Abstract
The pinewood nematode (PWN), Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, the causal agent of pine-wilt disease (PWD), is a threat to Pinus forests in Asia and Europe. Bursaphelenchus mucronatus and B. fraudulentus are closely related non-pathogenic pine-wood nematodes. In the present work, four medium-chain aliphatic alcohols (C10 to C13) were evaluated in direct-contact bioassays against B. xylophilus, B. mucronatus and B. fraudulentus. The compounds showed high nematicidal activity against the species tested. The lowest values for half-maximal effective concentrations (EC50) were determined in B. xylophilus and B. fraudulentus, suggesting a higher sensibility to these compounds. Further bioassays will include compounds with different chain lengths and functional groups to explore the diversity in the activity of oxygen-containing aliphatic compounds for a more targeted sustainable-control strategy for the PWN.
1. Introduction
The pinewood nematode (PWN), Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Steiner and Bührer) Nickle, is the causal agent of pine wilt disease (PWD). This migratory endoparasite is believed to be indigenous to North America, where it causes PWD to non-endemic pine species. In the beginning of the 20th century, the PWN spread to Japan and later to China, Korea and, more recently, to Portugal, in 1999; it is temporarily contained in Spanish-border pine forests [1,2,3,4,5,6]. Since its introduction, European authorities have established phytosanitary plans to control the progression of the PWN by heavily restricting and regulating wood transportation and export, eliminating symptomatic trees, creating buffer zones adjacent to affected areas, and controlling vector beetle populations, including longhorn beetles Monochamus spp. (Coleoptera; Cerambycidae). However, these measures have exerted only a limited impact on PWN spread; new pockets of infection continue to be detected by official national-monitoring programs. Thus, PWD continues to be considered a serious threat to the highly susceptible pine forests of Europe and Asia [7,8,9].
Bursaphelenchus genus (Nematoda: Aphelenchidae) is mostly mycetophagous, yet some can also feed on plants (wood). Examples of this include B. cocophilus, a pathogen of coconuts and palms and the PWN, which parasitizes pines. Bursaphelenchus mucronatus Mamiya & Enda and B. fraudulentus Rühm are taxonomically closely related to the PWN, sharing many morphological traits and tree hosts. Contrary to the PWN, these are considered non-pathogenic [10]. Bursaphelenchus xylophilus and B. mucronatus nematodes feed on epithelial cells and reproduce in the resin canals of pine trees or feed on fungi present in their hosts [11]; however, only the PWN commonly increases its population uncontrollably, damaging the tree. Conversely, B. fraudulentus is mycetophagous and does not cause harm to host tree; it is even considered a biological control agent of Armillaria spp., the causal agent of Armillaria-root rot in a multitude of woody hosts [12].
Currently, pest management in agriculture and forestry is still heavily dependent on the application of synthetic pesticides. For the control of the PWN, highly damaging insecticides can be used to reduce the populations of the insect vector, which transmits the PWN. Alternatively, strong nematicides, from synthetic or hemisynthetic sources, are used by direct application through the injection of the trunks of infected or endangered pines. The most commonly used nematicides include morantel tartrate, levamisole hydrochloride, mesulfenfos, emamectin benzoate and nemadectin [13]. Despite their high effectiveness in eliminating the PWN, synthetic pesticides are non-specific; they can effectively target numerous beneficial microorganisms and negatively influence food chains, ultimately damaging several other organisms, such as bees, birds, plants and even humans. In general terms, downstream effects result in the loss of endemic biodiversity in forest ecosystems, potentiating acquired resistance on the target pests and the bioaccumulation of residues above the safety limits in human food chains [14,15,16,17].
The establishment of more sustainable management strategies is thus essential to minimize the effects of pesticide misuse, by developing novel biopesticides and biocontrol agents [18,19,20,21,22]. In recent years, a growing demand for “greener” pesticides has fueled the search for novel biopesticides. These plant-protection products (PPPs) are regarded as more sustainable forms of control, since they can allow specific activities against the target pest. Moreover, PPPs have shown fewer adverse effects on the environment and are reported to be less concerning for human health when compared to conventional pesticides [23,24]. For use against the PWN, essential oils (EOs) have been screened with relative success; several of these complex mixtures of volatiles have shown higher activities than common-use nematicides [15]. Plants synthesize volatile organic compounds (VOCs) with several important environmental roles, particularly when subjected to biotic stress. These VOCs function as chemical signals between neighboring plants and/or other organisms and are essential in plants’ defense mechanisms [25,26,27]. For example, when attacked by phytophagous parasites, small- and medium-chain aliphatic aldehydes and alcohols can have a protective role [28], and their nematicidal strength against the PWN has begun to be screened [29].
