Analytical Chemistry in the 21st Century: Challenges, Solutions, and Future Perspectives of Complex Matrices Quantitative Analyses in Biological/Clinical Field
Abstract
1. Introduction
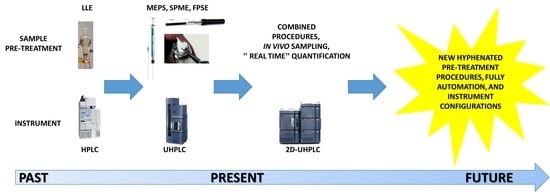
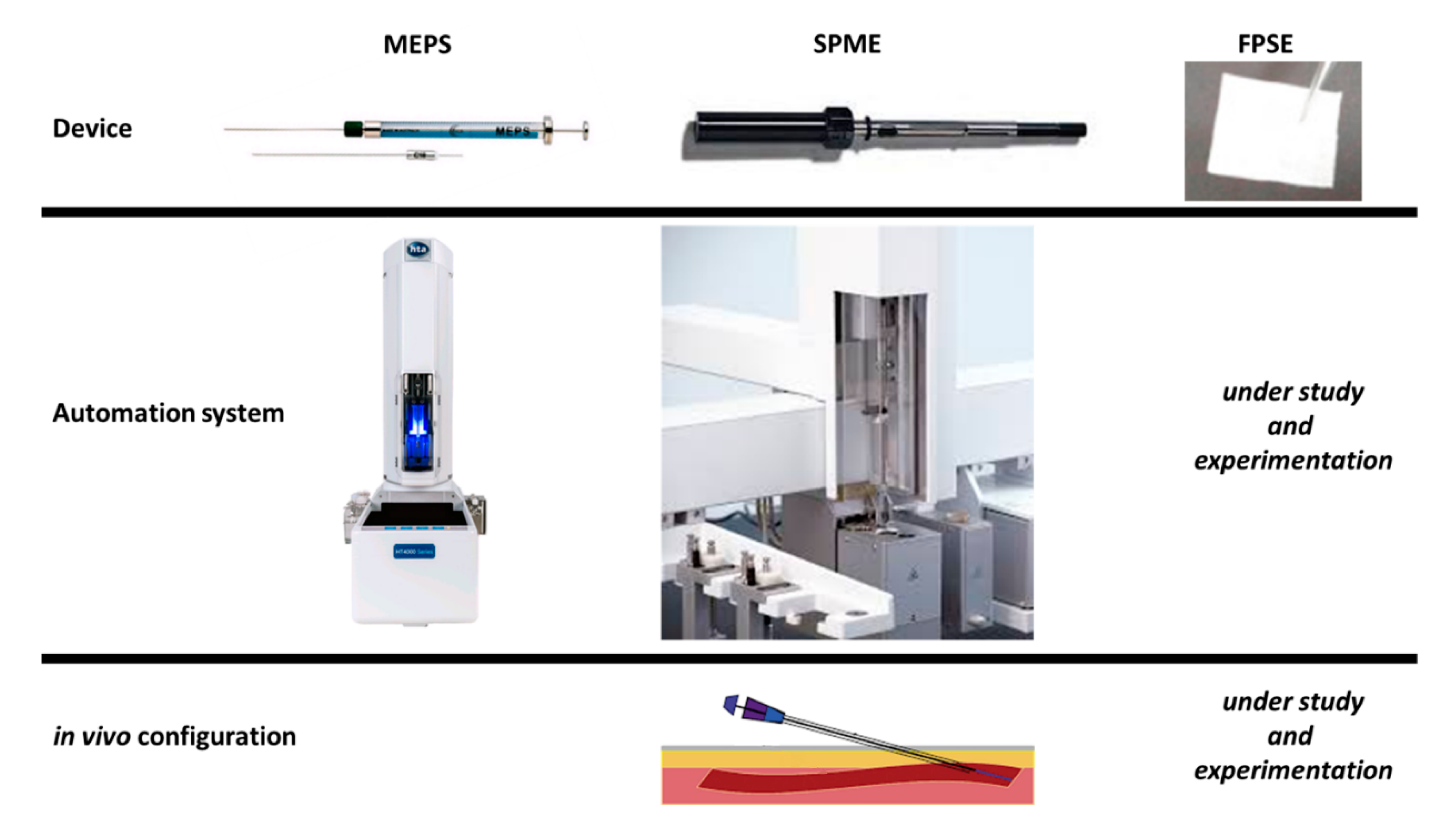
2. Pre-Treatment Procedures
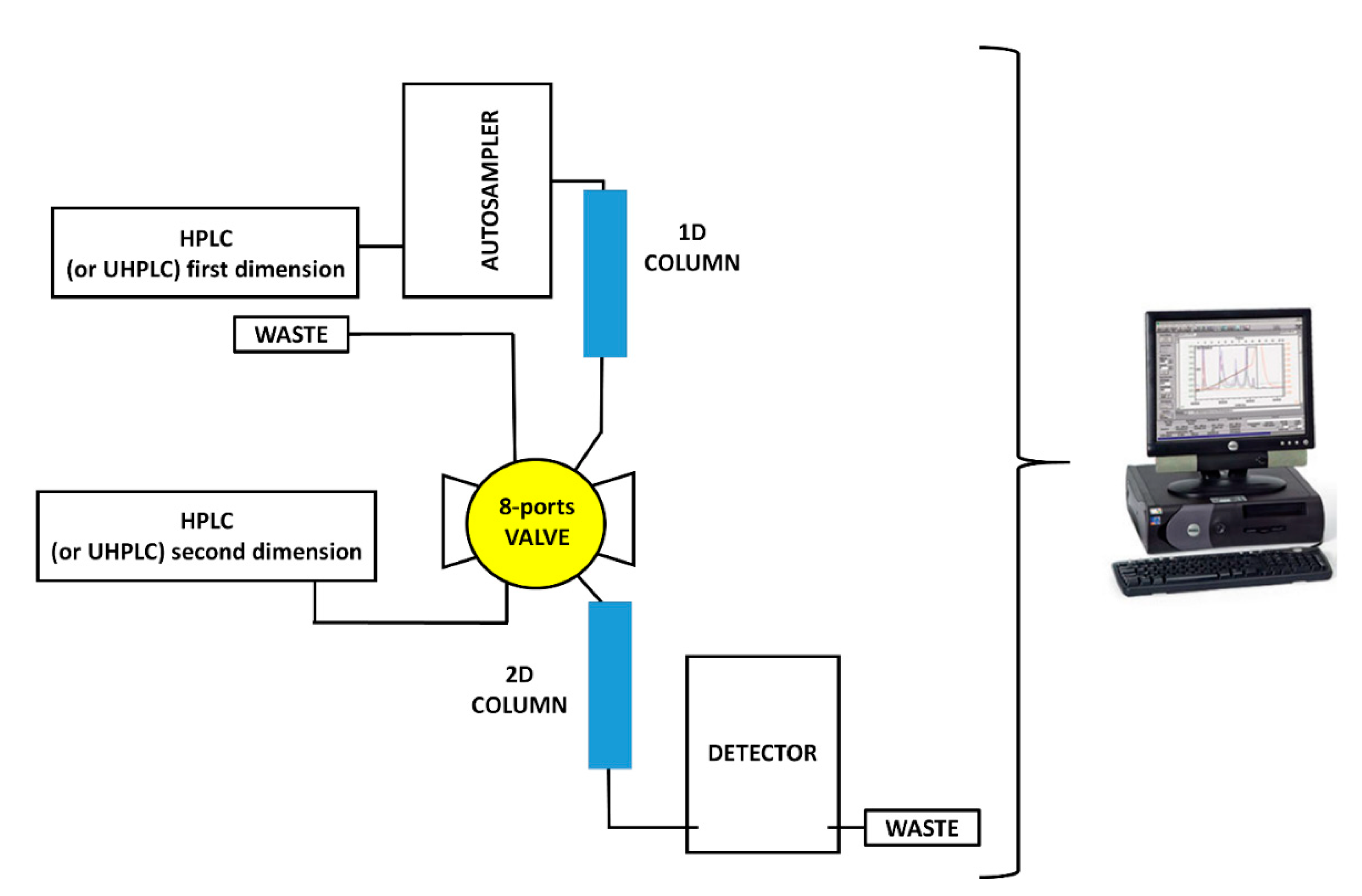
3. Instrument Configurations
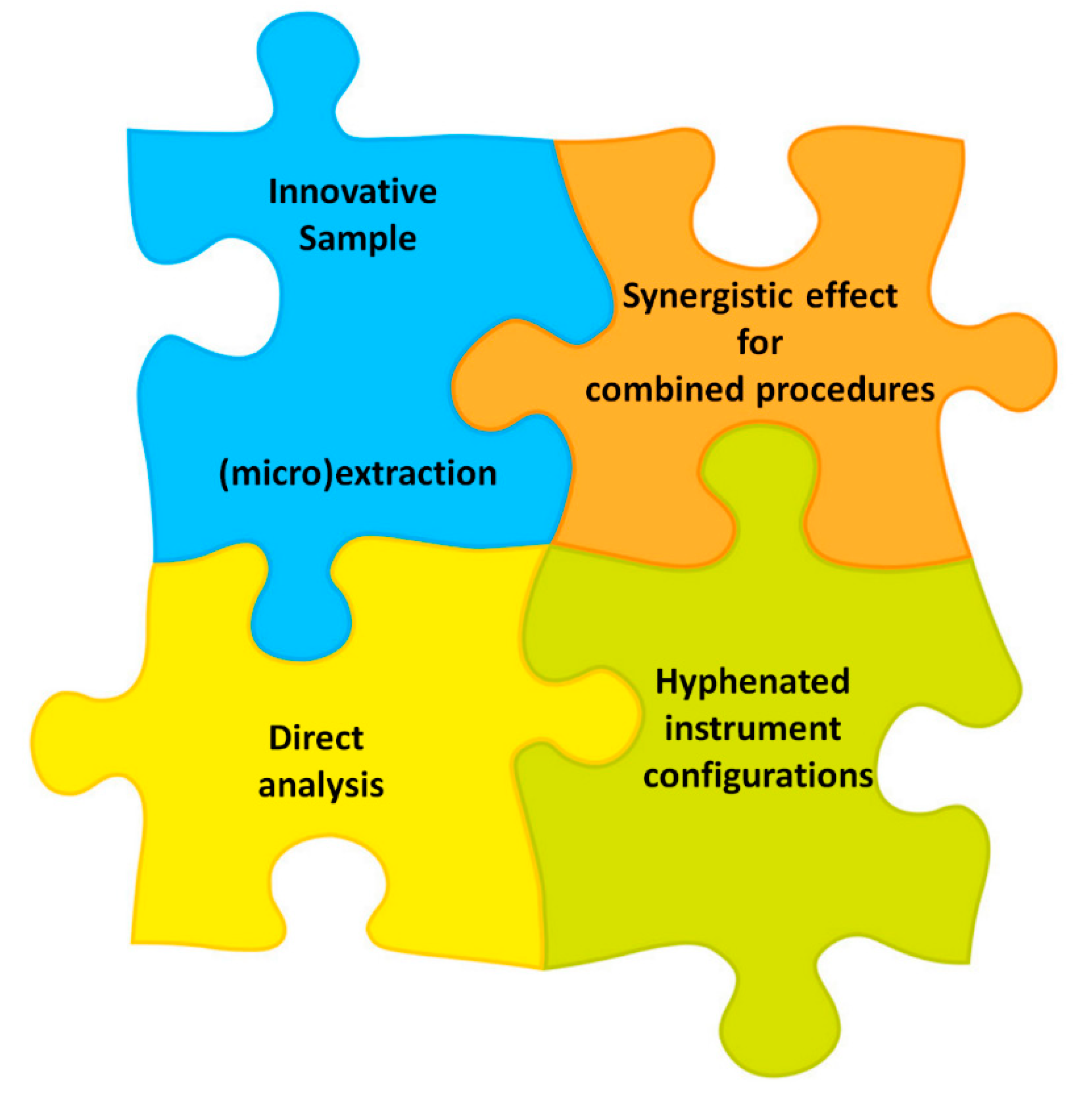
4. Conclusions
- ✓
- better selectivity towards molecules with different chemical-physical properties,
- ✓
- reduction of matrix effects (in the case of hyphenated techniques),
- ✓
- greater flexibility in terms of sample volume required,
- ✓
- ease of use and suitability of automation,
- ✓
- simplification of the sample preparation procedure (up to complete non-pre-treatment of the same),
- ✓
- feasibility for the determination of free and total concentrations
- ✓
- possible “synergistic effect” related to the techniques combination.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kabir, A.; Locatelli, M.; Ulusoy, H.I. Recent Trends in Microextraction Techniques Employed in Analytical and Bioanalytical Sample Preparation. Separations 2017, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, M.; Mandrioli, R.; Samanidou, V.; Bocklitz, T.W. Analytica—A Journal of Analytical Chemistry and Chemical Analysis. Anal. J. Anal. Chem. Chem. Anal. 2020, 1, 12–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, M.; Governatori, L.; Carlucci, G.; Genovese, S.; Mollica, A.; Epifano, F. Recent application of analytical methods to phase I and phase II drugs development: A review. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2011, 26, 283–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tartaglia, A.; Kabir, A.; D’Ambrosio, F.; Ramundo, P.; Ulusoy, S.; Ulusoy, H.; Merone, G.; Savini, F.; D’Ovidio, C.; De Grazia, U.; et al. Fast off-line FPSE-HPLC-PDA determination of six NSAIDs in saliva samples. J. Chromatogr. B 2020, 1144, 122082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassotti, E.; Merone, G.M.; D’Urso, A.; Savini, F.; Locatelli, M.; Tartaglia, A.; Dossetto, P.; D’Ovidio, C.; De Grazia, U. A new LC-MS/MS confirmation method for the determination of 17 drugs of abuse in oral fluid and its application to real samples. Forensic Sci. Int. 2020, 312, 110330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M.; Basheer, C.; Narasimhan, K.; Choolani, M.; Lee, H.K. Application of microwave-assisted micro-solid-phase extraction for determination of parabens in human ovarian cancer tissues. J. Chromatogr. B 2015, 1000, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M.; Płotka-Wasylka, J. Combined extraction and microextraction techniques: Recent trends and future perspectives. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 103, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, M.; Tartaglia, A.; Piccolantonio, S.; Di Iorio, L.A.; Sperandio, E.; Ulusoy, H.I.; Furton, K.G.; Kabir, A. Innovative Configurations of Sample Preparation Techniques Applied in Bioanalytical Chemistry: A Review. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2019, 15, 731–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashri, N.Y.; Abdel-Rehim, M. Sample treatment based on extraction techniques in biological matrices. Bioanalysis 2011, 3, 2003–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namera, A.; Saito, T. Recent advances in unique sample preparation techniques for bioanalysis. Bioanalysis 2013, 5, 915–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Vera, M.; Lucena, R.; Cárdenas, S.; Valcárcel, M. Sorptive microextraction for liquid-chromatographic determination of drugs in urine. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 1164–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyacı, E.; Gorynski, K.; Lafuente, A.R.; Bojko, B.; Pawliszyn, J. Introduction of solid-phase microextraction as a high-throughput sample preparation tool in laboratory analysis of prohibited substances. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 809, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartaglia, A.; Kabir, A.; Ulusoy, S.; Ulusoy, H.I.; Merone, G.M.; Savini, F.; D’Ovidio, C.; De Grazia, U.; Gabrielli, S.; Maroni, F.; et al. Novel MIPs-Parabens based SPE Stationary Phases Characterization and Application. Molecules 2019, 24, 3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canlı, A.G.; Sürücü, B.; Ulusoy, H.I.; Yilmazabd, E.; Kabir, A.; Locatelli, M. Analytical Methodology for Trace Determination of Propoxur and Fenitrothion Pesticide Residues by Decanoic Acid Modified Magnetic Nanoparticles. Molecules 2019, 24, 4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajid, M. Magnetic ionic liquids in analytical sample preparation: A literature review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 113, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Pohl, J.; Engel, R.; Rothman, L.; Thomas, M. Preparation of ionic liquid based solid-phase microextraction fiber and its application to forensic determination of methamphetamine and amphetamine in human urine. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 4824–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuckovic, D. High-throughput solid-phase microextraction in multi-well-plate format. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 45, 136–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-W.; Xing, J.; Cai, L.-S.; Wu, C. Molecularly imprinted monolith in-tube solid-phase microextraction coupled with HPLC/UV detection for determination of 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine in urine. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.-M.; Wang, S.-T.; Hu, W.-K.; Feng, Y.-Q. In-tube solid-phase microextraction based on hybrid silica monolith coupled to liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry for automated analysis of ten antidepressants in human urine and plasma. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 7493–7501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, B.; Zohrabi, P.; Shamsipur, M. Recent developments and applications of different sorbents for SPE and SPME from biological samples. Talanta 2018, 187, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, M.; Tartaglia, A.; D’Ambrosio, F.; Ramundo, P.; Ulusoy, H.; Furton, K.; Kabir, A. Biofluid sampler: A new gateway for mail-in-analysis of whole blood samples. J. Chromatogr. B 2020, 1143, 122055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nováková, L.; Nováková, L. A review of current trends and advances in modern bio-analytical methods: Chromatography and sample preparation. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 656, 8–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G.; Tinari, N.; Grossi, L.; Innosa, D.; Macerola, D.; Tartaglia, A.; Di Donato, V.; D’Ovidio, C.; Locatelli, M. Fabric phase sorptive extraction-high performance liquid chromatography-photo diode array detection method for simultaneous monitoring of three inflammatory bowel disease treatment drugs in whole blood, plasma and urine. J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1084, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locatelli, M.; Tinari, N.; Grassadonia, A.; Tartaglia, A.; Macerola, D.; Piccolantonio, S.; Sperandio, E.; D’Ovidio, C.; Carradori, S.; Ulusoy, H.I.; et al. FPSE-HPLC-DAD method for the quantification of anticancer drugs in human whole blood, plasma, and urine. J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1095, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, M.; Furton, K.G.; Tartaglia, A.; Sperandio, E.; Ulusoy, H.I.; Kabir, A. An FPSE-HPLC-PDA method for rapid determination of solar UV filters in human whole blood, plasma and urine. J. Chromatogr. B 2019, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartaglia, A.; Kabir, A.; Ulusoy, S.; Sperandio, E.; Piccolantonio, S.; Ulusoy, H.I.; Furton, K.G.; Locatelli, M. FPSE-HPLC-PDA analysis of seven paraben residues in human whole blood, plasma, and urine. J. Chromatogr. B 2019, 1125, 121707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Déglon, J.; Thomas, A.; Mangin, P.; Staub, C. Direct analysis of dried blood spots coupled with mass spectrometry: Concepts and biomedical applications. