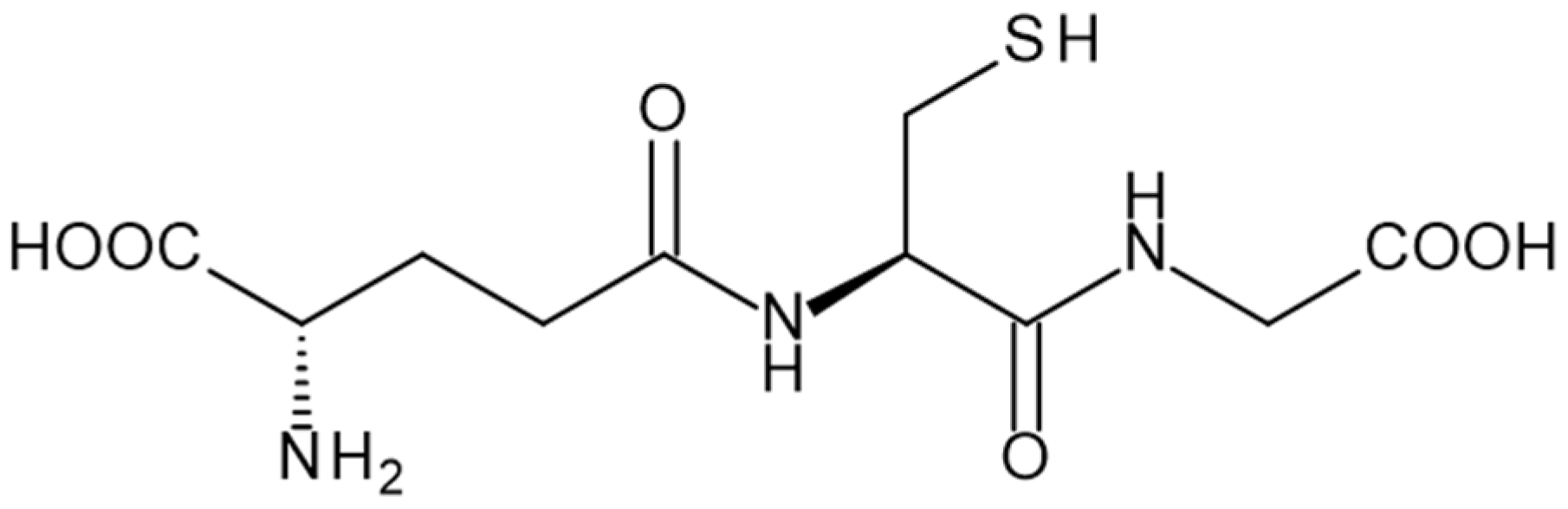
General Applicability of High-Resolution Continuum-Source Graphite Furnace Molecular Absorption Spectrometry to the Quantification of Oligopeptides Using the Example of Glutathione
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Instrumentation
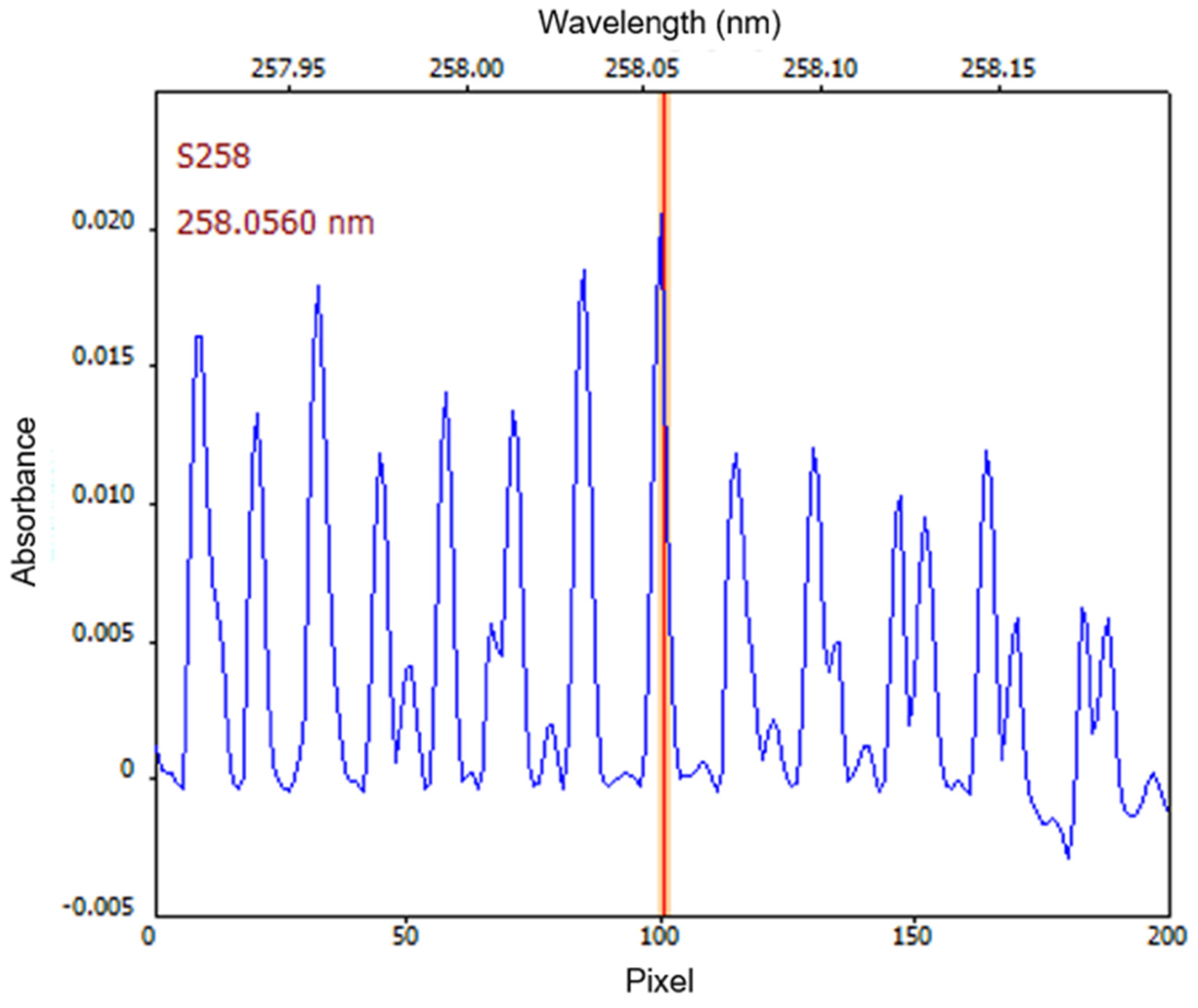
2.3. HR CS MAS Procedure
3. Results
3.1. Selection of the Diatomic Molecule
3.2. Optimization of the Pyrolysis/Vaporization Temperatures Considering Modifiers
3.3. Calibration and Figures of Merit
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAS | Atomic absorption spectrometry |
| CE | Capillary electrophoresis |
| CS | Carbon monosulfide |
| Cys | L-Cysteine |
| GF | Graphite furnace |
| Glu | L-Glutaminic acid |
| Gly | Glycin |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| GSSG | Glutathione disulfide |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| HR CS MAS | High-resolution continuum-source MAS |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| LOQ | Limit of quantification |
| MAS | Molecular absorption spectrometry |
| RSD | Relative standard deviation |
| SD | Standard deviation |
References
- Kent, S.B.H. The critical role of peptide chemistry in the life sciences. J. Pept. Sci. 2015, 21, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orenius, S.; Moldeus, P. The multiple roles of glutathione in drug metabolism. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1984, 5, 432–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deponte, M. Glutathione catalysis and the reaction mechanisms of glutathione-dependent enzymes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Gen. Subj. 2013, 1830, 3217–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Yue, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, W.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, Q.; Huang, C.; Sheng, J.; Song, X. Simultaneous detection of glutathione and hydrogen polysulfides from different emission channels. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 12984–12991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Fang, Y.-Z.; Yang, S.; Lupton, J.R.; Turner, N.D. Glutathione metabolism and its implications for health. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Townsend, D.M.; Tew, K.D.; Tapiero, H. The importance of glutathione in human disease. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2003, 57, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yoon, J. Fluorescent and colorimetric probes for detection of thiols. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 2120–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamad, A.; Elshahawy, M.; Negm, A.; Mansour, F.R. Analytical methods for determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfide in pharmaceuticals and biological fluids. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2019, 38, 20190019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Li, C.; Shen, S.; Liu, X.; Peng, Y.; Zheng, J. Mass spectrometry based detection of glutathione with sensitivity for single-cell analysis. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 29, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuragi, M.; Zushi, T.; Seguchi, R.; Arai, T.; Taguchi, K.; Kusakabe, K. Locational analysis of glutathione in liposomes by using small-angle X-ray scattering. Chem. Lett. 2017, 46, 185–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camera, E.; Picardo, M. Analytical methods to investigate glutathione and related compounds in biological and pathological processes. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2002, 781, 181–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitmann, U.; Becker-Ross, H.; Florek, S.; Huang, M.D.; Okruss, M. Determination of non-metals via molecular absorption using high-resolution continuum source absorption spectrometry and graphite furnace atomization. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2006, 21, 1314–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbek, N.; Baysal, A. Determination of sulfur by high-resolution continuum source atomic absorption spectrometry: Review of studies over the last 10 years. Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 88, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, H.S.; Lepri, F.G.; Welz, B.; Carasek, E.; Huang, M.-D. Determination of sulfur in biological samples using high-resolution molecular absorption spectrometry in a graphite furnace with direct solid sampling. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2010, 25, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welz, B.; Lepri, F.G.; Araujo, R.G.O.; Ferreira, S.L.C.; Huang, M.-D.; Okruss, M.; Becker-Ross, H. Determination of phosphorus, sulfur and the halogens using high-temperature molecular absorption spectrometry in flames and furnaces—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 647, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resano, M.; Florez, M.R. Direct determination of sulfur in solid samples by means of high-resolution continuum source graphite furnace molecular absorption spectrometry using palladium nanoparticles as chemical modifier. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2012, 27, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mior, R.; Mores, S.; Welz, B.; Carasek, E.; de Andrade, J.B. Determination of sulfur in coal using direct solid sampling and high-resolution continuum source molecular absorption spectrometry of the CS molecule in a graphite furnace. Talanta 2013, 106, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camera, A.S.; Arcenio, P.P.; de Oliveira, W.; Filho, P.; de Andrade Maranhao, T.; de Oliveira, F.J.S.; Frescura, V.L.A. Method development and validation for sulfur determination via CS molecule in petroleum green coke by high resolution continuum source molecular absorption spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2017, 134, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, A.A.; Pereira, E.R.; Carasek, E.; Welz, B. The use of Ca + Pd + Zr as modifiers in the determination of sulfur by HR-CS GF MAS with solid sampling. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2019, 34, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignataro, M.F.; Herrera, M.G.; Dodero, V.I. Evaluation of peptide/protein self-assembly and aggregation by spectroscopic methods. Molecules 2020, 25, 4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggeri, F.S.; Mannini, B.; Schmid, R.; Vendruscolo, M.; Knowles, T.P.J. Single molecule secondary structure determination of proteins through infrared absorption nanospectroscopy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz-Fonfria, V.A. Infrared difference spectroscopy of proteins: From bands to bonds. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 3466–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, E.H.; Pisonero, J.; Smith, C.M.M.; Taylor, R.N. Atomic spectrometry update: Review of advances in atomic spectrometry and related techniques. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2021, 36, 868–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad, C.; Florek, S.; Becker-Ross, H.; Huang, M.-D.; Buzanich, A.G.; Radtke, M.; Lippitz, A.; Hodoroaba, V.-D.; Schmid, T.; Heinrich, H.-J.; et al. Zirconium permanent modifiers for graphite furnaces used in absorption spectrometry: Understanding their structure and mechanism of action. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2018, 33, 2034–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.D.; Becker-Ross, H.; Florek, S.; Abad, C.; Okruss, M. Investigation of high-resolution absorption spectra of diatomic sulfides of group 14 elements in graphite furnace and the comparison of their performance for sulfur determination. Spectrochim. Acta B 2017, 135, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.D.; Becker-Ross, H.; Florek, S.; Heitmann, U.; Okruss, M. Direct determination of total sulfur in wine using a continuum-source atomic-absorption spectrometer and an air-acetylene flame. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 382, 1877–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalewska, Z. Feasibility of high-resolution continuum source molecular absorption spectrometry in flame and furnace for sulphur determination in petroleum products. Spectrochim. Acta B 2011, 66, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbek, N.; Akam, S. Determination of total sulfur in food samples by solid sampling high-resolution continuum source graphite furnace molecular absorption spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 4816–4821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbek, N.; Baysal, A. A new approach for the determination of sulphur in food samples by high-resolution continuum source flame atomic absorption spectrometer. Food Chem. 2015, 168, 460–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozbek, N.; Baysal, A. Determination of sulfur in human hair using high resolution continuum source graphite furnace molecular absorption spectrometry and its correlation with total protein and albumin. Spectrochim. Acta B 2017, 130, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welz, B.; Sperling, M. Atomabsorptionsspektrometrie, 4th ed.; Wiley-VHS: Weinheim, Germany, 1997; pp. 393–394. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, E.R.; Welz, B.; Vieira, A.A. A systematic look at the carbon monosulfide molecule and chemical modifiers for the determination of sulfur by HR-CS GF MAS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2018, 33, 1394–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fick, S.S.; Nakadi, F.V.; Fujiwara, F.; Smichowski, P.; Vale, M.G.R.; Welz, B.; de Andrade, J.B. Investigation of spectral interference in the determination of Pb in road dust using high-resolution continuum source graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry and direct solid sample analysis. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2018, 33, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, T.; Yashima, Y.; Ahmadi, E.; Natsui, S.; Suzuki, R.O. Synthesis of Sc sulfides by CS2 sulfurization. J. Solid State Chem. 2020, 285, 121268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanazi, A.M.; Mostafa, G.A.E.; Al-Badr, A.A. Profiles of Drug Substances, Excipients and Related Methodology, 40th ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 43–158. [Google Scholar]
