Abstract
Obesity is closely associated with appetite dysregulation, influenced by behavioral, hormonal, and neurological factors. The Council on Nutrition Appetite Questionnaire (CNAQ) is a validated tool, translated into Arabic, but its application in weight-loss interventions remains underexplored. This secondary cross-sectional analysis evaluated whether the Arabic CNAQ can differentiate appetite levels after a 6-month telenutrition weight-loss intervention supported by telemonitoring and health coaching, and whether appetite is associated with weight-loss outcomes. A total of 36 participants were assessed: the intervention group (n = 21), who completed the program, and the control group (n = 15), who received no continuous support. Appetite was measured using the CNAQ after 6 months. Independent-samples t-tests and Mann–Whitney U tests were applied to compare appetite scores, while Chi-square tests were used for appetite categories. Results showed mean CNAQ scores of 27.87 (SD = 2.64) for the control group and 26.86 (SD = 4.46) for the intervention group (p = 0.402). Most participants reported moderate appetite (93.3% control; 76.2% intervention), with no significant between-group differences (p = 0.367). Although differences were not statistically significant, the findings demonstrate the feasibility of using the Arabic CNAQ in telehealth weight management. Larger studies with repeated measures are needed to confirm its utility in clinical and dietetic practice.
1. Introduction
Obesity is a global public health concern that is associated with several cardiometabolic risk factors such as hyperlipidemia and high blood pressure, all of which have been strongly linked to increased morbidity and mortality risks of cardiometabolic diseases [1]. Recent global estimations report that by 2030, the number of individuals with obesity will increase to ~1 billion [2]. Across the Middle East region, 1 in 5 men (58 million men, 21.69%) and 1 in 3 women (84 million women, 33.15%) are predicted to have obesity by 2030 [1]). In the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), there has been an increase in the prevalence of obesity over the last decades [3]. According to the recent World Health Survey report of KSA, in 2019, the prevalence of overweight [Body Mass Index (BMI) 25.0 kg/m2 to <30 kg/m2] and obesity [BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2] were 38% and 20%, respectively, amongst Saudi adults aged 32 ± 9 years [3]. In 2023, another study [4] reported a 32.8% and 23% prevalence rate of overweight and obesity, respectively, highlighting the urgent needs for focused interventions to manage obesity. Obesity is a multifactorial condition caused by numerous factors, such as genetics, diet, physical activity, smoking, and mental health [5,6,7,8,9]. The human appetite system is a network that connects biological, psychological, and environmental factors to collectively regulate hunger as well as eating patterns. When the human appetite system becomes dysregulated, individuals lose track of their eating pattern and tend to eat more calories than their body needs, which makes them become obese [10]. Obesity can be driven by a strong desire for food, sometimes leading to inappropriate food choices (such as frequent consumption of calorie dense food) or finding it difficult to inhibit the eating process [10]. Every individual has varied appetite systems; this is because of the hormonal, genetic, neuropsychological, and lifestyle influences, which cause them to eat more or less. The appetite system serves as a bridge connecting external and internal environments. Since obesity and the human appetite system are closely linked, obesity treatment strategies should target both behavioral and physiological aspects, empowering individuals to make healthy behavioral changes rather than following diet plans and extensive exercise. Individual empowerment includes providing health coaching and enhancing active learning by helping individuals to manage their stress-eating habits, as well as giving them awareness on mindful eating. If we rely only on health education, then it is not sufficient to promote long-term changes in lifestyle behaviors [11]; so, we need to look for more factors in appetite systems that can be improved on the way to becoming less obese. This is why health coaching has also emerged as an efficient approach in preventing and treating obesity along with other factors. The advantages of health coaching in managing obesity are highlighted by recent study carried out by [12].). In a randomized controlled trial, coaching participants lost 5.4 kg and reduced their BMI by 1.9 kg/m2 (p < 0.05), resulting in a 15.6% reduction in excess weight loss compared with 2.5% in controls (p = 0.015) [12]. Additionally, coaching demonstrated both behavioral and clinical benefits by improving psychosocial outcomes, such as self-regulation, motivation, and patient activation, and increasing weekly physical activity (+50.3 vs. +7.1 min, p = 0.004) [12]. Health coaching is a patient-centric strategy whereby a working relationship is established between a health coach and patient to facilitate healthy changes concerning lifestyle behaviors, assisting them with self-management, giving them cognitive support, as well as integrating advanced technologies like telenutrition to track patients’ progress in real time.
