An Overview of Level 3 DC Fast Chargers: Technologies, Topologies, and Future Directions
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Power converters topologies
- The performance and characteristics of the various energy storage systems integrated in EVs,
- The design and deployment of commercial charging infrastructures
- A systematic examination of research prototypes proposed in the scientific literature.
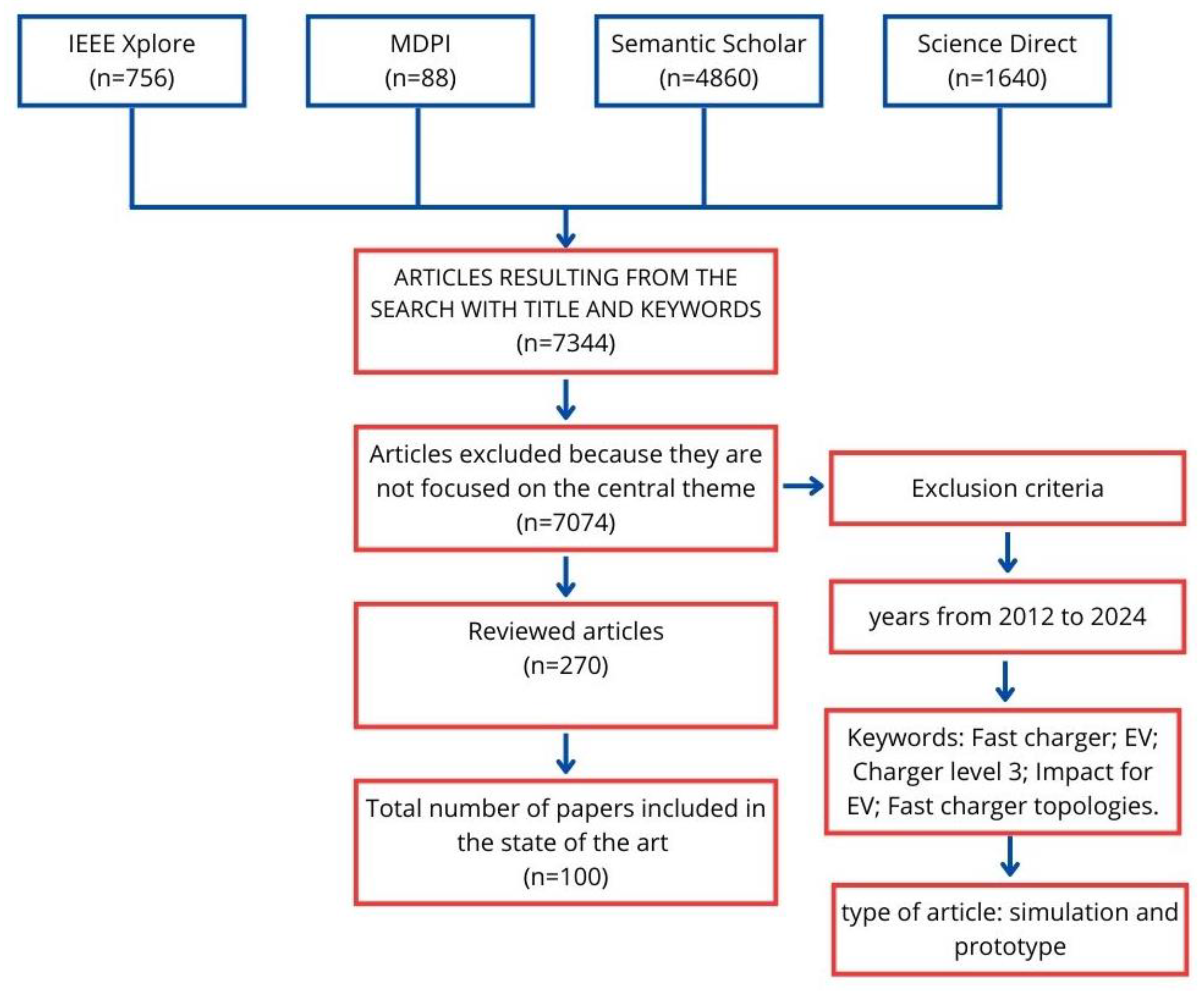
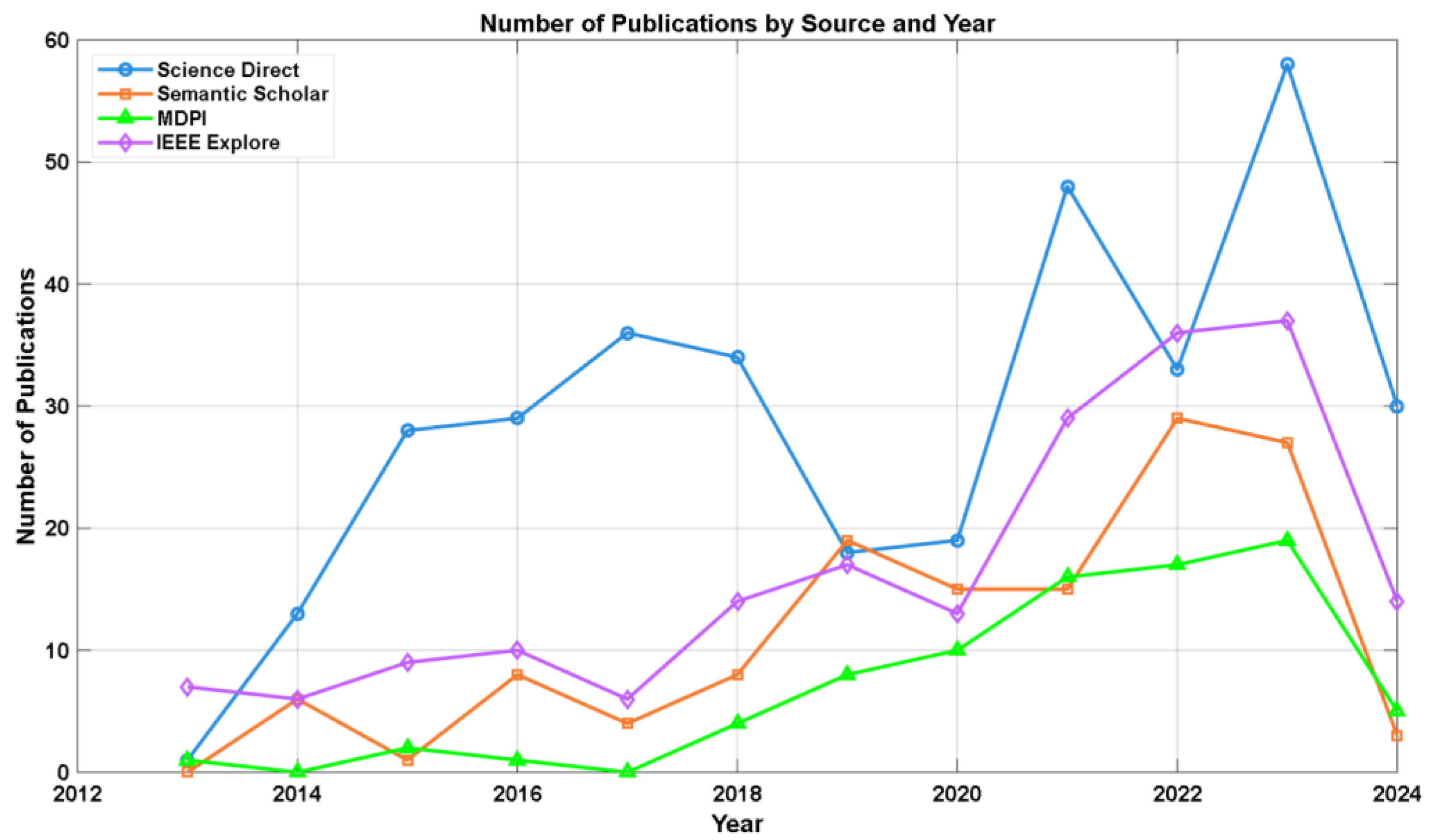
Systematic Review Methodology
- Focus on EV fast charging systems, charger architectures, or power converter topologies.
- Provide technical or experimental contributions (simulation or prototype).
- Did not directly address the central theme of fast charging.
- Were outside the publication years of interest.
- Were duplicated across databases.
