Ti-Fe-Based Alloys Modified with Al and Cr for Next-Generation Biomedical Implants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Particle Size
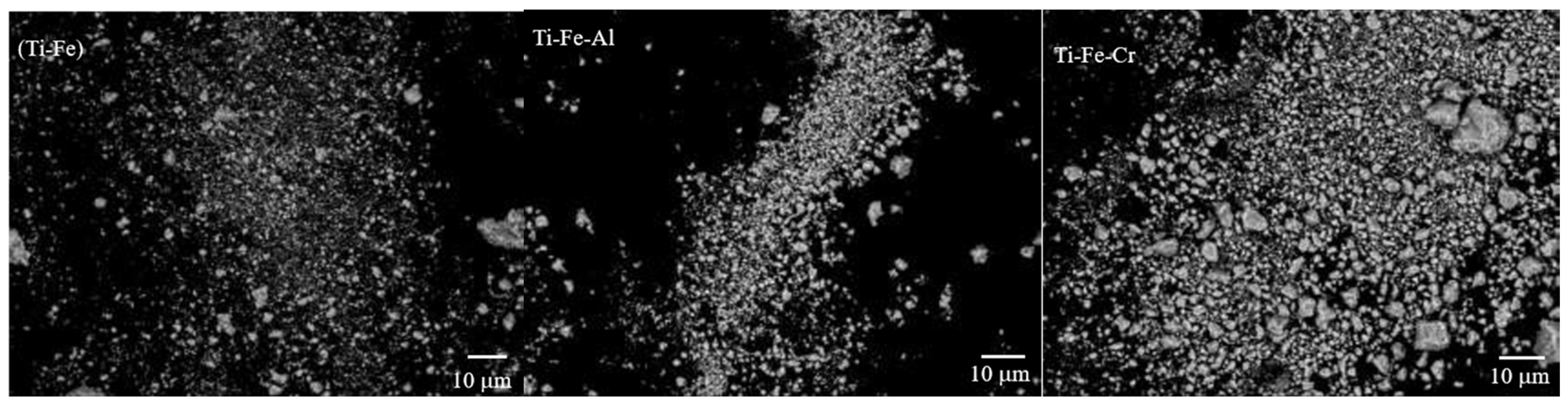
3.2. Powder Morphology
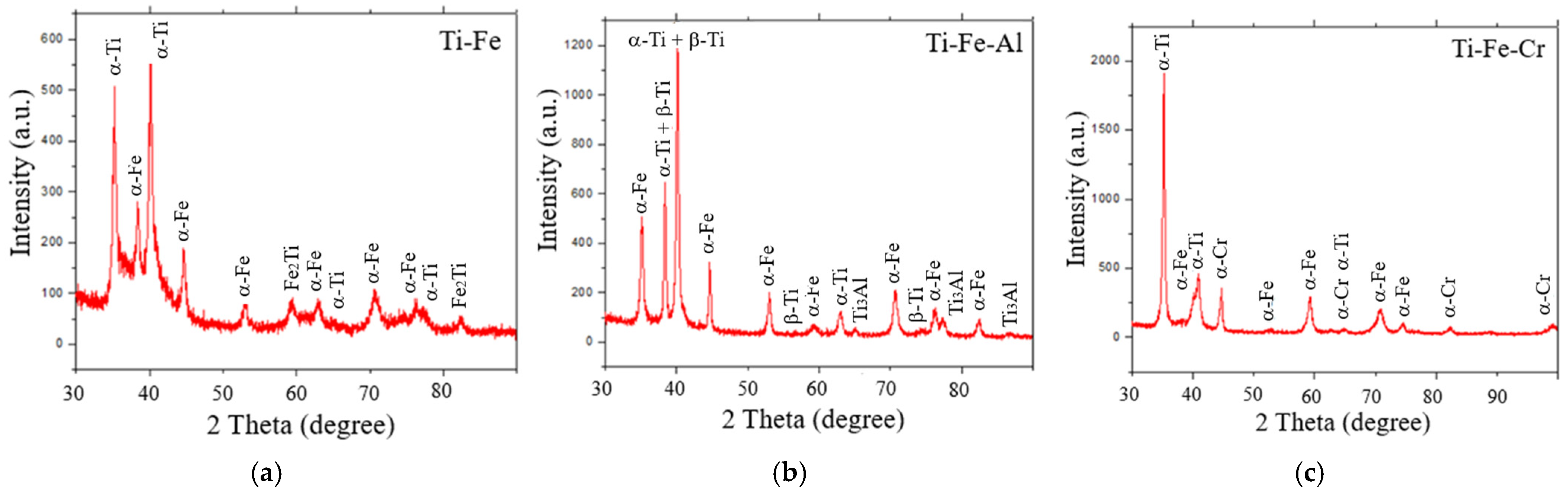
3.3. Crystalline Phases in Powders
3.4. Density
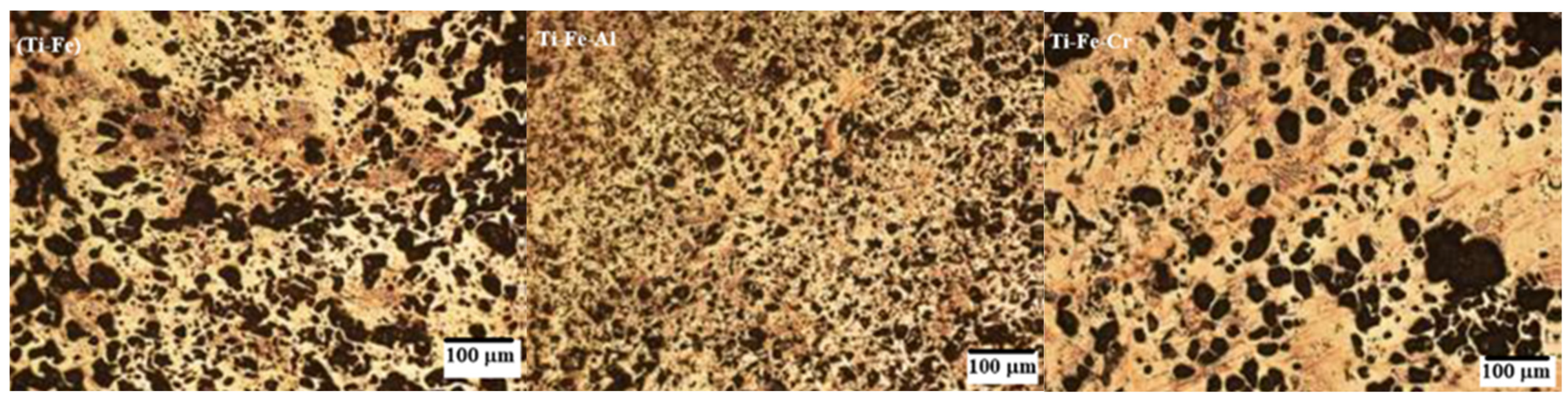
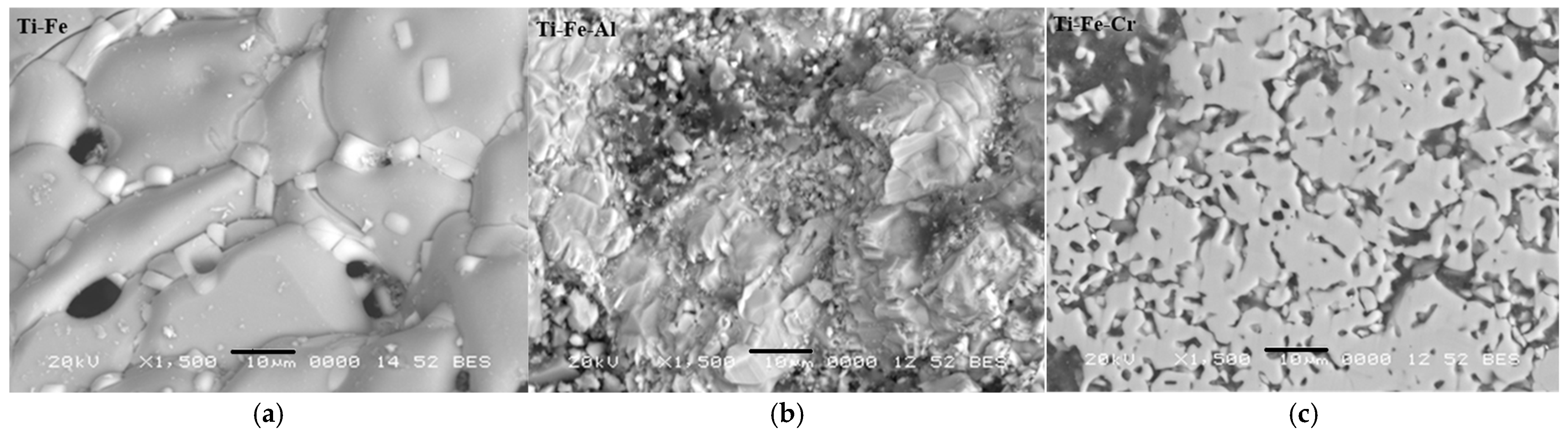
3.5. Microstructure
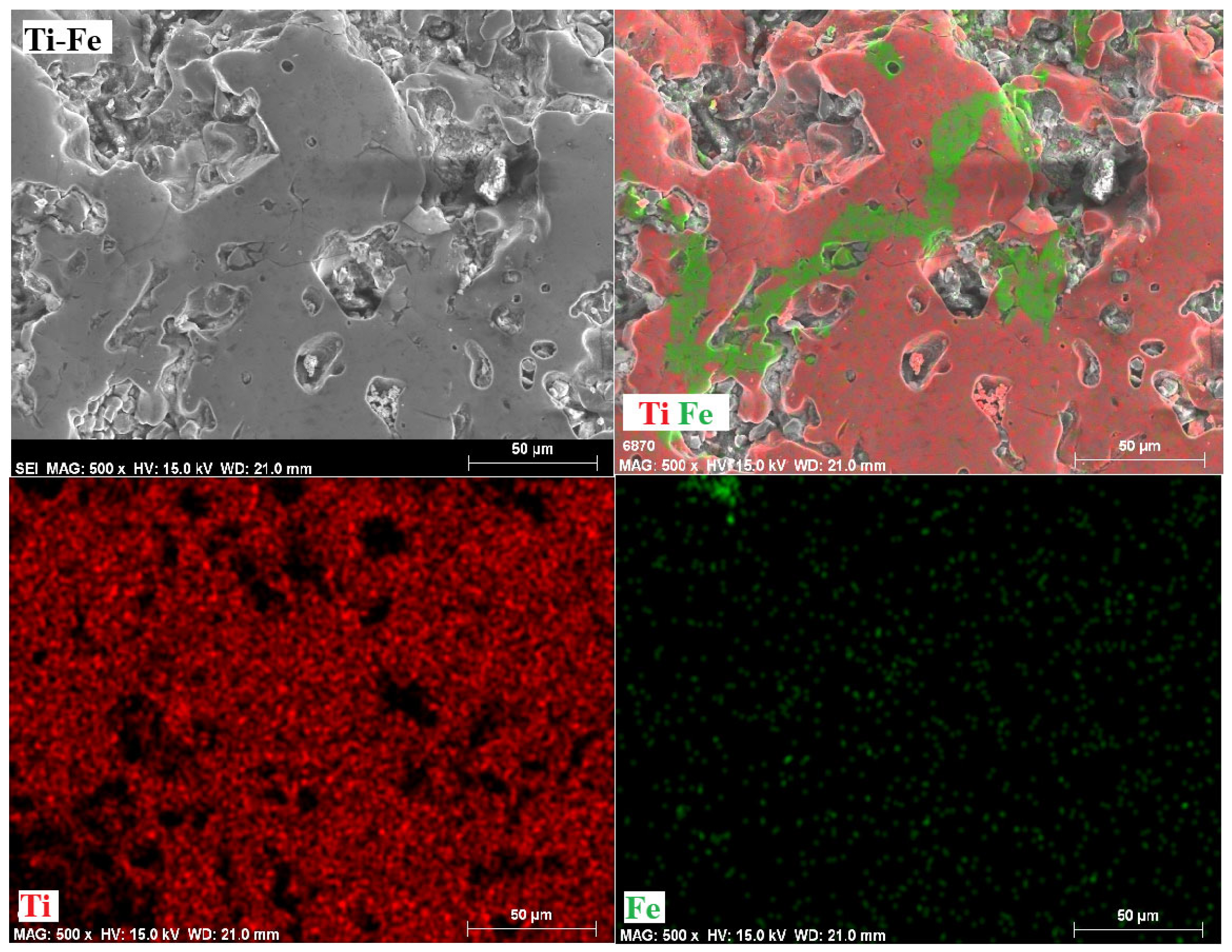
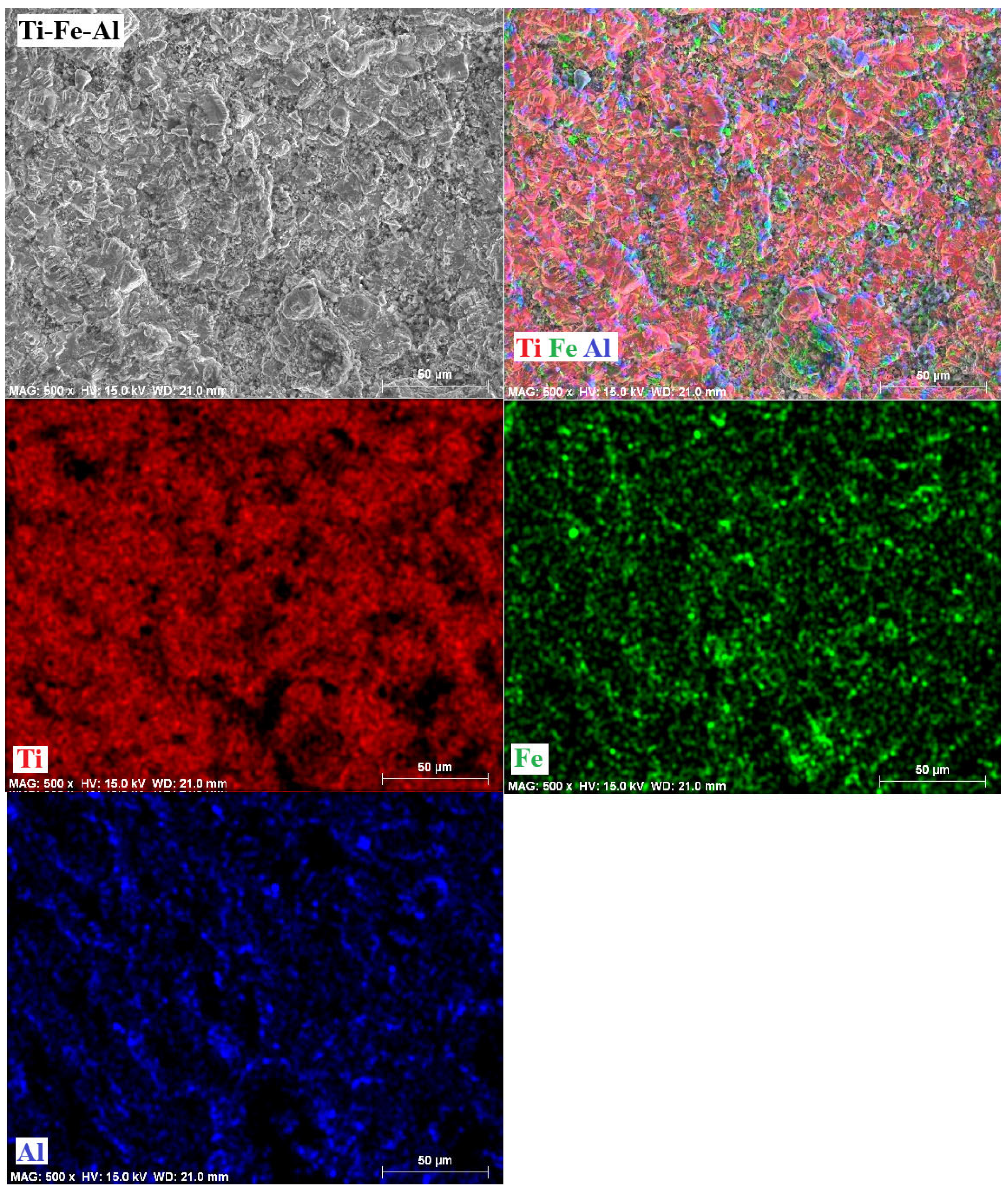
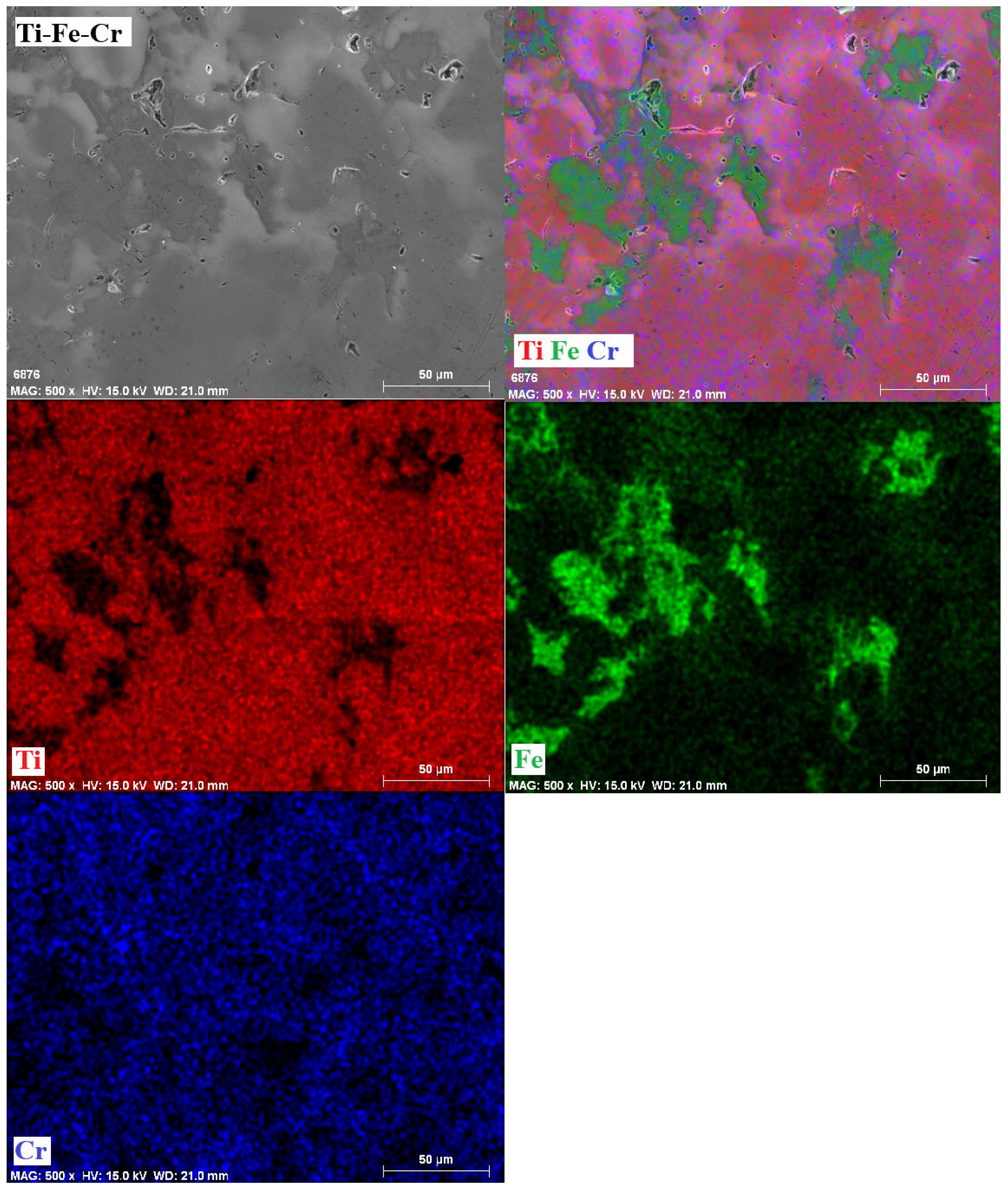