Telenutrition is nowadays highly liked by health coaches when it comes to obesity management. Additional proof of the efficacy of telenutrition in managing obesity comes from a pilot randomized controlled trial involving 59 middle-aged and older men with cardiovascular risk factors and obesity, which was carried out by Ventura Marra et al. (2019) [13]. Weight, waist circumference, body fat, and caloric intake were significantly reduced over a 12-week period in both the enhanced usual care group and the intervention group (weekly dietitian support via telenutrition) (p < 0.0001). Interestingly, compared with 41.4% of the controls, 70.4% of participants in the intervention group lost at least 5% of their baseline weight (p = 0.035). The intervention group lost an average of 8.3 kg (6.2%) of weight compared with 5.0 kg (4.3%) of the controls, and their daily caloric intake dropped by about 600 kcal compared with about 445 kcal [13]. Telenutrition is a scalable and successful strategy for managing obesity, particularly in rural populations, as evidenced by retention (94.9%), adherence (88.5%), and satisfaction (92%) surpassing feasibility thresholds. Telenutrition and traditional consultations were compared in a clinical study of 233 overweight and obese women in Colombia, carried by Kuzmar et al. (2015) [14]. With a dropout/failure risk roughly half that of traditional care (RR = 0.45, 95% CI [0.27–0.85], p < 0.05), telenutrition had higher success rates after 16 weeks (76.5%) than traditional care (23.5%). Even though traditional care resulted in slightly larger reductions in BMI and hips, telenutrition was just as successful and provided better adherence, confirming its potential as a scalable substitute for in-person programs [14]. Many studies have highlighted the utmost importance of telenutrition, given that traditional face-to-face lifestyle lead to increased healthcare costs, in addition to being more time-consuming and resource-demanding, but with the help of the digital platforms the costs can be reduced drastically; real time tracking, and self-monitoring has expanded reach by a lot [15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23]. Telenutrition involves a dietitian interactively using electronic information and telecommunication technologies to implement the Nutrition Care Process with patients or clients at a remote location [14]. Research indicates that technology-based interventions might be more effective in weight management than traditional dietetic consultations, because of continuous self-monitoring, real time feedback, cost-effectiveness, and accessiblitiy [13,24,25,26,27,28,29]. Using digital technologies, such as electronic scales [26,27], smartphones, and smartwatches [27], can enhance the patient’s self-efficacy and empower healthy behavioral changes [24,25,26,27,28,29]. In the results of past studies, successful weight loss has been attributed to the efficacy of self-monitoring food intake and exercise using these technologies [24,25,26,27,28,29].
Telenutrition can be further enhanced via telemonitoring [30,31,32,33,34,35], whereby a medical health provider uses digital technologies to monitor and interpret several client outcomes, including body weight, to enhance the management of provided care [31,32]. A study highlighted that delivering health coaching sessions over the phone with a portion control plate was significantly associated with beneficial changes; in this way, patients could control portion sizes without having to track calories at each meal, and the brain’s appetite system adjusted over time to anticipate more sensible serving sizes. Moreover, combining online health coaching with “MyPlate” dietary recommendations was associated with a reduction in central adiposity, as well as enhancements in satiety and quality of life [33]. Similarly, coaching adults with obesity regarding the dysregulation of their hunger and satiety while following a traditional weight-loss intervention (i.e., a balanced energy-deficit diet and increased physical activity) was suggested as a promising approach to weight loss in a recent randomized controlled trial (RCT) [33]. A study has incorporated psychoeducation to improve awareness of overeating-related thoughts, situations, environments, and moods. Self-monitoring, coping skills, and experiential learning were also integrated, enhancing responsiveness to internal cues of hunger or satiety, as well as decreasing food cue sensitivity. A paper by Suzuki et al. (2012) highlighted the importance of targeting appetite levels when managing obesity [34], but there is still a lack of research on telenutrition weight-loss programs because of its complexity in measuring appetite, some gaps in digital health, and limited awareness in many parts around the globe. The current study is part of a pilot randomized controlled trial that has confirmed significant reductions in weight, BMI, fat%, visceral fat, and WC, with increased muscle % within the period of 3 months [35].
