Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Survival in Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Objectives
2.2. Data Sources and Study Population
2.3. Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abasheva, D.; Ortiz, A.; Fernandez-Fernandez, B. GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with chronic kidney disease and either overweight or obesity. Clin. Kidney J. 2024, 17 (Suppl. S2), 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2015 Obesity Collaborators; Afshin, A.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Reitsma, M.B.; Sur, P.; Estep, K.; Lee, A.; Marczak, L.; Mokdad, A.H.; Moradi-Lakeh, M.; et al. Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity in 195 Countries over 25 Years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrington, W.G.; Smith, M.; Bankhead, C.; Matsushita, K.; Stevens, S.; Holt, T.; Hobbs, F.D.R.; Coresh, J.; Woodward, M. Body-mass index and risk of advanced chronic kidney disease: Prospective analyses from a primary care cohort of 1.4 million adults in England. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prospective Studies Collaboration; Whitlock, G.; Lewington, S.; Sherliker, P.; Clarke, R.; Emberson, J.; Halsey, J.; Qizilbash, N.; Collins, R.; Peto, R. Body-mass index and cause-specific mortality in 900 000 adults: Collaborative analyses of 57 prospective studies. Lancet 2009, 373, 1083–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndumele, C.E.; Neeland, I.J.; Tuttle, K.R.; Chow, S.L.; Mathew, R.O.; Khan, S.S.; Coresh, J.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Carnethon, M.R.; Després, J.-P.; et al. A Synopsis of the Evidence for the Science and Clinical Management of Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2023, 148, 1636–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marso, S.P.; Bain, S.C.; Consoli, A.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Jódar, E.; Leiter, L.A.; Lingvay, I.; Rosenstock, J.; Seufert, J.; Warren, M.L.; et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1834–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkovic, V.; Tuttle, K.R.; Rossing, P.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Mann, J.F.; Bakris, G.; Baeres, F.M.; Idorn, T.; Bosch-Traberg, H.; Lausvig, N.L.; et al. Effects of Semaglutide on Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muskiet, M.H.A.; Tonneijck, L.; Smits, M.M.; Van Baar, M.J.B.; Kramer, M.H.H.; Hoorn, E.J.; Joles, J.A.; Van Raalte, D.H. GLP-1 and the kidney: From physiology to pharmacology and outcomes in diabetes. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 605–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michos, E.D.; Bakris, G.L.; Rodbard, H.W.; Tuttle, K.R. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in diabetic kidney disease: A review of their kidney and heart protection. Am. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2023, 14, 100502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, I.H.; Khunti, K.; Sadusky, T.; Tuttle, K.R.; Neumiller, J.J.; Rhee, C.M.; Rosas, S.E.; Rossing, P.; Bakris, G. Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 3075–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2024 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2024, 105, S117–S314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VA Informatics and Computing Infrastructure (VINCI). Available online: www.research.va.gov/programs/vinci/ (accessed on 16 October 2025).
- Levey, A.S.; Coresh, J.; Greene, T.; Stevens, L.A.; Zhang, Y.L.; Hendriksen, S.; Kusek, J.W.; Van Lente, F.; Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration. Using standardized serum creatinine values in the modification of diet in renal disease study equation for estimating glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2006, 145, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inker, L.A.; Eneanya, N.D.; Coresh, J.; Tighiouart, H.; Wang, D.; Sang, Y.; Crews, D.C.; Doria, A.; Estrella, M.M.; Froissart, M.; et al. New Creatinine- and Cystatin C-Based Equations to Estimate GFR without Race. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1737–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynard, C. Ascertaining Veterans’ Vital Status: Data Sources for Mortality Ascertainment and Cause of Death. Database & Methods Cyberseminar Series. 2017. Available online: https://view.officeapps.live.com/op/view.aspx?src=https%3A%2F%2Fhsrd.research.va.gov%2Ffor_researchers%2Fcyber_seminars%2Fcatalog%2Ftranscripts%2F3783.doc&wdOrigin=BROWSELINK (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- Zhang, Z.; Reinikainen, J.; Adeleke, K.A.; Pieterse, M.E.; Groothuis-Oudshoorn, C.G.M. Time-varying covariates and coefficients in Cox regression models. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Highcharts. Highcharts Documentation. Available online: https://www.highcharts.com/docs/index (accessed on 18 November 2025).
- R: The R Project for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 16 October 2025).
- 2020 FDA Guidance for Diabetes Drug Development: Cardiorenal Populations and Outcomes: Lessons Learned and Future Directions—American College of Cardiology. Available online: https://www.acc.org/latest-in-cardiology/articles/2021/09/10/13/46/2020-fda-guidance-for-diabetes-drug-development (accessed on 16 October 2025).
