Rethinking Metabolic Imaging: From Static Snapshots to Metabolic Intelligence
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Metabolic Signals: A Fragmented View of a Dynamic Whole
3. Bridging the Gap: Data-Driven and Physics-Based Metabolic Modeling
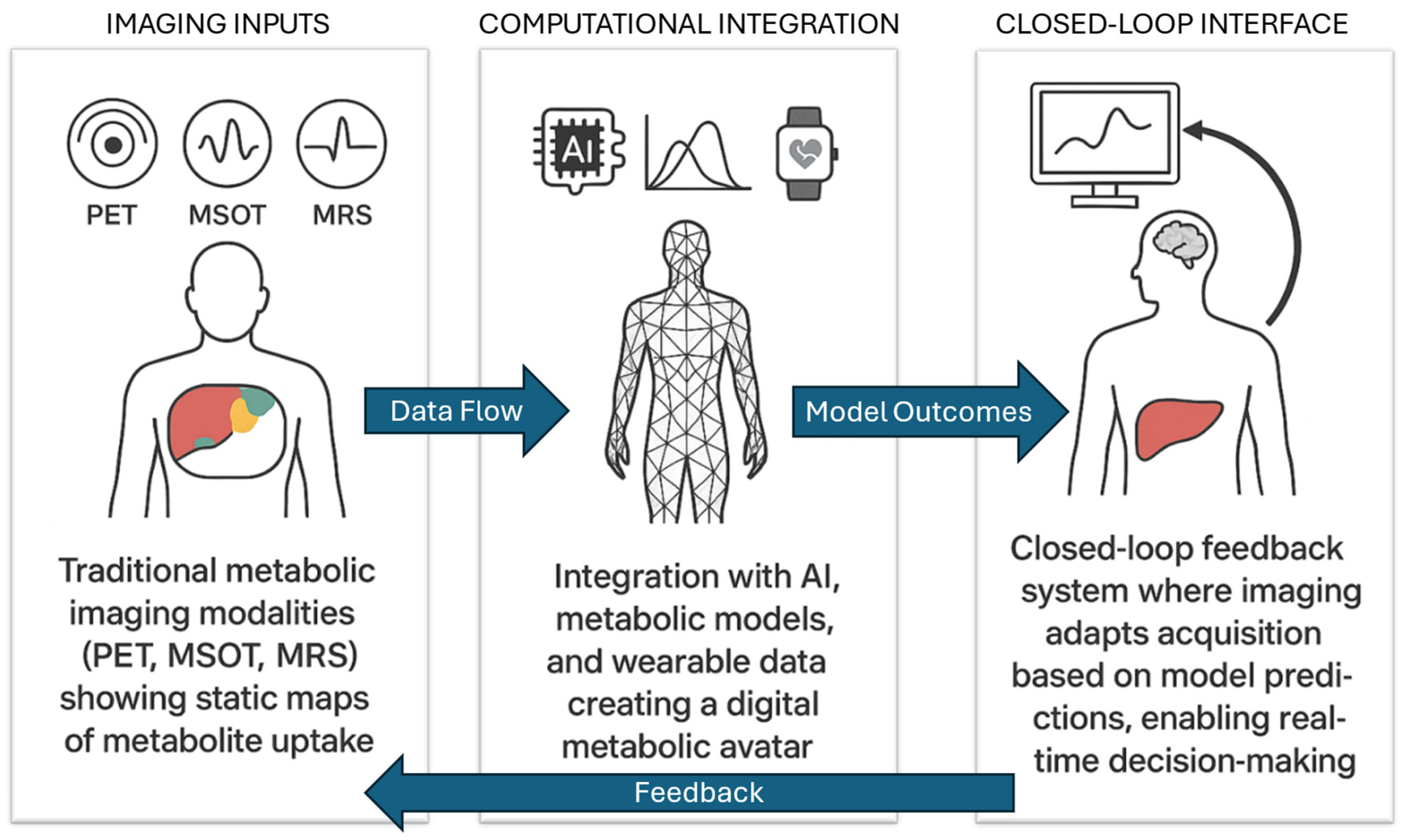
4. Toward Interactive, Adaptive Imaging Platforms
5. Clinical and Translational Implications
6. Conclusions: Toward a Living Metabolic Map
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bianchetti, G.; Taralli, S.; Vaccaro, M.; Indovina, L.; Mattoli, M.V.; Capotosti, A.; Scolozzi, V.; Calcagni, M.L.; Giordano, A.; De Spirito, M.; et al. Automated Detection and Classification of Tumor Histotypes on Dynamic PET Imaging Data Through Machine-Learning Driven Voxel Classification. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 145, 105423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, H.; AkhavanAllaf, A.; Sanaat, A.; Shiri, I.; Zaidi, H. The Promise of Artificial Intelligence and Deep Learning in PET and SPECT Imaging. Phys. Med. 2021, 83, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagana Gowda, G.A.; Raftery, D. NMR Based Metabolomics. In Cancer Metabolomics: Methods and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; Volume 1280, p. 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.M.; Recht, L.D.; Josan, S.; Merchant, M.; Jang, T.; Yen, Y.F.; Hurd, R.E.; Spielman, D.M.; Mayer, D. Metabolic Response of Glioma to Dichloroacetate Measured In Vivo by Hyperpolarized 13C Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Imaging. Neuro Oncol. 2013, 15, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graça, G.; Duarte, I.F.; Goodfellow, B.J.; Carreira, I.M.; Couceiro, A.B.; Domingues, M.D.R.; Spraul, M.; Tseng, L.H.; Gil, A.M. Metabolite Profiling of Human Amniotic Fluid by Hyphenated Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 6085–6092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giacinto, F.; Riente, A.; Mignini, I.; Ainora, M.E.; Esposto, G.; Borriello, R.; Zocco, M.A.; Minordi, L.M.; Sala, E.; Scaldaferri, F.; et al. Advancing Multispectral Optoacoustic Tomography (MSOT): Phasor Analysis for Real-Time Spectral Unmixing. Comput. Biol. Med. 2025, 195, 110586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildgruber, M.; Masthoff, M.; Helfen, A.; Claussen, J.; Karlas, A.; Markwardt, N.A.; Ntziachristos, V.; Eisenblätter, M.; Wildgruber, M. Use of Multispectral Optoacoustic Tomography to Diagnose Vascular Malformations. JAMA Dermatol. 2018, 154, 1457–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diot, G.; Metz, S.; Noske, A.; Liapis, E.; Schroeder, B.; Ovsepian, S.V.; Meier, R.; Rummeny, E.; Ntziachristos, V. Multispectral Optoacoustic Tomography (MSOT) of Human Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 6912–6922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skala, M.; Ramanujam, N. Multiphoton Redox Ratio Imaging for Metabolic Monitoring In Vivo. In Advanced Protocols in Oxidative Stress II; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 594, pp. 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchetti, G.; Clementi, M.E.; Sampaolese, B.; Serantoni, C.; Abeltino, A.; De Spirito, M.; Sasson, S.; Maulucci, G. Investigation of DHA-Induced Regulation of Redox Homeostasis in Retinal Pigment Epithelium Cells Through the Combination of Metabolic Imaging and Molecular Biology. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjit, S.; Malacrida, L.; Gratton, E. Differences between FLIM Phasor Analyses for Data Collected with the Becker and Hickl SPC830 Card and with the FLIMbox Card. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2018, 81, 980–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursprung, S.; Woitek, R.; McLean, M.A.; Priest, A.N.; Crispin-Ortuzar, M.; Brodie, C.R.; Gill, A.B.; Gehrung, M.; Beer, L.; Riddick, A.C.P.; et al. Hyperpolarized13C-Pyruvate Metabolism as a Surrogate for Tumor Grade and Poor Outcome in Renal Cell Carcinoma—A Proof of Principle Study. Cancers 2022, 14, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woitek, R.; McLean, M.A.; Gill, A.B.; Grist, J.T.; Provenzano, E.; Patterson, A.J.; Ursprung, S.; Torheim, T.; Zaccagna, F.; Locke, M.; et al. Hyperpolarized13c Mri of Tumor Metabolism Demonstrates Early Metabolic Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer. Radiol. Imaging Cancer 2020, 2, e200017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, G.J.R.; Alberts, I.L.; Wagner, T.; Fischer, B.M.; Nazir, M.S.; Lilburn, D. The Impact of Long Axial Field of View (LAFOV) PET on Oncologic Imaging. Eur. J. Radiol. 2025, 183, 111873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.C.; Tsai, M.H.; Chen, F.C.; Hsiung, C.A. GEMSiRV: A Software Platform for GEnome-Scale Metabolic Model Simulation, Reconstruction and Visualization. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1752–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Kim, G.B.; Kim, W.J.; Kim, H.U.; Lee, S.Y. Current Status and Applications of Genome-Scale Metabolic Models. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opdam, S.; Richelle, A.; Kellman, B.; Li, S.; Zielinski, D.C.; Lewis, N.E. A Systematic Evaluation of Methods for Tailoring Genome-Scale Metabolic Models. Cell Syst. 2017, 4, 318–329.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abeltino, A.; Serantoni, C.; Riente, A.; De Giulio, M.; Capezzone, S.; Esposito, R.; De Spirito, M.; Maulucci, G. Transforming Personalized Weight Forecasting: From the Personalized Metabolic Avatar to the Generalized Metabolic Avatar. Comput. Biol. Med. 2025, 188, 109879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeltino, A.; Bianchetti, G.; Serantoni, C.; Riente, A.; De Spirito, M.; Maulucci, G. Putting the Personalized Metabolic Avatar into Production: A Comparison between Deep-Learning and Statistical Models for Weight Prediction. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, D.M.; Henriques, R.; Costa, R.S. Predicting Metabolic Fluxes from Omics Data via Machine Learning: Moving from Knowledge-Driven Towards Data-Driven Approaches. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2023, 21, 4960–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazza, G.; Moro, F.; Ruggeri, D.; Teusink, B.; Vidács, L. MINN: A Metabolic-Informed Neural Network for Integrating Omics Data into Genome-Scale Metabolic Modeling. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2025, 27, 3609–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoogian, E.N.C.; Panda, S. Circadian Rhythms, Time-Restricted Feeding, and Healthy Aging. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 39, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruynseels, K.; de Sio, F.S.; van den Hoven, J. Digital Twins in Health Care: Ethical Implications of an Emerging Engineering Paradigm. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Modality | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| PET | High sensitivity; established clinical use; quantitative tracer uptake | Radiation exposure; high cost; relatively low spatial resolution; limited suitability for repeated longitudinal studies |