In the present study, the nematicidal activity of four medium-chain aliphatic alcohols (C10 to C13) was investigated against B. xylophilus, as well as against its closest relatives, B. mucronatus and B. fraudulentus. Their chemical structures were compared considering their nematicidal activity to uncover and explore potentially differential susceptibilities to these compounds, for the development of targeted nematotoxic compounds.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Nematicidal Chemicals
The pure analytical-grade standards 1-decanol (purity ≥ 98%), 1-undecanol (purity 99%), 1-dodecanol (purity ≥ 98%) and 1-tridecanol (purity 97%) were acquired from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). The HPLC-grade methanol was acquired from Fisher Chemicals (Hampton, NH, USA).
2.2. Bursaphelenchus spp. In Vitro Culture
Nematodes were obtained in vitro by culturing on axenically grown fungal mats of a non-sporulating strain of Botrytis cinerea (de Bary) Whetzel. In 250-milliliter Erlenmeyer flasks, ca. 15 g of Hordeum vulgare L. were added to 15 mL water and steam-sterilized. At room temperature, axenic cultures of the fungus, grown in potato-dextrose agar (PDA) culture medium, were used to inoculate the hydrated barley grains, which were then maintained at 25 ± 1 °C (7–10 days). Following, ca. 1500 ± 500 surface-sterilized [30] B. xylophilus (Portuguese isolate BX013.003), B. mucronatus (Chinese isolate BmCh3FJ12), or B. fraudulentus (German isolate BfG1DE10W) from the reference collection maintained at the Plant Nematology Laboratory of the National Institute for Agrarian and Veterinary Research (INIAV, I.P.) at Oeiras, Portugal, were added to these cultures and kept at 25 ± 1 °C, in darkness, for 7 to 10 days. Each nematode-species in vitro culture was then extracted through the modified Baermann-funnel technique [31] and kept in aqueous suspensions. The assessment of nematode numbers and/or survival rates was performed using an Olympus SZX12 (Tokyo, Japan) stereomicroscope. For nematode morphological traits, at least 10 specimens of each species were heat-killed and placed in a drop of water on a glass slide and observed using an Olympus BX-51 bright-field-light microscope (Hamburg, Germany) and photographed with an Olympus DP10 digital camera.
2.3. Toxicological Characterization of Nematicidal Compounds
Direct-contact bioassays were employed to determine the nematicidal activity of each compound, by assessing compound mortality at different concentrations in flat-bottomed 96-well microtiter plates (Carl Roth GmbH & Co. KG, Karlsruhe, Germany). The survival of mixed-life-stage nematodes (100 ± 10 nematodes per well) was assayed at 1 µL of compound/mL, by adding 5 µL of stock solution (containing 20 µL of compound per mL of methanol) to 95 µL of aqueous nematode suspension. Control assays were performed with 5 µL of pure methanol. Plates were mixed at 800 cycles/min for 1 min, covered with aluminum foil to reduce volatilization of compounds and to establish complete darkness and maintained at 25 ± 1 °C and 50 r.p.m., for 24 h. Nematode mortality was visually assessed with a stereomicroscope. Nematodes were considered dead if no movement was detected, even after physical prodding. To determine toxicity parameters, lower concentrations (0.500, 0.250, 0.125, 0.063, 0.031, 0.016, 0.008 and 0.004 µL/mL) were screened for each compound using the procedure described above.
2.4. Data Treatment and Statistical Analysis
Nematode percentage mortality was determined by applying the formula, mortality % = 100 × [(dead nematodes)/(total nematodes)]. Corrected mortality was determined through the formula, corrected mortality % = 100 × [(mortality % in treatment−mortality % in control)/(100−mortality % in control)]. The nematicidal strength of each compound was evaluated according to Kong et al. [32], according to which it was complete when mortality was 100%, strong activity ≥ 80%, moderate activity between 80 and 61%, weak activity under 60 and above 40% and low or inactive under 40%. The EC50 values were obtained with Origin Graphing & Analysis software v. 2019 (OriginLab, Northampton, MA, USA). A nonlinear regression analysis was performed by fitting a dose-response log-logistic equation, y = A + (B−A)/1 + exp {b [log (x)−log (EC50)]} [33], where A is the lower limit and B is the upper limit of the dose-response curve, b is the slope and EC50 is the half-maximal effective concentration.