- Federal Register: Guidance for Industry on Diabetes Mellitus-Evaluating Cardiovascular Risk in New Antidiabetic Therapies to Treat Type 2 Diabetes; Availability. Available online: https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2008/12/19/E8-30086/guidance-for-industry-on-diabetes-mellitus-evaluating-cardiovascular-risk-in-new-antidiabetic (accessed on 16 October 2025).
- Pfeffer, M.A.; Claggett, B.; Diaz, R.; Dickstein, K.; Gerstein, H.C.; Køber, L.V.; Lawson, F.C.; Ping, L.; Wei, X.; Lewis, E.F.; et al. Lixisenatide in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Acute Coronary Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2247–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marso, S.P.; Daniels, G.H.; Brown-Frandsen, K.; Kristensen, P.; Mann, J.F.E.; Nauck, M.A.; Nissen, S.E.; Pocock, S.; Poulter, N.R.; Ravn, L.S.; et al. Liraglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, R.R.; Bethel, M.A.; Mentz, R.J.; Thompson, V.P.; Lokhnygina, Y.; Buse, J.B.; Chan, J.C.; Choi, J.; Gustavson, S.M.; Iqbal, N.; et al. Effects of Once-Weekly Exenatide on Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1228–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, A.F.; Green, J.B.; Janmohamed, S.; D‘Agostino, R.B.; Granger, C.B.; Jones, N.P.; Leiter, L.A.; Rosenberg, A.E.; Sigmon, K.N.; Somerville, M.C.; et al. Albiglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease (Harmony Outcomes): A double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2018, 392, 1519–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstein, H.C.; Colhoun, H.M.; Dagenais, G.R.; Diaz, R.; Lakshmanan, M.; Pais, P.; Probstfield, J.; Riesmeyer, J.S.; Riddle, M.C.; Rydén, L.; et al. Dulaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes (REWIND): A double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, M.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Donsmark, M.; Dungan, K.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Franco, D.R.; Jeppesen, O.K.; Lingvay, I.; Mosenzon, O.; Pedersen, S.D.; et al. Oral Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstein, H.C.; Sattar, N.; Rosenstock, J.; Ramasundarahettige, C.; Pratley, R.; Lopes, R.D.; Lam, C.S.; Khurmi, N.S.; Heenan, L.; Del Prato, S.; et al. Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes with Efpeglenatide in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 896–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, S.L.; Rørth, R.; Jhund, P.S.; Docherty, K.F.; Sattar, N.; Preiss, D.; Køber, L.; Petrie, M.C.; McMurray, J.J.V. Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacIsaac, R.J.; Jerums, G.; Ekinci, E.I. Glycemic Control as Primary Prevention for Diabetic Kidney Disease. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2018, 25, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemens, K.K.; Ernst, J.; Khan, T.; Reichert, S.; Khan, Q.; LaPier, H.; Chiu, M.; Stranges, S.; Sahi, G.; Castrillon-Ramirez, F.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists in end-staged kidney disease and kidney transplantation: A narrative review. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2023, 33, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idorn, T.; Knop, F.K.; Jørgensen, M.B.; Jensen, T.; Resuli, M.; Hansen, P.M.; Christensen, K.B.; Holst, J.J.; Hornum, M.; Feldt-Rasmussen, B. Safety and Efficacy of Liraglutide in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and End-Stage Renal Disease: An Investigator-Initiated, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind, Parallel-Group, Randomized Trial. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomholt, T.; Idorn, T.; Knop, F.K.; Jørgensen, M.B.; Ranjan, A.G.; Resuli, M.; Hansen, P.M.; Borg, R.; Persson, F.; Feldt-Rasmussen, B.; et al. The Glycemic Effect of Liraglutide Evaluated by Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Persons with Type 2 Diabetes Receiving Dialysis. Nephron 2021, 145, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terawaki, Y.; Nomiyama, T.; Akehi, Y.; Takenoshita, H.; Nagaishi, R.; Tsutsumi, Y.; Murase, K.; Nagasako, H.; Hamanoue, N.; Sugimoto, K.; et al. The efficacy of incretin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes undergoing hemodialysis. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2013, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiramatsu, T.; Ozeki, A.; Asai, K.; Saka, M.; Hobo, A.; Furuta, S. Liraglutide Improves Glycemic and Blood Pressure Control and Ameliorates Progression of Left Ventricular Hypertrophy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on Peritoneal Dialysis. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2015, 19, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonston, D.; Mulder, H.; Lydon, E.; Chiswell, K.; Lampron, Z.; Shay, C.; Marsolo, K.; Shah, R.C.; Jones, W.S.; Gordon, H.; et al. Kidney and Cardiovascular Effectiveness of SGLT2 Inhibitors vs GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Type 2 Diabetes. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2024, 84, 696–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.W.; See, C.Y.; Chen, J.Y.; Wu, V.C. Mortality and cardiovascular events in diabetes mellitus patients at dialysis initiation treated with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | All | No KRT | KRT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| eGFR | 15–24 | <15 | ||
| 100 | 32.4 | 19.7 | 48.0 | |
| Age, yrs. | ||||
| <50 | 2.1 | 0.6 | 2.2 | 3.2 |
| 50–64 | 20.3 | 10.6 | 19.7 | 27.0 |
| 65–79 | 59.4 | 56.3 | 61.4 | 60.7 |
| ≥80 | 18.2 | 32.5 | 16.7 | 9.2 |
