Defining the miRnome of Saphenous Vein Smooth Muscle Cells from Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation and Culture of Primary Human SV-SMC
2.2. Preparation of RNA for miRNA Array
2.3. miRNA Array
2.4. Identification of Differentially Expressed miRNAs
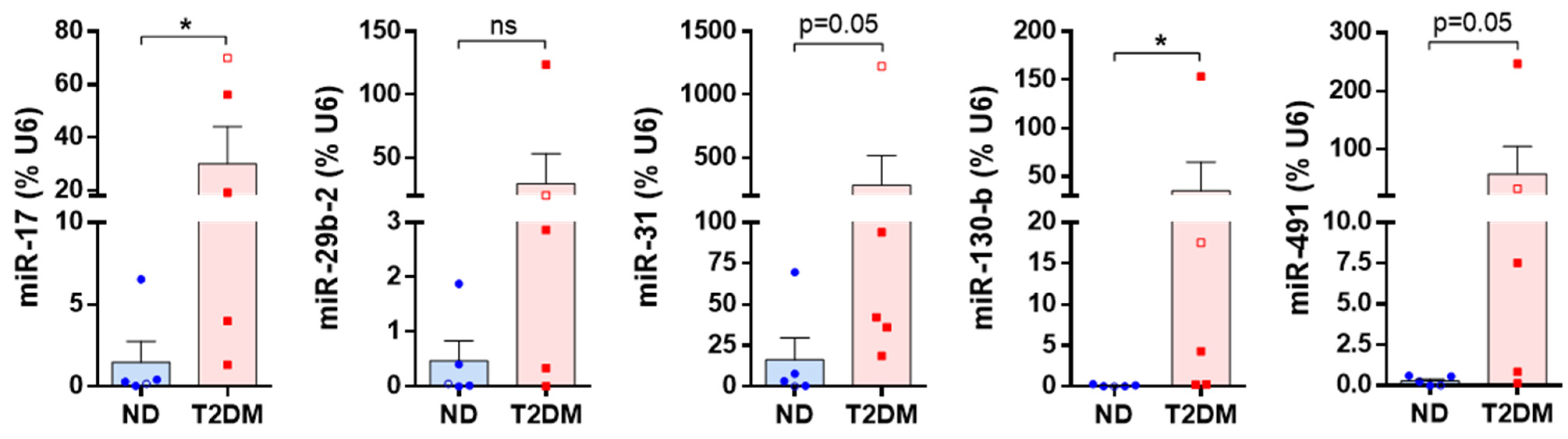
2.5. Validation of miRNA Array Targets
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
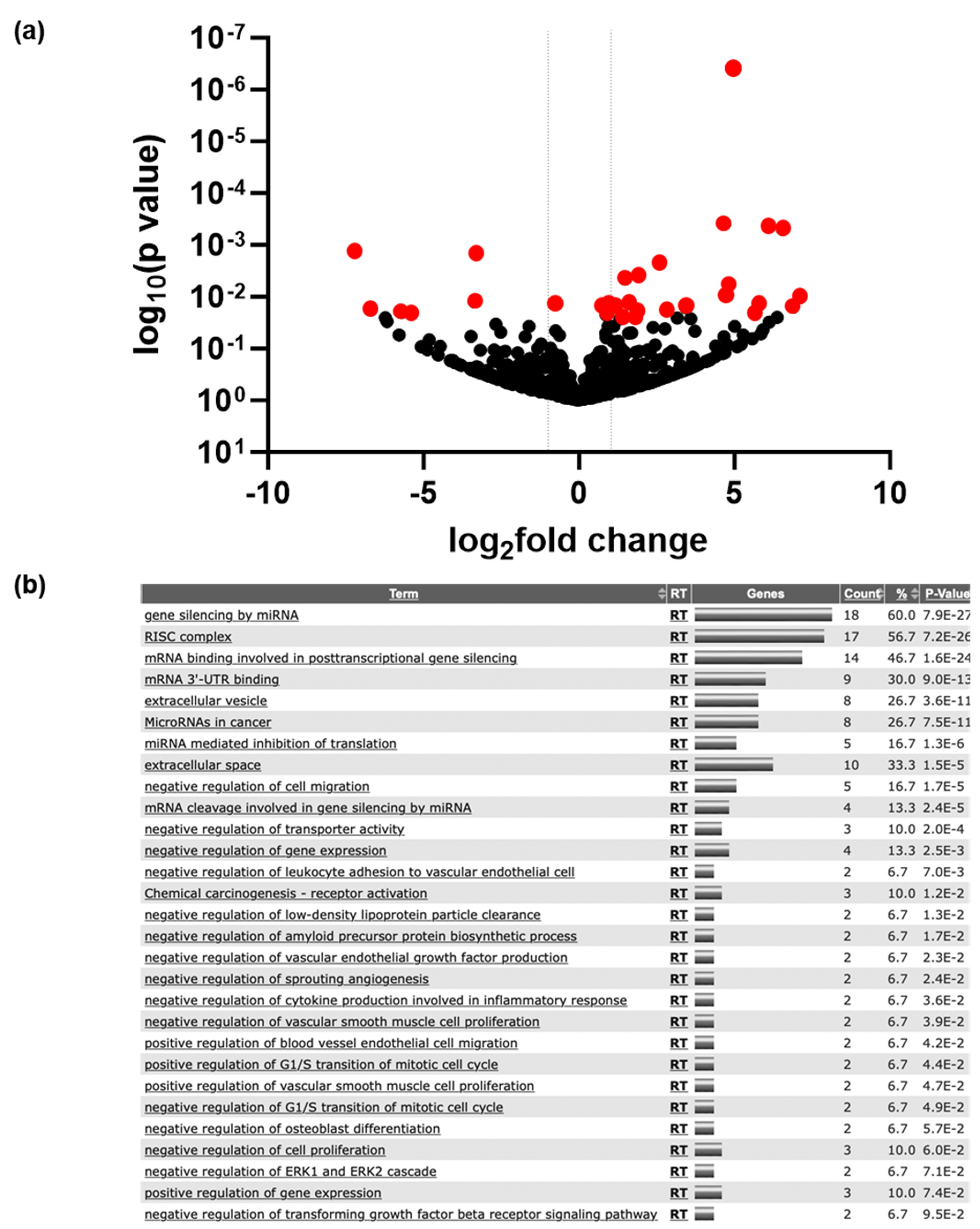
3.1. Initial Identification of Differentially Expressed miRNAs
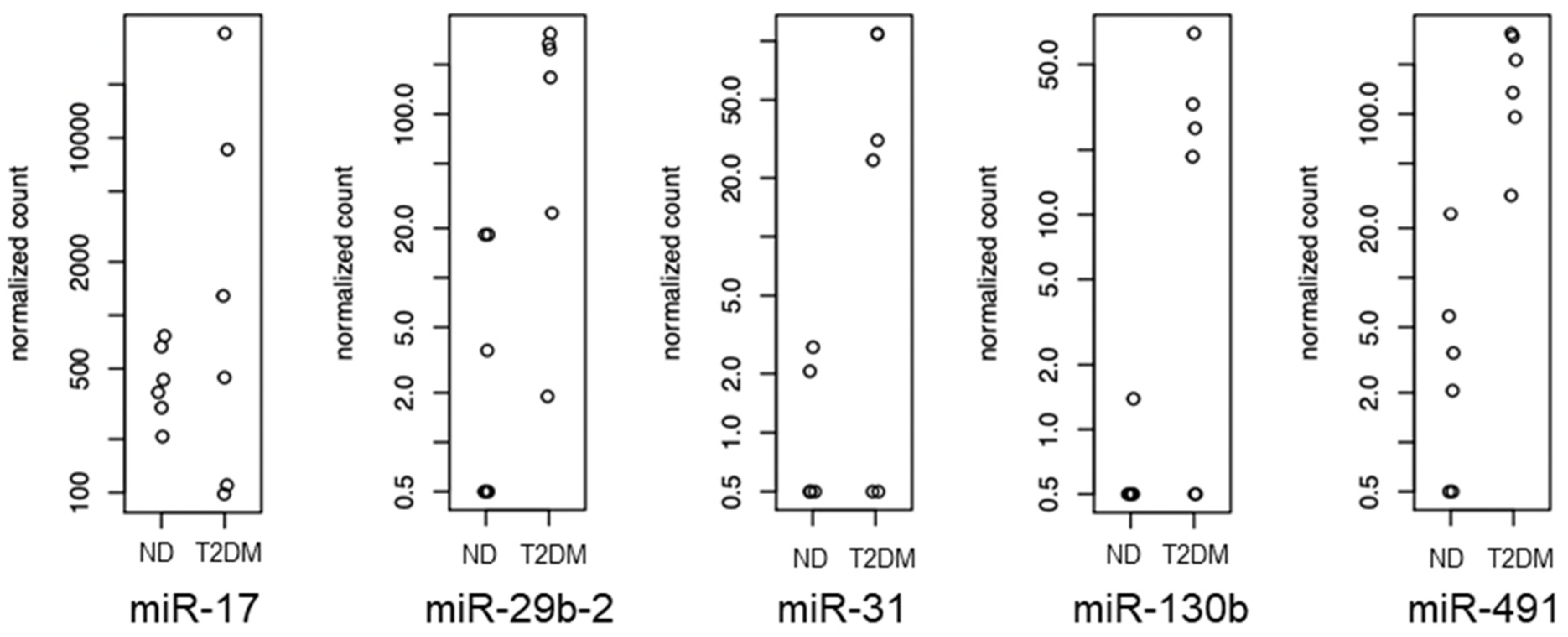
3.2. Differentially Expressed miRNAs
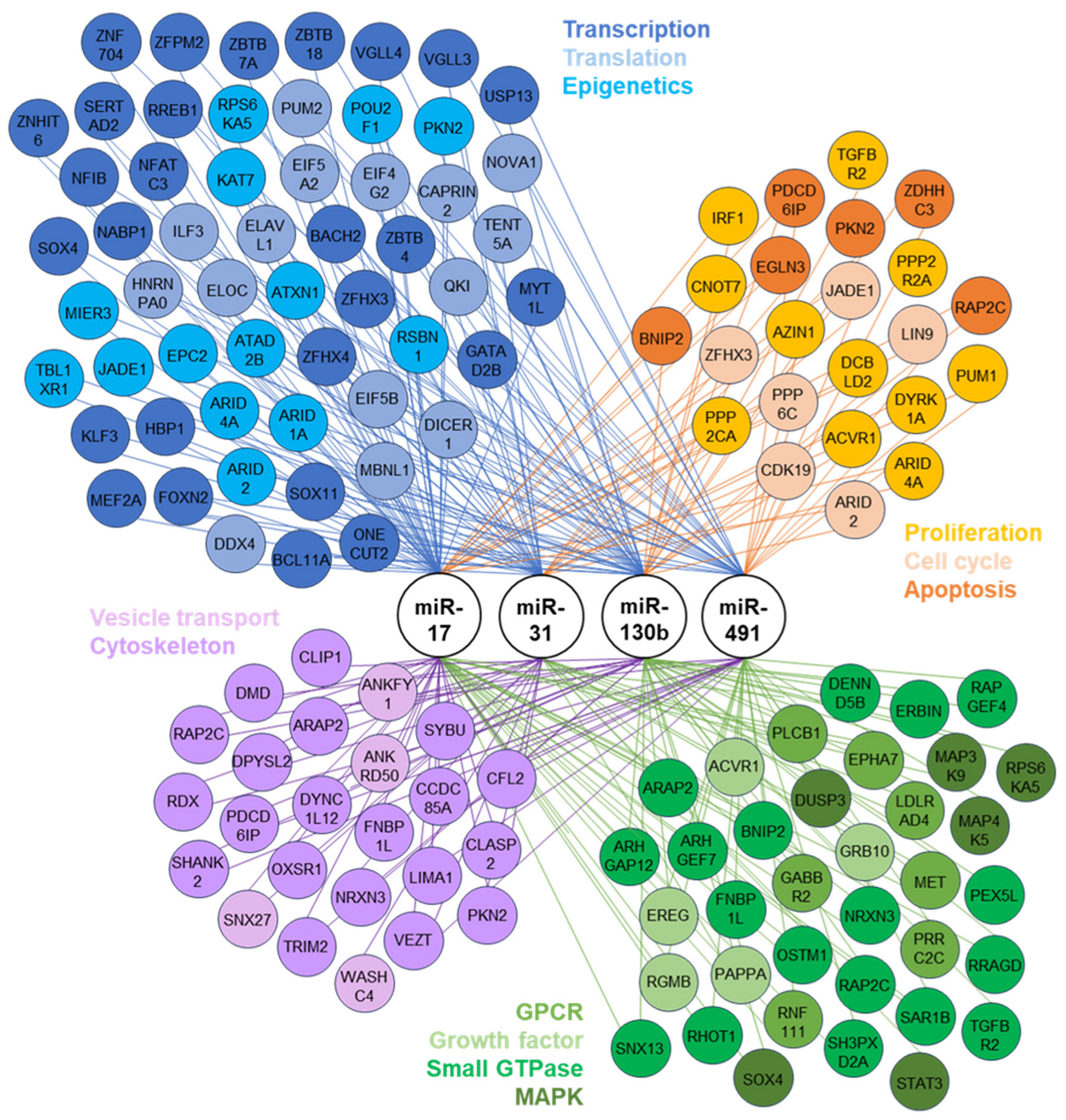
3.3. Identification of Potential Functional Outcomes of Differentially Expressed miRNAs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iacobucci, G. One in 10 UK adults could have diabetes by 2030, warns charity. Bmj 2021, 375, n2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.A.B.; Hashim, M.J.; King, J.K.; Govender, R.D.; Mustafa, H.; Al Kaabi, J. Epidemiology of Type 2 Diabetes—Global Burden of Disease and Forecasted Trends. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2020, 10, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caliskan, E.; de Souza, D.R.; Böning, A.; Liakopoulos, O.J.; Choi, Y.H.; Pepper, J.; Gibson, C.M.; Perrault, L.P.; Wolf, R.K.; Kim, K.B.; et al. Saphenous vein grafts in contemporary coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolanle, I.O.; Riches-Suman, K.; Loubani, M.; Williamson, R.; Palmer, T.M. Revascularisation of type 2 diabetics with coronary artery disease: Insights and therapeutic targeting of O-GlcNAcylation. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 31, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riches-Suman, K.; Hussain, A. Identifying and targeting the molecular signature of smooth muscle cells undergoing early vascular ageing. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2022, 1868, 166403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadey, K.; Lopes, J.; Bendeck, M.; George, S. Role of smooth muscle cells in coronary artery bypass grafting failure. Cardiovasc. Res. 2018, 114, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madi, H.A.; Riches, K.; Warburton, P.; O’Regan, D.J.; Turner, N.A.; Porter, K.E. Inherent differences in morphology, proliferation, and migration in saphenous vein smooth muscle cells cultured from nondiabetic and Type 2 diabetic patients. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2009, 297, C1307-1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riches, K.; Alshanwani, A.R.; Warburton, P.; O’Regan, D.J.; Ball, S.G.; Wood, I.C.; Turner, N.A.; Porter, K.E. Elevated expression levels of miR-143/5 in saphenous vein smooth muscle cells from patients with Type 2 diabetes drive persistent changes in phenotype and function. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2014, 74, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riches, K.; Warburton, P.; O’Regan, D.J.; Turner, N.A.; Porter, K.E. Type 2 diabetes impairs venous, but not arterial smooth muscle cell function: Possible role of differential RhoA activity. Cardiovasc. Revasc Med. 2014, 15, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmings, K.E.; Riches-Suman, K.; Bailey, M.A.; O’Regan, D.J.; Turner, N.A.; Porter, K.E. Role of MicroRNA-145 in DNA Damage Signalling and Senescence in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells of Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Cells 2021, 10, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riches-Suman, K. Diverse roles of microRNA-145 in regulating smooth muscle (dys)function in health and disease. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2021, 49, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laggerbauer, B.; Engelhardt, S. MicroRNAs as therapeutic targets in cardiovascular disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zytnicki, M. mmquant: How to count multi-mapping reads? BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang da, W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang da, W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Bioinformatics enrichment tools: Paths toward the comprehensive functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitão, A.L.; Costa, M.C.; Enguita, F.J. A guide for miRNA target prediction and analysis using web-based applications. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1182, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Deng, P.