Supplementation Effects of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. Flower Aqueous Extract on Body Composition and Metabolism in Eutrophic and Obese Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of H. sabdariffa L. Aqueous Infusion and Spray-Dried Extract
2.2. Antioxidant Characterization of the H. sabdariffa Extract
2.3. Experimental Design
2.3.1. Animals
2.3.2. Experimental Protocol
2.3.3. Experimental Diets
2.3.4. Food Intake and Body Parameters
2.3.5. Biochemical Parameters
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Antioxidant Characterization of the H. sabdariffa Extract
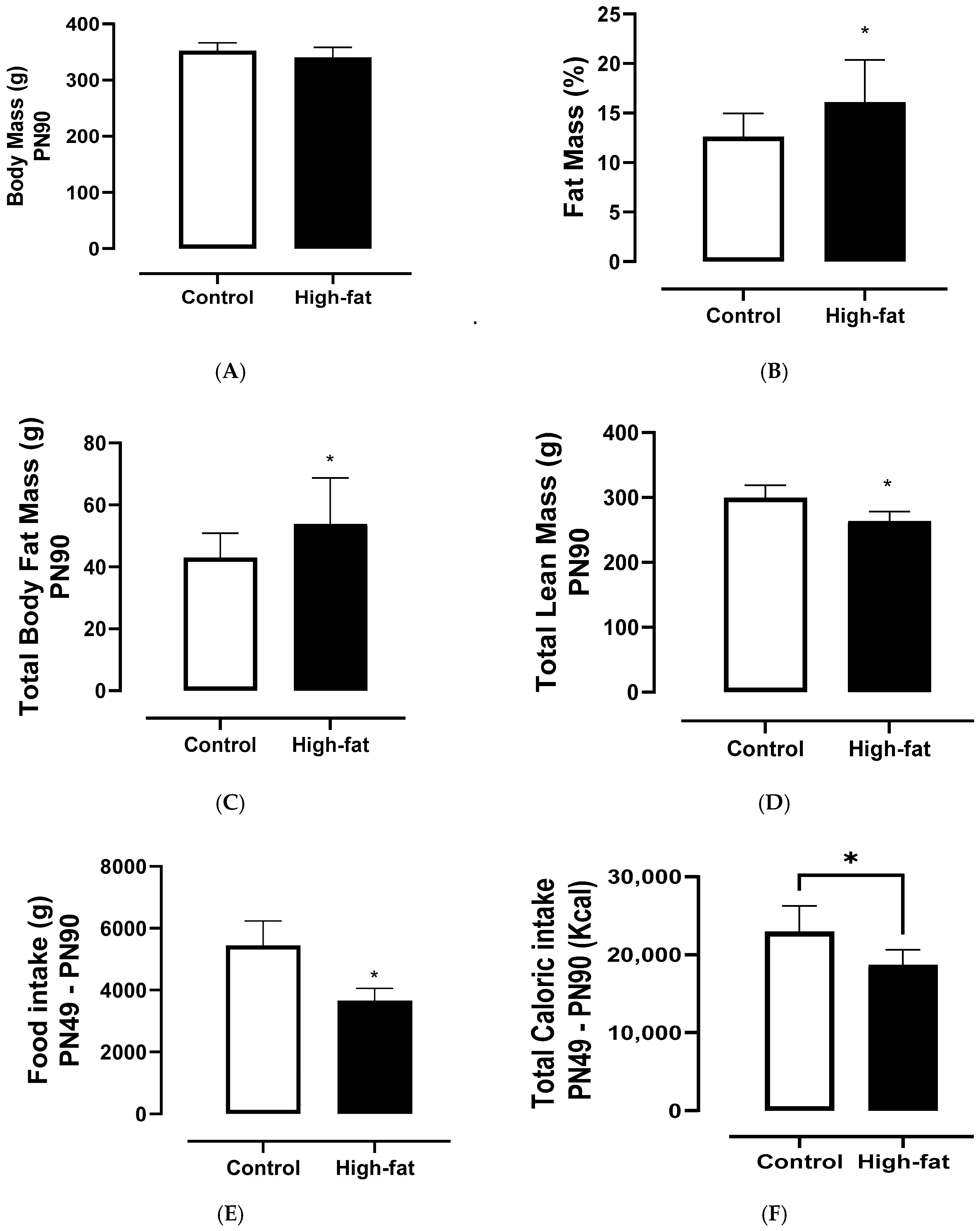
3.2. Food Intake and Body Parameters
3.3. Biochemical Parameters
4. Discussion
4.1. Antioxidant Characterization of the H. sabdariffa Extract
4.2. Food Intake and Body Parameters
4.3. Biochemical Parameters
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Safaei, M.; Sundararajan, E.A.; Driss, M.; Boulila, W.; Shapi’i, A. A Systematic Literature Review on Obesity: Understanding the Causes & Consequences of Obesity and Reviewing Various Machine Learning Approaches Used to Predict Obesity. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 136, 104754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.J.; Barrientos, R.M. The Impact of Nutrition on COVID-19 Susceptibility and Long-Term Consequences. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 87, 53–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naomi, R.; Teoh, S.H.; Embong, H.; Balan, S.S.; Othman, F.; Bahari, H.; Yazid, M.D. The Role of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Obesity and Its Impact on Cognitive Impairments—A Narrative Review. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Martínez, E.; Cachofeiro, V. Oxidative Stress in Obesity. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakubiak, G.K.; Osadnik, K.; Lejawa, M.; Osadnik, T.; Goławski, M.; Lewandowski, P.; Pawlas, N. “Obesity and Insulin Resistance” Is the Component of the Metabolic Syndrome Most Strongly Associated with Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maganha, E.G.; Halmenschlager, R.d.C.; Rosa, R.M.; Henriques, J.A.P.; Ramos, A.L.L.d.P.; Saffi, J. Pharmacological Evidences for the Extracts and Secondary Metabolites from Plants of the Genus Hibiscus. Food Chem. 2010, 118, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzini, E.; Barnaba, L.; Ciarapica, D.; Polito, A. Micronutrients and Plant Food Bioactive Compounds Against Obesity Diseases. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2022, 23, 316–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilokthornsakul, P.; Rattanachaisit, N.; Thimkorn, P.; Pongpattanawut, S.; Dilokthornsakul, W.; Dhippayom, T. Clinical Effects of Hibiscus sabdariffa Linn. on Obesity Treatment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Complement. Ther. Med. 2024, 84, 103063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongmo, F.F.D.; Touohou, S.V.N.; Etame, R.M.E.; Lienou, L.L.; Koule, J.C.M.; Mbiatat, H.D.G.; Tchuenbou-Magaia, F.L.; Gouado, I. An Herbal Tea Blend of Hibiscus sabdariffa, Zingiber Officinale, and Mentha Spicata: A Potent Source of Antioxidant and Anti-Obesity Properties. Eur. J. Med. Health Res. 2024, 2, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, G.; Chopra, R. A Review on Phytochemistry and Therapeutic Uses of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 102, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez-Diéguez, T.; Palma-Morales, M.; Camacho Bernal, G.I.; Valdez López, E.N.; Rodríguez-Pérez, C.; Cruz-Cansino, N.d.S.; Nieto, J.A. Modulation of the Hyperglycemia Condition in Diabetic Lab Rats with Extracts of the Creole Jamaica Flower (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.) from the Morelia Region (Mexico). Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanissa, N.T.S.; Fabien, D.D.F.; Landry, L.L.; Ghislain, M.T.; William, D.A.; Christophe, M.K.J.; Calvin, B.Z.; De Goeithe, M.H.; Madeleine, E.E.R.; Inocent, G. Antioxidant and Antiobesogenic Properties of Aqueous Extracts of Hibiscus sabdariffa, Zingiber Officinale and Mentha Spicata in Wistar High-Fat Diet Rats. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2022, 10, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel-García, C.A.; Reynoso-Camacho, R.; Pérez-Ramírez, I.F.; Morales-Luna, E.; de los Ríos, E.A.; Salgado, L.M. Serum Phospholipids Are Potential Therapeutic Targets of Aqueous Extracts of Roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa) Against Obesity and Insulin Resistance. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaly, H.K.F.; Younis, F.A.A.Y.; Soliman, A.M.; El-Sabbagh, S.M. Phytochemical and Antibacterial Properties of Calyces Hibiscus sabdariffa L.: An in Vitro and in Silico Multitarget-Mediated Antibacterial Study. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2025, 25, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, L.L.; Martins, F.S.; Conceição, E.C.; Silveira, D. Optimization of the Spray-Drying Process for Developing Jabuticaba Waste Powder Employing Response Surface Methodology. J. Food Process Eng. 2015, 40, e12276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Rossi, J.A. Colorimetry of Total Phenolics with Phosphomolybdic-Phosphotungstic Acid Reagents. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1965, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a Free Radical Method to Evaluate Antioxidant Activity. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufino, M.d.S.M.; Alves, R.E.; de Brito, E.S.; Pérez-Jiménez, J.; Saura-Calixto, F.; Mancini-Filho, J. Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Capacities of 18 Non-Traditional Tropical Fruits from Brazil. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 996–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akindahunsi, A.A.; Olaleye, M.T. Toxicological Investigation of Aqueous-Methanolic Extract of the Calyces of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2003, 89, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakeye, T.O.; Pal, A.; Bawankule, D.U.; Yadav, N.P.; Khanuja, S.P.S. Toxic Effects of Oral Administration of Extracts of Dried Calyx of Hibiscus sabdariffa Linn. (Malvaceae). Phytother. Res. 2009, 23, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, B.H.; Al Wabel, N.; Blunden, G. Phytochemical, Pharmacological and Toxicological Aspects of Hibiscus sabdariffa L.: A Review. Phytother. Res. 2005, 19, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.B.; Jacob, S. A Simple Practice Guide for Dose Conversion between Animals and Human. J. Basic. Clin. Pharm. 