Microplastic Exposure for Pinnipeds (Pinnipedia): A Rapid Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Literature Search Parameters
2.2. Literature Selection
3. Results and Discussion
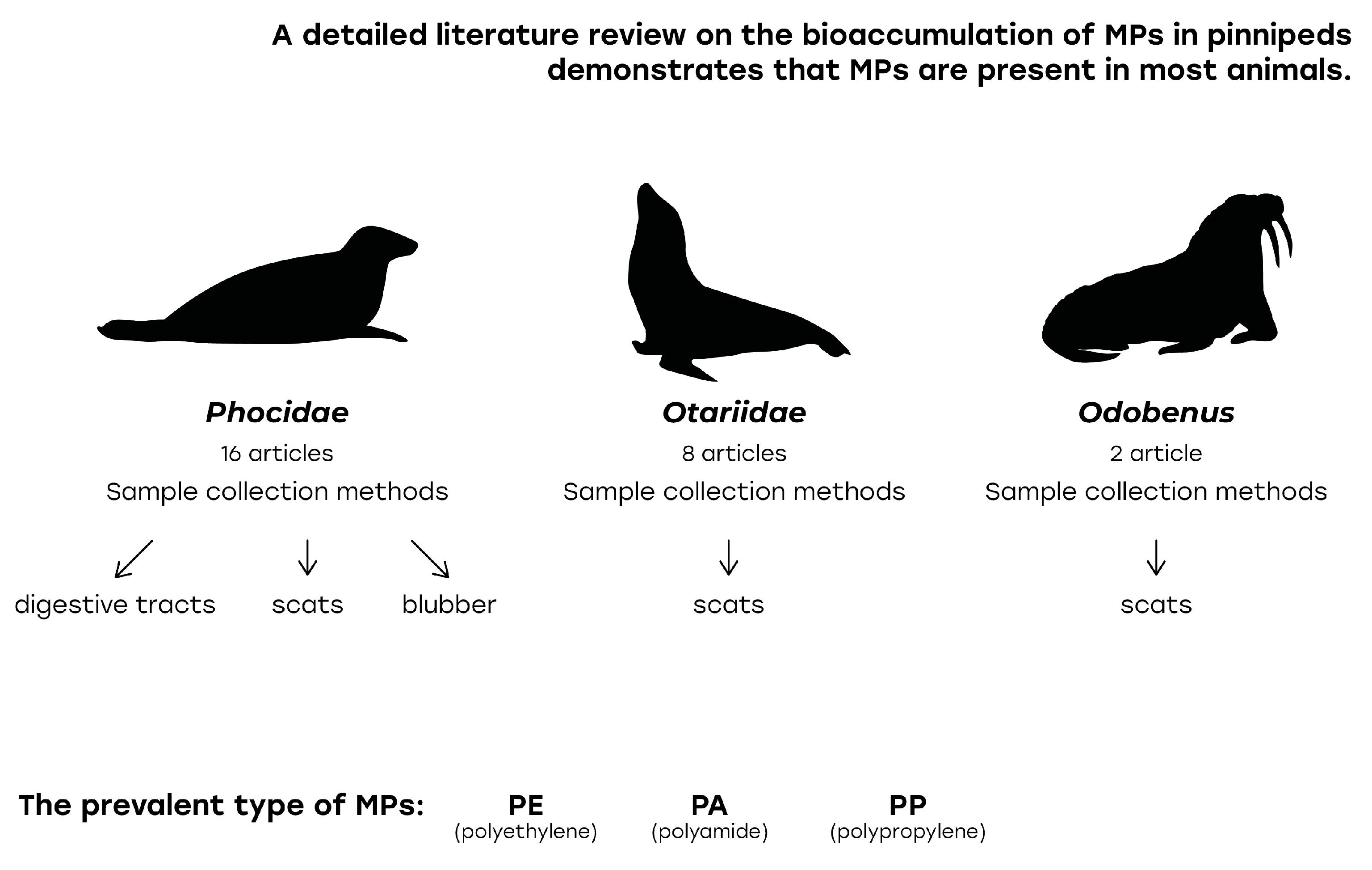
3.1. Microplastics in the Gastrointestinal Tract
3.2. Microplastics in Scat Samples
3.3. Microplastics in Blubber
3.4. Methodological Variation
3.4.1. Sample Collection
3.4.2. Extraction Methods
- Physical (filtration)
- Chemical or enzymatic digestion
- A combination of methods
3.4.3. Microplastic Identification Methods
3.4.4. Contamination Prevention
3.5. Phthalates and Other Contaminants as Biomarkers
3.6. Knowledge Gaps and Recommendations for Future Research
- clarification of trophic transfer pathways;
- translocation and bioaccumulation of MPs within animal bodies;
- the effects of MP ingestion and accumulation on animal health.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MPs | Microplastics |
| GIT | Gastrointestinal tract |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared |
| PVC | Polyvinyl chloride |
| PC | Polycarbonates |
| PMMA | Polymethyl methacrylate |
| PS | Polystyrene |
| PP | Polypropylene |
| PE | Polyethylene |
| CP | Polyetheretherketone reinforced with carbon fiber |
| PES | Polysulfones |
| PET | Polyethylene terephthalate |
| PAN/ PAA | Polyacrylonitrile/polyacrylamide |
| PA | Polyamide |
| PMMA | Polymethyl methacrylate |
| ABS | Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene |
| EPDM | Ethylene propylene diene monomer |
References
- Jepsen, E.M.; de Bruyn, P.N. Pinniped entanglement in oceanic plastic pollution: A global review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 145, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butterworth, A. A review of the welfare impact on pinnipeds of plastic marine debris. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, C.; Baker, J.; Bamford, H. (Eds.) Proceedings of the International Research Workshop on the Occurrence, Effects and Fate of Microplastic Marine Debris; NOAA Technical Memorandum NOS-OR&R-30; NOAA Marine Debris Division: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, D.K.A.; Galgani, F.; Thompson, R.C.; Barlaz, M. Accumulation and Fragmentation of Plastic Debris in Global Environments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.L.; Gwinnett, C.; Robinson, L.F.; Woodall, L.C. Plastic Microfibre Ingestion by Deep-Sea Organisms. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühn, S.; van Franeker, J.A. Quantitative Overview of Marine Debris Ingested by Marine Megafauna. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 151, 110858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Costa, A.H. Microplastics in decapod crustaceans: Accumulation, toxicity and impacts, a review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 832, 154963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, M.M.H.; Leistenschneider, C.; Miranda, J.A.; Paler, M.K.; Legaspi, C.; Germanov, E.; Araujo, G.; Burkhardt-Holm, P.; Erni-Cassola, G. Microplastics in fecal samples of whale sharks (Rhincodon typus) and from surface water in the Philippines. Microplast. Nanoplast. 2021, 1, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessa, F.; Ratcliffe, N.; Otero, V.; Sobral, P.; Marques, J.C.; Waluda, C.M.; Trathan, P.N.; Xavier, J.C. Microplastics in gentoo penguins from the Antarctic region. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meaza, I.; Toyoda, J.; Wise, J. Microplastics in Sea Turtles, Marine Mammals and Humans: A One Environmental Health Perspective. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 8, 575614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zantis, L.J. Assessing microplastic exposure of large marine filter-feeders. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 818, 151815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.A.; Niven, S.J.; Galloway, T.S.; Rowland, S.J.; Thompson, R.C. Microplastic Moves Pollutants and Additives to Worms, Reducing Functions Linked to Health and Biodiversity. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 2388–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-X.; Getzinger, G.J.; Ferguson, P.L.; Orihuela, B.; Zhu, M.; Rittschof, D. Effects of Toxic Leachate from Commercial Plastics on Larval Survival and Settlement of the Barnacle Amphibalanus amphitrite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 924–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, L.M.R.; Jones, P.R. Characterisation of Microplastics and Toxic Chemicals Extracted from Microplastic Samples from the North Pacific Gyre. Environ. Chem. 2015, 12, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fackelmann, G.; Pham, C.K.; Rodríguez, Y.; Mallory, M.L.; Provencher, J.F.; Baak, J.E.; Sommer, S. Current Levels of Microplastic Pollution Impact Wild Seabird Gut Microbiomes. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 7, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lemos, B.; Ren, H. Tissue Accumulation of Microplastics in Mice and Biomarker Responses Suggest Widespread Health Risks of Exposure. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep46687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toto, B.; Refosco, A.; Dierkes, J.; Kögel, T. Efficient Extraction of Small Microplastic Particles from Rat Feed and Feces for Quantification. Heliyon 2023, 9, e12811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrill, G.B.; Hermabessiere, L.; Rochman, C.M.; Nowacek, D.P. Microplastics in Marine Mammal Blubber, Melon, & Other Tissues: Evidence of Translocation. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 335, 122252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Milian, G.; Tsangaris, C.; Anestis, A.; Fossi, M.C.; Baini, M.; Caliani, I.; Panti, C.; Bundone, L.; Panou, A. Monk Seal Faeces as a Non-Invasive Technique to Monitor the Incidence of Ingested Microplastics and Potential Presence of Plastic Additives. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 193, 115227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zantis, L.J.; Carroll, E.L.; Nelms, S.E.; Bosker, T. Marine Mammals and Microplastics: A Systematic Review and Call for Standardization. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddaway, A.P.; Wood, A.M.; Hedges, L.V. How to Do a Systematic Review: A Best Practice Guide for Conducting and Reporting Narrative Reviews, Meta-Analyses, and Meta-Syntheses. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2019, 70, 747–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, F.; Cardena, M.; Cardenas-Alayza, S. Registro Preliminar de Microplasticos en Fecas del Leon Marino Sudamericano (Otaria byronia) Recolectadas en Punta San Juan, Perú. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 2021, 37, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdages, M.P.T.; Provencher, J.F.; Sudlovenick, E.; Ferguson, S.H.; Young, B.G.; Pelletier, N.; Murphy, M.J.; D’Addario, A.; Vermaire, J.C. No Plastics Detected in Seal (Phocidae) Stomachs Harvested in the Eastern Canadian Arctic. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 150, 110772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo Rebolledo, E.L.; Van Franeker, J.A.; Jansen, O.E.; Brasseur, S.M. Plastic Ingestion by Harbour Seals (Phoca vitulina) in The Netherlands. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 67, 200–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohue, M.J.; Masura, J.; Gelatt, T.; Ream, R.; Baker, J.D.; Faulhaber, K.; Lerner, D.T. Evaluating Exposure of Northern Fur Seals, Callorhinus ursinus, to Microplastic Pollution through Fecal Analysis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 138, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebuhar, J.D.; Negrete, J.; Pirani, L.S.R.; Picone, A.L.; Proietti, M.; Romano, R.M.; Della Védova, C.O.; Casaux, R.; Secchi, E.R.; Botta, S. Anthropogenic Debris in Three Sympatric Seal Species of the Western Antarctic Peninsula. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 922, 171273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desclos-Dukes, L.; Butterworth, A.; Cogan, T. Investigating Microplastic Presence Amongst Grey Seals (Halichoerus grypus) of the North Sea. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/348317888_Investigating_Microplastic_Presence_Amongst_Grey_Seals_Halichoerus_Grypus_of_the_North_Sea (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Desclos-Dukes, L.; Butterworth, A.; Cogan, T. Using a Non-Invasive Technique to Identify Suspected Microplastics in Grey Seals (Halichoerus grypus) Living in the Western North Sea. Vet. Rec. 2022, 190, 1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huddak, C.A.; Sette, L. Opportunistic Detection of Anthropogenic Micro Debris in Harbor Seal (Phoca vitulina vitulina) and Gray Seal (Halichoerus grypus atlantica) Fecal Samples from Haul-Outs in Southeastern Massachusetts, USA. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 145, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, C.; Burton, H. Origins and Biological Accumulation of Small Plastic Particles in Fur Seals from Macquarie Island. Ambio 2003, 32, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Garin, O.; García-Cuevas, I.; Drago, M.; Rita, D.; Parga, M.; Gazo, M.; Cardona, L. No Evidence of Microplastics in Antarctic Fur Seal Scats from a Hotspot of Human Activity in Western Antarctica. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 140210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Milian, G.; Lusher, A.; MacGabban, S.; Rogan, E. Microplastics in Grey Seal (Halichoerus grypus) Intestines: Are They Associated with Parasite Aggregations? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mclvor, A.J.; Pires, R.; Lopes, C.; Raimundo, J.; Campos, P.F.; Pais, M.P.; Canning-Clode, J.; Dinis, A. Assessing Microplastic Exposure of the Critically Endangered Mediterranean Monk Seal (Monachus monachus) on a Remote Oceanic Island. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 159077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira-Mendieta, A.; Garcia-Garin, O.; Muñoz-Pérez, J.P.; Urquía, D.O.; Drago, M.; Borrell, A.; Páez-Rosas, D. Detection and Quantification of Microplastic Pollution in the Endangered Galapagos Sea Lion. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 896, 166223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelms, S.E.; Galloway, T.S.; Godley, B.J.; Jarvis, D.S.; Lindeque, P.K. Investigating Microplastic Trophic Transfer in Marine Top Predators. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 238, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelms, S.E.; Barnett, J.; Brownlow, A.; Davison, N.J.; Deaville, R.; Galloway, T.S.; Lindeque, P.K.; Santillo, D.; Godley, B.J.; Thompson, R.C. What goes in, must come out: Combining scat-based molecular diet analysis and quantification of ingested microplastics in a marine top predator. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2019, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Borchardt, J.Á.; Ramírez-Álvarez, N.; Mendoza, L.M.R.; Gallo-Reynoso, J.P.; Barba-Acuña, I.D.; García-Hernández, J.; Égido-Villarreal, J.; Kubenik, T. Detection of Microplastic Particles in Scats from Different Colonies of California Sea Lions (Zalophus californianus) in the Gulf of California, Mexico: A Preliminary Study. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 186, 114433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Venegas, D.; Seguel, M.; Pavés, H.; Pulgar, J.; Urbina, M.; Ahrendt, C.; Galbán-Malagón, C. First Detection of Plastic Microfibers in a Wild Population of South American Fur Seals (Arctocephalus australis) in the Chilean Northern Patagonia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 136, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Venegas, D.J.; Toro-Valdivieso, C.; Ayala, F.; Brito, B.; Iturra, L.; Arriagada, M.; Seguel, M.; Barrios, C.; Sepúlveda, M.; Oliva, D.; et al. Monitoring the Occurrence of Microplastic Ingestion in Otariids along the Peruvian and Chilean Coasts. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 153, 110966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipp, C.; Unger, B.; Siebert, U. Occurrence of Microplastics in Harbour Seals (Phoca vitulina) and Grey Seals (Halichoerus grypus) from German Waters. Animals 2022, 12, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardine, A.M.; Provencher, J.F.; Insley, S.J.; Tauzer, L.; Halliday, W.D.; Bourdages, M.P.; Houde, M.; Muir, D.; Vermaire, J.C. No Accumulation of Microplastics Detected in Western Canadian Ringed Seals (Pusa hispida). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 188, 114692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardine, A.M.; Matthews, C.J.; Provencher, J.F.; Hornby, C.; Gamberg, M.; Bourdages, M.P.; Alexander, D.; Naullaq, M.; Vermaire, J.C. No Microplastics Detected in the First Assessment of Atlantic Walrus Stomachs from Nunavut, Canada. Arct. Sci. 2023, 9, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yu, Y.; Wu, H.; Wu, W.; Wang, L.; An, L.; Cai, W. Microplastics in Spotted Seal Cubs (Phoca largha): Digestion after Ingestion? Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelms, S.E.; Barnett, J.; Brownlow, A.; Davison, N.J.; Deaville, R.; Galloway, T.S.; Lindeque, P.K.; Santillo, D.; Godley, B.J. Microplastics in Marine Mammals Stranded around the British Coast: Ubiquitous but Transitory? Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelia, T.S.M.; Wan Mohd Khalik, W.M.A.; Chuan Ong, M.; Shao, Y.T.; Pan, H.-J.; Bhubalan, K. Marine Microplastics as Vectors of Major Ocean Pollutants and Its Hazards to the Marine Ecosystem and Humans; Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson, P.; Singdahl-Larsen, C.; Lusher, A.L. Understanding the Occurrence and Fate of Microplastic in Coastal Arctic Ecosystems: The Case of Surface Waters, Sediments and Walrus (Odobenus rosmarus). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 792, 148308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, M.; Lusher, A.; Nixon, M.; Wernery, U. The plight of camels eating plastic waste. J. Arid. Environ. 