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 97.2 | 97.4 | 97.5 | 96.9 |
| Race | ||||
| White | 54.8 | 63.9 | 49.2 | 51.0 |
| Black | 35.8 | 27.5 | 40.7 | 39.5 |
| Other | 9.4 | 8.6 | 10.2 | 9.5 |
| Hispanic Ethnicity | 7.9 | 6.0 | 7.9 | 9.1 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | ||||
| <25 | 20.3 | 18.4 | 19.5 | 21.9 |
| 25–29 | 31.2 | 30.7 | 33.1 | 30.8 |
| 30–39 | 38.5 | 40.0 | 38.4 | 37.5 |
| ≥40 | 7.3 | 8.2 | 6.1 | 7.2 |
| Not measured | 2.6 | 2.6 | 2.8 | 2.6 |
| HgbA1c, % | ||||
| <7 | 49.5 | 45.3 | 52.0 | 51.3 |
| ≥7 | 39.5 | 45.9 | 38.0 | 35.7 |
| Not measured | 11.0 | 8.8 | 10.0 | 13.0 |
| Medications | ||||
| Biguanide | 3.3 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 5.6 |
| Sulfonylurea | 10.1 | 14.7 | 8.0 | 7.9 |
| SGLT2i | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 0.8 |
| Insulin | 34.4 | 38.0 | 35.2 | 31.7 |
| ACEi/ARB | 27.7 | 31.6 | 19.5 | 28.5 |
| Statin | 52.1 | 54.8 | 50.0 | 51.2 |
| Comorbid Condition | ||||
| Heart failure | 31.1 | 21.9 | 11.6 | 45.2 |
| Ischemic heart disease | 31.6 | 21.9 | 12.0 | 46.2 |
| Stroke | 11.5 | 7.4 | 3.8 | 17.5 |
| Peripheral vascular disease | 19.2 | 10.9 | 6.1 | 30.1 |
| Skin ulcer | 16.0 | 8.4 | 4.9 | 25.7 |
| Vision disorder | 16.3 | 9.7 | 6.6 | 24.7 |
| Nicotine dependence | 10.1 | 5.9 | 3.6 | 15.7 |
| Substance abuse | 7.8 | 3.8 | 2.4 | 12.7 |
| Serious mental illness | 2.8 | 1.6 | 1.1 | 4.3 |
| Post-traumatic stress disorder | 9.7 | 5.3 | 3.2 | 15.4 |
| Malignancy | 20.7 | 14.5 | 8.8 | 29.8 |
| Dementia | 5.7 | 4.8 | 2.7 | 7.6 |
| Variable | % | Unadjusted | Model 1 | Model 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| eGFR | ||||
| 15–24 | 9.7 | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) |
| <15 | 5.2 | 0.56 (0.50, 0.63) | 0.51 (0.45, 0.57) | 0.65 (0.58, 0.74) |
| KRT | 7.6 | 0.79 (0.71, 0.87) | 0.67 (0.61, 0.75) | 0.85 (0.76, 0.95) b |
| Age, yrs. | ||||
| <50 | 15.2 | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) |
| 50–64 | 11 | 0.83 (0.64, 1.07) ns | 0.84 (0.65, 1.08) ns | 0.78 (0.60, 1.01) ns |
| 65–79 | 8.3 | 0.68 (0.53, 0.88) b | 0.64 (0.50, 0.83) | 0.61 (0.48, 0.79) |
| ≥80 | 3.1 | 0.29 (0.22, 0.38) | 0.26 (0.20, 0.35) | 0.31 (0.23, 0.41) |
| Sex | ||||
| Female | 9.8 | 1.14 (0.89, 1.45) | 1.04 (0.82, 1.33) | 1.02 (0.80, 1.30) |
| Race | ||||
| White | 8.3 | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) |
| Black | 6.9 | 0.73 (0.67, 0.81) | 0.65 (0.59, 0.72) | 0.82 (0.74, 0.91) |
| Other | 8.9 | 0.99 (0.85, 1.15) ns | 0.92 (0.79, 1.07) ns | 0.99 (0.85, 1.15) ns |
| Hispanic ethnicity | 7.2 | 0.91 (0.77, 1.07) ns | 0.77 (0.65, 0.91) b | 0.91 (0.76, 1.08) ns |
| BMI | ||||
| <25 | 2.2 | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) |
| 25–29 | 5.3 | 2.15 (1.76, 2.62) | 2.06 (1.69, 2.51) | 1.75 (1.43, 2.13) |
| 30–39 | 11.2 | 4.45 (3.70, 5.36) | 4.02 (3.34, 4.84) | 2.88 (2.38, 3.48) |
