Exploring the Role of Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics in the Treatment of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease—A Scoping Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
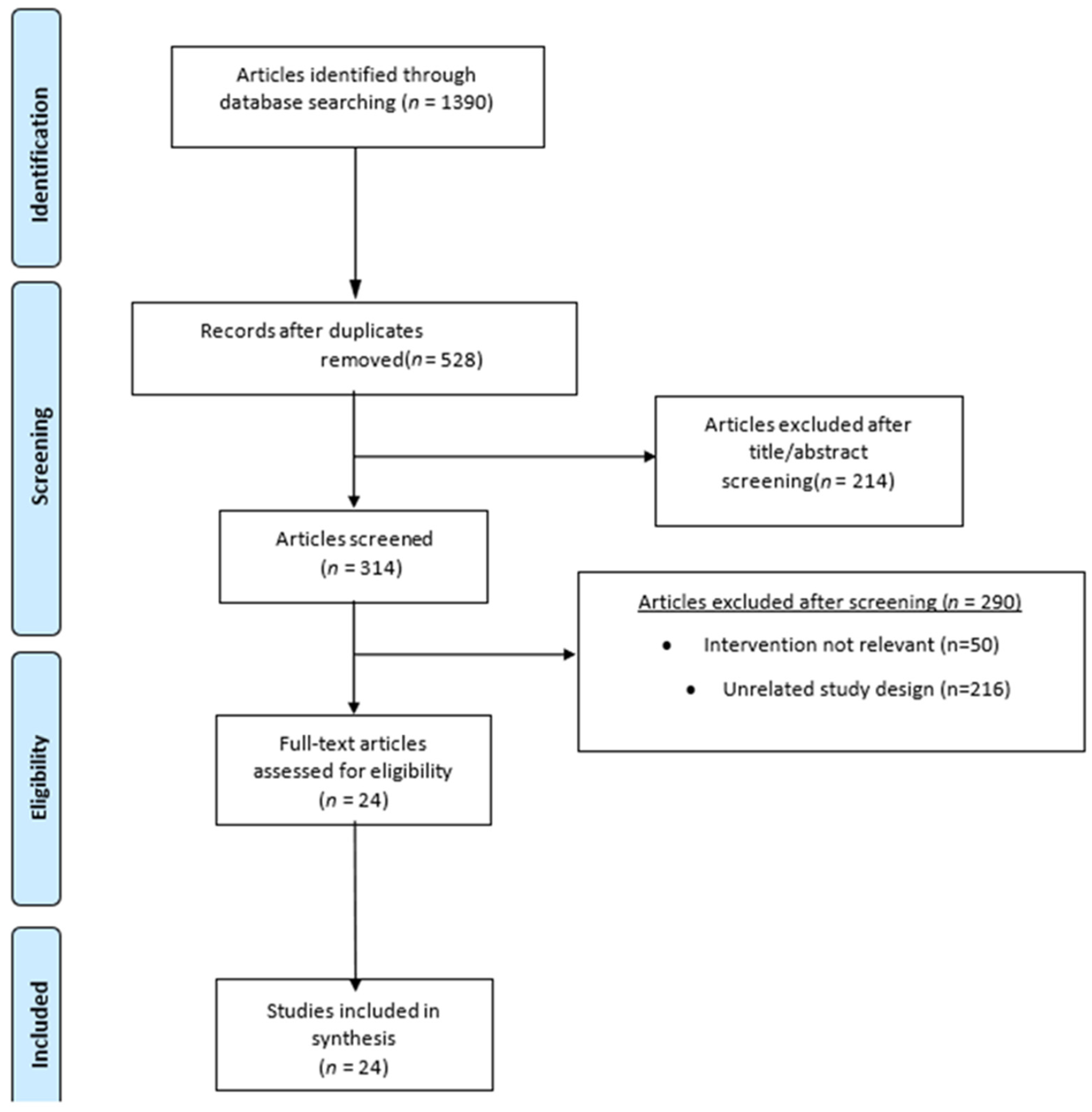
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Sample
3.3. Randomization Process
3.4. Evaluation of Risks of Bias
| Study | Sample | Intervention | Duration | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Escouto et al., 2023 (Brazil) [38] NCT02764047 | 8 | Probiotics (Lactobacillus acidophilus Bifidobacterium lactis) vs. Placebo | 6 months | Reduced AST to Platelet Ratio Index (APRI) score; no microbiota change. Glucose: no statistically significant differences between groups at the end of the study. |
| Behrouz et al., 2020 (Iran) [24] IRCT201410052394N13. | 89 | Probiotics (Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bifidobacterium longum, and Bifidobacterium breve), Prebiotics (Oligofructose; ORAFTI P95), Control | 12 weeks | Lower ALT, AST, GGT in probiotic group. Lower TG, total cholesterol, ALT, AST, GGT in prebiotic group. No significant alterations in the levels of Glu. |
| Ahn et al., 2019 (Korea) [37] CT0001588 | 65 | Probiotics (Lactobacillus acidophilus, L. rhamnosus, L. paracasei, Pediococcus pentosaceus, Bifidobacterium lactis, and B. breve) vs. Placebo | 12 weeks | Reduced intrahepatic fat fraction (IHF), TG, Glu values did not change in either group. |
| Kobyliak et al., 2018 (Ukraine) [33] NCT03434860 | 58 | Multi-probiotic (Lactobacillus + Lactococcus, Bifidobacterium, Propionibacterium, Acetobacter) vs. Placebo | 8 weeks | Lower FLI, AST, GGT, TNF-α, IL-6. |
| Scorletti et al., 2022 (UK) [31] NCT01680640 | 104 | Synbiotics (fructo-oligosaccharides (4 g/twice day) + Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BB-12) vs. Placebo | 12 months | No liver fat change; weight loss linked with synbiotics. Glu: no statistically significant differences between groups at the end of the study. |
| Manzhalii et al., 2019 (Ukraine) [34] The trial was not registered in a publicly accessible database | 75 | Probiotic cocktail (Lactobacillus casei, L. rhamnosus, L. bulgaricus, Bifidobacterium longum, Streptococcus thermophilus and fructooligosaccharides (LBSF)) vs. Control | 12 weeks | Lower ALT, stiffness; GGT unchanged. Decreased BMI and serum cholesterol levels, serum glucose remained constantly within the normal range between groups. |
| Mofidi et al., 2017 (Iran) [24] NCT02530138 | 50 | Synbiotic (Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Streptococcus thermophilus, Bifidobacterium breve, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bifidobacterium longum and Lactobacillus bulgaricus) and prebiotic (125 mg fructo-oligosaccharide) vs. Placebo | 28 weeks | Reduced steatosis, inflammation, TAG. |
| Mohamad Nor et al., 2021 (Malaysia) [40] NCT04074889 | 39 | Multi-strain probiotics (six different Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium species) vs. Placebo | 6 months | No change in steatosis and fibrosis; fasting glucose did not show any significant differences within both groups after the Intervention. |
| Mantri et al., 2024 (Germany) [35] The trial was pre-registered at Open Science Framework (https://osf.io/utsn4) | 117 | Synbiotic (Bifidobacterium lactis, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus salivarius, and Lactococcus lactis) vs. Placebo | 7 weeks | Reduced ALT; alteration in microbiome composition. |
