Expression of Bone Morphogenetic Protein 14 in Liver Disease and Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Cell Culture
2.2. Mouse Models of Liver Fibrosis
2.3. Human Tissue Samples
2.4. Analysis of mRNA Expression
2.5. Analysis of Protein Expression
2.6. Functional in Vitro Analysis
2.7. Histological Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
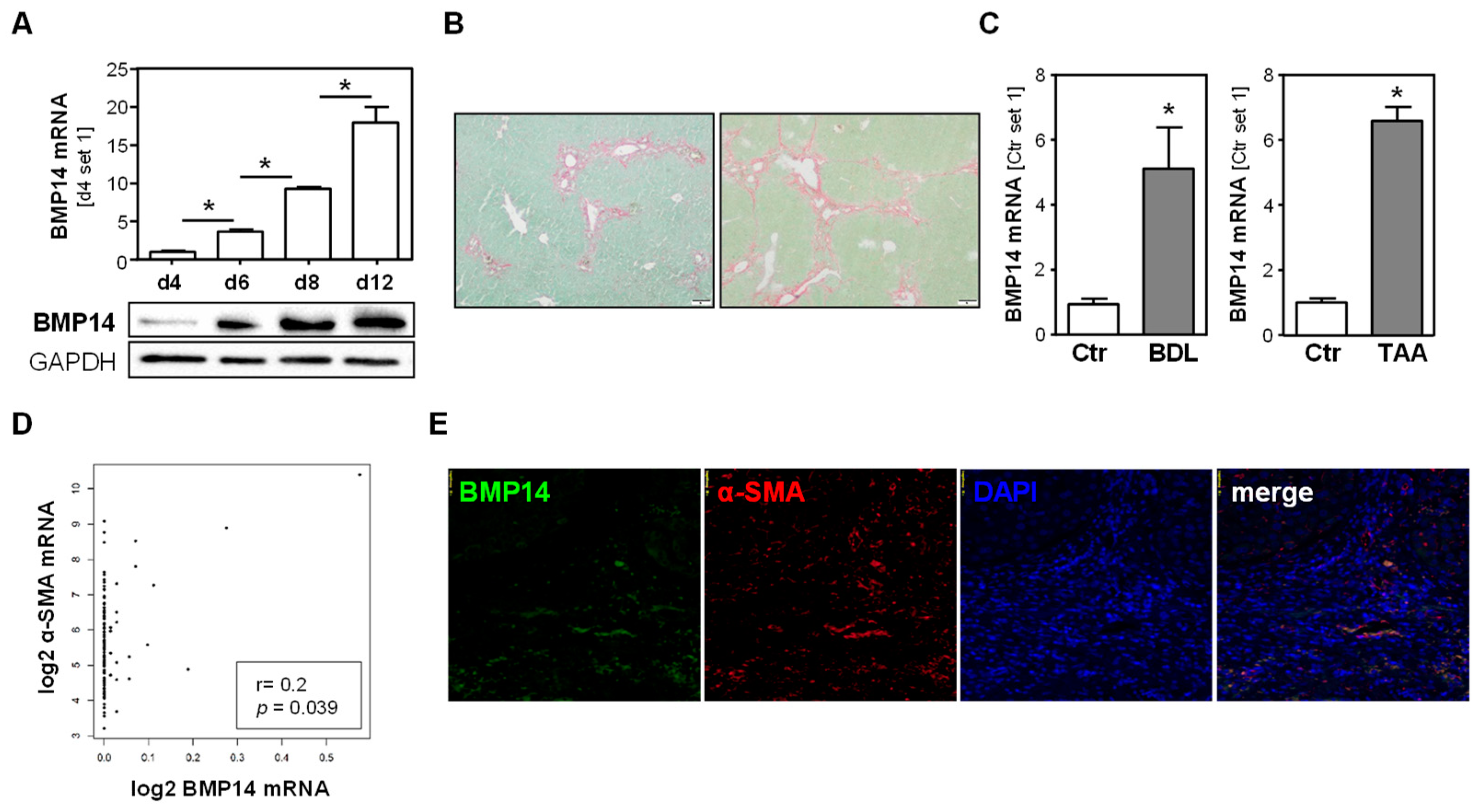
3.1. BMP14 Expression in Hepatic Fibrosis and Hepatic Stellate Cells
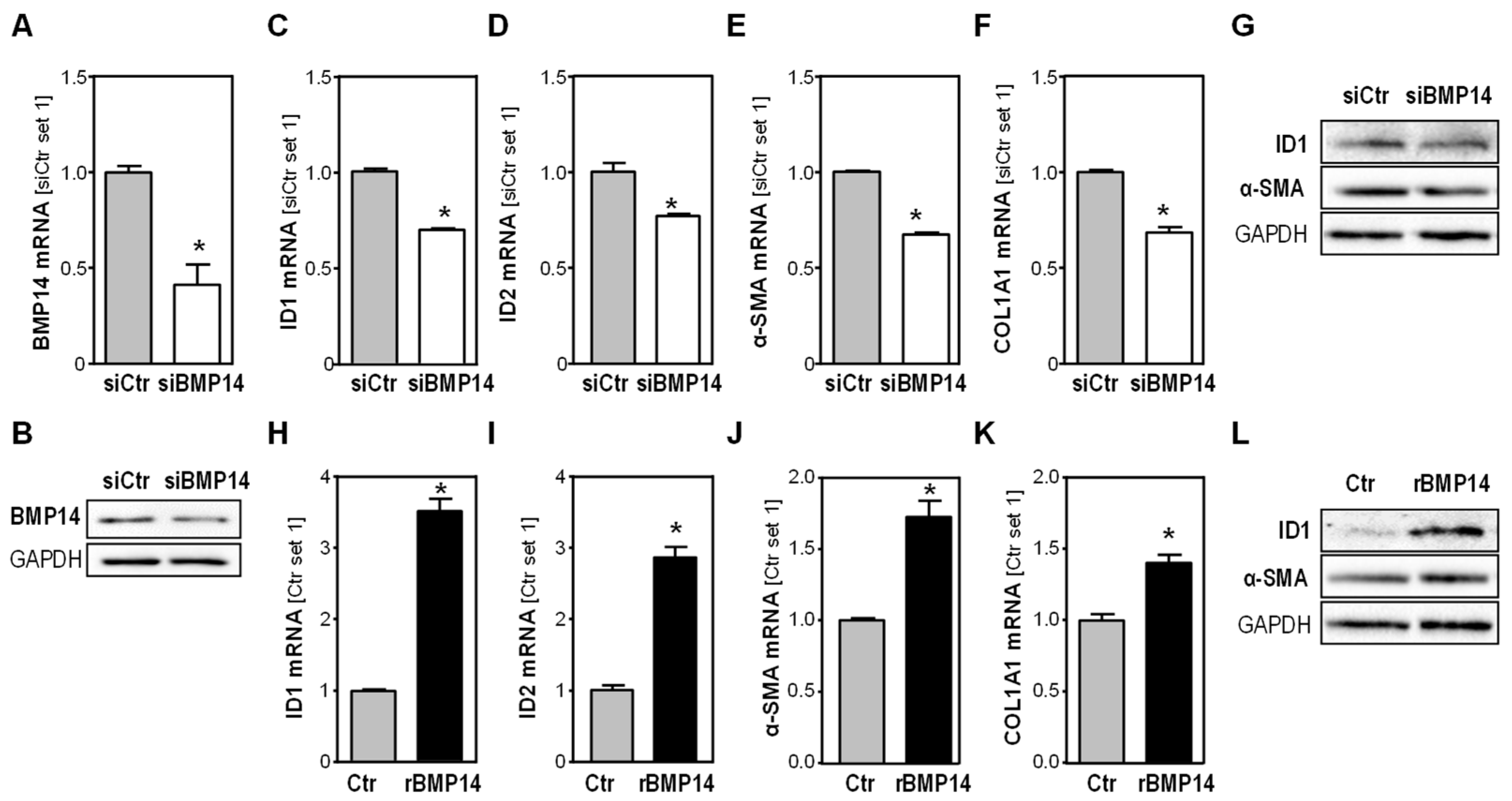
3.2. Effect of BMP14 in Activated Hepatic Stellate Cells
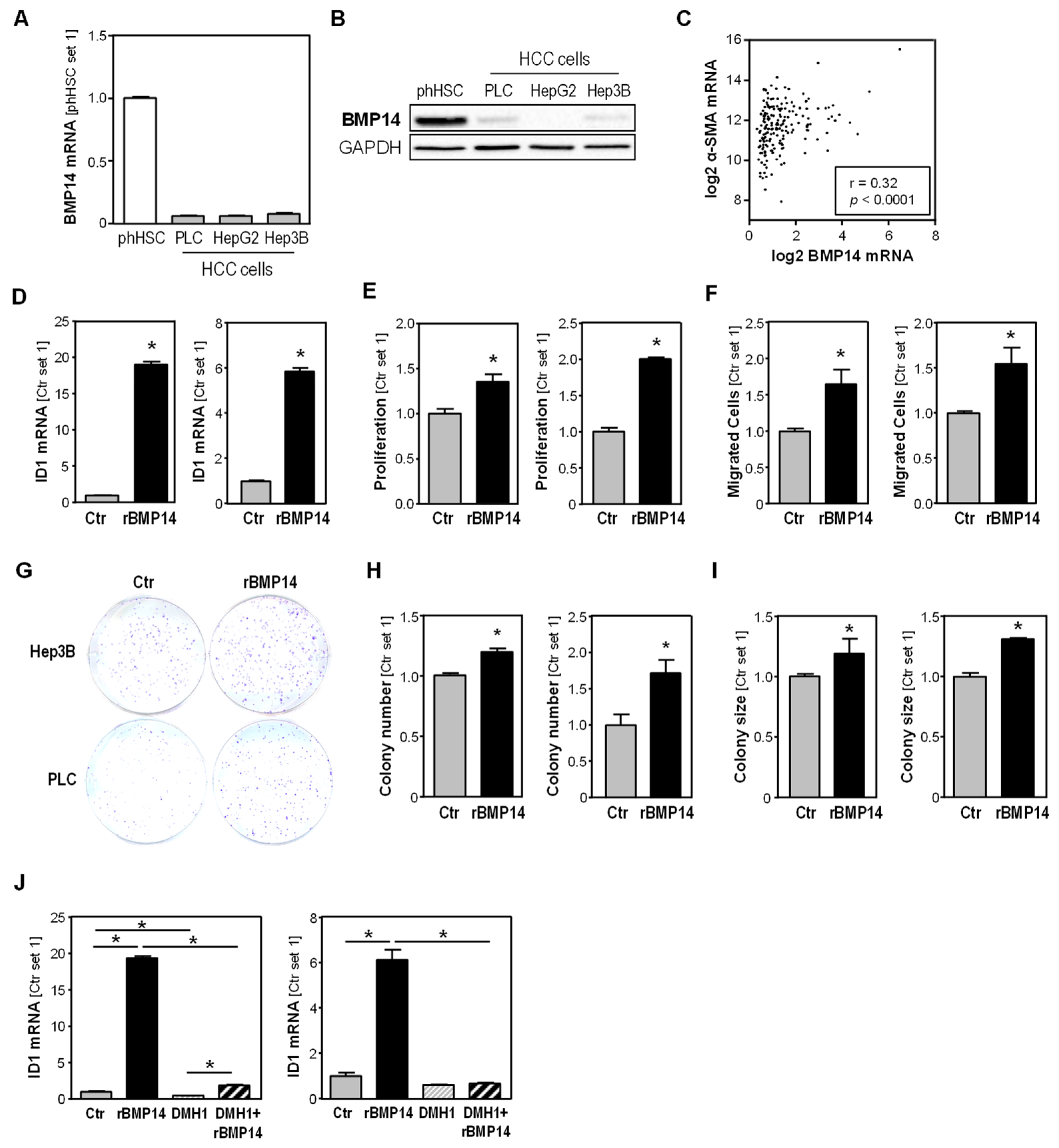
3.3. BMP14 Expression in HCC Cells and Tissues and Effect of BMP14 on HCC Cells
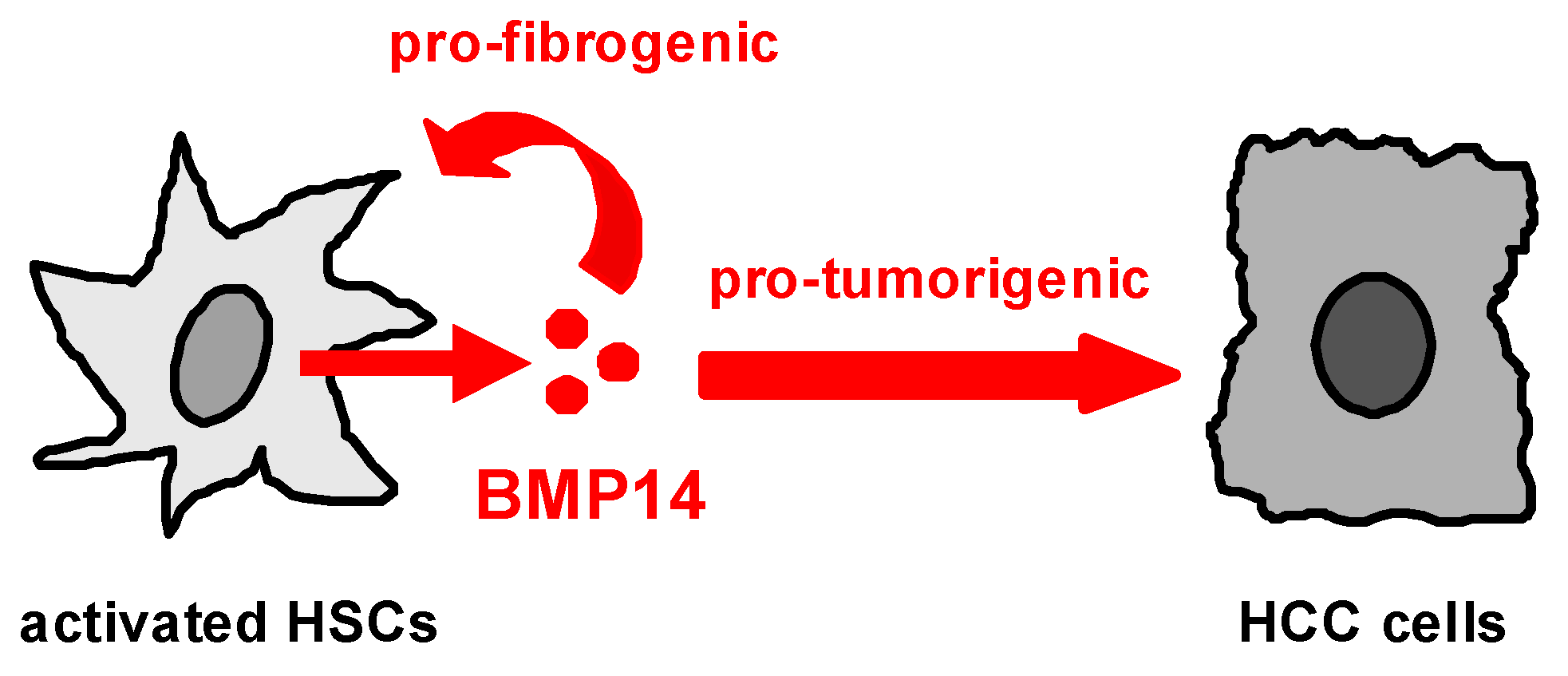
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsuchida, T.; Friedman, S.L. Mechanisms of hepatic stellate cell activation. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhar, D.; Baglieri, J.; Kisseleva, T.; Brenner, D.A. Mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its role in liver cancer. Exp. Biol. Med. 2020, 245, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, A.E.; Baldeosingh, R.; Lamm, R.; Patel, K.; Zhang, K.; Dominguez, D.A.; Kirton, K.J.; Shah, A.P.; Dang, H. Hepatic Stellate Cells and Hepatocarcinogenesis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amann, T.; Bataille, F.; Spruss, T.; Muhlbauer, M.; Gabele, E.; Scholmerich, J.; Kiefer, P.; Bosserhoff, A.K.; Hellerbrand, C. Activated hepatic stellate cells promote tumorigenicity of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Puerto, M.C.; Iyengar, P.V.; Garcia de Vinuesa, A.; Ten Dijke, P.; Sanchez-Duffhues, G. Bone morphogenetic protein receptor signal transduction in human disease. J. Pathol. 2019, 247, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Guo, J.; Yao, X.; Guo, Z.; Guo, F. Growth differentiation factor 5 in cartilage and osteoarthritis: A possible therapeutic candidate. Cell Prolif. 2021, 54, e12998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wu, X.; Wu, J.; Sun, C.; Luo, F.; Pei, Z. Systemic Overexpression of GDF5 in Adipocytes but Not Hepatocytes Alleviates High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver in Mice. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 2021, 8894685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enescu, A.S.; Margaritescu, C.L.; Craitoiu, M.M.; Enescu, A.; Craitoiu, S. The involvement of growth differentiation factor 5 (GDF5) and aggrecan in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of salivary gland pleomorphic adenoma. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2013, 54, 969–976. [Google Scholar]
- Margheri, F.; Schiavone, N.; Papucci, L.; Magnelli, L.; Serrati, S.; Chilla, A.; Laurenzana, A.; Bianchini, F.; Calorini, L.; Torre, E.; et al. GDF5 regulates TGFss-dependent angiogenesis in breast carcinoma MCF-7 cells: In vitro and in vivo control by anti-TGFss peptides. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhlbauer, M.; Bosserhoff, A.K.; Hartmann, A.; Thasler, W.E.; Weiss, T.S.; Herfarth, H.; Lock, G.; Scholmerich, J.; Hellerbrand, C. A novel MCP-1 gene polymorphism is associated with hepatic MCP-1 expression and severity of HCV-related liver disease. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Hui, A.Y.; Albanis, E.; Arthur, M.J.; O’Byrne, S.M.; Blaner, W.S.; Mukherjee, P.; Friedman, S.L.; Eng, F.J. Human hepatic stellate cell lines, LX-1 and LX-2: New tools for analysis of hepatic fibrosis. Gut 2005, 54, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thasler, W.E.; Weiss, T.S.; Schillhorn, K.; Stoll, P.T.; Irrgang, B.; Jauch, K.W. Charitable State-Controlled Foundation Human Tissue and Cell Research: Ethic and Legal Aspects in the Supply of Surgically Removed Human Tissue for Research in the Academic and Commercial Sector in Germany. Cell Tissue Bank. 2003, 4, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, P.; Koch, A.; Fritz, V.; Hartmann, A.; Bosserhoff, A.K.; Hellerbrand, C. Wild type Kirsten rat sarcoma is a novel microRNA-622-regulated therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma and contributes to sorafenib resistance. Gut 2018, 67, 1328–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannus, M.; Beitzinger, M.; Engelmann, J.C.; Weickert, M.T.; Spang, R.; Hannus, S.; Meister, G. siPools: Highly complex but accurately defined siRNA pools eliminate off-target effects. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 8049–8061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazagova, M.; Wang, L.; Anfora, A.T.; Wissmueller, M.; Lesley, S.A.; Miyamoto, Y.; Eckmann, L.; Dhungana, S.; Pathmasiri, W.; Sumner, S.; et al. Commensal microbiota is hepatoprotective and prevents liver fibrosis in mice. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, J.; Dorn, C.; Gabele, E.; Bataille, F.; Freese, K.; Seitz, T.; Thasler, W.E.; Buttner, R.; Weiskirchen, R.; Bosserhoff, A.; et al. Four-And-A-Half LIM-Domain Protein 2 (FHL2) Deficiency Aggravates Cholestatic Liver Injury. Cells 2020, 9, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahli, A.; Seitz, T.; Beckroge, T.; Freese, K.; Thasler, W.E.; Benkert, M.; Dietrich, P.; Weiskirchen, R.; Bosserhoff, A.; Hellerbrand, C. Bone Morphogenetic Protein-8B Expression is Induced in Steatotic Hepatocytes and Promotes Hepatic Steatosis and Inflammation In Vitro. Cells 2019, 8, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorn, C.; Weiss, T.S.; Heilmann, J.; Hellerbrand, C. Xanthohumol, a prenylated chalcone derived from hops, inhibits proliferation, migration and interleukin-8 expression of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2010, 36, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freese, K.; Seitz, T.; Dietrich, P.; Lee, S.M.L.; Thasler, W.E.; Bosserhoff, A.; Hellerbrand, C. Histone Deacetylase Expressions in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Functional Effects of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors on Liver Cancer Cells In Vitro. Cancers 2019, 11, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Li, C.; Kang, B.; Gao, G.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z. GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W98–W102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Koyama, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Ma, H.Y.; Liang, S.; Kim, I.H.; Brenner, D.A.; Kisseleva, T. Promising Therapy Candidates for Liver Fibrosis. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korchynskyi, O.; ten Dijke, P. Identification and functional characterization of distinct critically important bone morphogenetic protein-specific response elements in the Id1 promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 4883–4891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollnagel, A.; Oehlmann, V.; Heymer, J.; Ruther, U.; Nordheim, A. Id genes are direct targets of bone morphogenetic protein induction in embryonic stem cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 19838–19845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiercinska, E.; Wickert, L.; Denecke, B.; Said, H.M.; Hamzavi, J.; Gressner, A.M.; Thorikay, M.; ten Dijke, P.; Mertens, P.R.; Breitkopf, K.; et al. Id1 is a critical mediator in TGF-beta-induced transdifferentiation of rat hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology 2006, 43, 1032–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, K.; Terai, S.; Takami, T.; Kawaguchi, K.; Okita, K.; Sakaida, I. Importance of inhibitor of DNA binding/differentiation 2 in hepatic stellate cell differentiation and proliferation. Hepatol. Res. 2007, 37, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, M.J.; Craft, B.; Hastie, M.; Repecka, K.; McDade, F.; Kamath, A.; Banerjee, A.; Luo, Y.; Rogers, D.; Brooks, A.N.; et al. Visualizing and interpreting cancer genomics data via the Xena platform. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Tang, B.; Li, J.H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xie, X.Y.; Zhang, B.H.; Qiu, S.J.; Wu, W.Z.; Ren, Z.G. ID1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and confers chemoresistance to oxaliplatin by activating pentose phosphate pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, J.; Meng, J.; Zhu, L.; Nie, H.; Yang, C.; Li, J.; Gu, J.; Lin, Q.; Long, W.; Dong, X.; et al. Activation of androgen receptor induces ID1 and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion. Mol. Oncol. 