3.6. Mappings
3.7. Mechanical Properties
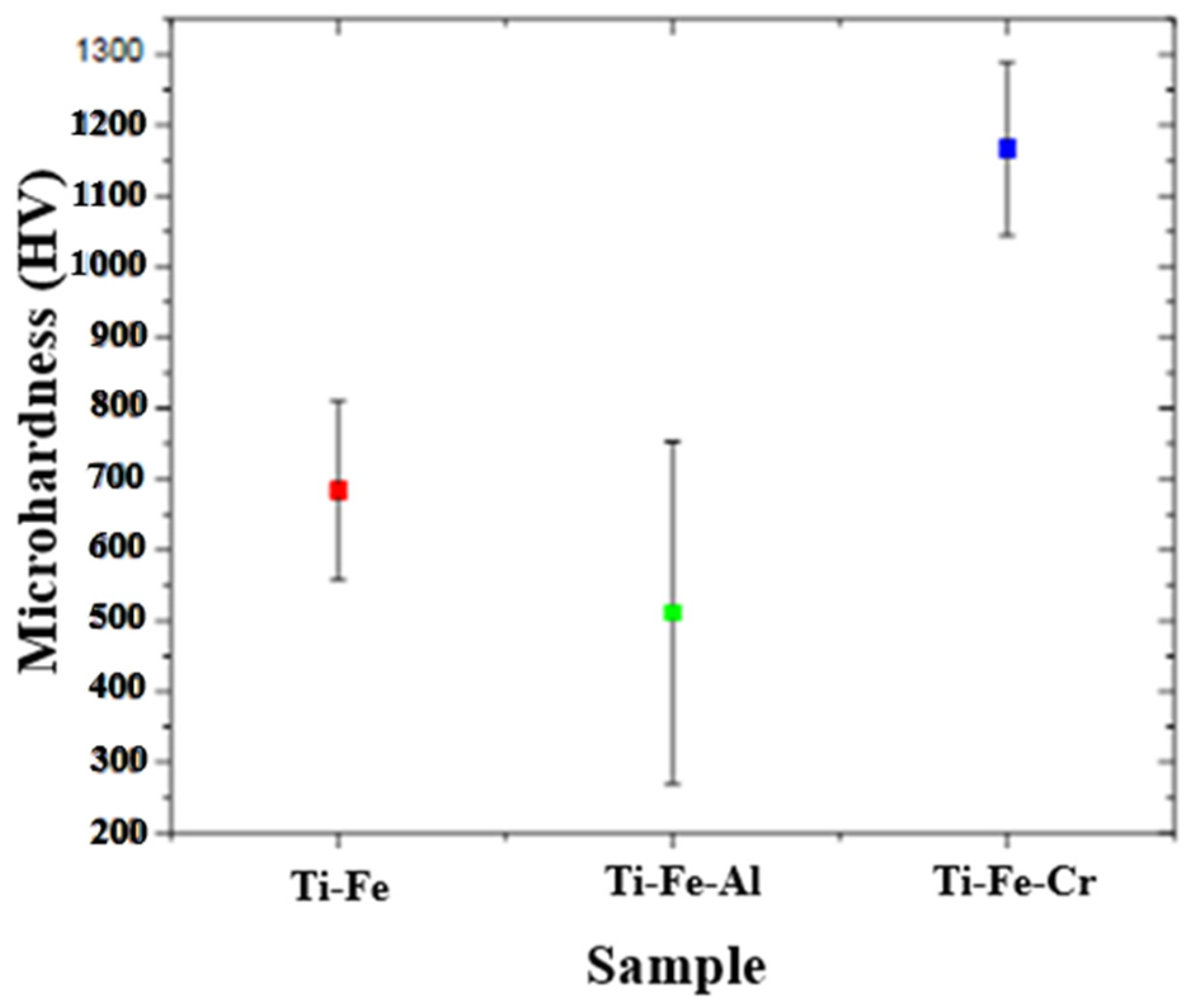
3.7.1. Microhardness
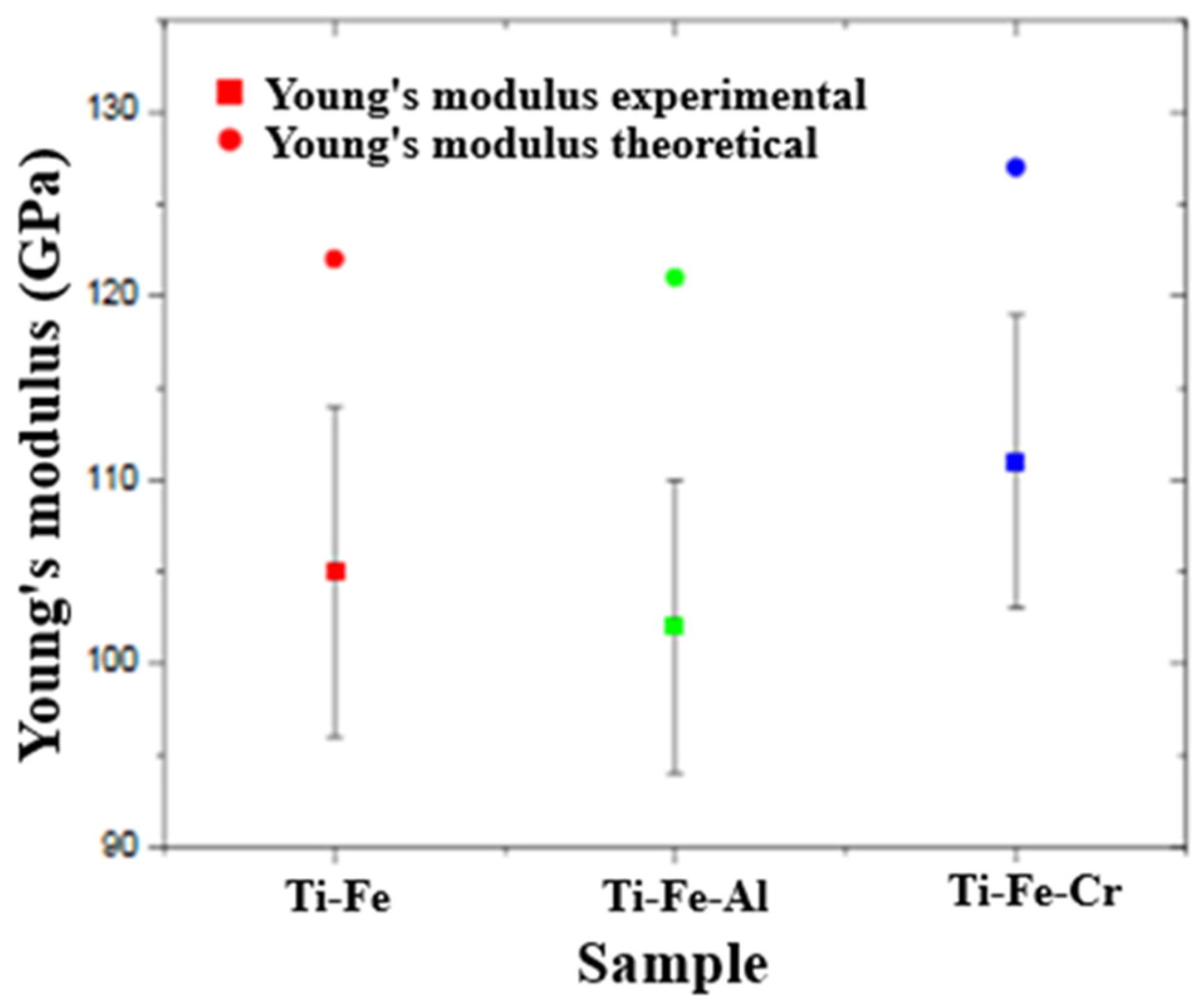
3.7.2. Elastic Modulus
3.8. Corrosion Test
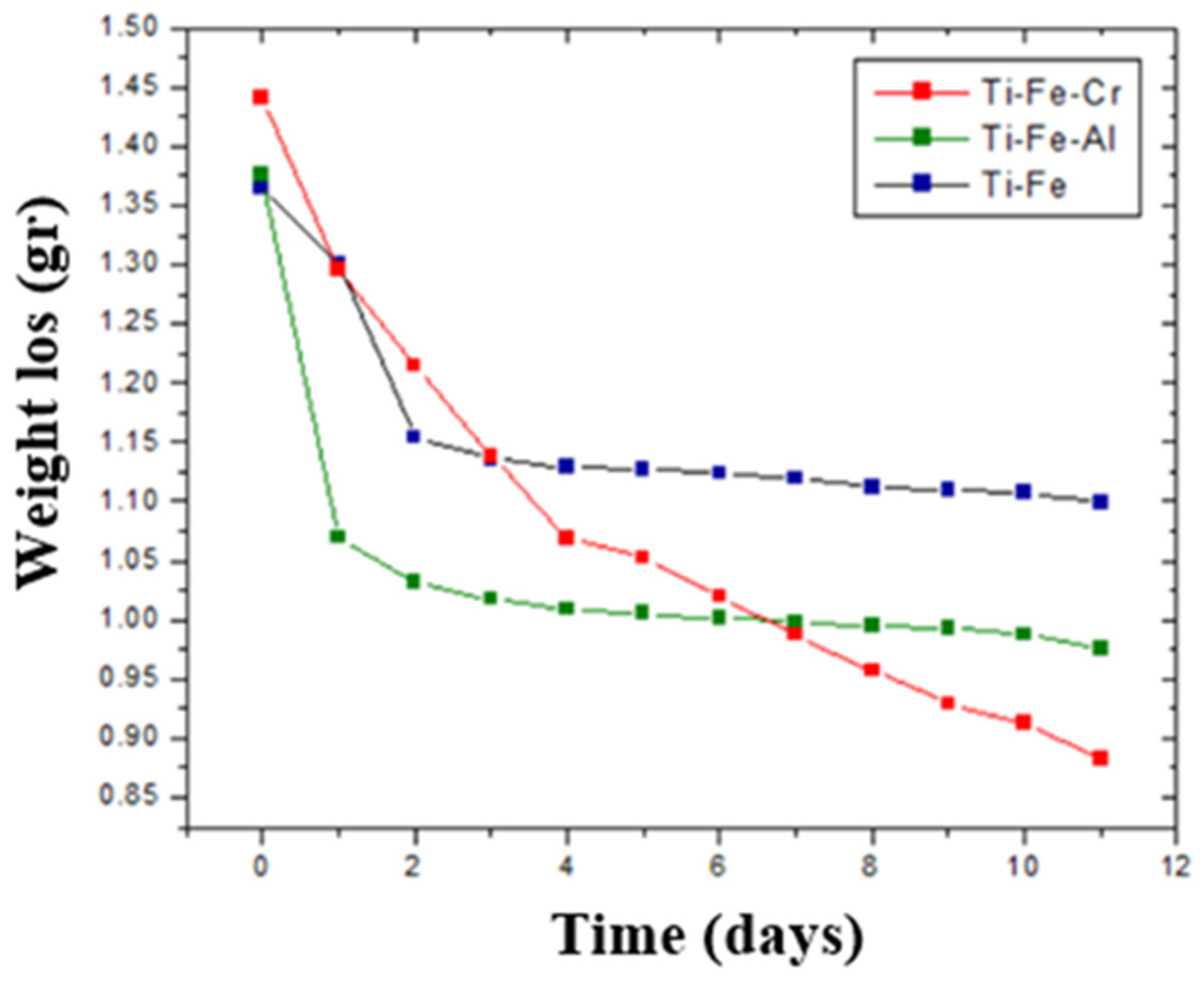
3.9. Corrosion by Chemical Agent
4. Conclusions
- ○
- Images obtained using optical microscopy reveal a microstructure with significant porosity, which is relevant for biomedical applications, as it can promote biocompatibility through cell adhesion to the host. In addition, a homogeneous alloy