Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of High-Performance Cold Mix Asphalt Modified with Portland Cement
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation and Conditioning
2.3. Testing Programme
2.3.1. Indirect Tensile Stiffness Modulus (ITSM) Test
2.3.2. Moisture Susceptibility Test
2.3.3. Temperature Susceptibility Test
2.3.4. Microstructure Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of OPC Addition on the ITSM Results
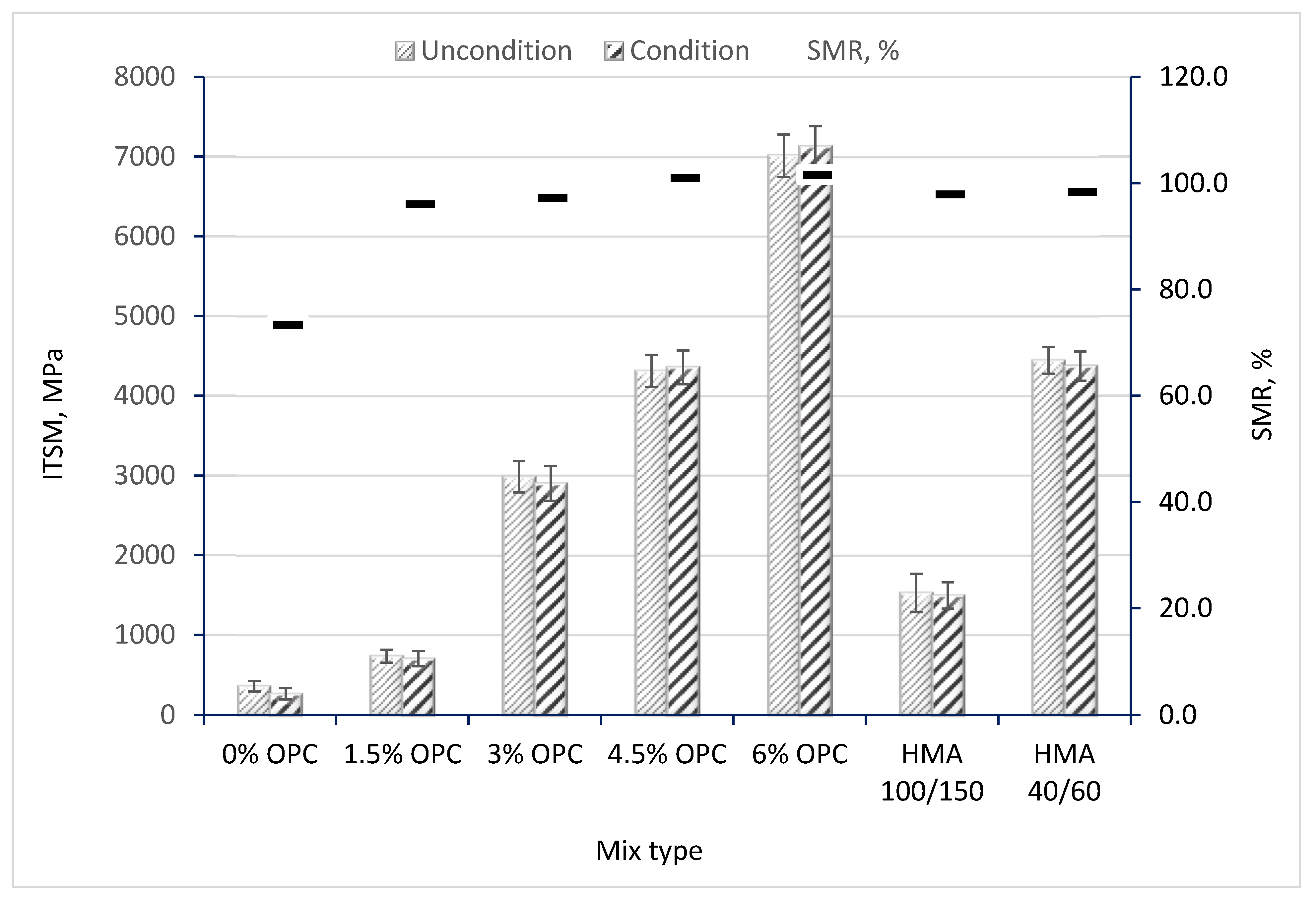
3.2. Effect of OPC Addition on Moisture Susceptibility
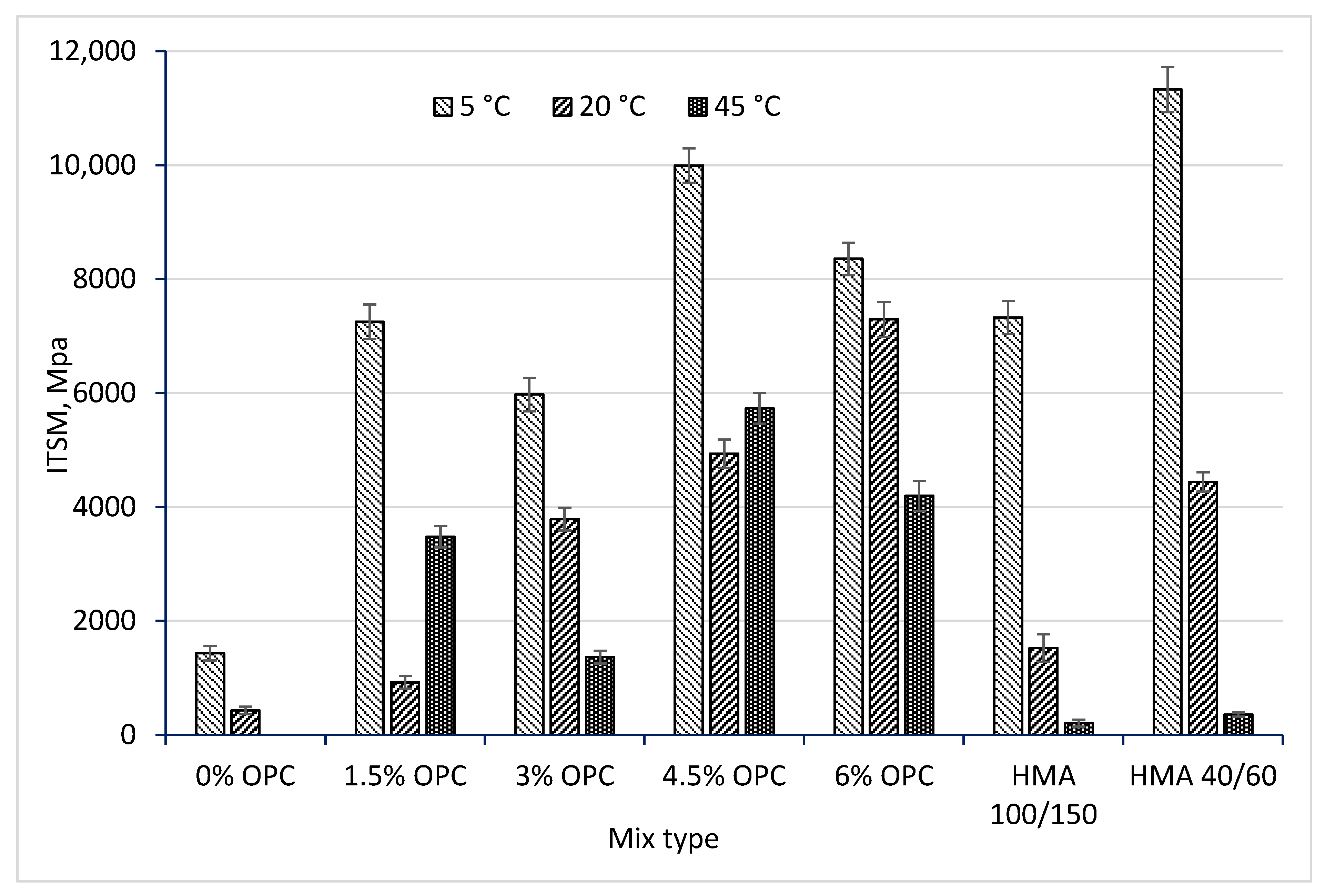
3.3. Effect of OPC Addition on the Temperature Susceptibility
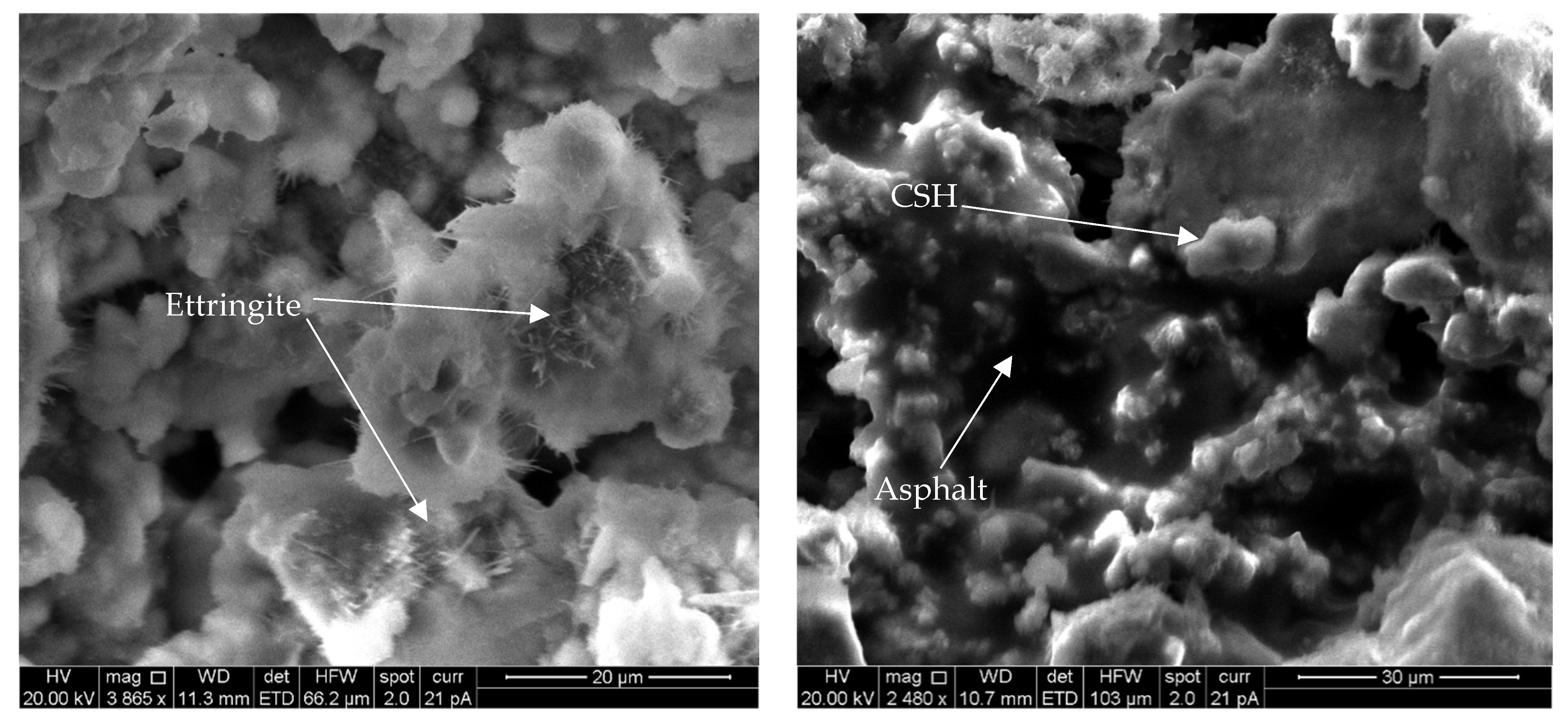
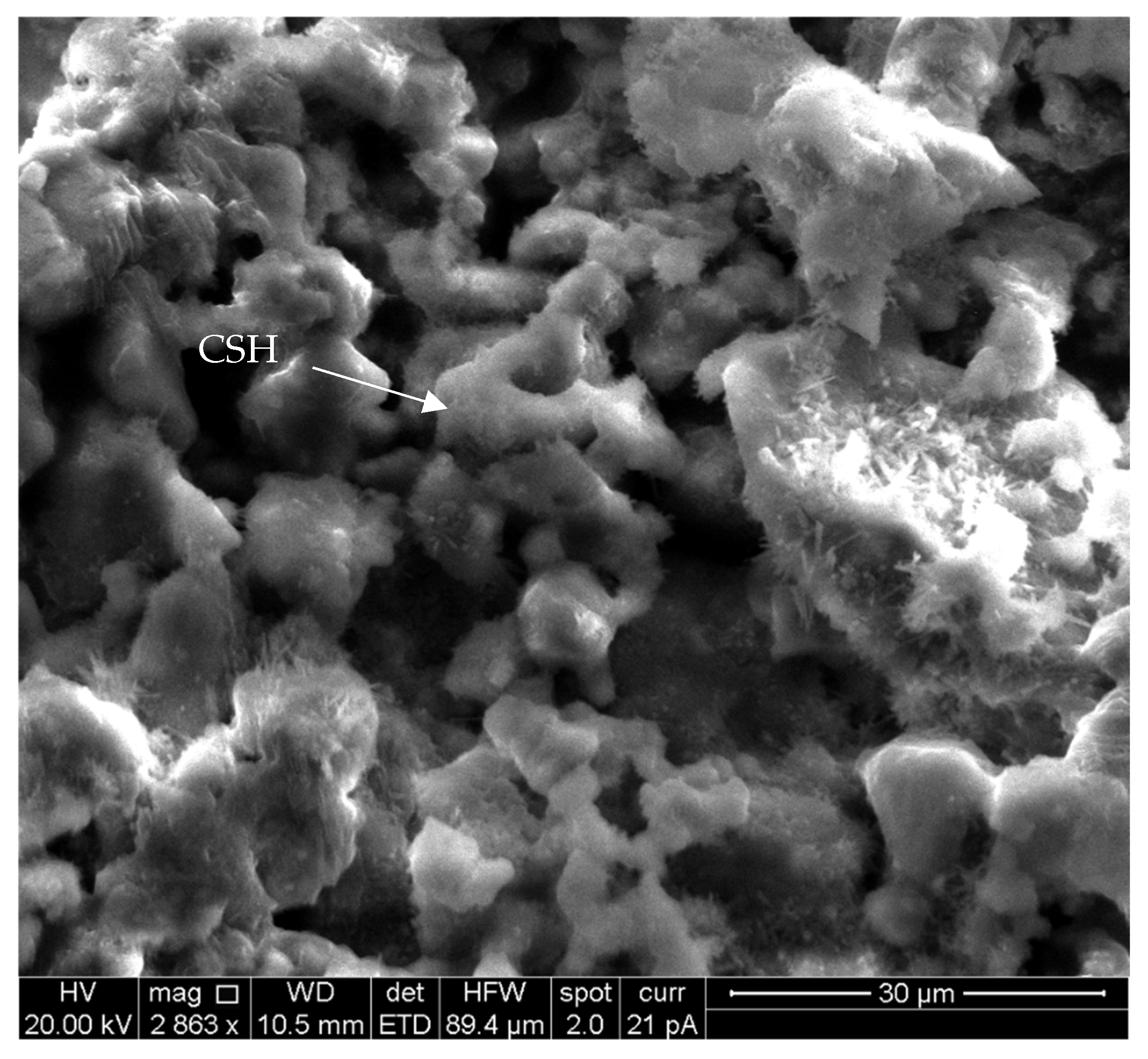
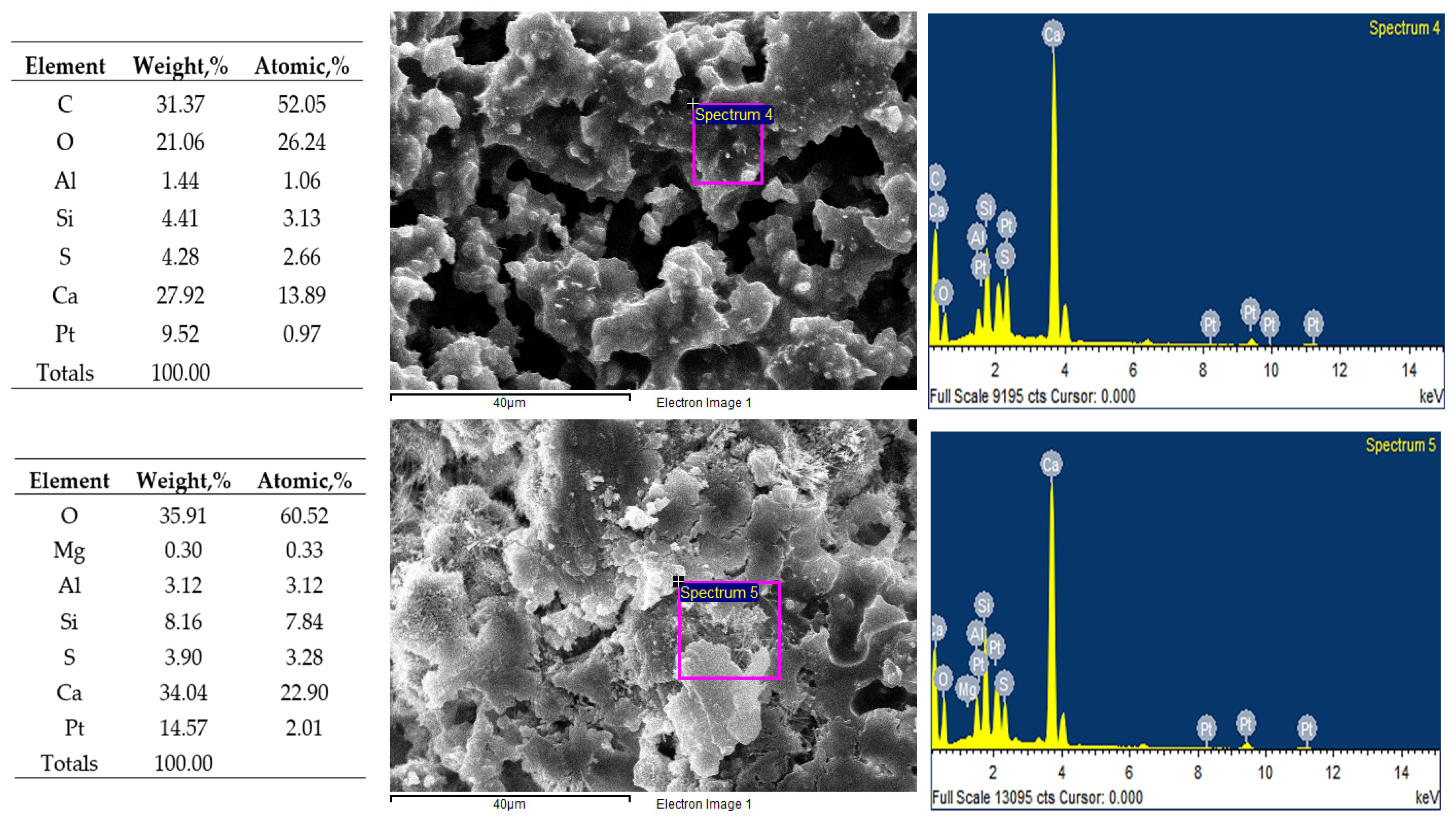
3.4. SEM–EDS Observations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ansari, A.H.; Jakarni, F.M.; Muniandy, R.; Hassim, S.b.; Elahi, Z. Natural rubber as a renewable and sustainable bio-modifier for pavement applications: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 289, 125727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Singh, B. Cold mix asphalt: An overview. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 280, 124378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulrahman, S.; Hainin, M.R.; Idham Mohd Satar, M.K.; Hassan, N.A.; Usman, A. Mechanical performance and global warming potential of unaged warm cup lump modified asphalt. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 297, 126653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.V.; Perry, S.; Klemeš, J.J.; Lee, C.T. A review on air emissions assessment: Transportation. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 194, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulaimi, A.; Al Nageim, H.; Ruddock, F.; Seton, L. Assessment the Performance of Cold Bituminous Emulsion Mixtures with Cement and Supplementary Cementitious Material for Binder Course Mixture. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Cement Microscopy, Lyon, France, 17–21 April 2016; pp. 283–296. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Sabaeei, A.M.; Napiah, M.B.; Sutanto, M.H.; Alaloul, W.S.; Usman, A. A systematic review of bio-asphalt for flexible pavement applications: Coherent taxonomy, motivations, challenges and future directions. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 249, 119357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.S.; Chandrappa, A.K.; Sahoo, U.C. Design and performance of cold mix asphalt—A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 315, 125687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alenezi, T.; Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Dawson, A.; Garcia, A. A novel type cold mix pavement material made with calcium-alginate and aggregates. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 212, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanaya, I.N.A.; Zoorob, S.E.; Forth, J.P. A laboratory study on cold-mix, cold-lay emulsion mixtures. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Transp. 2009, 162, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziari, H.; Nasiriamiri, E.; Ayar, P. Effect of encapsulated waste oils and compaction method on the curing and strength of cold mix asphalt. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 26687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanbara, H.K.; Ruddock, F.M.; Atherton, W. Airfield and Highway Pavements 2017. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Highway Pavements and Airfield Technology 2017, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 27–30 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Wahed, T.; Dulaimi, A.; Shanbara, H.K.; Al Nageim, H. The Impact of Cement Kiln Dust and Cement on Cold Mix Asphalt Characteristics at Different Climate. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Nageim, H.; Dulaimi, A.; Ruddock, F.; Seton, L. Development of a new cementitious filler for use in fast-curing cold binder course in pavement application. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Cement Microscopy, Lyon, France, 17–21 April 2016; pp. 167–180. [Google Scholar]
- Day, D.; Lancaster, I.M.; McKay, D. Emulsion cold mix asphalt in the UK: A decade of site and laboratory experience. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. (Engl. Ed.) 2019, 6, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanaya, I.N.A. Improving the Performance of Cold Bituminous Emulsion Mixtures Incorporating Waste Materials. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Leeds, Leeds, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.; Jiang, W.; Ye, W.; Shan, J.; Wang, Z. Effect of cement and emulsified asphalt contents on the performance of cement-emulsified asphalt mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 220, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miljković, M.; Radenberg, M.; Fang, X.; Lura, P. Influence of emulsifier content on cement hydration and mechanical performance of bitumen emulsion mortar. Mater. Struct. 2017, 50, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Liang, D. Effect of mass ratio of asphalt to cement on the properties of cement modified asphalt emulsion mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 134, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Liu, B.; Tan, J.; Dai, J.; Chen, J.; Ji, R. Experimental Studies and Microstructure Analysis for Rapid-Hardening Cement Emulsified Asphalt Mortar. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. Asce 2020, 146, 04020130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Tan, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J. Demulsification process of asphalt emulsion in fresh cement-asphalt emulsion paste. Mater. Struct. 2015, 48, 3875–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Zhou, J.; Yang, Z.; Yuan, Q.; Que, Y. Interaction between cement and asphalt emulsion and its influences on asphalt emulsion demulsification, cement hydration and rheology. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 329, 127220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercado, R.A.; Sadtler, V.; Marchal, P.; Choplin, L.; Salager, J.L. Heteroflocculation of a cationic oil-in-water emulsion resulting from Fontainebleau’s sandstone powder addition as a model for asphalt emulsion breakup. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 11688–11694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Tan, Y.; Corr, D.J.; Shah, S.P. Investigation on the mixing stability of asphalt emulsion with cement through viscosity. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2016, 28, 04016149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherkhani, H.; Firoozei, F.; Bolouri Bazaz, J. Evaluation of the mechanical properties of the cement treated cold-in-place recycled asphalt mixtures. Int. J. Transp. Eng. 2016, 3, 301–312. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.; Tan, Y. Interaction between asphalt and mineral fillers and its correlation to mastics’ viscoelasticity. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2021, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Lu, D.; Ma, R.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Yan, X. Effects of cement contents on the performance of cement asphalt emulsion mixtures with rapidly developed early-age strength. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 244, 118365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulaimi, A.; Al Nageim, H.; Ruddock, F.; Seton, L. Microanalysis of Alkali-Activated Binary Blended Cementitious Filler in a Novel Cold Binder Course Mixture. In Proceedings of the The 38th International Conference on Cement Microscopy, Lyon, France, 17–21 April 2016; pp. 189–205. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Hong, J.; Zhu, X.; Yang, D.; Bai, Y.; Liu, J.; Miao, C. Retardation mechanism of anionic asphalt emulsion on the hydration of Portland cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 163, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayar, P. Effects of additives on the mechanical performance in recycled mixtures with bitumen emulsion: An overview. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 178, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda López, M.A.; Fedrigo, W.; Kleinert, T.R.; Matuella, M.F.; Núñez, W.P.; Ceratti, J.A.P. Flexural fatigue evaluation of cement-treated mixtures of reclaimed asphalt pavement and crushed aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 158, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Li, H.; Han, B. The rheological properties and mechanisms of cement asphalt emulsion paste with different charge types of emulsion. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 147, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, W.; Christodoulou, C.; Goodier, C.; Austin, S.; Dunne, D. Durability performance of sustainable structural concrete: Effect of coarse crushed concrete aggregate on rapid chloride migration and accelerated corrosion. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 155, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Leng, Z.; Li, F.; Zhu, H.; Bao, S. Early-age strength and long-term performance of asphalt emulsion cold recycled mixes with various cement contents. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 137, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, H.; Guo, H.; Wu, C.; Wei, C. Effect of gradations on the final and long-term performance of asphalt emulsion cold recycled mixture. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 217, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Wang, Y.; Leng, Z.; Zhong, J. Influence of ternary blended cementitious fillers in a cold mix asphalt mixture. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 318, 128421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S. Effect of curing conditions on properties of cement asphalt emulsion mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 164, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dołżycki, B.; Jaczewski, M.; Szydłowski, C. The long-term properties of mineral-cement-emulsion mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 156, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulaimi, A.; Nageim, H.A.; Ruddock, F.; Seton, L. Laboratory studies to examine the properties of a novel cold-asphalt concrete binder course mixture containing binary blended cementitious filler. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2017, 29, 04017139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, C.; Bahia, H.U. Development of a volumetric mix design protocol for dense-graded cold mix asphalt. Journal of Transportation Engineering, Part B: Pavements 2018, 144, 04018039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Cao, X.; Xi, W.; Wei, W. Prediction model of compaction process parameters for pavement of cement emulsified asphalt mixture based on effective compaction work. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 280, 122403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PD 6691:2010; Guidance on the Use of BS EN 13108: Bituminous Mixtures–Material Specifications. BSI: London, UK, 2010.