2. Current State of Electric Vehicles
2.1. Battery Technology
2.1.1. Pouch Cell
2.1.2. Prism Cell
2.1.3. Cylindrical Cell
3. EV Charging Infrastructure
3.1. DC-DC Power Converters
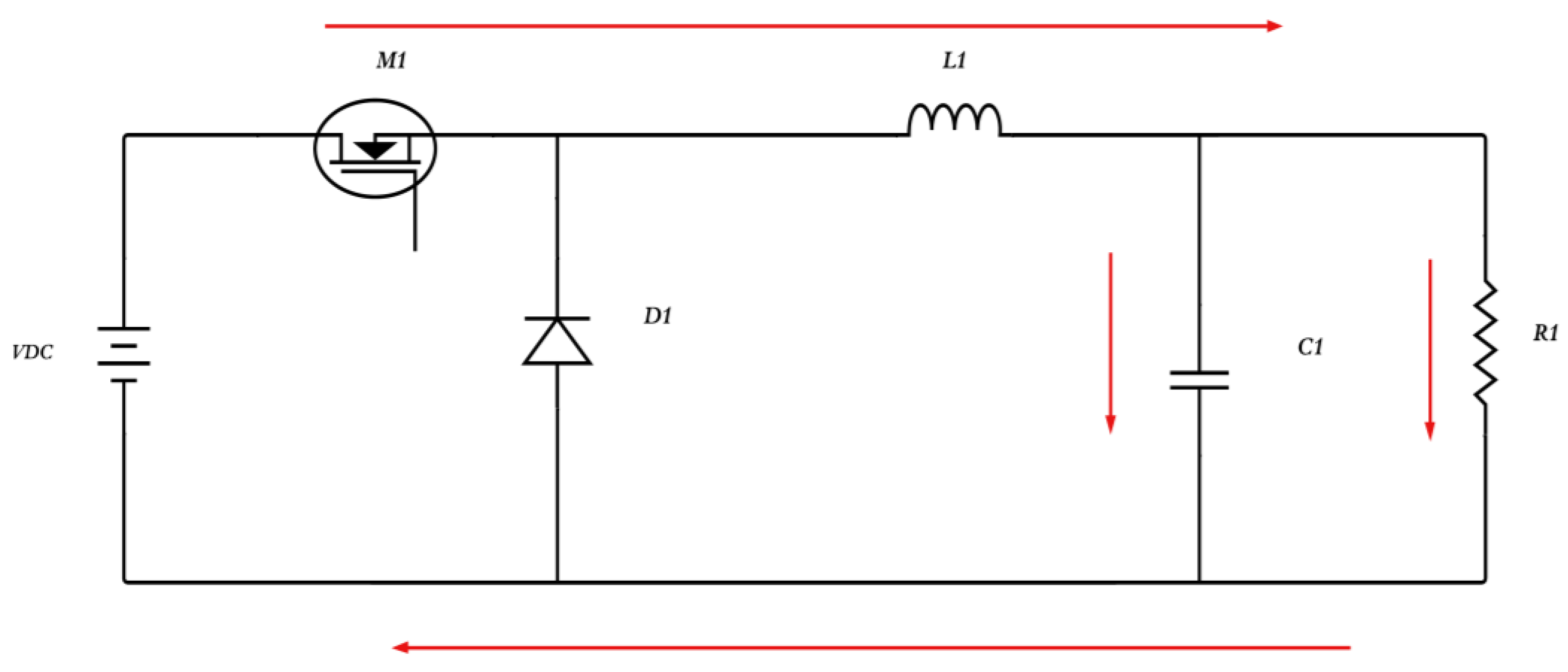
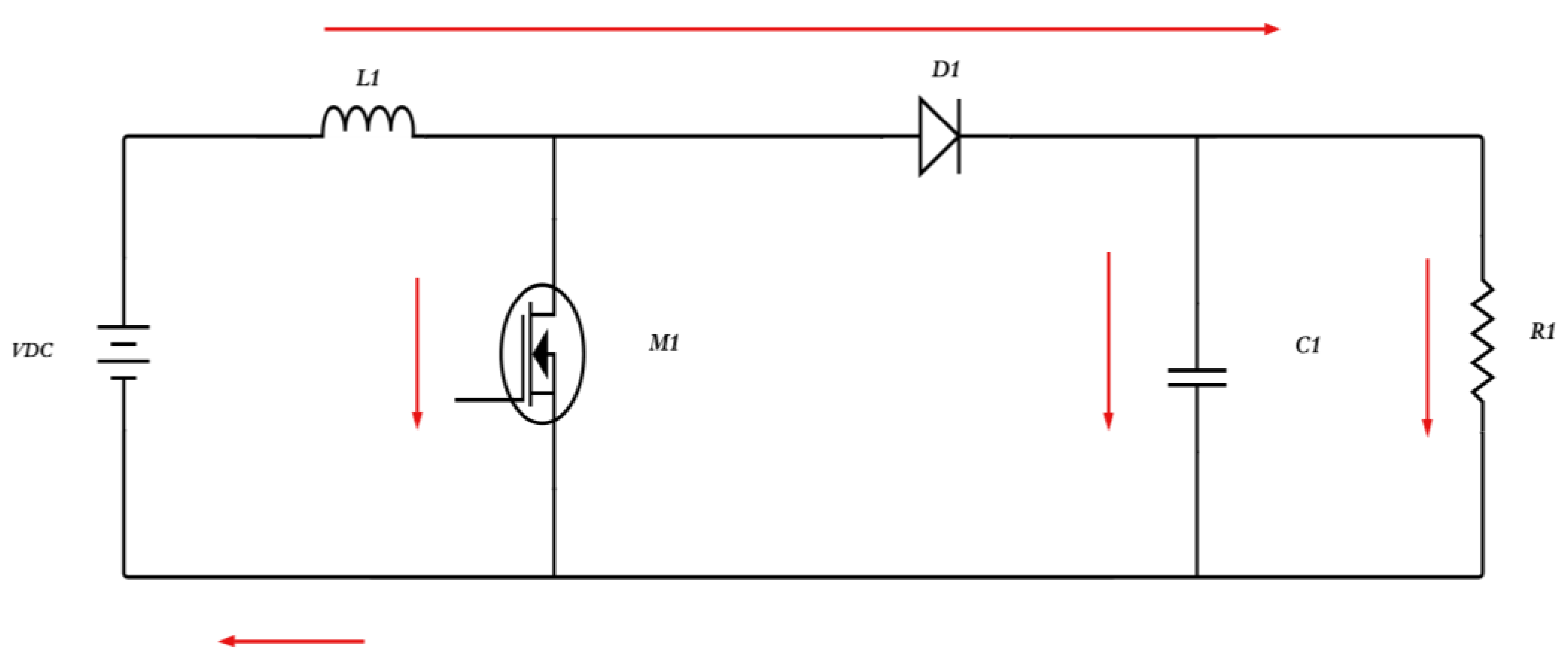
3.1.1. Buck Converter
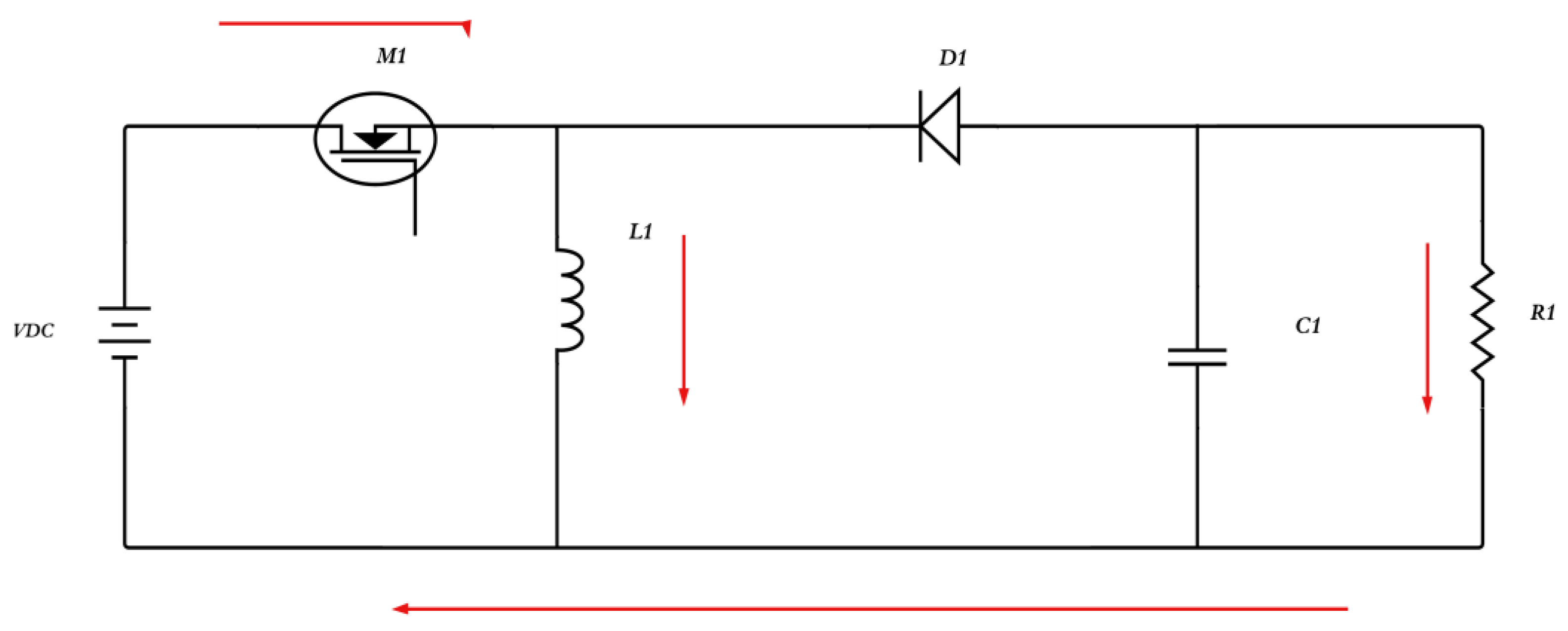
3.1.2. Boost Converter
3.1.3. Buck-Boost Converter
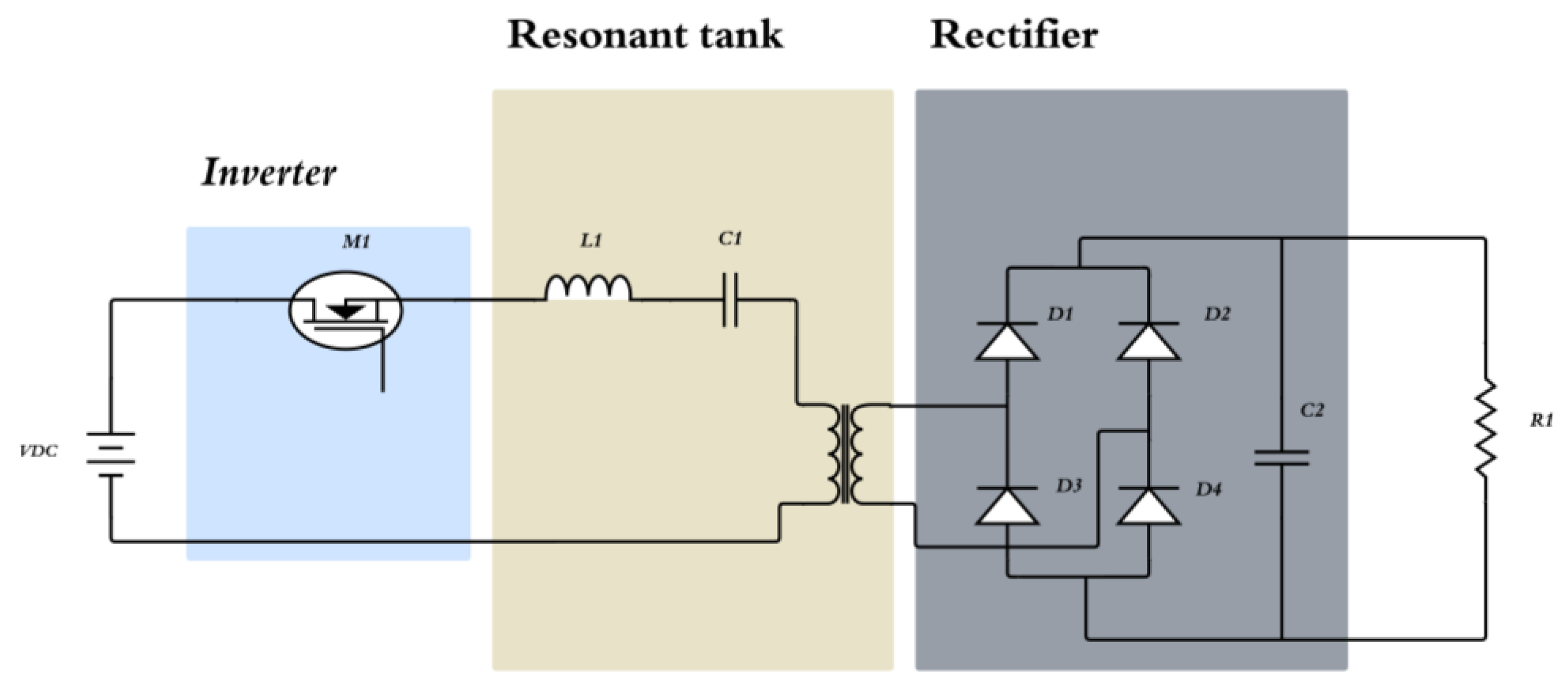
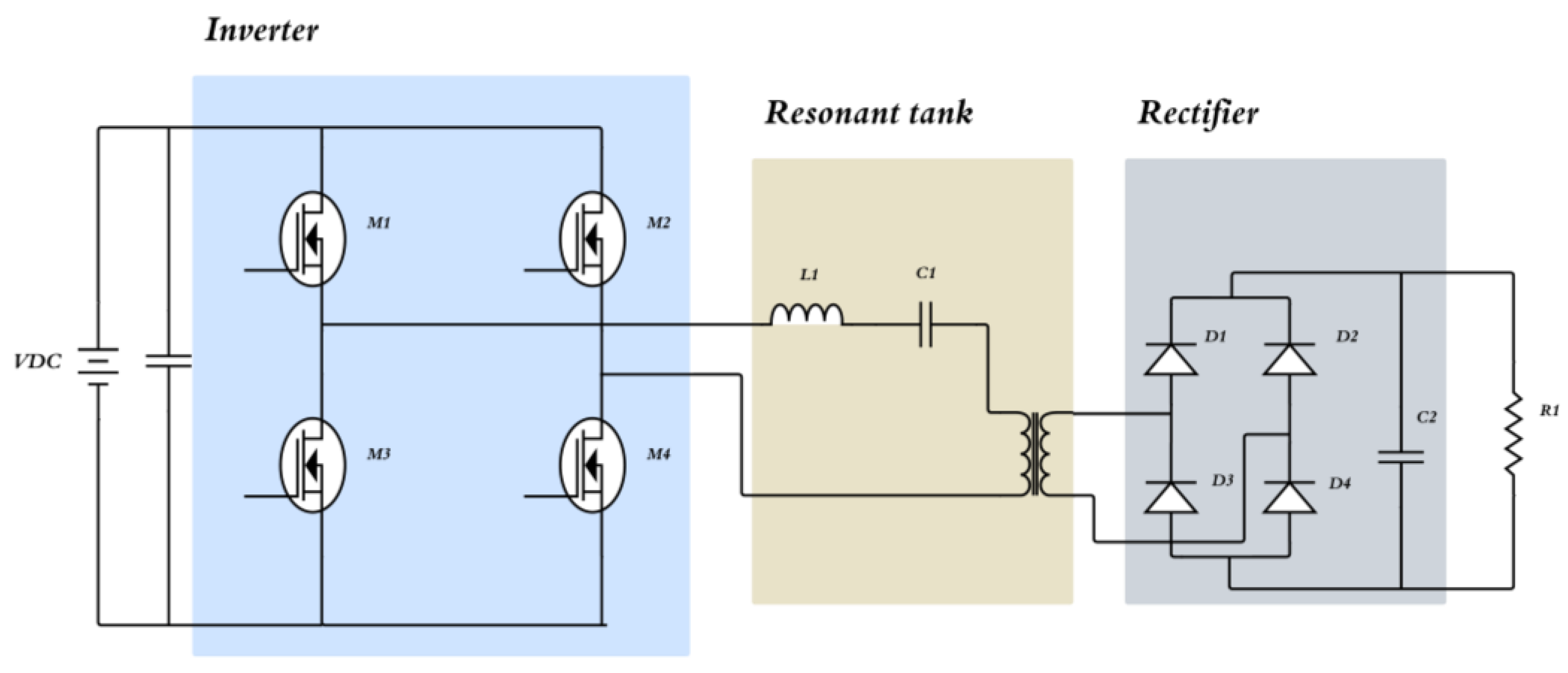
3.1.4. Resonant Converter
3.1.5. Half-Bridge Converter
3.1.6. Full Bridge Converter
3.1.7. Multilevel Converter
| Ref. | Year | Voltage (V) | Current (A) | Power (kW) | Efficiency (%) | Architecture | Protocol | Design |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [82] | 2013 | 390 | 66 | 25 | 95 | HPFC | - | Prototype |
| [83] | 2014 | 320 | 6.28 | 2.1 | 92 | FBD | - | Simulation |
| [84] | 2017 | 220 | 13.5 | 3 | 93.1 | PFC | Plug in | Prototype |
| [85] | 2017 | 380 | 132 | 50 | 94 | - | CHAdeMO | Prototype |
| [86] | 2018 | 700 | 22 | 15 | 96 | spo2LB6 | Prototype | |
| [87] | 2018 | 277 | - | 80 | - | G2V | J2894 | Simulation |
| [88] | 2018 | 400 | 150 | - | 90 | LLC | - | Prototype |
| [89] | 2019 | 200 | 20 | 4 | 94 | SST | CCS | Prototype |
| [90] | 2019 | 500 | 300 | 150 | - | P2P | - | Simulation |
| [91] | 2019 | 800 | 6 | 4.6 | - | PFC | CHAdeMO | Simulation |
| [92] | 2019 | 310 | 30 | 1.5 | 96.4 | LLC | - | Prototype |
| [91] | 2019 | 800 | 24 | 3.6 | PFC | - | Simulation | |
| [55] | 2019 | 100 | - | 15 | - | Boost | - | Prototype |
| [93] | 2020 | 48 | 12 | 1.5 | 90 | Buck | - | Prototype |
| [94] | 2020 | 400 | - | 3.6 | 95 | LLC | - | Simulation |
| [95] | 2020 | 400 | 12.5 | 15 | 94 | Buck | - | Simulation |
| [96] | 2021 | 240 | 18.8 | 4.5 | 98.6 | 2LB6 | CCS | Prototype |
| [55] | 2021 | 400 | - | 5 | - | 2LB6 | CCS | Prototype |
| [97] | 2021 | 230 | 14 | 3 | 80 | - | Plug in | Prototype |
| [98] | 2021 | 220 | 27 | 6 | - | G2V | - | - |
| [99] | 2023 | 230 | 16 | 3.6 | - | V2H | - | - |
4. Results
5. Conclusions
