Abstract
The present study reported, for the first time, the fabrication and characterization of electrospun nanofibers based on arabinoxylans (AXs) alone. The Fourier transform infrared spectrum of ferulated water-extractable AXs recovered from wheat endosperm confirmed the molecule identity. The carbon and oxygen signals in X-ray photoelectron spectrometry (XPS) were recorded for this molecule. The AXs had weight-average molar mass, intrinsic viscosity, radius of gyration, and hydrodynamic radius values of 769 kDa, 4.51 dL/g, 55 nm, and 31 nm, respectively. The calculated AX characteristic ratio and persistence length were 10.7 and 3.2 nm, respectively, while the Mark–Houwink–Sakurada α and K constants were 0.31 and 9.4, respectively. These macromolecular characteristics indicate a molecular random coil structure in the polysaccharide. Using aqueous acetic acid 50% (v/v) as a solvent favored the Taylor cone establishment and the fabrication of electrospun nanofibers. The morphology of nanofibers was revealed by scanning electron microscopy images. Atomic force microscopy analysis of AX nanofibers exposed the material deposition in layers; these nanofibers had an average diameter of 177 nm. These nanofibers could be used as advanced biomaterials for biomedical applications such as wound dressing.
1. Introduction
Arabinoxylans (AXs) are polysaccharides essentially found in cereal grains. These macromolecules comprise a linear xylose backbone connected via β(1-4) glycosidic bonds and branches with arabinose substituents linked by O-2 and O-3 bonds. The arabinose/xylose proportion (A/X) may vary between 0.3 and 1.1. AXs may contain ferulic acid (FA) esterified to some arabinoses (Figure 1). A low diferulic acid (di-FA) content can also be present in AX chains [1]. Additionally, small amounts of carboxylic acids in the form of methyl glucuronic acid side groups may be present in AXs [2].
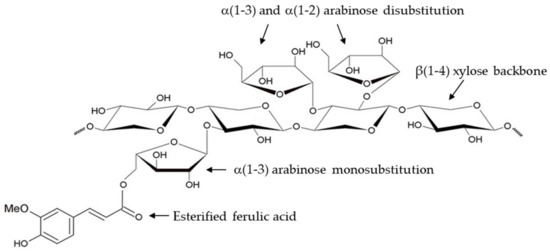
Figure 1.
Representative chemical structure of ferulated arabinoxylans.
AXs present different molecular weights, A/X proportions, and FA contents, among other characteristics; this variation results from the source and extraction method used [3]. AXs from bran cereals are primarily insoluble in water (WUAXs, water-unextractable arabinoxylans) due to their high FA content and the covalent bonds they form with other components of the cell walls [4]. AXs from cereal endosperm are soluble in water (WEAXs, water-extractable arabinoxylans) due to extensive arabinose substitution and weak assembly with the other cell wall components [5].
AXs present various functional and bioactive properties; various investigations report their prebiotic effect, and they have been explored for use in foods as an anti-obesogenic agent [6]. In the pharmaceutical industry, AXs have been evaluated for manufacturing tablets or as emulsifiers and tissue engineering agents for treating severe wounds as a scaffolding material [7]. AXs have many functional properties that include, but are not limited to, rheological properties such as thickening or texturing, which confer viscosity, the ability to make emulsions and confer stability, and the ability to form different porous materials such as gels, packaging, or edible films and fibers. In addition, they are polysaccharides presenting bioactivity and biocompatibility [3].
Recently, AXs have aroused great interest in manufacturing porous materials like gels, films, and fibers. Still, a limited bibliographic collection regarding its use is linked to the electrospinning method. In a previous report [8], a mixture of AXs and gelatin was electrospun to form a porous composite with a fiber diameter of around 1.4 μm, which showed excellent cytocompatibility and drug release potential. However, the biopolymers used to manufacture that material were obtained from third parties, so there was no control over its production chain. The development of fibers electrodeposited based on xylans loaded with polyethylene oxide [9] or a mixture of barley hull AXs and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) [10] has also been reported. Even though it has been reported that it is possible to manufacture electrospun nanofibers using AXs as a minor component of polymer blends with PVA or gelatin, until the date of the preparation of this document, the fabrication of electrospun nanofibers using only AXs has not been reported. In this regard, generating new insight into the fabrication and characterization of AX electrospun nanofibers is necessary. The current study aims to demonstrate that AXs can be used alone to fabricate electrospun nanofibers by physical entanglement.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Arabinoxylan (AX) Source
Ferulated water-extractable AXs from the endosperm of the Tacupeto wheat variety were obtained as previously described. The AX and protein content were 63.0 and 4.2 g/100 g sampled dry matter, respectively. The polysaccharides had an A/X value of 0.66 and FA and di-FA contents of 0.526 µg/mg and 0.036 µg/mg, respectively [11].