| Nabavi et al., 2014 (Iran) [25] Not registered | 72 | Probiotic yogurt (Lactobacillus acidophilus La5 and Bifidobacterium lactis Bb12) vs. Conventional | 8 weeks | Lower ALT, AST, TC, LDL. Changes in serum. Glucose levels were not significant. |
| Duseja et al., 2019 (India) [44] No. CTRI/2008/091/000074 | 39 | Probiotics (each capsule containing 112.5 billion live, lyophilised, lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria, namely Lactobacillus paracasei DSM 24733, Lactobacillus plantarum DSM 24730, Lactobacillus acidophilus DSM 24735, and Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus DSM 24734, Bifidobacterium longum DSM 24736, Bifidobacterium infantis DSM 24737, Bifidobacterium breve DSM 24732, and Streptococcus thermophilus DSM 24731) + Lifestyle mod. | 1 year | Improved hepatocyte balloning, lobullar inflammation, NAS, ALT; lower TNF-α. No significant change in the HOMA-IR levels in both groups of patients at 3 and 12 months. |
| Aller et al., 2011 (Spain) [42] Not registered | 30 | Probiotics (Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus) vs. Placebo | 3 months | Reduced ALT, AST, GGT. |
| Derosa et al., 2022 (Italy) [43] Not registered | 60 | VSL#3® (one strain of Streptococcus thermophilus BT01, three strains of Bifidobacteria (B. breve BB02; B. animalis subspecies [subsp.] lactis BL03, previously identified as B. longum BL03; and B. animalis subsp. lactis BI04, previously identified as B. infantis BI04), and four strains of Lactobacilli (L. acidophilus BA05, L. plantarum BP06, L. paracasei BP07, and L. helveticus BD08, previously identified as L. delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus BD08) vs. Placebo | 3 months | Lower TG, hs-CRP, transaminases, GGT, (AST)/alanine aminotransferase (ALT) ratio, and hepatic steatosis index (HSI). Non-significant decrease in fasting plasma glucose (FPG) in intervention group. |
| Chong et al., 2021 (UK) [32] ISRCTN05474560 | Unknown | VSL#3® (one strain of Streptococcus thermophilus BT01, three strains of Bifidobacteria (B. breve BB02; B. animalis subspecies [subsp.] lactis BL03, previously identified as B. longum BL03; and B. animalis subsp. lactis BI04, previously identified as B. infantis BI04), and four strains of Lactobacilli (L. acidophilus BA05, L. plantarum BP06, L. paracasei BP07, and L. helveticus BD08, previously identified as L. delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus BD08) vs. Placebo | 10 weeks | Improved biomarkers related to cardiovascular risk. |
| Sepideh et al., 2015 (Iran) [26] IRCT: 2012122911920N1 | 42 | Probiotic capsules (Lactobacillus casei 3 × 109 CFU/g, Lactobacillus acidophilus 3 × 1010 CFU/g, Lactobacillus rhamnosus 7 × 109 CFU/g, Lactobacillus bulgaricus 5 × 108 CFU/g, Bifidobacterium breve 2 × 1010 CFU/g, Bifidobacterium longum 1 × 109 CFU/g, and Streptococcus thermophilus 3 × 108 CFU/g) vs. Placebo | 8 weeks | Lower insulin, insulin resistance, TNF-a, and IL-6. |
| Mitrovic et al., 2024 (Serbia) [41] Not registered | 84 | Synbiotic (Lactobacillus acidophilus CBT LA1 (16 × 109), Lactobacillus casei CBT LC5 (16 × 109) and Bifidobacterium lactis CBT BL3 (32 × 109) with 6.4 g of inulin) vs. Placebo | 12 weeks | Reduced steatosis, hs-CRP. |
| Abhari et al., 2020 (Iran) [27] IRCT20100524004010N23 | 45 | Synbiotic (B. coagulans and inulin) vs. Placebo | 12 weeks | Lower ALT, GGT, TNF-α, nuclear factor-kB activity. Non-significant Glu decrease. |
| Eslamparast et al., 2014 (Iran) [28] NCT01791959 | 52 | Synbiotic (Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Streptococcus thermophilus, Bifidobacterium breve, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bifidobacterium longum, and Lactobacillus bulgaricus) and prebiotic (fructooligosaccharide) and probiotic cultures [magnesium stearate (source: mineral and vegetable) and a vegetable capsule (hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose)] vs. Placebo | 28 weeks | Reduced ALT, AST, GGT, hs-CRP, TNF-α, and fibrosis score. |