The aim of this study is to compare the appetite levels of obese adults who took part in a 6-month telenutrition weight-loss program accompanied by weekly telemonitoring and monthly health coaching to those who received telenutrition alone; the study used the Arabic version of the Council on Nutrition Appetite Questionnaire (CNAQ).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
The current study is secondary interview-based cross-sectional analysis, which was conducted on two groups after the completion of a previously published 6-month pilot randomized controlled trial (RCT) [36]. The control group received a tailored hypocaloric diet delivered through telenutrition, while the intervention group received the same dietary plan with additional support via weekly telemonitoring and monthly telehealth coaching.
2.2. Participants: Eligibility and Recruitment
The study conducted between January 2024 and January 2025 included 36 participants (21 in the intervention group and 15 in the control group). Adults (20–50 y) with overweight or obesity (WHO BMI categories) who were able to participate in remote visits were recruited via university/research-center announcements and screened for eligibility. Exclusion criteria were pregnancy/lactation; inability to use telecommunication apps or lack of internet; current participation in another weight-loss program or use of weight-loss medication within 3 months; chronic conditions requiring medical nutrition therapy (e.g., diabetes, CVD) or endocrine disorders (e.g., thyroid disease); and unavailability for the 6-month follow-up. Eligibility criteria mirrored those specified for the parent RCT.
Participant enrollment and follow-up are presented in the CONSORT flow diagram (Figure 1). All subjects who agreed to join the study provided written informed consent and completed the CNAQ. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of The Research Ethics Committee (REC) at the Unit of Biomedical Ethics, Faculty of Medicine at King Abdul-Aziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia ([NCBE Registration No: HA-02-J-008] and [Reference No 527-21], date: 9 February 2022).
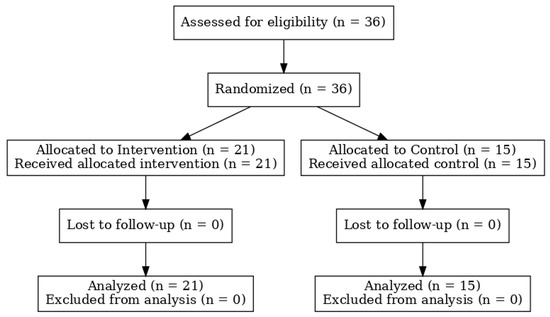
Figure 1.
CONSORT flow diagram of participant enrollment, allocation, follow-up, and analysis.
2.3. Interventions
The control group (telenutrition only): individualized hypocaloric diet delivered remotely by registered dietitians (RDs). The intervention group (telenutrition + support): same dietetic care plus weekly telemonitoring and monthly telehealth coaching delivered online by an integrative nutrition health coach using the “Circle of Life” framework (12 life domains) to guide goal setting and barrier management.
Adherence was documented using attendance logs for monthly sessions and weekly telemonitoring responses.
2.4. Appetite Assessment Using the Arabic Version of the Council of Nutrition Appetite Questionnaire (CNAQ)
Appetite levels were assessed using the validated Arabic version of the Council of Nutrition Appetite Questionnaire (CNAQ) [37], a validated screening tool consisting of 8 items that measure various aspects of appetite, including general appetite, satiety after eating, frequency of hunger, food taste and flavor perception, number of meals per day, nausea, and usual mood. Each item is rated on a 5-point scale (1 to 5), resulting in a total score ranging from 8 to 40, with lower scores indicating reduced appetite. Based on their total CNAQ score, participants were categorized into two groups: poor appetite (scores 8–28) and good appetite (Scores 29–40). The questionnaire was interview-based (~5 min) and administered by trained research assistants via telephone at 6 months.
Given the post-intervention timing and remote delivery, outcome assessors were not blinded to allocation; to limit bias, a standardized, verbatim script was used, and assessors were not involved in coaching delivery.
