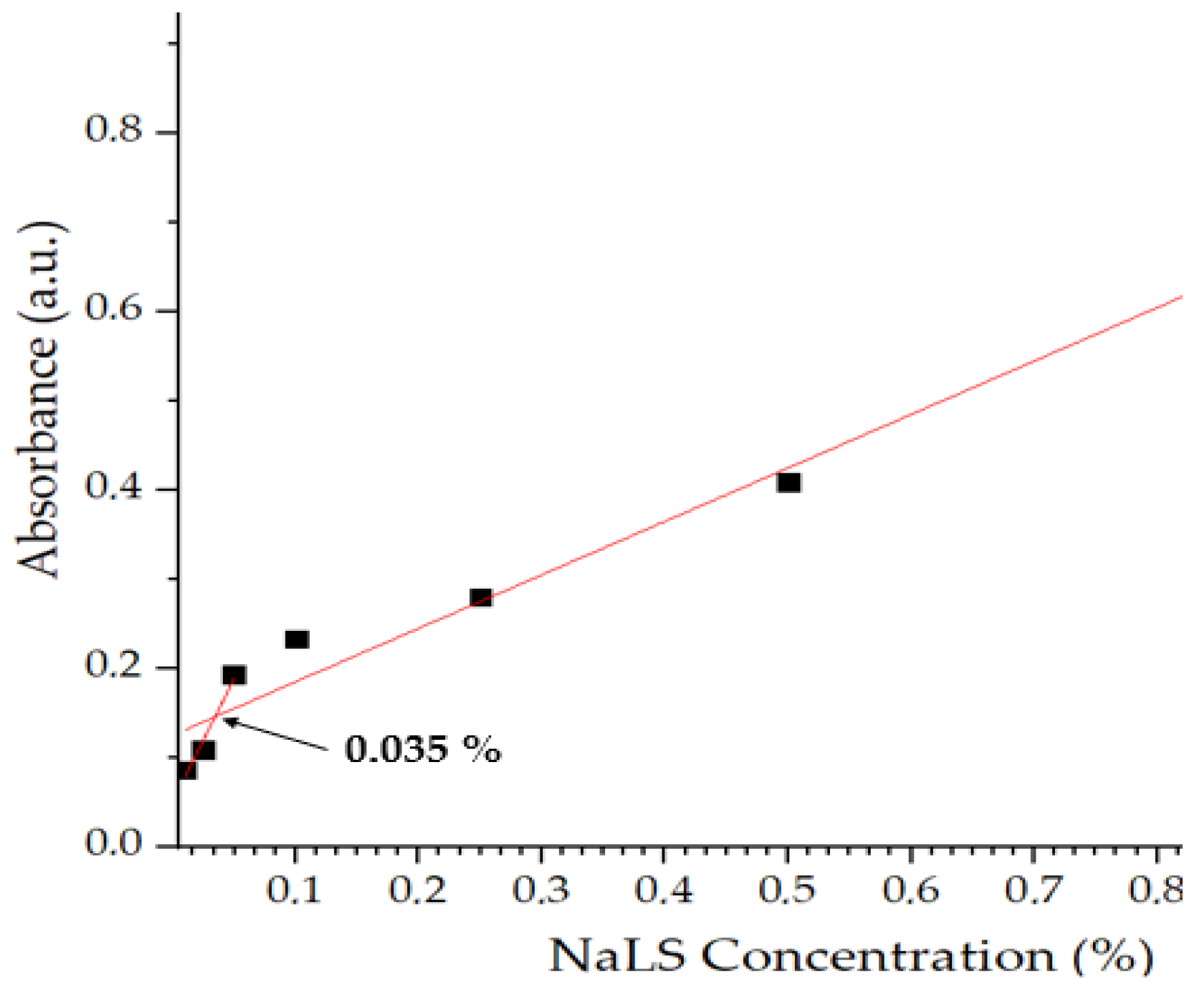
As a tensioactive agent, NaLS molecules tend to aggregate in solution, defined as critical micellar concentration (CAC). This parameter was determined in this study using UV-Vis spectroscopy. The concentrations of NaLS used were: 0.01, 0.025, 0.05, 0.1, 0.25, 0.5 and 1%. As depicted in Figure 2, at lower concentrations of NaLS (0.01–0.05%), UV absorbance increases linearly with NaLS concentration as the NaLS starts to orient in a favorable manner towards forming aggregates. At the CAC value, 0.035%, molecules begin to assemble in molecular aggregates. Above CAC (0.05–1%), absorbance values increase sharply due to larger and larger aggregates forming larger and larger aggregates.