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 402, 2485–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirev, P.A. Dried Blood Spots: Analysis and Applications. Anal. Chem. 2012, 85, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kesel, P.M.; Sadones, N.; Capiau, S.; Lambert, W.E.; Stove, C.P. Hemato-critical issues in quantitative analysis of dried blood spots: Challenges and solutions. Bioanalysis 2013, 5, 2023–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Płotka, J.M. A new tool for the evaluation of the analytical procedure: Green Analytical Procedure Index. Talanta 2018, 181, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirnaghi, F.S.; Pawliszyn, J. Reusable Solid-Phase Microextraction Coating for Direct Immersion Whole-Blood Analysis and Extracted Blood Spot Sampling Coupled with Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry and Direct Analysis in Real Time–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 8301–8309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoufi, A.; Ebrahimi, M.; Bozorgmehr, M.R. Application of response surface modeling and chemometrics methods for the determination of Atenolol, Metoprolol and Propranolol in blood sample using dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction combined with HPLC-DAD. J. Chromatogr. B 2019, 1132, 121823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagini, D.; Antoni, S.; Lomonaco, T.; Ghimenti, S.; Salvo, P.; Bellagambi, F.G.; Scaramuzzo, R.T.; Ciantelli, M.; Cuttano, A.; Fuoco, R.; et al. Micro-extraction by packed sorbent combined with UHPLC-ESI-MS/MS for the determination of prostanoids and isoprostanoids in dried blood spots. Talanta 2020, 206, 120236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musteata, F.M.; De Lannoy, I.; Gien, B.; Pawliszyn, J. Blood sampling without blood draws for in vivo pharmacokinetic studies in rats. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 47, 907–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Es-Haghi, A.; Cai, J.; Pawliszyn, J. Simplified kinetic calibration of solid-phase microextraction for in vivo pharmacokinetics. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 7664–7669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirnaghi, F.S.; Pawliszyn, J. Development of coatings for automated 96-blade solid phase microextraction-liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry system, capable of extracting a wide polarity range of analytes from biological fluids. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1261, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caris, J.A.; Chaves, A.R.; Queiroz, M.E.C. Evaluation of solid-phase microextraction using a polythiophene film and liquid chromatography with spectrophotometric detection for the determination of antidepressants in plasma samples. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2012, 23, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashayekhi, H.A.; Khalilian, F. Development of Solid-Phase Extraction Coupled with Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction Method for the Simultaneous Determination of Three Benzodiazepines in Human Urine and Plasma. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2016, 54, 1068–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahi, H.A.; Moniri, E.; Asgari, M.A.; Hajiaghababaei, L. Selective Sorption and Determination of Atenolol in Pharmaceutical and Biological Samples by Molecular Imprinting Using New Copolymer Beads as a Functional Matrix. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2014, 38, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sereshti, H.; Bakhtiari, S. Three-dimensional graphene/Fe3O4-based magnetic solid phase extraction coupled with high performance liquid chromatography for determination of carvedilol in human blood plasma. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 75757–75765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Hussain, A.; Alajmi, M.F. SPMMTE and Q-TOF–UPLC–MS for monitoring of atenolol and atorvastatin in human plasma using pentafluoro phenyl column. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2017, 40, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, V.R.A.; Goméz-Ríos, G.A.; Tascon, M.; Queiroz, M.E.C.; Pawliszyn, J. Analysis of endocannabinoids in plasma samples by biocompatible solid-phase microextraction devices coupled to mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1091, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuckovic, D.; Pawliszyn, J. Automated study of ligand–receptor binding using solid-phase microextraction. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2009, 50, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mena-Bravo, A.; Priego-Capote, F.; De Castro, M.L. Two-dimensional liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry for vitamin D metabolite profiling including the C3-epimer-25-monohydroxyvitamin D3. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1451, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebpour, Z.; Taraji, M.; Adib, N. Stir bar sorptive extraction and high performance liquid chromatographic determination of carvedilol in human serum using two different polymeric phases and an ionic liquid as desorption solvent. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1236, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, L.; Liu, W.; Huang, M.; Zhang, L. Preparation and application of solid-phase microextraction fiber based on molecularly imprinted polymer for determination of anabolic steroids in complicated samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 7461–7470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Lafuente, A.; Mirnaghi, F.S.; Pawliszyn, J. Determination of cocaine and methadone in urine samples by thin-film solid-phase microextraction and direct analysis in real time (DART) coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 9723–9727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Ríos, G.A.; Pawliszyn, J. Development of Coated Blade Spray Ionization Mass Spectrometry for the Quantitation of Target Analytes Present in Complex Matrices. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 14503–14507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Ríos, G.A.; Pawliszyn, J. Solid phase microextraction (SPME)-transmission mode (TM) pushes down detection limits in direct analysis in real time (DART). Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 12937–12940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, L.; Steffen, D.; Ye, T.; Raftery, D. Metabolic profiling of gender: Headspace-SPME/GC–MS and 1H NMR analysis of urine. Metabolomics 2011, 8, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, S.M.; Caldeira, M.; Carrola, J.; Santos, M.; Cruz, N.; Duarte, I.F. Exploring the human urine metabolomic potentialities by comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography coupled to time of flight mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1252, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, A.; Dualde, P.; Yusa, V.; Coscollà, C. Retrospective analysis of pesticide metabolites in urine using liquid chromatography coupled to high-resolution mass spectrometry. Talanta 2016, 160, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- León, N.; Roca, M.; Igualada, C.; Martins, C.P.; Pastor, A.; Yusa, V. Wide-range screening of banned veterinary drugs in urine by ultra high liquid chromatography coupled to high-resolution mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1258, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, S.; Karimi, M. Synthesis and application of molecularly imprinted polymer for highly selective solid phase extraction trace amount of sotalol from human urine samples: Optimization by central composite design (CCD). Med. Chem. Res. 2017, 26, 2477–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šatínský, D.; Sobek, V.; Lhotská, I.; Solich, P. Micro-extraction by packed sorbent coupled on-line to a column-switching chromatography system—A case study on the determination of three beta-blockers in human urine. Microchem. J. 2019, 147, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takáts, Z.; Wiseman, J.M.; Gologan, B.; Cooks, R.G. Mass Spectrometry Sampling Under Ambient Conditions with Desorption Electrospray Ionization. Science 2004, 306, 471–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takáts, Z.; Wiseman, J.M.; Cooks, R.G. Ambient mass spectrometry using desorption electrospray ionization (DESI): Instrumentation, mechanisms and applications in forensics, chemistry, and biology. J. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 40, 1261–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, W.S.; Chen, H.; Ding, J.; Yang, S.; Zhu, L.; Gamez, G.; Chingin, K.; Ren, Y.; Zenobi, R. Rapid Characterization of Complex Viscous Liquids at the Molecular Level. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 8277–8280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Venter, A.; Cooks, R.G. Extractive electrospray ionization for direct analysis of undiluted urine, milk and other complex mixtures without sample preparation. Chem. Commun. 2006, 21, 2042–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemes, P.; Vertes, A. Laser Ablation Electrospray Ionization for Atmospheric Pressure, in Vivo, and Imaging Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 8098–8106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, B.; Vertes, A. In Situ Metabolic Profiling of Single Cells by Laser Ablation Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 8265–8271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feider, C.L.; Krieger, A.C.; DeHoog, R.J.; Eberlin, L.S. Ambient Ionization Mass Spectrometry: Recent Developments and Applications. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 4266–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberici, R.M.; Simas, R.C.; Sanvido, G.B.; Romão, W.; Lalli, P.M.; Benassi, M.; Cunha, I.B.S.; Eberlin, M.N. Ambient mass spectrometry: Bringing MS into the “real world. ” Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 265–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monge, M.E.; Harris, G.A.; Dwivedi, P.; Fernández, F.M. Mass Spectrometry: Recent Advances in Direct Open Air Surface Sampling/Ionization. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 2269–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, M.K.; Chen, L.C.; Yu, Z.; Nonami, H.; Hiraoka, K.; Erra-Balsells, R. Detection of protein from detergent solutions by probe electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (PESI-MS). J. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 46, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, M.K.; Yoshimura, K.; Chen, L.C.; Yu, Z.; Nakazawa, T.; Katoh, R.; Fujii, H.; Takeda, S.; Nonami, H.; Hiraoka, K. Application of Probe Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry (PESI-MS) to Clinical Diagnosis: Solvent Effect on Lipid Analysis. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 23, 2043–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Yao, Z.-P. Detection of native proteins using solid-substrate electrospray ionization mass spectrometry with nonpolar solvents. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1004, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Yang, Y.; Fang, L.; Lin, L.; Zhou, H.; Luan, T. Coupling Solid-Phase Microextraction with Ambient Mass Spectrometry Using Surface Coated Wooden-Tip Probe for Rapid Analysis of Ultra Trace Perfluorinated Compounds in Complex Samples. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 11159–11166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; So, P.-K.; Yang, Y.; Deng, J.; Choi, Y.-C.; Luan, T.; Yao, Z.-P. Surface-Modified Wooden-Tip Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry for Enhanced Detection of Analytes in Complex Samples. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 1759–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Manicke, N.E.; Lin, J.-M.; Cooks, R.G.; Ouyang, Z. Development, Characterization, and Application of Paper Spray Ionization. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 2463–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Cooks, R.G.; Ouyang, Z. Paper Spray for Direct Analysis of Complex Mixtures Using Mass Spectrometry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 877–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, M.Y.M.; Tang, H.-W.; Man, S.-H.; Lam, C.-W.; Che, C.-M.; Ng, K.-M. Electrospray ionization on porous spraying tips for direct sample analysis by mass spectrometry: Enhanced detection sensitivity and selectivity using hydrophobic/hydrophilic materials as spraying tips. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2013, 27, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.Y.M.; Man, S.-H.; Che, C.-M.; Lau, K.-C.; Ng, K.-M. Negative electrospray ionization on porous supporting tips for mass spectrometric analysis: Electrostatic charging effect on detection sensitivity and its application to explosive detection. Analyst 2014, 139, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Yao, Z.