Detection of Gene Doping Using Dried Blood Spots from a Mouse Model with rAAV9 Vector-Mediated Human Erythropoietin Expression as a Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
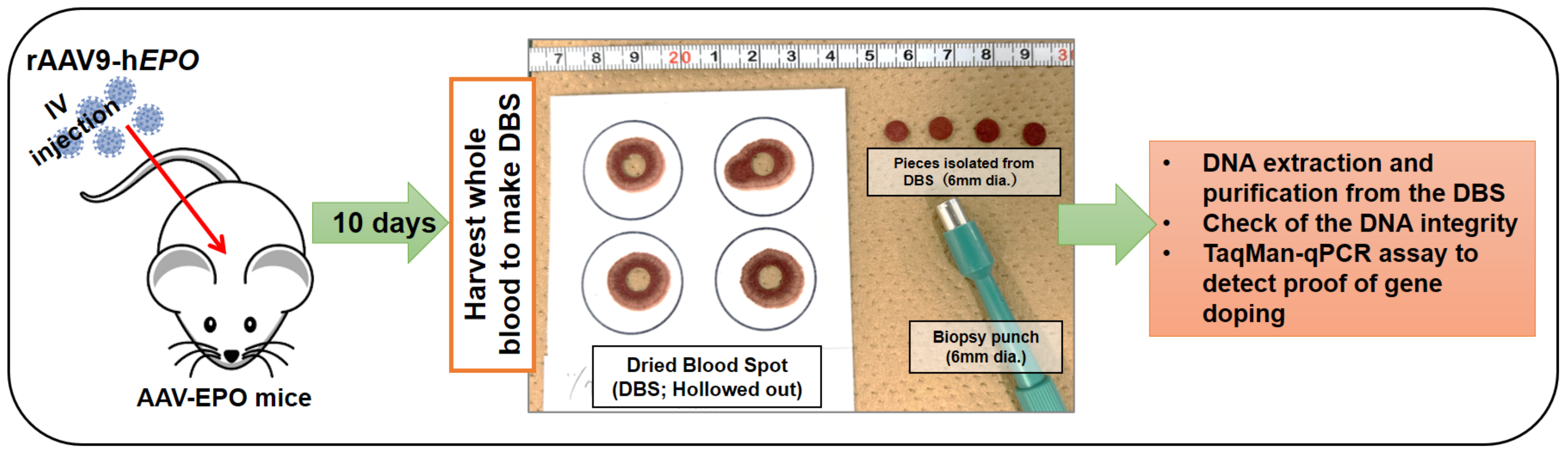
2.1. Graphical Presentation of Experimental Methods
2.2. Creation of the rAAV9-hEPO Vector
2.3. Generation of the Gene Doping Mouse Model
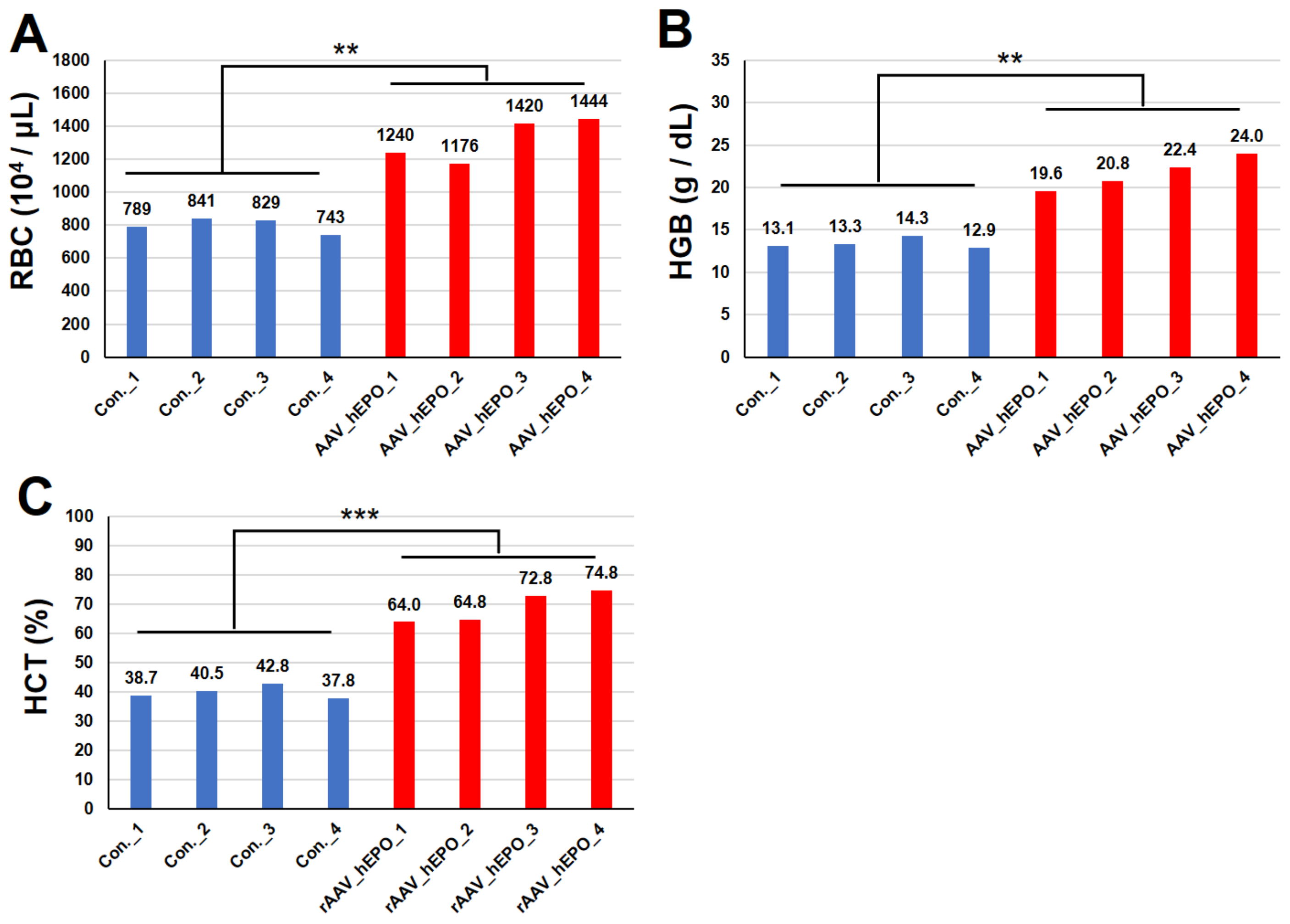