2.2. AX Characterization
Macromolecular characteristics in the AXs were analyzed using a high-performance size-exclusion liquid chromatography (SEC) system coupled to a multiangle laser light scattering (MALLS) detector [1]. A chromatographic system (260 Infinity, Agilent Technologies, Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA) connected to DAWN/HELEOS-II, ViscoStar-II, and Optilab T-rEX detectors (Wyatt Technology Corp., Santa Barbara, CA, USA) was used. The columns utilized were OH-pak SBH-Q-804 and 805 (Shodex Showa Denco K.K., Tokyo, Japan). The flow rate and temperature were 0.7 mL/min and 25 °C, respectively. NaNO3 was used as a mobile phase. The weight-average molar mass (Mw), the number-average molar mass (Mn), the intrinsic viscosity ([η]), the radius of gyration (RG), the hydrodynamic radius (Rh), and the dispersity index (I = Mw/Mn) were generated using Astra 6.1 software (Wyatt Technology Corp., Santa Barbara, CA, USA).
Molecular identification of the AXs and AX nanofibers was performed using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) with a Nicolet iS50 infrared spectrometer (Nicolet Instrument Corp., Madison, WI, USA) coupled to an attenuated total reflectance system by using 64 scans and a resolution of 4 cm−1. The spectrum was recorded from 4000 cm−1 to 400 cm−1 [11].
Chemical composition was analyzed by X-ray photoelectron spectrometry (XPS) using a Perkin-Elmer Phi-5100 XPS (PerkinElmer, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) with a dual aluminum and magnesium source with a power of 15 kV and an atmospheric pressure of 7.5 × 10−8 Torr [12].
2.3. Fabrication of Electrospun Nanofibers
The dynamic viscosity of AXs at different concentrations (0.5–7.0% w/v) and diverse solvents (milli-Q water, ethanol 40% /v, and acetic acid 50% /v) was determined. A frequency sweep was made from 1 Hz to 1000 Hz using a strain-controlled rheometer (AR-1500ex, TA Instruments, New Castle, DE, USA) using a 40 mm parallel plate geometry with a GAP of 1000 µm. The borders were covered using mineral oil to prevent drying. The experiments were performed at 25 °C for 15 min [13].
For electrospinning, AX dispersions of 3.5% and 6% (w/v) in milli-Q water, ethanol 40% (v/v), and acetic acid 50% (v/v) were prepared. Dispersions were stirred for 24 h at 20 °C and then heated at 80 °C for 1 h. Finally, they were treated with an ultrasonic homogenizer (Benson 1510, Branson Ultrasonics Corp., Danbury, CT, USA) for 10 min to eliminate air bubbles.
The electrospinning process was a modification of that previously reported in [10]. AX dispersions were loaded in 3 mL syringes with a 21-gauge blunt nozzle; an electrospray was used (Spraybase™ system, Profector™, Dublin, Ireland), and the parameters used were a voltage of 17 kV and a distance between electrodes of 5 cm. For flow control, a pump (WorldPrecision Instruments, AL-1000, Sarasota, FL, USA) was used at a speed of 0.30 mL/h or 1.2 mL/h. The material was collected on an aluminum plate attached to the negative electrode (Figure 2).
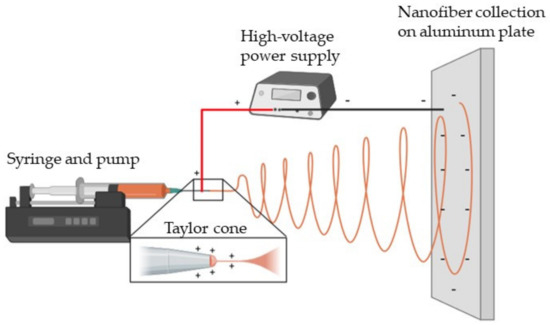
Figure 2.
A schematic representation of the electrospinning process used for AX nanofiber fabrication. Created with www.BioRender.com (accessed on 22 October 2024).
2.4. Characterization of Electrospun AX Nanofibers
The nanofibers’ morphology was studied by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) with a JSM 5300 microscope (JEOL, Tokyo, Japan) using secondary electron imaging (SEI) with an intensity of 5 kV and a low vacuum [8]. Surface analysis was conducted in non-contact mode with an atomic force microscope (AFM), Alpha 300 RA (WiTec, Ulm, Germany). The probe had a spring constant of 42 Nm−1 and a resonant frequency of 285 kHz [14].
The nanofibers were placed in an ATR module for Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) analysis. The FTIR spectrum was generated in absorbance mode, in a wavenumber range from 4000 cm−1 to 400 cm−1, using a Nicolet iS50 FTIR spectrometer (Nicolet Instrument Corp., Madison, WI, USA) coupled with an attenuated total reflectance system [11].
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Physicochemical analyses were performed in triplicate, and the results were expressed as the mean values. The diameter of the AX nanofibers was analyzed using ImageJ software version 1.54g. (National Institutes of Health and the Laboratory for Optical and Computational Instrumentation, University of Wisconsin), using at least 300 nanofibers.