- Ortner, H.M.; Bulska, E.; Rohr, U.; Schlemmer, G.; Weinbruch, S.; Welz, B. Modifiers and coatings in graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry—mechanisms of action (a tutorial review). J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2002, 57, 1835–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlemmer, G.; Welz, B. Palladium and magnesium nitrates, a more universal modifier for graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 1986, 41, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunduz, S.; Akman, S. Determination of sulphur in various vegetables by solid sampling high-resolution electrothermal molecular absorption spectrometry. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, C.S.; Vale, M.G.R.; Welz, B.; Andrade, J.B.; Dessuy, M.B. Investigation of chemical modifiers for sulfur determination in diesel fuel samples by high-resolution continuum source graphite furnace molecular absorption spectrometry using direct analysis. Spectrochim. Acta B 2015, 108, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Passos, A.S.; Dessuy, M.B.; Nakadi, F.V.; de Andrade, J.B.; Vale, M.G.R. Investigation of different chemical modifiers based on the Pd/Mg mixture for the determination of sulfur in shale oil by high-resolution continuum source graphite furnace molecular absorption spectrometry. Talanta 2019, 204, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resano, M.; Garcia-Ruiz, E.; Aramendi, M.; Belarra, M.A. Quo vadis high-resolution continuum source atomic/molecular absorption spectrometry? J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2019, 34, 59–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Curno, R.; Magee, E.A.; Edmond, L.M.; Cummings, J.H. Studies of a urinary biomarker of dietary inorganic sulphur in subjects on diets containing 1–38 mmol sulphur/day and of the half-life of ingested 34SO42−. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 62, 1106–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baecker, D.; Obermoser, V.; Kirchner, E.A.; Hupfauf, A.; Kircher, B.; Gust, R. Fluorination as tool to improve bioanalytical sensitivity and COX-2-selective antitumor activity of cobalt alkyne complexes. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 15856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moschner, J.; Stulberg, F.; Fernandes, R.; Huhmann, S.; Leppkes, J.; Koksch, B. Approaches to obtaining fluorinated α-amino acids. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 10718–10801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
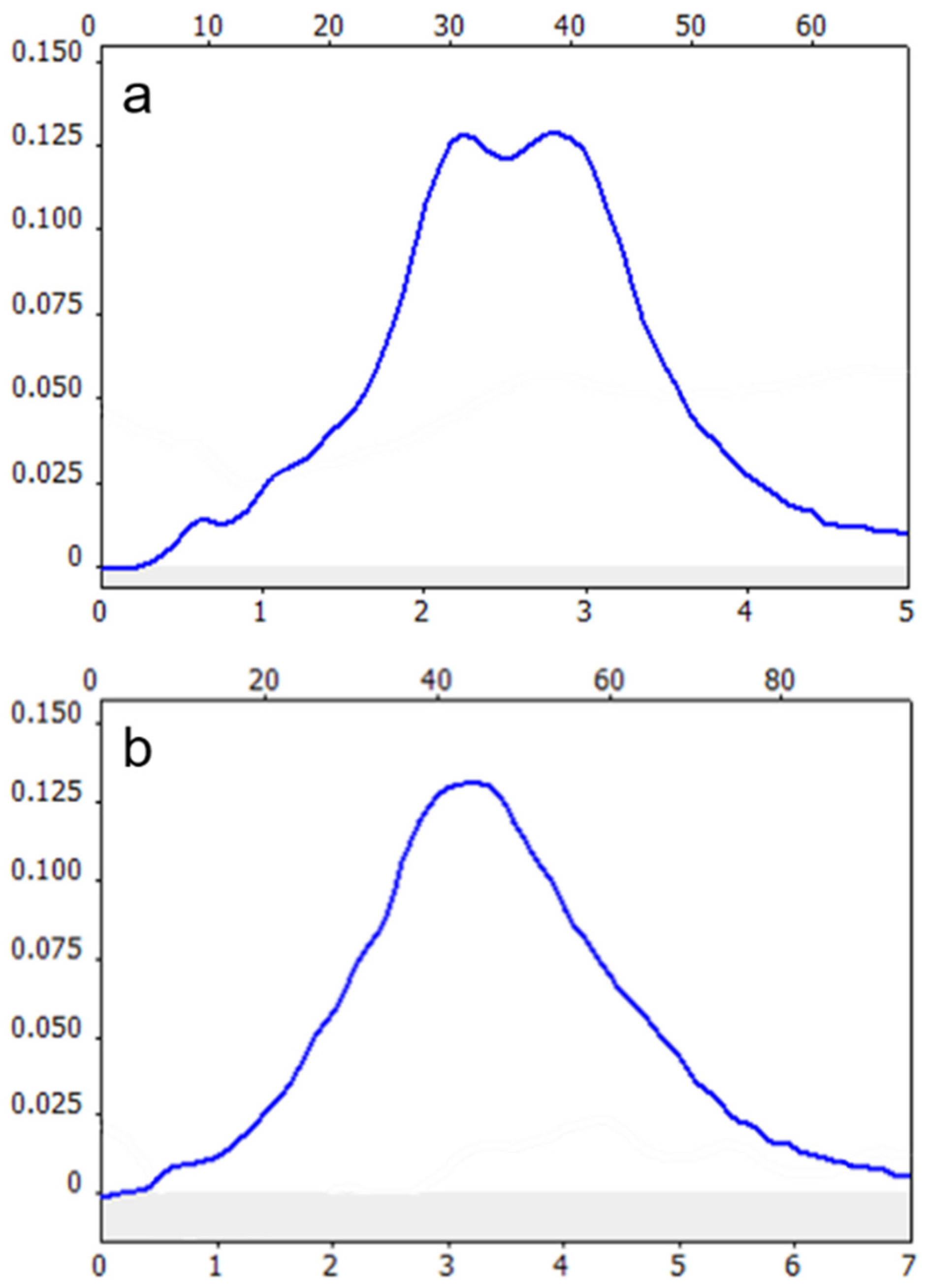
 ) as chemical modifiers besides zirconium coating. The data represent mean ± standard error of 3 replications (merely 2 conductions for zirconium only) with each 3 injections.
