Effects of Fucoidan and Fucoidan Oligosaccharides in Growth and Quorum Sensing Mediated Virulence Factor of Campylobacter Jejuni
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Fucoidan-Oligosaccharides
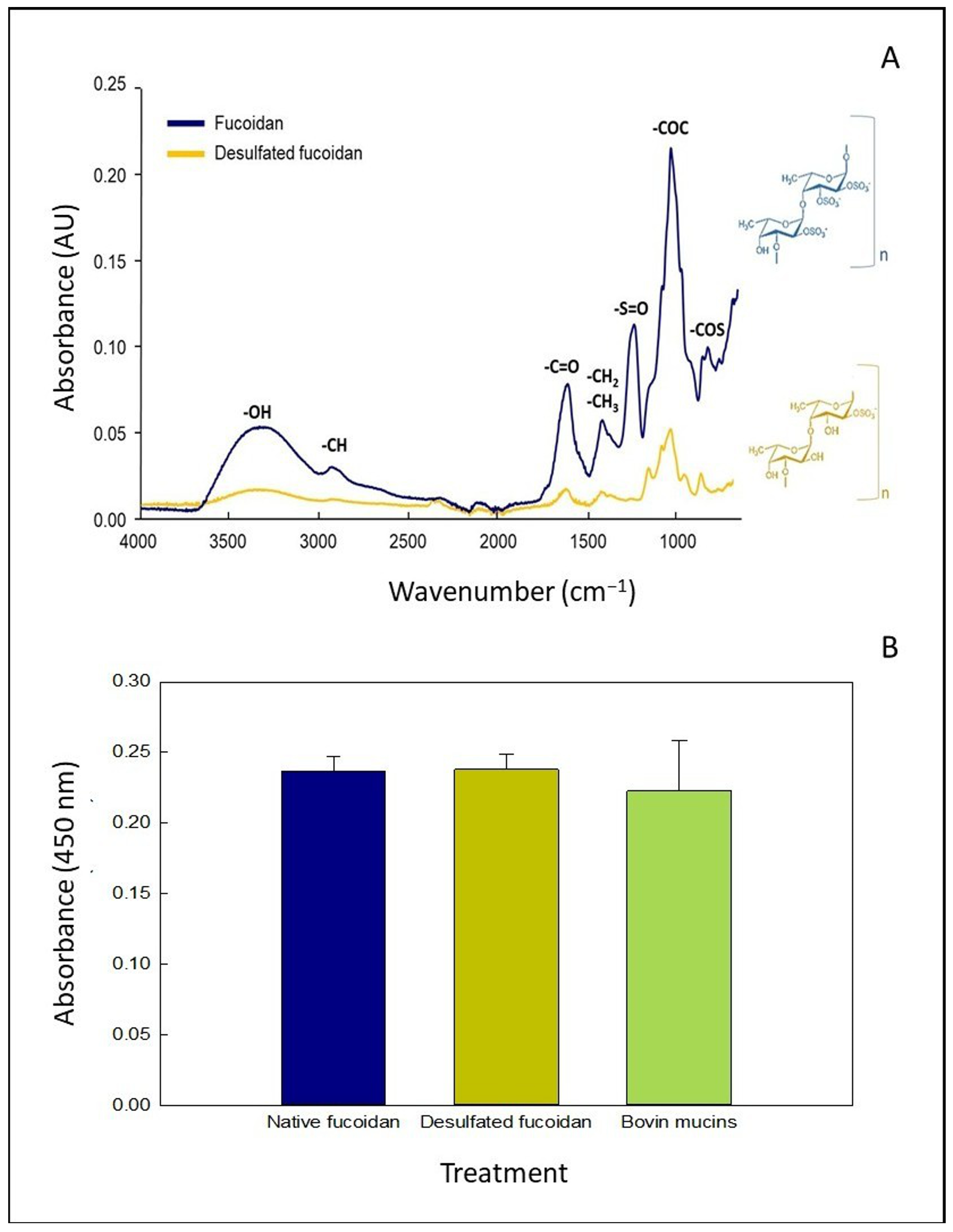
2.3. Characterization of Fucoidan-Oligosaccharides
2.4. Growth of C. jejuni in the Presence of Fucose-Based Compounds
2.5. Effect of Fucose-Based Compounds on Abiotic Film Formation
2.6. Bacterial Mobility Assays
2.7. Microbial Adhesion to Hydrocarbons
2.8. Enzyme-Linked Lectin Assay
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
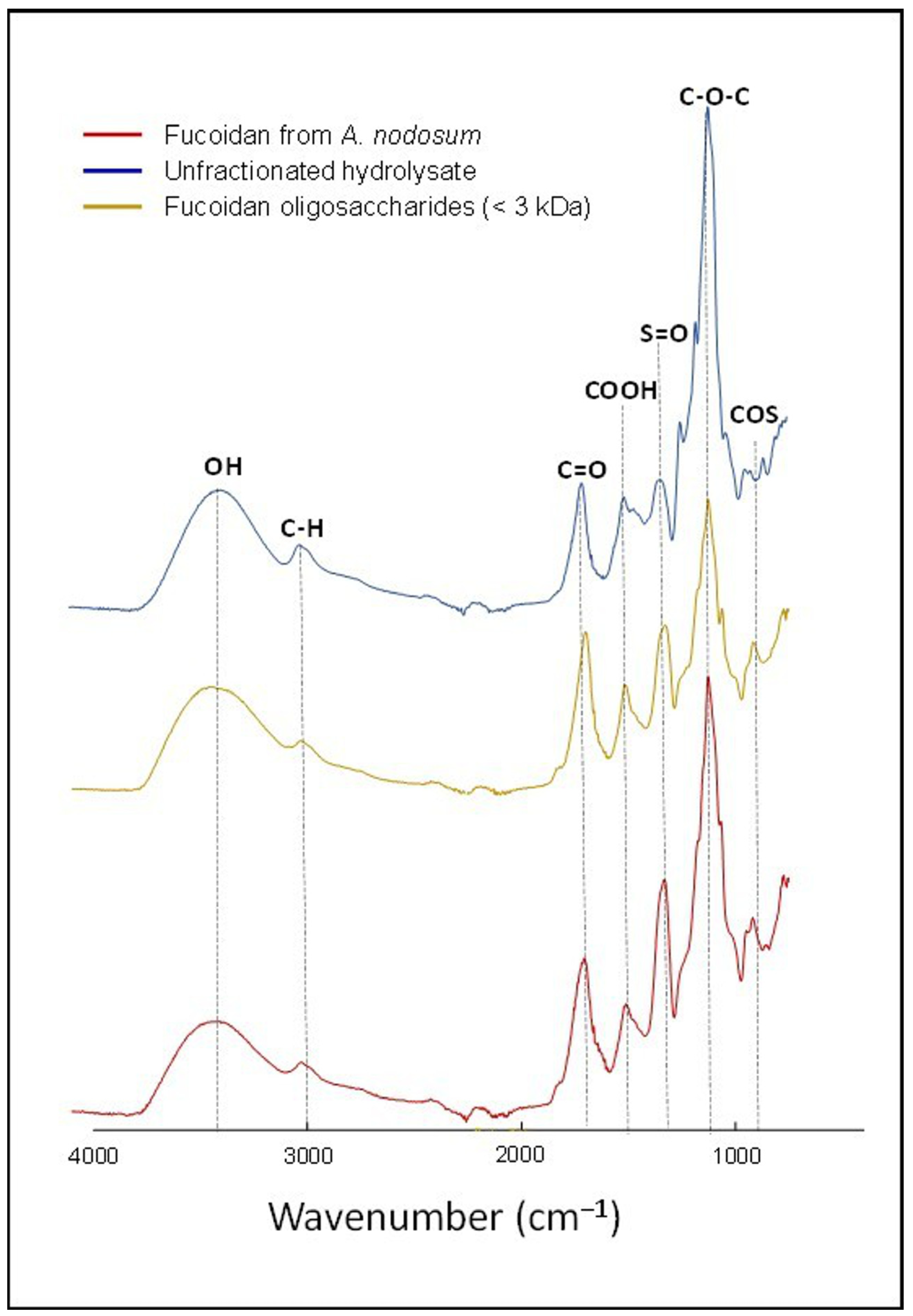
3.1. Characterization of OFuc
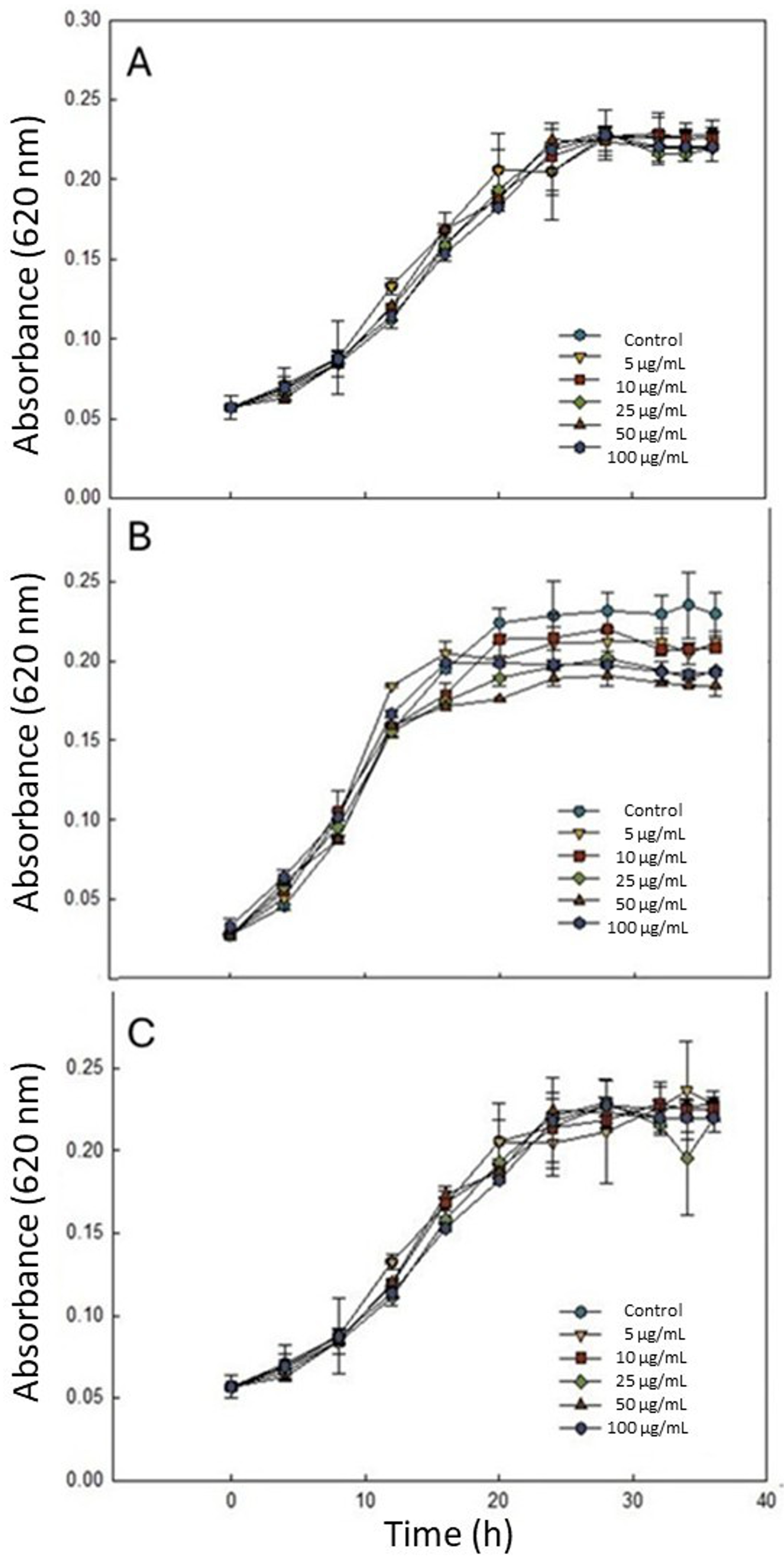
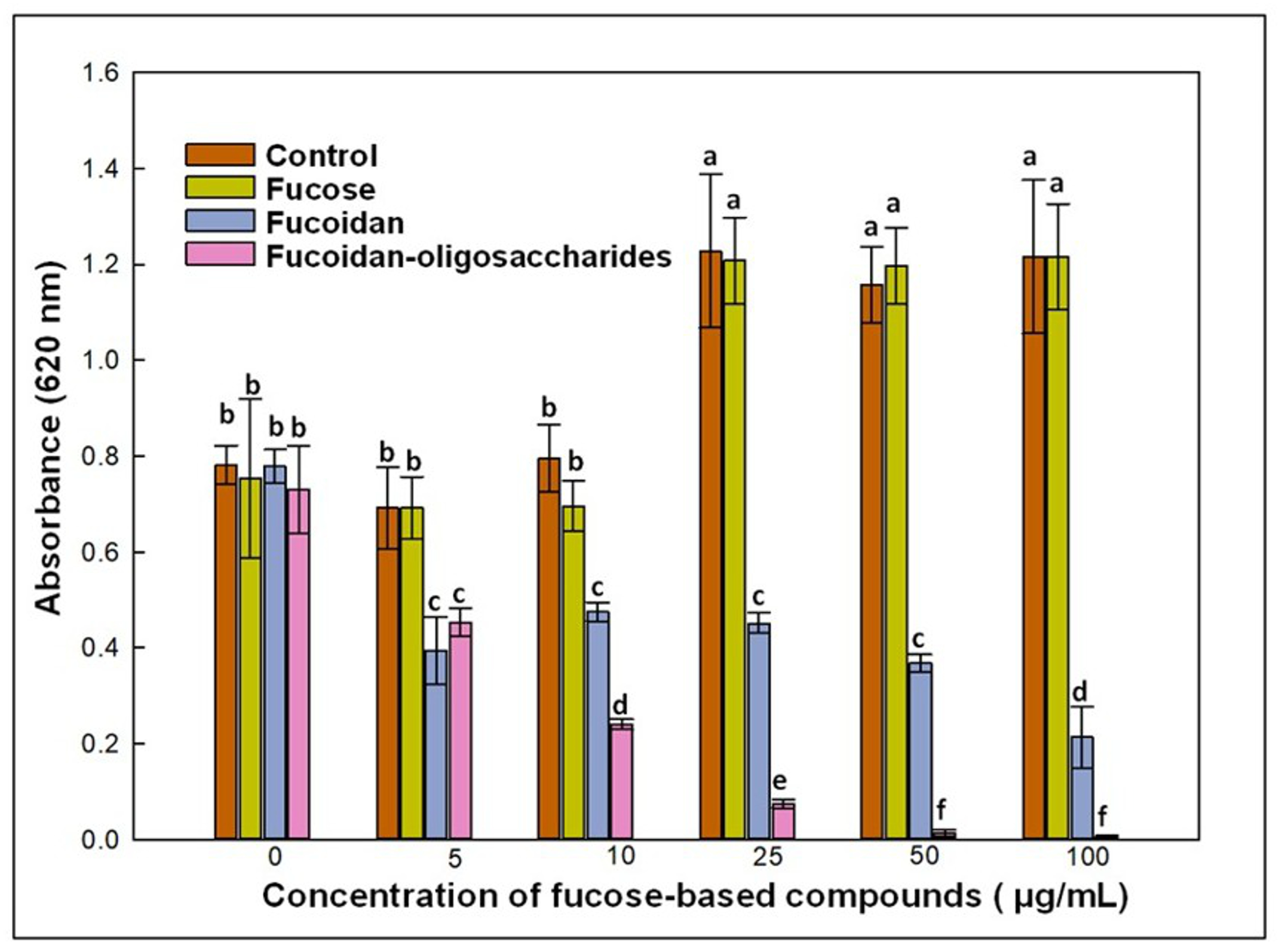
3.2. Effect of Fucose-Based Compounds on C. jejuni Growth
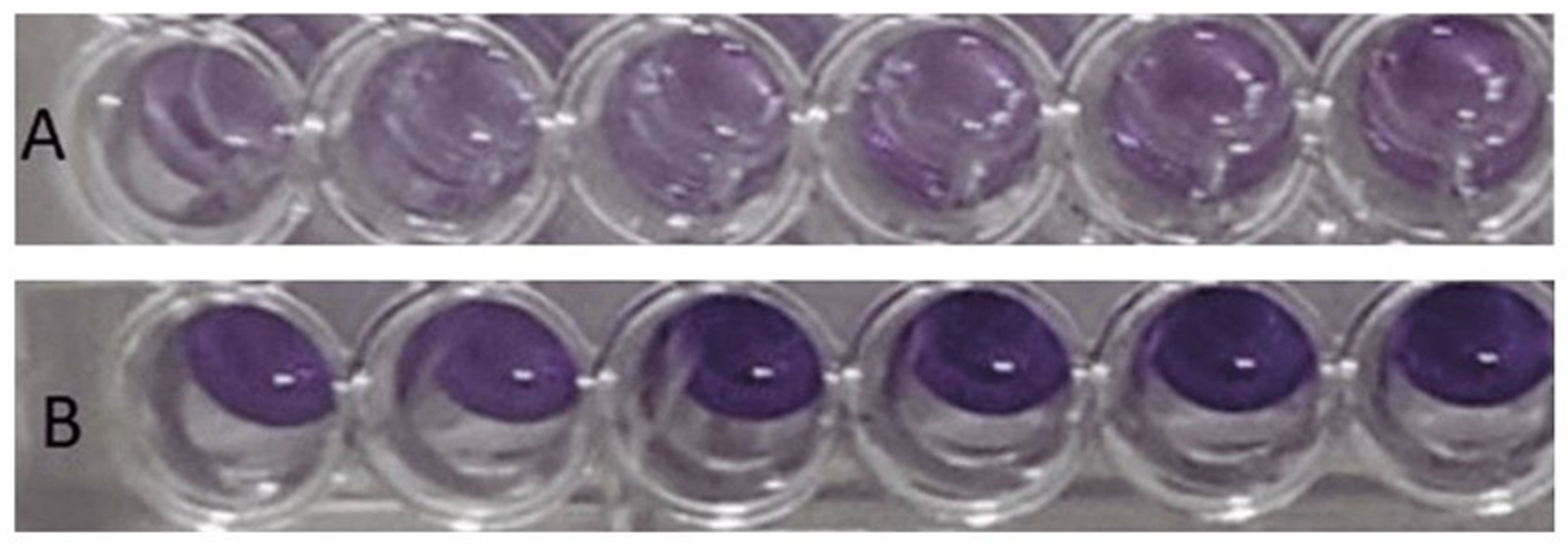
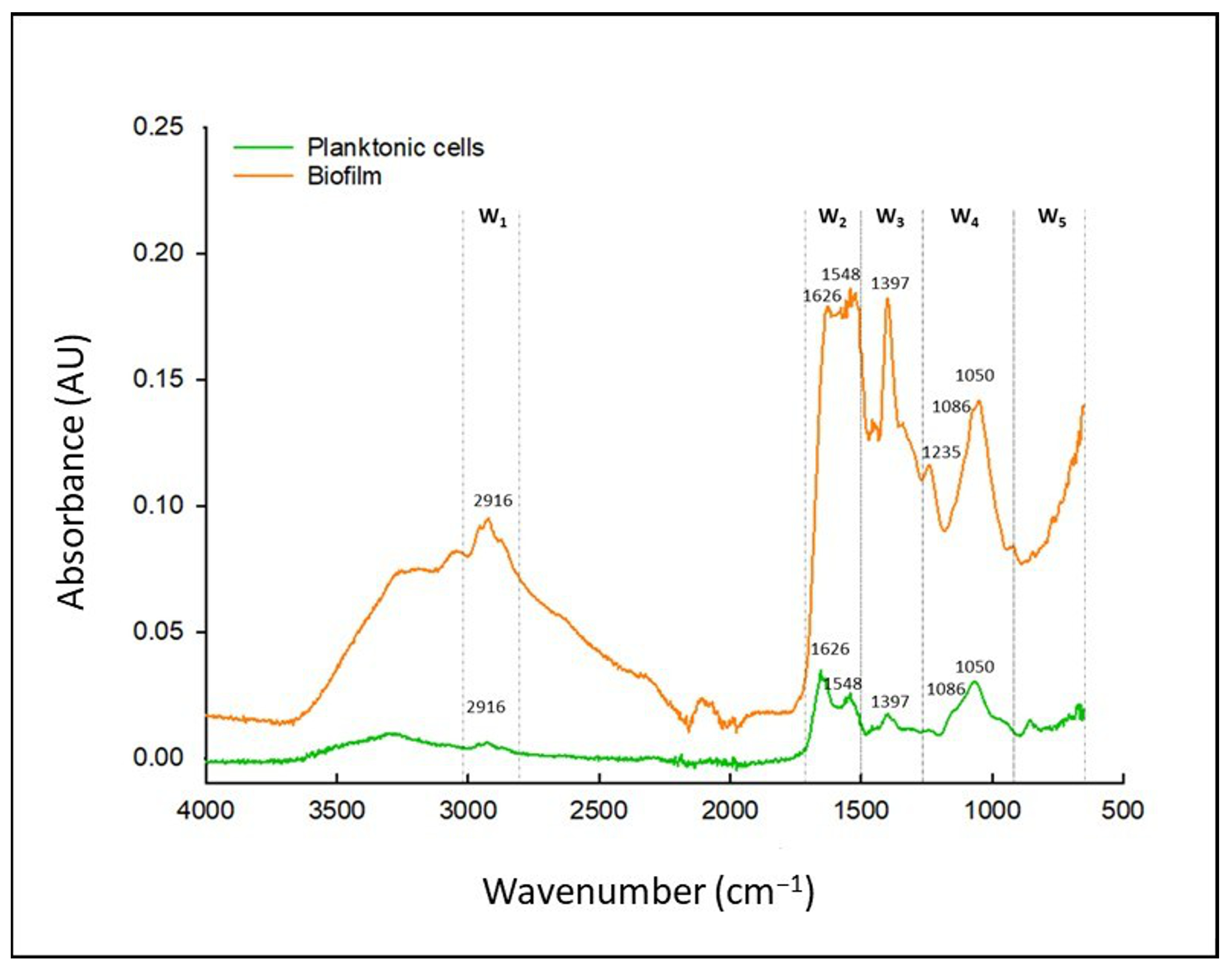
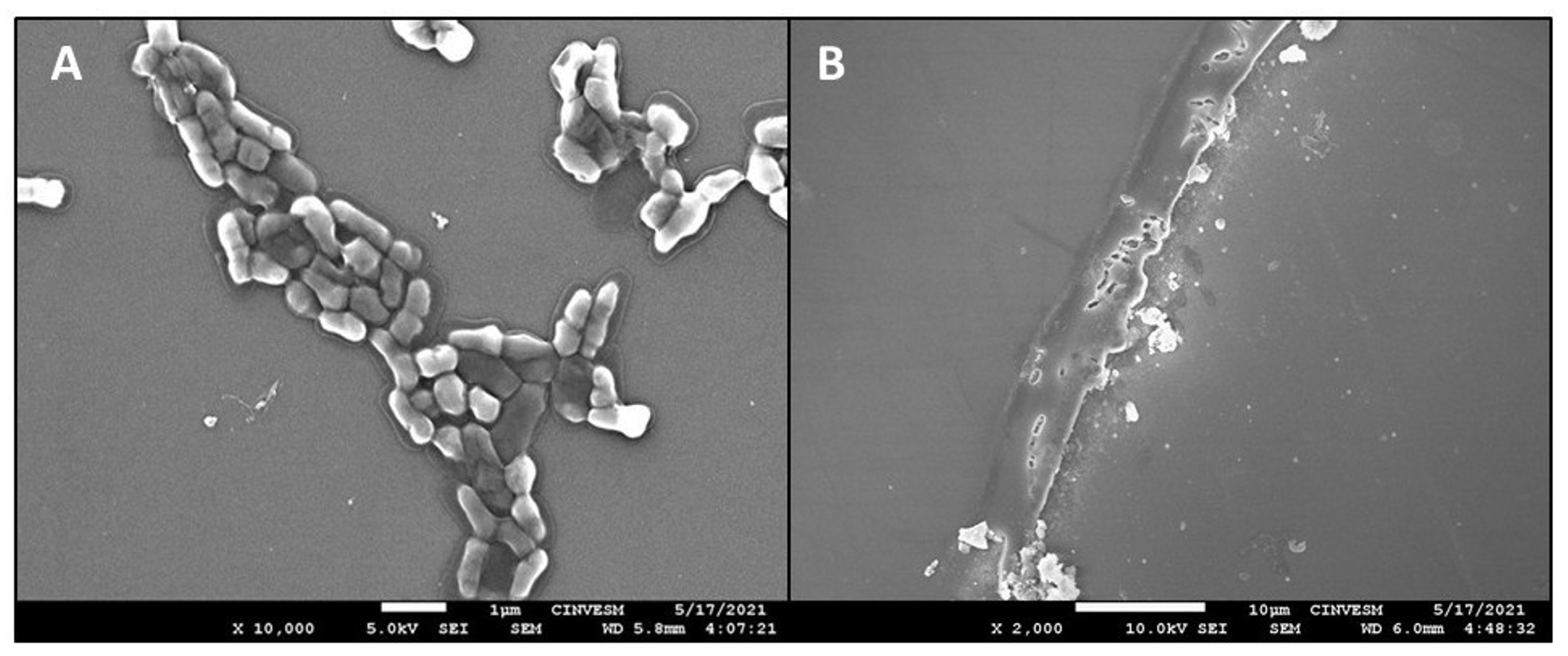
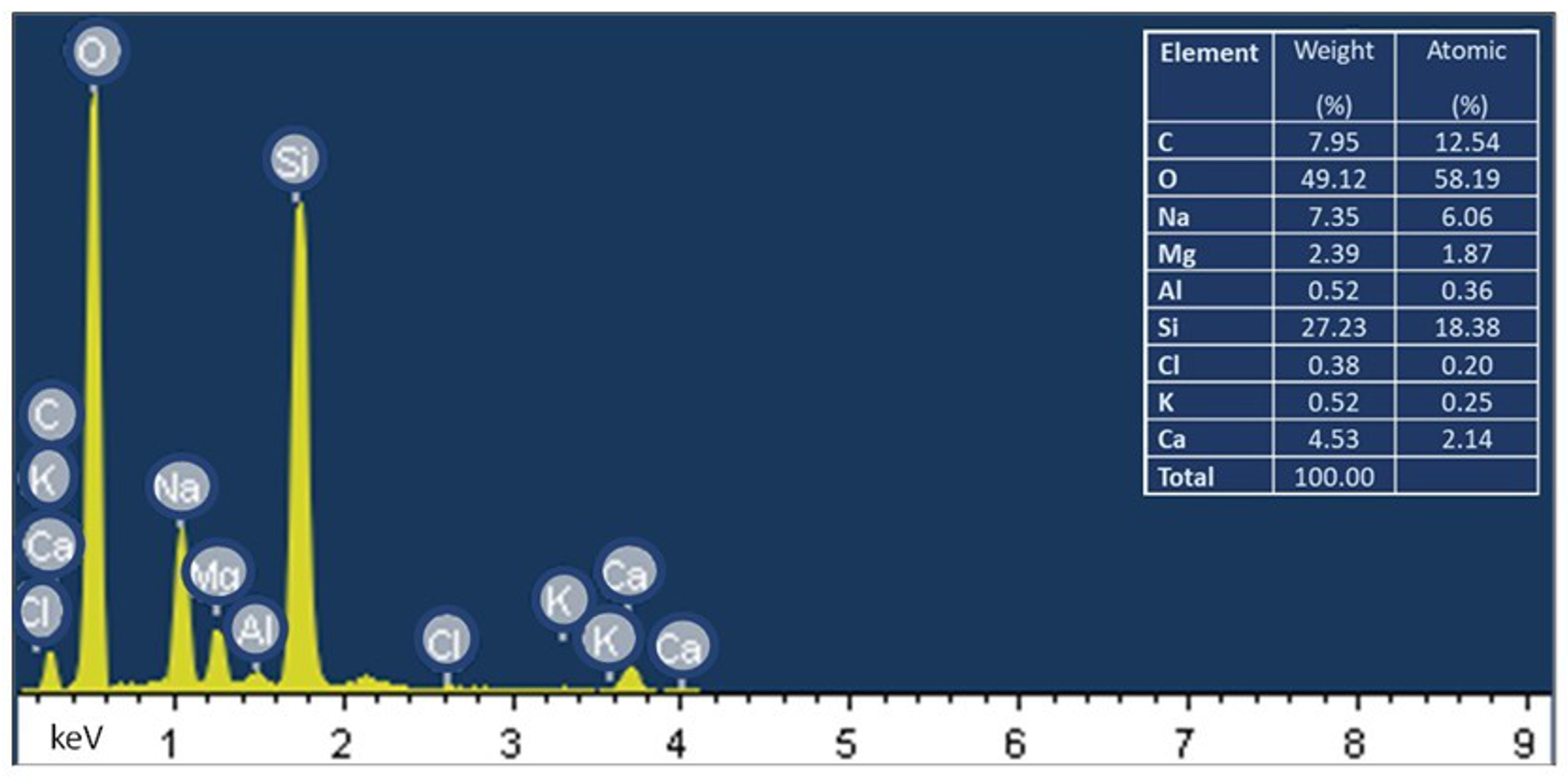
3.3. Characterization of Abiotic Biofilms of C. jejuni
3.4. Effect of Fucose-Based Compounds on Biofilm Formation
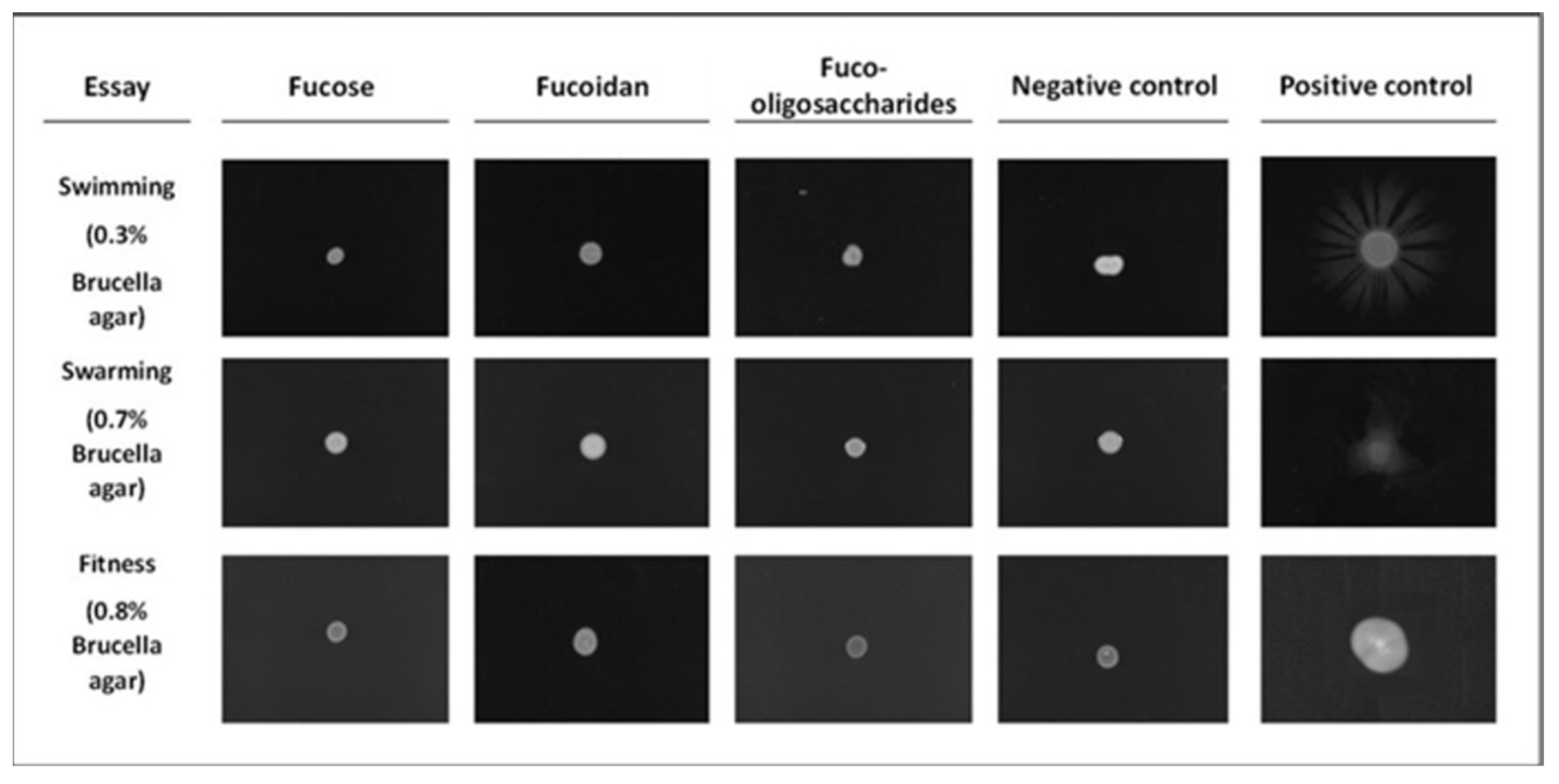
3.5. Motility Assays
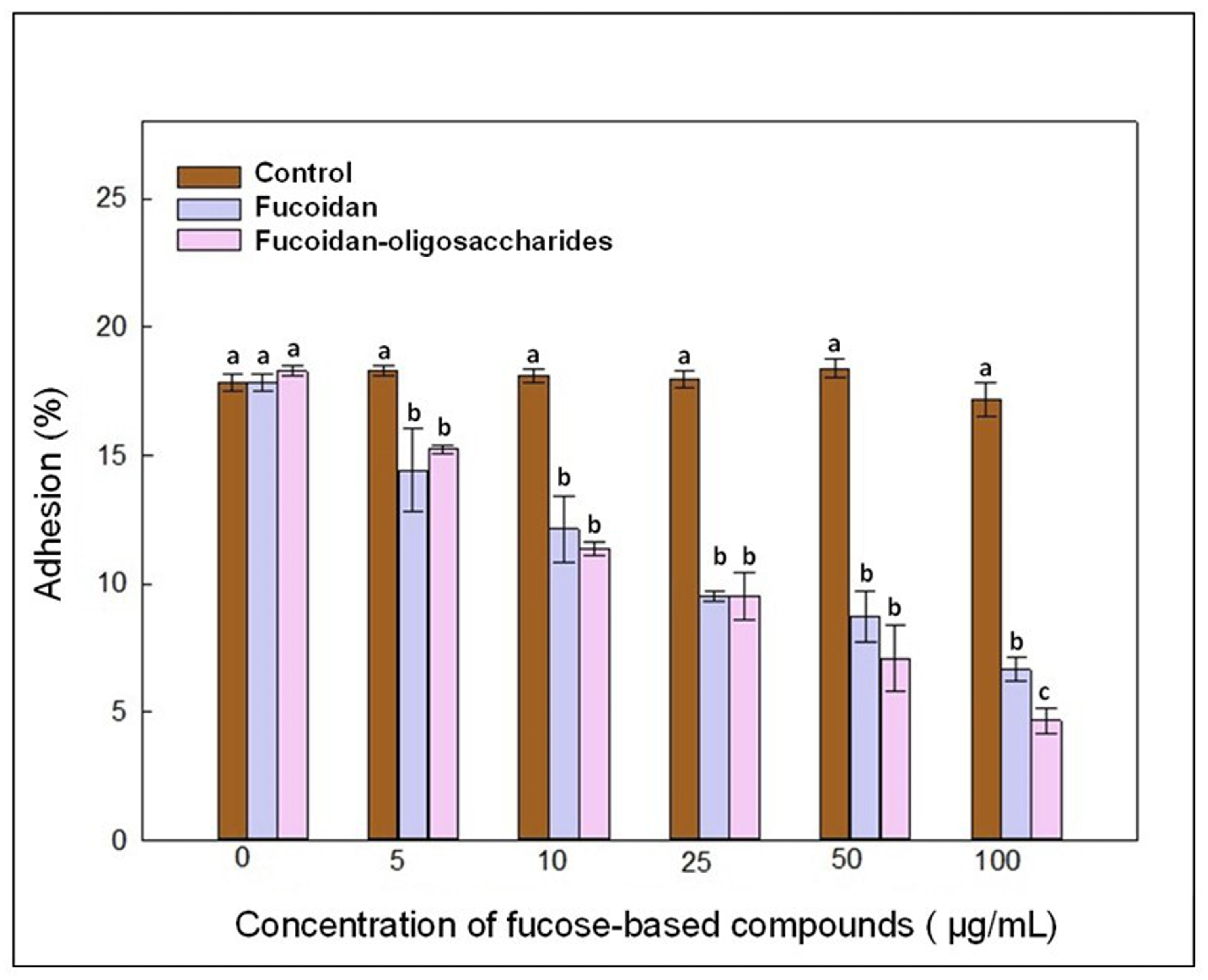
3.6. Adhesion Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Campylobacter. 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/campylobacter (accessed on 9 March 2024).
- Igwaran, A.; Okoh, A.I. Human campylobacteriosis: A public health concern of global importance. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davys, G.; Marshall, J.C.; Fayaz, A.; Weir, R.P.; Benschop, J. Campylobacteriosis associated with the consumption of unpasteurized milk: Findings from a sentinel surveillance site. Epidemiol. Infect. 2020, 148, e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronowski, C.; James, C.E.; Winstanley, C. Role of environmental survival in transmission of Campylobacter jejuni. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2014, 356, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimunović, K.; Ramić, D.; Xu, C.; Smole Možina, S. Modulation of Campylobacter jejuni motility, adhesion to polystyrene surfaces, and invasion of INT407 cells by Quorum-Sensing inhibition. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Feng, J.; Zhang, J.; Lu, X. Campylobacter biofilms. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 264, 127149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, N.; Marce, C.; Magras, C.; Cappelier, J.M. An overview of methods used to clarify pathogenesis mechanisms of Campylobacter jejuni. J. Food Prot. 2010, 73, 786–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwivedi, R.; Nothaft, H.; Garber, J.; Xin Kin, L.; Stahl, M.; Flint, A.; van Vliet, A.H.; Stintzi, A.; Szymanski, C.M. L-fucose influences chemotaxis and biofilm formation in Campylobacter jejuni. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 101, 575–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval Larios, G.; Huerta Ocampo, J.Á.; Sarabia Sainz, J.A.; García Galaz, A.; Guzmán-Partida, A.M.; Madera Santana, T.J.; Ramos-Clamont Montfort, G. Core-shell nanoparticles from fucoidan neoglycans: Synthesis, characterization with capability of glycomimetic ligands for Campylobacter jejuni. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2023, 6, 100384. [Google Scholar]
- Garber, J.M.; Nothaft, H.; Pluvinage, B.; Stahl, M.; Bian, X.; Porfirio, S.; Enriquez, A.; Butcher, J.; Huang, H.; Glushka, J.; et al. The gastrointestinal pathogen Campylobacter jejuni metabolizes sugars with potential help from commensal Bacteroides vulgatus. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, N.; Zhang, W.; Mu, W. Recent advances in a functional deoxy hexose L-fucose: Occurrence, physiological effects, and preparation. Trends Food Sci. 2023, 138, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Ren, X.; Yu, Y.; Gao, W.; Zhu, C.; Sun, H.; Kong, Q.; Fu, X.; Mou, H. Fucose-containing bacterial exopolysaccharides: Sources, biological activities, and food applications. Food. Chem. X 2022, 13, 100233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, G.; Yu, G.; Zhang, J.; Ewart, H.S. Chemical structures and bioactivities of sulfated polysaccharides from marine algae. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 196–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitton, H.J.; Stringer, D.S.; Park, A.Y.; Karpiniec, S.N. Therapies from Fucoidan: New Developments. Mar. Drugs. 2019, 17, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citkowska, A.; Szekalska, M.; Winnicka, K. Possibilities of fucoidan utilization in the development of pharmaceutical dosage forms. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ale, M.T.; Mikkelsen, J.D.; Meyer, A.S. Important determinants for fucoidan bioactivity: A critical review of structure-function relations and extraction methods for fucose-containing sulfated polysaccharides from brown seaweeds. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2106–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayed, A.; El-Aasr, M.; Ibrahim, A.-R.S.; Ulber, R. Fucoidan characterization: Determination of purity and physicochemical and chemical properties. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Weelden, G.; Bobiński, M.; Okła, K.; van Weelden, W.J.; Romano, A.; Pijnenborg, J.M.A. Fucoidan structure and activity in relation to anti-cancer mechanisms. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silchenko, A.S.; Kusaykin, M.I.; Kurilenko, V.V.; Zakharenko, A.M.; Isakov, V.V.; Zaporozhets, T.S.; Isakov, V.V.; Zvyagintseva, T.N. Hydrolysis of fucoidan by fucoidanase isolated from the marine bacterium, Formosa algae. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2413–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielesz, A.; Biniaś, W.; Paluch, J. Mild acid hydrolysis of fucoidan: Characterization by electrophoresis and FT-Raman spectroscopy. Carbohydr. Res. 2011, 346, 1937–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, N.S.; Tabarsa, M.; You, S.; Ghandehari Yazdi, A.P.; Cao, R.; Gavlighi, H.A.; Babakhani, A. Hydrolysis and cross-flow ultrafiltration as an alternative process to isolate fucoidans from edible seaweed Nizamuddinia zarnardinii with enhanced immunostimulatory efficacy. Algal Res. 2024, 82, 103632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeser, R.J.; Medler, R.T.; Billington, S.J.; Jost, B.H.; Joens, L.A. Characterization of Campylobacter jejuni biofilms under defined growth conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1908–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elvers, K.T.; Park, S.F. Quorum sensing in Campylobacter jejuni: Detection of a luxS encoded signaling molecule. Microbiology 2002, 148, 1475–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Yang, L.; Lv, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, X.; Li, M.; Zhou, M.; Pan, L.; Chen, A.; Zhang, Z. Antibiofilm activity and mechanism of linalool against food spoilage Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenette, P.S.; Weiss, L. Sulfated glycans induce rapid hematopoietic progenitor cell mobilization: Evidence for selectin-dependent and independent mechanisms. Blood 2000, 96, 2460–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCoy, J.P.; Varani, J.; Goldstein, I.J. Enzyme-linked lectin assay (ELLA). II. Detection of carbohydrate groups on the surface of unfixed cells. Exp. Cell Res. 1984, 151, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval Larios, G.; Palafox Félix, S.; Armenta Corral, R.I.; García-Hernández, J.; Balandrán-Quintana, R.R.; Ramos Clamont Montfort, G. El fucoidan de Sargassum sinicola es reconocido in vitro por la bacteria Campylobacter jejuni. TIP Rev. Espec. Cienc. Químico-Biológicas 2024, 27, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtczak, K.; Byrne, J.P. Structural considerations for building synthetic glycoconjugates as inhibitors for Pseudomonas aeruginosa lectins. Chem. Med. Chem. 2022, 17, e202200081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauck, D.; Joachim, I.; Frommeyer, B.; Varrot, A.; Philipp, B.; Möller, H.M.; Imberty, A.; Exner, T.E.; Titz, A. Discovery of two classes of potent glycomimetic inhibitors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa LecB with distinct binding modes. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 1775–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.J.; Gibson, M.I. Toward glycomaterials with selectivity as well as affinity. JACS Au 2021, 1, 2089–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomin, V.H.; Valente, A.P.; Pereira, M.S.; Mourão, P.A. Mild acid hydrolysis of sulfated fucans: A selective 2-desulfation reaction and an alternative approach for preparing tailored sulfated oligosaccharides. Glycobiology 2005, 15, 1376–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagley, S.; Newcombe, J.; Laing, E.; Yusuf, E.; Sambles, C.M.; Studholme, D.J.; La Ragione, R.M.; Titball, R.W.; Champion, O.L. Differences in carbon source utilization distinguish Campylobacter jejuni from Campylobacter coli. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahl, M.; Friis, L.M.; Nothaft, H.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Szymanski, C.M.; Stintzi, A. L-fucose utilization provides Campylobacter jejuni with a competitive advantage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 7194–7199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velayudhan, J.; Kelly, D.J. Analysis of gluconeogenic and anaplerotic enzymes in Campylobacter jejuni: An essential role for phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase. Microbiology 2002, 148, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraoka, W.T.; Zhang, Q. Phenotypic and genotypic evidence for L-fucose utilization by Campylobacter jejuni. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 1065–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middendorf, P.S.; Wijnands, L.M.; Boeren, S.; Zomer, A.L.; Jacobs-Reitsma, W.F.; den Besten, H.M.W.; Abee, T. Activation of the L-fucose utilization cluster in Campylobacter jejuni induces proteomic changes and enhances Caco-2 cell invasion and fibronectin binding. Heliyon 2024, 10, e34996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayrapetyan, O.N.; Obluchinskaya, E.D.; Zhurishkina, E.V.; Skorik, Y.A.; Lebedev, D.V.; Kulminskaya, A.A.; Lapina, I.M. Antibacterial properties of fucoidans from the brown algae Fucus vesiculosus L. of the Barents Sea. Biology 2021, 10, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanisamy, S.; Vinosha, M.; Rajasekar, P.; Anjali, R.; Sathiyaraj, G.; Marudhupandi, T.; Selvam, S.; Prabhu, N.M.; You, S. Antibacterial efficacy of a fucoidan fraction (Fu-F2) extracted from Sargassum polycystum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Liu, Y.; Cao, M.J.; Liu, G.M.; Chen, Q.; Sun, L.; Chen, H. Antibacterial activity and mechanisms of depolymerized fucoidans isolated from Laminaria japonica. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 172, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graikini, D.; Soro, A.B.; Sivagnanam, S.P.; Tiwari, B.K.; Sánchez, L. Bioactivity of fucoidan-rich extracts from Fucus vesiculosus against rotavirus and foodborne pathogens. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimesaat, M.M.; Backert, S.; Alter, T.; Bereswill, S. Molecular targets in Campylobacter infections. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Püning, C.; Su, Y.; Lu, X.; Gölz, G. Molecular mechanisms of Campylobacter biofilm formation and Quorum Sensing. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2021, 431, 293–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helm, D.; Labischinski, H.; Schallehn, G.; Naumann, D. Classification and identification of bacteria by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1991, 137, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novais, Â.; Freitas, A.R.; Rodrigues, C.; Peixe, L. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy: Unlocking fundamentals and prospects for bacterial strain typing. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 38, 427–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, C.; Novais, Â.; Magalhães, A.; Lopes, J.; Peixe, L. Diverse high-risk B2 and D Escherichia coli clones depicted by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ding, S.; Wang, G.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G. In situ characterization and analysis of Salmonella biofilm formation under meat processing environments using a combined microscopic and spectroscopic approach. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 167, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, R.T.; Mendonça, E.P.; Monteiro, G.P.; Siqueira, M.C.; Pereira, C.B.; Peres, P.; Fernandez, H.; Rossi, D.A. Intrinsic and extrinsic aspects on Campylobacter jejuni biofilms. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tram, G.; Klare, W.P.; Cain, J.A.; Mourad, B.; Cordwell, S.J.; Korolik, V.; Day, C.J. RNA sequencing data sets identifying differentially expressed transcripts during Campylobacter jejuni biofilm formation. Microbiol. Resour. Announce 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turonova, H.; Briandet, R.; Rodrigues, R.; Hernould, M.; Hayek, N.; Stintzi, A.; Pazlarova, J.; Tresse, O. Biofilm spatial organization by the emerging pathogen Campylobacter jejuni: Comparison between NCTC 11168 and 81-176 strains under microaerobic and oxygen-enriched conditions. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turonova, H.; Neu, T.R.; Ulbrich, P.; Pazlarova, J.; Tresse, O. The biofilm matrix of Campylobacter jejuni determined by fluorescence lectin-binding analysis. Biofouling 2016, 32, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taglialegna, A.; Lasa, I.; Valle, J. Amyloid structures as biofilm matrix scaffolds. J. Bacteriol. 2016, 198, 2579–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matilla-Cuenca, L.; Toledo-Arana, A.; Valle, J. Anti-biofilm molecules targeting functional amyloids. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensson, S.L.; Pryjma, M.; Gaynor, E.C. Flagella-mediated adhesion and extracellular DNA release contribute to biofilm formation and stress tolerance of Campylobacter jejuni. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLennan, M.K.; Ringoir, D.D.; Frirdich, E.; Svensson, S.L.; Wells, D.H.; Jarrell, H.; Szymanski, C.M.; Gaynor, E.C. Campylobacter jejuni biofilms up-regulated in the absence of the stringent response utilize a calcofluor white-reactive polysaccharide. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Z.; Wang, J.; Nie, X.; Ding, Y.; Xue, L.; Chen, M.; Wu, S.; et al. Campylobacter jejuni biofilm formation under aerobic conditions and inhibition by ZnO nanoparticles. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, E.; Andrews, K.J.; Jeon, B. Enhanced biofilm formation by ferrous and ferric iron through oxidative stress in Campylobacter jejuni. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grumbein, S.; Opitz, M.; Lieleg, O. Selected metal ions protect Bacillus subtilis biofilms from erosion†. Metallomics 2014, 6, 1441–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, J.Y.; Jung, M.J.; Jeong, I.H.; Yamazaki, K.; Kawai, Y.; Kim, B.M. Antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities of sulfated polysaccharides from marine algae against dental plaque bacteria. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Manivasagan, P.; Lee, J.W.; Pham, D.T.N.; Oh, J.; Kim, Y.M. Fucoidan-stabilized gold nanoparticle-mediated biofilm inhibition, attenuation of virulence and motility properties in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, G.; Rajendran, I.; Jayakumar, T.; Mani, A.; Govindaraju, R.; Dhayalan, S. Evaluation of antibiofilm and antiquorum sensing activities of fucoidan characterized from Padina boryana against nosocomial pathogens. Appl. Biochem. Biotech. 2024, 196, 4727–4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashistha, A.; Sharma, N.; Nanaji, Y.; Kumar, D.; Singh, G.; Barnwal, R.P.; Yadav, A.K. Quorum sensing inhibitors as therapeutics: Bacterial biofilm inhibition. Bioorganic Chem. 2023, 136, 106551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrixson, D.R.; DiRita, V.J. Identification of Campylobacter jejuni genes involved in commensal colonization of the chick gastrointestinal tract. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 52, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Miller, J.F. Campylobacter jejuni colonization of mice with limited enteric flora. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 5261–5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuter, M.; van Vliet, A.H. Signal balancing by the CetABC and CetZ chemoreceptors controls energy taxis in Campylobacter jejuni. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, E.J.; Nakane, D.; Kabata, Y.; Hendrixson, D.R.; Nishizaka, T.; Beeby, M. Campylobacter jejuni motility integrates specialized cell shape, flagellar filament, and motor, to coordinate action of its opposed flagella. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigematsu, M.; Umeda, A.; Fujimoto, S.; Amako, K. Spirochaete-like swimming mode of Campylobacter jejuni in a viscous environment. J. Med. Microbiol. 1998, 47, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Palacios, G.M.; Cervantes, L.E.; Ramos, P.; Chavez-Munguia, B.; Newburg, D.S. Campylobacter jejuni binds intestinal H(O) antigen (Fuc alpha 1, 2Gal beta 1, 4GlcNAc), and fucosyloligosaccharides of human milk inhibit its binding and infection. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 14112–14120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, C.J.; Tiralongo, J.; Hartnell, R.D.; Logue, C.A.; Wilson, J.C.; von Itzstein, M.; Korolik, V. Differential carbohydrate recognition by Campylobacter jejuni strain 11168: Influences of temperature and growth conditions. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.T.; Nanthakumar, N.N.; Newburg, D.S. The Human milk oligosaccharide 2′-fucosyllactose quenches Campylobacter jejuni-induced inflammation in human epithelial cells HEp-2 and HT-29 and in mouse intestinal mucosa. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 1980–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattin, S.; Bernardi, A. Glycoconjugates and glycomimetics as microbial anti-adhesives. Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gange, C.T.; Quinn, J.M.W.; Zhou, H.; Kartsogiannis, V.; Gillespie, M.T.; Ng, K.W. Characterization of sugar binding by osteoclast inhibitory lectin. JBC 2004, 279, 29043–29049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Tan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Luo, P.; Liu, H. Molecular targets and related biologic activities of fucoidan: A review. Mar Drugs. 2020, 18, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Test | Agar Concentration (%) | Culture Media | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Swimming | 0.3 | Brucella | MH |