- BS EN 933-1; Tests for Geometrical Properties of Aggregates: Part 1. Determination of Particle Size Distribution. Sieving Method. British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2021.
- EN 1426:2015; BS EN 1426: Bitumen and Bituminous Binders—Determination of Needle Penetration. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2015.
- EN 1428:2012; BS EN 1428: Bitumen and Bituminous Binders—Determination of Water Content in Bituminous Emulsions—Azeotropic Distillation Method. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2012.
- EN 1430:2009; BS EN 1430: Bitumen and Bituminous Binders—Determination of Particle Polarity of Bituminous Emulsions. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2009.
- EN 1427:2015; BS EN 1427: Bitumen and Bituminous Binders—Determination of the Softening Point—Ring and Ball Method. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2015.
- EN 13614:2021; BS EN13614: Bitumen and Bituminous Binders—Determination of Adhesivity of Bituminous Emulsions by Water Immersion Test. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2021.
- Asphalt Institute. Asphalt Cold Mix Manual, Manual Series No. 14(MS-14), 3rd ed.; Asphalt Institute: Lexington, KY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Habeeb, Z.H.; Al-Hdabi, A. Cold Asphalt Mixtures Characteristics with Cement and Sugar Industry Waste Material as Mineral Filler. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1090, 012137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BS EN 12697: Part 26; Bituminous Mixtures-Test Methods for Hot Mix Asphalt- Stiffness. British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2012.
- Li, R.; Leng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zou, F. Characterization and correlation analysis of mechanical properties and electrical resistance of asphalt emulsion cold-mix asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 263, 119974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Bahia, H. Distribution of mortar film thickness and its relationship to mixture cracking resistance. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2020, 23, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BS EN 12697: Part 12; Bituminous Mixtures-Test Methods for Hot Mix Asphalt-Determination of the Water Sensitivity of Bituminous Specimens. British Standard Institution: London, UK, 2008.