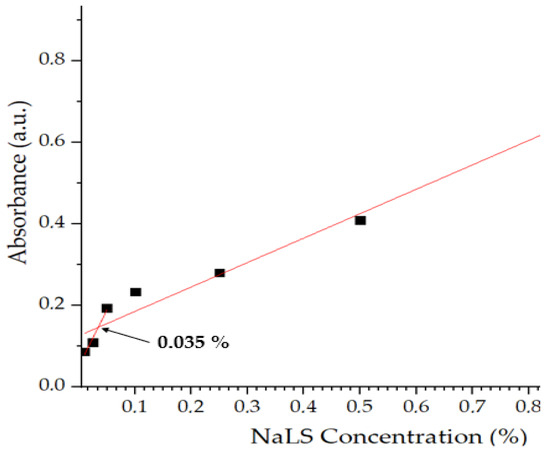
Figure 2.
Critical aggregation concentration of sodium lignosulfonate (NaLS).
This behavior is explained by the fact that as the concentration of NaLS in solution increases, the hydrophobic moieties of this amphiphilic compound begin to interact with each other through hydrophobic interactions, reducing the exposure of the hydrophilic core to the aqueous environment. When the concentration of NaLS exceeds the CAC, larger structures are formed by H bonds. The aggregation behavior is based on reducing the electrostatic repulsions and enhancing hydrophobic interactions. The experimental data obtained are similar to those obtained in the literature [9], even though discrepancies were observed due to the intrinsic variability of the raw NaLS.
3.4. Emulsion Preparation
This study tested the ability of NaLS to work as a cosurfactant in the formation of oil-in-water emulsion. The formulation was prepared by phase inversion, a low-energy method that implies the spontaneous formation of fine droplets dispersed in the aqueous environment [13]. The surfactant chosen for emulsifying was Tween 85 (polyoxyethylene sorbitan trioleate), a nonionic surfactant having a hydrophilic polyethylene glycol chain and a hydrophobic oleic acid tail, with a hydrophilic–lipophilic balance (HLB) value of 11, which is close to the one required by essential oils. The oil phase consisted of thyme essential oil diluted in fractionated coconut oil (medium chain triglycerides). The dilution step was necessary since for some applications, such as those required for agriculture, essential oils give a hormetic response, with high doses being considered phytotoxic [14], but also because it reduces the density differences between the aqueous and the oil phase, decreasing the risk of emulsion destabilization due to gravitational forces [15]. The aqueous phase of emulsions was prepared using different concentrations of NaLS. Based on studies in the literature, the HLB value of NaLS is 11.62 [16]. Close values of surfactant and cosurfactant were chosen to match the required HLB of the oil phase [17].
3.5. Emulsion Characterization
One drop of emulsion was added into water or oil phase to determine the emulsion type. All prepared emulsions were well dispersed in water, concluding that they are oil-in-water emulsions, fine droplets of oil being dispersed into an aqueous, continuous phase.
Particle size and PDI for all emulsions were determined by dynamic light scattering. Table 1 shows the obtained values. All tested concentrations were above the CAC value hence NaLS molecules adsorbed at the oil–water interface are expected to be in their aggregated form, facilitating the formation and stabilization of smaller droplets by decreasing the interfacial tension [18]. The droplet size and PDI of the emulsions containing NaLS in the aqueous phase were smaller compared to the one without NaLS. These observations indicate that sodium lignosulphonate is a favorable co-surfactant in stabilizing oil-in-water emulsions.

Table 1.
Droplet size and PDI of the DLS-analyzed emulsions at 0 and 24 h after synthesis.