Synthesis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| kW | Kilowatt |
| h | Hours |
| V | Volt |
| A | Ampere |
| Hz | Hertz |
| kWh | Kilowatt-hour |
| AC | Alternating Current |
| DC | Direct Current |
| J2894 | Wireless Power Transfer for Light-Duty Plug-In Vehicles |
| CCS | Combined Charging System |
| CHAdeMO | Charge de Move |
| PSBC | Power Supply and Battery Charger |
| EV | Electric Vehicle |
| 2LB6 | Two-Level-Based Six |
| V2H | Vehicle-to-Home |
| PFC | Power Factor Correction |
| SST | Solid-State Transformer |
| G2V | Grid-to-Vehicle |
| P2P | Peer-to-Peer |
| HPFC | High Power Factor Correction |
| TLB | Two-Level Bridge |
| CMM | Current Mode Control |
| DCM | Discontinuous Conduction Mode |
| LLC | LLC Resonant Converter |
| SiC | Silicon Carbide (Wide Bandgap Semiconductor) |
| GaN | Gallium Nitride (Wide Bandgap Semiconductor) |
| Pb-acid | Lead-Acid |
| Ni-Cd | Nickel-Cadmium |
| NiMH | Nickel-Metal Hydride |
| Li-ion | Lithium-Ion |
| Na-NiCl | Sodium-Nickel-Chloride |
| LFP | Lithium Iron Phosphate |
| LMR | Lithium-Manganese-Rich |
| NCA | Nickel-Cobalt-Aluminum |
| NCM811 | Nickel-Cobalt-Manganese (8-1-1 ratio) |
| NCM/NMC | Nickel-Cobalt-Manganese |
| NCMA | Nickel-Cobalt-Manganese-Aluminum |
| PEC | Packed E-Cell |
| MOSFETs | Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor |
| OBC | On-Board Charger |
| EMI | Electromagnetic Interference |
| ZVS | Zero Voltage Switching |
References
- Ros Marin, J.A.; Barrera Doblado, O. Vehículos Eléctricos e Híbridos; Ediciones Paraninfo, SA: Madrid, Spain, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, P.R.; Skea, J.; Slade, R.; Al Khourdajie, A.; van Diemen, R.; McCollum, D.; Pathak, M.; Some, S.; Vyas, P.; Fradera, R. Climate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares Salgado, L.S. Ventajas y Desventajas de los Vehículos Eléctricos Como TPI Según la Percepción de sus Conductores en la Ciudad de Bogotá. 2019. Available online: http://polux.unipiloto.edu.co:8080/00051269.pdf (accessed on 2 May 2024).