| ≥40 | 18.2 | 7.27 (5.93, 8.91) | 6.23 (5.08, 7.65) | 4.04 (3.28, 4.98) |
| Not measured | 5.7 | 2.76 (1.94, 3.91) | 2.70 (1.90, 3.83) | 2.37 (1.67, 3.37) |
| HgbA1c, % | ||||
| <7 | 4.6 | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) |
| ≥7 | 13.1 | 2.94 (2.67, 3.23) | 2.83 (2.57, 3.11) | 2.15 (1.94, 2.37) |
| Not measured | 2.8 | 0.62 (0.48, 0.78) | 0.63 (0.50, 0.80) | 0.67 (0.52, 0.86) b |
| Medications | ||||
| Biguanide | 21.2 | 2.44 (2.01, 2.95) | 2.15 (1.78, 2.61) | 1.53 (1.25, 1.88) |
| Sulfonylurea | 9.6 | 1.15 (1.01, 1.32) b | 1.20 (1.05, 1.37) b | 1.05 (0.92, 1.20) ns |
| SGLT2i | 37.7 | 4.75 (3.30, 6.86) | 4.33 (3.00, 6.25) | 2.09 (1.43, 3.05) |
| Insulin | 12.9 | 2.53 (2.32, 2.76) | 2.40 (2.20, 2.62) | 1.59 (1.45, 1.75) |
| ACEi/ARB | 11.4 | 1.62 (1.48, 1.77) | 1.59 (1.45, 1.73) | 1.24 (1.13, 1.36) |
| Statin | 9.4 | 1.45 (1.33, 1.58) | 1.44 (1.31, 1.57) | 1.09 (1.00, 1.20) ns |
| Comorbid condition | ||||
| Heart failure | 8.3 | 1.15 (1.02, 1.29) a | 1.14 (1.01, 1.28) a | 1.16 (0.97, 1.37) ns |
| Ischemic heart disease | 8.3 | 1.15 (1.03, 1.30) a | 1.13 (1.01, 1.27) a | 1.19 (1.00, 1.41) a |
| Stroke | 8.2 | 1.06 (0.88, 1.28) ns | 1.06 (0.88, 1.27) ns | 1.12 (0.90, 1.38) ns |
| Peripheral vascular disease | 7.7 | 1.04 (0.90, 1.21) ns | 1.03 (0.89, 1.20) ns | 0.98 (0.78, 1.24) ns |
| Skin ulcer | 8.3 | 1.16 (1.00, 1.36) ns | 1.11 (0.95, 1.29) ns | 1.07 (0.85, 1.36) ns |
| Vision disorder | 7.1 | 0.89 (0.75, 1.05) ns | 0.92 (0.78, 1.09) ns | 0.86 (0.71, 1.04) ns |
| Nicotine dependence | 6 | 0.75 (0.60, 0.94) a | 0.69 (0.55, 0.86) b | 0.76 (0.60, 0.97) a |
| Substance abuse | 5.7 | 0.69 (0.53, 0.91) b | 0.64 (0.49, 0.84) b | 0.81 (0.60, 1.09) ns |
| Serious mental illness | 7.1 | 0.87 (0.59, 1.29) ns | 0.75 (0.51, 1.12) ns | 0.96 (0.64, 1.45) ns |
| PTSD | 10.1 | 1.27 (1.05, 1.53) a | 1.18 (0.98, 1.42) ns | 1.18 (0.96, 1.45) ns |
| Malignancy | 6.9 | 0.88 (0.76, 1.03) ns | 0.89 (0.76, 1.04) ns | 0.88 (0.74, 1.05) ns |
| Dementia | 5.1 | 0.71 (0.52, 0.97) a | 0.81 (0.60, 1.11) ns | 0.87 (0.63, 1.21) ns |
| I/D (%) | Overall | No KRT | KRT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| eGFR | 15–24 | <15 | |||
| All | 6.1/57.7 | 0.52 (0.47, 0.57) | 0.60 (0.52, 0.70) | 0.64 (0.50, 0.82) | 0.43 (0.36, 0.50) |
| Age, yrs. | |||||
| <65 | 9.7/38.6 | 0.43 (0.34, 0.55) | 0.58 (0.35, 0.97) a | 0.64 (0.40, 1.02) ns | 0.34 (0.23, 0.48) |
| 65–79 | 6.0/58.2 | 0.59 (0.52, 0.67) | 0.66 (0.55, 0.79) | 0.79 (0.58, 1.08) ns | 0.51 (0.43, 0.62) |
| ≥80 | 2.1/79.4 | 0.69 (0.54, 0.89) b | 0.76 (0.58, 1.01) ns | 1.41 (0.70, 2.84) ns | 0.43 (0.20, 0.89) a |
| Sex | |||||
| Male | 6.1/58.2 | 0.53 (0.48, 0.58) | 0.61 (0.52, 0.71) | 0.64 (0.50, 0.82) | 0.44 (0.37, 0.51) |
| Female | 7.2/41.1 | 0.25 (0.10, 0.68) b | 0.56 (0.21, 1.49) ns | - | - |