) as chemical modifiers besides zirconium coating. The data represent mean ± standard error of 3 replications (merely 2 conductions for zirconium only) with each 3 injections.
 ) as chemical modifiers besides zirconium coating. The data represent mean ± standard error of 3 replications (merely 2 conductions for zirconium only) with each 3 injections.
) as chemical modifiers besides zirconium coating. The data represent mean ± standard error of 3 replications (merely 2 conductions for zirconium only) with each 3 injections.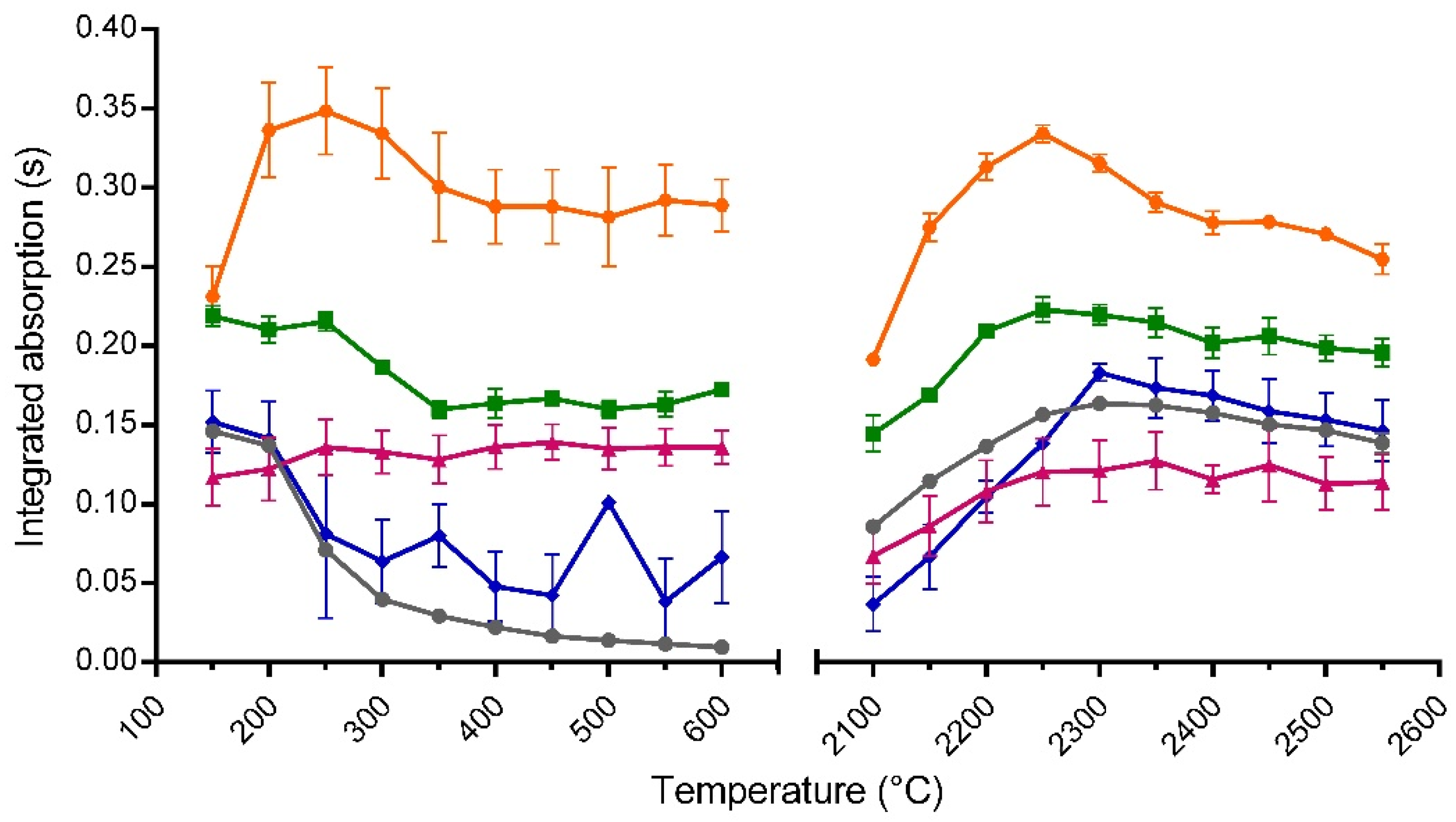
| Operation | Temperature (°C) | Heating Rate (°C s−1) | Holding Time (s) | Argon Flow |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drying 1 | 90 | 10 | 20 | Maximal |
| Drying 2 | 120 | 5 | 20 | Maximal |
| Pyrolysis | 400 | 50 | 20 | Maximal |
| Atomization | 1000 | 100 | 10 | Stop |
| Cleaning | 2000 | 100 | 5 | Stop |
| Volume (µL) | Integration Time (s) | Integrated Absorption (s) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pd | Ca | Mean 1 | RSD (%) 2 | |
| 5 | 5 | 0.23 | 5.3 | |
| 10 | 5 | 0.25 | 5.8 | |
| 15 | 5 | 0.23 | 3.5 | |
| 10 | 2 | 5 | 0.28 | 5.7 |
| 4 | 5 | 0.26 | 1.3 | |
| 6 | 5 | 0.26 | 2.0 | |
| 8 | 5 | 0.23 | 5.9 | |
| 10 | 2 | 7 | 0.31 | 4.4 |
| 4 | 7 | 0.28 | 5.2 | |
| Operation | Temperature (°C) | Heating Rate (°C s−1) | Holding Time (s) | Argon Flow |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drying 1 | 90 | 10 | 10 | Maximal |
| Drying 2 | 100 | 5 | 10 | Maximal |
| Drying 3 | 120 | 5 | 10 | Maximal |
| Pyrolysis | 250 | 50 | 15 | Maximal |
| Auto-zero | 250 | 0 | 5 | Stop |
| Vaporization | 2250 | 3000 | 7 | Stop |
