Abstract
Myelin is a membranous structure critically important for human health. Historically, it was believed that myelin remained largely unchanged in the adult brain. However, recent research has shown that myelin is remarkably dynamic, capable of adjusting axonal conduction velocity and playing a role in learning, memory, and recovery from injury, in response to both physiological and pathological signals. Axons are more efficiently insulated in myelinated fibers, where segments of the axonal membrane are wrapped by the myelin sheath. Although extensive data are available on the electrical properties of myelin, its structural and mechanical characteristics—as well as the role of its lipid composition—are also relevant, although much less explored. The objective of our review is derived from this point since alterations in lipid components can lead to axonal dysfunction, giving rise to neurological disorders such as multiple sclerosis and other demyelinating conditions. In this review, concerning the lipid composition of myelin, we focus on two distinct classes of lipids: sphingolipids and long-chain fatty acids, emphasizing the differential contributions of saturated versus polyunsaturated species. We analyze studies that correlate the mechanical vulnerability of myelin with its lipid composition, particularly sphingomyelin, thereby underscoring its role in protecting neurons against physical stress and providing a robust microstructural network that reinforces the white matter as a whole. From a biochemical perspective, we examine the susceptibility of myelin to oxidative stress, metabolic disorders, and extreme nutritional deficiencies in relation to the role of long-chain fatty acids. Both perspectives highlight that the aforementioned lipids participate in a complex biomechanical balance that is essential for maintaining the stability of myelin and, consequently, the integrity of the central and peripheral nervous systems.
1. Introduction
Myelin is a modified cellular membrane that wraps around axons in multiple tightly packed layers [1]. Figure 1 [2] shows a schematic of the structure of the peripheral nervous system myelin sheath, illustrating the myelinated axon, the myelin sheath, the lipid bilayer, and the major lipid classes described in Section 2.
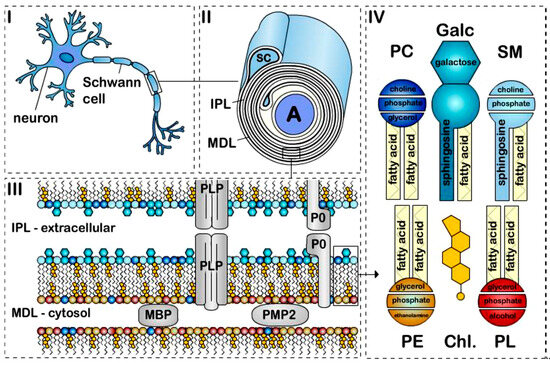
Figure 1.
The structure of peripheral nervous system myelin sheath. Schematic representation of a (I) myelinated axon, (II) myelin sheath, (III) bilayer membrane, and (IV) major lipids classes. Myelin is formed by apposition of the external surfaces and internal surfaces of the myelin bilayer that constitute the intraperiodic line (IPL) and the major dense line (MDL), respectively (II,III). The myelin bilayer has an asymmetric lipid composition (III,IV). Myelin proteins are also asymmetrically distributed with, for example, PLP and P0 in the IPL and MBP and PMP2 at the MDL (III). Cholesterol (Chl.), Galactosylceramide (Galc, cyan), Plasmalogen (PE, yellow), Phosphatidylcholine (PC, dark blue), Sphingomyelin (SM, light blue) and other phospholipids (PL, red). P0, PMP2 proteins and the enrichment of sphingomyelin in the myelin are specific to PNS myelin [2].
Optimal electrical insulation depends on the specific types and proportions of lipids and proteins in myelin, as well as the water fraction within the sheath. If the myelin sheath is damaged, axonal insulation is disrupted and nerve impulses slow or fail to propagate, leading to neurological dysfunction [3,4].
The myelin sheath is characterized by a high lipid content (70–85%) and, consequently, a low protein fraction (15–30%). In contrast, most biological membranes have approximately equal proportions of protein and lipid (50% lipid/50% protein) [5]. This high lipid-to-protein ratio in myelin contributes to its tight packing and compact organization through noncovalent lipid–protein interactions [6]. Moreover, enrichment in specific lipid classes is also necessary for long-term myelin maintenance [7]. Myelin’s lipid composition is distinctive: it contains high levels of cholesterol and is enriched in glycolipids, in a 40:40:20 ratio (cholesterol:phospholipid:glycolipid) compared to most biological membranes (25:65:10) [8]. Figure 2 schematically summarizes the distinctive lipid composition of the myelin membrane in comparison to biological membranes.
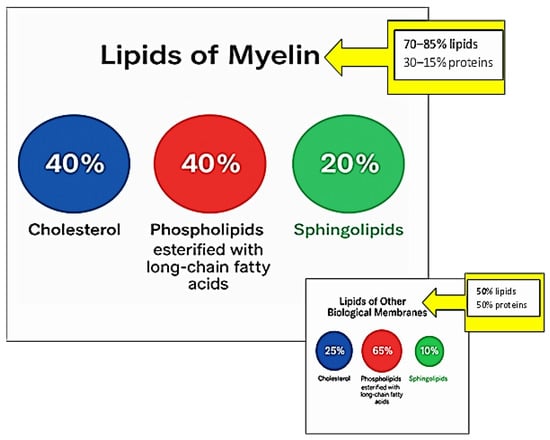
Figure 2.
Distinctive lipid composition of the myelin membrane in comparison to other biological membranes.
The high lipid content of myelin renders it less permeable to ions and a superior electrical insulator. It also affects the physical properties of the membrane, including its stiffness and deformability [3]. Myelin is highly susceptible to compositional changes, and even minor alterations in lipid proportions can cause structural disintegration [9] and, consequently, severe neurological disease [10].
In this review, concerning the lipid composition of myelin, we focus on two distinct classes of lipids: sphingolipids and long-chain fatty acids, emphasizing the differential contributions of saturated versus polyunsaturated species. Figure 3 presents a summary table outlining the objective of this review.
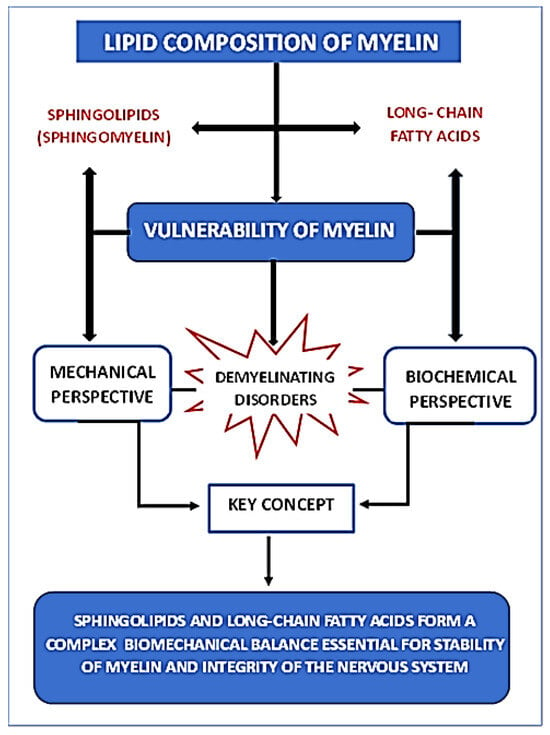
Figure 3.
Summary diagram showing the relationship between myelin lipid composition and its vulnerability from both mechanical and biochemical perspectives.
We analyze studies that correlate the mechanical vulnerability of myelin with its lipid composition, particularly sphingomyelin, thereby underscoring its role in protecting neurons against physical stress and providing a robust microstructural network that reinforces the white matter as a whole. It is evident that the structural integrity and stability of the myelin membrane are fundamental for normal nervous system function. Its degradation or dysgenesis leads to devastating neurocognitive consequences. A pioneering study by O’Brien [8] related myelin membrane stability to intermolecular cohesion among its lipid constituents, given myelin’s exceptionally high lipid content. According to O’Brien, both physiological and clinical findings supported the concept that an excess of polyunsaturated lipids or a deficiency of long-chain sphingolipids could render the membrane more prone to disruption. The key prediction arising from these speculations was that myelin could become unstable in disease states if its lipid composition shifted toward higher proportions of polyunsaturated fatty acids and lower proportions of very-long-chain fatty acids. Sixty years ago, the author acknowledged that these considerations would not fully explain myelin stability, since the molecular models used as references were simplifications of a highly complex structure whose exact molecular organization and sequence remained unknown.