| Race | |||||
| White | 6.4/63.8 | 0.55 (0.48, 0.61) | 0.62 (0.52, 0.74) | 0.67 (0.48, 0.93) a | 0.47 (0.39, 0.57) |
| Black | 5.7/48.9 | 0.44 (0.36, 0.55) | 0.57 (0.40, 0.80) b | 0.54 (0.34, 0.85) b | 0.34 (0.24, 0.48) |
| Other race | 6.5/55.6 | 0.36 (0.25, 0.53) | 0.34 (0.16, 0.70) b | 0.79 (0.41, 1.55) ns | 0.30 (0.17, 0.54) |
| Hispanic ethnicity | 6.1/55.7 | 0.44 (0.29, 0.66) | 0.43 (0.16, 1.19) ns | 0.45 (0.17, 1.21) ns | 0.46 (0.28, 0.76) b |
| BMI | |||||
| <25 | 1.5/70.5 | 0.52 (0.36, 0.74) | 0.37 (0.17, 0.79) a | 0.93 (0.51, 1.68) ns | 0.54 (0.33, 0.86) a |
| 25–29 | 4.0/58.5 | 0.59 (0.48, 0.73) | 0.59 (0.43, 0.81) b | 0.81 (0.51, 1.31) ns | 0.51 (0.36, 0.72) |
| 30–39 | 9.1/51.0 | 0.54 (0.47, 0.63) | 0.70 (0.58, 0.86) | 0.55 (0.38, 0.80) b | 0.43 (0.34, 0.54) |
| ≥40 | 14.0/48.5 | 0.62 (0.47, 0.80) | 0.64 (0.43, 0.95) a | 0.95 (0.48, 1.88) ns | 0.55 (0.36, 0.84) b |
| HbA1c, % | |||||
| <7 | 3.6/58.3 | 0.57 (0.47, 0.69) | 0.66 (0.49, 0.90) b | 0.62 (0.38, 0.99) a | 0.49 (0.37, 0.66) |
| ≥7 | 10.3/56.4 | 0.52 (0.46, 0.58) | 0.57 (0.48, 0.68) | 0.68 (0.50, 0.92) a | 0.44 (0.36, 0.54) |
| Medications | |||||
| Biguanide | 19.3/29.9 | 0.46 (0.28, 0.76) b | 1.07 (0.42, 2.74) ns | 1.81 (0.74, 4.44) ns | 0.34 (0.18, 0.64) |
| Sulfonylurea | 9.3/51.0 | 0.54 (0.41, 0.72) | 0.56 (0.38, 0.82) b | 0.78 (0.30, 2.04) ns | 0.54 (0.33, 0.86) b |
| Insulin | 10.4/56.3 | 0.52 (0.46, 0.60) | 0.62 (0.52, 0.75) | 0.62 (0.45, 0.84) b | 0.42 (0.34, 0.53) |
| Comorbid conditions | |||||
| CVD | 5.8/60.9 | 0.53 (0.45, 0.62) | 0.69 (0.53, 0.90) b | 0.70 (0.40, 1.23) ns | 0.46 (0.38, 0.56) |
| Heart failure | 5.8/62.9 | 0.59 (0.50, 0.70) | 0.78 (0.60, 1.02) ns | 0.82 (0.40, 1.68) ns | 0.49 (0.39, 0.61) |
| Comorbidities-0 | 6.8/55.9 | 0.52 (0.46, 0.60) | 0.56 (0.46, 0.68) | 0.69 (0.53, 0.91) b | 0.41 (0.30, 0.56) |
| Comorbidities-1 | 4.9/56.3 | 0.36 (0.23, 0.55) | 0.62 (0.34, 1.13) ns | 0.12 (0.02, 0.72) a | 0.28 (0.14, 0.53) |
| Comorbidities-2 | 4.9/61.9 | 0.58 (0.42, 0.79) | 0.68 (0.44, 1.06) ns | 1.10 (0.45, 2.72) ns | 0.44 (0.28, 0.70) |
| Comorbidities-3 | 6.0/59.3 | 0.54 (0.45, 0.65) | 0.73 (0.52, 1.01) ns | 0.64 (0.28, 1.48) ns | 0.48 (0.39, 0.60) |
| Overall | No KRT | KRT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| eGFR | 15–24 | <15 | - | |
| All | 0.55 (0.50, 0.61) | 0.65 (0.56, 0.75) | 0.74 (0.58, 0.95) a | 0.45 (0.38, 0.53) |
| Age, yrs. | ||||
| <65 | 0.42 (0.33, 0.54) | 0.57 (0.34, 0.95) a | 0.62 (0.39, 1.00) a | 0.33 (0.23, 0.47) |
| 65–79 | 0.57 (0.51, 0.65) | 0.64 (0.53, 0.77) | 0.76 (0.56, 1.03) ns | 0.50 (0.42, 0.61) |
| ≥80 | 0.67 (0.52, 0.87) b | 0.73 (0.55, 0.97) a | 1.25 (0.62, 2.55) ns | 0.43 (0.20, 0.90) a |
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 0.56 (0.50, 0.62) | 0.65 (0.56, 0.76) | 0.74 (0.58, 0.95) a | 0.46 (0.39, 0.54) |