with fine grains was observed, suggesting effective control in the synthesis and sintering processes.
- ○
- The phases present in the alloys were as follows. For the Ti-Fe alloy, the matrix consists of a mixture of α-Ti and α-Fe phases, with the formation of Fe2Ti intermetallic precipitates. The Ti-Fe-Al alloy has a matrix with a mixture of α and β phases of titanium and precipitates of the intermetallic Ti3Al. In contrast, the Ti-Fe-Cr alloy has a predominantly body-centered cubic structure without the formation of intermetallic precipitates.
- ○
- The data obtained in the microhardness tests show that the Ti-Fe-Cr alloy presented the highest resistance to localized deformation, followed by Ti-Fe and, finally, Ti-Fe-Al. This behavior indicates a direct relationship between the composition of the alloys and their mechanical properties.
- ○
- In the Young’s modulus measurements, it was observed that the Ti-Fe-Cr alloy also had the highest values, followed by Ti-Fe and Ti-Fe-Al. This finding is consistent with microhardness data, reinforcing the correlation between hardness and stiffness in the evaluated alloys. The presence of Cr significantly improves elastic properties, while Al tends to decrease them.
- ○
- Corrosion tests showed electrochemical potential values between 480 and 520 mV, indicating remarkable resistance to corrosive environments. In addition, the recorded current density values reflect a low tendency to corrosion, confirming that the alloys exhibit good stability in chemically aggressive conditions.
- ○
- Despite prolonged exposure to Kroll’s reagent, the samples showed minimal mass loss, highlighting their stability in acidic environments.
- ○
- The Ti-Fe-Cr alloy emerges as the most advantageous alternative, as it exhibits the highest values of microhardness, Young’s modulus, and relative density, thereby ensuring superior mechanical performance compared to the other alloys. Despite presenting the highest corrosion rate, the measured corrosion potentials confirm that, similar to the other systems, it maintains a high degree of chemical stability.