2016, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abreu, G.M.; Barros, B.F.d.B.; Teles, C.G.; Almeida, C.d.O.R.P.d.; Nascimento, B.A.; Teodoro, A.J.; Figueiredo, M.S. Early High Fat Diet Exposure Changes Body Composition, Biochemical Parameters and Redox Balance in Wistar Male Rats. Concilium 2024, 24, 450–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 20th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Rockville, MD, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Novelli, E.L.B.; Diniz, Y.S.; Galhardi, C.M.; Ebaid, G.M.X.; Rodrigues, H.G.; Mani, F.; Fernandes, A.A.H.; Cicogna, A.C.; Novelli Filho, J.L.V.B. Anthropometrical Parameters and Markers of Obesity in Rats. Lab. Anim. 2007, 41, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nascimento, A.F.; Luvizotto, R.A.M.; Leopoldo, A.S.; Lima-Leopoldo, A.P.; Seiva, F.R.; Justulin, L.A.; Silva, M.D.P.; Okoshi, K.; Wang, X.D.; Cicogna, A.C. Long-Term High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity Decreases the Cardiac Leptin Receptor Without Apparent Lipotoxicity. Life Sci. 2011, 88, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedewald, W.T.; Levy, R.I.; Fredrickson, D.S. Estimation of the Concentration of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol in Plasma, Without Use of the Preparative Ultracentrifuge. Clin. Chem. 1972, 18, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tietz, N.W. Clinical Guide to Laboratory Tests, 3rd ed.; Tietz, N.W., Ed.; WB Saunders Company: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Mak, Y.W.; Chuah, L.O.; Ahmad, R.; Bhat, R. Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activities of Hibiscus (Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L.) and Cassia (Senna bicapsularis L.) Flower Extracts. J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 2013, 25, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Mahdi, F.; Khanna, A.K.; Singh, R.; Chander, R.; Saxena, J.K.; Mahdi, A.A.; Singh, R.K. Antidyslipidemic and Antioxidant Activities of Hibiscus Rosa Sinensis Root Extract in Alloxan Induced Diabetic Rats. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2013, 28, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Roy, A.; Paul, A.; Saha, N.; Tarafdar, A.; Mazumder, S. Food and Medicinal Properties of Hibiscus (Hibiscus sabdariffa & Hibiscus rosa-sinensis). Sustain. Agric. Food Environ. Res. 2023, 11, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-J.; Wang, J.-M.; Lin, W.-L.; Chu, C.-Y.; Chou, F.-P.; Tseng, T.-H. Protective Effect of Hibiscus Anthocyanins Against Tert-Butyl Hydroperoxide-Induced Hepatic Toxicity in Rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2000, 38, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janson, B.; Prasomthong, J.; Malakul, W.; Boonsong, T.; Tunsophon, S. Hibiscus sabdariffa L. Calyx Extract Prevents the Adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 Adipocytes, and Obesity-Related Insulin Resistance in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 138, 111438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera-Arellano, A.; Miranda-Sánchez, J.; Ávila-Castro, P.; Herrera-Álvarez, S.; Jiménez-Ferrer, J.; Zamilpa, A.; Román-Ramos, R.; Ponce-Monter, H.; Tortoriello, J. Clinical Effects Produced by a Standardized Herbal Medicinal Product of Hibiscus sabdariffa on Patients with Hypertension. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Lisinopril-Controlled Clinical Trial. Planta Med. 2006, 73, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, T.D.; Richardson, M.L. A Review of the Effectiveness of Hibiscus for Treatment of Metabolic Syndrome. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 270, 113762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hariri, N.; Thibault, L. High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Animal Models. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2010, 23, 270–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajiboye, T.O.; Raji, H.O.; Adeleye, A.O.; Adigun, N.S.; Giwa, O.B.; Ojewuyi, O.B.; Oladiji, A.T. Hibiscus sabdariffa Calyx Palliates Insulin Resistance, Hyperglycemia, Dyslipidemia and Oxidative Rout in Fructose-Induced Metabolic Syndrome Rats. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 1522–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, M.E.d.C.; Natal, D.I.G.; Toledo, R.C.L.; Ramirez, N.M.; Ribeiro, S.M.R.; Benjamin, L.d.A.; de Oliveira, L.L.; Rodrigues, D.A.; Antônio, J.D.; Veloso, M.P.; et al. Bacupari Peel Extracts (Garcinia brasiliensis) Reduce High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Rats. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 29, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, D.F.; Pereira-Lancha, L.O.; Chaves, D.S.; Diwan, D.; Ferraz, R.; Campos-Ferraz, P.L.; Poortmans, J.R.; Lancha, A.H. Effect of High-Fat Diets on Body Composition, Lipid Metabolism and Insulin Sensitivity, and the Role of Exercise on These Parameters. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2011, 44, 966–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.J.; Wu, Y.; Fried, S.K. Adipose Tissue Heterogeneity: Implication of Depot Differences in Adipose Tissue for Obesity Complications. Mol. Aspects Med. 2013, 34, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, A.J.S.J.; Mohan, S.; Chellappan, D.K.; Kalusalingam, A.; Ariamuthu, S. Hibiscus vitifolius (Linn.) Root Extracts Shows Potent Protective Action against Anti-Tubercular Drug Induced Hepatotoxicity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 141, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalpando-Arteaga, E.V.; Mendieta-Condado, E.; Esquivel-Solís, H.; Canales-Aguirre, A.A.; Gálvez-Gastélum, F.J.; Mateos-Díaz, J.C.; Rodríguez-González, J.A.; Márquez-Aguirre, A.L. Hibiscus sabdariffa L. Aqueous Extract Attenuates Hepatic Steatosis Through Down-Regulation of PPAR-γ and SREBP-1c in Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Food Funct. 2013, 4, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, D.L.; Chen, C.-Y.O.; Saltzman, E.; Blumberg, J.B. Hibiscus sabdariffa L. Tea (Tisane) Lowers Blood Pressure in Prehypertensive and Mildly Hypertensive Adults. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Assays | HSLsd Extract |
|---|---|
| Total phenolic content (mg gallic acid 100 g−1) | 4712.33 ± 184.30 |
| DPPH (µmol of Trolox g−1) | 11,220.0 ± 133.3 |
| TEAC (µmol Trolox Equivalent g−1) | 322.50 ± 2.90 |
| FRAP (µmol ferrous sulfate g−1) | 14.06 ± 0.20 |
| Parameters | CS (n = 8) | CH (n = 8) | HFS (n = 8) | HFH (n = 8) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body weight (g) | 400.4 ± 20.0 | 381.6 ± 16.03 | 393.6 ± 36.12 | 389.1 ± 17.47 | >0.05 |
| Body lenght (cm) | 24.5 ± 0.50 | 24.31 ± 0.45 | 24.71 ± 0.48 | 24.75 ± 0.46 | >0.05 |
| Lee index (g/cm3) | 0.3 ± 0.01 | 0.29 ± 0.01 | 0.29 ± 0.01 | 0.29 ± 0.00 | >0.05 |
| Body mass index (g/cm3) | 0.66 ± 0.04 | 0.64 ± 0.04 | 0.64 ± 0.04 | 0.63 ± 0.02 | >0.05 |
| Adiposity index | 6.33 ± 0.41 | 6.29 ± 0.29 | 10.23 ± 0.68 *# | 8.86 ± 0.35 *# | <0.05 |
| Relative mesenteric fat (g) | 4.39 ± 0.73 | 4.36 ± 0.70 | 6.69 ± 2.16 *# | 6.01 ± 1.07 *# | <0.05 |
| Relative retroabdominal fat (g) | 5.85 ± 1.16 | 5.43 ± 1.08 | 10.371 ± 3.88 *# | 8.77 ± 1.90 *# | <0.05 |
| Relative epididymal fat (g) | 4.58 ± 0.61 | 4.41 ± 1.09 | 7.43 ± 3.01 *# | 5.85 ± 0.89 | <0.05 |
