Identification and Expression Analysis of Na+/K+-ATPase and NKA-Interacting Protein in Ark Shells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Identification of the NKA Subunits in Ark Shells
2.2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of the NKA Subunits in Ark Shells
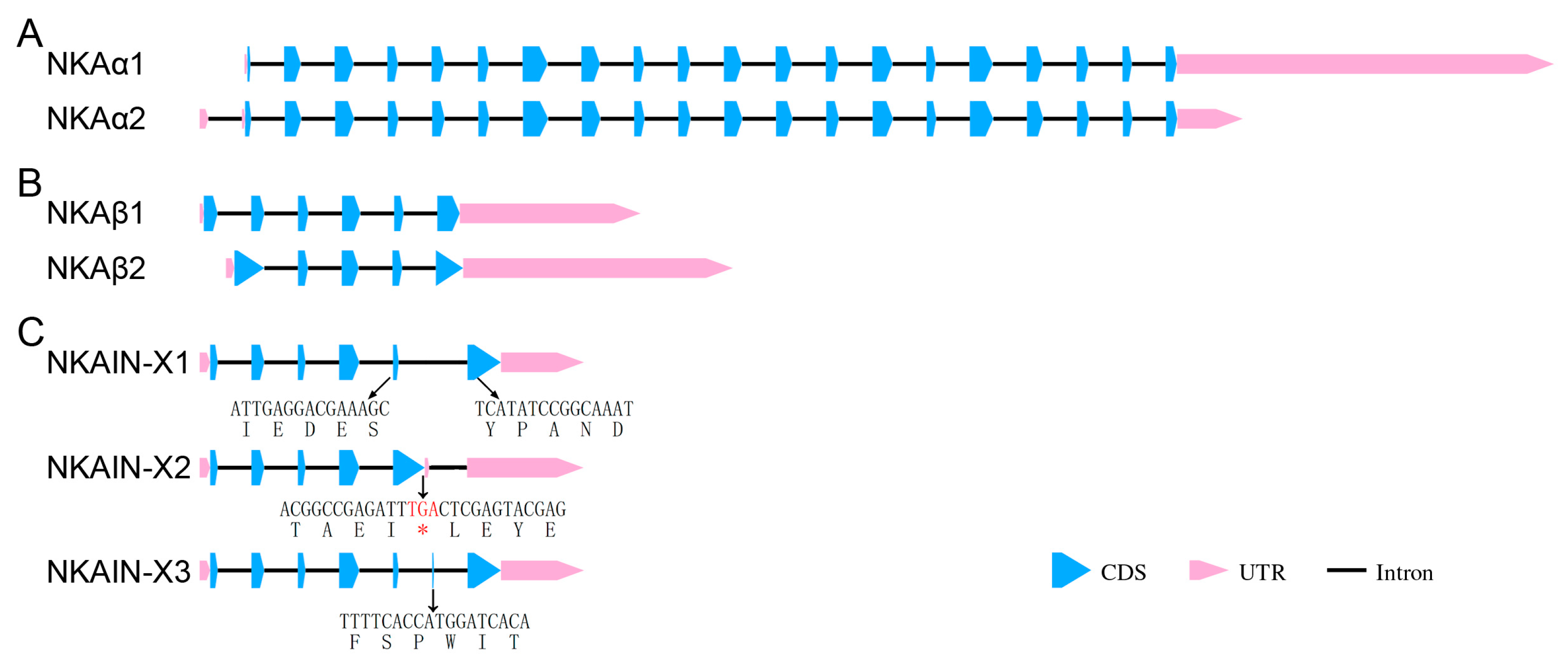
2.2.3. Gene Structure and Alternative Splicing Analysis
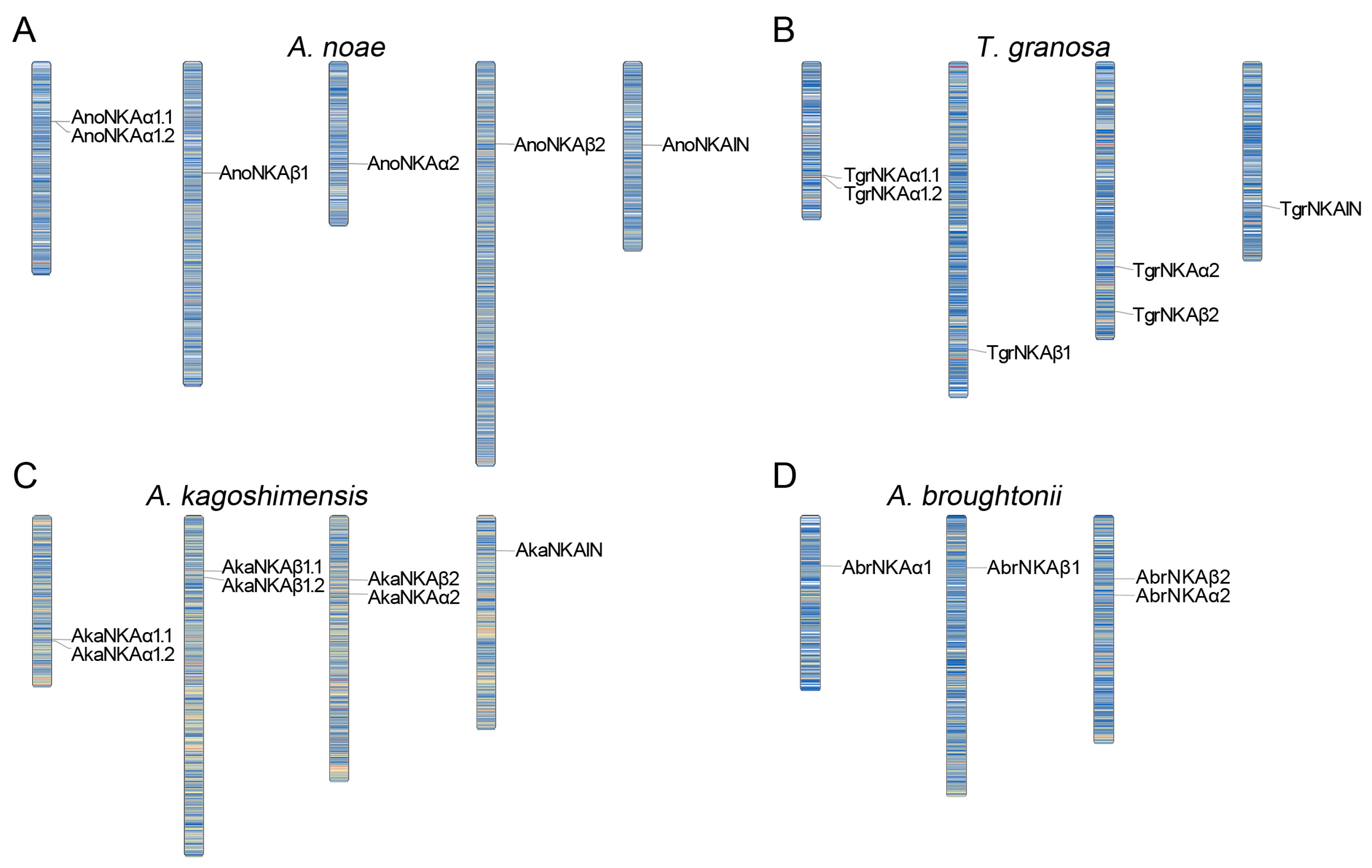
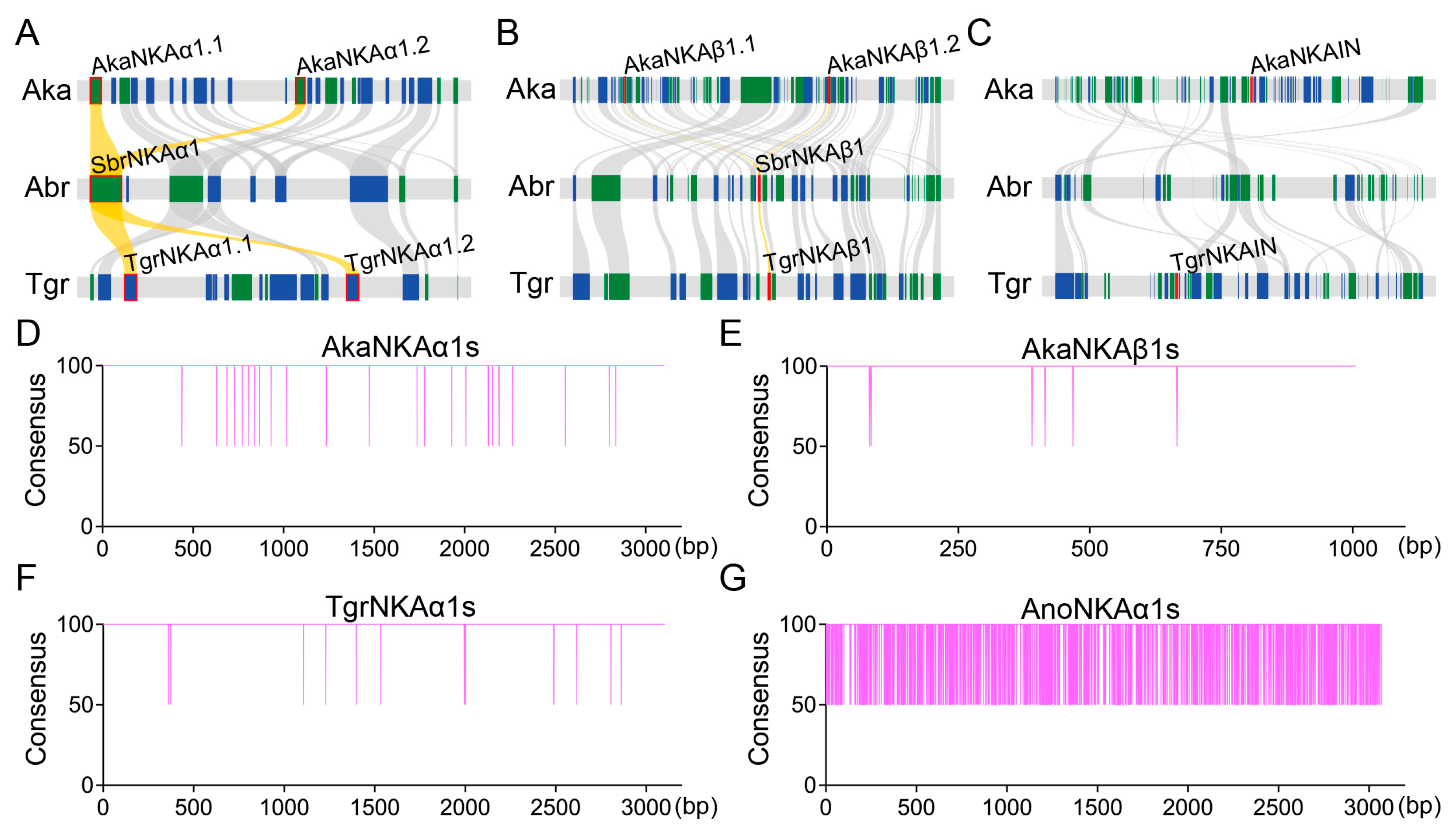
2.2.4. Synteny Analysis of the NKA Subunits in Ark Shells
2.2.5. Protein Structure Analysis
2.2.6. Expression Analysis
3. Results
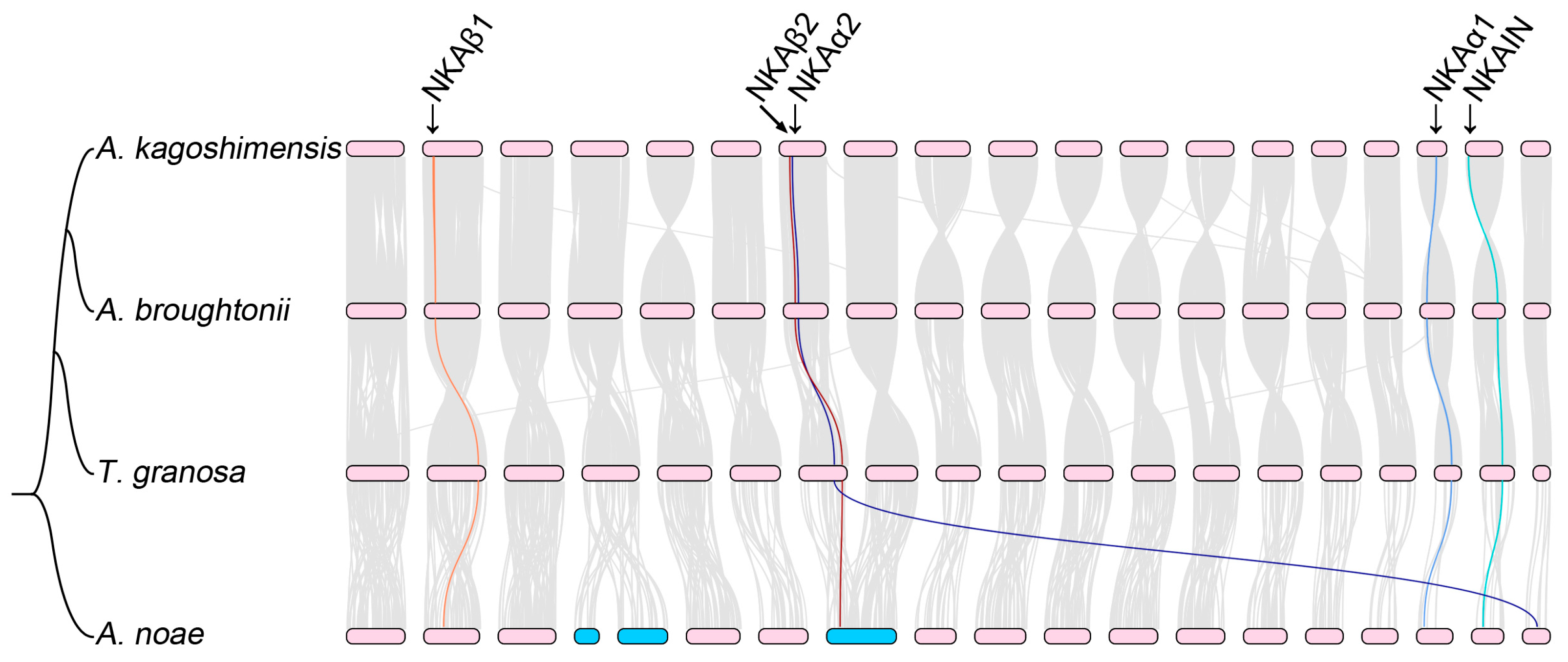
3.1. Conservation of Chromosomal Synteny in Ark Shells
3.2. Identification of the NKA Subunits and NKAIN
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of the NKA Subunits and NKAIN
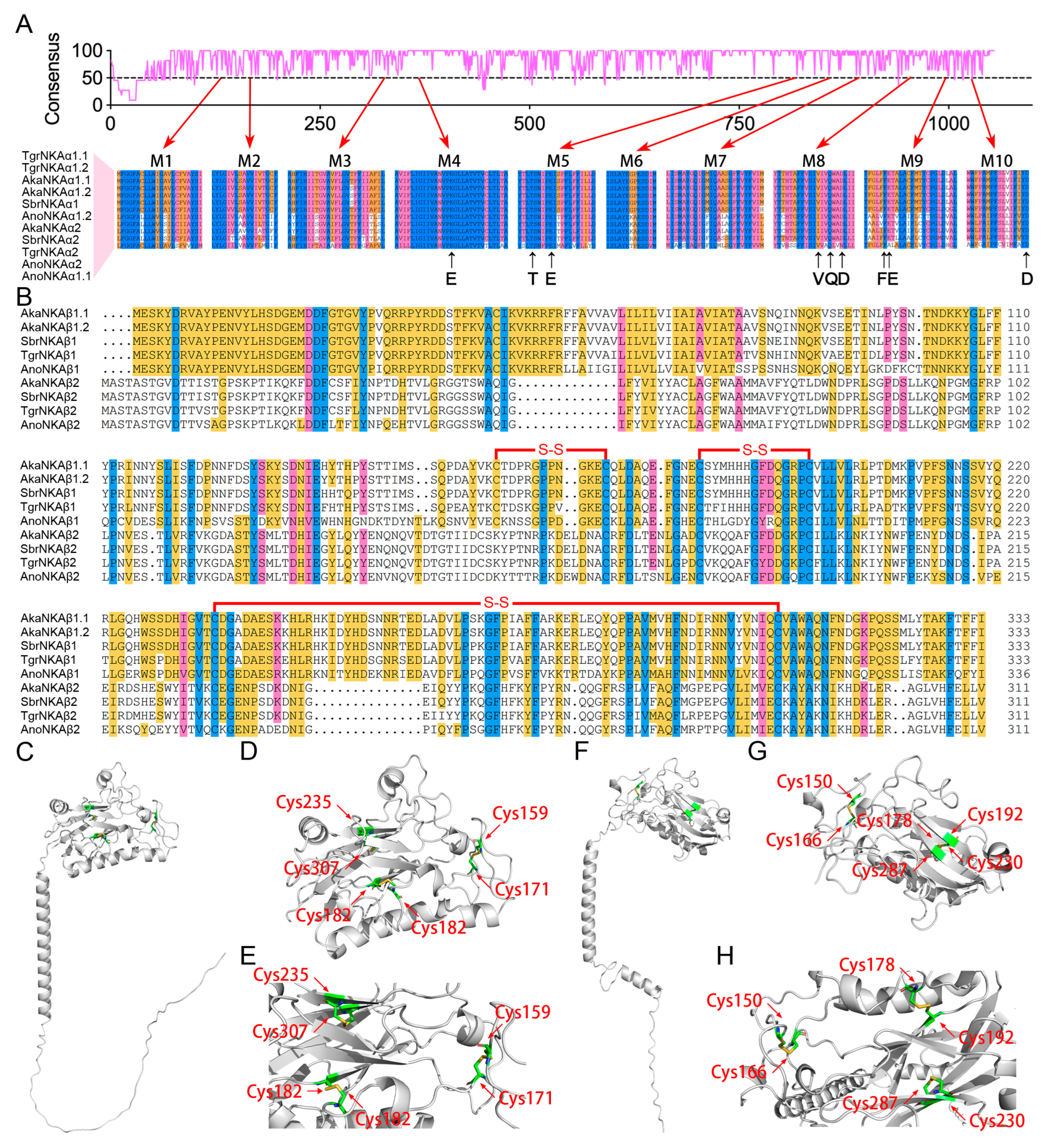
3.4. Structural Analysis of the NKA-α and NKA-β Subunits
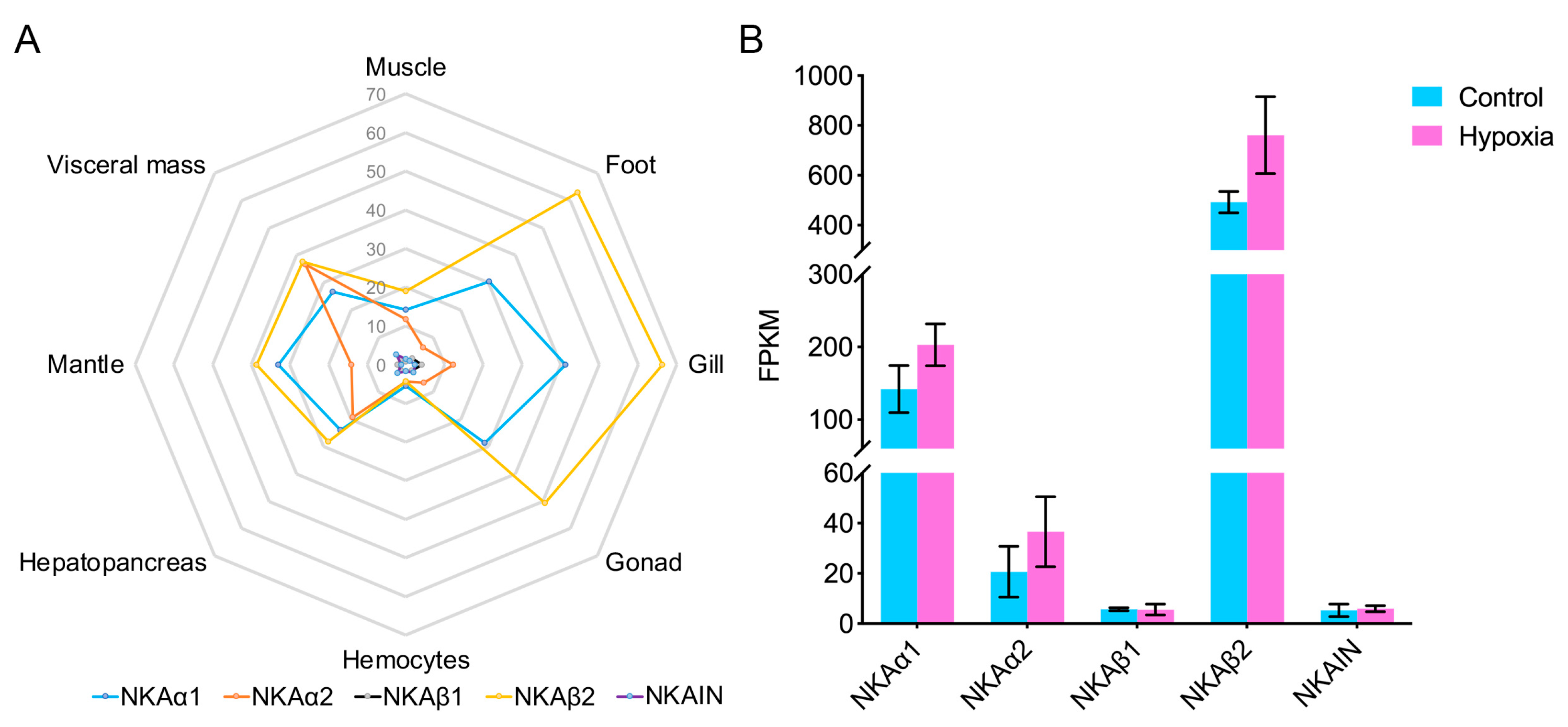
3.5. Expression of the NKA Subunits and NKAIN in Ark Shells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NKA | Sodium–potassium ATPase, Na⁺/K⁺-ATPase |
| NKAIN | NKA-interacting protein |
| Aka | A. kagoshimensis |
| Abr | A. broughtonii |
| Tgr | T. granosa |
| Ano | A. noae |
References