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H. MiR-17 Knockdown Promotes Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypic Modulation Through Upregulated Interferon Regulator Factor 9 Expression. Am. J. Hypertens. 2020, 33, 1119–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, K.G.; Ruhle, B.; Stein, J.J.; Gentile, K.L.; Middleton, F.A.; Gahtan, V. Thrombospondin-1 differentially regulates microRNAs in vascular smooth muscle cells. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2016, 412, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Wei, W.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Lu, L.; Lv, X.; Xue, X. Proliferation of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells under ox-LDL Is Regulated by Alismatis rhizoma Decoction via InhibitingERK1/2 and miR-17∼92a Cluster Activation. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 7275246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; He, F.; Liang, B.; Jing, Y.; Zhang, P.; Liu, W.; Zhao, H. p53-Dependent LincRNA-p21 Protects Against Proliferation and Anti-apoptosis of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells in Atherosclerosis by Upregulating SIRT7 via MicroRNA-17-5p. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2021, 14, 426–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Sun, C.; Zhang, J.; Lin, S.; Zhao, L.; Wang, L.; Lin, R.; Lv, J.; Xin, S. Proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells under inflammation is regulated by NF-κB p65/microRNA-17/RB pathway activation. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Wang, T.; Kuang, S.; Zhao, G.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, H. A microRNA-17-5p/homeobox B13 axis participates in the phenotypic modulation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 24, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushing, L.; Costinean, S.; Xu, W.; Jiang, Z.; Madden, L.; Kuang, P.; Huang, J.; Weisman, A.; Hata, A.; Croce, C.M.; et al. Disruption of miR-29 Leads to Aberrant Differentiation of Smooth Muscle Cells Selectively Associated with Distal Lung Vasculature. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Ren, S.; Hao, X.; Zhen, Z.; Ji, L.; Ji, H. MicroRNA-29b inhibits human vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation via targeting the TGF-β/Smad3 signaling pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 21, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, J.; Lv, M.