Current Knowledge on Radiation-Therapy-Induced Erectile Dysfunction in Prostate-Cancer Patients: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Radiation-Therapy-Induced Erectile Dysfunction Pathophysiology
3. Radiation Therapy Options in PCa Patients and Associated RI-ED Rates
3.1. External Beam Radiation Therapy
3.2. Hypofractionated Radiation Therapy
3.3. Proton-Beam Therapy
| Name/Author | Year | Country | Study Design | F/U | Participants Number | Therapeutic Option | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hall et al. [28] NRG/RTOG 0125 trial | 2022 | USA | Prospective Phase III RCT | 24 months | 1532 | EBRT | ED occurrence |
| 769 | 70.2 Gy in 39 fractions | 38.1% | |||||
| 763 | 79.2 Gy in 44 fractions | 49.7% | |||||
| p = 0.051 | |||||||
| Donovan et al. [29] ProtecT trial | 2016 | UK | Comparative trial | 6 years | ED occurrence/worsening | ||
| 545 | AS | 15% | |||||
| 553 | RP | 55% | |||||
| 545 | EBRT | 45% | |||||
| Dearnaley et al. [31] CHHiP trial | 2016 | UK, Ireland, Switzerland, New Zealand | International multicenter phase III RCT | 5 years | 3216 | EBRT | Sexual symptoms ≥2 |
| LENT-SOMA scale | |||||||
| 1065 | CF 74 Gy | 67% | |||||
| 1074 | HFX 60 Gy | 65% | |||||
| 1077 | HFX 57 Gy | 64% | |||||
| Lee et al. [33] NRG Oncology RTOG0415 | 2016 | USA | Randomized Phase III noninferiority comparing study | 5.8 years | 1092 | EBRT | GU toxicity, early and late |
| 542 | CF 73.8 Gy | 61.6%, 52.3% | |||||
| 550 | HFX 60 Gy | 62.2%, 58.1% | |||||
| Catton et al. [34] PROFIT trial | 2017 | Canada, | Noninferiority RCT | 6 years | 1206 | EBRT | Late ≥ 3 GU toxicity |
| Australia, | 608 | HFX 60 Gy | 2.1% | ||||
| France | 598 | CF 78 Gy | 3.0% | ||||
| Rasmusson et al. [36] HYPO-RT-PC trial | 2020 | Sweden | Open-lab Phase III RCT | 5 years | 673 | EBRT | ED occurrence |
| 330 | CF | 27% | |||||
| 343 | UHF | 27% | |||||
| Pepe et al. [42] | 2022 | Italy | Experimental trial | 18 months | 56 | Hydrogel injection SpaceOAR before HFX 60 Gy | EF preservation 62.5% |
| Brand et al. [45] PACE-B trial | 2022 | UK, | Open-label, multicohort, randomized, controlled, Phase III trial | 2 years | RTOG grade ≥2 GU toxicity | ||
| Ireland, | 430 | CF 78 Gy | 2% | ||||
| Canada | 414 | SBRT 36 Gy | 13% | ||||
| Ho et al. [46] | 2018 | USA | Observational trial | 5 years | 254 | PBT | Ability to function sexuality loss (EPIC) |
| 1 year F/U 24% | |||||||
| 3 year F/U 82% | |||||||
| 5 year F/U 54% |
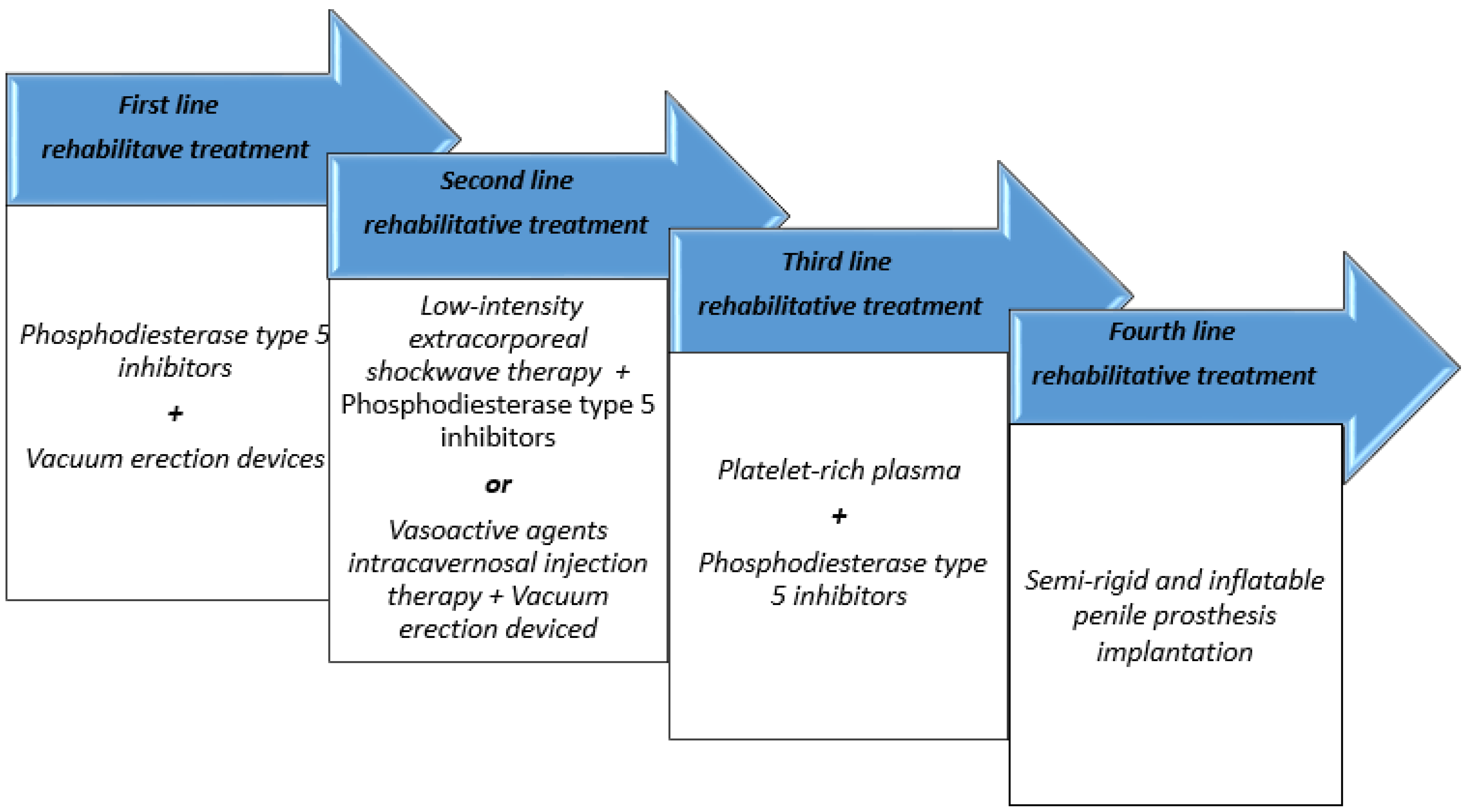
4. Sexual Rehabilitation in RI-ED Patients
4.1. Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitors
4.2. Vasoactive Injectables, Vacuum Therapy, and Pelvic-Floor Physiotherapy
4.3. Regenerative Therapies and Future Directions
| Name/Author | Year | Country | Study Design | Participants Number | Therapeutic Option | Dosing Schedule | Interval from RT | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. Kedia et al. [34] | 1999 | USA | Prospective observational trial | 21 | Sildenafil | 50 mg with a titration to 100 mg if needed; 1 sildenafil tablet approximately 1 h before sexual activity | 24.6 +/− 5.8 months | Mean duration of vaginal intercourse (CCEF), 12.7 ± 2.5 min; mean frequency of penetration score (IIEF 5), from 1.3 to 4.0; maintenance of erection score (IIEF 5), from 1.1 to 3.9. |
| Weber DC. et al. [35] | 1999 | Switzerland | Prospective observational trial | 35 | Sildenafil | 100 mg orally once a week for 6 consecutive weeks | 18.5 months | Response rate, from 40% during the first week to 77% at 6 weeks; mean weekly IIEF 5 score of 13.8, 16.0, 17.0, 16.8, 17.0, and 17.6 at weeks 1 to 6, respectively. |
| Zelefky MJ et al. [36] | 1999 | USA | Prospective observational trial | 50 | Sildenafil | Patients were initially given 50 mg of sildenafil and instructed to use the medication on at least three occasions | 19 months | Erection firmness improvement: significant in 74%, partial in 4%, no response in 22%; erection durability improvement: significant in 66%, partial in 6%, no improvement in 28%; libido improvement: in 18%. |
