An Evaluation of Point-of-Care HbA1c, HbA1c Home Kits, and Glucose Management Indicator: Potential Solutions for Telehealth Glycemic Assessments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials & Methods
3. Statistical Analysis
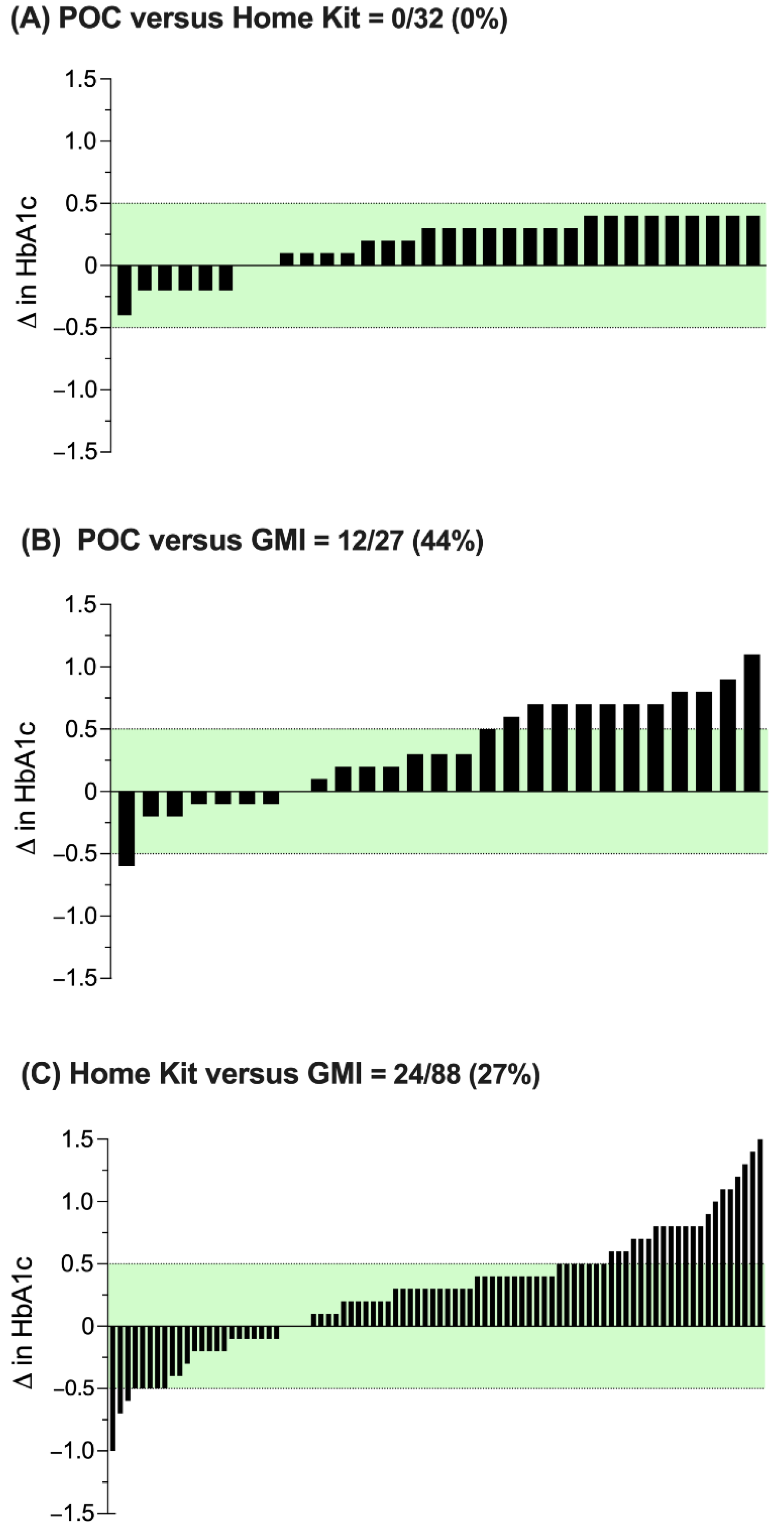
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Diabetes Association. 6. Glycemic Targets: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44 (Suppl. S1), S73–S84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitley, H.P.; Yong, E.V.; Rasinen, C. Selecting an A1C Point-of-Care Instrument. Diabetes Spectr. 2015, 28, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battelino, T.; Danne, T.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Amiel, S.A.; Beck, R.; Biester, T.; Bosi, E.; Buckingham, B.A.; Cefalu, W.T.; Close, K.L.; et al. Clinical Targets for Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data Interpretation: Recommendations from the International Consensus on Time in Range. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1593–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 6. Glycemic Targets: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2022. Diabetes Care 2022, 45 (Suppl. S1), S83–S96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, R.W.; Bocchino, L.E.; Lum, J.W.; Kollman, C.; Barnes-Lomen, V.; Sulik, M.; Haller, M.J.; Bode, B.; Cernich, J.T.; Killeen, A.A.; et al. An Evaluation of Two Capillary Sample Collection Kits for Laboratory Measurement of HbA1c. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2021, 23, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergenstal, R.M.; Beck, R.W.; Close, K.L.; Grunberger, G.; Sacks, D.B.; Kowalski, A.; Brown, A.S.; Heinemann, L.; Aleppo, G.; Ryan, D.B.; et al. Glucose Management Indicator (GMI): A New Term for Estimating A1C From Continuous Glucose Monitoring. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 2275–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prahalad, P.; Zaharieva, D.P.; Addala, A.; New, C.; Scheinker, D.; Desai, M.; Hood, K.K.; Maahs, D.M. Improving Clinical Outcomes in Newly Diagnosed Pediatric Type 1 Diabetes: Teamwork, Targets, Technology, and Tight Control—The 4T Study. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prahalad, P.; Ding, V.Y.; Zaharieva, D.P.; Addala, A.; Johari, R.; Scheinker, D.; Desai, M.; Hood, K.; Maahs, D.M. Teamwork, Targets, Technology, and Tight Control in Newly Diagnosed Type 1 Diabetes: Pilot 4T Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 107, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanenbaum, M.; Zaharieva, D.P.; Addala, A.; Hooper, J.; Leverenz, B.; Cortes, A.; Arrizon-Ruiz, N.; Pang, E.; Bishop, F.; Maahs, D. Initiating CGM over telehealth is well accepted by parents of newly diagnosed youth with T1D. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2022, 24 (Suppl. 1), A157. [Google Scholar]
