Application of NerveCheck Master in the Diagnosis of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Objective
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Population
3.2. Inclusion Criteria
- Prior diagnosis of diabetes mellitus
- Age over 18 years
3.3. Exclusion Criteria
- Previous or current foot ulceration
- Partial or complete foot amputation
- Ankle–Brachial Index (ABI) < 0.9 or >1.3
- Neuropathy attributable to causes other than diabetes mellitus
- Current or previous Charcot joint disease
- Non-palpable dorsalis pedis and posterior tibial pulses
- Impairment of psychological and cognitive capacity
3.4. Sample Selection
3.5. Data Collection
3.6. Ethical Considerations
4. Results
| Mean | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diabetes Mellitus Duration | 13.94 | 16.98 | 1 | 93 |
| HbA1c | 7.33 | 0.99 | 6 | 10 |
| Systolic Blood Pressure Left Arm | 136.28 | 11.99 | 120 | 160 |
| Systolic Blood Pressure Right Arm | 138.75 | 13.60 | 120 | 170 |
| Systolic Blood Pressure Left Ankle | 160.62 | 21.43 | 120 | 190 |
| Systolic Blood Pressure Right Ankle | 160.62 | 25.95 | 100 | 200 |
| Ankle-Brachial Index Left Arm | 1.20 | 0.11 | 1 | 1.46 |
| Ankle-Brachial Index Right Arm | 1.17 | 0.17 | 0.77 | 1.53 |
| Temperature Dorsum Left Foot | 29.85 | 3.29 | 22 | 28.12 |
| Temperature Dorsum Right Foot | 30.18 | 3.41 | 21.5 | 35.2 |
| Temperature Forefoot Left Foot | 29.13 | 2.83 | 25.3 | 35.3 |
| Temperature Forefoot Right Foot | 28.79 | 2.60 | 24.1 | 34.3 |
| Temperature Midfoot Left Foot | 28.32 | 2.04 | 25.3 | 33.2 |
| Temperature Midfoot Right Foot | 28.16 | 2.57 | 24.2 | 34.3 |
| Average Temperature Left Foot | 28.61 | 2.17 | 25.4 | 33.7 |
| Average Temperature Right Foot | 29.06 | 2.24 | 24.8 | 34 |
4.1. Analysis by Sex
4.2. Analysis by Age
4.3. Analysis by Body Mass Index
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Armstrong, D.G.; Tan, T.W.; Boulton, A.J.M.; Bus, S.A. Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Review. JAMA 2023, 330, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Hu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Luo, W.; Du, X.; Luo, Z.; Hu, J.; Peng, S. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: Pathogenetic mechanisms and treatment. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 14, 1265372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodman, M.A.; Dreyer, M.A.; Varacallo, M. Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Sloan, G.; Selvarajah, D.; Tesfaye, S. Pathogenesis, diagnosis and clinical management of diabetic sensorimotor peripheral neuropathy. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 400–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strand, N.; Anderson, M.A.; Attanti, S.; Gill, B.; Wie, C.; Dawodu, A.; Pagan-Rosado, R.; Harbell, M.W.; Maloney, J.A. Diabetic Neuropathy: Pathophysiology Review. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2024, 28, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novello, B.J.; Pobre, T. Electrodiagnostic Evaluation of Peripheral Neuropathy. 30 January 2023. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Padrós, C. Nuevo Método para el Diagnóstico Cuantitativo Sensitivo de Pacientes con Neuropatía Diabética. Trabajo Fin de Grado, Universidad de Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain, 2017; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Bonilla, E.; Planell, E.; Hidalgo, S.; Lázaro, J.L.; Martínez, L.; Mosquera, A. Exploración Podológica en Pacientes con Diabetes. In Guía de Protocolos del Pie Diabético, 1st ed.; Consejo General de Colegios Oficiales de Podólogos: Madrid, Spain, 2011; pp. 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Mohseni, S.; Badii, M.; Kylhammar, A.; Thomsen, N.O.B.; Eriksson, K.F.; Malik, R.A.; Rosén, I.; Dahlin, L.B. Longitudinal study of neuropathy, microangiopathy, and autophagy in sural nerve: Implications for diabetic neuropathy. Brain Behav. 2017, 7, e00763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponirakis, G.; Odriozola, M.N.; Odriozola, S.; Petropolus, I.N.; Azmi, S.; Fadavi, H.; Alam, U.; Asghar, O.; Marshall, A.; Miro, A.; et al. NerveCheck: An Inexpensive Quantitative Sensory Testing Device for Patients with Diabetic Neuropathy. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 113, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asociación Médica Mundial. Declaración de Helsinki de la Asamblea Médica Mundial: Principios Éticos para las Investi-gaciones Médicas en Seres Humanos; Enmienda Octubre 2013; Asociación Médica Mundial: Ferney-Voltaire, France, 2013; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- de España, G. Ley 14/2007, de investigación biomédica. Disposiciones generales. Boletín Oficial del Estado 2007, 159, 28826–28848. [Google Scholar]