- Zeng, J.; Zhang, G.; Yu, S.S.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y. LLC resonant converter topologies and industrial applications—A review. Chin. J. Electr. Eng. 2020, 6, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinson, R.S.; West, T.H. Impact of public electric vehicle charging infrastructure. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2018, 64, 158–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.R.; Sun, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, G.; Liu, X.; Zhang, P.; Kang, Y.; Dai, H. Regionally differentiated promotion of electric vehicles in China considering environmental and human health impacts. Environ. Res. Lett. 2023, 18, 074022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agency, I.E. Global EV Outlook 2024: Accelerating Ambitions Despite Headwinds; International Energy Agency: Paris, France, 2024; Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/global-ev-outlook-2024 (accessed on 14 August 2025).
- León, J.Á.; Rodríguez, N.O.; Marzoug, R. Democratización de la energía y transición hacia la electromovilidad sostenible. In Proceedings of the Agua y Energía: Actualidad y Retos para un Desarrollo Sostenible, Guadalajara, Mexico, 5 December 2024; Comunicación Científica: Ciudad de México, México, 2024; pp. 165–183. [Google Scholar]
- Dulcich, F.M.; Otero, D.; Canzian, A.M. Evolución reciente y situación actual de la producción y difusión de vehículos eléctricos a nivel global y en Latinoamérica. Asian J. Lat. Am. Stud. 2019, 32, 21–51. [Google Scholar]
- Safayatullah, M.; Elrais, M.T.; Ghosh, S.; Rezaii, R.; Batarseh, I. A comprehensive review of power converter topologies and control methods for electric vehicle fast charging applications. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 40753–40793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
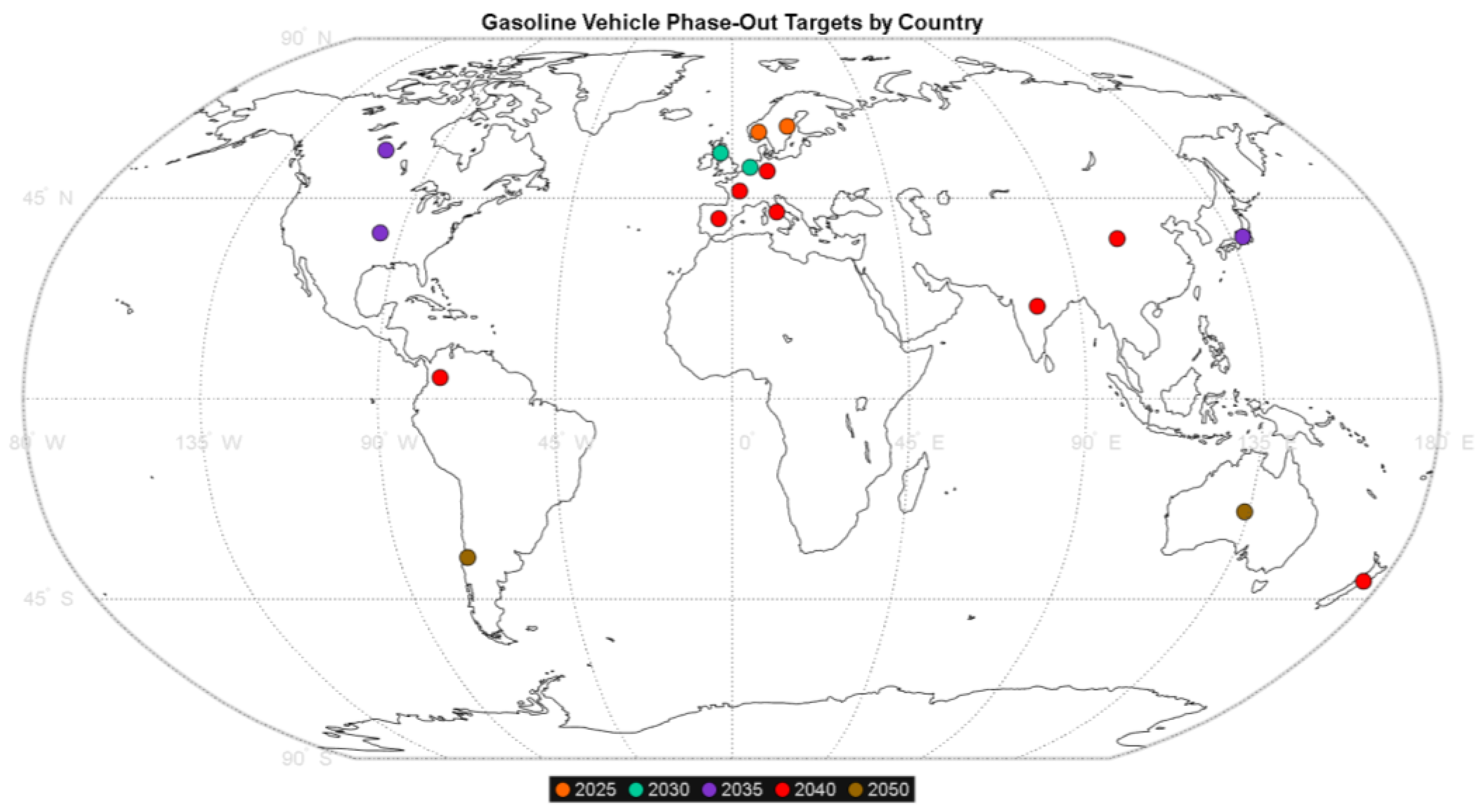
- Melo, M.F. La Eliminación Progresiva Mundial de los Autos de Gasolina. Available online: https://es.statista.com/grafico/32696/objetivos-para-la-eliminacion-de-la-venta-de-autos-nuevos-con-motor-de-combustion-interna/ (accessed on 28 August 2024).
- Qazi, A.; Hussain, F.; Rahim, N.A.; Hardaker, G.; Alghazzawi, D.; Shaban, K.; Haruna, K. Towards sustainable energy: A systematic review of renewable energy sources, technologies, and public opinions. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 63837–63851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Arif, S.M.; Aslam, M. Emerging renewable and sustainable energy technologies: State of the art. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 71, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzetti, S.; Mariasiu, F. Electric vehicle battery technologies: From present state to future systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 51, 1004–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, K.W.; Reddy, T.B. Linden’s Handbook of Batteries; McGraw-Hill Education: Columbus, OH, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Winter, M.; Brodd, R.J. What are batteries, fuel cells, and supercapacitors? Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4245–4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KEYENCE Corporation. Comparison of Different Types of Electric Vehicle Battery Cells. Available online: https://www.keyence.com/products/marker/laser-marker/resources/laser-marking-resources/comparison-of-different-types-of-electric-vehicle-battery-cells.jsp (accessed on 14 August 2025).
- Bozorg, M.V.; Torres, J.F. Multifaceted thermal regulation in electrochemical batteries using cooling channels and foam-embedded phase change materials. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.15040. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2407.15040 (accessed on 14 August 2025). [CrossRef]
- Reid, H.T.; Singh, G.; Palin, E.; Dai, Y.; Zong, W.; Somerville, L.; Shearing, P.R.; Robinson, J.B. Key considerations for cell selection in electric vertical take off and landing vehicles: A perspective. EES Batter. 2025, 1, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halimah, P.N.; Rahardian, S.; Budiman, B.A. Battery cells for electric vehicles. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. Technol. 2019, 2, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tredeau, F.P.; Salameh, Z.M. Evaluation of lithium iron phosphate batteries for electric vehicles application. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference, Dearborn, MI, USA, 7–10 September 2009; pp. 1266–1270. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Energy (DoE). Final Report Compilation for the Research and Development of High-Power and High-Energy Electrochemical Storage Devices; United States Advanced Battery Consortium, LLC: Southfield, MI, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- JPatel; Patel, R.; Saxena, R.; Nair, A. Thermal analysis of high specific energy NCM-21700 Li-ion battery cell under hybrid battery thermal management system for EV applications. J. Energy Storage 2024, 88, 111567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ren, D.; Feng, X.; Wang, L.; Ouyang, M. Thermal runaway modeling of large format high-nickel/silicon-graphite lithium-ion batteries based on reaction sequence and kinetics. J. Power Sources 2022, 527, 231127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ank, M.; Sommer, A.; Gamra, K.A.; Schöberl, J.; Leeb, M.; Schachtl, J.; Streidel, N.; Stock, S.; Schreiber, M.; Bilfinger, P. Lithium-ion cells in automotive applications: Tesla 4680 cylindrical cell teardown and characterization. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2023, 170, 120536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R. Battery Pack Design of Cylindrical Lithium-Ion Cells and Modelling of Prismatic Lithium-Ion Battery Based on Characterization. Department of Mechanical Engineering. Tests. Master’s Thesis, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada, 2022. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/11375/27797 (accessed on 23 July 2025).