| Cleaning | 2600 | 1000 | 5 | Maximal |
| Parameter | Value (S) | Value (GSH) |
|---|---|---|
| Linear working range | 2.5–100 µg mL−1 | 0.078–3.120 mmol L−1 |
| Correlation coefficient of calibration (R2) | 0.9971 | 0.9971 |
| Characteristic mass | 5.9 ng | 56.9 ng |
| LOD | 2.1 µg mL−1 | 0.06 mmol L−1 |
| LOQ | 4.3 µg mL−1 | 0.13 mmol L−1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baecker, D.; Guenther, S. General Applicability of High-Resolution Continuum-Source Graphite Furnace Molecular Absorption Spectrometry to the Quantification of Oligopeptides Using the Example of Glutathione. Analytica 2022, 3, 24-35. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica3010003
Baecker D, Guenther S. General Applicability of High-Resolution Continuum-Source Graphite Furnace Molecular Absorption Spectrometry to the Quantification of Oligopeptides Using the Example of Glutathione. Analytica. 2022; 3(1):24-35. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica3010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaecker, Daniel, and Sebastian Guenther. 2022. "General Applicability of High-Resolution Continuum-Source Graphite Furnace Molecular Absorption Spectrometry to the Quantification of Oligopeptides Using the Example of Glutathione" Analytica 3, no. 1: 24-35. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica3010003
APA StyleBaecker, D., & Guenther, S. (2022). General Applicability of High-Resolution Continuum-Source Graphite Furnace Molecular Absorption Spectrometry to the Quantification of Oligopeptides Using the Example of Glutathione. Analytica, 3(1), 24-35. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica3010003