- Consejo General de Colegios Oficiales de Podólogos. Código Deontológico de Podología; Consejo General de Colegios Oficiales de Podólogos: Madrid, Spain, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Dube, S.; Hulke, S.M.; Wakode, S.L.; Khadanga, S.; Thakare, A.E.; Bharshankar, R.N.; Pakhare, A. Effectiveness of Semmes Weinstein 10 gm monofilament in diabetic peripheral neuropathy taking nerve conduction and autonomic function study as reference tests. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2022, 11, 6204–6208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castelli, G.; Desai, K.M.; Cantone, R.E. Peripheral Neuropathy: Evaluation and Differential Diagnosis. Am. Fam. Physician 2020, 102, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perkins, B.A.; Olaleye, D.; Zinman, B.; Bril, V. Simple screening test for peripheral neuropathy in the diabetes Clinic. Diabetes Care 2001, 24, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chicharro, E. Elaboración de un Modelo Predictivo para la Identificación de Pacientes con Neuropatía Diabética. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Miguel Hernández, Alicante, Spain, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fealey, R.D. Thermoregulation in neuropathies. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 157, 777–787. [Google Scholar]
- Balbinot, L.F.; Robinson, C.C.; Achaval, M.; Zaro, M.A.; Brioschi, M.L. Repeatability of infrared plantar thermography in diabetes patients: A pilot study. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2013, 7, 1130–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papanas, N.; Papatheodorou, K.; Papazoglou, D.; Monastiriotis, C.; Maltezos, E. Foot temperature in type 2 diabetic patients with or without peripheral neuropathy. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2009, 117, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odriozola, A.; Ortega, L.; Martinez, L.; Odriozola, S.; Torrens, A.; Corroleu, D.; Martínez, S.; Ponce, M.; Meije, Y.; Presas, M.; et al. Widespread sensory neuropathy in diabetic patients hospitalized with severe COVID-19 infection. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 172, 108631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponirakis, G.; Odriozola, A.; Ortega, L.; Martinez, L.; Odriozola, S.; Torrens, A.; Coroleu, D.; Martínez, S.; Sanz, X.; Ponce, M.; et al. Quantitative sensory testing defines the trajectory of sensory neuropathy after severe COVID-19. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2024, 207, 111029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
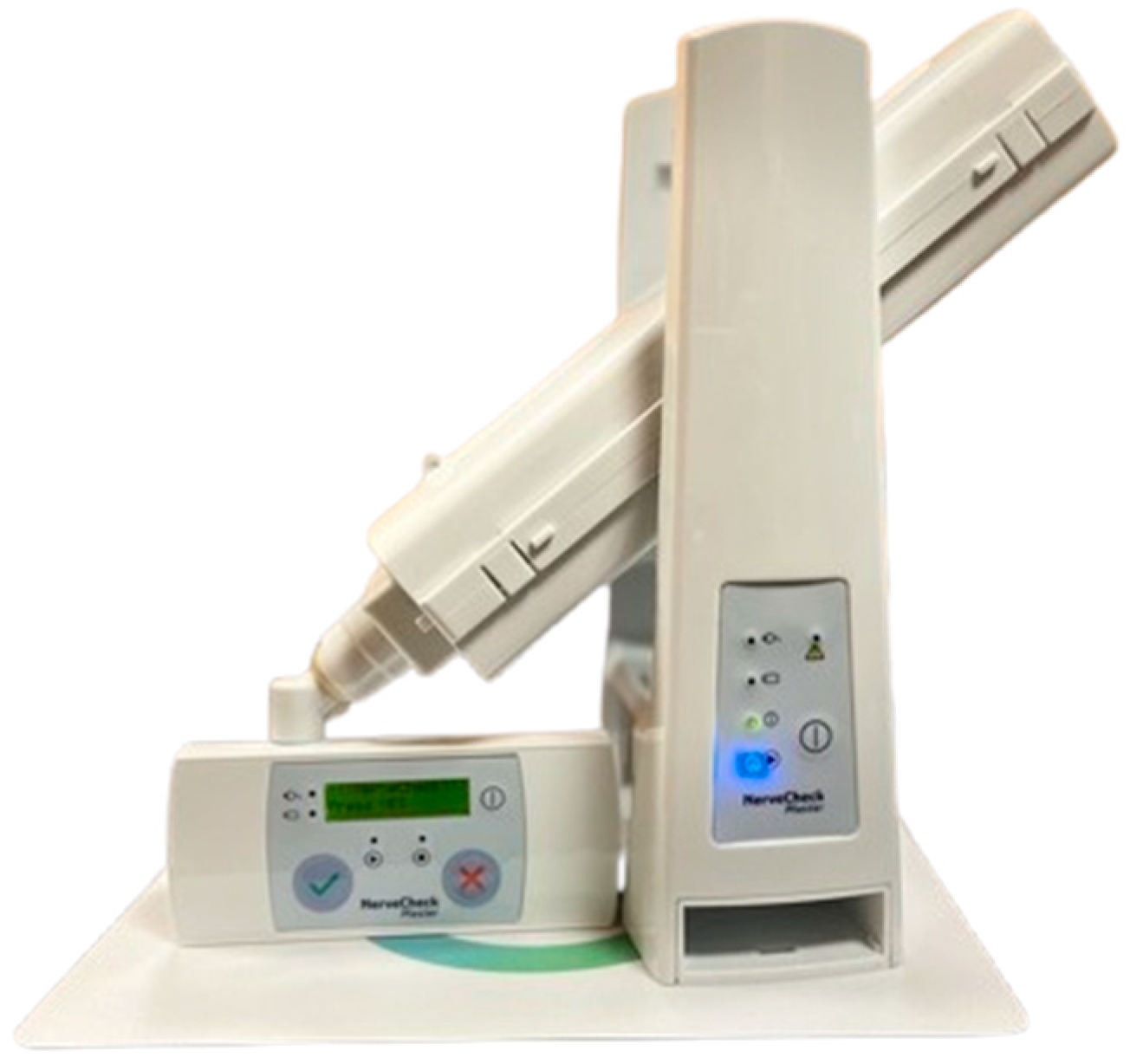
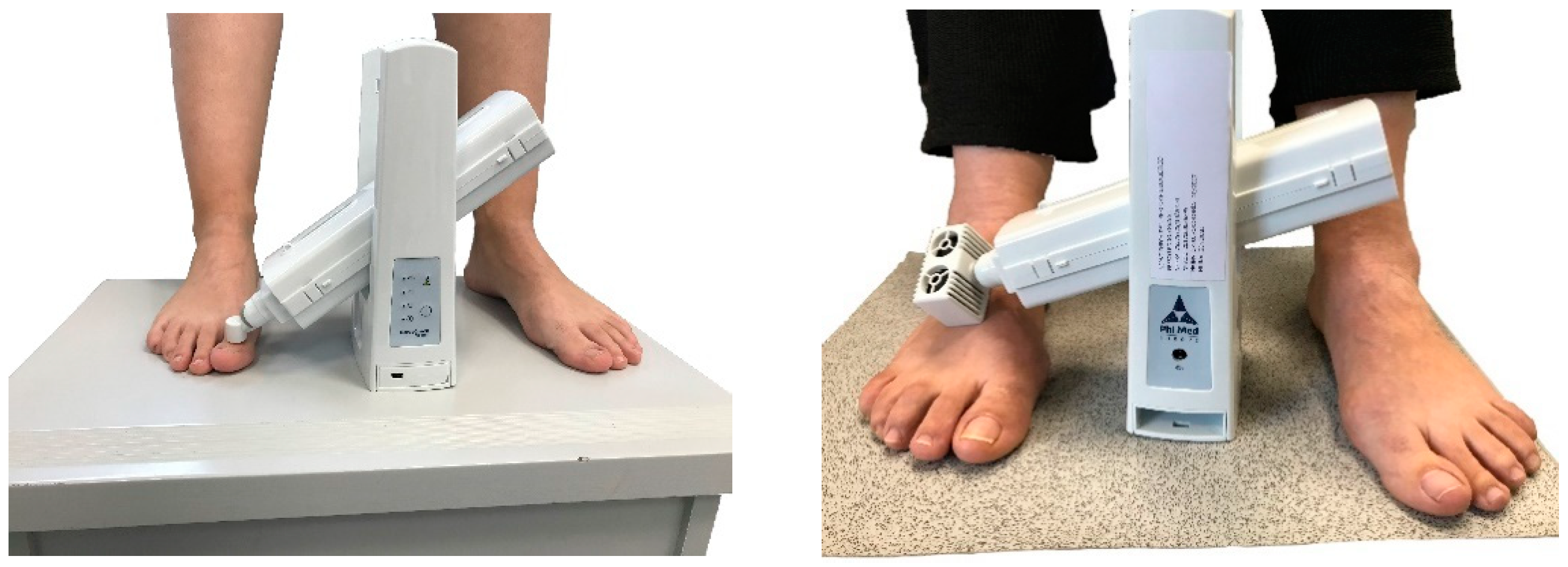