-P. Mobility of Proteins in Porous Substrates under Electrospray Ionization Conditions. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 5585–5589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Nie, L.; Liao, L.; Du, R.; Liu, B.; Yang, P. Ambient ionization based on mesoporous graphene coated paper for therapeutic drug monitoring. J. Chromatogr. B 2016, 1015, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Zou, Y.; Xie, X.; Zhao, J.; Piao, X.; Piao, J.; Yao, Z.-P.; Quinto, M.; Wang, G.; Li, D. A high throughput mass spectrometry screening analysis based on two-dimensional carbon microfiber fractionation system. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1501, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ro, K.W.; Busman, M.; Knapp, D.R. Electrospray Ionization with a Pointed Carbon Fiber Emitter. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 3599–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mahony, J.; Clarke, L.; Whelan, M.; O’Kennedy, R.; Lehotay, S.J.; Danaher, M. The use of ultra-high pressure liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometric detection in the analysis of agrochemical residues and mycotoxins in food—Challenges and applications. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1292, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillarme, D.; Schappler, J.; Rudaz, S.; Veuthey, J.-L. Coupling ultra-high-pressure liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2010, 29, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehotay, S.J.; Son, K.A.; Kwon, H.; Koesukwiwat, U.; Fu, W.; Mastovska, K.; Hoh, E.; Leepipatpiboon, N. Comparison of QuEChERS sample preparation methods for the analysis of pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 2548–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, L.P.; Madureira, F.; Vargas, E.D.A.; Faria, A.F.; Augusti, R. Development and validation of a multianalyte method for quantification of mycotoxins and pesticides in rice using a simple dilute and shoot procedure and UHPLC-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2019, 270, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- François, I.; Sandra, K.; Sandra, P. Comprehensive liquid chromatography: Fundamental aspects and practical considerations—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 641, 14–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro-Reig, M.; Jaumot, J.; Baglai, A.; Vivó-Truyols, G.; Schoenmakers, P.; Tauler, R. Untargeted Comprehensive Two-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography Coupled with High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Rice Metabolome Using Multivariate Curve Resolution. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 7675–7683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoll, D.R.; Carr, P.W. Two-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography: A State of the Art Tutorial. Anal. Chem. 2016, 89, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoll, D.R.; Talus, E.S.; Harmes, D.C.; Zhang, K. Evaluation of detection sensitivity in comprehensive two-dimensional liquid chromatography separations of an active pharmaceutical ingredient and its degradants. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 407, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.-X.; Schmitz, O.J. Comprehensive two-dimensional liquid chromatography tandem diode array detector (DAD) and accurate mass QTOF-MS for the analysis of flavonoids and iridoid glycosides in Hedyotis diffusa. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 407, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandra, K.; Steenbeke, M.; Vandenheede, I.; Vanhoenacker, G.; Sandra, P. The versatility of heart-cutting and comprehensive two-dimensional liquid chromatography in monoclonal antibody clone selection. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1523, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papac, D.I.; Shahrokh, Z. Mass spectrometry innovations in drug discovery and development. Pharm. Res. 2001, 18, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesinger, T.; Mechtler, T.; Schwarz, M.; Xie, X.; Grosse, R.; Cobos, P.N.; Kasper, D.; Lukacs, Z. Investigating the suitability of high-resolution mass spectrometry for newborn screening: Identification of hemoglobinopathies and β-thalassemias in dried blood spots. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2020, 58, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucci, S.; Behringer, S.; Sturm, M.; Grünert, S.C.; Spiekerkoetter, U. Implementation of a fast method for the measurement of carnitine palmitoyltransferase 2 activity in lymphocytes by tandem mass spectrometry as confirmation for newborn screening. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2019, 42, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Marca, G.; Giocaliere, E.; Malvagia, S.; Villanelli, F.; Funghini, S.; Ombrone, D.; Della Bona, M.; Forni, G.; Canessa, C.; Ricci, S.; et al. Development and validation of a 2nd tier test for identification of purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency patients during expanded newborn screening by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2016, 54, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thevis, M.; Schanzer, W. Mass Spectrometry in Doping Control Analysis. Curr. Org. Chem. 2005, 9, 825–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crutchfield, C.A.; Thomas, S.; Sokoll, L.J.; Chan, D.W. Advances in mass spectrometry-based clinical biomarker discovery. Clin. Proteom. 2016, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilento, E.M.; Jin, L.; Stewart, T.; Shi, M.; Sheng, L.; Zhang, J. Mass spectrometry: A platform for biomarker discovery and validation for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. J. Neurochem. 2019, 151, 397–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzi, M.; Riquelme, G.; Zabalegui, N.; Monge, M.E. Improving diagnosis of genitourinary cancers: Biomarker discovery strategies through mass spectrometry-based metabolomics. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 178, 112905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galindo, A.N.; Macron, C.; Cominetti, O.; Dayon, L. Analyzing Cerebrospinal Fluid Proteomes to Characterize Central Nervous System Disorders: A Highly Automated Mass Spectrometry-Based Pipeline for Biomarker Discovery. Breast Cancer 2019, 1959, 89–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicalini, I.; Rossi, C.; Pieragostino, D.; Agnifili, L.; Mastropasqua, L.; Di Ioia, M.; De Luca, G.; Onofrj, M.; Federici, L.; Del Boccio, P. Integrated Lipidomics and Metabolomics Analysis of Tears in Multiple Sclerosis: An Insight into Diagnostic Potential of Lacrimal Fluid. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballester-Caudet, A.; Campíns-Falcó, P.; Pérez, B.; Sancho, R.; Lorente, M.; Sastre, G.; González, C. A new tool for evaluating and/or selecting analytical methods: Summarizing the information in a hexagon. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazzi, M.; Colella, S.; Alladio, E.; Puccinelli, M.P.; Mengozzi, G.; Medana, C. Statistical Optimization of Urinary Organic Acids Analysis by a Multi-Factorial Design of Experiment. Anal. J. Anal. Chem. Chem. Anal. 2020, 1, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozzi, P.; Zappi, A.; Gottardi, F.; Locatelli, M.; Melucci, D. A Quick and Efficient Non-Targeted Screening Test for Saffron Authentication: Application of Chemometrics to Gas-Chromatographic Data. Molecules 2019, 24, 2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Matrix | Analyte/S | Extraction Configuration | Phase System | Instrument Configuration | Stationary Phase | Elution | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saliva | NSAIDs | FPSE | PTHF | HPLC-PDA | C18 | isocratic | [4] |
| Ovarian cancer tissue | NSAIDs | MASE-SPE | - | HPLC-UV | C18 | isocratic | [6] |
| Human Whole blood | NSAIDs | BFS | - | HPLC-PDA | C18 | isocratic | [21] |
| Parabens | FPSE | CW20M | HPLC-PDA | C18 | isocratic | [26] | |
| IBD drugs | FPSE | CW20M | HPLC-PDA | C18 | gradient | [23] | |
| Aromatase inhibitors | FPSE | PEG-PPG-PEG | HPLC-PDA | C18 | gradient | [24] | |
| UV filters | FPSE | CW20M | HPLC-PDA | C18 | isocratic | [25] | |
| Antidepressants | SPME | PAN-C18 | HPLC-MS/MS and DART-MS/MS | C18 | gradient | [31] | |
| β-blockers | Ionic liquid-DLLME | - | HPLC-DAD | C18 | isocratic | [32] | |
| Prostaglandin | DBS-MEPS | C18 | UHPLC-ESI-MS/MS | C18 | gradient | [33] | |