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Ecorr | Corrosion potential |
| Icorr | Corrosion current density |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| HV | Hardness Vickers |
| RHE | Reversible Hydrogen Electrode |
References
- Bandyopadhyay, A.; Mitra, I.; Goodman, S.B.; Kumar, M.; Bose, S. Improving biocompatibility for next generation of metallic implants. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2023, 133, 101053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Y.; Cui, Y.W.; Zhang, L.C. Recent development in beta titanium alloys for biomedical applications. Metals 2020, 10, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bassyouni, G.T.; Mouneir, S.M.; El-Shamy, A.M. Advances in surface modifications of titanium and its alloys: Implications for biomedical and pharmaceutical applications. Multiscale Multidiscip. Model. Exp. Des. 2025, 8, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Singh, K. Review on Titanium and Titanium Based Alloys as Biomaterials for Orthopaedic Applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 102, 844–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Niu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Du, Y.; Zhang, W.; Huo, W. Electrochemical corrosion behavior and elasticity properties of Ti-6Al-xFe alloys for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 62, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trevisan, F.; Calignano, F.; Aversa, A.; Marchese, G.; Lombardi, M.; Biamino, S.; Ugues, D.; Manfredi, D. Additive manufac-turing of titanium alloys in the biomedical field: Processes, properties and applications. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2018, 16, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawed, S.F.; Rabadia, C.D.; Khan, M.A.; Khan, S.J. Effect of alloying elements on the compressive mechanical properties of biomedical titanium alloys: A systematic review. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 29526–29542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Guo, Y.; Li, K.; Liu, W.; Dan, Z.; Sun, Z.; Chang, H.; Zhou, L. Improved mechanical, bio-corrosion properties and in vitro cell responses of Ti-Fe alloys as candidate dental implants. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 122, 111917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çaha, I.; Alves, A.; Chirico, C.; Pinto, A.; Tsipas, S.; Gordo, E.; Toptan, F. Corrosion and tribocorrosion behavior of Ti-40Nb and Ti-25Nb-5Fe alloys processed by powder metallurgy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2020, 51, 3256–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshammari, Y.; Manogar, B.; Raynova, S.; Yang, F.; Bolzoni, L. Behaviour of novel low-cost blended elemental Ti–5Fe-xAl alloys fabricated via powder metallurgy. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 110, 103865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Lee, J.G.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, D.G. Effect of molybdenum on the mechanical and corrosion properties of Ti-xMo-2Fe beta alloys. J. Korean Inst. Met. Mater. 2024, 62, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Qian, S.; Chang, H.; Duan, W.; Feng, L.; Li, F.; Zhou, L. Improved low cycle fatigue property of Ti–6Al–4V alloy by trace Fe addition. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, 8396–8408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Yang, X.; Yan, Y.; Liang, M. Development of novel Gd-Fe/Ti composites with tunable thermal expansion property. Mater. Res. Express 2024, 11, 096514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behjat, A.; Sanaei, S.; Mosallanejad, M.H.; Atapour, M.; Sheikholeslam, M.; Saboori, A.; Iuliano, L. A novel titanium alloy for load-bearing biomedical implants: Evaluating the antibacterial and biocompatibility of Ti536 produced via electron beam powder bed fusion additive manufacturing process. Biomater. Adv. 2024, 157, 213928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolzoni, L.; Yang, F. Development of Cu-bearing powder metallurgy Ti alloys for biomedical applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 97, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedram Sotoudeh Bagha, P.S.; Khakbiz, M.; Safaie, N.; Sheibani, S.; Ebrahimi-Barough, S. Effect of high energy ball milling on the properties of biodegradable nanostructured Fe-35 wt.%Mn alloy. J. Alloys Comp. 2018, 768, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaie, N.; Khakbiz, M.; Sheibani, S.; Bagha, P.S. Synthesizing of Nanostructured Fe-Mn Alloys by Mechanical Alloying Process. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2015, 11, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sur, D.; Holcombe, E.F.; Blades, W.H.; Anber, E.A.; Foley, D.L.; DeCost, B.L.; Liu, J.; Hattrick-Simpers, J.; Sieradzki, K.; Joress, H.; et al. An experimental high-throughput to high-fidelity study towards discovering Al-Cr containing corrosion-resistant compositionally complex alloys. High Entropy Alloys Mater. 2023, 1, 336–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E1876-22; Standard Test Method for Dynamic Young’s Modulus, Shear Modulus, and Poisson’s Ratio by Impulse Exci-tation of Vibration. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- ASTM E384-16; Standard Test Method for Microindentation Hardness of Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2016.