| Watkins Bruner et al. [39] | 2013 | USA | Randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled crossover trial | 115 | Sildenafil | 12 weeks of sildenafil or placebo, followed by 1 week of no treatment, 12 weeks of a alternative flexible dosing schedule starting with a 50 mg dose (1 pill) 1 h prior to desired sexual activity and increasing up to 100 mg (2 pills) daily as needed. | 12 months (range 5.5–48) | 66%, any response; 10%, both placebo and sildenafil response; 21%, only sildenafil response; 3%, only placebo response. |
| Ilic D. et al. [40] | 2012 | Australia | Randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial | 27 | Sildenafil | Standard 50 mg sildenafil tablets, one tablet each night. Patients were reviewed after 1 month, and if no adverse effects had been noted, they were instructed to take 2 tablets each evening. Six-month trial period. | 1 month | Based on IIEF-5 measure, sildenafil vs. placebo: Baseline: 24 both; 4 weeks: 24–21; 12 weeks: 24–20; 2 years: 19–20. |
| Pisansky et al. [41] Therapy Oncology Group [0831] | 2014 | USA Canada | Stratified, placebo-controlled, double-blind, parallel-group study with 1:1 randomization. | 242 | Tadalafil | 5 mg for 24 consecutive weeks | 1 week after RT initiation | EEF5-based EF. Tadalafil vs. placebo. Baseline, 24.8–25.1; 30 weeks, 20.7–20.9; 50 weeks, 21.2–20.4. |
| Incrocci et al. [42] | 2006 | Netherland | Randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled, cross-over-study | 358 | Tadalafil | 20 mg on demand tadalafil or placebo for 6 weeks. | 12 months | Erectile function, IIEF score: Baseline, 8.4; after tadalafil, 17.7; after placebo, 9.5. Erectile function, SEP diary, tadalafil vs. placebo: Question 1: 64–30; Question 2: 47–19; Question 3: 46–12; Question 4: 43–7; Question 5: 48–15. |
| Ricardi et al. [43] | 2010 | Italy | Randomized comparative study | 52 | Tadalafil | On-demand 20 mg or once-a-day 5 mg tadalafil for 12 weeks | 6 months | IIEF-based EF. On-demand 20 mg vs. once-a-day 5 mg: Baseline: 6–6; 1 month: 22–24; 3 months: 25–27. |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mottet, N.; van den Bergh, R.C.N.; Briers, E.; van den Broeck, T.; Cumberbatch, M.G.; de Santis, M.; Fanti, S.; Fossati, N.; Gandaglia, G.; Gillessen, S.; et al. EAU-EANM-ESTRO-ESUR-SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer-2020 Update. Part 1: Screening, Diagnosis, and Local Treatment with Curative Intent. Eur. Urol. 2021, 79, 243–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinikainen, P.; Lehtonen, M.; Lehtinen, I.; Luukkaala, T.; Sintonen, H.; Kellokumpu-Lehtinen, P.-L. Health-Related Quality of Life of Patients Treated With Different Fractionation Schedules for Early Prostate Cancer Compared to the Age-Standardized General Male Population. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2023, 21, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Incrocci, L. Radiotherapy for Prostate Cancer and Sexual Health. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2015, 4, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Fort, M.K.; Rogers, M.J.; Santiago, R.; Mahase, S.S.; Mendez, M.; Zheng, Y.; Kong, X.; Kashanian, J.A.; Niaz, M.J.; McClelland, S.; et al. Prostatic Irradiation-Induced Sexual Dysfunction: A Review and Multidisciplinary Guide to Management in the Radical Radiotherapy Era (Part I Defining the Organ at Risk for Sexual Toxicities). Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2020, 25, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, P.A.; Tasch, E.S.; Stocking, C.; Rubin, S.; Siegler, M.; Weichselbaum, R. Sex or Survival: Trade-Offs between Quality and Quantity of Life. J. Clin. Oncol. 1991, 9, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, I.; Feldman, M.I.; Deckers, P.J.; Babayan, R.K.; Krane, R.J. Radiation-Associated Impotence. A Clinical Study of Its Mechanism. JAMA 1984, 251, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Both, S.; Wang, K.K.