- Bathel, F. Charging the Future: An Analysis of Electric Vehicle Charging Technologies and Related Pilot Projects; Universidade NOVA de Lisboa: Lisbon, Portugal, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hummes, D.N.; Hunt, J.; Hervé, B.B.; Schneider, P.S.; Montanari, P.M. A comparative study of different battery geometries used in electric vehicles. Lat. Am. J. Energy Res. 2023, 10, 94–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, C. Balancing Future Grids: A Comprehensive Review of Vehicle-to-Grid Applications and Their Impact Factors; Universidade NOVA de Lisboa: Lisbon, Portugal, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J. A Brief Comparison Between Tesla and NIO In the Electric Vehicle Industry. Highlights Bus. Econ. Manag. 2023, 23, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, R.B.; Sakib, S.; Rabbi, M.; Islam, S.; Roy, P.; Hasan, S. A Comprehensive Review of Blade Battery Technology for the Vehicle Industry. N. Am. Acad. Res 2023, 6, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Link, S.; Neef, C.; Wicke, T. Trends in automotive battery cell design: A statistical analysis of empirical data. Batteries 2023, 9, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emadi, P. Tesla Model 3 2170 Li-ion Cell Dataset and Battery SOC Estimation Blind Modeling Tool. Borealis 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Thapa, A.; Gao, H. Silicon-Based Anode and Its Full-Cell Performance Test Using a High-Capacity Pouch Cell. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2024, 171, 010504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberger, N.; Wagner, N.; Fredl, A.; Riederle, L.; Lienkamp, M. Quantifying the State of the Art of Electric Powertrains in Battery Electric Vehicles: Comprehensive Analysis of the Two-Speed Transmission and 800 V Technology of the Porsche Taycan. World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frías Marín, P.; Román Úbeda, J. Vehículo eléctrico: Situación actual y perspectivas futuras. Econ. Ind. 2019, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- AeroVironment. Public Fast Charging Station, 50kW DC, eV50-ps. Public, Fast and Reliable Electric Vehicle Charging in Minutes, Huntington Dr., Suite 202, Monrovia, CA 91016. 2011. Available online: https://investor.avinc.com/static-files/2c8e54b0-66fe-4431-98c7-d45e74b6f56c (accessed on 16 May 2024).
- ABB. Terra CE 54 CJG 4N1-7M-0-0, Infraestructuras Para la Carga del Vehículo Eléctrico›DC Charging Products›All-in-One DC Chargers 50 kW, CE. Terra CE 54 CJG 4N1-7M-0-0 Terra 50 kW Charger, CCS 2 + CHAdeMO + AC Type 2 cable 43 kW, 3.9 m Cables, CE. 2017. Available online: https://ita-sacchi.mo.cloudinary.net/PRODUCT/DOCUMENT/hlr-system/ABB/MD22_BMECAT_20240410/EL6AGC063056.PDF?ts=1742882696330 (accessed on 16 May 2024).
- Electricmobility. Efacec QC45. Topmost of Fast Chargers, Compatible with All Brands of Electric Vehicles. Available online: https://www.edeq.com.co/Portals/0/EFAPOWER_EV_QC45_Standalone_Installation_and_User_Manual-V_07_00.pdf (accessed on 28 August 2025).
- Chargesolutions company. Datasheet EVBox Troniq 100 Fast Charging Solution, Charges up to 250 km in just 30 Minutes with CCS 2, CHAdeMO and AC Type 2 Connectors. EVBPI_DC100_EN_012020. 2020. Available online: https://evchargesolutions.com/v/downloads/evbox-troniq-spec-sheet.pdf (accessed on 16 May 2024).
- NationalLED. TurboEVC™ 60kW Ultra-Fast DC Electric Vehicle Charger, Suitable for Wet Locations. 832-459-4447, sales@nationalled.com. 2021. Available online: https://www.nationalled.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/National-LED-TurboEVC-DC-Fast-60kW-EV-Charger.pdf (accessed on 16 May 2024).
- EVTEC. Espresso&Charge Ready for All Cars, Trucks, and Busses with Up to 150kW DC and 65kW AC. +41 41 260 88 38, evtec@evtec.ch. 2023. Available online: https://www.evtec.ch/application/files/9716/1329/3826/factsheet_espressocharge_6in1_en.pdf (accessed on 16 May 2024).
- Smart Charge America. Tritium Veefil PK350 Level 3 DC Fast Electric Car Charging Station Dual Ports-CHAdeMO and SAE Combo Connector (CCS) 2024. Available online: https://smartchargeamerica.com/electric-car-chargers/commercial/tritium-veefil-pk350/?srsltid=AfmBOopEHy4PnC0mBhfydWy3C06jFEU2OCZKsZNJAGiT0deC3eibQArB& (accessed on 16 May 2024).
- Circontrol. Raption Compact 150. Compact Fast Charger up to 150kW (UFC) Combines 150kW Ultra-Fast Charging with 75kW Simultaneous Charging to Offer Flexibility Depending on Charging Demand. Available online: https://circontrol.com/es/ev-chargers/raption-compact-150/ (accessed on 14 August 2025).
- Blink. 60 kW–360 kW DC Fast Charging Stations, Impressive. Powerful Range of up to 360kW and up to 600 Amps of Output Current, the Blink Fast-Charging System is One of the Only Units Built with an All-in-One Format for Easy Installation, Deployment, and Cost Savings. Available online: https://a-us.storyblok.com/f/1016941/x/77c4c0d3bb/blink-charging-dcfc-60kw-360kw-aug2023.pdf (accessed on 16 May 2025).
- Power, B. 100 kW DC Fast Charger CLIN-S-815 L3R-100-480. In Process ETL Certification; Complies with UL 2202, UL 2231 UL50E, NEC Article 625, CSA STD C22.2 No. 107.1 FCC Part 15 Class A. 1719 S Grand Ave, Santa Ana CA, 92705. 2022. Available online: https://evgateway.net/pdf/BTC-S-815.pdf (accessed on 16 May 2024).
- TESLA. SUPERCARGADOR 1MW Power Cabinet with a Similar Design to Our Utility-Scale Products Supports Peak Rates of up to 250kW per car.2024. Available online: https://www.tesla.com/sites/default/files/downloads/Supercharger_First_Responder_Guide_es.pdf (accessed on 16 May 2024).
- Electronics, D. Ultra Fast Charger UFC 200 Speed-Up Your Power with UFC 200 Delta DC Charger|High Power Charger 200kW Leaflet (NA Version) for Larger DC Charging Parks. 2023. Available online: https://www.deltaww.com/en-US/products/EV-Charging/UFC-200 (accessed on 16 May 2024).
- ABB. Infraestructura de Recarga de Vehículo Eléctrico Terra High Power—GEN III Cargador de 175-350 kW Charger Connect Calle San Romualdo, 13. 2021. Available online: https://search.abb.com/library/Download.aspx?DocumentID=9AKK107992A2226&LanguageCode=es&DocumentPartId=&Action=Launch (accessed on 16 May 2024).
- Alpitronic. Alpitronic Hypercharger HYC 300 One of the Most Versatile DC Chargers in the Market. Hypercharger Ensures That Today’s Operators and Investors Are Compatible for Tomorrow’s Requirements. Available online: https://chargingshop.eu/product/alpitronic-hypercharger-hyc-300-kw-dc-station/ (accessed on 28 August 2025).
- Signet, S. Signet EV DC 350kW Charger. Our Reliable and Green Solution Features Cutting-Edge Technology and Advanced Features for a Seamless Charging Experience. Available online: https://sksignet.us/distributed/350kw-dp--175kw-pc (accessed on 28 August 2025).
- WALBOX. Supernova North America Cargador Rápido de CC de Próxima Generación Connect Two 65 kW Chargers to Deliver up to 130 kW to One Vehicle. 2021. Available online: https://vctgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/Supernova-Brochure_A5_EN-US.pdf (accessed on 16 May 2024).
- EVGO. Delta Signet DC350k-CC Combined Charging System Allie Curttright 531-203-0940 Allie.Curttright@evgo.com. Available online: https://www.consumersenergy.com/-/media/CE/Documents/pev/powermidrive-residential-program-approved-charging-station.ashx (accessed on 16 May 2024).
- Smart Charge America. Tritium Veefil PK350. Tritium Veefil PK350 350kW Level 3 DC Fast Electric Car Charging Station with Dual Ports- CHAdeMO and SAE Combo Connector. Available online: https://smartchargeamerica.com/electric-car-chargers/commercial/tritium-veefil-pk350 (accessed on 26 September 2025).
- Wang, H. A boost converter design with low output ripple based on harmonics feedback. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.10020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Americas, D. EVGO Delta 350kW DC Charger. EVgo and Delta Electronics Announce Strategic Collaboration to Advance Nationwide Access to EV Charging. Available online: https://www.delta-americas.com/en-US/products/EV-Charging/ALL/ (accessed on 28 August 2025).
- Shen, J.; Zhang, C. Design of High Efficiency DC-DC Buck Converter for Electric Vehicle Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 8–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ayyanar, R.; Lee, H. High-frequency buck converters using SiC devices in EV onboard chargers. J. Power Sources 2021, 502. [Google Scholar]
- Infineon Technologies. 11kW SiC DC-DC Buck Converter Design Guide; Infineon Technologies AG: Neubiberg, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J. Advanced PWM Control for Interleaved Buck Converter in Fast Charging. Energies 2021, 14, 4172. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L. Review of DC-DC Converters: Analysis and Applications of Buck and Boost Converters. Appl. Comput. Eng. 2025, 148, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; de Souza, R.P.C.; Kergus, P.; Kader, Z.; Caux, S. Robust Switching Control of DC-DC Boost Converter for EV Charging Stations. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.03158. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.03158 (accessed on 25 June 2025). [CrossRef]
- Rekha, J.; Thentral, T.M.T.; Vijayakumar, K. Electric Vehicle Motor, Converter, Controller and Charging Station with Challenges and Configurations: Review. Int. J. Renew. Energy Res. (IJRER) 2022, 12, 505–528. Available online: https://www.ijrer.org/ijrer/index.php/ijrer/article/view/12703 (accessed on 25 June 2025).