3. Results
3.1. Bursaphelenchus spp. Morphology
Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, B. mucronatus and B. fraudulentus are commonly grouped in a unit designated as the “pinewood-nematode complex”, within the xylophilus group (which includes nine morphologically similar Bursaphelenchus species). Within the “pinewood-nematode complex” these three species can be identified by their different female-tail morphologies and, more minutely, by the shape of the spicules in their male tails (Figure 1). Under the microscope, amongst other features, B. mucronatus females showed a round mucronated tail, B. fraudulentus a pointed tail, and B. xylophilus a rounded tail, which may be mucronated (Figure 1).
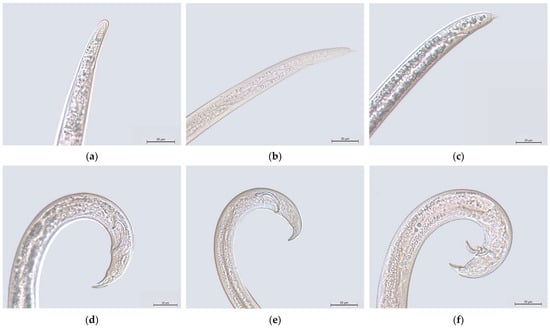
Figure 1.
Light-microscopy micrographs of the tails of female (a–c) and male (d–f) Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (a,d), B. mucronatus (b,e) and B. fraudulentus (c,f). Bar = 20 μm.
3.2. Toxicity of Oxygen-Containing Aliphatic Compounds
The four medium-chain aliphatic alcohols screened showed high nematicidal activities (Table 1). Among the tested compounds, 1-dodecanol showed the lowest EC50 values for B. xylophilus and B. fraudulentus, while for B. mucronatus, 1-tridecanol had the highest effect. For B. xylophilus and B. fraudulentus, 1-dodecanol was followed by 1-tridecanol, 1-undecanol and 1-decanol, respectively, in terms of activity. For B. mucronatus, 1-tridecanol was followed by 1-undecanol, 1-dodecanol and 1-decanol, respectively, in terms of activity. The results suggest some homology in the nematoxicity of these compounds against B. xylophilus and B. fraudulentus.

Table 1.
Nematicidal activity of 1-decanol, 1-undecanol, 1-dodecanol and 1-tridecanol against Bursaphelenchus spp.
4. Discussion
Oxygen-containing aliphatic compounds are known antagonists of the PWN. Seo et al. [34] uncovered several structure-activity relationships between medium-carbon-chain-length alcohols, aldehydes and carboxylic acids and mortality on the PWN. Depending on the compound-chain length and functional group, activity against the PWN could be almost completely lost after a certain number of Cs in the aliphatic compound. For medium-carbon-chain alcohols, this cut-off effect occurred at the C12 chain length, n-dodecanol, with n-undecanol showing the strongest activity. This effect contradicts the Meyer–Overton rule, according to which n-alkanols with increasing chain lengths are expected to induce a constant increase in potency, which can be explained by the increase in molecule volume exceeding that of its putative protein-binding site [35,36]. Therefore, this activity loss can be related to the oxygen-containing molecule’s suitability to its target receptor. In the present work, this effect was not detected; however, 1-undecanol was identified as a highly nematicidal n-alkanol against the PWN. To some extent, this was similar to the findings in the study by Seo et al. [34].
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time that C10-to-C13 n-alkanols were screened against B. mucronatus and B. fraudulentus. Although some tendencies were identified that distinguished the responses of these species to the tested compounds, no substantial difference was ascertained.