| Bakhshimoghaddam et al., 2018 (Iran) [29] IRCT2017020932417N2 | 102 | Synbiotic yogurt (Bifidobacterium animalis/mL and 1.5 g inulin) vs. Control | 24 weeks | Lower NAFLD grade, ALT, AST, GGT, and alkaline phosphatase. Non-significant Glu decrease. |
| Javadi et al., 2018 (Iran) [22] IRCT201301223140N6 | 75 | Probiotics (Bifidobacterium longum (B.L) and Lactobacillus acidophilus (L.A), Prebiotics, Combo | 3 months | Lower ALT, AST, hs-CRP, TNF-a, and TAC with the combination of pro- and prebiotics. |
| Crommen et al., 2022 (Germany) [36] NCT03585413 | 60 | Probiotics (Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bifidobacterium breve, B. longum, L. delbrueckii susp. bulgaricus, L. helveticus, L. plantarum, L. rhamnosus, L. casei, Lactococcus lactis susp. lactis, and Streptococcus thermophiles) + Micronutrients vs. Control | 12 weeks | Better NAFLD fibrosis score, TG, and the visceral adiposity index. Changes in the HbA1c concentrations did not differ between groups after 12 wk. Fasting glucose, insulin concentrations, and HOMA-IR were not affected by either supplementation protocol. |
| Asgharian et al., 2016 (Iran) [30] IRCT2013122811763N15 | 80 | Synbiotic capsules (Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Lactobacillus bulgaricus, Bifidobacterium breve, Bifidobacterium longum, Streptococcus thermophilus) vs. Placebo | 8 weeks | Lower steatosis grade with synbiotic treatment. |
| Alam et al., 2022 (Bangladesh) [39] No. BSMMU/2017/12512 | 85 | Probiotics (Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Streptococcus thermophilus, Bifidobacterium breve, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bifidobacterium longum, and Lactobacillus bulgaricus) vs. Placebo with adjunct dietary modifications | 6 months | Significant improvement in liver function and reduced ALT, AST, and inflammation markers. No effect of probiotics on the glucose levels of both obese and non-obese patients. |
| Study | Selection Bias | Performance Bias | Attrition Bias | Detection Bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Escouto et al., 2023/Brazil [38] | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Unclear/unknown risk |
| Behrouz et al., 2020/Iran [24] | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk |
| Ahn et al., 2019/Korea [37] | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk |
| Kobyliak et al., 2018/Ukraine [33] | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk |
| Scorletti et al., 2022/UK [31] | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk |
| Alam et al., 2022/Bangladesh [39] | High risk | Unclear/unknown risk | Low risk | Unclear/unknown risk |
| Manzhalii et al., 2019/Ukraine [34] | High risk | Unclear/unknown risk | Low risk | Unclear/unknown risk |
| Mofidi et al., 2017/Iran [24] | Unclear/unknown risk | Unclear/unknown risk | Low risk | Unclear/unknown risk |
| Mohamad Nor et al., 2021/Malaysia [40] | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk |
| Mantri et al., 2024/Germany [35] | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk |
| Nabavi et al., 2014/Iran [25] | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk |
| Scorletti et al., 2020/UK [31] | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk |
| Sepideh et al., 2015/Iran [26] | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk |
| Mitrovic et al., 2024/Serbia [41] | Low risk | Unclear/unknown risk | Low risk | Unclear/unknown risk |
| Abhari et al., 2020/Iran [27] | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk |
| Eslamparast et al., 2014/Iran [28] | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk |
| Bakhshimoghaddam et al., 2018/Iran [29] | Low risk | Unclear/unknown risk | Low risk | Low risk |
| Aller et al., 2011/Spain [42] | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk |
| Javadi et al., 2018/Iran [22] | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk |
| Crommen et al., 2022/Germany [36] | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk |
| Derosa et al., 2022/Italy [43] | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk |
| Asgharian et al., 2016/Iran [30] | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk |
| Chong et al., 2021/UK [32] | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk |
| Duseja et al., 2019/India [44] | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk |
3.5. Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics
3.6. Hepatic Steatosis and Fibrosis Markers
3.7. Hepatic Function
3.8. Lipid Profiles
3.9. Inflammation Markers
3.10. Glucose Homeostasis
4. Discussion
Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karlsen, T.H.; Sheron, N.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Carrieri, P.; Dusheiko, G.; Bugianesi, E.; Pryke, R.; Hutchinson, S.J.; Sangro, B.; Martin, N.K.; et al. The EASL–Lancet Liver Commission: Protecting the next Generation of Europeans against Liver Disease Complications and Premature Mortality. Lancet 2022, 399, 61–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, W.K.; Chuah, K.H.; Rajaram, R.B.; Lim, L.L.; Ratnasingam, J.; Vethakkan, S.R. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): A State-of-the-Art Review. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2023, 32, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinella, M.E.; Lazarus, J.V.; Ratziu, V.; Francque, S.M.; Sanyal, A.J.; Kanwal, F.; Romero, D.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arab, J.P.; et al. A Multisociety Delphi Consensus Statement on New Fatty Liver Disease Nomenclature. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 1542–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, M.H.; Yeo, Y.H.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Zou, B.; Wu, Y.; Ye, Q.; Huang, D.Q.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, J.; et al. 2019 Global NAFLD Prevalence: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 2809–2817.e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, Y.; Cho, Y.J.; Nam, G.E. Recent Epidemiology and Risk Factors of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2022, 31, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Allen, A.M.; Wang, Z.; Prokop, L.J.; Murad, M.H.; Loomba, R. Fibrosis Progression in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver vs. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Paired-Biopsy Studies. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 643–654.e1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.-K.; Treeprasertsuk, S.; Imajo, K.; Nakajima, A.; Seki, Y.; Kasama, K.; Kakizaki, S.; Fan, J.-G.; Song, M.J.; Yoon, S.K.; et al. Clinical Features and Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease across the Asia Pacific Region—The GO ASIA Initiative. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 47, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global Epidemiology of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Meta-Analytic Assessment of Prevalence, Incidence, and Outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrani, S.; Gill, S.S.; Sooi, C.Y.; Skantha, R.; Kumar, C.V.C.; Limun, M.F.; Affendi, N.A.N.M.; Chuah, K.H.; Khoo, S.; Rajaram, R.B.; et al. Frequency of Significant Steatosis and Compensated Advanced Chronic Liver Disease among Adults with Chronic Liver Disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 38, 1818–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, M.; Melaku, M.; Liu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Everaert, N.; Yi, B.; Zhang, H. Intestinal Dysbiosis in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Focusing on the Gut–Liver Axis. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 1689–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, F.; Khan, S.; Fredrickson, G.; Wang, H.; Dietsche, K.; Parthiban, P.; Robert, S.; Kaiser, T.; Winer, S.; Herman, A.; et al. Microbiota-Driven Activation of Intrahepatic B Cells Aggravates NASH Through Innate and Adaptive Signaling. Hepatology 2021, 74, 704–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.; Zhang, X. The Role of Gut–Liver Axis in Gut Microbiome Dysbiosis Associated NAFLD and NAFLD-HCC. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasinariu, O.E.; Ceccarelli, S.; Alisi, A.; Moraru, E.; Nobili, V. Gut–Liver Axis and Fibrosis in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: An Input for Novel Therapies. Dig. Liver Dis. 2013, 45, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albillos, A.; de Gottardi, A.; Rescigno, M. The Gut–Liver Axis in Liver Disease: Pathophysiological Basis for Therapy. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 558–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paolella, G.; Mandato, C.; Pierri, L.; Poeta, M.; Di Stasi, M.; Vajro, P. Gut–Liver Axis and Probiotics: Their Role in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 15518–15531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.; Sardi, J.; Pitangui, N.; MagreRoque, S.; Silva, A.; Rosalen, P. Probiotics as an Alternative Antimicrobial Therapy: Current Reality and Future Directions. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 73, 104080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlawat, S.; Asha; Sharma, K.K. Gut–Organ Axis: A Microbial Outreach and Networking. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 72, 636–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowiak, P.; Śliżewska, K. Effects of Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics on Human Health. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munn, Z.; Peters, M.D.J.; Stern, C.; Tufanaru, C.; McArthur, A.; Aromataris, E. Systematic Review or Scoping Review? Guidance for Authors When Choosing between a Systematic or Scoping Review Approach. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2018, 18, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arksey, H.; O’Malley, L. Scoping Studies: Towards a Methodological Framework. Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. 2005, 8, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Javadi, L.; Khoshbaten, M.; Safaiyan, A.; Ghavami, M.; Abbasi, M.M.; Gargari, B.P. Pro- and Prebiotic Effects on Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Markers in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 27, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrouz, V.; Aryaeian, N.; Zahedi, M.J.; Jazayeri, S. Effects of Probiotic and Prebiotic Supplementation on Metabolic Parameters, Liver Aminotransferases, and Systemic Inflammation in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 3611–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mofidi, F.; Poustchi, H.; Yari, Z.; Nourinayyer, B.; Merat, S.; Sharafkhah, M.; Malekzadeh, R.; Hekmatdoost, A. Synbiotic Supplementation in Lean Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Pilot, Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Clinical Trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabavi, S.; Rafraf, M.; Somi, M.H.; Homayouni-Rad, A.