| Female | 0.29 (0.11, 0.75) a | 0.64 (0.24, 1.70) ns | - | - |
| Race | ||||
| White | 0.59 (0.52, 0.66) | 0.67 (0.57, 0.80) | 0.77 (0.56, 1.06) ns | 0.50 (0.41, 0.60) |
| Black | 0.50 (0.40, 0.61) | 0.64 (0.46, 0.90) a | 0.64 (0.40, 1.03) ns | 0.38 (0.27, 0.53) |
| Other race | 0.42 (0.29, 0.61) | 0.41 (0.20, 0.85) a | 0.91 (0.47, 1.77) ns | 0.32 (0.18, 0.58) |
| Hispanic ethnicity | 0.52 (0.34, 0.78) b | 0.54 (0.20, 1.47) ns | 0.58 (0.22, 1.58) ns | 0.50 (0.30, 0.83) b |
| Body mass index | ||||
| <25 | 0.55 (0.39, 0.78) | 0.40 (0.20, 0.83) a | 1.13 (0.65, 1.95) ns | 0.55 (0.35, 0.88) a |
| 25–29 | 0.61 (0.49, 0.75) | 0.61 (0.44, 0.83) b | 0.99 (0.62, 1.59) ns | 0.53 (0.37, 0.74) |
| 30–39 | 0.56 (0.49, 0.65) | 0.73 (0.60, 0.89) b | 0.59 (0.41, 0.85) b | 0.44 (0.35, 0.56) |
| ≥40 | 0.63 (0.48, 0.82) | 0.63 (0.43, 0.94) a | 1.10 (0.58, 2.10) ns | 0.56 (0.37, 0.85) b |
| HgbA1c, %. | ||||
| <7 | 0.60 (0.50, 0.73) | 0.70 (0.52, 0.94) a | 0.72 (0.45, 1.17) ns | 0.53 (0.39, 0.70) |
| ≥7 | 0.54 (0.48, 0.61) | 0.61 (0.51, 0.73) | 0.76 (0.56, 1.03) ns | 0.45 (0.37, 0.55) |
| Medications | ||||
| Biguanide | 0.48 (0.28, 0.79) b | 1.09 (0.41, 2.89) ns | 2.47 (0.83, 7.35) ns | 0.35 (0.19, 0.66) b |
| Sulfonylurea | 0.59 (0.44, 0.78) | 0.64 (0.43, 0.93) a | 1.01 (0.44, 2.32) ns | 0.54 (0.34, 0.86) a |
| Insulin | 0.55 (0.48, 0.62) | 0.65 (0.54, 0.78) | 0.72 (0.53, 0.97) a | 0.43 (0.35, 0.54) |
| Comorbid conditions | ||||
| CVD | 0.56 (0.48, 0.66) | 0.74 (0.56, 0.96) a | 0.90 (0.50, 1.61) ns | 0.48 (0.40, 0.59) |
| Heart failure | 0.61 (0.52, 0.72) | 0.84 (0.64, 1.08) ns | 0.91 (0.44, 1.88) ns | 0.50 (0.40, 0.62) |
| Comorbidities-0 | 0.56 (0.49, 0.65) | 0.61 (0.51, 0.74) | 0.78 (0.60, 1.02) ns | 0.43 (0.31, 0.58) |
| Comorbidities-1 | 0.37 (0.24, 0.57) | 0.56 (0.31, 1.02) ns | 0.18 (0.03, 1.16) ns | 0.29 (0.15, 0.57) |
| Comorbidities-2 | 0.61 (0.45, 0.83) b | 0.73 (0.47, 1.13) ns | 1.13 (0.57, 2.26) ns | 0.48 (0.30, 0.76) b |
| Comorbidities-3 | 0.57 (0.48, 0.68) | 0.78 (0.57, 1.08) ns | 0.80 (0.32, 2.04) ns | 0.50 (0.41, 0.62) |
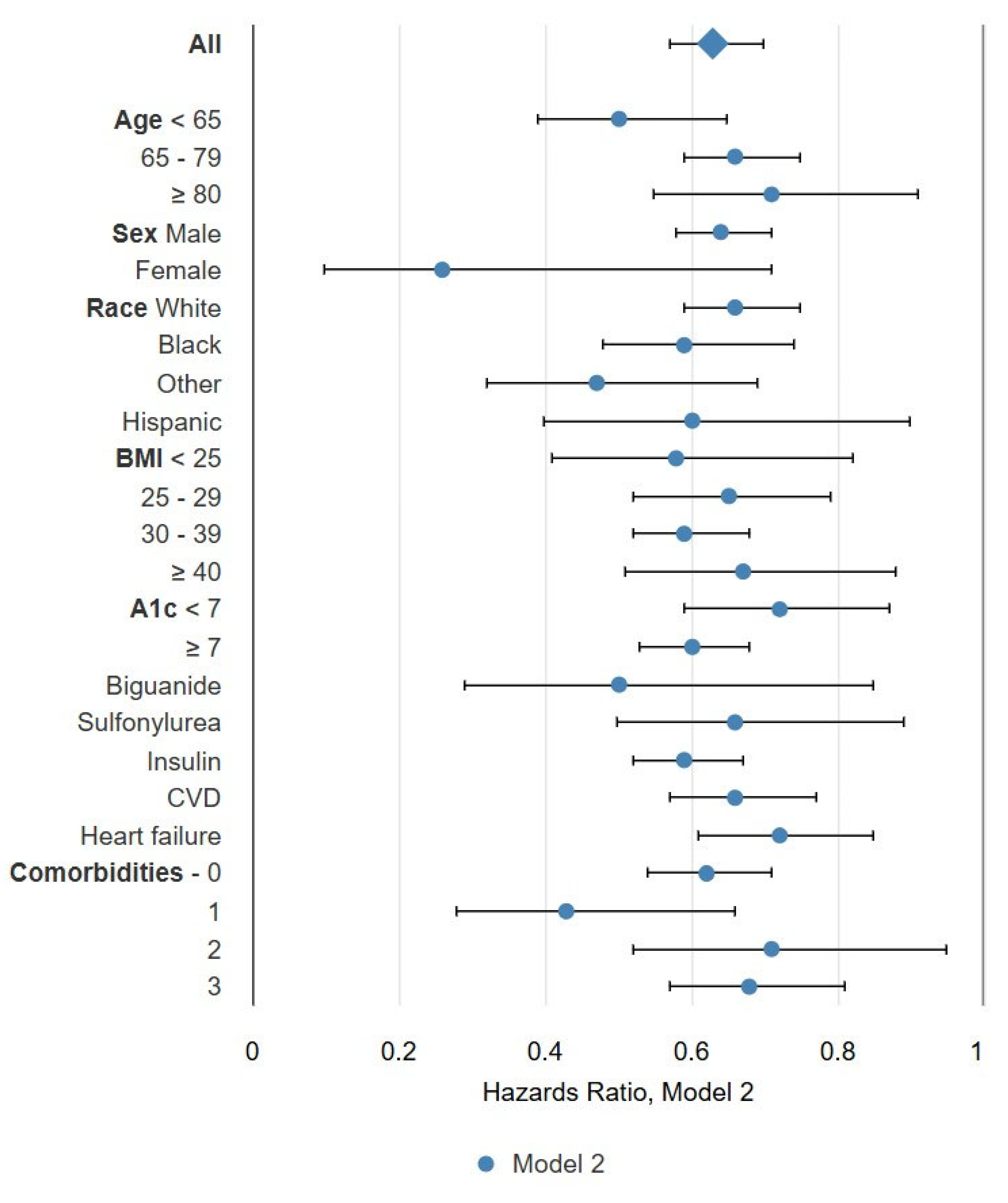
| Overall | No KRT | KRT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| eGFR | 15–24 | <15 | - | |
| All | 0.63 (0.57, 0.70) | 0.67 (0.58, 0.78) | 0.80 (0.63, 1.02) ns | 0.57 (0.49, 0.67) |
| Age, yrs. | ||||
| <65 | 0.50 (0.39, 0.65) | 0.65 (0.38, 1.11) ns | - | 0.41 (0.28, 0.59) |
| 65–79 | 0.66 (0.59, 0.75) | 0.66 (0.54, 0.79) | 0.81 (0.60, 1.10) ns | 0.66 (0.55, 0.79) |
| ≥80 | 0.71 (0.55, 0.91) b | 0.76 (0.57, 1.00) ns | - | 0.48 (0.23, 0.97) a |
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 0.64 (0.58, 0.71) | 0.67 (0.58, 0.78) | 0.80 (0.63, 1.02) ns | 0.59 (0.50, 0.69) |
| Female | 0.26 (0.10, 0.71) b | 0.70 (0.25, 1.97) ns | - | - |
| Race | ||||
| White | 0.66 (0.59, 0.75) | 0.70 (0.59, 0.82) | 0.84 (0.62, 1.15) ns | 0.61 (0.50, 0.74) |