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, A.; Wu, Z. MiR-29b Downregulation Induces Phenotypic Modulation of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells: Implication for Intracranial Aneurysm Formation and Progression to Rupture. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 41, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Chen, Z.; Wu, W.; Wang, M.; Wang, R.; Cui, J.; Li, W.; Wang, S. MicroRNA-31 promotes arterial smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration by targeting mitofusin-2 in arteriosclerosis obliterans of the lower extremitie. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, X.; Yang, J.; Xu, L.; Zhang, C. MicroRNA-31 regulated by the extracellular regulated kinase is involved in vascular smooth muscle cell growth via large tumor suppressor homolog 2. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 42371–42380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yan, C.H.; Li, Y.; Xu, K.; Tian, X.X.; Peng, C.F.; Tao, J.; Sun, M.Y.; Han, Y.L. MicroRNA-31 controls phenotypic modulation of human vascular smooth muscle cells by regulating its target gene cellular repressor of E1A-stimulated genes. Exp. Cell Res. 2013, 319, 1165–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Ren, J.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Xue, L.; Cui, S.; Sang, W.; Xu, T.; Zhang, J.; Yu, J.; et al. Prevention of aortic dissection and aneurysm via an ALDH2-mediated switch in vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 2442–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Wu, N.; Yan, Y.; Wu, L.L.; Zhu, G.Q.; Xiong, X.Q. Angiotensin II-induced miR-31-5p upregulation promotes vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration. Exp. Cell Res. 2022, 419, 113303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Hu, J.; Xu, J.; Wang, H.; Dai, L. microRNA-130b May Induce Cerebral Vasospasm after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage via Modulating Kruppel-like Factor 4. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 43, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Yu, N.; Jang, Y.E.; Lee, E.; Jung, Y.; Lee, D.J.; Taylor, W.R.; Jo, H.