2.4. Assessment of General Hematopoietic Parameters
2.5. Creation of DBSs
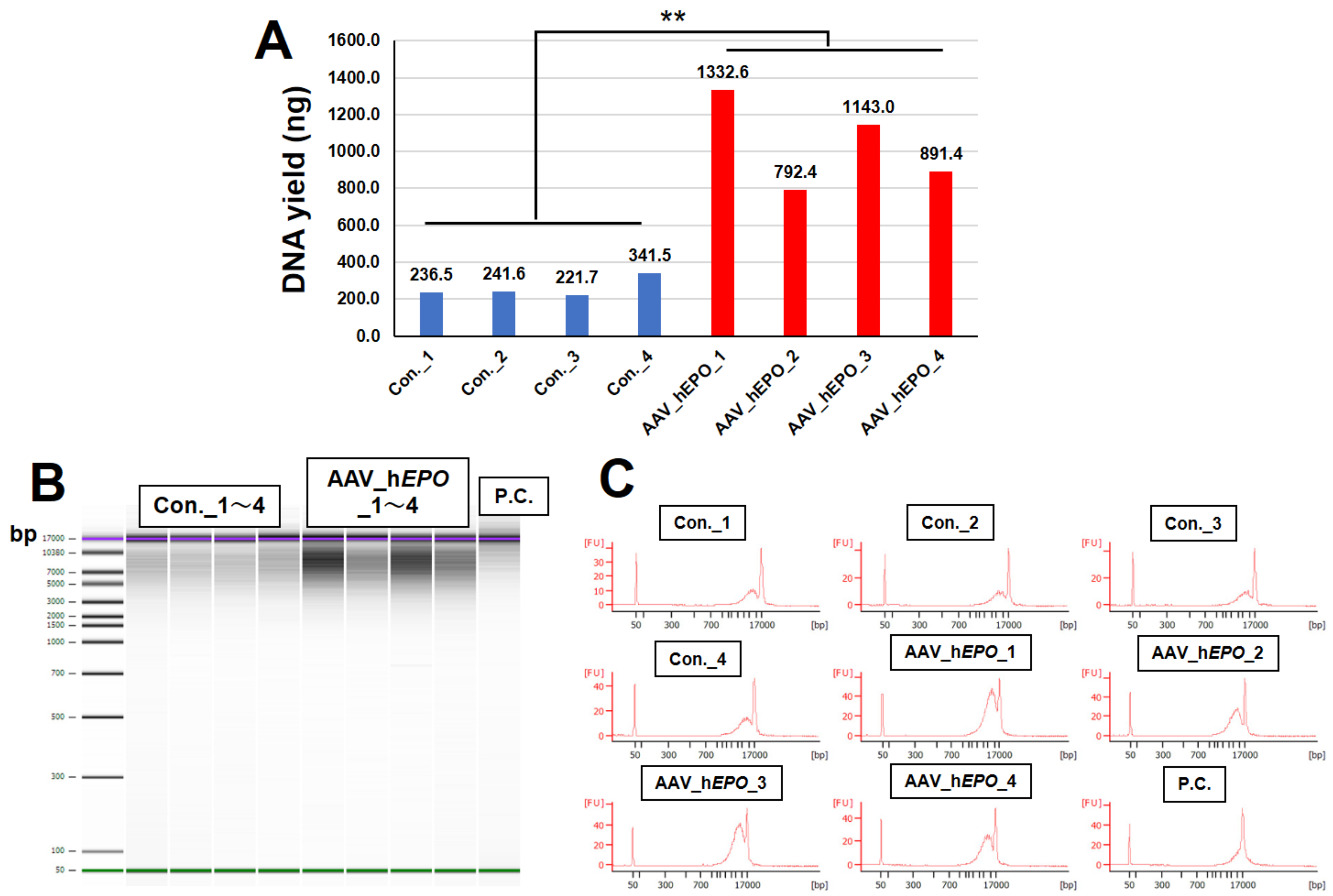
2.6. DNA Isolation from the DBSs
2.7. Analysis of DNA Integrity
2.8. Taqman Quantitative PCR Assay
2.9. Sanger Sequencing Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Hematopoietic Parameters Increased after the rAAV Injection
3.2. Confirmation of DNA Yield and Fragmentation after Purification
3.3. Direct Proof of Gene Doping was Detected in the DBS-Derived DNA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Center for Biologics Evaluation; Research ZOLGENSMA. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/zolgensma (accessed on 5 April 2024).
- Novartis Pharma; DR’s Net; ZOLGENSMA. Available online: https://www.drs-net.novartis.co.jp/dr/products/product/zolgensma/document (accessed on 5 April 2024).