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M. Effects of Probiotic Yogurt Consumption on Metabolic Factors in Individuals with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 7386–7393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepideh, A.; Karim, P.; Hossein, A.; Leila, R.; Hamdollah, M.; Mohammad, E.G.; Mojtaba, S.; Mohammad, S.; Ghader, G.; Seyed Moayed, A. Effects of Multistrain Probiotic Supplementation on Glycemic and Inflammatory Indices in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Double-Blind Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2016, 35, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abhari, K.; Shekarforoush, S.S.; Sajedianfard, J.; Hosseinzadeh, S.; Nazifi, S. The Effects of Probiotic, Prebiotic and Synbiotic Diets Containing Bacillus coagulans and Inulin on Rat Intestinal Microbiota. Iran. J. Vet. Res. 2015, 16, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eslamparast, T.; Poustchi, H.; Zamani, F.; Sharafkhah, M.; Malekzadeh, R.; Hekmatdoost, A. Synbiotic Supplementation in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Pilot Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshimoghaddam, F.; Shateri, K.; Sina, M.; Hashemian, M.; Alizadeh, M. Daily Consumption of Synbiotic Yogurt Decreases Liver Steatosis in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 1276–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgharian, A.; Askari, G.; Esmailzade, A.; Feizi, A.; Mohammadi, V. The Effect of Symbiotic Supplementation on Liver Enzymes, C-reactive Protein and Ultrasound Findings in Patients with Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Clinical Trial. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2016, 7, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Scorletti, E.; Afolabi, P.R.; Miles, E.A.; Smith, D.E.; Almehmadi, A.; Alshathry, A.; Childs, C.E.; Del Fabbro, S.; Bilson, J.; Moyses, H.E.; et al. Synbiotics Alter Fecal Microbiomes, But Not Liver Fat or Fibrosis, in a Randomized Trial of Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1597–1610.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, P.L.; Laight, D.; Aspinall, R.J.; Higginson, A.; Cummings, M.H. A Randomised Placebo-Controlled Trial of VSL#3® Probiotic on Biomarkers of Cardiovascular Risk and Liver Injury in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021, 21, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobyliak, N.; Abenavoli, L.; Mykhalchyshyn, G.; Kononenko, L.; Boccuto, L.; Kyriienko, D.; Dynnyk, O. A Multi-Strain Probiotic Reduces the Fatty Liver Index, Cytokines and Aminotransferase Levels in NAFLD Patients: Evidence from a Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Gastrointestin. Liver Dis. 2018, 27, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzhalii, E.; Virchenko, O.; Falalyeyeva, T.; Beregova, T.; Stremmel, W. Treatment Efficacy of a Probiotic Preparation for Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Pilot Trial. J. Dig. Dis. 2017, 18, 698–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantri, A.; Köhlmoos, A.; Schelski, D.S.; Seel, W.; Stoffel-Wagner, B.; Krawitz, P.; Stehle, P.; Holst, J.J.; Weber, B.; Koban, L.; et al. Impact of Synbiotic Intake on Liver Metabolism in Metabolically Healthy Participants and Its Potential Preventive Effect on Metabolic-Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD): A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blinded Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crommen, S.; Rheinwalt, K.P.; Plamper, A.; Simon, M.