The Use of Waste Fillers in Asphalt Mixtures: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Asphalt–Filler Interaction and the Characteristics of Fillers
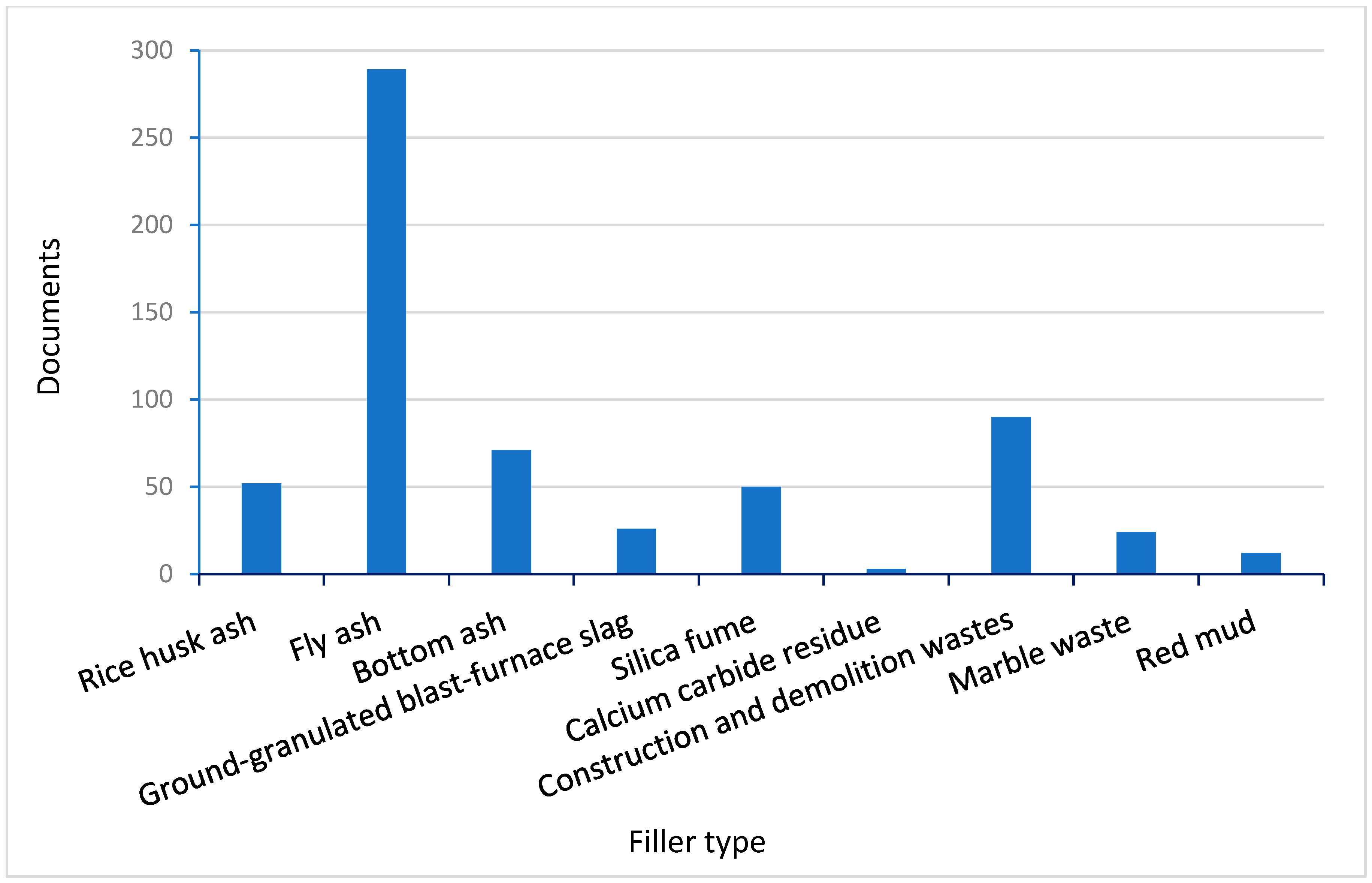
4. The Use of Various Waste Fillers
4.1. Rice Husk Ash (RHA)
4.2. Fly Ash (FA)
4.3. Bottom Ash (BA)