2021, 185, 104374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadappa, P.; Krishnaswamy, N.; Karunanidhi, M.; Bhanuprakash, A.G.; Bindhuja, B.V.; Dey, S. Effect of plastic foreign body impaction on rumen function and heavy metal concentrations in various body fluids and tissues of buffaloes. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 189, 109972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornek-Gausterer, R.; Oberacher, H.; Reinstadler, V.; Hartmann, C.; Liebmann, B.; Lomako, I.; Kübber-Heiss, A. A preliminary study on the detection of potential contaminants in the european brown hare (Lepus europaeus) by suspect and microplastics screening. Environ. Adv. 2021, 4, 100045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusher, A.L.; Hernandez-Milian, G. Microplastic Extraction from Marine Vertebrate Digestive Tracts, Regurgitates and Scats: A Protocol for Researchers from All Experience Levels. BioProtoc 2018, 8, e3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristic | Categories |
|---|---|
| Target species | Species name and taxonomy |
| Target location | Country, Region |
| Material | Scat, gut content, blubber |
| Method of polymer identification | None, microscopy, Raman spectroscopy; Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) |
| Polymer characteristics | Color, shape, type |
| Contamination identification protocol | Field controls, lab controls |
| GIT | Scats | Blubber | Study Location | Families | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| + | Peru | Otariidae | Ayala et al., 2021 [22] | ||
| + | Canadian Arctic | Phocidae | Bourdages et al., 2020 [23] | ||
| + | Netherlands | Phocidae | Bravo et al., 2013 [24] | ||
| + | Spitsbergen | Odobenus | Carlsson et al., 2021 [25] | ||
| + | Antarctica | Phocidae | Cebuhar et al., 2024 [26] | ||
| + | United Kingdom | Phocidae | Desclos-Dukes et al., 2021 [27] | ||
| + | United Kingdom | Phocidae | Desclos-Duces et al., 2022 [28] | ||
| + | Pacific Coast, USA | Otariidae | Donohue et al., 2019 [29] | ||
| + | Australian Subantarctic | Otariidae | Eriksson and Burton, 2003 [30] | ||
| + | Antarctica | Otariidae | Garcia-Garin et al., 2020 [31] | ||
| + | Ireland | Phocidae | Hernandes-Milian et al., 2019 [32] | ||
| + | Greece, Zakynthos Island | Phocidae | Hernandez-Milian et al., 2023 [19] | ||
| + | Atlantic Coast, USA | Phocidae | Hudak and Sette, 2019 [33] | ||
| + | Madeira | Phocidae | McIvor et al., 2023 [34] | ||
| + | United Kingdom | Phocidae | Nelms et al., 2018 [35] | ||
| + | United Kingdom | Phocidae | Nelms et al., 2019 [32] | ||
| + | United Kingdom | Phocidae | Nelms et al., 2019a [36] | ||
| + | USA, Alaska | Phocidae | Merrill et al., 2023 [18] | ||
| + | Galapagos Marine Reserve | Otariidae | Moreira-Mendieta et al., 2023 [34] | ||
| + | Gulf of California | Otariidae | Ortega-Borchard et al., 2023 [37] | ||
| + | Peru, Chile | Otariidae | Perez-Venegas et al., 2018 [38] | ||
| + | Peru, Chile | Otariidae | Perez-Venegas et al., 2020 [39] | ||
| + | German | Phocidae | Philipp et al., 2022 [40] | ||
| + | Canada | Phocidae | Jardine et al., 2023 [41] | ||
| + | Canada | Odobenus | Jardine et al., 2023a [42] | ||
| + | Bohai Sea, China | Phocidae | Wang et al., 2021 [43] |
| Characteristics | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Source | Study Location | Most Common Shape (>10%) | Most Common Colors (>10%) | Common Polymers (>10%) |
| Phocidae | |||||
| Phoca hispida, | Jardine et al., 2023 [41] | Canada | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Erignathus barbatus, Phoca vitulina | |||||
| Phoca vitulina | Bourdages et al., 2020 [23] | Netherlands | Stomach: fibers (54%), Intestimal: fragments (54%); | 0 | 0 |