3. Results
3.1. AX Characteristics
Figure 3 presents the Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectrum of the AXs. The sample produced a pattern consistent with that reported by different authors for AXs [3,11]. The main band at 1035 cm−1 was associated with C-OH bending. The tiny signals registered at 1158, and 897 cm−1 were related to the C-O-C antisymmetric stretching mode of the glycosidic link and β(1→4). The absorption band at 1650 cm−1 was attributed to phenolic acids and associated proteins in the sample. In addition, the stretches at 3400 cm−1 and 2850 cm−1 corresponded to the vibration of OH and CH structures, respectively [1].
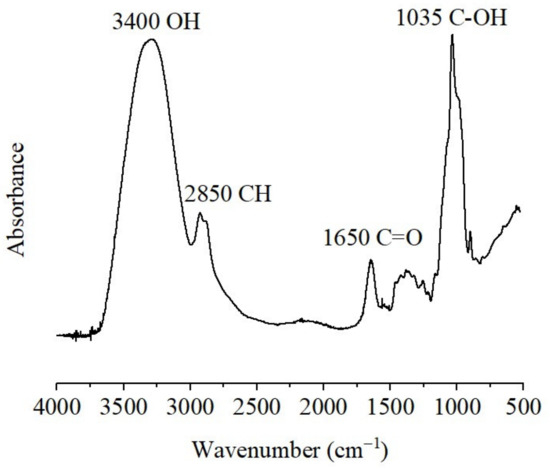
Figure 3.
Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectrum registered for AXs.
Figure 4 shows the characteristic energies obtained from the XPS of the chemical elements that made up the AX powder samples. The main compounds detected were carbon (285.1 and 289.3 eV), nitrogen (402.6 eV), and oxygen (535.4 eV). The binding energies registered for carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen in the present study correspond to those reported in the literature for these elements [15].
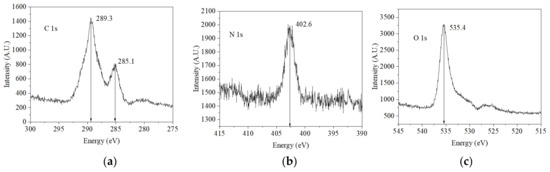
Figure 4.
The energy spectrum of X-ray photoelectrons emitted by AXs. The principal elements contained in the sample were (a) carbon, (b) nitrogen, and (c) oxygen.
Figure 5 presents the AX elution profile generated from high-performance size-exclusion liquid chromatography coupled to a multiangle laser light scattering detector (SEC-MALS), where the dRI, UV, light scattering (LS), and the degree of polymerization (DP) are shown. The AXs produced a monomodal LS and DP signal with the LS peak at a lower elution time than the DP and the prominent dRI peak (Fraction 1, between 7.5 and 10.5 min). The low elution time for the LS peak could have been due to the formation of polysaccharide macro-aggregates. The dRI signal presented various peaks (Fractions 2–4) and large elution volumes, indicating dispersity. The UV peaks in the sample could be related to peptides that may be linked to AXs, as reported in the literature [3], and to FA esterified to these polysaccharides [11,16].
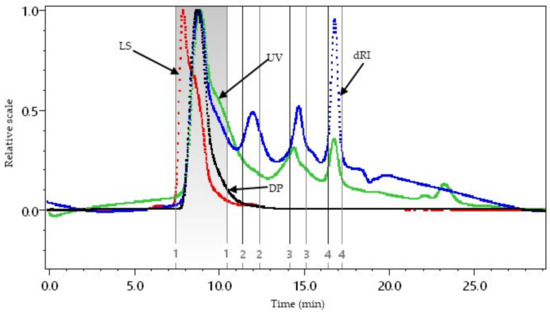
Figure 5.
High-performance size-exclusion liquid chromatography coupled to multiangle laser light scattering detector (SEC-MALS) for AXs. Differential refractive index (dRI, blue line), light scattering (LS, red line), ultraviolet (UV, green line), and degree of polymerization (DP, black line).
The macromolecular characteristics of the AXs are reported in Table 1. The weight-average molar mass (Mw), intrinsic viscosity [η], radius of gyration (RG), hydrodynamic radius (Rh), characteristic ratio (C∞), and persistence length (q) were in the range reported for WEAXs from wheat endosperm in previous studies [16,17]. Estimated C∞ and q values have been associated with a semiflexible random coil conformation [16]. Regarding the α constant in the Mark–Houwink–Sakurada equation, it has been reported that a value of 1.26 corresponds to rigid polysaccharide structures, while 0.50 indicates random coil structures. In addition, a high K value in this equation implies expanded coil conformation, while a low K value represents compact coil conformation [17]. Therefore, these macromolecular characteristics describe an AX registering a high-molecular-weight, semiflexible, random, and expanded coil conformation, which agrees with the behavior reported for wheat AXs [16,17].

Table 1.
Molecular characteristics of AXs.