2012, 6, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Ho, J.N.; Lewis, J.A.; Karim, K.A.; Daniels, R.N.; Gentry, P.R.; Hopkins, C.R.; Lindsley, C.W.; Hong, C.C. In vivo structure-activity relationship study of dorsomorphin analogues identifies selective VEGF and BMP inhibitors. ACS Chem. Biol. 2010, 5, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, D.K.; Marcelino, J.; Baker, M.; Gong, Y.; Smits, P.; Lefebvre, V.; Jay, G.D.; Stewart, M.; Wang, H.; Warman, M.L.; et al. The secreted glycoprotein lubricin protects cartilage surfaces and inhibits synovial cell overgrowth. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahata, Y.; Hagino, H.; Kimura, A.; Urushizaki, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Wakamori, K.; Murakami, T.; Hata, K.; Nishimura, R. Regulatory Mechanisms of Prg4 and Gdf5 Expression in Articular Cartilage and Functions in Osteoarthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, J.T.; Lin, K.; Nandedkar, M.; Camargo, M.; Cervenka, J.; Luyten, F.P. A human chondrodysplasia due to a mutation in a TGF-beta superfamily member. Nat. Genet. 1996, 12, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Yahyaee, S.A.; Al-Kindi, M.N.; Habbal, O.; Kumar, D.S. Clinical and molecular analysis of Grebe acromesomelic dysplasia in an Omani family. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2003, 121A, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storm, E.E.; Kingsley, D.M. GDF5 coordinates bone and joint formation during digit development. Dev. Biol. 1999, 209, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, C.M.; Vaughan, E.E.; Browe, D.C.; Mooney, E.; Howard, L.; Barry, F. Growth differentiation factor-5 enhances in vitro mesenchymal stromal cell chondrogenesis and hypertrophy. Stem Cells Dev. 2013, 22, 1968–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, C.M.; Scheremeta, B.H.; Boyce, A.T.; Mauck, R.L.; Tuan, R.S. Delayed fracture healing in growth differentiation factor 5-deficient mice: A pilot study. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2011, 469, 2915–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Lin, C.Y.; Cheng, K. siRNA- and miRNA-based therapeutics for liver fibrosis. Transl. Res. 2019, 214, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, R.; Yang, J.; Liu, H.; Davies, N.M.; Gong, Y. Hepatic Stellate Cells in Liver Fibrosis and siRNA-Based Therapy. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 172, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickel, J.; Kotzsch, A.; Sebald, W.; Mueller, T.D. A single residue of GDF-5 defines binding specificity to BMP receptor IB. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 349, 933–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishitoh, H.; Ichijo, H.; Kimura, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Makishima, F.; Yamaguchi, A.; Yamashita, H.; Enomoto, S.; Miyazono, K. Identification of type I and type II serine/threonine kinase receptors for growth/differentiation factor-5. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 21345–21352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dituri, F.; Cossu, C.; Mancarella, S.; Giannelli, G. The Interactivity between TGFbeta and BMP Signaling in Organogenesis, Fibrosis, and Cancer. Cells 2019, 8, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Shen, H.; Sun, Y.; Li, P.; Burczynski, F.; Namaka, M.; Gong, Y. Bone morphogenetic protein 4 mediates bile duct ligation induced liver fibrosis through activation of Smad1 and ERK1/2 in rat hepatic stellate cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2006, 207, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.W.; Hsia, Y.; Yang, W.Y.; Lin, Y.I.; Li, C.C.; Tsai, T.F.; Chang, K.W.; Shieh, G.S.; Tsai, S.F.; Wang, H.D.; et al. Identification of the common regulators for hepatocellular carcinoma induced by hepatitis B virus X antigen in a mouse model. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arndt, S.; Wacker, E.; Dorn, C.; Koch, A.; Saugspier, M.; Thasler, W.E.; Hartmann, A.; Bosserhoff, A.K.; Hellerbrand, C. Enhanced expression of BMP6 inhibits hepatic fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Gut 2015, 64, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desroches-Castan, A.; Tillet, E.; Ricard, N.; Ouarne, M.; Mallet, C.; Belmudes, L.; Coute, Y.; Boillot, O.; Scoazec, J.Y.; Bailly, S.; et al. Bone Morphogenetic Protein 9 Is a Paracrine Factor Controlling Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cell Fenestration and Protecting Against Hepatic Fibrosis. Hepatology 2019, 70, 1392–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, Y.; Zhu, L.; Yang, Z.; He, J.; Wang, L.; Shang, Q.; Pan, H.; Wang, H.; Ma, X.; et