Regarding myelin vulnerability from a biochemical and lipid composition perspective, the roles of certain lipids in myelin membrane maintenance and plasticity have recently gained prominence. In this context, long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids play a particularly intriguing dual role: they are essential for myelination processes yet contribute minimally to the myelin membrane’s lipid architecture, where their proportion is very low compared to that of neuronal membranes in gray matter. Once again, the lipid composition of the myelin membrane appears to play a critical biomechanical role in its integrity and, consequently, in its involvement in related diseases such as multiple sclerosis.
2. Distinctive Myelin Lipids
Cholesterol and Sphingolipids contribute to the formation of the characteristical compact and multilamellar structure of myelin to a greater extent than in conventional biological membranes. Even minor alterations in the lipid composition of myelin can affect the adhesive properties between membranes, potentially leading to the destabilization and breakdown of myelin structures, as well as the development of severe neurological disorders [11].
2.1. Cholesterol
The brain contains approximately 20% of the body’s cholesterol, making it the organ with the highest cholesterol content [12]. The largest reservoir of free cholesterol in mammals is found in myelin [13]. In myelin, cholesterol is inserted into the lipid bilayers of the membrane to increase myelin viscosity and stabilize its lipids and proteins [14]. Myelin cannot be synthesized without cholesterol, and cholesterol availability is a critical requirement and limiting factor for myelin membrane growth during central nervous system (CNS) maturation [15]. Once incorporated into myelin, cholesterol turnover is much slower, with a half-life of approximately five years in the adult human brain [16].
2.2. Sphingolipids
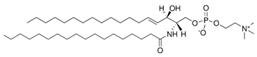
Galactosylceramide and its sulfated form, sulfatide, are two glycosphingolipids found at high and exclusive levels in oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells. Together, they represent approximately 20% of total myelin lipids in oligodendrocytes [15,17,18]. Galactosylceramides are extremely hydrophobic molecules and contribute most significantly to myelin formation and stability among myelin lipids. Alongside highly hydrophobic myelin proteins, they generate strong hydrophobic forces between myelin membranes. These intermolecular forces contribute to the “closing” or “sealing” of myelin membranes—creating attractive forces that pull membranes together and repulsive forces toward extracellular fluid and cytosol [19,20]. Moreover, galactosylceramides have a high proportion of long-chain fatty acids that intercalate into the inner leaflet of the bilayer, further reinforcing myelin membrane stability [20].
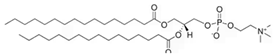
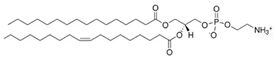
Sphingomyelin is a lipid class enriched in PNS myelin. It consists of a phosphocholine headgroup linked to a sphingosine-based backbone, analogous to the backbone found in galactosylceramide. Its functions are similarly crucial, as it promotes membrane interactions within the myelin structure [21,22].
2.3. Phospholipids (PC, PE, PS) Esterified with Long-Chain Fatty Acids
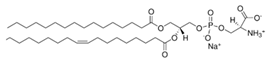
Phosphatidylcholines and phosphatidylethanolamines are abundant phospholipids in myelin, particularly in the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Phosphatidylcholines consist of a choline or ethanolamine headgroup, a glycerophosphate backbone, and fatty acid tails. They serve as structural components of myelin and play roles in membrane initiation, compaction, and maintenance [23]. Phosphatidylcholines are precursors for the synthesis of other key structural and signaling phospholipid classes—such as sphingomyelin, which shares the same headgroup, and phosphatidylinositols and their phosphorylated derivatives—all of which are critical for PNS myelination [24,25,26,27,28,29,30].
Myelin lipids—aside from cholesterol—use fatty acids as fundamental structural components. Because myelin assembly and maintenance require large quantities of fatty acids, myelinating cells are particularly vulnerable to fatty acid– and lipid-related disorders. Myelin contains high levels of saturated very-long-chain fatty acids (VLCFAs) [31]. Intermolecular interactions among long fatty acid tails impart rigidity to the membrane. Saturated fatty acid chains lack double bonds and thus are straight, maximizing interactions between lipids with saturated tails. Consequently, a high content of saturated VLCFAs reduces myelin fluidity and provides a thick permeability barrier to electrically insulate the axon from ions [9]. VLCFAs play a role in myelin maintenance; oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells appear to have an “ideal set-point” for VLCFA content. Mice deficient in VLCFA synthesis exhibit myelin defects [32]. Conversely, abnormal VLCFA accumulation can also cause demyelination—either directly, by disrupting myelin stability and structure, and/or indirectly, by limiting peroxisomal phospholipids synthesis [33,34,35]. Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids (LC-PUFAs) play a fundamental role in both myelination and energy metabolism, yet their incorporation into myelin membranes can induce destabilization. In particular, docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is essential for myelin maintenance and function. DHA is critical to cellular membrane architecture, including oligodendrocyte membranes. Because the brain cannot synthesize sufficient DHA, it must be transported from peripheral sources—crossing the blood–brain barrier (BBB) primarily as unesterified fatty acid via specific transporters. Diets rich in DHA increase its concentration in neurons and glial cells. Additionally, DHA serves as a precursor for anti-inflammatory mediators (e.g., resolvins and protectins) that modulate microglial and astrocyte activity, thereby fostering an environment conducive to oligodendrocyte differentiation.
Fatty acid oxidation is an aerobic mitochondrial process in which a fatty acid is degraded into acetyl-CoA units. The total energy yield from oxidizing a 16-carbon fatty acid molecule generates approximately 129 ATP molecules—more than triple the energy derived from a single glucose molecule. However, fatty acid oxidation is slower, requires more oxygen than glucose oxidation, and is a major source of reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation [36].
3. Mechanical Vulnerability of the Myelin Lipid Membrane
3.1. Lipid Composition, Rigidity, and Demyelination
The integrity of cellular membranes is fundamental to axonal function. Failure of axonal membranes can underlie neurological diseases [37]. Given the complexity of in vivo studies, investigating systems that mimic certain aspects of the myelin membrane may shed light on potential factors related to neurodegenerative disease etiology—especially with regard to remyelination processes. It is well known that, in many situations where myelin partially degrades (e.g., ischemia, trauma), remyelination mechanisms are activated. Such studies are critically important for elucidating these mechanisms and for informing therapeutic approaches in neurodegenerative disorders that remain incurable.
Accordingly, reported findings in the literature depend directly on the choice of the model membrane system used for a particular purpose. The myelin sheath is a multilamellar membrane wrapped tightly around neuronal axons [38]. In the central nervous system (CNS), oligodendrocytes produce this membrane. The cytoplasmic leaflets of oligodendrocyte membranes adhere via interactions between myelin lipids and the myelin basic protein (MBP). Numerous studies have examined MBP’s interaction with liposomes or planar bilayers as membrane models [39,40,41,42,43,44,45]. In recent years, complex biomimetic membrane systems that replicate myelin have attracted particular scientific interest [46,47,48,49,50,51,52]. These biomimetic systems take into account the complexity of myelin’s lipid composition and the asymmetry in lipid distribution between the inner (cytoplasmic) and outer (extracellular) leaflets. Myelin membranes consist of a diverse array of lipids with varying headgroups and alkyl chain lengths—and a high cholesterol content. Myelin is highly anisotropic, with the inner and outer leaflets exhibiting markedly different lipid compositions. Consequently, more realistic model membranes have been developed recently to mimic either the cytoplasmic or extracellular leaflet composition of myelin [6,50,52,53,54]. In those studies, different lipid mixtures were chosen to emulate healthy native myelin versus disease-altered myelin, such as in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), the standard mouse model of multiple sclerosis. The effect of MBP on native versus disease-like multilamellar cytoplasmic model membranes was investigated, and structural instabilities were observed in the modified compositions, akin to those seen in vivo during MS [49].
In Krugmann et al. [55], two distinct large unilamellar vesicle (LUV) populations were prepared—one with native cytoplasmic myelin lipids and one with EAE-modified myelin lipids [6]. Table 1 shows the lipid composition of both membranes.

Table 1.
Proportion of native cytoplasmic myelin lipids and myelin lipids modified by EAE [55].