- Sun, S.E.; Li, Q.; Kong, L.; Yu, H. Evolution of mitochondrial gene arrangements in Arcidae (Bivalvia: Arcida) and their phylogenetic implications. Mol. Phylogeneti. Evol. 2020, 150, 106879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, P.G.; Holmes, A.M. The Arcoidea (Mollusca: Bivalvia): A review of the current phenetic-based systematics. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2006, 148, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Lee, W.C.; Choy, E.J.; Kang, C.K. Reproductive cycle and gross biochemical composition of the ark shell Scapharca subcrenata (Lischke, 1869) reared on subtidal mudflats in a temperate bay of Korea. Aquaculture 2011, 322–323, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheaton, W.W.; Chandel, N.S. Hypoxia. 2. Hypoxia regulates cellular metabolism. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2011, 300, C385–C393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Liu, X. Expression of Na+/K+-ATPase was affected by salinity change in Pacific abalone Haliotis discus hannai. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amende, L.M.; Pierce, S.K. Cellular volume regulation in salinity stressed molluscs: The response of Noetia ponderosa (Arcidae) red blood cells to osmotic variation. J. Comp. Physiol. 1980, 138, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skou, J.C. The identification of the Sodium–Potassium Pump (Nobel Lecture). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 2320–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausen, M.V.; Hilbers, F.; Poulsen, H. The structure and function of the Na, K-ATPase isoforms in health and disease. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenza, G.L. Life with oxygen. Science 2007, 318, 62–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyblom, M.; Poulsen, H.; Gourdon, P.; Reinhard, L.; Andersson, M.; Lindahl, E.; Fedosova, N.; Nissen, P. Crystal structure of Na+, K(+)-ATPase in the Na(+)-bound state. Science 2013, 342, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therien, A.G.; Blostein, R. Mechanisms of sodium pump regulation. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2000, 279, C541–C566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, N.; Canfield, V.A.; Beckers, M.-C.; Gros, P.; Levenson, R. Identification of the mammalian Na, K-ATPase β3 subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 22754–22758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guynn, S.R.; Scofield, M.A.; Petzel, D.H. Identification of mRNA and protein expression of the Na/K-ATPase α1-, α2- and α3-subunit isoforms in Antarctic and New Zealand nototheniid fishes. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2002, 273, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorokhova, S.; Bibert, S.; Geering, K.; Heintz, N. A novel family of transmembrane proteins interacting with beta subunits of the Na, K-ATPase. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2007, 16, 2394–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Xue, J.; Li, W.; Gu, C.; Wang, P.; Jia, Y.; Liu, X. Identification and expression analysis of Na+/K+-ATPase and NKA-interacting protein in oyster. Invertebr. Surviv. J. 2024, 21, 99–108. [Google Scholar]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Trinity: Reconstructing a full-length transcriptome without a genome from RNA-Seq data. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Toh, H. Recent developments in the MAFFT multiple sequence alignment program. Brief. Bioinform. 2008, 9, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; He, Y.; et al. TBtools-II: A “one for all, all for one” bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.D.; Watanabe, C.K. GMAP: A genomic mapping and alignment program for mRNA and EST sequences. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 1859–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Jin, J.; Guo, A.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Luo, J.; Gao, G. GSDS 2.0: An upgraded gene features visualization server. Bioinformatics 2014, 31, 1296–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Debarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, T.H.; Jin, H.; Marler, B.; Guo, H.; et al. MCScanX: A toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Su, H.; Wang, W.; Ye, L.; Wei, H.; Peng, Z.; Anishchenko, I.; Baker, D.; Yang, J. The trRosetta server for fast and accurate protein structure prediction. Nat. Protoc. 2021, 16, 5634–5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delano, W.L. The PyMol molecular graphics system. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2002, 30, 442–454. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.; Paggi, J.M.; Park, C.; Bennett, C.; Salzberg, S.L. Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovaka, S.; Zimin, A.V.; Pertea, G.M.; Razaghi, R.; Pertea, M.; Salzberg, S.L. Transcriptome assembly from long-read RNA-seq alignments with StringTie2. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fambrough, D.M.; Lemas, M.V.; Hamrick, M.A.; Emerick, M.A.; Renaud, K.J.; Inman, E.M.; Hwang, B.; Takeyasu, K.U. Analysis of subunit assembly of the Na-K-ATPase. Am. J. Physiol. 1994, 266, C579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasler, U.; Wang, X.; Crambert, G.; Béguin, P.; Jaisser, F.; Horisberger, J.D.; Geering, K. Role of β-subunit domains in the assembly, stable expression, intracellular routing, and functional properties of Na, K-ATPase. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 30826–30835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborti, S.; Rahaman, S.M.; Alam, M.N.; Mandal, A.; Ghosh, B.; Dey, K.; Chakraborti, T. Na+/K+-ATPase: Aperspective in Regulation of Membrane Na+-K+ ATPase; Chakraborti, S., Dhalla, N.S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 3–30. [Google Scholar]
- Pius, J.; Peter, M.C.S. Air exposure promotes subunit isoform expression of Na+/K+-ATPase and vH+-ATPase, and recovery reverses NKCC1 and NCC expressions in the brain/gut axis of zebrafish. Proc. Zool. Soc. 2025, 78, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanova, A.; Petrushanko, I.; Boldyrev, A.; Gassmann, M. Oxygen- and redox-induced regulation of the Na/K ATPase. Curr. Enzym. Inhib. 