| MRS | Non-invasive; direct metabolite quantification (e.g., lactate, creatine) | Poor spatial localization; low sensitivity; long acquisition times |
| MSOT | Real-time imaging; combines optical contrast with ultrasound resolution | Limited penetration depth (~2–3 cm); best suited for superficial tissues or preclinical models |
| Fluorescence imaging | High specificity; subcellular resolution; sensitive metabolic readouts | Requires exogenous probes; limited deep tissue applicability; photobleaching and invasiveness |
| Hyperpolarized MRI | Dynamic tracking of metabolic fluxes (e.g., pyruvate, lactate) | Short polarization lifetime; technically complex; expensive; limited availability |
| Module | Components | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Data Sources | Imaging (PET, MSOT, MRS, hyperpolarized MRI, fluorescence imaging); wearables (HR, steps, glucose, sleep); clinical records | Provide multimodal, real-time, and contextual inputs reflecting the metabolic state |
| Computational Layers | Physics-based models (ODEs, GEMs, constraint-based); machine learning (deep learning, physics-informed ML); hybrid avatars | Simulate, predict, and reconcile metabolic trajectories using complementary mechanistic and data-driven methods |
| Interfaces | Imaging–model feedback; model-informed acquisition (adaptive scanning, timing windows); clinical dashboards | Enable bidirectional flow: data feeding into models, and models guiding imaging parameters and interventions |
| Category | Challenges | Mitigation Strategies |
| Technological | Lack of standardization across imaging modalities and acquisition protocols | Adoption of open standards; development of harmonized acquisition protocols; federated multi-center initiatives |
| Workflow | Difficulty integrating real-time streaming data into clinical workflows | Modular software design; use of interoperability frameworks (e.g., FHIR); embedding within clinical dashboards |
| Regulatory | Computational opacity of deep learning models; difficulty in regulatory approval | Prioritize physics-informed and explainable AI; ensure traceability and uncertainty quantification |
| Ethical and Privacy | Data security and privacy risks when linking wearables and EHRs; patient consent management | Privacy-preserving federated learning; strong encryption; GDPR/HIPAA compliance; transparent informed consent |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maulucci, G. Rethinking Metabolic Imaging: From Static Snapshots to Metabolic Intelligence. Biophysica 2025, 5, 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/biophysica5030042
Maulucci G. Rethinking Metabolic Imaging: From Static Snapshots to Metabolic Intelligence. Biophysica. 2025; 5(3):42. https://doi.org/10.3390/biophysica5030042
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaulucci, Giuseppe. 2025. "Rethinking Metabolic Imaging: From Static Snapshots to Metabolic Intelligence" Biophysica 5, no. 3: 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/biophysica5030042
APA StyleMaulucci, G. (2025). Rethinking Metabolic Imaging: From Static Snapshots to Metabolic Intelligence. Biophysica, 5(3), 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/biophysica5030042