In future research, transcriptomics and/or metabolomics approaches will be used to identify the molecular mechanisms of the activity of these compounds on the PWN. Furthermore, different oxygen-containing compounds, with similar carbon-chain lengths, will be tested to determine possible analogous nematotoxic effects and screen for possible variations in susceptibility among Bursaphelenchus spp. Finally, evaluating the phytotoxicity of these compounds on the host tree [37] is crucial before a greener nematicide against the PWN can be formulated.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.M.S.F.; methodology, J.M.S.F.; software, J.M.S.F.; formal analysis, T.C., D.G., A.P. and J.M.S.F.; investigation, T.C., D.G., A.P. and J.M.S.F.; resources, C.M. and M.L.I.; writing—original draft preparation, T.C. and J.M.S.F.; writing—review and editing, D.G., A.P., C.M. and M.L.I. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially funded by the Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia (FCT/MCTES) through national funds, under the project LISBOA-01-0145-FEDER-028724, UIDB/00100/2020, UIDP/00100/2020 and IMS-LA/P/0056/2020 (CQE).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author (Jorge M. S. Faria) upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhao, B.G. Pine Wilt Disease in China. In Pine Wilt Disease; Zhao, B.G., Futai, K., Sutherland, J.R., Takeuchi, Y., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2008; pp. 18–25. ISBN 978-4-431-75655-2. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, S.-C. Pine Wilt Disease in Korea. In Pine Wilt Disease; Zhao, B.G., Futai, K., Sutherland, J.R., Takeuchi, Y., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2008; pp. 26–32. ISBN 978-4-431-75655-2. [Google Scholar]
- Futai, K. Pine Wilt in Japan: From First Incidence to the Present. In Pine Wilt Disease; Zhao, B.G., Futai, K., Sutherland, J.R., Takeuchi, Y., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2008; pp. 5–12. ISBN 978-4-431-75655-2. [Google Scholar]
- Mota, M.; Braasch, H.; Bravo, M.A.; Penas, A.C.; Burgermeister, W.; Metge, K.; Sousa, E. First Report of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in Portugal and in Europe. Nematology 1999, 1, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, L.; Cardoso, J.M.S.; Lopes, A.; Pestana, M.; Abreu, F.; Nunes, N.; Mota, M.; Abrantes, I. The Pinewood Nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, in Madeira Island. Helminthologia 2012, 49, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abelleira, A.; Picoaga, A.; Mansilla, J.P.; Aguin, O. Detection of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, Causal Agent of Pine Wilt Disease on Pinus Pinaster in Northwestern Spain. Plant Disease 2011, 95, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Futai, K. Pine Wood Nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2013, 51, 61–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, A.M.; Faria, J.M.S. Profiling the Variability of Eucalyptus Essential Oils with Activity against the Phylum Nematoda. Biol. Life Sci. Forum 2021, 2, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, A.; Nakamura, K.; Nakao, K.; Kominami, Y.; Tanaka, N.; Ohashi, H.; Takano, K.T.; Takeuchi, W.; Matsui, T. Potential Distribution of Pine Wilt Disease under Future Climate Change Scenarios. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryss, A.; Vieira, P.; Mota, M.; Kulinich, O. A Synopsis of the Genus Bursaphelenchus Fuchs, 1937 (Aphelenchida: Parasitaphelenchidae) with Keys to Species. Nematology 2005, 7, 393–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.-Y.; Xie, P.-Z.; Cheng, F.-X.; Xu, R.-M.; Xie, B.-Y. Competitive Displacement of the Native Species Bursaphelenchus mucronatus by an Alien Species Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Nematoda: Aphelenchida: Aphelenchoididae): A Case of Successful Invasion. Biol. Invasions 2009, 11, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomalak, M. Parasitic Association of the Mycetophagous Wood Nematode, Bursaphelenchus fraudulentus with the Honey Fungus Armillaria ostoyae. For. Pathol. 2017, 47, e12325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamata, N. Integrated Pest Management of Pine Wilt Disease in Japan: Tactics and Strategies. In Pine Wilt Disease; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2008; pp. 304–322. ISBN 9784431756545. [Google Scholar]
- Woodcock, B.A.; Bullock, J.M.; Shore, R.F.; Heard, M.S.; Pereira, M.G.; Redhead, J.; Ridding, L.; Dean, H.; Sleep, D.; Henrys, P.; et al. Country-Specific Effects of Neonicotinoid Pesticides on Honey Bees and Wild Bees. Science 2017, 356, 1393–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, J.M.S.; Barbosa, P.; Vieira, P.; Vicente, C.S.L.; Figueiredo, A.C.; Mota, M. Phytochemicals as Biopesticides against the Pinewood Nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus: A Review on Essential Oils and Their Volatiles. Plants 2021, 10, 2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihara, M.; Matsuda, K. Neonicotinoids: Molecular Mechanisms of Action, Insights into Resistance and Impact on Pollinators. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2018, 30, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-R.; Lee, S.-C.; Lee, J.-E.; Seo, S.