- MathWorks. Boost Converter—Implement Boost Power Converter—Simulink—MathWorks. Available online: https://la.mathworks.com/help/sps/ref/boostconverter.html (accessed on 26 June 2025).
- Alsharif, M.; Alghamdi, A. Bidirectional Buck–Boost Converter for EV Fast Charging Using GaN Devices. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2023, 9, 1250–1260. [Google Scholar]
- Flores Torres, Á.D.; Estevez Carreón, J.; Díaz Téllez, J.; García Ramírez, R.S.; Pérez Pérez, J. Análisis y diseño de un convertidor Buck-Boost. La Mecatrónica En México 2019, 8, 65–80. Available online: http://www.mecamex.net/revistas/LMEM/revistas/LMEM-V08-N02-02.pdf (accessed on 26 June 2025).
- Shen, J.; Zhang, C. Design and Analysis of a Bidirectional Interleaved Buck–Boost Converter for V2G Applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 8504–8515. [Google Scholar]
- Sohail, K.; Farzaneh, H. Model for Optimal Power Coefficient Tracking and Loss Reduction of the Wind Turbine Systems. Energies 2022, 15, 4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J. Application Note for an LLC Resonant Converter Using Resonant Controller HR1000A. The Future of Analog IC Technology, 1 September 2013. pp. 6–20. Available online: https://www.monolithicpower.cn/cn/documentview/productdocument/index/version/2/document_type/Application%20Note/lang/en/sku/HR1000/document_id/3790/ (accessed on 26 July 2025).
- Jin, J.; Systems, M.P. Application Note for an LLC Resonant Converter Using Resonant Controller HR1000A; Monolithic Power Systems: Kirkland, WA, USA, 2019; Available online: https://media.monolithicpower.com/mps_cms_document/a/n/an151_r1.0.pdf (accessed on 26 July 2025).
- Ponce-Silva, M. Conversión Resonante, Convertidor Resonante Clase E; CENIDET: Cuernavaca, Mexico, 2024; p. 54. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Chen, R.; Lee, F.C. Integrated magnetic for LLC resonant converter. In Proceedings of the APEC. Seventeenth Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (Cat. No. 02CH37335), Dallas, TX, USA, 10–14 March 2002; pp. 346–351. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Fu, J.; Wei, L. Optimization of high-efficiency half-bridge LLC resonant converter. In Proceedings of the 2021 40th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Shanghai, China, 26–28 July 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 5922–5926. [Google Scholar]
- Quiroga, A.; Bayona, J.; Espitia, H. Review of Converter Circuits with Power Factor Correction. Technologies 2025, 13, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, D.; Soeiro, T.B.; Bauer, P. Design and implementation of a reconfigurable phase shift full-bridge converter for wide voltage range EV charging application. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2022, 9, 1200–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, M.A.; Nallathambi, K.; Vishnuram, P.; Rathore, R.S.; Bajaj, M.; Rida, I.; Alkhayyat, A. A novel technological review on fast charging infrastructure for electrical vehicles: Challenges, solutions, and future research directions. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 82, 260–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles Aguilar, C.J. Estudio del Convertidor cd-cd Resonante llc en alta Frecuencia para Sistemas de Iluminación Led. INSTITUTO TECNOLÓGICO SUPERIOR DE IRAPUATO, 16 February 2024. Available online: https://rinacional.tecnm.mx/jspui/bitstream/TecNM/8048/1/05_CJRA_MTESIS.pdf (accessed on 26 September 2025).
- Quiroga, A.; González, L.; García, M.S.; Carrasco, J.M.; Suárez, J.A. Comparative Analysis of DC-DC Converter Topologies for Fast EV Charging: Emphasis on Resonant Full-Bridge Efficiency. Technologies 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Hren, A.; Truntič, M.; Mihalič, F. A survey on the state-of-the-art and future trends of multilevel inverters in BEVs. Electronics 2023, 12, 2993. [Google Scholar]
- Elizondo-Martinez, D.; Barrios, E.L.; Galdeano, M.; Ursúa, A.; Sanchis, P. Novel two-stage three-level converter with inherently balanced DC voltage for EV fast-charging applications. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2023, 10, 6418–6433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifzadeh, M.; Al-Haddad, K. Packed E-Cell (PEC) converter topology operation and experimental validation. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 93049–93061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, K.J.; Chien, M.D.; Hsieh, C.C.; Cheng, M.Y.; Liang, C.K.; Lo, Y.K.; Liu, Y.C.; Tseng, P.J. Implementation and design of high-power fast charger for lithium-ion battery pack. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2014, 42, 1154–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez Rincón, I.; Arízaga Silva, J.A.; Olivos Pérez, L.I. Diseño y simulación de un convertidor CD-CD tipo Full-Bridge dual de baja potencia. Repos. Nac. CONACYT 2014, 6–14. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, C.; Tang, Y.; Khaligh, A. A Single-Phase Integrated Onboard Battery Charger Using Propulsion System for Plug-in Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 66, 10899–10910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Semsar, S.; Lehn, P.W. Constant current fast charging of electric vehicles via a DC grid using a dual-inverter drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 6940–6949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, Q.; Lu, S. Power conversion efficiency calculation models for electric vehicle fast charger system. In Proceedings of the 2018 13th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), Wuhan, China, 31 May–2 June 2018; pp. 316–321. [Google Scholar]
- Mortezaei, A.; Abdul-Hak, M.; Simoes, M.G. A bidirectional NPC-based level 3 EV charging system with added active filter functionality in smart grid applications. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo (ITEC), Long Beach, CA, USA, 13–15 June 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 201–206. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Jia, Z.; Tian, Y.; Zeng, H.; Lv, Z. Virtual synchronous motor based-control of a three-phase electric vehicle off-board charger for providing fast-charging service. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Yeh, C.-S.; Yu, O.; Kim, J.-W.; Choe, J.-M.; Lai, J.-S. Modeling and Control of Three-Level Boost Rectifier Based Medium-Voltage Solid-State Transformer for DC Fast Charger Application. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2019, 5, 890–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, M.; Viatkin, A.; Ricco, M.; Grandi, G. A dc/dc fast charger for electric vehicles with minimum input/output ripple based on multiphase interleaved converters. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Clean Electrical Power (ICCEP), Otranto, Italy, 2–4 July 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 187–192. [Google Scholar]
- Quijije Barreto, J.C. Simulación en MATLAB–SIMULINK de un Cargador de Baterías de dos Etapas Basado en un Rectificador Boost y un Convertidor Resonante Para Aplicaciones en Industria de Automoción; Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya: Barcelona, Spain, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.-H.; Kim, M.-S.; Hussain Nengroo, S.; Kim, C.-H.; Kim, H.-J. LLC resonant converter for LEV (Light Electric Vehicle) fast chargers. Electronics 2019, 8, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Lin, F.; Blaabjerg, F. Artificial-intelligence-based design for circuit parameters of power converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 69, 11144–11155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaguer Molins, J.I. Diseño y evaluación de un Convertidor DC-DC Resonante LLC en Semipuente para un Cargador Embarcado de 3, 6 kW en un Vehículo Eléctrico. Master’s Thesis, Universitat Politècnica de València, Valencia, Spain, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Elkhateb, A.; Athanasopoulos, N. Ultra Buck DC/DC Converter for Electric Vehicles. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.07822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papamanolis, P.; Bortis, D.; Krismer, F.; Menzi, D.; Kolar, J.W. New EV Battery Charger PFC Rectifier Front-End Allowing Full Power Delivery in 3-Phase and 1-Phase Operation. Electronics 2021, 10, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabarimuthu, M.; Senthilnathan, N. Development of fast and hybrid charger for lithium ion batteries in light weight electric vehicles. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2021, 31, e12932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elserougi, A.; Abdelsalam, I.; Massoud, A. An isolated-boost-converter-based unidirectional three-phase off-board fast charger for electric vehicles. IET Electr. Syst. Transp. 2021, 12, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petreus, D.; Patarau, T.; Szilagyi, E.; Cirstea, M. Electrical Vehicle Battery Charger Based on Smart Microgrid. Energies 2023, 16, 3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
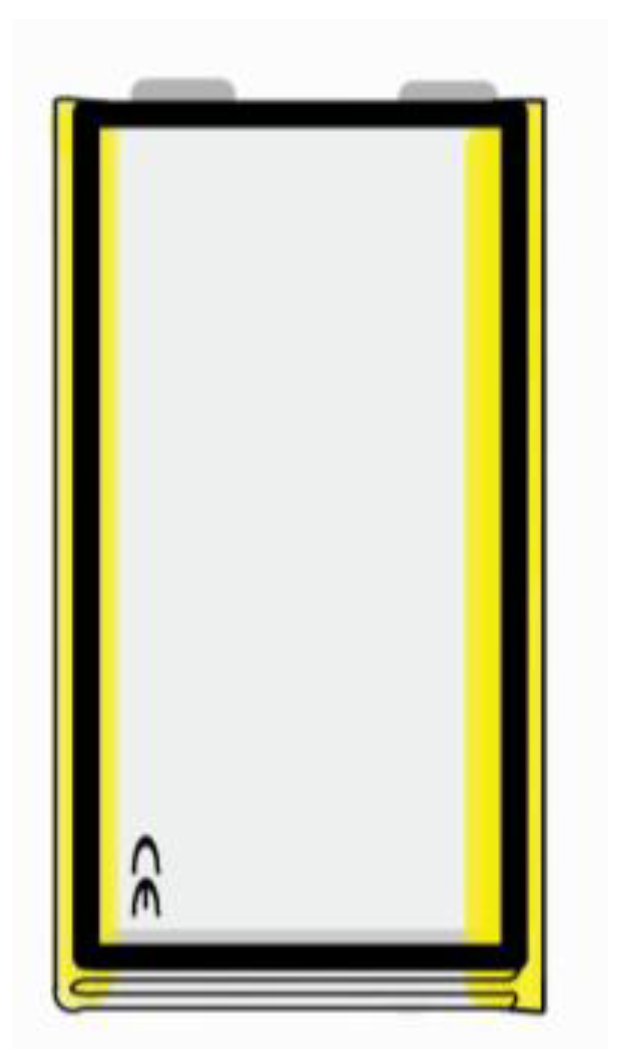

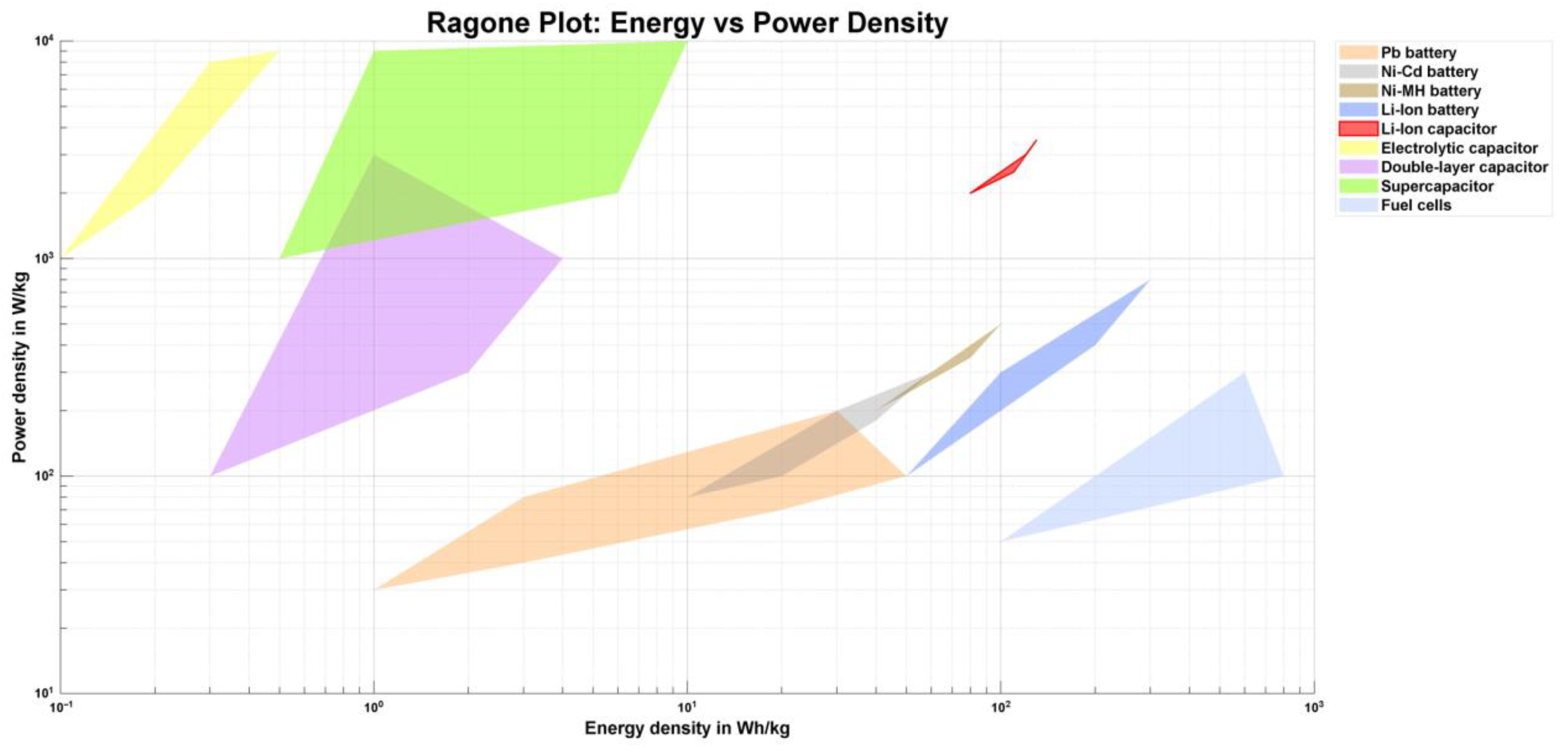



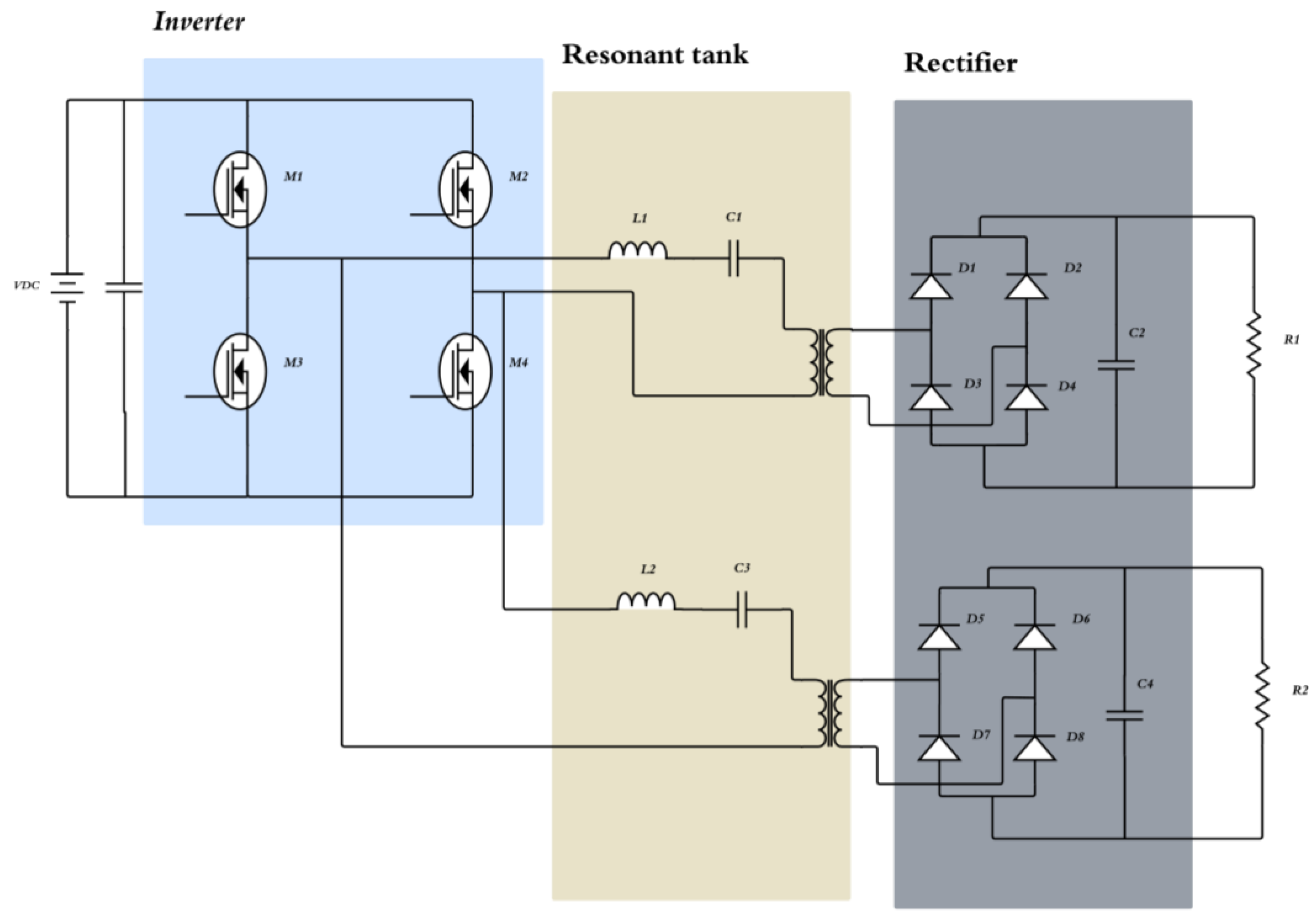
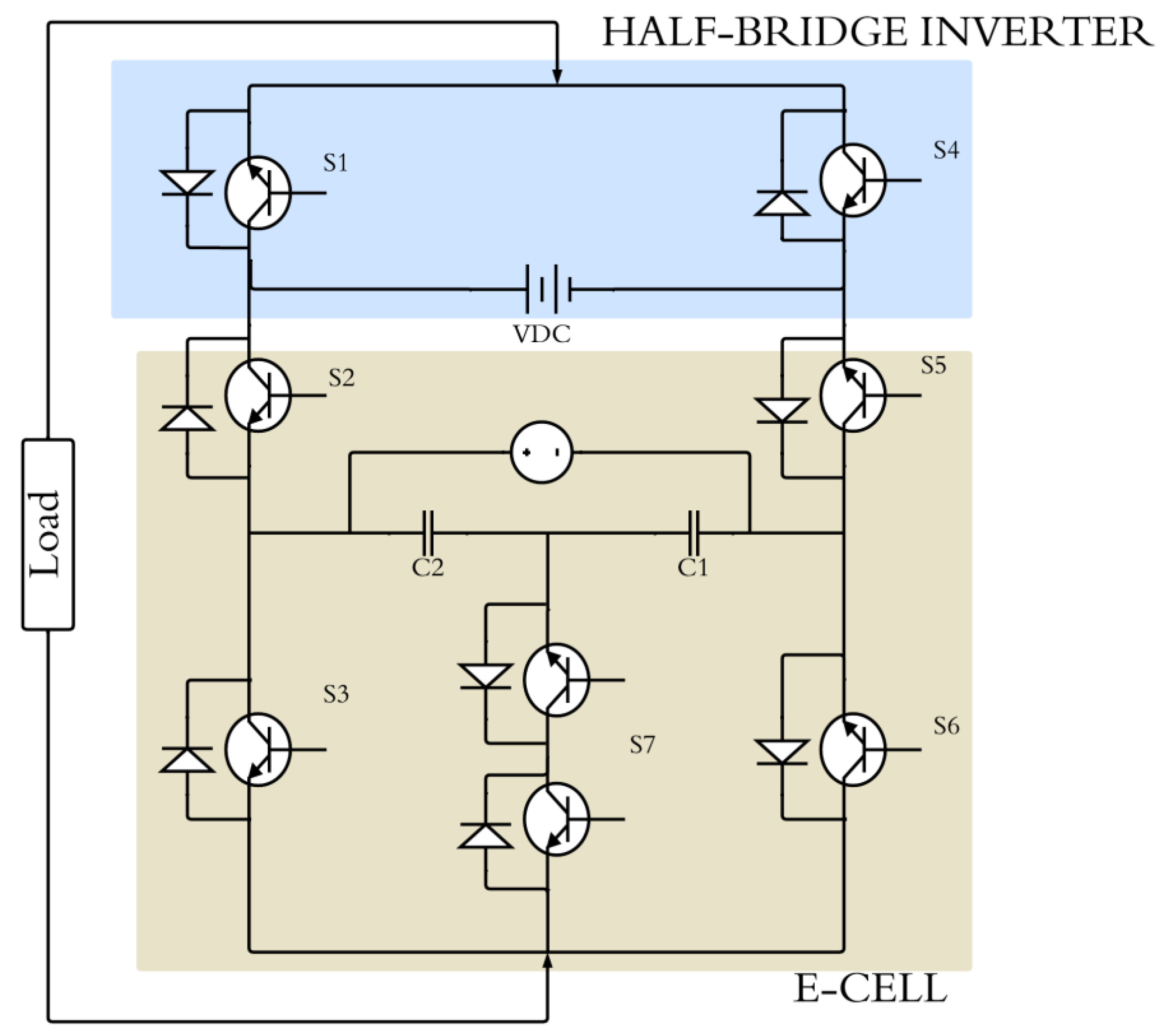
| Battery Technology | Specific Energy (Wh/kg) | Self-Discharge Coefficient (%/24 h) | Number of Recharging Cycles |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pb-acid | 40 | 1 | 500 |
| Ni-Cd | 60 | 5 | 1350 |
| NiMH | 70 | 2 | 1350 |
| Li-ion | 125 | 1 | 1000 |
| Na-NiCl | 125 | 0 | 1000 |
| Ref. | Year | Battery Model | Chemical Composition | Capacity | Cells | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [21] | 2009 | BYD Tang (BYD, Shenzhen, China) | LFP | 100–150 kWh | 200 | Pouch |