| Swarming | 0.7 | Brucella | MH |
| Fitness | 0.8 | Brucella | MH |
| Standard | 1.5 | Brucella | MH |
| Zeta Potential (mV) | Size (d.nm) | Polydispersity Index | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fucoidan from A. nodosum | −66.6 ± 0.5 | 450.6 ± 42.3 | 0.48 |
| Unfractionated hydrolysate | −44.5 ± 10.4 | 257.1 ± 67.9 | 0.92 |
| Fraction < 3 kDa | −41.9 ± 8.5 | 121.3 ± 95.9 | 1.00 |
| Concentration mg/mL | Fucose μ (η−1) | Fucoidan μ (η−1) | Fucoidan-Oligosaccharides μ (η−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 0.060 ± 0.011 a | 0.127 ± 0.022 b | 0.0994± 0.085 a |
| 50 | 0.064 ± 0.022 a | 0.129 ± 0.033 b | 0.0998± 0.060 a |
| 25 | 0.067 ± 0.013 a | 0.127 ± 0.029 b | 0.0727± 0.056 a |
| 10 | 0.064 ± 0.012 a | 0.144± 0.046 a | 0.0757± 0.043 a |
| 5 | 0.066 ± 0.018 a | 0.154 ± 0.130 a | 0.0857± 0.035 a |
| Control | 0.065 ± 0.012 a | 0.154 ± 0.130 a | 0.0724 ± 0.039 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palafox Félix, S.; Sandoval Larios, G.; Cabrera, R.; García-Galaz, A.; Huerta-Ocampo, J.Á.; Guzmán-Partida, A.M.; Armenta Corral, R.I.; Sarabia-Sainz, J.A.; Ramos Clamont Montfort, G. Effects of Fucoidan and Fucoidan Oligosaccharides in Growth and Quorum Sensing Mediated Virulence Factor of Campylobacter Jejuni. Polysaccharides 2025, 6, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides6020024
Palafox Félix S, Sandoval Larios G, Cabrera R, García-Galaz A, Huerta-Ocampo JÁ, Guzmán-Partida AM, Armenta Corral RI, Sarabia-Sainz JA, Ramos Clamont Montfort G. Effects of Fucoidan and Fucoidan Oligosaccharides in Growth and Quorum Sensing Mediated Virulence Factor of Campylobacter Jejuni. Polysaccharides. 2025; 6(2):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides6020024
Chicago/Turabian StylePalafox Félix, Sharon, Giovanna Sandoval Larios, Rosina Cabrera, Alfonso García-Galaz, José Ángel Huerta-Ocampo, Ana María Guzmán-Partida, Rosa Idalia Armenta Corral, Jose Andrei Sarabia-Sainz, and Gabriela Ramos Clamont Montfort. 2025. "Effects of Fucoidan and Fucoidan Oligosaccharides in Growth and Quorum Sensing Mediated Virulence Factor of Campylobacter Jejuni" Polysaccharides 6, no. 2: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides6020024
APA StylePalafox Félix, S., Sandoval Larios, G., Cabrera, R., García-Galaz, A., Huerta-Ocampo, J. Á., Guzmán-Partida, A. M., Armenta Corral, R. I., Sarabia-Sainz, J. A., & Ramos Clamont Montfort, G. (2025). Effects of Fucoidan and Fucoidan Oligosaccharides in Growth and Quorum Sensing Mediated Virulence Factor of Campylobacter Jejuni. Polysaccharides, 6(2), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides6020024