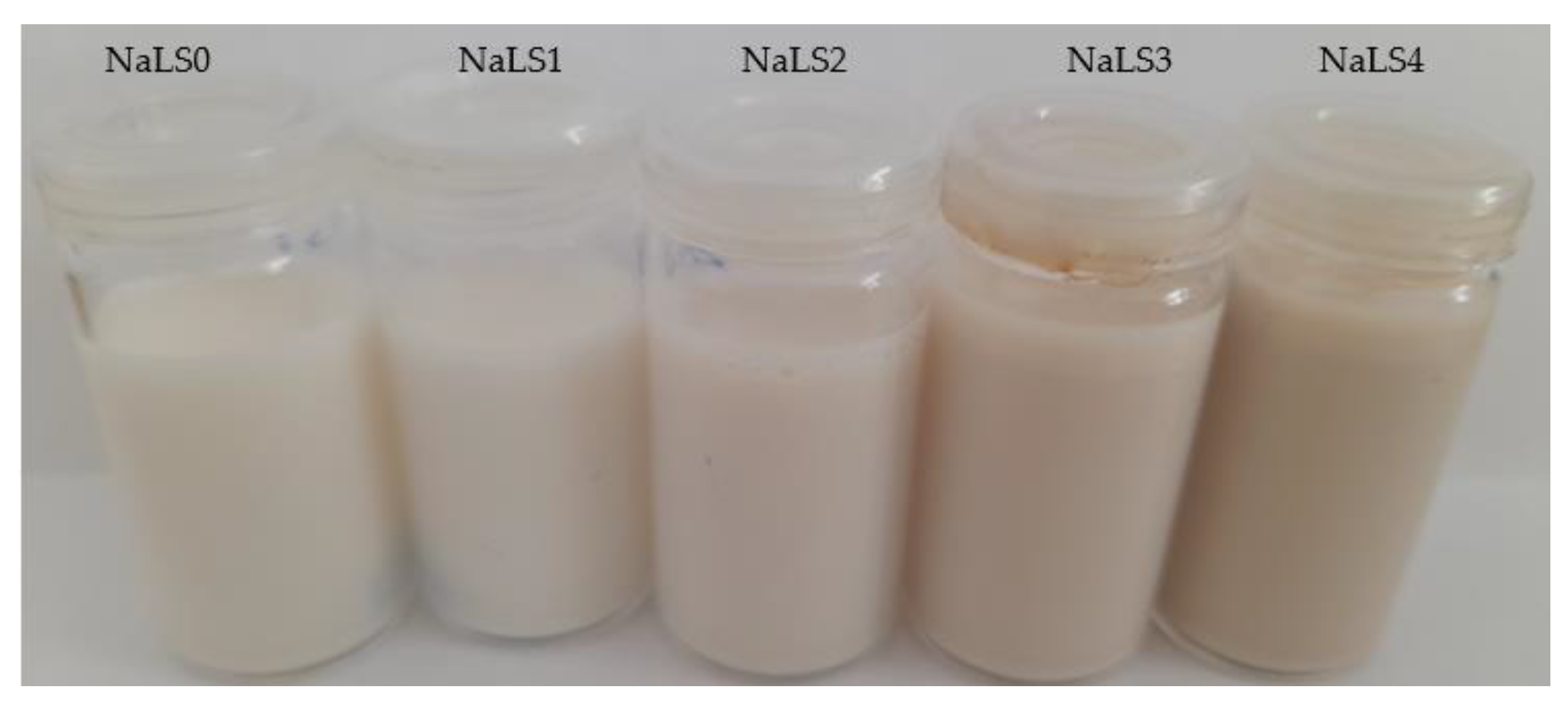
Emulsion stability was addressed by measuring the droplet size and PDI 24 h after preparation. The visual appearance of emulsions at 24 h after preparation is presented in Figure 3.

Figure 3.
Visual appearance of emulsions, 24 h after preparation.
Emulsions containing lower concentrations of NaLS were proven to be more stable, as evidenced by the fact that there were no notable changes in the tested parameters or in their visual appearance. All other emulsions had different values for droplet size and polydispersity index, indicating that they are less stable, being prone to phase separation in time. As seen in Figure 3, emulsions with high concentrations of NaLS are destabilized since the creaming phenomenon is observed.