- The World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA). The World Anti-Doping Code International Standard Prohibited List 2024; WADA: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Sugasawa, T.; Nakano, T.; Fujita, S.-I.; Matsumoto, Y.; Ishihara, G.; Aoki, K.; Yanazawa, K.; Ono, S.; Tamai, S.; Manevich, L.; et al. Proof of Gene Doping in a Mouse Model with a Human Erythropoietin Gene Transferred Using an Adenoviral Vector. Genes 2021, 12, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugasawa, T.; Aoki, K.; Yanazawa, K.; Takekoshi, K. Detection of Multiple Transgene Fragments in a Mouse Model of Gene Doping Based on Plasmid Vector Using TaqMan-qPCR Assay. Genes 2020, 11, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, K.; Sugasawa, T.; Yanazawa, K.; Watanabe, K.; Takemasa, T.; Takeuchi, Y.; Aita, Y.; Yahagi, N.; Yoshida, Y.; Kuji, T.; et al. The Detection of Trans Gene Fragments of hEPO in Gene Doping Model Mice by Taqman qPCR Assay. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugasawa, T.; Aoki, K.; Watanabe, K.; Yanazawa, K.; Natsume, T.; Takemasa, T.; Yamaguchi, K.; Takeuchi, Y.; Aita, Y.; Yahagi, N.; et al. Detection of Transgenes in Gene Delivery Model Mice by Adenoviral Vector Using ddPCR. Genes 2019, 10, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levernæs, M.C.S.; Solheim, S.A.; Broderstad, L.; Zandy, E.; Mørkeberg, J.; Dehnes, Y. Detection of Doping Substances in Paired Dried Blood Spots and Urine Samples Collected during Doping Controls in Danish Fitness Centers. Drug Test. Anal. 2024; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donati, F.; Concetti, L.; de la Torre, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, L.; Botrè, F. Detection of Exon 5 c.577del Variant of Human Erythropoietin Gene in Whole Blood, Dried Blood Spots and Urine Samples for Doping Control. Front. Anal. Sci. 2023, 3, 1202074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, T.; Barquín, D.; Ndarabu, A.; Fernández-Alonso, M.; Rubio-Garrido, M.; Carlos, S.; Makonda, B.; Holguín, Á.; Reina, G. HCV Diagnosis and Sequencing Using Dried Blood Spots from Patients in Kinshasa (DRC): A Tool to Achieve WHO 2030 Targets. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandane Tak, M.; Vaidyanathan, A.; Mukherjee, A. Revolutionizing HIV-1 Viral Load Monitoring in India: The Potential of Dried Blood Spot Analysis for Expanding Access and Improving Care. Healthcare 2024, 12, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doornekamp, L.; Embregts, C.W.E.; Aron, G.I.; Goeijenbier, S.; van de Vijver, D.A.M.C.; van Gorp, E.C.M.; GeurtsvanKessel, C.H. Dried Blood Spot Cards: A Reliable Sampling Method to Detect Human Antibodies against Rabies Virus. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Primer Designing Tool. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/tools/primer-blast/ (accessed on 10 April 2024).
- Homo Sapiens Erythropoietin (EPO), mRNA—Nucleotide—NCBI. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/NM_000799.4 (accessed on 8 April 2024).
- Dried Blood Spot (DBS) Testing & the Potential for the ABP, Matthew Fedoruk, 16th Annual USADA Symposium on Anti-Doping Science. Available online: https://www.wada-ama.org/sites/default/files/54_fedoruk_day_3_distribution.pdf (accessed on 10 April 2024).
- Blicharz, T.M.; Gong, P.; Bunner, B.M.; Chu, L.L.; Leonard, K.M.; Wakefield, J.A.; Williams, R.E.; Dadgar, M.; Tagliabue, C.A.; El Khaja, R.; et al. Microneedle-Based Device for the One-Step Painless Collection of Capillary Blood Samples. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 2, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dried Blood Spots (DBS) in Sports Drug Testing: Complementary Matrix Providing Unique Features and Utilities to Modern Anti-Doping Fights. Available online: https://www.wada-ama.org/en/resources/scientific-research/dried-blood-spots-dbs-sports-drug-testing-complementary-matrix (accessed on 10 April 2024).