Experimental techniques employed included small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS), small-angle neutron scattering (SANS), cryo–transmission electron microscopy (cryo-TEM), neutron reflectometry, and neutron spin-echo spectroscopy. The authors probed how membrane rigidity and MBP interaction constitute key molecular factors in MS pathogenesis. They demonstrated that LUVs with native versus EAE-modified lipid compositions form distinct assemblies upon MBP binding. These differences can be largely explained by comparing each membrane’s bending rigidity. Native myelin-like bilayers exhibited approximately 25% greater bending rigidity than EAE-like bilayers across all tested temperatures. Previous studies indicate that adding cholesterol to a bilayer increases bending rigidity; however, in this case, the native membrane contains less cholesterol than the EAE membrane. Conversely, unsaturated lipids decrease bending rigidity by disrupting order in the bilayer. Therefore, the reduced sphingomyelin content in the EAE-modified membrane—which is predominantly saturated—leads to lower bending rigidity, since its sphingomyelin fraction is considerably smaller than that of the native membrane. Higher bending rigidity correlates with membrane structural properties, because rigid membranes minimize local curvature. Experimentally, strong MBP binding to EAE-like biomimetic membranes prevents LUVs from forming multilamellar stacks and, by extension, may impede the formation of well-organized myelin sheaths in MS. In summary, MBP binds more strongly to EAE-modified LUVs than to native LUVs, causing greater aggregation in EAE-mimicking LUVs. Whereas EAE-like vesicles remain stably aggregated, native LUVs undergo a secondary reorganization over several days: LUV fusion leads to extensive multilamellar formation. Notably, these critical differences originate at the molecular level from membrane lipid composition—differences that could trigger severe pathology such as MS.
The vital role of lipids in demyelination processes is further evidenced by the computational work of Saeedimasine et al. [37]. They investigated the relationship between lipid composition and the lipid bilayer’s structural–mechanical properties to clarify how lipid makeup influences membrane behavior. One bilayer—comprising sphingomyelin/phospholipids/cholesterol—was used to mimic a plasma membrane, and another—galactosylceramide/phospholipids/cholesterol—mimicked a myelin sheath. Molecular dynamics simulations (both all-atom and coarse-grained) characterized bilayers at equilibrium and under deformation. For comparison, phospholipid-only and phospholipid/cholesterol bilayers were also simulated. By varying only one lipid species in these bilayers, the researchers isolated the specific effect of each lipid on bilayer properties and, ultimately, clarified each lipid’s role in the mechanical (stress) response of natural membranes. It should be noted that simulated lipid bilayers are simplified models of cellular membranes; they exclude integral membrane proteins, the full diversity of lipid types, and membrane asymmetry. The results clearly show that biophysical and structural traits of a bilayer depend on its lipid composition—regardless of the molecular model used. Both galactosylceramide and sphingomyelin lipids increase acyl chain order and water impermeability. A 30% galactosylceramide fraction raises bilayer rigidity. Galactosylceramide lipids cluster via sugar–sugar interactions and hydrogen bonds with phosphocholine, increasing bilayer thickness. These findings provide a molecular-level perspective on how lipid content shapes natural membrane properties. Because these lipids are characteristic of the myelin sheath, the results enhance our molecular understanding of how lipid composition influences the axonal membrane and elucidate the relationship between lipid content and myelin’s protective function.
3.2. Damage to Myelin Architecture Due to Traumatic Injury and Demyelination Mechanisms
In the central nervous system, myelinated axons interact with—and even actively interdigitate among—adjacent neurons and glial cells such as oligodendrocytes [56,57]. Taib et al. [58] reported that irregularities in myelin within white matter can lead to structural fragmentation, loosening of individual myelin lamellae, or separation of the sheath from the underlying axon. Stretch-induced axonal injury appears to trigger degradation of myelin basic protein (MBP) and subsequent demyelination.
Numerous prior studies have examined the mechanophysiological behavior of lipid bilayers—the principal structural component of the myelin sheath [59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73]. Although those investigations yield valuable mechanobiological insights into lipid bilayer biomechanics, their findings do not directly address the biomechanics of intact myelin. A smaller subset of studies has focused on the biological interactions between myelin and other cellular components [74,75,76,77,78,79,80]. Hence, a quantitative understanding of pure mechanical loading effects on myelin remains incomplete.
To clarify how mechanical forces induce deformation and damage in myelin, Maliha et al. [81] performed computational simulations of a single myelin layer under tensile loading. They applied incremental tensile strains and determined the model’s mechanical response via stress–strain analysis. At approximately 10% applied strain, the simulated myelin began to fail cohesively by nucleating defects within its bilayers. Further tensile loading caused those defects to propagate continuously throughout the bilayer, both radially and transversely. Notably, as loading increased, failure initiated and propagated to final rupture entirely within the lipid bilayer, without initiating any rupture within the protein components. This work defines cellular-level mechanisms by which mechanical loading damages myelin.
4. Biochemical Vulnerability of Myelin: Protective Role of PUFAs
The pathophysiology of MS involves the aberrant activation of helper T lymphocytes, particularly the Th1 and Th17 subsets, along with concurrent suppression of regulatory T cells. Medium-chain saturated fatty acids (SFAs), specifically those ranging from C14 to C18, have been reported to inhibit regulatory T cell differentiation and decrease the expression of anti-inflammatory cytokines [82].
A reduced SFA/PUFA ratio has been associated with the preservation of a non-pathogenic Th17 cell profile, suggesting that lipid composition plays a key role in modulating the immunological behavior of specific T cell subpopulations [83]. Consequently, targeting fatty acid metabolism may offer immunomodulatory benefits and represent a complementary approach to MS therapy.
In the CNS, even under demyelinating conditions such as MS, there is broad consensus regarding the anti-inflammatory properties of n-3 PUFAs, including alpha-linolenic acid (ALA, 18:3n-3), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA, 20:5n-3), and DHA, 22:6n-3. It is important to note that, due to the CNS’s limited capacity for endogenous PUFA synthesis, their availability largely depends on peripheral uptake across the BBB [84,85].
Dietary supplementation with n-3 PUFAs has been shown to reduce neuro-inflammatory burden [86,87,88], potentially by suppressing activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome [89] or inhibiting the differentiation of Th17 cells [90]. Moreover, omega-3-enriched diets have been associated with diminished CNS infiltration by pro-inflammatory cytokine-producing cells [91,92]. These anti-inflammatory effects may be partly mediated by the conversion of n-3 PUFAs into specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators [93,94], which are capable of inhibiting cytokine release from Th1 and Th17 cells [95].
The neuroprotective potential of omega-3 fatty acids is further supported by findings that they promote oligodendrocyte precursor cell maturation, enhance neuronal and oligodendrocyte viability, and reduce demyelination in experimental models [96,97,98,99]. Abd-Elmawla et al. [100] performed clinical trials to demonstrate that supplementation with omega-3 PUFAs can influence triglyceride and HDL-C levels by modulating ApoA1 gene expression. They found that the intake of omega-3 PUFAs and fish oils reduced inflammatory markers and relapse rates in patients with relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS). Furthermore, these supplements decreased triglyceride levels, alone or in combination with other lipid-lowering medications. These authors also indicate that previous studies report omega-3 supplementation in MS patients can help reverse disabilities, halt inflammatory processes, reduce oxidative stress-related damage, and improve metabolic function. They state that the therapeutic potential of omega-3 PUFAs is noteworthy, as are generally well-tolerated and have a good safety profile. However, the specific mechanisms through which they alleviate dyslipidemia still need further investigation.
In contrast, omega-6 PUFAs—particularly arachidonic acid (AA, 20:4n-6)—are known to promote pro-inflammatory responses in both immune and glial cells. AA serves as a precursor for several potent inflammatory eicosanoids, including prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes [101,102].
Western dietary patterns, which are typically high in omega-6 PUFAs, have been implicated in the elevated incidence of MS observed in industrialized countries [91]. Conversely, diets rich in omega-3—especially those emphasizing fish oil consumption—have been associated with a lower risk of MS onset and improved clinical outcomes in affected individuals [92,93].
Furthermore, the human brain is particularly vulnerable to oxidative stress as explained by Stojkovic et al. due to its high oxygen consumption and substantial content of oxidation-prone polyunsaturated fatty acids, especially n-6 PUFAs. Among the lipid peroxidation products, 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) is both highly toxic and abundant. Excessive formation of 4-HNE–protein adducts disrupts normal protein function and contributes to oxidative damage, neuro-inflammation, demyelination, and neurodegeneration—processes central to MS onset and progression. The mentioned study suggests that the profile of long-chain fatty acids in erythrocytes may serve as a specific marker for the progression of multiple sclerosis, proposing circulatory fatty acids as potential molecular indicators to distinguish between RRMS and progressive MS (PMS) [103].
Other authors [100,104,105,106] suggest that future research on MS could focus on the role of lipids as biomarkers of MS, as well as possible indicators of disease load and response to treatment.