-H.; Plastaras, J.P.; Deville, C.; Bar Ad, V.; Tochner, Z.; Vapiwala, N. Real-Time Study of Prostate Intrafraction Motion during External Beam Radiotherapy with Daily Endorectal Balloon. Int. J. Radiat Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 81, 1302–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariados, N.; Sylvester, J.; Shah, D.; Karsh, L.; Hudes, R.; Beyer, D.; Kurtzman, S.; Bogart, J.; Hsi, R.A.; Kos, M.; et al. Hydrogel Spacer Prospective Multicenter Randomized Controlled Pivotal Trial: Dosimetric and Clinical Effects of Perirectal Spacer Application in Men Undergoing Prostate Image Guided Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy. Int. J. Radiat Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 92, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulhall, J.; Ahmed, A.; Parker, M.; Mohideen, N. The Hemodynamics of Erectile Dysfunction Following External Beam Radiation for Prostate Cancer. J. Sex Med. 2005, 2, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelefsky, M.J.; Eid, J.F. Elucidating the Etiology of Erectile Dysfunction after Definitive Therapy for Prostatic Cancer. Int. J. Radiat Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1998, 40, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, M.W.; Marolf, A.J.; Ehrhart, E.J.; Rao, S.; Kraft, S.L.; Engel, S.; Yoshikawa, H.; Golden, A.E.; Wasserman, T.H.; LaRue, S.M. Pudendal Nerve and Internal Pudendal Artery Damage May Contribute to Radiation-Induced Erectile Dysfunction. Int. J. Radiat Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 91, 796–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, D.; Gonzalez, J.; Goldstein, I. The Role of Pelvic Floor Muscles in Male Sexual Dysfunction and Pelvic Pain. Sex Med. Rev. 2016, 4, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, A.L. Pelvic Floor Muscle Training in Males: Practical Applications. Urology 2014, 84, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavoisier, P.; Courtois, F.; Barres, D.; Blanchard, M. Correlation between Intracavernous Pressure and Contraction of the Ischiocavernosus Muscle in Man. J. Urol. 1986, 136, 936–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoisier, P.; Roy, P.; Dantony, E.; Watrelot, A.; Ruggeri, J.; Dumoulin, S. Pelvic-Floor Muscle Rehabilitation in Erectile Dysfunction and Premature Ejaculation. Phys. Ther. 2014, 94, 1731–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wespes, E.; Nogueira, M.C.; Herbaut, A.G.; Caufriez, M.; Schulman, C.C. Role of the Bulbocavernosus Muscles on the Mechanism of Human Erection. Eur. Urol. 1990, 18, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.M.; Nammur, L.G.; Mateus-Vasconcelos, E.C.L.; Ferreira, C.H.J.; Muglia, V.F.; de Oliveira, H.F. Pelvic Floor Muscles after Prostate Radiation Therapy: Morpho-Functional Assessment by Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Surface Electromyography and Digital Anal Palpation. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2021, 47, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, S.; Leydon, G.; Birch, B.; Prescott, P.; Lai, L.; Eardley, S.; Lewith, G. Depression and Anxiety in Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prevalence Rates. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e003901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavlarides, A.M.; Ames, S.C.; Diehl, N.N.; Joseph, R.W.; Castle, E.P.; Thiel, D.D.; Broderick, G.A.; Parker, A.S. Evaluation of the Association of Prostate Cancer-Specific Anxiety with Sexual Function, Depression and Cancer Aggressiveness in Men 1 Year Following Surgical Treatment for Localized Prostate Cancer. Psychooncology 2013, 22, 1328–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, S.R.; Speer, S.A.; Peters, S. Development of an Explanatory Model of Sexual Intimacy Following Treatment for Localised Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Synthesis of Qualitative Evidence. Soc. Sci. Med. 2016, 163, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Fort, M.K.; Suarez, P.; Carrion, M.; Weiner, D.; Postl, C.; Arribas, R.; Sayyah, M.; Forta, D.V.; Niaz, M.J.; Feily, A.; et al. Prostatic Irradiation-Induced Sexual Dysfunction: A Review and Multidisciplinary Guide to Management in the Radical Radiotherapy Era (Part III on Psychosexual Therapy and the Masculine Self-Esteem). Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2020, 25, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amico, A.V.; Manola, J.; Loffredo, M.; Renshaw, A.A.; DellaCroce, A.; Kantoff, P.W. 6-Month Androgen Suppression plus Radiation Therapy vs Radiation Therapy Alone for Patients with Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer: A Randomized Controlled Trial. JAMA 2004, 292, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.B.; Babaian, R.J. The Effects of Treatment for Cancer on Male Fertility and Sexuality. Cancer Nurs. 1992, 15, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelefsky, M.J.; Chan, H.; Hunt, M.; Yamada, Y.; Shippy, A.M.; Amols, H. Long-Term Outcome of High Dose Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy for Patients with Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer. J. Urol. 2006, 176, 1415–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teloken, P.E.; Ohebshalom, M.; Mohideen, N.; Mulhall, J.P. Analysis of the Impact of Androgen Deprivation Therapy on Sildenafil Citrate Response Following Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer. J. Urol. 2007, 178, 2521–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullins, B.T.; Basak, R.; Broughman, J.R.; Chen, R.C. Patient-Reported Sexual Quality of Life after Different Types of Radical Prostatectomy and Radiotherapy: Analysis of a Population-Based Prospective Cohort. Cancer 2019, 125, 3657–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, W.A.; Deshmukh, S.; Bruner, D.W.; Michalski, J.M.; Purdy, J.A.; Bosch, W.; Bahary, J.-P.; Patel, M.P.; Parliament, M.B.; Lock, M.I.; et al. Quality of Life Implications of Dose-Escalated External Beam Radiation for Localized Prostate Cancer: Results of a Prospective Randomized Phase 3 Clinical Trial, NRG/RTOG 0126. Int. J. Radiat Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022, 112, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, J.L.; Hamdy, F.C.; Lane, J.A.; Mason, M.; Metcalfe, C.; Walsh, E.; Blazeby, J.M.; Peters, T.J.; Holding, P.; Bonnington, S.; et al. Patient-Reported Outcomes after Monitoring, Surgery, or Radiotherapy for Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1425–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, F.R.; Wortel, R.C.; Wessels, F.J.; Claes, A.; van de Pol, S.M.G.; Rasing, M.J.A.; Meijer, R.P.; van Melick, H.H.E.; de Boer, J.C.J.; Verkooijen, H.M.; et al. Interrater Agreement of Contouring of the Neurovascular Bundles and Internal Pudendal Arteries in Neurovascular-Sparing Magnetic Resonance-Guided Radiotherapy for Localized Prostate Cancer. Clin. Transl. Radiat Oncol. 2022, 32, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearnaley, D.; Syndikus, I.; Mossop, H.; Khoo, V.; Birtle, A.; Bloomfield, D.; Graham, J.; Kirkbride, P.; Logue, J.; Malik, Z.; et al. Conventional versus Hypofractionated High-Dose Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy for Prostate Cancer: 5-Year Outcomes of the Randomised, Non-Inferiority, Phase 3 CHHiP Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1047–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incrocci, L.; Wortel, R.C.; Alemayehu, W.G.; Aluwini, S.; Schimmel, E.; Krol, S.; van der Toorn, P.-P.; de Jager, H.; Heemsbergen, W.; Heijmen, B.; et al. Hypofractionated versus Conventionally Fractionated Radiotherapy for Patients with Localised Prostate Cancer (HYPRO): Final Efficacy Results from a Randomised, Multicentre, Open-Label, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.R.; Dignam, J.J.; Amin, M.B.; Bruner, D.W.; Low, D.; Swanson, G.P.; Shah, A.B.; D’Souza, D.P.; Michalski, J.M.; Dayes, I.S.; et al. Randomized Phase III Noninferiority Study Comparing Two Radiotherapy Fractionation Schedules in Patients With Low-Risk Prostate Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2325–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catton, C.N.; Lukka, H.; Gu, C.-S.; Martin, J.M.; Supiot, S.; Chung, P.W.M.; Bauman, G.S.; Bahary, J.