4.4. Waste Slags
4.5. Silica Fume (SF)
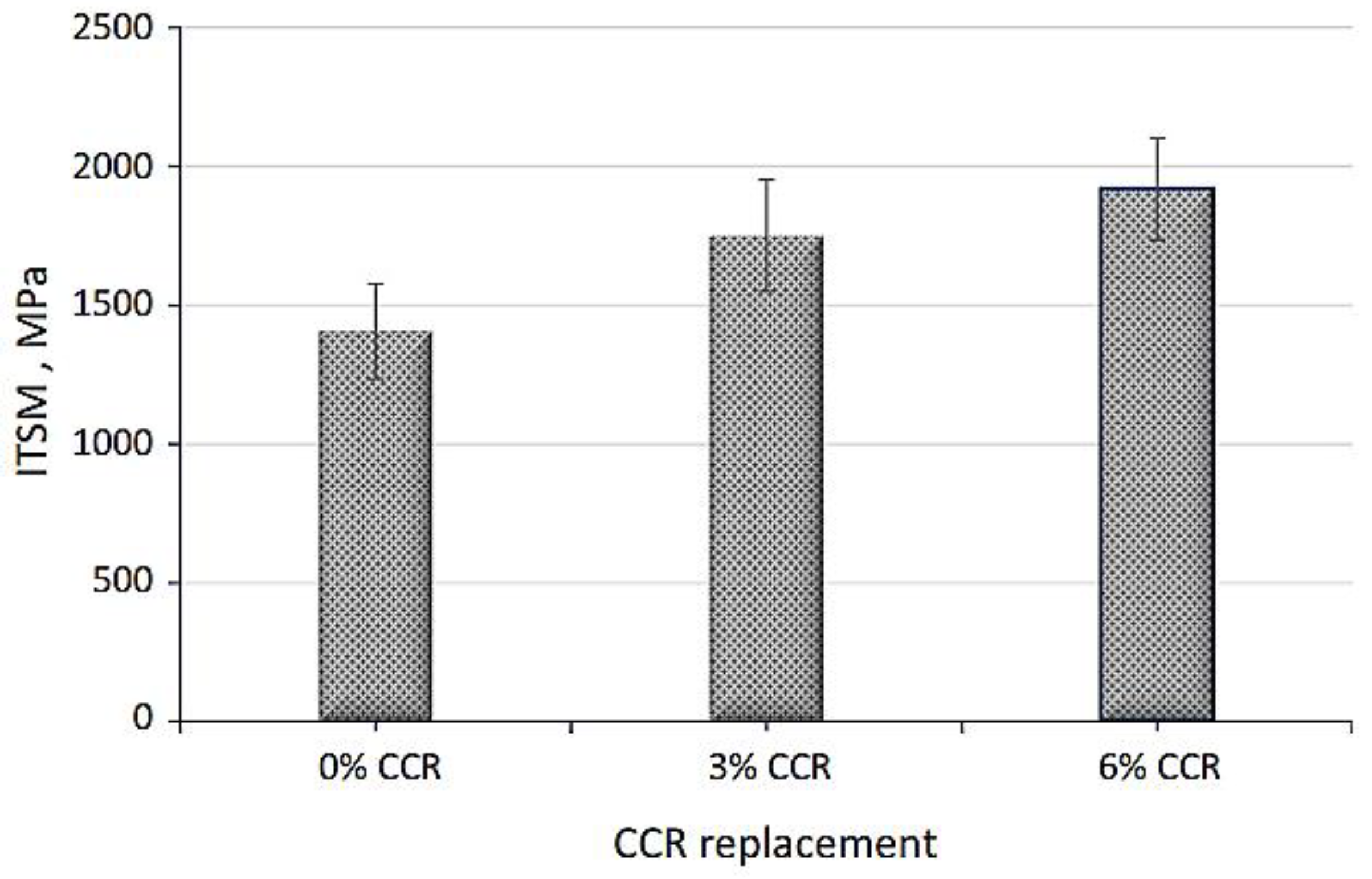
4.6. Calcium Carbide Residue (CCR)
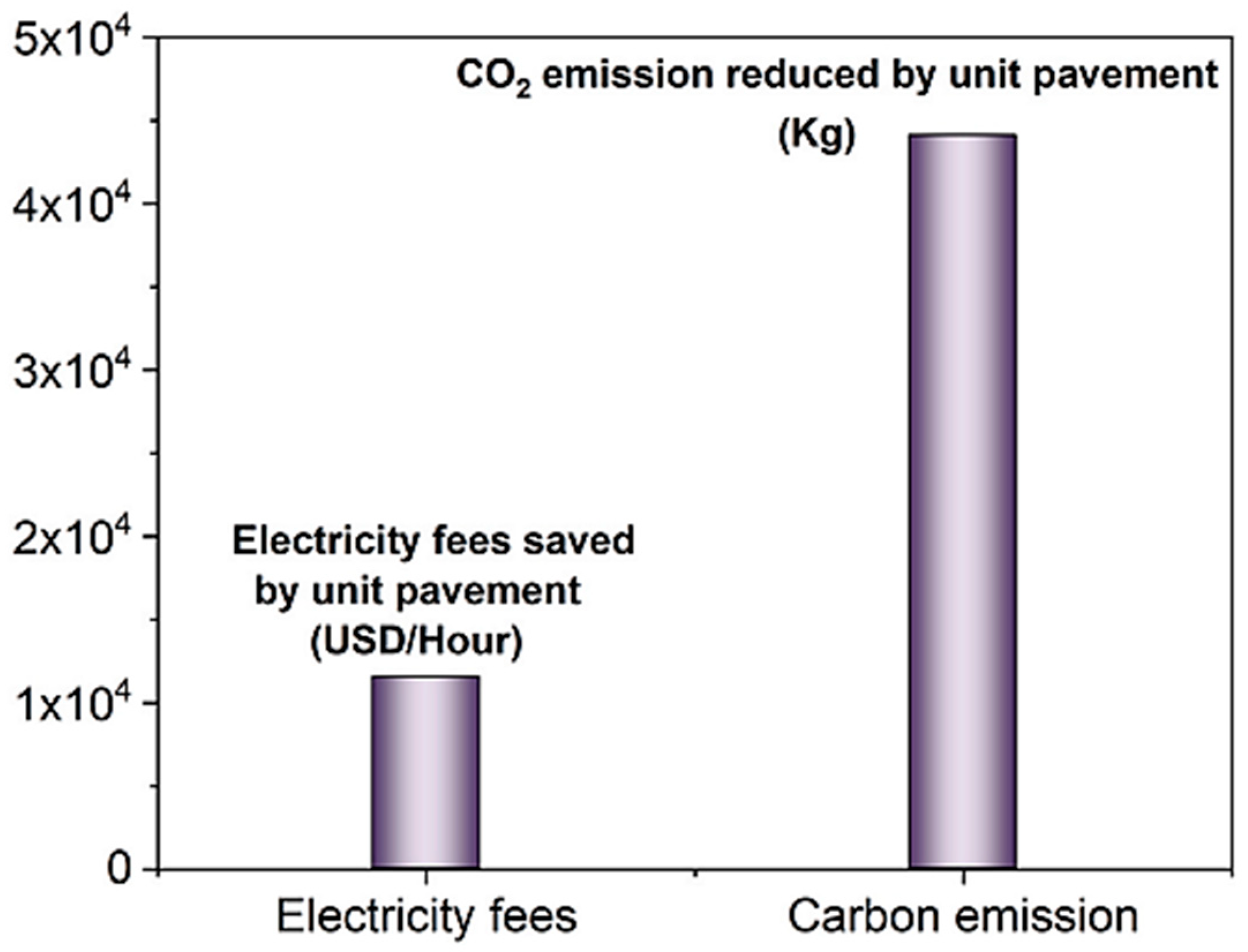
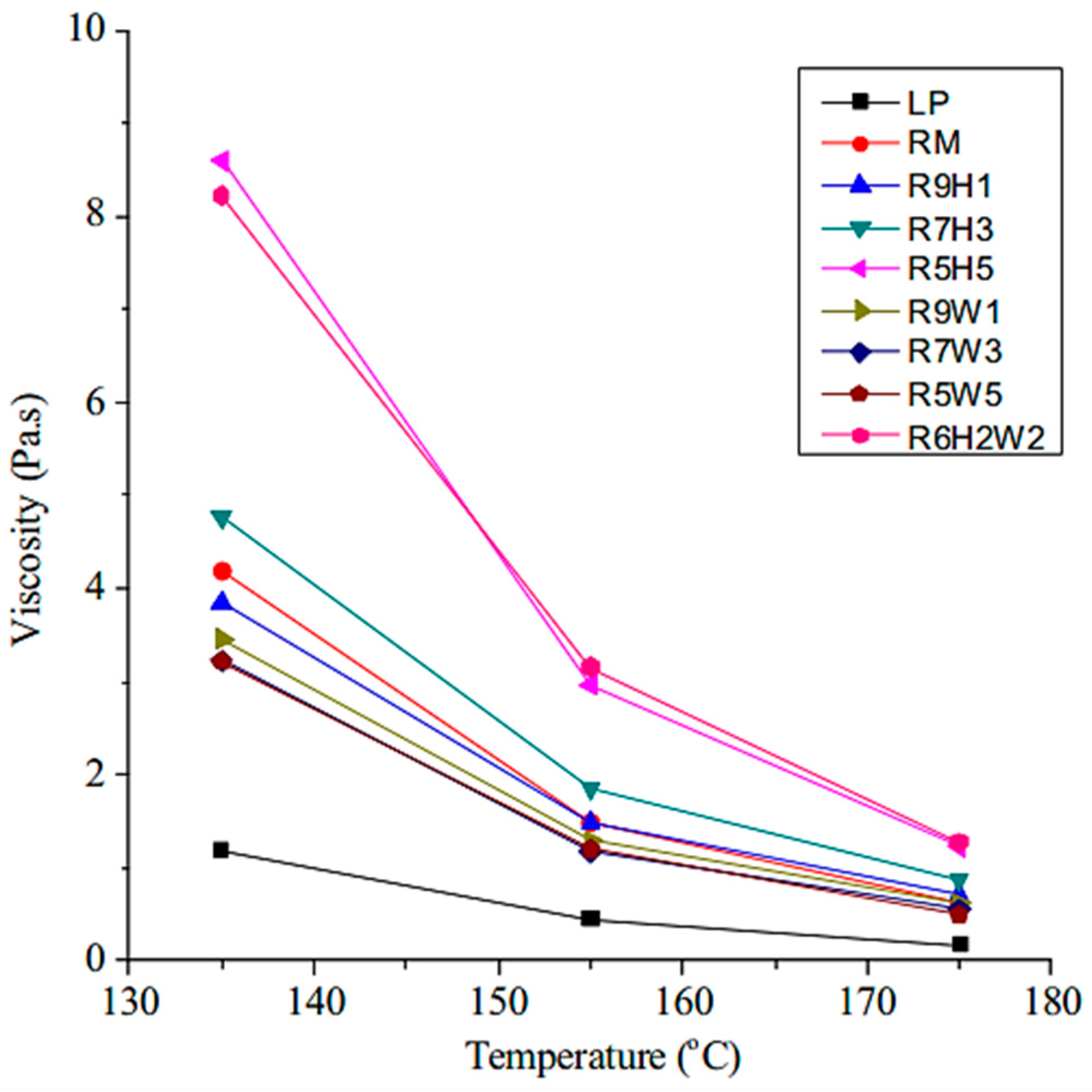
4.7. Microwave-Sensitive Additives (MSAs)
4.8. Construction and Demolition Wastes