-C.; Rösler, D.; Fimmers, R.; Egert, S.; Metzner, C. A Specifically Tailored Multistrain Probiotic and Micronutrient Mixture Affects Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease–Related Markers in Patients with Obesity after Mini Gastric Bypass Surgery. J. Nutr. 2022, 152, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.B.; Jun, D.W.; Kang, B.-K.; Lim, J.H.; Lim, S.; Chung, M.-J. Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study of a Multispecies Probiotic Mixture in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escouto, G.S.; Port, G.Z.; Tovo, C.V.; Fernandes, S.A.; Peres, A.; Dorneles, G.P.; Houde, V.P.; Varin, T.V.; Pilon, G.; Marette, A.; et al. Probiotic Supplementation, Hepatic Fibrosis, and the Microbiota Profile in Patients with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Nutr. 2023, 153, 1984–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.; Datta, P.K.; Alam, M.; Hasan, M.J. Effect of Probiotics Supplementation on Liver Stiffness and Steatosis in Patients with NAFLD. Hepatol. Forum 2024, 5, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad Nor, M.H.; Ayob, N.; Mokhtar, N.M.; Raja Ali, R.A.; Tan, G.C.; Wong, Z.; Shafiee, N.H.; Wong, Y.P.; Mustangin, M.; Nawawi, K.N.M. The Effect of Probiotics (MCP® BCMC® Strains) on Hepatic Steatosis, Small Intestinal Mucosal Immune Function, and Intestinal Barrier in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrović, M.; Dobrosavljević, A.; Odanović, O.; Knežević-Ivanovski, T.; Kralj, Đ.; Erceg, S.; Perućica, A.; Svorcan, P.; Stanković-Popović, V. The Effects of Synbiotics on the Liver Steatosis, Inflammation, and Gut Microbiome of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Liver Disease Patients—Randomized Trial. Rom. J. Intern. Med. 2024, 62, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aller, R.; De Luis, D.A.; Izaola, O.; Conde, R.; Gonzalez Sagrado, M.; Primo, D.; De La Fuente, B.; Gonzalez, J. Effect of a Probiotic on Liver Aminotransferases in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patients: A Double-Blind Randomized Clinical Trial. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 15, 1090–1095. [Google Scholar]
- Derosa, G.; Guasti, L.; D’Angelo, A.; Martinotti, C.; Valentino, M.C.; Di Matteo, S.; Bruno, G.M.; Maresca, A.M.; Gaudio, G.V.; Maffioli, P. Probiotic Therapy with VSL#3® in Patients with NAFLD: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 846873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duseja, A.; Acharya, S.K.; Mehta, M.; Chhabra, S.; Shalimar; Rana, S.; Das, A.; Dattagupta, S.; Dhiman, R.K.; Chawla, Y.K. High Potency Multistrain Probiotic Improves Liver Histology in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): A Randomised, Double-Blind, Proof of Concept Study. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2019, 6, e000315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Appendix C: Methodology checklist: Randomised controlled trials. In The Guidelines Manual; NICE: London, UK, 2012; Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/process/pmg6/resources/the-guidelines-manual-appendices-bi-2549703709/chapter/appendix-c-methodology-checklist-randomised-controlled-trials (accessed on 27 May 2025).