-P.; Ahmed, S.; Cheung, P.; et al. Randomized Trial of a Hypofractionated Radiation Regimen for the Treatment of Localized Prostate Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1884–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fransson, P.; Nilsson, P.; Gunnlaugsson, A.; Beckman, L.; Tavelin, B.; Norman, D.; Thellenberg-Karlsson, C.; Hoyer, M.; Lagerlund, M.; Kindblom, J.; et al. Ultra-Hypofractionated versus Conventionally Fractionated Radiotherapy for Prostate Cancer (HYPO-RT-PC): Patient-Reported Quality-of-Life Outcomes of a Randomised, Controlled, Non-Inferiority, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmusson, E.; Gunnlaugsson, A.; Wieslander, E.; Höglund, P.; Widmark, A.; Fransson, P.; Kjellén, E.; Nilsson, P. Erectile Dysfunction and Absorbed Dose to Penile Base Structures in a Randomized Trial Comparing Ultrahypofractionated and Conventionally Fractionated Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Radiat Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2020, 107, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baccaglini, W.; de Carvalho, I.T.; Glina, F.P.A.; Pazeto, C.L.; Marantes, A.; Nascimento, M.; Farias, A.; Mendez, L.C.; Tafuri, A.; Glina, S. Radiotherapy-Related Toxicity for Localized Prostate Cancer: Meta-Analysis Comparing Conventional or Moderately Hypofractionated vs. Ultrahypofractionated Protocols. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 24, 1425–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, W.A.; Tree, A.C.; Dearnaley, D.; Parker, C.C.; Prasad, V.; Roach, M.; Lawton, C.A.F. Considering Benefit and Risk before Routinely Recommending SpaceOAR. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babar, M.; Katz, A.; Ciatto, M. Dosimetric and Clinical Outcomes of SpaceOAR in Men Undergoing External Beam Radiation Therapy for Localized Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review. J. Med. Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2021, 65, 384–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, W.M.; Kurko, B.S.; Scholl, W.J.; Merrick, G.S. Effect of the Timing of Hydrogel Spacer Placement on Prostate and Rectal Dosimetry of Low-Dose-Rate Brachytherapy Implants. J. Contemp. Brachytherapy 2021, 13, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminsharifi, A.; Kotamarti, S.; Silver, D.; Schulman, A. Major Complications and Adverse Events Related to the Injection of the SpaceOAR Hydrogel System Before Radiotherapy for Prostate Cancer: Review of the Manufacturer and User Facility Device Experience Database. J. Endourol. 2019, 33, 868–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepe, P.; Tamburo, M.; Pennisi, M.; Marletta, D.; Marletta, F. Clinical Outcomes of Hydrogel Spacer Injection Space OAR in Men Submitted to Hypofractionated Radiotherapy for Prostate Cancer. In Vivo 2021, 35, 3385–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, P.; Tamburo, M.; Panella, P.; Pepe, L.; Marletta, G.; Pennisi, M.; Marletta, F. Erectile Dysfunction Following Hydrogel Injection and Hypofractionated Radiotherapy for Prostate Cancer: Our Experience in 56 Cases. Arch. Ital. Urol. Androl. 2022, 94, 166–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmark, A.; Gunnlaugsson, A.; Beckman, L.; Thellenberg-Karlsson, C.; Hoyer, M.; Lagerlund, M.; Kindblom, J.; Ginman, C.; Johansson, B.; Björnlinger, K.; et al. Ultra-Hypofractionated versus Conventionally Fractionated Radiotherapy for Prostate Cancer: 5-Year Outcomes of the HYPO-RT-PC Randomised, Non-Inferiority, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, D.H.; Tree, A.C.; Ostler, P.; van der Voet, H.; Loblaw, A.; Chu, W.; Ford, D.; Tolan, S.; Jain, S.; Martin, A.; et al. Intensity-Modulated Fractionated Radiotherapy versus Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Prostate Cancer (PACE-B): Acute Toxicity Findings from an International, Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 3, Non-Inferiority Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1531–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, C.K.; Bryant, C.M.; Mendenhall, N.P.; Henderson, R.H.; Mendenhall, W.M.; Nichols, R.C.; Morris, C.G.; Kanmaniraja, D.; Hamlin, D.J.; Li, Z.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes Following Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer in Young Men with a Focus on Sexual Health. Acta Oncol. 