3.2. Electrospun Nanofibers
Figure 6 corresponds to dynamic viscosity values as a function of AX concentration in different solvents. Dissolving high-Mw AXs using conventional mechanical methods in concentrations greater than 7% (w/v) is difficult. Therefore, it was decided to use this concentration as the maximum for evaluation. The results indicate that the dynamic viscosity of AXs depended on the shear rate, and in slow flows, it tended to be more viscous. Similar results have been reported for AX [13]. It was also found that, for any solvent used, with a 3% (w/v) concentration, the viscosity dispersion dramatically increased, with the most abrupt behavior seen when using aqueous acetic acid 50% (v/v) as the solvent.
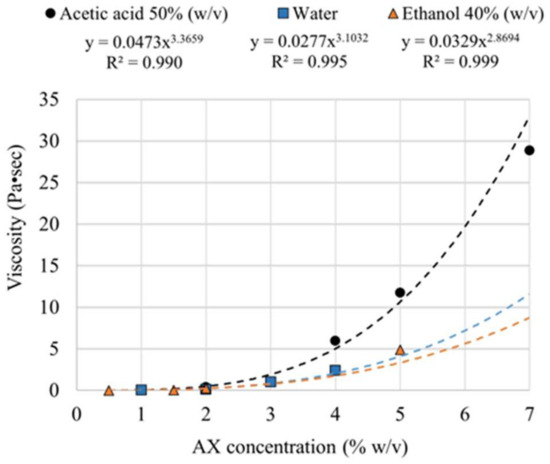
Figure 6.
The dynamic viscosity of AX dispersions in different solvents and at various concentrations at a frequency of 1 Hz.
The electrospinning behavior of different AX dispersions is reported in Table 2. When using AXs at 3.5% (w/v) dispersed in water with a voltage of 7.5 kV, the material could be ejected from the syringe; however, a Taylor cone could not be formed, and liquid droplets were deposited on the collector. After drying, the material did not have a defined shape. The same phenomenon occurred when the AX concentration in water was increased to 6% (w/v) and fibers could not be formed. By adding ethanol to the dispersion, the evaporation process could be accelerated. By using 40% (v/v) ethanol in water, Taylor cones were formed for all the concentrations of AXs tested. The material was electrosprayed with an AX concentration of 3.5% and 6.0% (w/v) and voltages greater than 6 kV, but nanofibers could not be formed. Using acetic acid 50% (v/v) aqueous solution as a solvent favored the Taylor cone, and the establishment and fabrication of nanofibers was possible at an AX concentration of 6.0% (w/v).

Table 2.
AX dispersion behavior during the electrospinning process.
The scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of the most representative materials obtained from the different AX dispersions submitted to the electrospinning process reported in Table 2 are presented in Figure 7.
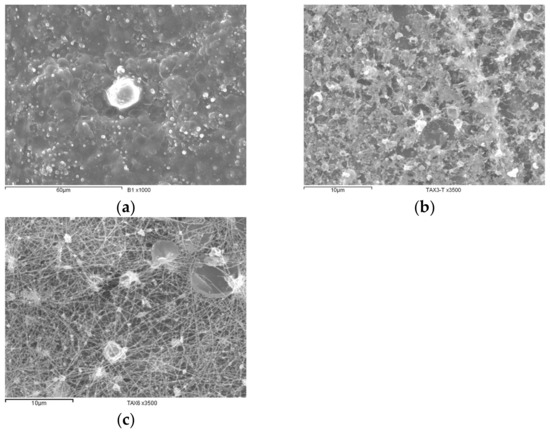
Figure 7.
SEM images of materials recovered after electrospinning process. (a) Granular film from 3.5% (w/v) AX dispersion in ethanol 40% (v/v) aqueous solution, (b) granular film from 3.5% (w/v) AX dispersion in acetic acid 50% (v/v) aqueous solution, and (c) nanofibers fabricated from 6% (w/v) AX dispersion in acetic acid 50% (v/v) aqueous solution.
In Figure 7a, it can be observed that a granular film recovered by employing a 3.5% (w/v) AX dispersion in water, while Figure 7b exposes a granular film fabricated after utilizing a 3.5% (w/v) AX dispersion in ethanol 40% (v/v). Figure 7c demonstrates that electrospun nanofibers could be fabricated by using 6% (w/v) AX dispersions in acetic acid 50% (v/v). The nanofiber imperfections could be related to polysaccharide dispersity.
3.3. Characteristics of Electrospun AX Nanofibers
The AX nanofibers produced an FTIR spectrum presenting a band pattern similar to that of the AXs, indicating that no changes in the molecular identity of these polysaccharides occurred after electrospinning (Figure 8). The FTIR bands detected for AXs (Figure 1) and AX nanofibers (Figure 6) have been previously reported for this macromolecule in other studies [18,19].