- Malaret, F. Exact calculation of corrosion rates by the weight-loss method. Exp. Results 2022, 3, e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Wagner, G.; Williams, C.B. Effect of Particle Size Distribution on Powder Packing and Sintering in Binder Jetting Additive Manufacturing of Metals. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2017, 139, 081019–081024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currey, J.D. Bones: Structure and Mechanics; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Dia, A.S.; Renaud, G.; Chappard, C.; Grimal, Q. Ultrasound imaging of cortical bone: Cortex geometry and measurement of porosity based on wave speed for bone remodeling estimation. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.08824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Kattner, U.; Choudharry, K.; Tavazza, F.; Campbell, C. Thermodynamic assessments of Ti-Al, Ti-Fe, and Ti-Al-Fe systems with four-sublattice description of ordered body-centered cubic phase and density functional theory data. J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 2024, 45, 732–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, K.; Chen, G.; Li, Z.; Qin, Z.; Lu, X.; Li, C. Thermodynamic modeling of Ti-Fe-Cr ternary system. Calphad 2017, 56, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, J.Z.; Yin, B.; Hu, Z.S.; Zhang, X.J.; Wu, W.; Liu, G.B.; Liu, Y.K.; Fu, L.; Zhang, Y.Z. Atlas of human skeleton hardness obtained using the micro-indentation technique. Orthop. Surg. 2021, 13, 1417–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, E.; Lanzutti, A. Biomedical applications of titanium alloys: A comprehensive review. Materials 2024, 17, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, R.B.; Hein, L.R.d.O.; Robin, A. Influence of aged Ti-15V-3Cr-3Sn-3Al alloy microstructure on chemical and electrochemical behavior in the Kroll reagent for metallographic etching. Prakt. Metallogr. 2003, 40, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

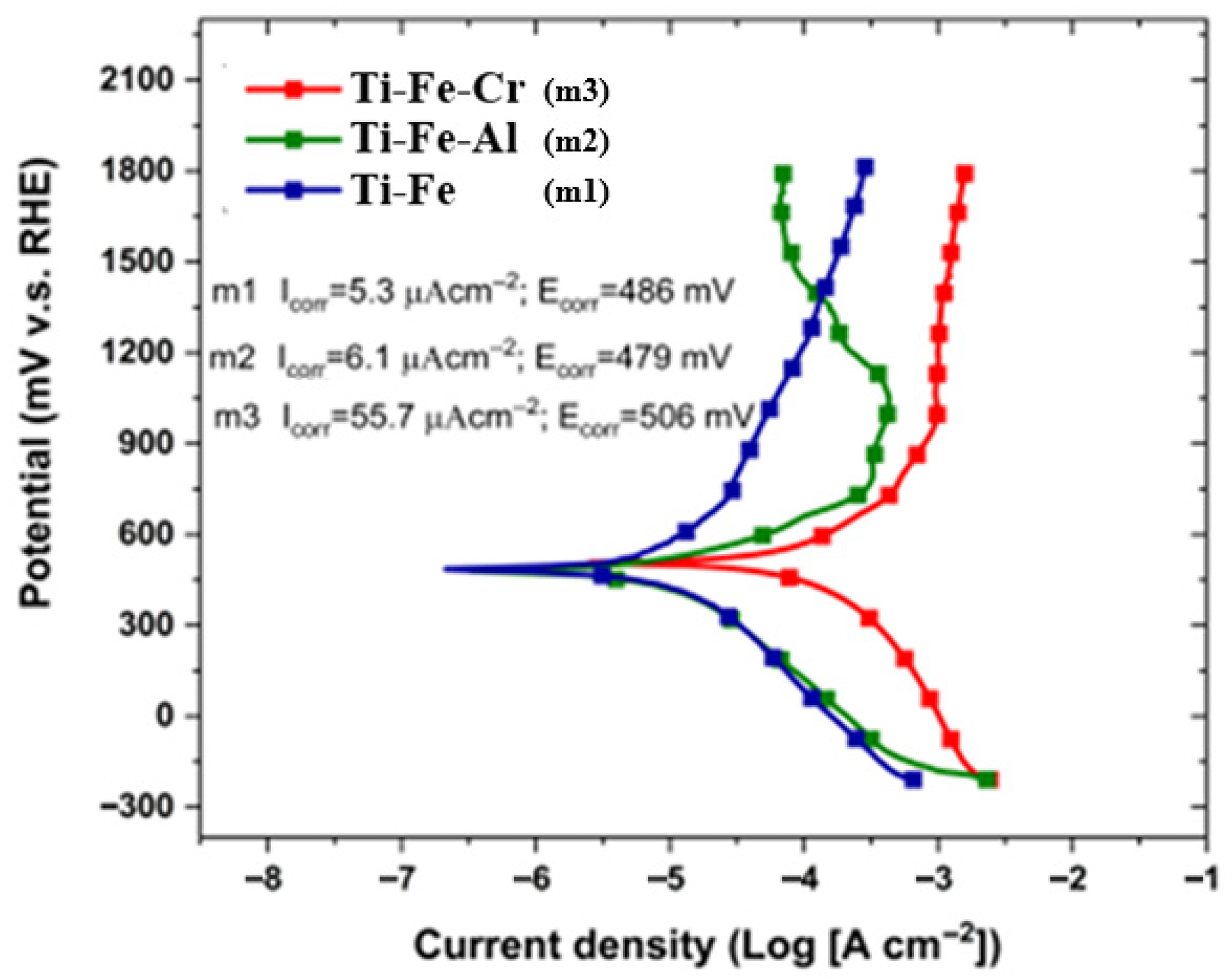
| Sample | Ecorr (mV) | Icorr (μA·cm−2) | βa (V) | βc (V) | Rp (Ω·cm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 486 | 5.3 | 0.262 | 0.130 | 7127.7 |
| M2 | 479 | 6.1 | 0.122 | 0.163 | 4973.3 |
| M3 | 506 | 55.7 | 0.118 | 0.100 | 422.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez-Escobedo, K.I.; Pech-Rodríguez, W.J.; Bedolla-Valdez, Z.I.; Calles-Arriaga, C.A.; Miranda-Hernández, J.G.; Rocha-Rangel, E. Ti-Fe-Based Alloys Modified with Al and Cr for Next-Generation Biomedical Implants. Eng 2025, 6, 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6100273
Rodríguez-Escobedo KI, Pech-Rodríguez WJ, Bedolla-Valdez ZI, Calles-Arriaga CA, Miranda-Hernández JG, Rocha-Rangel E. Ti-Fe-Based Alloys Modified with Al and Cr for Next-Generation Biomedical Implants. Eng. 2025; 6(10):273. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6100273
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez-Escobedo, Katia Itzel, Wilian Jesús Pech-Rodríguez, Zaira Itzel Bedolla-Valdez, Carlos Adrián Calles-Arriaga, José Guadalupe Miranda-Hernández, and Enrique Rocha-Rangel. 2025. "Ti-Fe-Based Alloys Modified with Al and Cr for Next-Generation Biomedical Implants" Eng 6, no. 10: 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6100273
APA StyleRodríguez-Escobedo, K. I., Pech-Rodríguez, W. J., Bedolla-Valdez, Z. I., Calles-Arriaga, C. A., Miranda-Hernández, J. G., & Rocha-Rangel, E. (2025). Ti-Fe-Based Alloys Modified with Al and Cr for Next-Generation Biomedical Implants. Eng, 6(10), 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6100273