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.; et al. Conserved miR-370-3p/BMP-7 axis regulates the phenotypic change of human vascular smooth muscle cells. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Pan, Q.; Qian, L.; Hu, C. Differentially expressed mRNAs and their upstream miR-491-5p in patients with coronary atherosclerosis as well as the function of miR-491-5p in vascular smooth muscle cells. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2022, 26, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Wang, Y.; He, Q.; Chen, M. microRNA-491-5p protects against atherosclerosis by targeting matrix metallopeptidase-9. Open Med. 2020, 15, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Camargo, L.L.; Beatie, W.; Mcbride, M.; Montezano, A.C.; Touyz, R.M. MicroRNA profile in human vascular smooth muscle cells from hypertensive subjects: Focus on oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress. J. Hypertens. 2021, 39, e249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miska, E.A.; Alvarez-Saavedra, E.; Townsend, M.; Yoshii, A.; Sestan, N.; Rakic, P.; Constantine-Paton, M.; Horvitz, H.R. Microarray analysis of microRNA expression in the developing mammalian brain. Genome Biol. 2004, 5, R68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, T.; Liu, Z.; Han, Z.; Ge, Q. MicroRNA Detection Specificity: Recent Advances and Future Perspective. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 3179–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, S.; Xia, Y.; Wu, K. MiR-31 Regulates Rho-Associated Kinase-Myosin Light Chain (ROCK-MLC) Pathway and Inhibits Gastric Cancer Invasion: Roles of RhoA. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 4679–4691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, J.; Cao, W.; Song, C.; Lei, S.; Li, Y.; Ren, Z. Long noncoding RNA LINC00857 promotes pancreatic cancer proliferation and metastasis by regulating the miR-130b/RHOA axis. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danielson, L.S.; Guijarro, M.V.; Menendez, S.; Higgins, B.; Sun, Q.; Mittal, K.; Popiolek, D.A.; Overholtzer, M.; Palmer, G.D.; Hernando, E. MiR-130b modulates the invasive, migratory, and metastatic behavior of leiomyosarcoma. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0278844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Medication Class | ND Donors | T2DM Donors |