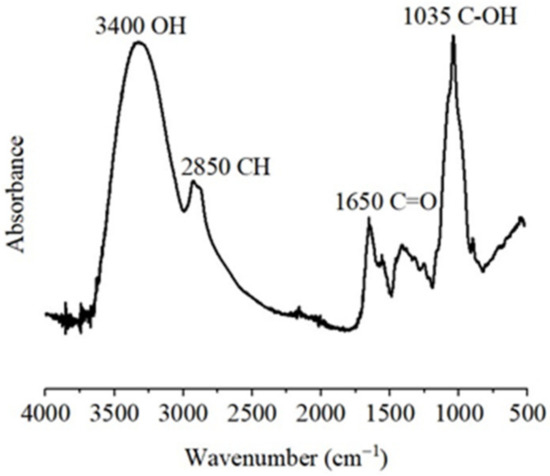
Figure 8.
Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectrum of AX nanofibers.
Figure 9a shows the atomic force microscopy (AFM) of the electrospun nanofibers. These had an irregular surface with lumps and imperfections. Figure 9b shows that the nanofibers were deposited in layers, and those deposited on top of the rugs were coplanar.
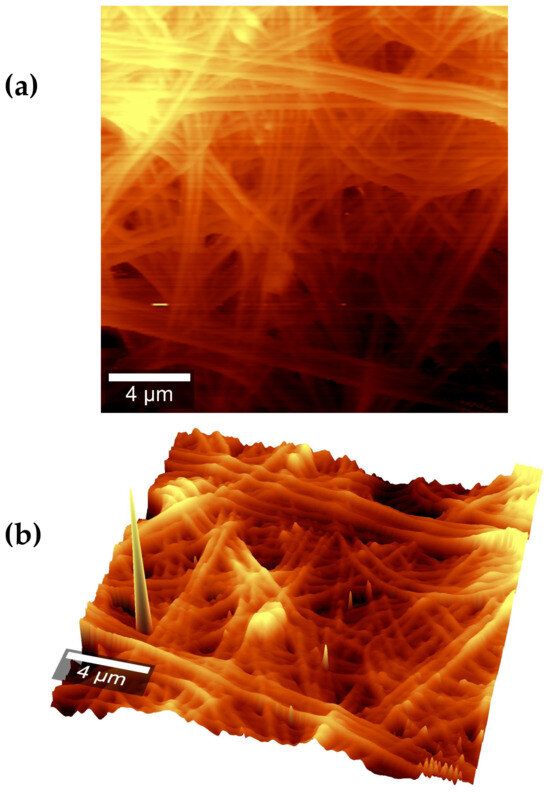
Figure 9.
AFM images of AX electrospun nanofibers (a) from a top view and (b) from an isometric view.
As for the many fibers in Figure 7c, it was possible to generate a histogram of AX nanofiber diameters (Figure 10). All the observed fibers had diameters of a nanometric order of magnitude ranging from 100 nm to 260 nm, with the majority the diameters around 170 nm and an average diameter of 177 nm. The diameter of the fibers meets statistical normality and fits a Gaussian bell.
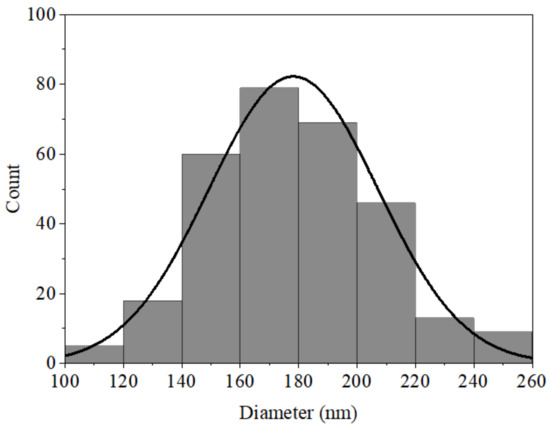
Figure 10.
Histogram of AX electrospun nanofiber diameters.
4. Discussion
The FTIR spectrum of AXs confirmed the polysaccharides’ molecular identity. This spectroscopy analysis is an outstanding method for molecular identification. The energy spectrum of X-ray photoelectrons emitted by AXs confirmed a carbon signal at 285.1 eV and an oxygen signal at 535.4 eV as the main elemental components. In addition, a signal at 289.3 eV was detected, which may have been related to carbons belonging to phenolic groups such as ferulic acid. The nitrogen signal around 402.6 eV could indicate the presence of some proteins along the molecular chains of AXs.
According to SEC-MALS analysis, AXs are disperse macromolecules, as previously reported by several studies [1,11,16,17]. Rh and RG values also agree with other AX values [16,17,18]. Rh denotes the radius of a corresponding hard sphere diffusing at the same rate as AXs. At the same time, RG corresponds to the mass-weighted average distance from the center of an AX molecule to every mass element in the polysaccharide. The C∞ and q values computed in the current study were also within the range reported for other AXs [16,17]. According to these macromolecular characteristics, AXs are semiflexible macromolecules.
The value of the α constant found for AXs is close to 0.50, therefore related to a random coil structure. Furthermore, the K value corresponds to a compact coil conformation [20]. The macromolecular characteristics found for AXs in the present study imply a molecular random coil structure, as reported in previous investigations using other AX sources [1,16,17]. Chain conformation and flexibility are relevant as they can be crucial during polysaccharide interaction and adhesion with cell surfaces.