al. Targeting secreted cytokine BMP9 gates the attenuation of hepatic fibrosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Yan, W.; Zhang, Q.; Chang, X. Bone morphogenetic protein 2 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth and migration through downregulation of the PI3K/AKT pathway. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 5189–5198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.M.; Ma, N.; Zhang, E.B.; Chen, T.W.; Jiang, H.; Yin, F.F.; Wang, J.J.; Zhang, F.K.; Ni, Q.Z.; Wang, X.; et al. BMP10 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma progression via PTPRS-STAT3 axis. Oncogene 2019, 38, 7281–7293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, B.; Garcia-Alvaro, M.; Cruz, S.; Walsh, P.; Fernandez, M.; Roncero, C.; Fabregat, I.; Sanchez, A.; Inman, G.J. BMP9 is a proliferative and survival factor for human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Nio, K.; Tang, H.; Yamashita, T.; Okada, H.; Li, Y.; Doan, P.T.B.; Li, R.; Lv, J.; Sakai, Y.; et al. BMP9-ID1 Signaling Activates HIF-1alpha and VEGFA Expression to Promote Tumor Angiogenesis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sommer, J.; Thasler, W.E.; Bosserhoff, A.; Hellerbrand, C. Expression of Bone Morphogenetic Protein 14 in Liver Disease and Cancer. Livers 2023, 3, 282-292. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers3020019
Sommer J, Thasler WE, Bosserhoff A, Hellerbrand C. Expression of Bone Morphogenetic Protein 14 in Liver Disease and Cancer. Livers. 2023; 3(2):282-292. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers3020019
Chicago/Turabian StyleSommer, Judith, Wolfgang E. Thasler, Anja Bosserhoff, and Claus Hellerbrand. 2023. "Expression of Bone Morphogenetic Protein 14 in Liver Disease and Cancer" Livers 3, no. 2: 282-292. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers3020019
APA StyleSommer, J., Thasler, W. E., Bosserhoff, A., & Hellerbrand, C. (2023). Expression of Bone Morphogenetic Protein 14 in Liver Disease and Cancer. Livers, 3(2), 282-292. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers3020019