-M.; Jeong, Y.-C.; Jung, C.-S.; Moloney, M.; Park, I.-K. Nematicidal Activity of 3-Acyltetramic Acid Analogues Against Pine Wood Nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Molecules 2017, 22, 1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, D.; Vicente, C.S.L.; Inácio, M.L.; Mota, M. The Potential of Esteya spp. for the Biocontrol of the Pinewood Nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Weng, M.; Sun, Y.; Carballar-Lejarazú, R.; Wu, S.; Lian, C. Bacillus Thuringiensis Toxins with Nematocidal Activity against the Pinewood Nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2022, 189, 107726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, J.M.S.; Barbosa, P.; Bennett, R.N.; Mota, M.; Figueiredo, A.C. Bioactivity against Bursaphelenchus xylophilus: Nematotoxics from Essential Oils, Essential Oils Fractions and Decoction Waters. Phytochemistry 2013, 94, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.C.; Baek, S.; Park, S.E.; Kim, S.; Lee, M.R.; Jo, M.; Im, J.S.; Ha, P.; Kim, J.S.; Shin, T.Y. Colonization of Metarhizium anisopliae on the Surface of Pine Tree Logs: A Promising Biocontrol Strategy for the Japanese Pine Sawyer, Monochamus alternatus. Fungal Biol. 2020, 124, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lengai, G.M.W.; Muthomi, J.W.; Mbega, E.R. Phytochemical Activity and Role of Botanical Pesticides in Pest Management for Sustainable Agricultural Crop Production. Sci. Afr. 2020, 7, e00239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damalas, C.; Koutroubas, S. Current Status and Recent Developments in Biopesticide Use. Agriculture 2018, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, L.; Thapa, K.; Kanojia, N.; Sharma, N.; Singh, S.; Grewal, A.S.; Srivastav, A.L.; Kaushal, J. An Extensive Review on the Consequences of Chemical Pesticides on Human Health and Environment. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 283, 124657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicke, M.; van Loon, J.J.A. Multitrophic Effects of Herbivore-Induced Plant Volatiles in an Evolutionary Context. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2000, 97, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delory, B.M.; Delaplace, P.; Fauconnier, M.-L.; du Jardin, P. Root-Emitted Volatile Organic Compounds: Can They Mediate Belowground Plant-Plant Interactions? Plant Soil 2016, 402, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broekgaarden, C.; Snoeren, T.A.L.; Dicke, M.; Vosman, B. Exploiting Natural Variation to Identify Insect-Resistance Genes. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2011, 9, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, K. Green Leaf Volatiles: Hydroperoxide Lyase Pathway of Oxylipin Metabolism. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2006, 9, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, S.; Lu, H.; Zhang, D.; Liu, F.; Lin, J.; Zhou, C.; Mu, W. Effects of the Plant Volatile trans-2-Hexenal on the Dispersal Ability, Nutrient Metabolism and Enzymatic Activities of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2017, 143, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, J.M.S.; Sena, I.; Vieira da Silva, I.; Ribeiro, B.; Barbosa, P.; Ascensão, L.; Bennett, R.N.; Mota, M.; Figueiredo, A.C. In Vitro Co-Cultures of Pinus pinaster with Bursaphelenchus xylophilus: A Biotechnological Approach to Study Pine Wilt Disease. Planta 2015, 241, 1325–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, A.G.; Hemming, J.R. A Comparison of Some Quantitative Methods of Extracting Small Vermiform Nematodes from Soil. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1965, 55, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.O.; Lee, S.M.; Moon, Y.S.; Lee, S.G.; Ahn, Y.J. Nematicidal Activity of Plant Essential Oils against Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae). J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2006, 9, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seefeldt, S.S.; Jensen, J.E.; Feurst, E.P. Log-Logistic Analysis of Herbicide Dose-Response Relationships. Weed Technol. 1995, 9, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.-M.; Kim, J.; Kim, E.; Park, H.-M.; Kim, Y.-J.; Park, I.-K. Structure—Activity Relationship of Aliphatic Compounds for Nematicidal Activity against Pine Wood Nematode (Bursaphelenchus xylophilus). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 1823–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, S.J.; Cox, K.J.A.; Lombardi, J.V.; Ho, C.; Kelly, M.B.; Rubin, E.; Stubbs, C.D. Inhibition of Protein Kinase C by Alcohols and Anaesthetics. Nature 1993, 364, 82–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balgavy, P.; Iadv, F.D. Cut-off Effects in Biological Activities of Surfactants. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996, 66, 23–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, J.M.S.; Sena, I.; Moiteiro, C.; Bennett, R.N.; Mota, M.; Cristina Figueiredo, A. Nematotoxic and Phytotoxic Activity of Satureja montana and Ruta graveolens Essential Oils on Pinus pinaster Shoot Cultures and P. pinaster with Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in Vitro Co-Cultures. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 77, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).