2.5. Data Analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using the statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) software (version 26; SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Descriptive statistics were calculated for all variables and are presented as mean (M) and standard deviations (SDs) for continuous variables, and as frequencies and percentages for categorical variables. To compare appetite scores between the control and intervention groups, the independent-samples t-test was used for normally distributed data, while the Mann–Whitney U test was applied for non-normally distributed data as determined by the Shapiro–Wilk test. The Chi-square test was employed to compare categorical appetite scores (low, moderate, high) between groups. Results are presented in both tabular and graphical formats, with p values of <0.05 considered statistically significant. Significance levels are clearly indicated in the tables and figures.
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
The mean age of participants was 36 years (SD = 5.5) in the control group and 34.9 years (SD = 9.7) in the intervention group. The mean weight was 92 kg (SD = 21.59) in the control group and 95.5 kg (SD = 26.41) in the intervention group.
The demographic profile of participants was broadly comparable between the control and intervention groups; details available in Table 1 below. Gender distribution was balanced across both groups. Allergies and ear, nose, and throat (ENT) conditions were the most commonly reported medical problems in both groups. A smaller proportion of participants reported current medication use, with slightly higher prevalence in the control group. Regarding family history, diabetes mellitus (DM) and cholesterol were the most frequently reported conditions across both groups. Parents as first-degree relatives (particularly fathers and mothers) were the main contributors to these family histories.

Table 1.
Demographic characteristics of participants in the study conducted at King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
3.2. Appetite Assessment (Response to CNAQ)
Table 2 shows that there were no significant differences in the evaluation of the eight appetite criteria between the two groups. Most of the participants (two-thirds or more) in both groups gave high scores (4–5) to two criteria, namely, “not feeling nauseous” and “general food taste.” These were closely followed by the criterion “general appetite”, where in both groups, slightly more than half of the participants evaluated it as high (4–5). For other appetite criteria, those who evaluated them as high (4–5) constituted less than 50%. Although the overall patterns were similar between groups, the largest difference emerged in the evaluation of mood, where a greater proportion of the control group (40%) reported high scores compared with the intervention group (23.8%).

Table 2.
Participant appetite assessment based on the Council on Nutrition Appetite Questionnaire (CNAQ).
When appetite was analyzed as a total score, the mean values were 27.87 (SD = 2.64) for the control group and 26.86 (SD = 4.46) for the intervention group, with a t-test showing no significant difference (p = 0.402). Similarly, when appetite levels were categorized into “moderate” and “high”, the Chi-square test confirmed no significant difference between groups (p = 0.367). The majority of participants in both groups had moderate appetite (93.3% in the control, and 76.2% in the intervention group), while a smaller proportion reported high appetite levels.
4. Discussion
The current study is the first telehealth weight-loss intervention in Saudi Arabia to use the Arabic version of the CNAQ to explore appetite regulation following a six-month telenutrition weight-loss program. Although the findings did not reveal statistically significant differences in appetite levels between intervention and control groups, both maintained moderate appetite, which is clinically relevant. Preservation of appetite in the context of weight loss may be considered a positive outcome, as severe reductions in appetite are associated with nutritional risk and adverse health effects. As proved in the literature, loss of appetite (LOA) may have adverse effects on a patient’s health and wellbeing [38], which was not seen after completing the telenutrition weight-loss program. The results suggest that there were no significant differences in levels of appetite regulation between participants who received additional support and participants in the control group; the intervention group had an average score of 26.86 for appetite level, while the control group’s average was 27.87. Our data are consistent with a previous study that examined the effect of appetite-stimulating medicine on appetite level, showing CNAQ appetite scores of 17–28 at baseline (94%), week 1 (66%), and week 2 (78%) of receiving the treatment [38]. Indeed, our rationale for investigating the health coaching impact on appetite was obtained from previous research that confirmed that socially active participants experienced a positive impact on high levels of appetite [39]. It is noted that the health coaching strategy in the intervention followed the “integrative nutrition” approach taught by the Institute for Integrative Nutrition [40], using the “Circle of Life” as a coaching tool that includes working on 12 aspects of life: spirituality, creativity, finances, career, education, health, physical activity, home cooking, home environment, relationships, social life, and joy. This was confirmed in previous research, which showed that appetite levels are significantly associated with cognitive frailty among older populations [41]. Another study also showed a significant association between physical activity and appetite levels among older populations [42]. Accordingly, our study used the CNAQ for the first time and showed that the telenutrition weight-loss program succeeded in helping participants maintain their appetite at a moderate level.