- Garzinsky, A.-M.; Thomas, A.; Guddat, S.; Görgens, C.; Dib, J.; Thevis, M. Dried blood spots for doping controls—Development of a comprehensive initial testing procedure with fully automated sample preparation. Chromatography 2023, 37, e5633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okano, M.; Miyamoto, A.; Ota, M.; Kageyama, S.; Sato, M. Doping Control Analysis of Trimetazidine in Dried Blood Spot. Drug Test. Anal. 2022; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, A.; Geyer, H.; Schänzer, W.; Crone, C.; Kellmann, M.; Moehring, T.; Thevis, M. Sensitive Determination of Prohibited Drugs in Dried Blood Spots (DBS) for Doping Controls by Means of a Benchtop Quadrupole/Orbitrap Mass Spectrometer. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 1279–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naumann, N.; Walpurgis, K.; Rubio, A.; Thomas, A.; Paßreiter, A.; Thevis, M. Detection of Doping Control Sample Substitutions via Single Nucleotide Polymorphism-based ID Typing. Drug Test. Anal. 2023, 15, 1521–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leuenberger, N.; Jan, N.; Kuuranne, T.; Castella, V. Characterization of DNA Concentration in Urine and Dried Blood Samples to Detect the c.577 Deletion within the EPO Gene. Drug Test. Anal. 2024; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchand, A.; Roulland, I.; Semence, F.; Ericsson, M. EPO Transgene Detection in Dried Blood Spots for Antidoping Application. Drug Test. Anal. 2021, 13, 1888–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiland, C.E.; Martin, L.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, L.; Ericsson, M.; Marchand, A. Dried Blood Spots for Erythropoietin Analysis: Detection of Micro-doses, EPO c.577del Variant and Comparison with In-competition Matching Urine Samples. Drug Test. Anal. 2023; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loria, F.; Stutz, A.P.; Rocca, A.; Grabherr, S.; Kuuranne, T.; Pruijm, M.; Leuenberger, N. Monitoring of Hemoglobin and Erythropoiesis-Related mRNA with Dried Blood Spots in Athletes and Patients. Bioanalysis 2022, 14, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yachie, N.; Robotic Biology Consortium; Natsume, T. Robotic Crowd Biology with Maholo LabDroids. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 310–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bierer, R.; Roohi, M.; Peceny, C.; Ohls, R.K. Erythropoietin Increases Reticulocyte Counts and Maintains Hematocrit in Neonates Requiring Surgery. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2009, 44, 1540–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, S.; Pham, E.; Macdougall, I.C. Erythropoietins: A Common Mechanism of Action. Exp. Hematol. 2008, 36, 1573–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundby, C.; Thomsen, J.J.; Boushel, R.; Koskolou, M.; Warberg, J.; Calbet, J.A.L.; Robach, P. Erythropoietin Treatment Elevates Haemoglobin Concentration by Increasing Red Cell Volume and Depressing Plasma Volume. J. Physiol. 2007, 578, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens-Hernandez, C.J.; Flatt, J.F.; Kupzig, S.; Bruce, L.J. Reticulocyte Maturation and Variant Red Blood Cells. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 834463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Target | Sequences | Predicted Amplicon Size (bp) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| hEPO | Forward | CATCTGTGACAGCCGAGTCC | 290 |
| Probe | 56-FAM/TG AGA ATA T/ZEN/C ACT GTC CCA GAC ACC/3IABkFQ | ||
| Reverse | AGGCCACTGACGGCTTTATC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Otani, N.; Kanki, Y.; Nguyen, K.D.M.; Sugasawa, T. Detection of Gene Doping Using Dried Blood Spots from a Mouse Model with rAAV9 Vector-Mediated Human Erythropoietin Expression as a Pilot Study. Analytica 2024, 5, 263-272. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica5020017
Otani N, Kanki Y, Nguyen KDM, Sugasawa T. Detection of Gene Doping Using Dried Blood Spots from a Mouse Model with rAAV9 Vector-Mediated Human Erythropoietin Expression as a Pilot Study. Analytica. 2024; 5(2):263-272. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica5020017
Chicago/Turabian StyleOtani, Norihiro, Yasuharu Kanki, Kieu D. M. Nguyen, and Takehito Sugasawa. 2024. "Detection of Gene Doping Using Dried Blood Spots from a Mouse Model with rAAV9 Vector-Mediated Human Erythropoietin Expression as a Pilot Study" Analytica 5, no. 2: 263-272. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica5020017
APA StyleOtani, N., Kanki, Y., Nguyen, K. D. M., & Sugasawa, T. (2024). Detection of Gene Doping Using Dried Blood Spots from a Mouse Model with rAAV9 Vector-Mediated Human Erythropoietin Expression as a Pilot Study. Analytica, 5(2), 263-272. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica5020017