2018, 57, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salonia, A.; Bettocchi, C.; Boeri, L.; Capogrosso, P.; Carvalho, J.; Cilesiz, N.C.; Cocci, A.; Corona, G.; Dimitropoulos, K.; Gül, M.; et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Sexual and Reproductive Health-2021 Update: Male Sexual Dysfunction. Eur. Urol. 2021, 80, 333–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzimouratidis, K.; Salonia, A.; Adaikan, G.; Buvat, J.; Carrier, S.; El-Meliegy, A.; McCullough, A.; Torres, L.O.; Khera, M. Pharmacotherapy for Erectile Dysfunction: Recommendations From the Fourth International Consultation for Sexual Medicine (ICSM 2015). J. Sex Med. 2016, 13, 465–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, M.J.; Ramirez-Fort, M.K.; Kashanian, J.A.; Broster, S.A.; Matta, J.; Mahase, S.S.; Fort, D.V.; Niaz, M.J.; McClelland, S.; Bander, N.H.; et al. Prostatic Irradiation-Induced Sexual Dysfunction: A Review and Multidisciplinary Guide to Management in the Radical Radiotherapy Era (Part II on Urological Management). Rep. Pract Oncol. Radiother. 2020, 25, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedia, S.; Zippe, C.D.; Agarwal, A.; Nelson, D.R.; Lakin, M.M. Treatment of Erectile Dysfunction with Sildenafil Citrate (Viagra) after Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer. Urology 1999, 54, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, D.C.; Bieri, S.; Kurtz, J.M.; Miralbell, R. Prospective Pilot Study of Sildenafil for Treatment of Postradiotherapy Erectile Dysfunction in Patients with Prostate Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 1999, 17, 3444–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelefsky, M.J.; McKee, A.B.; Lee, H.; Leibel, S.A. Efficacy of Oral Sildenafil in Patients with Erectile Dysfunction after Radiotherapy for Carcinoma of the Prostate. Urology 1999, 53, 775–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrick, G.S.; Butler, W.M.; Lief, J.H.; Stipetich, R.L.; Abel, L.J.; Dorsey, A.T. Efficacy of Sildenafil Citrate in Prostate Brachytherapy Patients with Erectile Dysfunction. Urology 1999, 53, 1112–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valicenti, R.K.; Choi, E.; Chen, C.; Lu, J.D.; Hirsch, I.H.; Mulholland, G.S.; Gomella, L.G. Sildenafil Citrate Effectively Reverses Sexual Dysfunction Induced by Three-Dimensional Conformal Radiation Therapy. Urology 2001, 57, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watkins Bruner, D.; James, J.L.; Bryan, C.J.; Pisansky, T.M.; Rotman, M.; Corbett, T.; Speight, J.; Byhardt, R.; Sandler, H.; Bentzen, S.; et al. Randomized, Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled Crossover Trial of Treating Erectile Dysfunction with Sildenafil after Radiotherapy and Short-Term Androgen Deprivation Therapy: Results of RTOG 0215. J. Sex Med. 2011, 8, 1228–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilic, D.; Hindson, B.; Duchesne, G.; Millar, J.L. A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Nightly Sildenafil Citrate to Preserve Erectile Function after Radiation Treatment for Prostate Cancer. J. Med. Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2013, 57, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisansky, T.M.; Pugh, S.L.; Greenberg, R.E.; Pervez, N.; Reed, D.R.; Rosenthal, S.A.; Mowat, R.B.; Raben, A.; Buyyounouski, M.K.; Kachnic, L.A.; et al. Tadalafil for Prevention of Erectile Dysfunction after Radiotherapy for Prostate Cancer: The Radiation Therapy Oncology Group [0831] Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2014, 311, 1300–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incrocci, L.; Koper, P.C.; Hop, W.C.; Slob, A.K. Sildenafil Citrate (Viagra) and Erectile Dysfunction Following External Beam Radiotherapy for Prostate Cancer: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Cross-over Study. Int. J. Radiat Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2001, 51, 1190–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricardi, U.; Gontero, P.; Ciammella, P.; Badellino, S.; Valentino, F.; Munoz, F.; Guarneri, A.; Rondi, N.; Moretto, F.; Filippi, A.R.