2006, 2, 37–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, J.G.; Semple, J.W.; Bystriansky, J.S.; Schulte, P.M. Na+/K+-ATPase α-isoform switching in gills of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) during salinity transfer. J. Exp. Biol. 2003, 206, 4475–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Family | Genus | Species | Genome | Length | Scaffolds | Scaffold N50 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arcidae | Anadara | A. kagoshimensis | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/datasets/genome/GCA_021292105.1, accessed on 12 January 2025 | 1,115,236,308 | 36 | 60,635,260 |
| A. broughtonii | http://gigadb.org/dataset/100607, accessed on 12 January 2025 | 884,566,040 | 1026 | 44,995,656 | ||
| Tegillarca | T. granosa | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/datasets/genome/GCA_029721355.1, accessed on 12 January 2025 | 915,485,251 | 923 | 45,661,362 | |
| Arca | A. noae | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/datasets/genome/GCA_964261245.2, accessed on 12 January 2025 | 1,495,912,614 | 118 | 84,746,044 |
| Run No. | Species | Tissue | Bytes (bp) | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRR491670 | T. granosa | Mix | 1,287,848,281 | Trinity assemble |
| SRR10855671 | A. broughtonii | Foot | 2,351,898,942 | |
| SRR10713949 | T. granosa | Gonad | 3,361,847,283 | Tissue expression analysis |
| SRR10713950 | T. granosa | Gill | 3,627,355,286 | |
| SRR10713951 | T. granosa | Gill | 2,993,728,725 | |
| SRR10713952 | T. granosa | Gill | 3,138,959,394 | |
| SRR10713953 | T. granosa | Foot | 3,176,163,402 | |
| SRR10713958 | T. granosa | Visceral Mass | 2,995,318,000 | |
| SRR10713959 | T. granosa | Mantle | 2,725,940,705 | |
| SRR10713960 | T. granosa | Muscle | 3,133,933,436 | |
| SRR10713961 | T. granosa | Mantle | 3,908,781,169 | |
| SRR10713962 | T. granosa | Mantle | 2,903,531,436 | |
| SRR10713963 | T. granosa | Hepatopancreas | 2,498,636,342 | |
| SRR10713964 | T. granosa | Hepatopancreas | 3,370,949,865 | |
| SRR10713965 | T. granosa | Hepatopancreas | 2,777,483,605 | |
| SRR10713966 | T. granosa | Hemocytes | 3,300,438,409 | |
| SRR10713967 | T. granosa | Hemocytes | 2,648,750,164 | |
| SRR10713968 | T. granosa | Hemocytes | 2,658,545,770 | |
| SRR10713969 | T. granosa | Gonad | 2,985,742,068 | |
| SRR10713970 | T. granosa | Gonad | 2,535,690,855 | |
| SRR10713971 | T. granosa | Muscle | 3,140,842,716 | |
| SRR10713972 | T. granosa | Muscle | 2,923,365,727 | |
| SRR10713954 | T. granosa | Foot | 3,273,166,707 | |
| SRR10713955 | T. granosa | Foot | 3,746,359,568 | |
| SRR10713956 | T. granosa | Visceral Mass | 3,753,476,460 | |
| SRR10713957 | T. granosa | Visceral Mass | 3,068,244,064 | |
| SRR23345051 | T. granosa | Haemolymph (Hypoxia) | 1,904,248,299 | Hypoxia treatment analysis |