4. Conclusions
The lignin derivative, sodium lignosulphonate, was obtained from spent sulfite liquor through a microfiltration/ultrafiltration sequence of membrane process. Its behavior as a tensioactive agent was proven using interfacial tension measurement. Due to its amphiphilic nature, sodium lignosulphonate was able to decrease the interfacial tension of water. UV-Vis spectroscopy was used to study its aggregation behavior and revealed that at concentrations higher than 0.035%, molecular aggregates begin to form, increasing in size as the NaLS concentration increases. At concentrations that exceed the critical aggregation concentration, sodium lignosulphonate can be used as a co-surfactant in an oil and water emulsion formed by a phase inversion strategy. Dynamic light scattering revealed that NaLS can decrease the droplet size of the emulsion. Emulsions with lower concentrations of NaLS were proven to be more stable, the optimal value being 0.1%. This system has a droplet size of 154 nm and a PDI value of 0.12.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A.T. and F.O.; methodology, M.A.T.; software, M.A.T.; validation, M.A.T., B.T. and F.O.; formal analysis, M.A.T. and B.T.; investigation, M.A.T. and B.T.; resources, F.O. and D.C.-A.; data curation, B.T.; writing—original draft preparation, M.A.T.; writing—review and editing, B.T., F.O. and D.C.-A.; visualization F.O.; supervision, F.O. and D.C.-A.; project administration, F.O.; funding acquisition, F.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF), the Competitiveness Operational Programme (POC), Axis 1, project POC-A1-A1.2.3-G-2015-P_40_352, My_SMIS 105684, “Sequential processes of closing the side streams from bioeconomy and innovative (bio)products resulting from it—SECVENT”, subsidiary projects 1229/2020 and 385/2021.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tribot, A.; Amer, G.; Abdou Alio, M.; De Baynast, H.; Delattre, C.; Pons, A.; Mathias, J.-D.; Callois, J.-M.; Vial, C.; Michaud, P.; et al. Wood-Lignin: Supply, Extraction Processes and Use as Bio-Based Material. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 112, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kienberger, M.; Maitz, S.; Pichler, T.; Demmelmayer, P. Systematic Review on Isolation Processes for Technical Lignin. Processes 2021, 9, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Rodríguez, J.; García, A.; Coz, A.; Labidi, J. Spent Sulphite Liquor Fractionation into Lignosulphonates and Fermentable Sugars by Ultrafiltration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 152, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abejón, R.; Rabadán, J.; Garea, A.; Irabien, A. Comparison of Supported Ionic Liquid Membranes and Polymeric Ultrafiltration and Nanofiltration Membranes for Separation of Lignin and Monosaccharides. Membranes 2020, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, T.; Fei, J.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, J.; He, H.; Ma, M.; Shi, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, X. Water-soluble Lignosulfonates: Structure, Preparation, and Application. ChemistrySelect 2023, 8, e202204941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruwoldt, J.; Planque, J.; Øye, G. Lignosulfonate Salt Tolerance and the Effect on Emulsion Stability. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 15007–15015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piombino, C.; Lange, H.; Sabuzi, F.; Galloni, P.; Conte, V.; Crestini, C. Lignosulfonate Microcapsules for Delivery and Controlled Release of Thymol and Derivatives. Molecules 2020, 25, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, B.; Mishra, A.P.; Shukla, I.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Contreras, M.D.M.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Fatti, H.; Nasrabi, N.N.; Sharifi-Rad, J. Thymol, thyme, and other plant sources: Health and potential uses. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 1688–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.; Kong, Q.; Zhou, M.; Yang, D. Aggregation Behavior of Sodium Lignosulfonate in Water Solution. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 15857–15861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostertag, F.; Weiss, J.; McClements, D.J. Low-Energy Formation of Edible Nanoemulsions: Factors Influencing Droplet Size Produced by Emulsion Phase Inversion. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 388, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Yuan, B.; Guo, M.; Yang, Q.; Nguyen, T.T.; Ji, X. Effect of Sodium Lignosulfonate on Bonding Strength and Chemical Structure of a Lignosulfonate/Chitosan-Glutaraldehyde Medium-Density Fiberboard Adhesive. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2021, 4, 1176–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, D.; Neale, G.; Hornof, V. Surface Tension of Mixed Surfactant Systems: Lignosulfonate and Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2002, 280, 775–778. [Google Scholar]
- Perazzo, A.; Preziosi, V.; Guido, S. Phase Inversion Emulsification: Current Understanding and Applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 222, 581–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-ElGawad, A.M.; El Gendy, A.E.-N.G.; Assaeed, A.M.; Al-Rowaily, S.L.; Alharthi, A.S.; Mohamed, T.A.; Nassar, M.I.; Dewir, Y.H.; Elshamy, A.I. Phytotoxic Effects of Plant Essential Oils: A Systematic Review and Structure-Activity Relationship Based on Chemometric Analyses. Plants 2020, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komaiko, J.; McClements, D.J. Low-Energy Formation of Edible Nanoemulsions by Spontaneous Emulsification: Factors Influencing Particle Size. J. Food Eng. 2015, 146, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiati, R.; Siregar, S.; Marhaendrajana, T.; Wahyuningrum, D. Challenge Sodium Lignosulfonate Surfactants Synthesized from Bagasse as an Injection Fluid Based on Hydrophil Liphophilic Balance. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 434, 012083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.J.; Trujillo, L.A.; Garcia, M.C.; Alfaro, M.C.; Muñoz, J. Effect of Emulsifier HLB and Stabilizer Addition on the Physical Stability of Thyme Essential Oil Emulsions. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2018, 39, 1627–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruwoldt, J.; Simon, S.; Øye, G. Viscoelastic Properties of Interfacial Lignosulfonate Films and the Effect of Added Electrolytes. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 606, 125478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).