This study builds upon our previously published work in 2024 [35,36,43,44], providing a more detailed investigation into the role of telenutrition supported with health coaching. Unlike standard dietary interventions, health coaching directly addresses eating behaviors and emotional factors, such as emotional eating, binge eating, and appetite regulation, that are often overlooked but strongly influence outcomes. A key strength of the current study is the integration of an Arabic version of a validated appetite assessment (CNAQ) within a telehealth farmwork, offering a novel contribution to the literature on digital nutrition care in Saudi Arabia. Another strength lies in the holistic approach of combining dietetic care, telemonitoring, and health coaching, reflecting real-world practices that go beyond calorie restriction alone. Indeed, several methodological constraints must be acknowledged, a lack of statistical significance where pilot studies are intended to generate feasibility data and inform future research as the current findings should be interpreted as preliminary. In addition, the present study has an important limitation, which is the absence of baseline measurements of appetite levels, which makes it difficult to prove that health coaching resulted in the moderate to high appetite levels of our participants. However, non-significant changes in appetite scores may introduce valuable data that are worth exploring to determine the impact of digital nutrition and health coaching on appetite levels [45]. Thus, many previous studies have used the CNAQ tool to assess appetite in different types of diseases, including malnutrition [39] and cancer [46], and among geriatric patients [47]. Furthermore, another limitation is the sample size, which was selected due to the nature of the study, which was a pilot study. We enrolled between 10% and 30% of the calculated sample size as per recommendations for a pilot study sample size [48]. In our primary outcome paper, the full sample size calculation was reported, based on a significance level of 5%, power of 80%, and an expected dropout rate of 25%, indicating that at least 35 participants per group were required to detect meaningful changes in weight loss, as supported by previous telemedical coaching studies. The present analysis, however, was designed as a preliminary and hypothesis-generating rather than definitive [35]. A pilot study was conducted to investigate a holistic approach in weight-loss intervention, known as “Integrative nutrition”, to tackle different factors associated with overweight and obesity, which include appetite level [40]. Therefore, using a larger sample size and investigating appetite through trials will be important for determining whether the intervention has an impact. Despite the mentioned limitations of the current study, it demonstrates a newly developed type of intervention in telemedicine, which requires more research and measurements at different time points. Future studies should incorporate baseline and longitudinal appetite assessments across multiple time points, alongside extended follow-up. Building on this pilot, adequately powered randomized trials are needed with repeated appetite measurements and the integration of behavioral and biochemical markers. In this context, the study by Alioto et al. (2023), which biochemically assessed insulin and vitamin D levels in obese adolescents following diet and physical activity, provides complementary evidence on the integration of biochemical outcomes with lifestyle interventions and could guide future research in obesity management [49]. Such research is essential to clarify the relationship between digital health coaching, appetite regulation, and sustained weight management, and to generate evidence-based recommendations that can be confidently translated into clinical practice.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, this study demonstrated that participants who completed the six-month telenutrition weight-loss program, with or without additional telemonitoring and health coaching, reported moderate appetite levels, with no significant differences between groups. While these findings cannot provide definitive clinical recommendations due to methodological limitations, they suggest that digital weight-loss interventions may help sustain appetite within a healthy range while promoting weight reduction. For clinical dietetics, these results emphasize the importance of monitoring appetite alongside traditional anthropometric outcomes to ensure that dietary interventions do not compromise nutritional adequacy. Practically, dietitians implementing telehealth programs should consider incorporating validated appetite tools, such as the CNAQ, to track patient progress and tailor additional support. Having a health coach can play an important role in supporting participants’ weight-loss efforts and in managing related factors such as emotional eating and binge eating, both of which are closely linked to appetite regulation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.N.A., N.M.S.E., N.A.H., N.M.M.J. and S.F.A.; Data curation, S.N.A. and N.A.H.; Formal analysis, S.N.A. and N.A.H.; Funding acquisition, N.M.S.E., S.N.A., N.A.H., N.M.M.J. and S.F.A.; Investigation, N.M.M.J. and S.F.A.; Methodology, N.M.S.E.; Project administration, N.M.S.E.; Supervision, S.N.A., N.M.S.E., N.A.H., N.M.M.J. and S.F.A.; Writing—original draft, S.N.A., N.M.S.E., N.A.H., N.M.M.J. and S.F.A.; Writing—review and editing, S.N.A. and N.M.S.E. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is funded by the Institutional Fund Projects under [grant no. IFPRC-206-141-2020].