- Carpi, R.Z.; Barbalho, S.M.; Sloan, K.P.; Laurindo, L.F.; Gonzaga, H.F.; Grippa, P.C.; Zutin, T.L.M.; Girio, R.J.S.; Repetti, C.S.F.; Detregiachi, C.R.P.; et al. The Effects of Probiotics, Prebiotics and Synbiotics in Non-Alcoholic Fat Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhang, W.Y.; Qin, S.; Yang, Y.X.; Ren, H.; Yang, Q.-B.; Hu, H. Effects of Probiotics on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2019, 12, 1756284819878046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Shang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, W.; Tian, Y.; Shang, H. Effects of Probiotics on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 15, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.-Y.; Li, L.; Yu, C.-H.; Shen, Z.; Chen, L.-H.; Li, Y.-M. Effects of Probiotics on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Meta-Analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 6911–6918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.-W.; Lin, S.-X.; Shen, Z.-H.; Luo, W.-W.; Wang, X.-Y. Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis: The Effects of Probiotics in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2019, 2019, 1484598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Zhou, S.; Liao, J.; Ye, Z.; Mao, L. Efficacy of Probiotics on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2023, 102, e32734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wen, Y.; Liu, G.; Wan, C. Efficacy of Probiotics in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Adult and Children: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, 1226–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly, R.M. Nutrition and Diseases of Ageing—Plenary 5. New Zealand Society for Nutrition Annual Conference. 2024. Available online: https://www.nsnzconference.co.nz/_files/ugd/7af793_2cb5ea5983c74815af487837bb388fd4.pdf#page=46 (accessed on 27 May 2025).
- Zhang, W.; Tang, Y.; Wu, H.; Mancuso, A.; Thévenot, T.; Qi, X. Editorial: Treatment and prognostic assessment of liver cirrhosis and its complications, volume II. Front. Med. 2025, 12, 1601785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, C.; Yang, L.; Wei, W.; Fu, P. Efficacy of Probiotics/Synbiotics Supplementation in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1434613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatino, A.; Regolisti, G.; Brusasco, I.; Fiaccadori, E. Alterations of Intestinal Barrier and Microbiota in Chronic Kidney Disease and Effects of Probiotics, Prebiotics and Synbiotics on Uremic Toxins: A Review. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, H. Gut–Liver Axis in Liver Cirrhosis: How to Manage Leaky Gut and Endotoxemia. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 425–442. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4381167 (accessed on 27 May 2025). [CrossRef]
- Kalo, E.; Read, S.; Ahlenstiel, G. Targeting Gut–Liver Axis for Treatment of Liver Fibrosis and Portal Hypertension. Livers 2021, 1, 147–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ntikoudi, A.; Papachristou, A.; Spirou, A.; Evangelou, E.; Tsartsalis, A.; Vlachou, E.; Mastorakos, G. Exploring the Role of Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics in the Treatment of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease—A Scoping Review. Livers 2025, 5, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers5030031
Ntikoudi A, Papachristou A, Spirou A, Evangelou E, Tsartsalis A, Vlachou E, Mastorakos G. Exploring the Role of Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics in the Treatment of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease—A Scoping Review. Livers. 2025; 5(3):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers5030031
Chicago/Turabian StyleNtikoudi, Anastasia, Anastasia Papachristou, Alketa Spirou, Eleni Evangelou, Athanasios Tsartsalis, Eugenia Vlachou, and George Mastorakos. 2025. "Exploring the Role of Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics in the Treatment of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease—A Scoping Review" Livers 5, no. 3: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers5030031
APA StyleNtikoudi, A., Papachristou, A., Spirou, A., Evangelou, E., Tsartsalis, A., Vlachou, E., & Mastorakos, G. (2025). Exploring the Role of Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics in the Treatment of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease—A Scoping Review. Livers, 5(3), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers5030031