4.9. Marble Waste (MW)
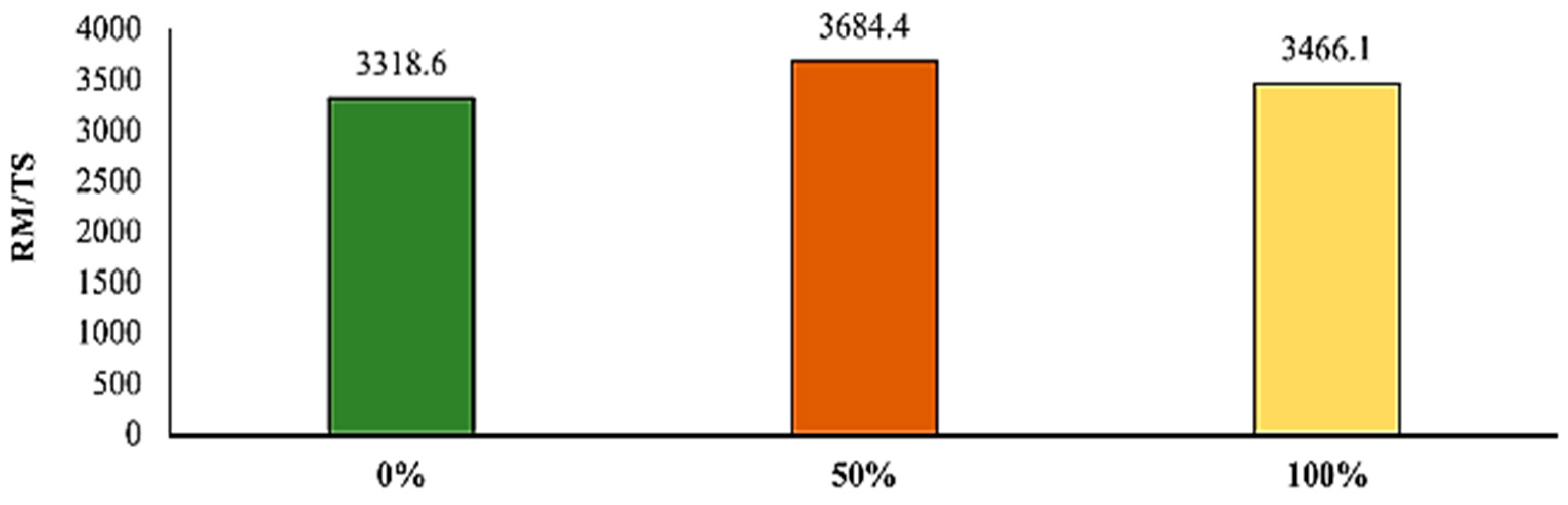
4.10. Red Mud (RM)
5. Conclusions
6. Future Perspectives
- The content of waste filler in asphalt mixtures should be optimized to achieve the desired performance characteristics while maximizing cost savings and environmental benefits.