| Black | 0.59 (0.48, 0.74) | 0.65 (0.46, 0.93) a | 0.70 (0.43, 1.12) ns | 0.49 (0.35, 0.70) |
| Other race | 0.47 (0.32, 0.69) | 0.41 (0.20, 0.87) a | - | 0.43 (0.24, 0.76) b |
| Hispanic ethnicity | 0.60 (0.40, 0.90) a | 0.64 (0.24, 1.74) ns | - | 0.68 (0.41, 1.15) ns |
| Body mass index | ||||
| <25 | 0.58 (0.41, 0.82) b | 0.36 (0.18, 0.74) b | - | 0.64 (0.41, 1.01) ns |
| 25–29 | 0.65 (0.52, 0.79) | 0.55 (0.40, 0.76) | - | 0.62 (0.45, 0.87) b |
| 30–39 | 0.59 (0.52, 0.68) | 0.73 (0.60, 0.89) b | 0.57 (0.39, 0.83) b | 0.50 (0.39, 0.63) |
| ≥40 | 0.67 (0.51, 0.88) b | 0.67 (0.45, 0.99) a | - | 0.59 (0.38, 0.91) a |
| HgbA1c, %. | ||||
| <7 | 0.72 (0.59, 0.87) | 0.78 (0.58, 1.06) ns | 0.81 (0.50, 1.32) ns | 0.66 (0.49, 0.88) b |
| ≥7 | 0.60 (0.53, 0.68) | 0.62 (0.52, 0.74) | - | 0.54 (0.45, 0.66) |
| Medications | ||||
| Biguanide | 0.50 (0.29, 0.85) a | 0.99 (0.32, 3.05) ns | - | 0.37 (0.19, 0.71) b |
| Sulfonylurea | 0.66 (0.50, 0.89) b | 0.70 (0.48, 1.03) ns | 0.79 (0.30, 2.08) ns | 0.63 (0.37, 1.05) ns |
| Insulin | 0.59 (0.52, 0.67) | 0.64 (0.53, 0.78) | - | 0.51 (0.41, 0.64) |
| Comorbid conditions | ||||
| CVD | 0.66 (0.57, 0.77) | 0.71 (0.53, 0.94) a | - | 0.61 (0.50, 0.74) |
| Heart failure | 0.72 (0.61, 0.85) | 0.82 (0.63, 1.08) ns | - | 0.64 (0.51, 0.79) |
| Comorbidities-0 | 0.62 (0.54, 0.71) | 0.64 (0.53, 0.77) | 0.81 (0.62, 1.06) ns | 0.52 (0.38, 0.71) |
| Comorbidities-1 | 0.43 (0.28, 0.66) | 0.59 (0.31, 1.12) ns | - | 0.38 (0.20, 0.74) b |
| Comorbidities-2 | 0.71 (0.52, 0.95) a | 0.73 (0.48, 1.13) ns | - | 0.59 (0.37, 0.93) a |
| Comorbidities-3 | 0.68 (0.57, 0.81) | 0.82 (0.58, 1.15) ns | - | 0.63 (0.51, 0.79) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reule, S.; Pickthorn, S.; Worwa, S.; Ishani, A.; Foley, R. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Survival in Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetology 2025, 6, 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6120161
Reule S, Pickthorn S, Worwa S, Ishani A, Foley R. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Survival in Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetology. 2025; 6(12):161. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6120161
Chicago/Turabian StyleReule, Scott, Sean Pickthorn, Stefanie Worwa, Areef Ishani, and Robert Foley. 2025. "Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Survival in Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes" Diabetology 6, no. 12: 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6120161
APA StyleReule, S., Pickthorn, S., Worwa, S., Ishani, A., & Foley, R. (2025). Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Survival in Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetology, 6(12), 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6120161