| Rat whole blood | Antidepressants | In vivo SPME | PPY | HPLC-MS/MS | C18 | gradient | [34] |
| Dog whole blood | Antidepressants | In vivo SPME | PEG-C18 | HPLC-MS/MS | C18 | gradient | [35] |
| Human Plasma | Parabens | FPSE | CW20M | HPLC-PDA | C18 | isocratic | [26] |
| IBD drugs | FPSE | CW20M | HPLC-PDA | C18 | gradient | [23] | |
| Aromatase inhibitors | FPSE | PEG-PPG-PEG | HPLC-PDA | C18 | gradient | [24] | |
| UV filters | FPSE | CW20M | HPLC-PDA | C18 | isocratic | [25] | |
| Antidepressants | SPME | PAN/PS/DVB | HPLC-MS/MS | PFP | gradient | [36] | |
| Antidepressants | SPME | PTP (polythiophene) | HPLC-UV | C18 RP-Select B | isocratic | [37] | |
| Benzodiazepines | SPE-DLLME | - | HPLC-UV | C18 | Isocratic | [38] | |
| β-blockers | MIP-SPE | - | HPLC-UV | C18 | isocratic | [39] | |
| β-blockers | Magnetic SPE | Graphene nanocomposite | HPLC-UV | C18 | isocratic | [40] | |
| β-blockers | SPMMTE | Iron nanocomposite adsorbent | UPLC-Q-TOF-MS | PFP | isocratic | [41] | |
| Endocannabinoids | Bio-SPME | HLB | nano-ESI-MS/MS | - | - | [42] | |
| Human Serum | Antidepressants | SPME | C16 amide | HPLC-MS/MS | C18 | gradient | [43] |
| Vitamin D and analogues | On line SPE | C18 | 2D-UPLC-ESI-MS/MS | PFP-C18 | gradient | [44] | |
| Human Urine | β-blockers | SBSE | polymeric | HPLC-UV | C18 | isocratic | [45] |
| Parabens | FPSE | CW20M | HPLC-PDA | C18 | isocratic | [26] | |
| Parabens | MIP-SPE | CW20M | HPLC-PDA | C18 | isocratic | [13] | |
| IBD drugs | FPSE | CW20M | HPLC-PDA | C18 | gradient | [23] | |
| Aromatase inhibitors | FPSE | PEG-PPG-PEG | HPLC-PDA | C18 | gradient | [24] | |
| UV filters | FPSE | CW20M | HPLC-PDA | C18 | isocratic | [25] | |
| Anabolic steroids | MIP-SPME | - | GC-MS | HP-5MS | temperature gradient | [46] | |
| Illicit drugs | Ionic liquid-SPME | - | GC-MS | DB-1MS | temperature gradient | [16] | |
| Illicit drugs | SPME | C18 | DART MS/MS Coated blade spray-MS/MS DART-MS/MS | - - - | - - - | [47] [48] [49] | |
| Metabolic profile | SPME | PA | GC-MS | HP-5 | temperature gradient | [50] | |
| Metabolic profile | SPME | DVB/CAR/PDMS | GC x GC-TOF-MS | HP-5 x DB-FFAP | temperature gradient | [51] | |
| Benzodiazepines | SPE-DLLME | - | HPLC-UV | C18 | isocratic | [38] | |
| Pesticides and metabolites | QuEChERS | - | UHPLC–HRMS | Hypersil Gold aQ | gradient | [52] | |
| Veterinary drugs | QuEChERS-SPE | - | UHPLC–HRMS | Hypersil Gold aQ | gradient | [53] | |
| β-blockers | MIP-SPE | - | HPLC-UV | C18 | isocratic | [39] | |
| β-blockers | MIP-SPE | - | HPLC-UV | C18 | isocratic | [54] | |
| β-blockers | On line MEPS | - | HPLC-FLD | C18 | gradient | [55] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Merone, G.M.; Tartaglia, A.; Locatelli, M.; D’Ovidio, C.; Rosato, E.; de Grazia, U.; Santavenere, F.; Rossi, S.; Savini, F. Analytical Chemistry in the 21st Century: Challenges, Solutions, and Future Perspectives of Complex Matrices Quantitative Analyses in Biological/Clinical Field. Analytica 2020, 1, 44-59. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica1010006
Merone GM, Tartaglia A, Locatelli M, D’Ovidio C, Rosato E, de Grazia U, Santavenere F, Rossi S, Savini F. Analytical Chemistry in the 21st Century: Challenges, Solutions, and Future Perspectives of Complex Matrices Quantitative Analyses in Biological/Clinical Field. Analytica. 2020; 1(1):44-59. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica1010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleMerone, Giuseppe Maria, Angela Tartaglia, Marcello Locatelli, Cristian D’Ovidio, Enrica Rosato, Ugo de Grazia, Francesco Santavenere, Sandra Rossi, and Fabio Savini. 2020. "Analytical Chemistry in the 21st Century: Challenges, Solutions, and Future Perspectives of Complex Matrices Quantitative Analyses in Biological/Clinical Field" Analytica 1, no. 1: 44-59. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica1010006
APA StyleMerone, G. M., Tartaglia, A., Locatelli, M., D’Ovidio, C., Rosato, E., de Grazia, U., Santavenere, F., Rossi, S., & Savini, F. (2020). Analytical Chemistry in the 21st Century: Challenges, Solutions, and Future Perspectives of Complex Matrices Quantitative Analyses in Biological/Clinical Field. Analytica, 1(1), 44-59. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica1010006