The theory that MS may be related to a change in lipid metabolism has prevailed for some time. Changes in the composition of plasma lipids result from various pathogenic processes that are not yet fully understood. However, it has been established that the development of MS plaques is associated with the activation of various inflammatory mediators, including cytokines and anaphylotoxins, which alter the liver’s ability to produce plasma lipoproteins. A substantial correlation has been demonstrated between the prevalence of this disorder and levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and total cholesterol [104].
Makris et al. [105] through a meta-analysis, suggest that patients with RRMS exhibit significantly lower levels of HDL-C compared to healthy controls. However, they note that it remains unclear whether inflammation in MS results from dyslipidaemia or vice versa. This lipoprotein may play a protective role by regulating the integrity of the BBB and preventing its breakdown. Therefore, low HDL-C concentrations would promote BBB disruption, allowing pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines to pass into the central nervous system, leading to the attraction of leukocytes. This inflammatory state results in demyelination.
Noroozi et al. [106] conducted a comprehensive multicenter study to clarify serum metabolomic differences between individuals with MS and healthy controls. The researchers sought to explore the relationship between these metabolic alterations and the severity of clinical symptoms.
They found that patients with MS exhibited significantly lower concentrations of phosphatidylcholines and amino acids, while also showing elevated levels of triglycerides. These metabolic and lipid disturbances were strongly linked to impaired neurological function, as assessed by quantitative motor and cognitive performance evaluations.
Distinct metabolic profiles were observed in patients with progressive forms of MS and in those receiving highly effective disease-modifying therapies, suggesting possible modulation of lipid metabolism through therapeutic intervention.
Dietary factors appear particularly relevant, although the etiological mechanisms of demyelinating diseases remain unclear. The incidence of MS varies significantly by geography, with higher prevalence in Europe, North America, and Oceania, and lower prevalence in Asia and Africa. A north–south/latitudinal gradient has been proposed, which, according to several authors, is associated with various environmental and lifestyle factors, notably dietary habits and the westernization of diet [107,108,109,110,111].
Numerous studies have demonstrated that combining various antioxidants, including DHA, may yield synergistic protective effects against oxidative damage during both preventive and maintenance phases of MS therapy. Due to its favorable lipid composition, fish oil has been proposed as a key nutritional component for promoting regeneration and preventing CNS disorders [112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120].
Moreover, there is growing consensus on the importance of maintaining an optimal dietary omega-6 to omega-3 PUFA ratio. Diets enriched in omega-6 fatty acids have been associated with increased production of pro-inflammatory mediators, highlighting the need for balance [102,121]. Personalized dietary interventions, coupled with robust biomarker monitoring, may improve the efficacy of strategies aimed at preserving myelin integrity [82].
Nonetheless, some authors argue that the current evidence remains insufficient to draw definitive conclusions regarding the clinical impact of antioxidant supplementation or other nutritional interventions on MS outcomes [122].
Altogether, these findings underscore the critical need for continued research to clarify the precise role of polyunsaturated fatty acids—both endogenous and dietary—in the onset and progression of multiple sclerosis.
5. Myelin Vulnerability in the Context of Metabolic Disorders and Nutritional Deprivation: Myelin Lipids as an Energy Reserve
In 2015, Schmitt [7] concluded his research with the question: “… An unresolved issue is whether myelin lipids can serve as an energy reserve. Since these lipids store substantial energy, it would be reasonable for the brain to exploit them as an alternative energy source under conditions of limited availability. For instance, one might ask whether neurons could utilize the energy released from the breakdown of myelin lipids to sustain their metabolism in the absence of glucose”.
Years later, in 2020, Chapman [123] emphasized the need for further research to “… directly observe, characterize, and describe myelin plasticity in vivo”.
More recently, in 2023, Graciani [124] highlighted that critical questions remain concerning aerobic exercise in the context of MS. Although aerobic activity has shown neuroprotective benefits, particularly in preventing or mitigating myelin degradation, little is known about the effects of other exercise modalities, such as resistance training. These forms of exercise may significantly improve physical capacity and autonomy in older individuals with MS. However, Graciani encountered inconsistent results, likely due to methodological limitations or external confounding factors, and concluded that the optimal intensity and duration of physical activity to maximize its benefits remain unclear.
Ongoing investigations are gradually addressing these open questions.
The increasing use of lipidomic technologies has enhanced our understanding of how exercise induces metabolic adaptations, particularly in lipid metabolism. A review by Latino et al. [125] assessed lipidomic shifts in blood and muscle tissue following both acute and chronic physical activity. Their findings revealed significant alterations in medium- and long-chain fatty acids, lipid oxidation products, acylcarnitines, phospholipids, and sphingolipids. Physical exercise promotes fatty acid oxidation, as evidenced by elevated carnitine levels—markers of enhanced mitochondrial activity. Additionally, complex lipids and ceramides accumulate post-exercise, the latter being associated with inflammatory responses. These insights may support the development of personalized training protocols aimed at improving athletic performance and general health outcomes.
Neuronal function and impulse conduction critically depend on a continuous supply of glucose. Remarkably, the mammalian brain lacks extensive energy reserves, apart from glycogen granules localized in astrocytes. Oligodendrocytes not only generate myelin to facilitate rapid axonal conduction but also provide metabolic support to axons via lactate shuttling. Myelin, being a lipid-rich membrane, may function as a localized energy depot during glucose scarcity. Studies in the mouse optic nerve—a white matter model—have shown that oligodendrocytes are more resilient than astrocytes under glucose deprivation, relying on myelin lipid catabolism through a process dependent on oxygen and mitochondrial β-oxidation of fatty acids. This lipid oxidation contributes to axonal ATP production and helps maintain basal axonal conductance [126,127,128].
Regular physical activity is a fundamental determinant of lifelong health. Moderate-intensity training reduces oxidative stress, lowers systemic inflammatory markers, and supports cardiovascular fitness and brain function. However, under extreme conditions—such as prolonged fasting or exhaustive physical exertion without appropriate energy replenishment—the brain shifts to alternative energy substrates, which may include mobilizing structural lipids and compromising myelin integrity.
Recent findings by Ramos-C. [129,130] indicate that marathon running induces a region-dependent reduction in myelin content across both gray and white matter in the brain. This transient demyelination is partially reversed, as levels of myelin water fraction (MWF) increase progressively within two weeks post-race. Such a widespread and marked decrease in myelin following prolonged physical exertion, and its subsequent recovery upon physical rest, introduces the concept of myelin metabolic plasticity—the idea that myelin may serve as an energy reservoir activated during nutrient scarcity.
Oligodendrocytes appear to withstand glucose deprivation by catabolizing myelin lipids into fatty acids, which are then β-oxidized in mitochondria to generate ATP, thereby sustaining axonal and neuronal energy demands.
Although intense physical efforts such as marathons do not appear to cause irreversible demyelination, chronic nutritional deprivation—such as that seen in anorexia nervosa—has been linked to disrupted myelination and structural and cognitive impairments in white matter. Anorexia nervosa thus represents a prototypical model of prolonged nutritional deficiency. Studies in both humans and animals have reported reduced white matter volume and thinning of myelin sheaths, particularly in adolescents and young adults [86,131]. Additionally, delayed oligodendrocyte maturation and incomplete myelination are associated with emotional and cognitive deficits, along with altered brain lipid composition characterized by elevated oxidized lipids [127]. Although these changes may be partially reversible through nutritional rehabilitation, remyelination is often incomplete if nutrient deprivation occurs during critical neurodevelopmental windows [118].
Furthermore, metabolic syndrome and central adiposity have also been associated with reduced myelin content. These findings underscore the need for clinical trials to assess whether interventions such as weight loss and visceral fat reduction could preserve myelin integrity during adulthood. This is particularly relevant for young and middle-aged adults, where metabolic syndrome and adiposity may impair optimal myelination and increase susceptibility to accelerated brain aging and neurodegenerative disorders, including Alzheimer’s disease [132]. Metabolic dysfunction and impaired myelin repair are early mechanisms implicated in the development of Alzheimer’s disease, emphasizing the need to understand these relationships to prevent cognitive decline. Metabolic disorders—including diabetes, obesity, protein-energy malnutrition, and extreme fasting—adversely affect lipid and energy homeostasis in the central nervous system.
Likewise during childhood and adolescence, a high body mass index (BMI) has been associated with an increased risk of developing MS. Associations between BMI and clinical progression markers in patients with MS have been reported, although significant discrepancies exist among studies [133]. It has also been observed that individuals with high total cholesterol, LDL, non-HDL, and triglycerides, as well as an unfavorable lipid profile, experience higher levels of clinical deterioration [134].