| Minimum Left Foot | Maximum Left Foot | Minimum Right Foot | Maximum Right Foot | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dorsum | 22 | 33.3 | 21.5 | 35.2 |
| Forefoot | 25.3 | 35.3 | 24.1 | 34.3 |
| Midfoot | 25.3 | 33.2 | 24.2 | 33.6 |
| MINIMUM | MAXIMUM | STANDARD DEVIATION | MEAN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 51 | 79 | 9.301 | 68.88 |
| Weight | 60 | 110 | 15.005 | 81.10 |
| Height | 1.54 | 1.87 | 0.098 | 1.65 |
| BMI | 22.80 | 45.20 | 5.576 | 29.91 |
| Diapason | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | Abnormal | ||||
| N | % | N | % | ||
| NerveCheck | Normal | 10 | 90.9 | 2 | 40.0 |
| Abnormal | 1 | 9.1 | 3 | 60.0 | |
| Woman | Man | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | p-Valor | |
| Normal | 4 | 57.1 | 6 | 100.0 | 0.122 |
| Abnormal | 3 | 42.9 | 0 | 0.0 | |
| Midfoot Temperature | N | MEAN | SD | p-Valor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Woman | 7 | 29.17 | 3.19 | 0.217 |
| Man | 6 | 27.18 | 2.05 |
| Age | N | MEAN | SD | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 10 | 70.10 | 9.21 | 0.161 |
| Abnormal | 3 | 62.67 | 8.15 |
| Body Mass Index | ||
|---|---|---|
| Midfoot Temperature of the Right Foot | Pearson Correlation | 0.249 |
| Sig. (two-tailed) | 0.412 | |
| N | 13 | |
| Midfoot Temperature | N | MEAN | SD | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 10 | 27.39 | 2.25 | 0.036 |
| Abnormal | 3 | 31.13 | 2.90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García de la Peña, R.; Ortiz Romero, M.; Juárez Jiménez, J.M.; Rayo Pérez, A.M. Application of NerveCheck Master in the Diagnosis of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. Diabetology 2025, 6, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6010003
García de la Peña R, Ortiz Romero M, Juárez Jiménez JM, Rayo Pérez AM. Application of NerveCheck Master in the Diagnosis of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. Diabetology. 2025; 6(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía de la Peña, Raquel, Mercedes Ortiz Romero, José María Juárez Jiménez, and Ana María Rayo Pérez. 2025. "Application of NerveCheck Master in the Diagnosis of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy" Diabetology 6, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6010003
APA StyleGarcía de la Peña, R., Ortiz Romero, M., Juárez Jiménez, J. M., & Rayo Pérez, A. M. (2025). Application of NerveCheck Master in the Diagnosis of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. Diabetology, 6(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6010003