| Halichoerus grypus | Hernandez-Milian et al., 2019 [32] | Ireland | Fibers (85%), fragments (14%) | - | - |
| Halichoerus grypus | Nelms et al., 2018 [35] | United Kingdom | Fibers (69%), fragments (31%) | Black (27.0%), clear (23.0%), red (23.0%), orange (12.0%) | EPDM (27.0%), PP (27.0%) PE (12.0%) |
| Halichoerus grypus Phoca vitualina | Nelms et al., 2019 [32] | United Kingdom | Fibers (84%), fragments (16%) | Blue (42.5%), black (26.4%), clear (12.8%), red (11,0%), | PA (61.2%) PET (10.2%) |
| Halichoerus grypus | Nelms et al., 2019a [36] | United Kingdom | Fibers (76.5%), fragments (23.5%) | Blue (52.9%), red (17.6%), black (11.8%) | Nylon (47.1%) PE, PET (all 17.6%) |
| Phoca largha | Wang et al., 2021 [43] | Bohai Sea, China | Fibers (60.0%), fragments (33.33%) | - | PET (40.0%), PP (20%), PAN/PAA (13.33%) |
| Odobenus | |||||
| Odobenus rosmarus | Jardine et al., 2023a [42] | Canada | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Characteristics | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Source | Study Location | Most Common Shape (>10%) | Most Common Colors (>10%) | Common Polymers (>10%) |
| Phocidae | |||||
| Phoca vitulina | Bravo et al., 2013 [24] | Netherlands | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Nelms et al., 2018 [35] | United Kingdom | Fragments (69%), fibers (31%) | Black (27%), clear (23%), red (23%), blue (15%), orange (12%) | PP (54%), PE (12%) | |
| Hudak and Sette, 2019 [33] | USA, Massachusetts | Fragments (100%) | Brown and white | CP (50%), OTHER (50%) | |
| Lobodon carcinophaga, Hydrurga leptonyx, Leptonychotes weddellii | Cebuhar et al., 2024 [26] | Antarctica, Cierva Bay | Fibers (59.6%), fragments (33.8%) | Black (93.10%), blue (89.66%), white (86.20%), green (31.03%), red/purple (27.59%), yellow/orange/brown (27.59%), clear (13.79%) | PS, PES PET prevailed |
| Monachus monachus | McIvor et al., 2023 [34] | Madeira | Fragments (69%), fibers (13%) | Blue (39%), clear (19%), red (17%) | PE (28%) PES (21%) |
| Hernandez-Milian et al., 2023 [19] | Greece, Zakynthos island | Fibers (84.9%) fragments (24, 14.6%) | Blue (39.16%), clear (34.5%) | PA (72.58%), PC (15.52%) | |
| Halichoerus grypus | Hudak and Sette, 2019 [33] | USA, Massachusetts | Fragments (100%) | Purple and red | CP (50%), дp. (50%) |
| Desclos-Duces et al., 2021 [27] | United Kingdom | Fibers (61%), fragments (39%) | Light blue (36%), clear (29%), blue (14%), white (11%) | PET, PP, PAN/PAA prevailed | |
| Desclos-Duces et al., 2022 [28] | United Kingdom | Fibers (61%), fragments (39%) | Light blue (36%), clear (29%), blue (14%), white (11%) | PET, PP, PAN/PAA prevailed | |
| Otariidae | |||||
| Zalophus wollebaeki | Moreira-Mendieta et al., 2023 [34] | Southeastern part of the Galapagos Marine Reserve | Fibers—69%, fragments—26% | Blue (45%), black (32%) | PP-PE (22%), PP (17%), PE (11%), PVC (11%) |
| Zalophus californianus | Ortega-Borchard et al., 2023 [37] | Mexico, Gulf of California | Fibers (92%), fragments (8%) | Blue, black, grey prevailed | PET (37), PP (23%), PE (17%), ABS (10%) |
| Callorhinus ursinus | Donohue et al., 2019 [29] | Pacific Coast, USA | Fragments (55%), fibers (41%) | Fragments: white (99%); fibers: black, white, purple, blue, red, yellow, clear | PE |
| Arctocephalus gasella | Garcia Garin et al., 2020 [31] | Deception, Antarctica | - | - | - |
| Arctocephalus tropicalis | Eriksson and Burton, 2003 [30] | Mariana Islands, Australian Subantarctic | Fragments и fibers | White (33%), brown (19%), blue (15%), green (15%), yellow (15%) | PE (93%) |