- Singh, B.; Jain, S. Effect of lime and cement fillers on moisture susceptibility of cold mix asphalt. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2022, 23, 2433–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dołżycki, B.; Jaczewski, M.; Szydłowski, C. The influence of binding agents on stiffness of mineral-cement-emulsion mixtures. Procedia Eng. 2017, 172, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Yang, W.; Chen, J.; Han, B. Effect of Superplasticizer and Wetting Agent on Pavement Properties of Cold Recycled Mixture with Bitumen Emulsion and Cement. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2020, 32, 04020136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Yuan, J.; Chen, X.; Ma, X. Reduction of moisture susceptibility of cold asphalt mixture with Portland cement and bentonite nanoclay additives. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 176, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadykova, A.Y.; Strelets, L.A.; Ilyin, S.O. Infrared Spectral Classification of Natural Bitumens for Their Rheological and Thermophysical Characterization. Molecules 2023, 28, 2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, Z.; Xu, G.; Shi, C. Evaluation of aging behaviors of asphalt binders through different rheological indices. Fuel 2018, 221, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qian, Z.; Hu, H. Thermal field characteristic analysis of steel bridge deck during high-temperature asphalt pavement paving. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2016, 20, 2811–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Ma, Y.; Ye, K.; Huang, S. Analysis of high-temperature performance of polymer-modified asphalts through molecular dynamics simulations and experiments. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 350, 128903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Jiang, K.; Li, H. High-temperature stability of asphalt mixture with the influence of styrene butadiene styrene. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 43, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, K.; Sun, M.; Zhang, M.; Qin, Y.; Li, Y. Interfacial and mechanical performance of grouted open-graded asphalt concrete with latex modified cement mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 234, 117394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhu, H.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, F.; Ye, F.; Li, P.; Zhang, X.; Dai, Z.; Bai, Y.; Huang, B. A state-of-art review on development and progress of backfill grouting materials for shield tunneling. Dev. Built Environ. 2023, 16, 100250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadique, M.; Al-Nageim, H. Hydration Kinetics of a Low Carbon Cementitious Material Produced by Physico-Chemical Activation of High Calcium Fly Ash. J. Adv. Concr. Technol. 2012, 10, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sieve Size (mm) | % Passing (Specification Limits) | % Passing (Midpoint of the Specification Limits) |
|---|---|---|
| 14 | 100 | 100 |
| 10 | 77–83 | 80 |
| 6.3 | 52–58 | 55 |
| 2 | 25–31 | 28 |
| 1 | 14–26 | 20 |
| 0.063 | 6 | 6 |
| Properties | Value |
|---|---|
| Coarse aggregates | |
| Water absorption (%) | 0.7 |
| Bulk specific gravity (g/cm3) | 2.60 |
| Apparent specific gravity (g/cm3) | 2.65 |
| Fine aggregates | |
| Water absorption (%) | 1.5 |
| Bulk specific gravity (g/cm3) | 2.53 |
| Apparent specific gravity (g/cm3) | 2.64 |
| Properties | Bitumen Emulsion | Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Cationic | |
| Appearance | Black to dark brown liquid | |
| Base bitumen Penetration, 0.1 mm | 50 | EN 1426 [43] |
| Viscosity—Efflux time 4 mm at 50 °C, s | 15–70 | |
| Bitumen content, % | 50 | EN 1428 [44] |
| Particle surface electric charge | positive | EN 1430 [45] |
| Boiling Point, °C | 100 | |
| Softening Point, °C | 50 | EN 1427 [46] |
| Adhesiveness | ≤90% | EN 13614 [47] |
| Density, g/cm3 | 1.016 |
| Mix ID | Limestone, % | OPC, % | PMWC | Bitumen Emulsion, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% OPC | 6% | 0% | 3% | 12.5% |
| 1.5% OPC | 4.5% | 1.5% | 3% | 12.5% |
| 3% OPC | 3% | 3% | 3% | 12.5% |
| 4.5% OPC | 1.5% | 4.5% | 3% | 12.5% |
| 6% OPC | 0% | 6% | 3% | 12.5% |
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Rise time (ms) | 124 ± 4 |
| Transient peak horizontal deformation (μm) | 5 |
| Loading time (s) | 3–300 |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.35 |
| No. of test plus | 5 |
| No. of conditioning plus | 10 |
| Test temperature (°C) | 20 ± 0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dulaimi, A.; Kadhim, Y.N.; Quraishy, Q.A.A.; Hawesah, H.A.; Ribeiro, T.P.; Bernardo, L.F.A. Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of High-Performance Cold Mix Asphalt Modified with Portland Cement. CivilEng 2025, 6, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/civileng6030046
Dulaimi A, Kadhim YN, Quraishy QAA, Hawesah HA, Ribeiro TP, Bernardo LFA. Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of High-Performance Cold Mix Asphalt Modified with Portland Cement. CivilEng. 2025; 6(3):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/civileng6030046
Chicago/Turabian StyleDulaimi, Anmar, Yasir N. Kadhim, Qassim Ali Al Quraishy, Hayder Al Hawesah, Tiago Pinto Ribeiro, and Luís Filipe Almeida Bernardo. 2025. "Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of High-Performance Cold Mix Asphalt Modified with Portland Cement" CivilEng 6, no. 3: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/civileng6030046
APA StyleDulaimi, A., Kadhim, Y. N., Quraishy, Q. A. A., Hawesah, H. A., Ribeiro, T. P., & Bernardo, L. F. A. (2025). Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of High-Performance Cold Mix Asphalt Modified with Portland Cement. CivilEng, 6(3), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/civileng6030046