Depending on the molecular weight of the polymer, it is necessary to have enough dispersed molecules for a successful electrospinning process [21]. AX molecules should be sufficiently large to be electrospun from the critical concentration of 2.5% (w/v) [22]. On the other hand, dispersions with dynamic viscosities of more than 100 cP or 0.1 Pa·s are reported to be suitable for electrospinning [23]. From the potential regression of the dynamic viscosity, a minimum concentration for electrospinning was estimated at around 2% (w/v) for any of the solvents studied. Water, alone or with salt content, is a widely used medium for the dispersion of AXs [10,24].
On the other hand, ethanol is a non-solvent of AXs; however, depending on how much ethanol is diluted in water, AXs of different molecular weights can be suspended [25]. When applying the electrospinning method, dispersion at low polymer concentrations forms electrospray. As the polymer concentration increases, a material with the microscopic shape of marbles in a thread is obtained. Fibers with nanometric diameters are formed with a sufficiently high polymer concentration [26].
The AX nanofibers were obtained using a concentration of 6% (w/v), which is four percentage points higher than the estimated minimum concentration for electrospinning, probably due to the AX dispersity. The calculus performed in [23] considers monodisperse polymers; however, AX viscosity is mainly conferred by a fraction of molecules with a high Mw. Thus, a higher polymer concentration is needed to promote the physical entanglement between AX chains of a smaller Mw during the electrospinning process.
The present study found that when using water and diluted ethanol, forming fibers of any size was impossible; the fabrication of nanofibers was only possible in an acetic acid aqueous dispersion (50% v/v). The effectiveness of the solvent used in the present study (acetic acid/water) may be related to a reduction in surface tension as it has been reported that surface tension in acetic acid is lower than in water (28.8 mN/m and 72 mN/m, respectively) and that a high solution surface tension inhibits the electrospinning process since jet instabilities lead to jet breakup in droplets [27]. In addition, it is possible that some changes in charge density in AXs dispersed in an acetic acid/water solvent might occur during the electrospinning process because even though AXs are considered neutral polysaccharides [1], they also contain low amounts of associated peptides and esterified ferulic acid [3]. It has also been reported that small amounts of carboxylic acids in the form of methyl glucuronic acid side groups may be present in AXs [2].
For biomolecules such as gelatin, interaction with acetic acid causes the polymer chain to contract, thus promoting less intramolecular interaction and better dispersion within the solvent [28]. However, further investigation is necessary to ensure that this is true for AXs. Furthermore, due to its low boiling temperature (118 °C) [29], aqueous acetic acid evaporates from a syringe to a collecting plate, promoting the physical entanglement of AX molecules and the formation of nanofibers.
The AX nanofibers fabricated in the present study using high-Mw AXs had similar diameters to those of low-Mw AXs in a copolymer with PVA [8]. In addition, the AX/PVA nanofibers reported in a previous study [8] were smaller than those made in another investigation using a combination of AXs and gelatin [10]. The following are some advantages of the AX nanofibers reported in the current investigation. As polysaccharides, AXs are renewable and biodegradable, making them a sustainable option for synthetic polymers such as PVA. In addition, proteins such as gelatin present a polyelectrolytic nature, which can alter jet streams, complicating the electrospinning process.
The present study demonstrates that AXs can be used alone to fabricate electrospun nanofibers. Physical entanglement rather than chemical crosslinking is expected to happen during the electrospinning process, which explains the similarity of the FTIR spectrum of AX nanofibers regarding AXs. The slight increase in the band at 1550 cm−1 could be attributed to higher crystallinity or additional intermolecular interactions in AX nanofibers concerning AX powder, as previously reported for other polymer nanofibers [30,31].
The morphology of AX nanofibers indicates that the polysaccharide concentration could be within the optimal spinning range; however, a subsequent response surface study is necessary to thoroughly establish these optimal conditions. In addition, AX electrospinning is not without limitations; material flow is easily disturbed, so constant vigilance is required when depositing to avoid inconsistencies.
Polysaccharide electrospun nanofibers can exhibit several exceptional properties that are influenced by the macromolecule characteristics and the experimental conditions used during the material preparation. Developing specific electrospinning conditions to fabricate nanofibers based on less explored polysaccharides such as AXs allows the generation of innovative knowledge. In this regard, the main novelty of the present study is that it offers a possibility for the electrospinning of AXs alone without additional polymers. This information is of great relevance in the electrospinning field.