| [22] | 2014 | GM LMR prismatic (General Motors, MI, USA) | LMR | 150 kWh | 273 | Prism |
| [23] | 2020 | Lucid Air 2170 (Samsung SDI, Yongin, South Korea) | NCA | 113 kWh | 6600 | Cylinder |
| [24] | 2022 | Ford Mach-E (Ford, MI, USA) | NCM811 | 91 kWh | 376 | Pouch |
| [25] | 2022 | Tesla 4680 (Tesla, TX, USA) | NCM o NCA | 82 kWh | 4680 | Cylinder |
| [26] | 2022 | Tesla/NMC (Tesla, NV, USA) | NMC | ~55–82 kWh | 108 | Prism |
| [27] | 2023 | Nio ET7 (NIO, Hefei, China) | NMC | 150 kWh | 108 | Pouch |
| [28] | 2023 | GM Ultium (Ultium Cells LLC, OH, USA) | NCMA | 100 kWh | 264 | Pouch |
| [29] | 2023 | Nio ET7 (NIO, Hefei, China) | NMC | 100 kWh | 192 | Prism |
| [30] | 2023 | Nio ET7(NIO, Hefei, China) | NMC + LFP | 75 kWh | 118 | Prism |
| [31] | 2023 | BYD Blade (BYD, Qinghai, China) | LFP | 82–100 kWh | 230 | Prism |
| [32] | 2023 | BMW NEUE KLASSE (BMW, Debrecen, Munich, Hungary and Germany) | NMC | 105 kWh | 4680 | Cylinder |
| [33] | 2023 | Tesla 2170 (Tesla, NV, USA) | NCA | 60–82 kWh | 2170 | Cylinder |
| [34] | 2024 | Hyundai loniq (Hyundai, Ulsan, South Korea) | LFP | 77 kWh | 360 | Pouch |
| [35] | 2025 | Porsche 18650 (Panasonic, Kadoma, Japan) | NCA | 93 kWh | 396 | Cylinder |
| Level 1 (AC) | Level 2 (AC) | Level 3 (DC) | Level 4 (DC) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recharge time | 11–36 h | 2–6 h | 30 min | 10 min |
| Energy consumed | 16–50 kWh | 16–30 kWh | 20–50 kWh | 50–160 kWh |
| Connection protocols | SAE J1772 | SAE J1772 | CCS, CHAdeMO | CCS, CHAdeMO |
| Voltage (V) | 120 | 240 | 200–1000 | Up to 1000 |
| Current (A) | 12–16 | 16–80 | 100–400 | 300–500 |
| CHAdeMO | Tesla Supercharger | CCS | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Connection type | DC | DC | AC/DC |
| Maximum load capacity | Up to 400 kW | Up to 250 kW | Up to 350 kW |
| Maximum current | Up to 400 A | Up to 423 A | Up to 500 A |
| Voltage standards | 200–1000 V | 480 V | 200–1000 V |
| Communication protocol | Control Area Network | Only Tesla | Power Line Communication |
| Manufacturers | Nissan, Mitsubishi, Kia | Tesla | BMW, Audi, Ford, Hyundai |
| Connection port diagram |  |  |  |
| Ref. | Year | Voltage (V) | Current (A) | Power (kW) | Efficiency (%) | Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [37] | 2011 | 100–500 | 120 | 50 | 90 | CHAdeMO |
| [38] | 2017 | 200–500 | 125 | 50 | 95 | CCS, CHAdeMO |
| [39] | 2019 | 50–500 | 125 | 50 | 94 | CCS, CHAdeMO |
| [40] | 2020 | 500 | 200 | 100 | 95 | CCS1,CHAdeMO |
| [41] | 2021 | 150–950 | 120 | 60 | 94 | CCS1,CHAdeMO |
| [42] | 2021 | 170–940 | 50–400 | 150 | 93 | CHAdeMO |
| [43] | 2021 | 920 | 200–500 | 350 | 98.5 | CCS2,CHAdeMO |
| [44] | 2021 | 200–1000 | 375 | 150 | 94 | CCS, CHAdeMO |
| [45] | 2022 | 920 | 188 | 75 | 95 | CCS ½, CHAdeMO |
| [46] | 2022 | 50–920 | 200 | 100 | 95 | CCS1,CHAdeMO |
| [47] | 2022 | 50–410 | 330 | 135 | 91 | Supercharger |
| [48] | 2023 | 200–1000 | 250–500 | 2000 | 94 | CCS, CHAdeMO |
| [49] | 2023 | 150–950 | 500 | 350 | 95 | CHAdeMO |
| [50] | 2023 | 150 | 500 | 350 | 96 | CCS, CHAdeMO |
| [51] | 2023 | 150–1000 | 350 | 350 | 95 | CCS, CHAdeMO |
| [52] | 2024 | 150–920 | 325 | 130 | 97 | CCS ½, CHAdeMO |
| [53] | 2024 | 150–950 | 380–500 | 350 | 94 | CCS ½, CHAdeMO |
| [54] | 2024 | 200–920 | 500 | 350 | 96 | CCS2, CHAdeMO |
| [55] | 2024 | 500 | - | 6.6 | - | CCS |
| [56] | 2024 | 200–1000 | 350 | 350 | 97 | CHAdeMO |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernández Ruiz, A.Y.; De león Aldaco, S.E.; Aguayo Alquicira, J.; Ponce Silva, M.; Rodríguez Benítez, O.; Flores Rodríguez, E. An Overview of Level 3 DC Fast Chargers: Technologies, Topologies, and Future Directions. Eng 2025, 6, 276. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6100276
Hernández Ruiz AY, De león Aldaco SE, Aguayo Alquicira J, Ponce Silva M, Rodríguez Benítez O, Flores Rodríguez E. An Overview of Level 3 DC Fast Chargers: Technologies, Topologies, and Future Directions. Eng. 2025; 6(10):276. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6100276
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernández Ruiz, Alan Yabin, Susana Estefany De león Aldaco, Jesús Aguayo Alquicira, Mario Ponce Silva, Omar Rodríguez Benítez, and Eligio Flores Rodríguez. 2025. "An Overview of Level 3 DC Fast Chargers: Technologies, Topologies, and Future Directions" Eng 6, no. 10: 276. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6100276
APA StyleHernández Ruiz, A. Y., De león Aldaco, S. E., Aguayo Alquicira, J., Ponce Silva, M., Rodríguez Benítez, O., & Flores Rodríguez, E. (2025). An Overview of Level 3 DC Fast Chargers: Technologies, Topologies, and Future Directions. Eng, 6(10), 276. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6100276