- Ferstad, J.O.; Vallon, J.J.; Jun, D.; Gu, A.; Vitko, A.; Morales, D.P.; Leverenz, J.; Lee, M.Y.; Leverenz, B.; Vasilakis, C.; et al. Population-level management of type 1 diabetes via continuous glucose monitoring and algorithm-enabled patient prioritization: Precision health meets population health. Pediatr. Diabetes 2021, 22, 982–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheinker, D.; Gu, A.; Grossman, J.; Ward, A.; Ayerdi, O.; Miller, D.; Leverenz, J.; Hood, K.; Lee, M.Y.; Maahs, D.M.; et al. Algorithm-Enabled, Personalized Glucose Management for Type 1 Diabetes at the Population Scale: Prospective Evaluation in Clinical Practice. JMIR Diabetes 2022, 7, e27284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prahalad, P.; Addala, A.; Scheinker, D.; Hood, K.K.; Maahs, D.M. CGM Initiation Soon After Type 1 Diabetes Diagnosis Results in Sustained CGM Use and Wear Time. Diabetes Care 2019, 43, e3–e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addala, A.; Zaharieva, D.P.; Gu, A.J.; Prahalad, P.; Scheinker, D.; Buckingham, B.; Hood, K.K.; Maahs, D.M. Clinically serious hypoglycemia is rare and not associated with time-in-range in youth with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes. JCEM 2021, 106, 3239–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, J.; Ward, A.; Crandell, J.L.; Prahalad, P.; Maahs, D.M.; Scheinker, D. Improved individual and population-level HbA1c estimation using CGM data and patient characteristics. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2021, 35, 107950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharieva, D.P.; Bishop, F.; Maahs, D.M. Advancements and Future Directions in the Teamwork, Targets, Technology, and Tight Control—The 4T Study: Improving Clinical Outcomes in Newly Diagnosed Pediatric Type 1 Diabetes. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2022, 34, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanenbaum, M.L.; Zaharieva, D.P.; Addala, A.; Ngo, J.; Prahalad, P.; Leverenz, B.; New, C.; Maahs, D.M.; Hood, K.K. ‘I was ready for it at the beginning’: Parent experiences with early introduction of continuous glucose monitoring following their child’s Type 1 diabetes diagnosis. Diabet. Med. 2021, 38, e14567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Grimsmann, J.M.; Karges, B.; Hofer, S.E.; Danne, T.; Holl, R.W.; Ajjan, R.A.; Dunn, T.C. Personal Glycation Factors and Calculated Hemoglobin A1c for Diabetes Management: Real-World Data from the Diabetes Prospective Follow-up (DPV) Registry. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2021, 23, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrzanowski, J.; Michalak, A.; Łosiewicz, M.A.; Kuśmierczyk, M.H.; Mianowska, M.B.; Szadkowska, M.A.; Fendler, W. Improved Estimation of Glycated Hemoglobin from Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Past Glycated Hemoglobin Data. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2021, 23, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabris, C.; Heinemann, L.; Beck, R.; Cobelli, C.; Kovatchev, B. Estimation of Hemoglobin A1c from Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data in Individuals with Type 1 Diabetes: Is Time In Range All We Need? Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2020, 22, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danne, T.; Nimri, R.; Battelino, T.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Close, K.L.; DeVries, J.H.; Garg, S.; Heinemann, L.; Hirsch, I.; Amiel, S.A.; et al. International Consensus on Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 1631–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Demographics | Mean ± SD Median [IQR] |
|---|---|
| Age, years | 9.7 ± 4.6 10 [6–14] |
| Sex Male Female | 29 (41%) 42 (59%) |
| Race/Ethnicity Non-Hispanic White Non-Hispanic Black Hispanic Asian/Pacific Islander Other Unknown | 34 (48%) 0 (0%) 7 (10%) 10 (14%) 2 (3%) 18 (25%) |
| Body Mass Index (BMI) | 18.6 ± 6.1 17 [15–21] |
| Insurance Type Private Public | 55 (77%) 16 (23%) |
| HbA1c at Diagnosis (%) | 12.5 ± 2.2 |
| HbA1c Home Kit (%) | 6.9 ± 1.2 |
| Months Since Diagnosis | 8.6 ± 5.1 8 [4–12] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaharieva, D.P.; Addala, A.; Prahalad, P.; Leverenz, B.; Arrizon-Ruiz, N.; Ding, V.Y.; Desai, M.; Karger, A.B.; Maahs, D.M. An Evaluation of Point-of-Care HbA1c, HbA1c Home Kits, and Glucose Management Indicator: Potential Solutions for Telehealth Glycemic Assessments. Diabetology 2022, 3, 494-501. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology3030037
Zaharieva DP, Addala A, Prahalad P, Leverenz B, Arrizon-Ruiz N, Ding VY, Desai M, Karger AB, Maahs DM. An Evaluation of Point-of-Care HbA1c, HbA1c Home Kits, and Glucose Management Indicator: Potential Solutions for Telehealth Glycemic Assessments. Diabetology. 2022; 3(3):494-501. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology3030037
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaharieva, Dessi P., Ananta Addala, Priya Prahalad, Brianna Leverenz, Nora Arrizon-Ruiz, Victoria Y. Ding, Manisha Desai, Amy B. Karger, and David M. Maahs. 2022. "An Evaluation of Point-of-Care HbA1c, HbA1c Home Kits, and Glucose Management Indicator: Potential Solutions for Telehealth Glycemic Assessments" Diabetology 3, no. 3: 494-501. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology3030037
APA StyleZaharieva, D. P., Addala, A., Prahalad, P., Leverenz, B., Arrizon-Ruiz, N., Ding, V. Y., Desai, M., Karger, A. B., & Maahs, D. M. (2022). An Evaluation of Point-of-Care HbA1c, HbA1c Home Kits, and Glucose Management Indicator: Potential Solutions for Telehealth Glycemic Assessments. Diabetology, 3(3), 494-501. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology3030037