- The use of new types of waste fillers, such as coconut shell powder, textile fibres, palm oil fuel ash, copper slag, sewage sludge ash, recycled plastic, crumb rubber, and wood ash, should be explored to further diversify the range of materials available for asphalt mixtures.
- Sustainable practices for incorporating waste fillers into asphalt mixtures, including the development of guidelines and standards for the use of waste materials in asphalt construction, are needed.
- Conduct comprehensive life cycle assessments to evaluate the environmental impact of using waste fillers in asphalt mixtures compared with traditional materials.
- Develop performance-based specifications for asphalt mixtures containing waste fillers to ensure long-term performance and durability.
- Promote the market acceptance and implementation of asphalt mixtures containing waste fillers through education, outreach, and collaboration with industry stakeholders.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, C.; Wu, W.; Han, W. Investigation of lignin as an alternative extender of bitumen for asphalt pavements. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 283, 124663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, F.D.B.; Maraqa, M.A.; Chowdhury, R.; Mauga, T.; Alzard, M. Greenhouse gas emissions associated with road transport projects: Current status, benchmarking, and assessment tools. Transp. Res. Procedia 2020, 48, 2018–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lendvai, L. Lignocellulosic agro-residue/polylactic acid (PLA) biocomposites: Rapeseed straw as a sustainable filler. Clean. Mater. 2023, 9, 100196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porto, M.; Caputo, P.; Loise, V.; Abe, A.A.; Tarsi, G.; Sangiorgi, C.; Gallo, F.; Oliviero Rossi, C. Preliminary Study on New Alternative Binders through Re-Refined Engine Oil Bottoms (REOBs) and Industrial By-Product Additives. Molecules 2021, 26, 7269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penki, R.; Rout, S.K. Next-generation bitumen: A review on challenges and recent developments in bio-bitumen preparation and usage. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023, 13, 9583–9600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schipfer, F.; Kranzl, L.; Leclère, D.; Sylvain, L.; Forsell, N.; Valin, H. Advanced biomaterials scenarios for the EU28 up to 2050 and their respective biomass demand. Biomass Bioenergy 2017, 96, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Nageim, H.; Dulaimi, A.; Ruddock, F.; Seton, L. Development of a new cementitious filler for use in fast-curing cold binder course in pavement application. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Cement Microscopy, Lyon, France, 17–21 April 2016; pp. 167–180. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, C. The Modern Asphalt Pavement; J. Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1907. [Google Scholar]
- Dulaimi, A.; Al Nageim, H.; Ruddock, F.; Seton, L. Assessment the Performance of Cold Bituminous Emulsion Mixtures with Cement and Supplementary Cementitious Material for Binder Course Mixture. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Cement Microscopy, Lyon, France, 17–21 April 2016; pp. 283–296. [Google Scholar]
- Einstein, A. Berichtigung zu meiner Arbeit: “Eine neue Bestimmung der Moleküldimensionen”. Ann. Der Phys. 1911, 339, 591–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, V.; Freire, A.C.; Quaresma, L.; Micaelo, R. Influence of the geometrical and physical properties of filler in the filler–bitumen interaction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 76, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Choudhary, R. Performance Characteristics of Bituminous Concrete with Industrial Wastes as Filler. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2013, 25, 1666–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Al-Qadi, I.L.; Faheem, A.F.; Bahia, H.U.; Yang, S.-H.; Reinke, G.H. Effect of mineral filler characteristics on asphalt mastic and mixture rutting potential. Transp. Res. Rec. 2011, 2208, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, J.; Kumar, B.; Gupta, A. Laboratory evaluation on recycling waste industrial glass powder as mineral filler in hot mix asphalt. In Proceedings of the Civil Engineering Conference—Innovation for Sustainability, Hamirpur, India, 9–10 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Wahed, T.; Dulaimi, A.; Shanbara, H.K.; Al Nageim, H. The Impact of Cement Kiln Dust and Cement on Cold Mix Asphalt Characteristics at Different Climate. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diab, A.; Enieb, M. Investigating influence of mineral filler at asphalt mixture and mastic scales. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2018, 11, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangiorgi, C.; Tataranni, P.; Mazzotta, F.; Simone, A.; Vignali, V.; Lantieri, C. Alternative Fillers for the Production of Bituminous Mixtures: A Screening Investigation on Waste Powders. Coatings 2017, 7, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.J. Performance evaluation of the use of tire-derived fuel fly ash as mineral filler in hot mix asphalt concrete. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2020, 7, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzun, İ.; Terzi, S. Evaluation of andesite waste as mineral filler in asphaltic concrete mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 31, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasilewska, M.; Małaszkiewicz, D.; Ignatiuk, N. Evaluation of Different Mineral Filler Aggregates for Asphalt Mixtures. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 245, 022042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Jia, Y.; Yang, T.; Du, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y. Fatigue performance evaluation of asphalt mixtures based on energy-controlled loading mode. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 157, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtar, N.; Mohd Hasan, M.R.; Shariff, K.A.; Mohd Ghazali, M.F.H.; Sindi, W.; Putra Jaya, R. Evaluating and quantifying the variations and sensitivity in asphalt-filler interaction indices. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2023, 132, 103480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Guo, M. Interfacial thickness and interaction between asphalt and mineral fillers. Mater. Struct. 2014, 47, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesami, E.; Birgisson, B.; Kringos, N. Numerical and experimental evaluation of the influence of the filler–bitumen interface in mastics. Mater. Struct. 2014, 47, 1325–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Jia, Y.; Pan, Y.; Yang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J. Quantitative comparison of evaluation indices for asphalt–filler interaction ability within filler critical volume fraction. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2020, 21, 906–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunnicliff, D.G. A review of mineral filler. J. Assoc. Asph. Paving Technol. 1962, 31, 118–150. [Google Scholar]