Obesity is frequently associated with low-grade inflammation due to increased infiltration and activation of innate and adaptive immune cells in peripheral tissues, such as adipose tissue, which may contribute to neuroinflammation [135].
Circulating inflammatory substances can propagate peripheral inflammation, activate macrophages in organs such as the liver and pancreas, and may cause cerebral inflammation [136]. Obesity can increase the permeability of the BBB, rendering the brain more vulnerable to inflammation [137,138].
A deficiency in essential lipids undermines the stability and adaptability of myelin membranes, while severe caloric restriction impairs the capacity of oligodendrocytes to synthesize and repair myelin [107,127].
6. Conclusions
This review highlights the importance of myelin’s lipid composition in terms of its mechanical and biochemical vulnerability, associated with demyelinating diseases.
The objective of the information gathered from the mechanical perspective of the myelin membrane is to demonstrate how its structural instability may originate from abnormal lipid composition, related to a reduced proportion of sphingomyelin, which alters membrane rigidity and, consequently, its axonal protective function.
About the complex biochemical vulnerability of myelin, the evidence underscores the fundamental role of polyunsaturated fatty acids, especially omega-3 PUFAs, in modulating inflammatory responses and promoting neuroprotection through immune regulation, antioxidant effects, and support for oligodendrocyte function.
Furthermore, the concept of myelin as a dynamic energy reservoir opens new avenues for understanding myelin plasticity under metabolic and nutritional stress. While dietary and lifestyle interventions aimed at optimizing PUFA intake and metabolic health are promising, further research is essential to clarify their therapeutic potential and develop personalized strategies to preserve myelin integrity throughout life.
A comprehensive, mechanistic understanding of remyelination in multiple sclerosis remains a critical unmet need for the millions worldwide affected by this neurodegenerative disease.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A.M. and V.I.P.; formal analysis, M.A.M. and V.I.P.; investigation, M.A.M. and V.I.P.; writing—original draft preparation, M.A.M. and V.I.P.; writing—review and editing, M.A.M. and V.I.P.; project administration, M.A.M. and V.I.P.; funding acquisition, M.A.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Financial support from Universidad Nacional del Sur: PGI 24/Q132 is gratefully acknowledged. M.A.M. is a member of the research career of CONICET.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Simons, M.; Nave, K.A. Oligodendrocytes: Myelination and axonal support. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 8, a020479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poitelon, Y.; Kopec, A.M.; Belin, S. Myelin Fat Facts: An Overview of Lipids and Fatty Acid Metabolism. Cells 2020, 9, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harayama, T.; Riezman, H. Understanding the diversity of membrane lipid composition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 715281–715296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonetto, G.; Belin, D.; Káradóttir, R.T. Myelin: A gatekeeper of activity dependent circuit plasticity? Science 2021, 374, eaba6905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, N.; Pham-Dinh, D. Biology of oligodendrocytes and myelin in the mammalian central nervous system. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 871–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Y.; Kristiansen, K.; Boggs, J.M.; Husted, C.; Zasadzinski, J.A.; Israelachvili, J. Interaction forces and adhesion of supported myelin lipid bilayers modulated by myelin basic protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3154–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, S.; Castelvetri, L.C.; Simons, M. Metabolism and functions of lipids in myelin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1851, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.S. Stability of the myelin membrane. Science 1965, 147, 1099–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrast, R.; Saher, G.; Nave, K.A.; Verheijen, M.H. Lipid metabolism in myelinating glial cells: Lessons from human inherited disorders andmouse models. J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamari, F.; Mochel, F.; Sedel, F.; Saudubray, J.M. Disorders of phospholipids, sphingolipids and fatty acids biosynthesis: Toward a new category of inherited metabolic diseases. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2013, 36, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kister, A.; Kister, I. Overview of myelin, major myelin lipids, and myelin associated proteins. Front. Chem. 2023, 10, 1041961–1041970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjorkhem, I.; Meaney, S. Brain cholesterol: Long secret life behind a barrier. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saher, G.; Stumpf, S.K. Cholesterol in myelin biogenesis and hypomyelinating disorders. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1851, 1083–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demel, R.A.; De Kruyff, B. The function of sterols in membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1976, 457, 109–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saher, G.; Brügger, B.; Lappe-Siefke, C.; Möbius, W.; Tozawa, R.I.; Wehr, M.C.; Wieland, F.; Ishibashi, S.; Nave, K.A. High cholesterol level is essential for myelin membrane growth. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, D.W.; Halford, R.W.; Ramirez, D.M.; Shah, R.; Kotti, T. Cholesterol 24-hydroxylase: An enzyme of cholesterol turnover in the brain. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 1017–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, W.T.; Cammer, W. Isolation and characterization of myelin. In Myelin; Morell, P., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1984; pp. 147–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, J.; Popko, B. Galactolipids are molecular determinants of myelin development and axo-glial organization. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1573, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhti, M.; Aggarwal, S.; Simons, M. Myelin architecture: Zippering membranes tightly together. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 1265–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, S.; Yurlova, L.; Simons, M. Central nervous system myelin: Structure, synthesis and assembly. Trends Cell Biol. 2011, 21, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattenberg, B.W. Intra- and intercellular tracking in sphingolipid metabolism in myelination. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2019, 71, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozgen, H.; Baron, W.; Hoekstra, D.; Kahya, N. Oligodendroglial membrane dynamics in relation to myelin biogenesis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 3291–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furse, S.; de Kroon, A.I. Phosphatidylcholine’s functions beyond that of a membrane brick. Mol. Membr. Biol. 2015, 32, 117–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, L.; Özçelik, M.; Jacob, C.; Pereira, J.A.; Locher, V.; Baumann, R.; Relvas, J.B.; Suter, U.; Tricaud, N. Dlg1-PTEN interaction regulates myelin thickness to prevent damaging peripheral nerve overmyelination. Science 2010, 328, 1415–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boggs, J.M.; Rangaraj, G.; Dicko, A. Effect of phosphorylation of phosphatidylinositol on myelin basic protein-mediated binding of actin filaments to lipid bilayers in vitro. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1818, 2217–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Musse, A.A.; Gao, W.; Homchaudhuri, L.; Boggs, J.M.; Harauz, G. Myelin basic protein as a “PI(4,5)P2-modulin”: A new biological function for a major central nervous system protein. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 10372–10382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, S.; Kippert, A.; Saab, A.S.; Werner, H.B.; Lang, T.; Nave, K.A.; Simons, M. Phosphatidylinosito 4,5-bisphosphate-dependent interaction of myelin basic protein with the plasma membrane in oligodendroglial cells and its rapid perturbation by elevated calcium. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 4794–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noseda, R.; Belin, S.; Piguet, F.; Vaccari, I.; Scarlino, S.; Brambilla, P.; Boneschi, F.M.; Feltri, M.L.; Wrabetz, L.; Quattrini, A.; et al. DDIT4/REDD1/RTP801 is a novel negative regulator of Schwann cell myelination. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 15295–15305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bolis, A.; Coviello, S.; Bussini, S.; Dina, G.; Pardini, C.; Previtali, S.C.; Malaguti, M.; Morana, P.; Del Carro, U.; Feltri, M.L.; et al. Loss of Mtmr2 phosphatase in Schwann cells but not in motor neurons causes Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 4B1 neuropathy with myelin outfoldings. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 8567–8577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccari, I.; Carbone, A.; Previtali, S.C.; Mironova, Y.A.; Alberizzi, V.; Noseda, R.; Rivellini, C.; Bianchi, F.; Del Carro, U.; D’Antonio, M.; et al. Loss of Figure 4 in both Schwann cells and motor neurons contributes to CMT4J neuropathy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastry, P.S. Lipids of nervous tissue: Composition and metabolism. Prog. Lipid Res. 1985, 24, 69–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imgrund, S.; Hartmann, D.; Farwanah, H.; Eckhardt, M.; Sandho, R.; Degen, J.; Gieselmann, V.; Sandho, K.; Willecke, K. Adult ceramide synthase 2 (CERS2)-deficient mice exhibit myelin sheath defects, cerebellar degeneration, and hepatocarcinomas. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 33549–33560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brites, P.; Mooyer, P.A.; el Mrabet, L.; Waterham, H.R.; Wanders, R.J. Plasmalogens participate in very-long-chain fatty acid-induced pathology. Brain 2009, 132 Pt 2, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Singh, J.; Gilg, A.G.; Uto, T.; Singh, I. Very long-chain fatty acid accumulation causes lipotoxic response via 5-lipoxygenase in cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 1685–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassmann, C.M.; Lappe-Siefke, C.; Baes, M.; Brügger, B.; Mildner, A.; Werner, H.B.; Natt, O.; Michaelis, T.; Prinz, M.; Frahm, J.; et al. Axonal loss and neuroinflammation caused by peroxisome-deficient oligodendrocytes. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joffre, C.; Rey, C.; Layé, S. N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and the Resolution of Neuroinflammation. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedimasine, M.; Montanino, A.; Kleiven, S.; Villa, A. Role of lipid composition on the structural and mechanical features of axonal membranes: A molecular simulation study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boggs, J.M. Myelin basic protein: A multifunctional protein. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2006, 63, 1945–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stollery, J.G.; Vail, W.J. Interactions of divalent cations or basic proteins with phosphatidylethanolamine vesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1977, 471, 372–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampe, P.D.; Nelsestuen, G.L. Myelin basic protein-enhanced fusion of membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 1982, 693, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampe, P.D.; Wei, G.J.; Nelsestuen, G.L. Stopped-flow studies of myelin basic protein association with phospholipid vesicles and subsequent vesicle aggregation. Biochemistry 1983, 22, 1594–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggio, B.; Yu, R.K. Interaction and fusion of unilamellar vesicles containing cerebrosides and sulfatides induced by myelin basic protein. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1989, 51, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, H.; Torrielli, M.; Steitz, R.; Cavatorta, P.; Sorbi, R.; Fasano, A.; Riccio, P.; Gliozzi, A. Myelin model membranes on solid substrates. Thin Solid Film. 1998, 327–329, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polverini, E.; Arisi, S.; Cavatorta, P.; Berzina, T.; Cristofolini, L.; Fasano, A.; Riccio, P.; Fontana, M.P. Interaction of myelin basic protein with phospholipid monolayers: Mechanism of protein penetration. Langmuir 2003, 19, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, H.; Steitz, R.; Fasano, A.; Liuzzi, G.M.; Polverini, E.; Cavatorta, P.; Riccio, P. Laminar order within langmuir-blodgett multilayers from phospholipid and myelin basic protein: A neutron reflectivity study. Langmuir 2007, 23, 8491–8496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Saboe, P.O.; Sines, I.T.; Erbakan, M.; Kumar, M. Biomimetic membranes: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 454, 359–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquardt, D.; Geier, B.; Pabst, G. Asymmetric lipid membranes: Towards more realistic model systems. Membranes 2015, 5, 180–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heberle, F.A.; Marquardt, D.; Doktorova, M.; Geier, B.; Standaert, R.F.; Heftberger, P.; Kollmitzer, B.; Nickels, J.D.; Dick, R.A.; Feigenson, G.W.; et al. Subnanometer structure of an asymmetric model membrane: Interleaflet coupling influences domain properties. Langmuir 2016, 32, 5195–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rona, S.; Maor, R.O.; Ram, A.; Rina, A.; Ruth, A.; Yeshayahu, T.; Roy, B. Structural transition in myelin membrane as initiator of multiple sclerosis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 12159–12165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eicher, B.; Heberle, F.A.; Marquardt, D.; Rechberger, G.N.; Katsaras, J.; Pabst, G. Joint small-angle X-ray and neutron scattering data analysis of asymmetric lipid vesicles. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2017, 50, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eicher, B.; Marquardt, D.; Heberle, F.A.; Letofsky-Papst, I.; Rechberger, G.N.; Appavou, M.-S.; Katsaras, J.; Pabst, G. Intrinsic curvature-mediated transbilayer coupling in asymmetric lipid vesicles. Biophys. J. 2018, 114, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaharabani, R.; Ram-On, M.; Talmon, Y.; Beck, R. Pathological transitions in myelin membranes driven by environmental and multiple sclerosis conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 11156–11161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Y.; Alig, T.; Lee, D.; Boggs, J.; Israelachvili, J.; Zasadzinski, J. Critical and off-critical miscibility transitions in model extracellular and cytoplasmic myelin lipid monolayers. Biophys. J. 2011, 100, 1490–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raasakka, A.; Ruskamo, S.; Kowal, J.; Barker, R.; Baumann, A.; Martel, A.; Tuusa, J.; Myllykoski, M.; Bürck, J.; Ulrich, A.S.; et al. Membrane association landscape of myelin basic protein portrays formation of the myelin major dense line. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krugmann, B.; Radulescu, A.; Appavou, M.-S.; Koutsioubas, A.; Stingaciu, L.R.; Dulle, M.; Förster, S.; Stadler, A.M. Membrane stiffness and myelin basic protein binding strength as molecular origin of multiple sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, M.T.; Ruhwedel, T.; Meschkat, M.; Sadowski, B.; Möbius, W. Transmission electron microscopy of oligodendrocytes and myelin. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1936, 343–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, M.; Lyons, D.A. Axonal selection and myelin sheath generation in the central nervous system. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2013, 25, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taib, T.; Leconte, C.; Van Steenwinckel, J.; Cho, A.H.; Palmier, B.; Torsello, E.; Lai Kuen, R.; Onyeomah, S.; Ecomard, K.; Benedetto, C.; et al. Neuroinflammation, myelin and behavior: Temporal patterns following mild traumatic brain injury in mice. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olbrich, K.; Rawicz, W.; Needham, D. Evans EWater permeability mechanical strength of polyunsaturated lipid bilayers. Biophys. J. 2000, 79, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, K.A.; Yates, E.A.; Legleiter, J. Amyloid-forming proteins alter the local mechanical properties of lipid membranes. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 808–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picas, L.; Rico, F.; Scheuring, S. Direct measurement of the mechanical properties of lipid phases in supported bilayers. Biophys. J. 2012, 102, L01–L03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brannigan, G.; Brown, F.L. Composition dependence of bilayer elasticity. J. Chem. Phys. 2005, 122, 74905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, E.G.; Butler, P.D.; Ashkar, R.; Bradbury, R.; Nagao, M. Scaling relationships for the elastic moduli and viscosity of mixed lipid membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 23365–23373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, J.; Razmazma, H.; Jraij, A.; Ebrahimi, A.; Monticelli, L. On calculating the bending modulus of lipid bilayer membranes from buckling simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 6299–6311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nademi, Y.; Tang, T.; Uludağ, H. Nature of bilayer lipids affects membranes deformation and pore resealing during nanoparticle penetration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2022, 132, 112530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayton, G.; Smondyrev, A.M.; Bardenhagen, S.G.; McMurtry, P.; Voth, G.A. Calculating the bulk modulus for a lipid bilayer with nonequilibrium molecular dynamics simulation. Biophys. J. 2022, 82, 1226–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drücker, P.; Iacovache, I.; Bachler, S.; Zuber, B.; Babiychuk, E.B.; Dittrich, P.S.; Draeger, A. Membrane deformation and layer-bylayer peeling of giant vesicles induced by the pore-forming toxin pneumolysin. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 3693–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondrashov, O.V.; Akimov, S.A. The Possibility of Pore Formation in Lipid Membranes by Several Molecules of Amphipathic Peptides. Biochem. Suppl. Ser. A Membr. Cell Biol. 2022, 16, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soubias, O.; Sodt, A.J.; Teague, W.E.; Hines, K.G.; Gawrisch, K. Physiological changes in bilayer thickness induced by cholesterol control GPCR rhodopsin function. Biophys. J. 2023, 122, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faizi, H.A.; Dimova, R.; Vlahovska, P.M. A vesicle microrheometer for high-throughput viscosity measurements of lipid and polymer membranes. Biophys. J. 2022, 121, 910–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galimzyanov, T.R.; Bashkirov, P.V.; Blank, P.S.; Zimmerberg, J.; Batishchev, O.V.; Akimov, S.A. Monolayerwise application of linear elasticity theory well describes strongly deformed lipid membranes and the effect of solvent. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 1179–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinigin, K.V.; Kondrashov, O.V.; Jiménez-Munguía, I.; Alexandrova, V.V.; Batishchev, O.V.; Galimzyanov, T.R.; Akimov, S.A. Elastic deformations mediate interaction of the raft boundary with membrane inclusions leading to their effective lateral sorting. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanino, A.; Saeedimasine, M.; Villa, A.; Kleiven, S. Localized axolemma deformations suggest mechanoporation as axonal injury trigger. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kant, A.; Johnson, V.E.; Arena, J.D.; Dollé, J.P.; Smith, D.H.; Shenoy, V.B. Modeling links softening of myelin and spectrin scaffolds of axons after a concussion to increased vulnerability to repeated injuries. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2024961118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Tian, X.; Wang, C. In Vitro Application of Langmuir Monolayer Model: The interfacial Behavior of Myelin Basic Protein with a Plasma Membrane Model. J. Membr. Biol. 2022, 255, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Weaver, D.F. Microsecond molecular dynamics studies of cholesterol-mediated myelin sheath degeneration in early Alzheimer’s disease. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 24, 222–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eberle, D.; Fodelianaki, G.; Kurth, T.; Jagielska, A.; Möllmert, S.; Ulbricht, E.; Wagner, K.; Taubenberger, A.V.; Träber, N.; Escolano, J.C.; et al. Acquired demyelination but not genetic developmental defects in myelination leads to brain tissue stiffness changes. Brain Multiphys. 2020, 1, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.; Pradhan, S.; Sannigrahi, A.; Jha, S.; Chattopadhyay, K.; Biswas, M.; Saleem, M. In vitro reconstitution demonstrates the amyloid-beta mediated myelin membrane deformation. BioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, F.; Hofmann, F.; Smith, A.J.; Ye, H.; Thompson, M.S. Probing multi-scale mechanics of peripheral nerve collagen and myelin by X-ray diffraction. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 87, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedimasine, M.; Montanino, A.; Kleiven, S.; Villa, A. Elucidating axonal injuries through molecular modelling of myelin sheaths and nodes of Ranvier. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 669897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliha, F.; Adnan, A. Mechanical Responses of a Single Myelin Layer: A Molecular Simulation Study. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaublomme, J.T.; Yosef, N.; Lee, Y.; Gertner, R.S.; Yang, L.V.; Wu Ch Pandolfi, P.P.; Mak, T.; Satija, R.; Shalek, A.K.; Kuchroo, V.K.; et al. Aviv Regev. Single-Cell Genomics Unveils Critical Regulators of Th17 Cell Pathogenicity. Cell 2015, 163, 1400–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.; Lei, H.-T.; Lai, L.T.F.; Gallenito, M.J.; Mu, X.; Matthies, D.; Gonen, T. Lipid flipping in the omega-3 fatty-acid transporter. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, S.K.; Trépanier, M.O.; Bazinet, R.P. n-3 Polyunsaturated fatty acids in animal models with neuroinflammation. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2013, 88, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layé, S.; Nadjar, A.; Joffre, C.; Bazinet, R.P. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in the Brain: Physiological Mechanisms and Relevance to Pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018, 70, 12–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyrolle, Q.; Decoeur, F.; Dejean, C.; Brière, G.; Leon, S.; Bakoyiannis, I.; Baroux, E.; Sterley, T.; Bosch-Bouju, C.; Morel, L.; et al. N-3 PUFA deficiency disrupts oligodendrocyte maturation and myelin integrity during brain development. Glia 2022, 70, 50–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Jiang, W.; Spinetti, T.; Tardivel, A.; Castillo, R.; Bourquin, C.; Guarda, G.; Tian, Z.; Tschopp, J.; Zhou, R. Omega-3 fatty acids prevent inflammation and metabolic disorder through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Immunity 2013, 38, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, M.J.; Fan, Y.Y.; Monk, J.M.; Hou, T.Y.; Barhoumi, R.; McMurray, D.N.; Chapkin, R.S. n-3 PUFAs reduce T-helper 17 cell differentiation by decreasing responsiveness to interleukin-6 in isolated mouse splenic CD4+ T cells. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 1306–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adkins, Y.; Soulika, A.M.; Mackey, B.; Kelley, D.S. Docosahexaenoic acid (22:6n-3) Ameliorated the Onset and Severity of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis in Mice. Lipids 2019, 54, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unoda, K.; Doi, Y.; Nakajima, H.; Yamane, K.; Hosokawa, T.; Ishida, S.; Kimura, F.; Hanafusa, T. Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) induces peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2013, 256, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basil, M.C.; Levy, B.D. Specialized pro-resolving mediators: Endogenous regulators of infection and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norris, P.C.; Skulas-Ray, A.C.; Riley, I.; Richter, C.K.; Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Jensen, G.L.; Serhan, C.N.; Maddipati, K.R. Identification of specialized pro-resolving mediator clusters from healthy adults after intravenous low-dose endotoxin and omega-3 supplementation: A methodological validation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 18050, Erratum in Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiurchiù, V.; Leuti, A.; Dalli, J.; Jacobsson, A.; Battistini, L.; Maccarrone, M.; Serhan, C.N. Proresolving lipid mediators resolving D1, resolvin D2, and maresin 1 are critical in modulating T cell responses. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 353ra111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, A.; Giammarco, M.L.; De Nuccio, C.; Ajmone-Cat, M.A.; Visentin, S.; De Simone, R.; Minghetti, L. Docosahexaenoic acid promotes oligodendrocyte differentiation via PPAR-γ signalling and prevents tumor necrosis factor-α-dependent maturational arrest. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2017, 1862, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegert, E.; Paul, F.; Rothe, M.; Weylandt, K.H. The effect of omega-3 fatty acids on central nervous system remyelination in fat-1 mice. BMC Neurosci. 2017, 18, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkildsen, Ø.; Brunborg, L.A.; Thorsen, F.; Mørk, S.J.; Stangel, M.; Myhr, K.M.; Bø, L. Effects of dietary intervention on MRI activity, de- and remyelination in the cuprizone model for demyelination. Exp. Neurol. 2009, 215, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Ren, H.; Wan, J.B.; Yao, X.; Zhang, X.; He, C.; So, K.F.; Kang, J.X.; Pei, Z.; Su, H. Enriched endogenous omega-3 fatty acids in mice protect against global ischemia injury. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 1288–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Omura, T.; Masaki, N.; Arima, H.; Banno, T.; Okamoto, A.; Hanada, M.; Takei, S.; Matsushita, S.; Sugiyama, E.; et al. Increased arachidonic acid-containing phosphatidylcholine is associated with reactive microglia and astrocytes in the spinal cord after peripheral nerve injury. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matveeva, O.; Bogie, J.F.J.; Hendriks, J.J.A.; Linker, R.A.; Haghikia, A.; Kleinewietfeld, M. Western lifestyle and immunopathology of multiple sclerosis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2018, 1417, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-Elmawla, M.A.; Ghaiad, H.R.; Nooh, M.M.; Amer, M.A.; El-Ghoneimy, L.T.; Mehana, N.A. Role of Vitamin D and Omega 3 Fatty Acids in Improving HDL Biogenesis among Multiple Sclerosis Patients via Orchestrating CHROME/APOA1-AS/ABCA1/APOA1 Milieu. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2025, 145, 110007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørnevik, K.; Chitnis, T.; Ascherio, A.; Munger, K.L. Polyunsaturated fatty acids and the risk of multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 2017, 23, 1830–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlAmmar, W.A.; Albeesh, F.H.; Ibrahim, L.M.; Algindan, Y.Y.; Yamani, L.Z.; Khattab, R.Y. Effect of omega-3 fatty acids and fish oil supplementation on multiple sclerosis: A systematic review. Nutr. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojkovic, L.; Rankovic, S.; Dincic, E.; Boskovic, M.; Kolakovic, A.; Seke, M.; Taki, M.; Zivkovic, M. The Erythrocyte Fatty Acid Profile in Multiple Sclerosis Is Linked to the Disease Course, Lipid Peroxidation, and Dietary Influence. Nutrients 2025, 17, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sarno, A.; Romano, F.; Arianna, R.; Serpico, D.; Lavorgna, M.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A.; Di Somma, C. Lipid Metabolism and Statin Therapy in Neurodegenerative Diseases: An Endocrine View. Metabolites 2025, 15, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makris, A.; Palli, N.; Liontos, A.; Rizos, E.C.; Tsioutis, C.; Papadopoulos, D.; Agouridis, A.P. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol and multiple sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Med. Sci.-Atheroscler. Dis. 2025, 10, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noroozi, R.; Tsai, H.H.; Yu, K.; Bronson, P.; Samuel, K.; Trinh, K.; Wei, R.; Tsai, E.; Briggs, F.B.S.; Bhargava, P.; et al. Metabolic and lipid alterations in multiple sclerosis linked to disease severity. Mult. Scler. J. 2025, 31, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Ramirez, V.; Macias-Islas, M.A.; Ortiz, G.G.; Pacheco-Moises, F.; Torres-Sanchez, E.D.; Sorto-Gomez, T.E.; Cruz-Ramos, J.A.; Orozco-Aviña, G.; Celis de la Rosa, A.J. Efficacy of fish oil on serum of TNF α, IL-1 β, and IL-6 oxidative stress markers in multiple sclerosis treated with interferon beta-1b. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 709493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Meeteren, M.E.; Teunissen, C.E.; Dijkstra, C.D.; Van Tol, E.A.F. Antioxidants and polyunsaturated fatty acids in multiple sclerosis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 59, 1347–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallin, M.T.; Culpepper, W.J.; Campbell, J.D.; Nelson, L.M.; Langer-Gould, A.; Marrie, R.A.; Cutter, G.R.; Kaye, W.E.; Wagner, L.; Tremlett, H.; et al. The prevalence of MS in the United States: A population-based estimate using health claims data. Neurology 2019, 92, e1029–e1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompura, S.L.; Hafler, D.A.; Dominguez-Villar, M. Fatty acid metabolism and T cells in multiple sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 869197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakoda, A.; Matsushita, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Shinoda, K.; Masaki, K.; Isobe, N.; Yamasaki, R.; Kira, J.-i. Environmental risk factors for multiple sclerosis in Japanese people. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2020, 38, 101872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, J.; Sultan, S.; Rytz, A.; Steiner, P.; Schneider, N. A blend containing docosahexaenoic acid, arachidonic acid, vitamin B12, vitamin B9, iron and sphingomyelin promotes myelination in an in vitro model. Nutr. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 931–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei Ali, M.D.; Hamidi Majid, M.D.; Seyedmirzaei Homa, M.D.; Moghadasi Abdorreza Naser, M.D. Can supplementation with antioxidants improve cognitive functions in patients with multiple sclerosis? A literature review. Ann. Med. Surg. 2025, 87, 2736–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namiecinska, M.; Piatek, P.; Lewkowicz, P. Nervonic Acid Synthesis Substrates as Essential Components in Profiled Lipid Supplementation for More Effective Central Nervous System Regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piatek, P.; Lewkowicz, N.; Michlewska, S.; Wieczorek, M.; Bonikowski, R.; Parchem, K.; Lewkowicz, P.; Namiecinska, M. Natural fish oil improves the differentiation and maturation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells to oligodendrocytes in vitro after interaction with the blood–brain barrier. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macaron, T.; Giudici, K.V.; Bowman, G.L.; Sinclair, A.; Stephan, E.; Vellas, B.; de Souto, B.P. Associations of Omega-3 Fatty Acids with Brain Morphology and Volume in Cognitively Healthy Older Adults: A narrative review. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 67, 101300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orywal, K.; Socha, K.; Iwaniuk, P.; Kaczyński, P.; Farhan, J.A.; Zoń, W.; Łozowicka, B.; Perkowski, M.; Mroczko, B. Vitamins in the Prevention and Support Therapy of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahabi, B.; Hernández-Martínez, C.; Jardí, C.; Aparicio, E.; Arija, V. Maternal Omega-6/Omega-3 Concentration Ratio During Pregnancy and Infant Neurodevelopment: The ECLIPSES Study. Nutrients 2025, 17, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzner, D.; Bader, J.M.; Penkert, H.; Bergner, C.G.; Su, M.; Weil, M.-T.; Surma, M.A.; Mann, M.; Klose, C.; Simons, M. Cell-Type- and Brain-Region-Resolved Mouse Brain Lipidome. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 108132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavrinou, P.S.; Andreou, E.; Aphamis, G.; Pantzaris, M.; Ioannou, M.; Patrikios, I.S.; Giannaki, C.D. The Effects of a 6-Month High Dose Omega-3 and Omega-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Antioxidant Vitamins Supplementation on Cognitive Function and Functional Capacity in Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment. Nutrients 2020, 12, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedighiyan, M.; Djafarian, K.; Dabiri, S.; Abdolahi, M.; Shab-Bidar, S. The Effects of Omega-3 Supplementation on the Expanded Disability Status Scale and Inflammatory Cytokines in Multiple Sclerosis Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2019, 18, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torkildsen, Ø.; Wergeland, S.; Bakke, S.; Beiske, A.G.; Bjerve, K.S.; Hovdal, H.; Midgard, R.; Lilleås, F.; Pedersen, T.; Bjørnarå, B.; et al. ω-3 Fatty Acid Treatment in Multiple Sclerosis (OFAMS Study): A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Arch. Neurol. 2012, 69, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, T.W.; Hill, R.A. Myelin plasticity in adulthood and aging. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 715, 134645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graciani, A.L.; Usberti Gutierre, M.; Coppi, A.A.; Arida, R.M.; Campos Gutierre, R. Myelin, aging, and physical exercise. Neurobiol. Aging 2023, 127, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latino, F.; Cataldi, S.; Carvutto, R.; De Candia, M.; D’Elia, F.; Patti, A.; Bonavolontà, V.; Fischetti, F. The Importance of Lipidomic Approach for Mapping and Exploring the Molecular Networks Underlying Physical Exercise: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asadollahi, E.; Trevisiol, A.; Saab, A.S.; Looser, Z.J.; Dibaj, P.; Kusch, K.; Ruhwedel, T.; Möbius, W.; Jahn, O.; Baes, M.; et al. Myelin lipids as nervous system energy reserves. bioRxiv 2022. bioRxiv:2022.02.24.481621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadollahi, E.; Trevisiol, A.; Saab, A.S.; Looser, Z.J.; Dibaj, P.; Ebrahimi, R.; Kusch, K.; Ruhwedel, T.; Möbius, W.; Jahn, O.; et al. Oligodendroglial fatty acid metabolism as a central nervous system energy reserve. Nat. Neurosci. 2024, 27, 1934–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nave, K.-A.; Asadollahi, E.; Sasmita, A. Expanding the function of oligodendrocytes to brain energy metabolism. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2023, 83, 102782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Cabrer, P.; Cabrera-Zubizarreta, A.; Padró, D.; Matute-González, M.; Rodríguez-Antigüedad, A.; Matute, C. Widespread drastic reduction of brain myelin content upon prolonged endurance exercise. bioRxiv 2023, 10, 561303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Cabrer, P.; Cabrera-Zubizarreta, A.; Padró, D.; Matute-González, M.; Rodríguez-Antigüedad, A.; Matute, C. Reversible reduction in brain myelin content upon marathon running. Nat. Metab. 2025, 7, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklyn, N.; Kesavelu, D.; Joji, P.; Verma, R.; Wadhwa, A.; Ray, C. Impact of Key Nutrients on Brain and Executive Function Development in Infants and Toddlers: A Narrative Review. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2022, 10, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burzynska, A.Z.; Anderson Ch Arciniegas, D.B.; Calhoun, V.; Choi, I.-Y.; Mendez Colmenares, A.; Hiner, G.; Kramer, A.F.; Li, K.; Lee, J.; Lee, P.; et al. Metabolic syndrome and adiposity: Risk factors for decreased myelin in cognitively healthy adults. Cereb. Circ. Cogn. Behav. 2023, 5, 100180–100190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stampanoni Bassi, M.; Iezzi, E.; Buttari, F.; Gilio, L.; Simonelli, I.; Carbone, F.; Micillo, T.; De Rosa, V.; Sica, F.; Furlan, R.; et al. Obesity worsens central inflammation and disability in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2020, 26, 1237–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noori, H.; Gheini, M.R.; Rezaeimanesh, N.; Saeedi, R.; Rezaei Aliabadi, H.; Sahraian, M.A.; Naser Moghadasi, A. The correlation between dyslipidemia and cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis patients. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2019, 36, 101415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zatterale, F.; Longo, M.; Naderi, J.; Raciti, G.A.; Desiderio, A.; Miele, C.; Beguinot, F. Chronic adipose tissue inflammation linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Front. Physiol. 2020, 10, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, A.; Fernandes, A.; Barateiro, A. The complex relationship between obesity and neurodegenerative diseases: An updated review. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1294420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Yu, J.; Su, Y.; Mei, F.; Li, M.; Zhao, K.; Zhao, L.; Deng, W.H.; Chen, C.; Wang, W.X. High-fat diet aggravates acute pancreatitis via TLR4-mediated necroptosis and inflammation in rats. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 8172714–8172724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Fang, C.; Ma, Y.; Chang, J. Obesity-induced blood-brain barrier dysfunction: Phenotypes and mechanisms. J. Neuroinflamm. 2024, 21, 110–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).