5. Conclusions
Ferulated water-extractable AXs presenting a high weight-average molar mass and intrinsic viscosity and a semiflexible random and expanded coil conformation can be used alone to fabricate electrospun nanofibers by physical entanglement. Wheat water-extractable ferulated AX molecules are large enough to be electrospun at a 6% (w/v) concentration using 6% (w/v) AX dispersions in acetic acid 50% (v/v) aqueous solution. Nanofibers formed are coplanar, deposited in layers, and present an average diameter of 177 nm. Worldwide, this study is the first report on nanofibers based on AXs alone, without any other polymer present, generating new insight into the fabrication and characterization of this biomaterial. It could serve as a starting point to develop methodologies relevant to other polysaccharides that, to date, have not been able to be electrospun. In future work, the optimization of the process should be investigated, both regarding polysaccharide concentration and the degree of solvent dilution. Nevertheless, this work opens the door to scientific research and technological developments related to these novel nanofibers.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.C.-M. and M.R.-C.; methodology, M.R.-C., A.R.-C., V.M.-A., A.J.B.-E., S.J.C., F.B.-B. and E.C.-M.; software, M.R.-C. and V.M.-A.; validation, A.R.-C., A.J.B.-E., S.J.C., F.B.-B., J.L.-M., A.D.M.-A. and E.C.-M.; formal analysis, M.R.-C., A.R.-C., V.M.-A., A.J.B.-E., S.J.C., R.M.-M., F.B.-B. and E.C.-M.; investigation, M.R.-C., A.R.-C., V.M.-A., A.J.B.-E., S.J.C., F.B.-B. and E.C.-M.; resources, A.R.-C., A.J.B.-E., S.J.C., F.B.-B. and E.C.-M.; data curation, M.R.-C. and V.M.-A.; writing—original draft preparation, M.R.-C.; writing—review and editing M.R.-C., V.M.-A., A.R.-C., A.J.B.-E., S.J.C., R.M.-M., F.B.-B., J.L.-M., A.D.M.-A. and E.C.-M.; visualization, E.C.-M. and M.R.-C.; supervision, A.R.-C., A.J.B.-E., S.J.C., J.L.-M. and E.C.-M.; project administration, E.C.-M.; funding acquisition, E.C.-M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by CONAHCYT (grant number 319684) for E. Carvajal-Millan.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors are pleased to acknowledge Alma Campa-Mada, Karla Martínez-Robinson, and Jorge Marquez-Escalante for technical assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Marquez-Escalante, J.; Carvajal-Millan, E.; Martínez-López, A.; Martinez Robinson, K.; Campa-Mada, A.; Rascon, A. Fine structural features and antioxidant capacity of ferulated arabinoxylans extracted from nixtamalized maize bran. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 4584–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aminzadeh, S.; Zhang, L.; Henriksson, G. A possible explanation for the structural inhomogeneity of lignin in LCC networks. Wood Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 1365–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez-Encinas, M.A.; Carvajal-Millan, E.; Rascon-Chu, A.; Astiazaran-Garcia, H.F.; Valencia-Rivera, D.E. Ferulated Arabinoxylans and Their Gels: Functional Properties and Potential Application as Antioxidant and Anticancer Agent. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 2314759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietiäinen, S.; Moldin, A.; Ström, A.; Malmberg, C.; Langton, M. Effect of physicochemical properties, pre-processing, and extraction on the functionality of wheat bran arabinoxylans in breadmaking—A review. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Yadav, M.P.; Singh, B.; Bhinder, S.; Simon, S.; Singh, N. Isolation and characterization of arabinoxylans from wheat bran and study of their contribution to wheat flour dough rheology. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 221, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schupfer, E.; Pak, S.C.; Wang, S.Y.; Micalos, P.S.; Jeffries, T.; Ooi, S.L.; Golombick, T.; Harris, G.; El-Omar, E. The effects and benefits of arabinoxylans on human gut microbiota—A narrative review. Food Biosci. 2021, 43, 101267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, R.; Afifi, S.M.; Kassem, I.A.A.; Elkasabgy, N.A.; Farag, M.A. Arabinoxylan and rhamnogalacturonan mucilage: Outgoing and potential trends of pharmaceutical, environmental, and medicinal merits. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 2550–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aduba, D.C.; An, S.-S.; Selders, G.S.; Yeudall, W.A.; Bowlin, G.L.; Kitten, T.; Yang, H. Electrospun gelatin–arabinoxylan ferulate composite fibers for diabetic chronic wound dressing application. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2019, 68, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Karaaslan, M.A.; Cho, M.; Liu, L.-Y.; Johnson, A.M.; Renneckar, S. Investigation into electrospinning water-soluble xylan: Developing applications from highly absorbent and hydrophilic surfaces to carbonized fiber. Cellulose 2019, 26, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butylina, S.; Koljonen, K.; Hiltunen, S.; Laatikainen, K. Study on spinnability of arabinoxylan extracted from barley husks. Cellulose 2022, 29, 8409–8425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Ortega, A.; Carvajal-Millan, E.; López-Franco, Y.; Rascón-Chu, A.; Lizardi-Mendoza, J.; Torres-Chavez, P.; Campa-Mada, A. Characterization of Water Extractable Arabinoxylans from a Spring Wheat Flour: Rheological Properties and Microstructure. Molecules 2013, 18, 8417–8428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-León, E.; Íñiguez-Palomares, R.A.; Navarro, R.E.; Rodríguez-Beas, C.; Larios-Rodríguez, E.; Alvarez-Cirerol, F.J.; Íñiguez-Palomares, C.; Ramírez-Saldaña, M.; Hernández Martínez, J.; Martínez-Higuera, A.; et al. Silver nanoparticles synthesized with Rumex hymenosepalus extracts: Effective broad-spectrum microbicidal agents and cytotoxicity study. Artif. Cells. Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 1194–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kale, M.S.; Yadav, M.P.; Hicks, K.B.; Hanah, K. Concentration and shear rate dependence of solution viscosity for arabinoxylans from different sources. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 47, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgara-Estrella, A.J.; Acosta-Elias, M.A.; Álvarez-Bajo, O.; Silva-Campa, E.; Angulo-Molina, A.; Rodríguez-Hernández, I.d.C.; Sarabia-Sainz, H.M.; Escalante-Lugo, V.M.; Pedroza-Montero, M.R. Atomic force microscopy and Raman spectra profile of blood components associated with exposure to cigarette smoking. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 11971–11981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Chen, M.; Zhu, K.; Ni, J.; Wang, S.; Cao, B.; Zhong, S.; Zhou, J.; Wang, S. Facile synthesis of nitrogen-doped interconnected porous carbons derived from reed and chlorella for high-performance supercapacitors. Fuel Process. Technol. 2022, 238, 107466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dervilly-Pinel, G.; Thibault, J.-F.; Saulnier, L. Experimental evidence for a semiflexible conformation for arabinoxylans. Carbohydr. Res. 2001, 330, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picout, D.R.; Ross-Murphy, S.B. On the chain flexibility of arabinoxylans and other β-(1→4) polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Res. 2002, 337, 1781–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Anda-Flores, Y.; Carvajal-Millan, E.; Lizardi-Mendoza, J.; Rascon-Chu, A.; Martínez-López, A.L.; Marquez-Escalante, J.; Brown-Bojorquez, F.; Tanori-Cordova, J. Covalently Cross-Linked Nanoparticles Based on Ferulated Arabinoxylans Recovered from a Distiller’s Dried Grains Byproduct. Processes 2020, 8, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, N.C.; Ray, P.; Pfau, C.; Kalavacharla, V.; Hossain, K.; Quadir, M. Development of Functional Nanomaterials from Wheat Bran Derived Arabinoxylan for Nucleic Acid Delivery. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 4367–4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Guo, Q.; Shi, Y.C. Molecular and conformational properties of hemicellulose fiber gum from dried distillers grains with solubles. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 80, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, W.K.; Youk, J.H.; Lee, T.S.; Park, W.H. The effects of solution properties and polyelectrolyte on electrospinning of ultrafine poly(ethylene oxide) fibers. Polymer 2024, 45, 2959–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keirouz, A.; Wang, Z.; Reddy, V.S.; Nagy, Z.K.; Vass, P.; Buzgo, M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Radacsi, N. The history of electrospinning: Past, present, and future developments. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2201723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amariei, N.; Manea, L.R.; Bertea, A.P.; Bertea, A.; Popa, A. The Influence of Polymer Solution on the Properties of Electrospun 3D Nanostructures. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 209, 012092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvada, J.; Alke, B.; Brazinha, C.; Alves, V.D.; Coelhoso, I.M. Development and Characterisation of Arabinoxylan-Based Composite Films. Coatings 2022, 12, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.-K.; Yang, Z.; Xing, J.-J.; Guo, X.-N.; Zhu, K.-X. Fabrication and stabilization mechanisms of Pickering emulsions based on gliadin/arabinoxylan complexes. Food Chem. 2022, 393, 133458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okutan, N.; Terzi, P.; Altay, F. Affecting parameters on electrospinning process and characterization of electrospun gelatin nanofibers. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 39, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.H.; Kim, H.E.; Kim, H.W. Production of electrospun gelatin nanofiber by water-based co-solvent approach. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erencia, M.; Cano, F.; Tornero, J.A.; Macanás, J.; Carrillo, F. Resolving the electrospinnability zones and diameter prediction for the electrospinning of the gelatin/water/acetic acid system. Langmuir 2014, 30, 7198–7205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stie, M.B.; Jones, M.; Sørensen, H.O.; Jacobsen, J.; Chronakis, I.S.; Nielsen, H.M. Acids ‘generally recognized as safe’ affect morphology and biocompatibility of elec-trospun chitosan/polyethylene oxide nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 215, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamalpour, R.; Koocheki, A.; Ghorani, B. Encapsulation of D-limonene in Lepidium perfoliatum seed gum/PVA electrospun nanofibers: Physicochemical characterization and modeling the kinetics of release. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2025, 10, 100966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayebi-Khorrami, V.; Shahgordi, S.; Mahdi Dabbaghi, M.; Saleh Fadaei, M.; Masoumi Shahrbabak, S.; Fallahianshafiei, S.; Reza Fadaei, M.; Saquib Hasnain, M.; Kumar Nayak, A.; Reza Askari, V. From nature to nanotech: Harnessing the power of electrospun polysaccharide-based nanofibers as sustainable packaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 299, 140127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).