|---|---|---|
| ACE inhibitors | 3/5 | 3/5 |
| Beta blockers | 3/5 | 3/5 |
| Diuretics | 1/5 | 2/5 |
| Nitrates | 3/5 | 1/5 |
| Statins | 4/5 | 3/5 |
| miRNA | Fold difference in T2DM SV-SMC vs. ND SV-SMC | p Value | Supporting References |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR-17 | ↑ 1.9 | 0.003747 | [19,20,21,22,23,24] |
| miR-29b-2 | ↑ 4.7 | 0.000386 | [25,26,27] |
| miR-31 | ↑ 2.6 | 0.002209 | [28,29,30,31,32] |
| miR-130b | ↑ 1.5 | 0.000452 | [20,33,34] |
| miR-491 | ↑ 5.0 | 0.000382 | [35,36,37] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hussain, A.; Asare-Amankwah, Y.; Qureshi, S.; Thornton, M.J.; Palmer, T.M.; Bolanle, I.O.; Wood, I.C.; Turner, N.A.; Porter, K.E.; Tedder, A.; et al. Defining the miRnome of Saphenous Vein Smooth Muscle Cells from Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetology 2024, 5, 178-189. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology5020014
Hussain A, Asare-Amankwah Y, Qureshi S, Thornton MJ, Palmer TM, Bolanle IO, Wood IC, Turner NA, Porter KE, Tedder A, et al. Defining the miRnome of Saphenous Vein Smooth Muscle Cells from Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetology. 2024; 5(2):178-189. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology5020014
Chicago/Turabian StyleHussain, Alisah, Yaw Asare-Amankwah, Shehryar Qureshi, M. Julie Thornton, Timothy M. Palmer, Israel O. Bolanle, Ian C. Wood, Neil A. Turner, Karen E. Porter, Andrew Tedder, and et al. 2024. "Defining the miRnome of Saphenous Vein Smooth Muscle Cells from Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus" Diabetology 5, no. 2: 178-189. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology5020014
APA StyleHussain, A., Asare-Amankwah, Y., Qureshi, S., Thornton, M. J., Palmer, T. M., Bolanle, I. O., Wood, I. C., Turner, N. A., Porter, K. E., Tedder, A., & Riches-Suman, K. (2024). Defining the miRnome of Saphenous Vein Smooth Muscle Cells from Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetology, 5(2), 178-189. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology5020014