| Arctocephalus australis | Perez-Venegas et al., 2018 [38] | Peru, Chile | Fibers (100%) | Blue (45%), white (24%), black (16%), red (15%) | - |
| Otaria flavescens, Arctocephalus phillippii | Perez-Venegas et al., 2020 [39] | Peru, Chile | Fibers prevailed | Blue (42–69%), white (21–50%), red (12–31%) for A. australis and O. flavescens, respectively | PE + PA (total 30%) |
| Otaria byronia | Ayala et al., 2021 [22] | Peru | Fragments (91%), fibers (9%) | - | - |
| Odobenus | |||||
| Odobenus rosmarus | Carlsson et al., 2021 [25] | Spitsbergen | Fibers—70%, in all samples except 1 | - | PA (31%), PE (23%) |
| Characteristics | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Source | Study Location | Most Common Shape (>10%) | Most Common Colors (>10%) | Common Polymers (>10%) |
| Phocidae | |||||
| Erignathus barbatus | Merrill et al., 2023 [18] | USA, Alaska | Fibers 70%, in all samples except 1 | Blue | PP, PE, PS, PMMA, PVC, PC |
| Mesh Size (μm) | Digestion | Identification | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | Microscope | Ayala et al., 2021 [22] |
| 850, 425 | - | FTIR (no MP detected) | Bourdages et al., 2020 [23] |
| 500, 300 | - | FTIR | Carlsson, P et al., 2021 [25] |
| 500, 330 | 10% KOH (1 week) | FTIR + FT Raman | Cebuhar J.D. et al., 2024 [26] |
| 20 | K proteinase (enzyme) | FTIR | Desclos-Dukes et al., 2021 [27] |
| 20 | K proteinase (enzyme) | FTIR | Desclos-Duces et al., 2022 [28] |
| 500, 250 | NaCl (5.4 M) | FTIR | Donohue et al., 2019 [29] |
| 100, 500 | - | FTIR | Eriksson and Burton, 2003 [30] |
| 3000, 1000, 500 | 20% KOH (1 week) | FTIR | Garcia-Garin et al., 2020 [31] |
| 250, 1000 | 10% KOH (3 weeks) | Microscope | Hernandes-Milian et al., 2019 [32] |
| 1000, 500, 250 | 10% KOH (3 weeks) | FTIR | Hernandez-Milian et al., 2023 [19] |
| 2000, 1000, 500 | 10% KOH | FTIR | Hudak and Sette, 2019 [33] |
| 20 | 10% KOH | FTIR | McIvor et al., 2023 [34] |
| 1 | 20% KOH | FTIR + GC-MS | Merrill et al., 2023 [18] |
| 2000, 1000, 5000, 2000 | K proteinase (enzyme) | FTIR | Nelms et al., 2018 [35] |
| 35 | K proteinase (enzyme) | FTIR | Nelms et al., 2019 [32] |
| 35 | K proteinase (enzyme) | FTIR | Nelms et al., 2019a [36] |
| - | H2O2 | FTIR | Moreira-Mendieta et al., 2023 [34] |
| 1000, 500, 212 | 30% KOH (3–5 days) | FTIR | Ortega-Borchard et al., 2023 [37] |
| - | 20% KOH (1 week) | Microscope | Perez-Venegas et al., 2018 [38] |
| - | 20% KOH (1 week) | FTIR | Perez-Venegas et al., 2020 [39] |
| 300, 100 | Washing machine, adding enzyme detergents | Microscope | Philipp et al., 2022 [40] |
| 80, 10 | 10% KOH (2 weeks) | FTIR | Jardine et al., 2023 [41] |
| 80, 10 | 10% KOH (2 weeks) | FTIR | Jardine et al., 2023a [42] |
| - | - | FTIR | Wang et al., 2021 [43] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vainberg, A.; Abakumov, E. Microplastic Exposure for Pinnipeds (Pinnipedia): A Rapid Review. Ecologies 2025, 6, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecologies6020026
Vainberg A, Abakumov E. Microplastic Exposure for Pinnipeds (Pinnipedia): A Rapid Review. Ecologies. 2025; 6(2):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecologies6020026
Chicago/Turabian StyleVainberg, Anastasia, and Evgeny Abakumov. 2025. "Microplastic Exposure for Pinnipeds (Pinnipedia): A Rapid Review" Ecologies 6, no. 2: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecologies6020026
APA StyleVainberg, A., & Abakumov, E. (2025). Microplastic Exposure for Pinnipeds (Pinnipedia): A Rapid Review. Ecologies, 6(2), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecologies6020026