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Tadalafil 20 Mg on Demand vs. Tadalafil 5 Mg Once-a-Day in the Treatment of Post-Radiotherapy Erectile Dysfunction in Prostate Cancer Men: A Randomized Phase II Trial. J. Sex Med. 2010, 7, 2851–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolai, M.; Urkmez, A.; Sarikaya, S.; Fode, M.; Falcone, M.; Albersen, M.; Gul, M.; Hatzichristodoulou, G.; Capogrosso, P.; Russo, G.I. Penile Rehabilitation and Treatment Options for Erectile Dysfunction Following Radical Prostatectomy and Radiotherapy: A Systematic Review. Front. Surg. 2021, 8, 636974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, C.; Omran, G.J.; Teh, J.; Davis, N.F.; Bolton, D.M.; Lawrentschuk, N. Erectile Dysfunction: A Global Review of Intracavernosal Injectables. World J. Urol. 2019, 37, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Hoang, A.N.; Romero, C.A.; Lin, H.; Dai, Y.; Wang, R. Vacuum Therapy in Erectile Dysfunction--Science and Clinical Evidence. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2010, 22, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Lopez, D.S.; Chen, M.; Wang, R. Penile Rehabilitation Therapy Following Radical Prostatectomy: A Meta-Analysis. J. Sex Med. 2017, 14, 1496–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardo-Filho, M.; Barbosa Júnior, M.L.; da Cunha Sá-Caputo, D.; de Aguiar, E.d.O.G.; de Lima, R.P.C.; Santos-Filho, S.D.; de Paoli, S.; Presta, G.A.; de Oliveira Bravo Monteiro, M.; Tavares, Â. The Relevance of the Procedures Related to the Physiotherapy in the Interventions in Patients with Prostate Cancer: Short Review with Practice Approach. Int. J. Biomed. Sci. 2014, 10, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bajic, P.; Mahon, J.; Faraday, M.; Sadeghi-Nejad, H.; Hakim, L.; McVary, K.T. Etiology of Erectile Dysfunction and Duration of Symptoms in Patients Undergoing Penile Prosthesis: A Systematic Review. Sex Med. Rev. 2020, 8, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raheem, O.A.; Natale, C.; Dick, B.; Reddy, A.G.; Yousif, A.; Khera, M.; Baum, N. Novel Treatments of Erectile Dysfunction: Review of the Current Literature. Sex Med. Rev. 2021, 9, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiadis, E.; Ahmed, R.; Khoja, A.K.; Yap, T. Erectile Dysfunction: Is Platelet-Rich Plasma the New Frontier for Treatment in Patients with Erectile Dysfunction? A Review of the Existing Evidence. Front. Reprod. Health 2022, 4, 944765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, E. Regenerative Technology to Restore and Preserve Erectile Function in Men Following Prostate Cancer Treatment: Evidence for Penile Rehabilitation in the Context of Prostate Cancer Survivorship. Ther. Adv. Urol. 2021, 13, 17562872211026420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, E.; Wang, J. A State-of-Art Review of Low Intensity Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy and Lithotripter Machines for the Treatment of Erectile Dysfunction. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2017, 14, 929–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zewin, T.S.; El-Assmy, A.; Harraz, A.M.; Bazeed, M.; Shokeir, A.A.; Sheir, K.; Mosbah, A. Efficacy and Safety of Low-Intensity Shock Wave Therapy in Penile Rehabilitation Post Nerve-Sparing Radical Cystoprostatectomy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2018, 50, 2007–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, A.; Sønksen, J.; Fode, M. Low-Intensity Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy in the Treatment of Postprostatectomy Erectile Dysfunction: A Pilot Study. Scand J. Urol. 2016, 50, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, S.; Roberts, M.; Chung, E. Platelet-Rich Plasma and Treatment of Erectile Dysfunction: Critical Review of Literature and Global Trends in Platelet-Rich Plasma Clinics. Sex Med. Rev. 2019, 7, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epifanova, M.V.; Gvasalia, B.R.; Durashov, M.A.; Artemenko, S.A. Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapy for Male Sexual Dysfunction: Myth or Reality? Sex Med. Rev. 2020, 8, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, M.; Anitua, E.; Delgado, D.; Sanchez, P.; Prado, R.; Orive, G.; Padilla, S. Platelet-Rich Plasma, a Source of Autologous Growth Factors and Biomimetic Scaffold for Peripheral Nerve Regeneration. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2017, 17, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.-N.; Wu, C.-C.; Sheu, M.-T.; Chen, K.-C.; Ho, H.-O.; Chiang, H.-S. Optimization of Platelet-Rich Plasma and Its Effects on the Recovery of Erectile Function after Bilateral Cavernous Nerve Injury in a Rat Model. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2016, 10, E294–E304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matz, E.L.; Pearlman, A.M.; Terlecki, R.P. Safety and Feasibility of Platelet Rich Fibrin Matrix Injections for Treatment of Common Urologic Conditions. Investig. Clin. Urol. 2018, 59, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-C.; Wu, Y.-N.; Ho, H.-O.; Chen, K.-C.; Sheu, M.-T.; Chiang, H.-S. The Neuroprotective Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Erectile Function in Bilateral Cavernous Nerve Injury Rat Model. J. Sex Med. 2012, 9, 2838–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.-G.; Li, S.-W.; Zheng, X.-M.; Hu, L.-Q.; Hu, W.-L.; Luo, Y. The Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Cavernous Nerve Regeneration in a Rat Model. Asian J. Androl. 2009, 11, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, S.; Piek, E.; Fujii, M.; Javelaud, D.; Mauviel, A.; Flanders, K.C.; Samuni, A.M.; Felici, A.; Reiss, M.; Yarkoni, S.; et al. Amelioration of Radiation-Induced Fibrosis: Inhibition of Transforming Growth Factor-Beta Signaling by Halofuginone. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 15167–15176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anscher, M.S.; Thrasher, B.; Rabbani, Z.; Teicher, B.; Vujaskovic, Z. Antitransforming Growth Factor-Beta Antibody 1D11 Ameliorates Normal Tissue Damage Caused by High-Dose Radiation. Int. J. Radiat Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2006, 65, 876–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anscher, M.S.; Thrasher, B.; Zgonjanin, L.; Rabbani, Z.N.; Corbley, M.J.; Fu, K.; Sun, L.; Lee, W.-C.; Ling, L.E.; Vujaskovic, Z. Small Molecular Inhibitor of Transforming Growth Factor-Beta Protects against Development of Radiation-Induced Lung Injury. Int. J. Radiat Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2008, 71, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melman, A. Gene Therapy for Male Erectile Dysfunction. Urol. Clin. N. Am. 2007, 34, 619–630, viii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harraz, A.; Shindel, A.W.; Lue, T.F. Emerging Gene and Stem Cell Therapies for the Treatment of Erectile Dysfunction. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2010, 7, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-S.; Xin, Z.; Dai, J.; Huang, Y.-C.; Lue, T.F. Stem-Cell Therapy for Erectile Dysfunction. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2013, 13, 1585–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, E. Stem-Cell-Based Therapy in the Field of Urology: A Review of Stem Cell Basic Science, Clinical Applications and Future Directions in the Treatment of Various Sexual and Urinary Conditions. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2015, 15, 1623–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Labate, C.; Panunzio, A.; De Carlo, F.; Zacheo, F.; De Matteis, S.; Barba, M.C.; Carbonara, U.; Rizzo, F.L.; Leo, S.; Forte, S.; et al. Current Knowledge on Radiation-Therapy-Induced Erectile Dysfunction in Prostate-Cancer Patients: A Narrative Review. Uro 2023, 3, 104-116. https://doi.org/10.3390/uro3020013
Labate C, Panunzio A, De Carlo F, Zacheo F, De Matteis S, Barba MC, Carbonara U, Rizzo FL, Leo S, Forte S, et al. Current Knowledge on Radiation-Therapy-Induced Erectile Dysfunction in Prostate-Cancer Patients: A Narrative Review. Uro. 2023; 3(2):104-116. https://doi.org/10.3390/uro3020013
Chicago/Turabian StyleLabate, Connie, Andrea Panunzio, Francesco De Carlo, Federico Zacheo, Sara De Matteis, Maria Cristina Barba, Umberto Carbonara, Floriana Luigina Rizzo, Silvana Leo, Saverio Forte, and et al. 2023. "Current Knowledge on Radiation-Therapy-Induced Erectile Dysfunction in Prostate-Cancer Patients: A Narrative Review" Uro 3, no. 2: 104-116. https://doi.org/10.3390/uro3020013
APA StyleLabate, C., Panunzio, A., De Carlo, F., Zacheo, F., De Matteis, S., Barba, M. C., Carbonara, U., Rizzo, F. L., Leo, S., Forte, S., Ditonno, P., Tafuri, A., & Pagliarulo, V. (2023). Current Knowledge on Radiation-Therapy-Induced Erectile Dysfunction in Prostate-Cancer Patients: A Narrative Review. Uro, 3(2), 104-116. https://doi.org/10.3390/uro3020013