| SRR23345052 | T. granosa | Haemolymph (Hypoxia) | 1,929,010,199 | |
| SRR23345053 | T. granosa | Haemolymph (Hypoxia) | 2,164,158,072 | |
| SRR23345054 | T. granosa | Haemolymph (Control) | 2,003,282,116 | |
| SRR23345055 | T. granosa | Haemolymph (Control) | 1,925,848,892 | |
| SRR23345056 | T. granosa | Haemolymph (Control) | 1,869,022,616 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, M.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Pan, J.; Jia, Y. Identification and Expression Analysis of Na+/K+-ATPase and NKA-Interacting Protein in Ark Shells. Biophysica 2025, 5, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/biophysica5020022
Song M, Liu X, Zhang J, Li W, Pan J, Jia Y. Identification and Expression Analysis of Na+/K+-ATPase and NKA-Interacting Protein in Ark Shells. Biophysica. 2025; 5(2):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/biophysica5020022
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Man, Xiao Liu, Jie Zhang, Wuping Li, Jingfen Pan, and Yanglei Jia. 2025. "Identification and Expression Analysis of Na+/K+-ATPase and NKA-Interacting Protein in Ark Shells" Biophysica 5, no. 2: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/biophysica5020022
APA StyleSong, M., Liu, X., Zhang, J., Li, W., Pan, J., & Jia, Y. (2025). Identification and Expression Analysis of Na+/K+-ATPase and NKA-Interacting Protein in Ark Shells. Biophysica, 5(2), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/biophysica5020022