| Relative visceral fat mass (g) | 14.84 ± 2.28 | 14.21 ± 2.11 | 19.87 ± 7.87 | 19.92 ± 3.06 | >0.05 |
| Relative brown adipose tissue (g) | 0.33 ± 0.07 | 0.32 ± 0.05 | 0.41 ± 0.11 | 0.36 ± 0.07 | >0.05 |
| Parameters | CS (n = 8) | CH (n = 8) | HFS (n = 8) | HFH (n = 8) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Triglycerides (mg dL−1) | 40.43 ± 15.97 | 31.38 ± 8.89 | 60.86 ± 33.34 | 43.50 ± 17.76 | >0.05 |
| Total cholesterol (mg dL−1) | 40.29 ± 8.01 | 45.88 ± 7.06 | 43.00 ± 8.08 | 36.75 ± 7.01 | >0.05 |
| HDL-c (mg dL−1) | 16.43 ± 3.31 | 15.88 ± 2.53 | 16.29 ± 2.69 | 14.63 ± 3.58 | >0.05 |
| VLDL-c (mg dL−1) | 8.08 ± 3.19 | 6.27 ± 1.78 | 12.17 ± 6.67 | 8.70 ± 3.55 | >0.05 |
| LDL-c (mg dL−1) | 22.77 ± 4.06 | 23.73 ± 4.94 | 14.54 ± 6.13 *# | 13.43 ± 3.11 *# | <0.05 |
| AST (U L−1) | 112.10 ± 22.09 | 111.30 ± 21.17 | 96.71 ± 24.90 | 107.60 ± 47.69 | >0.05 |
| ALT (U L−1) | 40.71 ± 13.73 | 33.13 ± 3.94 | 32.00 ± 7.61 | 26.71 ± 1.11 * | <0.05 |
| Alkaline phosphatase (U L−1) | 79.57 ± 12.84 | 85.00 ± 17.34 | 81.14 ± 15.99 | 80.13 ± 18.12 | >0.05 |
| Albumin (mg dL−1) | 3.25 ± 0.13 | 3.21 ± 0.16 | 3.40 ± 0.11 | 3.36 ± 0.12 | >0.05 |
| Total proteins (mg dL−1) | 5.76 ± 0.27 | 5.57 ± 0.37 | 5.83 ± 0.27 | 5.73 ± 0.19 | >0.05 |
| Uric acid (mg dL−1) | 1.57 ± 0.32 | 1.41 ± 0.36 | 1.30 ± 0.10 | 1.41 ± 0.17 | >0.05 |
| Total bilirubin (mg dL−1) | 0.12 ± 0.02 | 0.09 ± 0.02 | 0.09 ± 0.02 | 0.07 ± 0.02 * | <0.05 |
| Direct bilirubin (mg dL−1) | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.01 * | <0.05 |
| Creatinine (mg dL−1) | 0.62 ± 0.02 | 0.61 ± 0.02 | 0.70 ± 0.17 | 0.69 ± 0.11 | >0.05 |
| Iron (mg dL−1) | 250.60 ± 52.59 | 242.80 ± 37.21 | 259.50 ± 31.76 | 257.20 ± 25.11 | >0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Costa, J.F.B.d.; Monteiro, A.L.M.; Nascimento, B.A.; Oliveira, C.M.V.d.; Coutinho, K.P.; Teodoro, A.J.; Teixeira-Costa, B.E.; Figueiredo, M.S. Supplementation Effects of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. Flower Aqueous Extract on Body Composition and Metabolism in Eutrophic and Obese Rats. Obesities 2025, 5, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5040067
Costa JFBd, Monteiro ALM, Nascimento BA, Oliveira CMVd, Coutinho KP, Teodoro AJ, Teixeira-Costa BE, Figueiredo MS. Supplementation Effects of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. Flower Aqueous Extract on Body Composition and Metabolism in Eutrophic and Obese Rats. Obesities. 2025; 5(4):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5040067
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosta, João Fernando Bernardo da, Alana Louzada Millions Monteiro, Bruna Almeida Nascimento, Clarice Maia Vinagre de Oliveira, Karen Pereira Coutinho, Anderson Junger Teodoro, Barbara Elisabeth Teixeira-Costa, and Mariana Sarto Figueiredo. 2025. "Supplementation Effects of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. Flower Aqueous Extract on Body Composition and Metabolism in Eutrophic and Obese Rats" Obesities 5, no. 4: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5040067
APA StyleCosta, J. F. B. d., Monteiro, A. L. M., Nascimento, B. A., Oliveira, C. M. V. d., Coutinho, K. P., Teodoro, A. J., Teixeira-Costa, B. E., & Figueiredo, M. S. (2025). Supplementation Effects of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. Flower Aqueous Extract on Body Composition and Metabolism in Eutrophic and Obese Rats. Obesities, 5(4), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5040067