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of The Research Ethics Committee (REC) at the Unit of Biomedical Ethics, Faculty of Medicine at King Abdul-Aziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia ([NCBE Registration No: HA-02-J-008] and [Reference No 527-21], date: 9 February 2022).
Informed Consent Statement
All subjects who agreed to join the study provided written informed consent and completed the CNAQ.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy or ethical restrictions.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the cooperation of Khulud A. Almalki and Dana S. Aljohani in data collection.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Eckel, R.H.; Kahn, R.; Robertson, R.M.; Rizza, R.A. Preventing cardiovascular disease and diabetes: A call to action from the American Diabetes Association and the American Heart Association. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 1697–1699. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- World Obesity Federation. World Obesity Atlas. 2023. Available online: https://www.worldobesity.org/resources/resource-library/world-obesity-atlas-2023 (accessed on 7 September 2025).[Green Version]
- Health. World Health Survey-Saudi Arabia. 2019. Available online: https://www.moh.gov.sa/en/Ministry/Statistics/Population-HealthIndicators/Documents/World-Health-Survey-Saudi-Arabia.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2025).[Green Version]
- Alsulami, S.; Baig, M.; Ahmad, T.; Althagafi, N.; Hazzazi, E.; Alsayed, R.; Alghamdi, M.; Almohammadi, T. Obesity prevalence, physical activity, and dietary practices among adults in Saudi Arabia. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1124051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Franks, P.W.; McCarthy, M.I. Exposing the exposures responsible for type 2 diabetes and obesity. Science 2016, 354, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Kumar, P.; Fahmi, N.; Garg, B.; Dutta, S.; Sachar, S.; Vimaleswaran, K. Endocrine disruption and obesity: A current review on environmental obesogens. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2020, 3, 100009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Fang, F.; Arnberg, F.K.; Mataix-Cols, D.; de la Cruz, L.F.; Almqvist, C.; Fall, K.; Lichtenstein, P.; Thorgeirsson, G.; Valdimarsdóttir, U.A. Stress related disorders and risk of cardiovascular disease: Population based, sibling controlled cohort study. BMJ 2019, 365, l1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosoff, D.B.; Smith, G.D.; Mehta, N.; Clarke, T.K.; Lohoff, F.W. Evaluating the relationship between alcohol consumption, tobacco use, and cardiovascular disease: A multivariable Mendelian randomization study. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, C.; Hopkins, M.; Beaulieu, K.; Oustric, P.; Blundell, J.E. Issues in measuring and interpreting human appetite (satiety/satiation) and its contribution to obesity. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2019, 8, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, S.A.; Epstein, L.H.; Jeffery, R.W.; Blundell, J.E.; Wardle, J. Eating behavior dimensions. Associations with energy intake and body weight: A review. Appetite 2012, 59, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aujoulat, I.; d’Hoore, W.; Deccache, A. Patient empowerment in theory and practice: Polysemy or cacophony? Patient Educ. Couns. 2007, 66, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suminski, R.R.; Leonard, T.; Obrusnikova, I.; Kelly, K. The impact of health coaching on weight and physical activity in obese adults: A randomized control trial. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2024, 18, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura Marra, M.; Lilly, C.L.; Nelson, K.R.; Woofter, D.R.; Malone, J. A pilot randomized controlled trial of a telenutrition weight loss intervention in middle-aged and older men with multiple risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Nutrients 2019, 11, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmar, I.E.; Cortés-Castell, E.; Rizo, M. Effectiveness of telenutrition in a women’s weight loss program. PeerJ 2015, 3, e748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werbrouck, A.; Swinnen, E.; Kerckhofs, E.; Buyl, R.; Beckwée, D.; De Wit, L. How to empower patients? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Transl. Behav. Med. 2018, 8, 660–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittelman, M. Health coaching: An update on the national consortium for credentialing of health & wellness coaches. Glob. Adv. Health Med. 2015, 4, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolever, R.Q.; Simmons, L.A.; Sforzo, G.A.; Dill, D.; Kaye, M.; Bechard, E.M.; Southard, M.E.; Kennedy, M.; Vosloo, J.; Yang, N. A systematic review of the literature on health and wellness coaching: Defining a key behavioral intervention in healthcare. Glob. Adv. Health Med. 2013, 2, 38–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sforzo, G.A.; Moore, M.; Moore, G.E.; Harenberg, S. Comment on “Health coaching: 100 strategies for weight loss: A systematic review and meta-analysis”. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 1042–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Abrahamson, K.; Liu, P.J.; Ahmed, A. Can mobile technology improve weight loss in overweight adults? A systematic review. West. J. Nurs. Res. 2020, 42, 747–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, M.; Stathi, A.; Keogh, E.; Eccleston, C. Raising the topic of weight in general practice: Perspectives of GPs and primary care nurses. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e008546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshman, L.; Othman, A.; Furst, W.; Heisler, M.; Kraftson, A.; Zouani, Y.; Hershey, C.; Cho, T.-C.; Guetterman, T.; Piatt, G.; et al. Primary care providers’ perceived barriers to obesity treatment and opportunities for improvement: A mixed methods study. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0284474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics. Telehealth for Dietetics Practitioners. Available online: https://www.eatrightpro.org/practice/practice-resources/telehealth/practicing-telehealth (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Ho, Y.L.; Yu, J.Y.; Lin, Y.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Huang, C.C.; Hsu, T.P.; Chuang, P.Y.; Hung, C.S.; Chen, M.F. Cost-effectiveness and clinical outcomes of a fourth-generation synchronous telehealth program for chronic cardiovascular disease. J. Med. Internet Res. 2014, 16, e145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Classification of Digital Health v1.0: A Shared Language to Describe the Uses of Digital Technology for Health; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; Available online: http://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/260480 (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Johnston, J.D.; Massey, A.P.; DeVaneaux, C.A. Innovation in weight loss programs: A 3-dimensional virtual-world approach. J. Med. Internet Res. 2012, 14, e120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krukowski, R.A.; Ross, K.M. Measuring weight with electronic scales in clinical and research settings during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic. Obesity 2020, 28, 1182–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras, C.M.; Metzger, G.A.; Beane, J.D.; Dedhia, P.H.; Ejaz, A.; Pawlik, T.M. Telemedicine: Patient–provider clinical engagement during the COVID-19 pandemic and beyond. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2020, 24, 1692–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumbo-Rodríguez, L.; Sánchez-SanSegundo, M.; Ruiz-Robledillo, N.; Albaladejo-Blázquez, N.; Ferrer-Cascales, R.; Zaragoza-Martí, A. Use of technology-based interventions in the treatment of overweight and obesity: A systematic review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, H.S.; Rajasegaran, N.N.; Chin, Y.H.; Chew, W.N.; Kim, K.M. Effectiveness of combined health coaching and self-monitoring apps on weight-related outcomes in overweight and obese people: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Med. Internet Res. 2023, 25, e42432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchesson, M.J.; Tan, C.Y.; Morgan, P.; Callister, R.; Collins, C. Enhancement of self-monitoring in a web-based weight loss program by extra individualized feedback and reminders: Randomized trial. J. Med. Internet Res. 2016, 18, e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wharton, C.M.; Johnston, C.S.; Cunningham, B.K.; Sterner, D. Dietary self-monitoring, but not dietary quality, improves with use of smartphone app technology in an 8-week weight loss trial. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2014, 46, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, J.M.; Shapiro, J.S.; Wieland, M.L.; Croghan, I.T.; Douglas, K.S.V.; Schroeder, D.R.; Hathaway, J.C.; Ebbert, J.O. Telecoaching plus a portion control plate for weight care management: A randomized trial. Trials 2015, 16, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, W.; Gelberg, L.; Herman, D.; Belin, T.; Chandler, M.; Love, S.; Ramirez, E. PCORI Final Research Reports. In Comparing Calorie Counting Versus MyPlate Recommendations for Weight Loss; Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, K.; Jayasena, C.N.; Bloom, S.R. Obesity and appetite control. J. Diabetes Res. 2012, 2012, 824305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, N.M.S.; Al-Ofi, E.A.; Enani, S.; Mosli, R.H.; Saqr, R.R.; Qutah, K.M.; Eid, S.M.S. Effects of a telenutrition weight loss program supported with telemonitoring and health coaching on anthropometric and biochemical measures in overweight and obese adults: A pilot randomized controlled trial. Healthcare 2024, 12, 2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, N.M.S.; Al-Ofi, E.A.; Enani, S.M.; Mosli, R.H.; Saqr, R.R.; Qutah, K.M.; Eid, S.M.S. A 6-month randomized controlled trial to compare the effectiveness of telenutrition versus telenutrition supported by telemonitoring and health coaching in a weight loss programme. Br. J. Nutr. 2024, 132, 1224–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutbi, H.A.; Albaiti, N.H.; AlThawwad, Y.H.; Mosli, R.H.; Mumena, W.A. Appetite as a predictor of malnutrition in end-stage renal disease patients in Saudi Arabia. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 30, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraj, S. Loss of appetite in adult patients: Effectiveness and safety of an appetite-stimulating medication in India. J. Nutr. Metab. 2022, 2022, 2661912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaharada, R.; Sugimoto, T.; Uchida, K.; Murata, S.; Tsuboi, Y.; Isa, T.; Nakatsuka, K.; Horibe, K.; Ono, R. Indirect effects of social activity on appetite via depressive symptoms in older adults: A cross-sectional study. Appetite 2022, 168, 105705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, J. Integrative Nutrition: A Whole-Life Approach to Health and Happiness; Integrative Nutrition Incorporated: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Awata, S.; Watanabe, Y.; Kojima, N.; Osuka, Y.; Motokawa, K.; Sakuma, N.; Inagaki, H.; Edahiro, A.; Hosoi, E.; et al. Cognitive frailty in older Japanese people: Prevalence and its association with falls. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2019, 19, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, T.; Sakai, H.; Uchiyama, Y. Association of physical activity and appetite with visual function related to driving competence in older adults. BMC Geriatr. 2017, 17, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, N.M.S.; Al-Ofi, E.A.; Enani, S.; Mosli, R.H.; Saqr, R.R.; Qutah, K.M.; Eid, S.M.S. Impact of Telemonitoring and Telehealth Coaching on Depression, Anxiety, and Stress Scales in Overweight and Obese Individuals: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Obesities 2024, 4, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, N.M.; Al-Ofi, E.A.; Enani, S.; Mosli, R.H.; Saqr, R.R.; Qutah, K.M.; Eid, S.M. Patients’ responsiveness and health benefits of weekly telemonitoring and monthly telehealth coaching in a pilot telenutrition weight-loss program. Telemed. Rep. 2024, 5, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljasir, S.; Eid, N.; Volpi, E.V.; Tewfik, I. Nutrigenomics-guided lifestyle intervention programmes: A critical scoping review with directions for future research. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2024, 64, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliday, V.; Porock, D.; Arthur, A.; Manderson, C.; Wilcock, A. Development and testing of a cancer appetite and symptom questionnaire. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2012, 25, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanisah, R.; Suzana, S.; Lee, F.S. Validation of screening tools to assess appetite among geriatric patients. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2012, 16, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunselman, A.R. A brief overview of pilot studies and their sample size justification. Fertil. Steril. 2024, 121, 899–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alioto, A.; Rossi, C.; Capano, S.; Amato, A.; Baldassano, S.; Pagliaro, A.; Lauriello, G.; Kuliś, S.; Proia, P. Biochemical assessment of insulin and vitamin D levels in obese adolescents after diet and physical activity: A retrospective observational study. Biomed. Hum. Kinet. 2023, 15, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).