- Faheem, A.F.; Bahia, H.U. Modelling of Asphalt Mastic in Terms of Filler-Bitumen Interaction. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2010, 11, 281–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, M.A.; Chughtai, A.; Ahmad, J.; Ahmad, R.; Majeed, U.; Khan, I. Theory of adhesion and its practical implications. J. Fac. Eng. Technol. 2008, 2007, 21–45. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.; Chen, H.; Kuang, D.; Song, L.; Wang, L. Effect of chemical composition of aggregate on interfacial adhesion property between aggregate and asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 146, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Xu, L.; Deng, H.; Deng, D.; Ma, C.; Liu, W. Characterization of thermal, high-temperature rheological and fatigue properties of asphalt mastic containing fly ash cenosphere. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 233, 117345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensley, E.K. Multilayer adsorption with molecular orientation of asphalt on mineral aggregate and other substrates. J. Appl. Chem. Biotechnol. 1975, 25, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Lee, J.; Patankar, N.A. Contact angle hysteresis on rough hydrophobic surfaces. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2004, 248, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Jiang, W.; Yuan, D.; Lu, R.; Shan, J.; Xiao, J.; Ogbon, A.W. A review of asphalt-filler interaction: Mechanisms, evaluation methods, and influencing factors. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 299, 124279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sun, C.; Li, P.; Liang, M.; Jiang, H.; Yao, Z. Experimental study on rheological properties and moisture susceptibility of asphalt mastic containing red mud waste as a filler substitute. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 211, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtar, N.; Mohd Hasan, M.R.; Mohd Ghazali, M.F.H.; Mohd Zin, Z.; Shariff, K.A.; Sani, A. Influence of concentration and packing of filler particles on the stiffening effect and shearing behaviour of asphalt mastic. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 295, 123660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahan, H.M. Influence of mineral filler-asphalt ratio on asphalt mixture performance. Eng. Sci. 2013, 21, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchetto, H.; Miró, R.; Pérez-Jiménez, F.; Martínez, A.H. Effect of Calcareous Fillers on Bituminous Mix Aging. Transp. Res. Rec. 2007, 1998, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Merzah, S.; Al-Busaltan, S.; Nageim, H.A. Characterizing Cold Bituminous Emulsion Mixtures Comprised of Palm Leaf Ash. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2019, 31, 04019069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulaimi, A.; Al Nageim, H.; Ruddock, F.; Seton, L. Microanalysis of Alkali-Activated Binary Blended Cementitious Filler in a Novel Cold Binder Course Mixture. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Cement Microscopy, Lyon, France, 17–21 April 2016; pp. 189–205. [Google Scholar]
- Yaro, N.S.A.; Sutanto, M.H.; Habib, N.Z.; Napiah, M.; Usman, A.; Jagaba, A.H.; Al-Sabaeei, A.M. Modeling and optimization of asphalt content, waste palm oil clinker powder and waste rice straw ash for sustainable asphalt paving employing response surface methodology: A pilot study. Clean. Mater. 2023, 8, 100187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Shen, J.; Guo, P. High titanium heavy slag powder as a sustainability filler and its influence on the performance of asphalt mortar. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 5586–5599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, G.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, L.; Cui, P.; Kong, D.; Xue, Y. Characteristics of steel slag filler and its influence on rheological properties of asphalt mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 201, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Nageim, H.; Dulaimi, A.; Al-Busaltan, S.; Kadhim, M.A.; Al-Khuzaie, A.; Seton, L.; Croft, J.; Drake, J. The development of an eco-friendly cold mix asphalt using wastewater sludge ash. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 329, 117015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulaimi, A.; Shanbara, H.K.; Jafer, H.; Sadique, M. An evaluation of the performance of hot mix asphalt containing calcium carbide residue as a filler. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 261, 119918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.; Suresh, M.; Pal, M. Utilization of fly ash and glass powder as fillers in steel slag asphalt mixtures. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2021, 15, e00672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargın, Ş.; Saltan, M.; Morova, N.; Serin, S.; Terzi, S. Evaluation of rice husk ash as filler in hot mix asphalt concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 48, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadhansyah, P.J.; Irwan, R.N.; Idris, A.M.; Ezree, A.M.; Khatijah, A.B.S.; Norhidayah, A.H.; Haryati, Y. Stability and voids properties of hot mix asphalt containing black rice husk ash. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 244, 012044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahami, S.A.; Arabani, M.; Foroutan Mirhosseini, A. Usage of two biomass ashes as filler in hot mix asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 170, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hdabi, A. Laboratory investigation on the properties of asphalt concrete mixture with Rice Husk Ash as filler. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 126, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helal, M.M.; Mahdy, H.A.-e.; Ibrahim, M.F. Effect of Rice Husk Ash on the Performance of Hot Asphalt Mixes. Bull. Fac. Eng. Mansoura Univ. 2020, 45, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameli, A.; Babagoli, R.; Norouzi, N.; Jalali, F.; Poorheydari Mamaghani, F. Laboratory evaluation of the effect of coal waste ash (CWA) and rice husk ash (RHA) on performance of asphalt mastics and Stone matrix asphalt (SMA) mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 236, 117557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, R.; Karmakar, S.; Kumar Roy, T. Experimental evaluation of rice husk ash and fly ash as alternative fillers in hot-mix asphalt. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2019, 20, 979–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, A.M.; Sutanto, M.H.; Yusoff, N.I.M.; Memon, R.A.; Khan, M.I.; Al-Sabaeei, A.M. Rheological modeling and microstructural evaluation of oily sludge modified bitumen. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 18, e02039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, M.; Moghaddam, T.B.; Karim, M.R.; Baaj, H. Analysis of fatigue properties of unmodified and polyethylene terephthalate modified asphalt mixtures using response surface methodology. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2015, 58, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmagid, A.A.A.; Qiu, Y.; Yang, E. Using agricultural residue sustainably: Enhancing asphalt properties with rice husk ash and analyzing its mixture performance using response surface methodology. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 19, e02476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolev, K.; Flores Vivian, I.; Saha, R.; Wasiuddin, N.M.; Saltibus, N.E. The effect of fly ash on the rheological properties of bituminous materials. Fuel 2014, 116, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, R.; Roy, T.K. Effect of using fly ash as alternative filler in hot mix asphalt. Perspect. Sci. 2016, 8, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Li, L.; Zheng k Ge, D. Research on properties of bitumen mortar containing municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 218, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, F.; Veropalumbo, R.; Pontoni, L.; Oreto, C.; Biancardo, S.A.; Viscione, N.; Pirozzi, F.; Race, M. Sustainable asphalt mastics made up recycling waste as filler. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 301, 113826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Yang, Y. Experimental investigation on the influence of interfacial effects of limestone and fly ash filler particles in asphalt binder on mastic aging behaviors. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 290, 123184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, E.; Mantovani, L.; Tribaudino, M.; Montepara, A. Reuse of stabilized municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash in asphalt mixtures. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04018157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hdabi, A.; Nageim, H.A.; Ruddock, F.M.; Seton, L. Development of Sustainable Cold Rolled Surface Course Asphalt Mixtures Using Waste Fly Ash and Silica Fume. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2014, 26, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulaimi, A.; Al Nageim, H.; Ruddock, F.; Seton, L. New developments with cold asphalt concrete binder course mixtures containing binary blended cementitious filler (BBCF). Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 124, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolev, K.; Flores, I.; Bohler, J.D.; Faheem, A.; Covi, A. Application of fly ash in ASHphalt concrete: From challenges to opportunities. In Proceedings of the World of Coal Ash Conference, Lexington, KY, USA, 22–25 April 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, F.; Veropalumbo, R.; Oreto, C.; Cassese, D.; Papa, B.; Malvezzi, S. Reusing bottom ash as a filler from a Waste-to-Energy plant for making asphalt mastics. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, J.; Kumar, B.; Gupta, A. Utilization of solid waste materials as alternative fillers in asphalt mixes: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 234, 117271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.M.; Mertens, G.; Salman, M.; Cizer, Ö.; Van Gerven, T. Comparative study of ageing, heat treatment and accelerated carbonation for stabilization of municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash in view of reducing regulated heavy metal/metalloid leaching. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 128, 807–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhu, X.; Li, L.; Wang, H. Effect of the interfacial zone on the tensile-damage behavior of an asphalt mixture containing MSWI bottom ash aggregates. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2017, 29, 04016269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.-L.; Chen, S.-H.; Lin, D.-F.; Cai, X.-R. Use of incinerator bottom ash in open-graded asphalt concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 149, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jattak, Z.A.; Hassan, N.A.; Mohd Satar, M.K.I. Moisture susceptibility and environmental impact of warm mix asphalt containing bottom ash. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2021, 15, e00636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.K. Marshall Properties of SDBC using Emulsion based Cold Mix Technology. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2018, 6, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, A.I.; Mohammed, M.K.; Thom, N.; Parry, T. Characterisation of high-performance cold bitumen emulsion mixtures for surface courses. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2018, 19, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulaimi, A.; Al Nageim, H.; Ruddock, F.; Seton, L. A novel cold asphalt concrete mixture for heavily trafficked binder course. Int. J. Civ. Environ. Struct. Constr. Archit. Eng. 2015, 9, 734–738. [Google Scholar]
- Borkakoti, D. Strength and Stability Characteristics of Semi Dense Bituminous Concrete by using Cold Mix Design. Int. J. Innov. Eng. Technol. 2015, 6, 157–164. [Google Scholar]
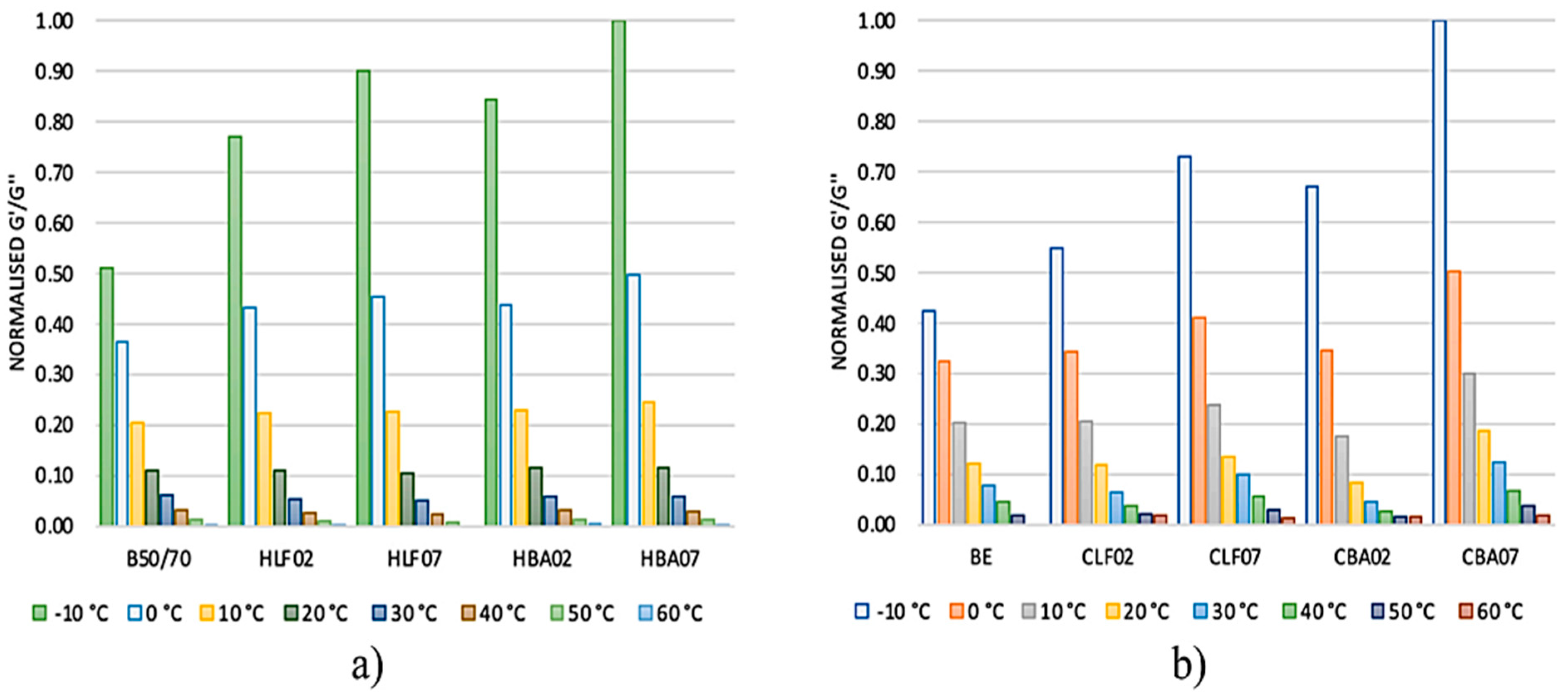
- Dulaimi, A.; Shanbara, H.K.; Al-Rifaie, A. The mechanical evaluation of cold asphalt emulsion mixtures using a new cementitious material comprising ground-granulated blast-furnace slag and a calcium carbide residue. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 250, 118808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocci, E. Use of ladle furnace slag as filler in hot asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 161, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberto, A.; Mantovani, L.; Romeo, E.; Tebaldi, G.; Montepara, A.; Tribaudino, M. Re-using Ladle Furnace Steel slags as filler in asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 323, 126420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-López, V.; Manso, J.M.; Cuesta, I.I.; González, J.J. The long-term accelerated expansion of various ladle-furnace basic slags and their soil-stabilization applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 68, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasetto, M.; Baliello, A.; Pasquini, E.; Skaf, M.; Ortega-López, V. Performance-Based Characterization of Bituminous Mortars Prepared with Ladle Furnace Steel Slag. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaf, M.; Ortega-López, V.; Fuente-Alonso, J.A.; Santamaría, A.; Manso, J.M. Ladle furnace slag in asphalt mixes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 122, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Yang, C.; Xie, J.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Zhang, L. Investigation of Permanent Deformation Behavior of Steel Slag Asphalt Mixture under Indoor Simulation. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 2021, 8842077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberto, A.; Romeo, E.; Montepara, A.; Roncella, R. Effect of fillers and their fractional voids on fundamental fracture properties of asphalt mixtures and mastics. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2020, 21, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquini, E.; Giacomello, G.; Skaf, M.; Ortega-Lopez, V.; Manso, J.M.; Pasetto, M. Influence of the Production Temperature on the Optimization Process of Asphalt Mixes Prepared with Steel Slag Aggregates Only. In Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Asphalt Pavements & Environment (APE), Padua, Italy, 11–13 September 2019; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Roberto, A.; Bisanti, F.; Pizzati, M.; Mantovani, L.; Romeo, E.; Tebaldi, G. Stiffening effects of LFS slags reused as filler in asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 402, 132702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.C.P.; Franco de Carvalho, J.M.; Costa, L.C.B.; Andrade, H.D.; de Melo, T.V.; Ribeiro, J.C.L.; Pedroti, L.G.; Peixoto, R.A.F. Steel slags in cement-based composites: An ultimate review on characterization, applications and performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 291, 123265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Liu, L.; Feng, Y. Evaluation of Steel Slag Powder as Filler in Hot-Mix Asphalt Mixtures. Adv. Civ. Eng. Mater. 2018, 7, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarbay, E.W.; Azam, A.M.; El-Badawy, S.M. Waste materials and by-products as mineral fillers in asphalt mixtures. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2018, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, B.; Sha, A.; Barbieri, D.M.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, F. Microwave heating properties of steel slag asphalt mixture using a coupled electromagnetic and heat transfer model. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 291, 123248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Luo, J.; Yang, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Creep and fatigue properties of asphalt mastic with steel slag powder filler. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 18, e01743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, B.; Xie, J.; Xiao, Y. Effects of steel slag fillers on the rheological properties of asphalt mastic. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 145, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Chen, M.; Wu, S.; Xie, J.; Kong, D.; Qiao, Z.; Niu, C. Moisture Susceptibility Evaluation of Asphalt Mixtures Containing Steel Slag Powder as Filler. Materials 2019, 12, 3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Yan, T.; Muhammad, Y.; Li, J.; Qin, P.; Ling, L.; Rong, H.; Yang, X. Study on the performance and sustainability of modified waste crumb rubber and steel slag powder/SBS composite modified asphalt mastic. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 338, 130563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osuolale, O.M.; Arinkoola, A.O.; Olawuyi, O.A. Performance evaluation of bamboo leaf ash and steel slag powder as alternative filler in asphaltic mixes. J. Eng. Res. 2023, 11, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, A.I.M. Enhancing the Performance of cold Bitumen Emulsion Mixture Using Supplementary Cementitious Materials; University of Nottingham: Nottingham, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Busaltan, S.; Nageim, H.A.; Atherton, W.; Sharples, G.P. Mechanical Properties of an Upgrading Cold-Mix Asphalt Using Waste Materials. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2012, 24, 1484–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Busaltan, S. Development of New Cold Bituminous Mixtures for Road and Highway Pavements; School of Built Environment: Kensington, Australia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hanjitsuwan, S.; Phoo-ngernkham, T.; Damrongwiriyanupap, N. Comparative study using Portland cement and calcium carbide residue as a promoter in bottom ash geopolymer mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 133, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.M.; Ahmadi Dehaghi, E.; Behnood, A. Cracking features of asphalt mixtures under induced heating-healing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 324, 126625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Ye, F.; Cai, Y.; Birgisson, B.; Lee, K. Self-healing properties of ferrite-filled open-graded friction course (OGFC) asphalt mixture after moisture damage. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 232, 518–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanbakhsh, H.; Karimi, M.M.; Jahangiri, B.; Nejad, F.M. Induction heating and healing of carbon black modified asphalt concrete under microwave radiation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 174, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Polaczyk, P.; He, J.; Lu, H.; Xiao, R.; Huang, B. Dispersion, compatibility, and rheological properties of graphene-modified asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 350, 128886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.M.; Amani, S.; Jahanbakhsh, H.; Jahangiri, B.; Alavi, A.H. Induced heating-healing of conductive asphalt concrete as a sustainable repairing technique: A review. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2021, 4, 100188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wu, S.; Xie, J.; Amirkhanian, S.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, H.; Li, N.; et al. Enhanced induction heating and self-healing performance of recycled asphalt mixtures by incorporating steel slag. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 366, 132999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, T. Microwave heating uniformity, road performance and internal void characteristics of steel slag asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 353, 129155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Liu, W.; Wu, S. Analysis on factors affecting moisture stability of steel slag asphalt concrete using grey correlation method. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 397, 136490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, X. Utilizing original and activated coal gangue wastes as alternative mineral fillers in asphalt binder: Perspectives of rheological properties and asphalt-filler interaction ability. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 365, 130069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, J.; Peng, T.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, H.; Waqas, H.; Abdul, S.; Chen, K.; Zhou, Y. Moisture susceptibility and fatigue performance of asphalt binder modified by bone glue and coal fly ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 308, 125135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Jiang, X.; Leng, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wang, D.; Zhong, J. Dual responsive microwave heating-healing system in asphalt concrete incorporating coal gangue and functional aggregate. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 422, 138648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Jiang, X.; Leng, Z. Sustainable microwave-heating healing asphalt concrete fabricated with waste microwave-sensitive fillers. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 140343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Jing, H.; Jia, H.; Zhou, L.; Chen, H.; Zhang, L. Microwave self-healing characteristics of bituminous mixtures with different steel slag aggregate and waste ferrite filler. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 407, 133304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Luo, S. Engineering properties and microwave heating induced ice-melting performance of asphalt mixture with activated carbon powder filler. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 197, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Fu, C.; Jiang, X.; Chen, Z.; Qu, F.; Huo, Y.; Leng, Z.; Zhong, J. Sustainable microwave-heating healing asphalt concrete incorporating functional aggregates and waste ferrite. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2024, 129, 104117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Lin, J.; Wu, S.; Liu, C. Utilization of recycled brick powder as alternative filler in asphalt mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 1532–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuity, A.; Jayaprakasan, S.; Das, A. Laboratory investigation on volume proportioning scheme of mineral fillers in asphalt mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 68, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabani, M.; Tahami, S.A.; Taghipoor, M. Laboratory investigation of hot mix asphalt containing waste materials. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2017, 18, 713–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, V.; Freire, A.C.; Quaresma, L.; Micaelo, R. Evaluation of waste materials as alternative sources of filler in asphalt mixtures. Mater. Struct. 2017, 50, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, J.; Kumar, B.; Gupta, A. Effect of filler on the bitumen-aggregate adhesion in asphalt mix. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2020, 21, 1482–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, J.; Kumar, B.; Gupta, A. Potential utilization of construction wastes in asphalt pavements as fillers using ranking framework. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 277, 122262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghnejad, M.; Arabani, M.; Taghipoor, M. Predicting the impact of temperature and stress on the glasphalt mixtures’ rutting behavior. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2018, 11, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khateeb, G.G.; Khedaywi, T.S.; Irfaeya, M.F. Shear properties of waste glass-asphalt mastics. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2019, 12, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simone, A.; Mazzotta, F.; Eskandarsefat, S.; Sangiorgi, C.; Vignali, V.; Lantieri, C.; Dondi, G. Experimental application of waste glass powder filler in recycled dense-graded asphalt mixtures. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2019, 20, 592–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, M.; Marandi, S.M. Performance improvement of a crumb rubber modified bitumen using recycled glass powder. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2013, 14, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, H.; Fu, C.; Shi, S.; Liu, Q.; Xu, P.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, D.; Cheng, Y.; Jiang, L. Effect and mechanism of waste glass powder silane modification on water stability of asphalt mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 366, 130086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Medeiros, W.R.P.; de Medeiros Melo Neto, O.; Luz, P.M.S.G.; Oliveira, R.K.F.d.; Guedes, L.R. Utilizing marble and granite industry waste in asphalt mixtures for enhanced road performance and sustainability. J. Eng. Res. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, N.; Baldo, N.; Satyam, N.; Miani, M. Mechanical Characterization of Industrial Waste Materials as Mineral Fillers in Asphalt Mixes: Integrated Experimental and Machine Learning Analysis. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, D.; Khan, R.; Khan, M.T.; Alam, M.; Hassan, T. Performance of hot-mix asphalt using polymer-modified bitumen and marble dust as a filler. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2023, 10, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Yao, Z.; Wu, S.; Jiang, H.; Liang, M.; Qiao, Y. Environmental aspects and pavement properties of red mud waste as the replacement of mineral filler in asphalt mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 180, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, M.S.S.; Thives, L.P. Evaluation of red mud as filler in Brazilian dense graded asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 260, 119894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, P.; Liang, M.; Jiang, H.; Yao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yu, S. Utilization of red mud as an alternative mineral filler in asphalt mastics to replace natural limestone powder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 237, 117821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Filler | Oxides | Ref. | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Fe2O3 | Al2O3 | K2O | SO3 | CaO | MgO | P2O5 | Na2O | TiO2 | ||
| Rice husk ash | 74.89 | 1.33 | 1.06 | 6.09 | 1.21 | 2.89 | 1.96 | 6.05 | [40] | ||
| TDF fly ash | 25.40 | 5.59 | 4.03 | 0.76 | 36.40 | 0.57 | [18] | ||||
| HSP | 27.38 | 0.79 | 12.55 | - | 28.12 | 7.37 | 21.46 | [41] | |||
| SSF | 15.77 | 23.179 | 1.362 | 46.290 | 4.170 | 1.867 | [42] | ||||
| Silica fume | 98.212 | 0.00 | 0.348 | 0.812 | 0.221 | 0.264 | 0.161 | [43] | |||
| CCR | 14.08 | 0.00 | 0.90 | 0.20 | 0.77 | 81.84 | 0.77 | 1.32 | 0.12 | [44] | |
| FA | 61.44 | 6.87 | 28.31 | 0.37 | 0.15 | 0.46 | [45] | ||||
| GP | 74.54 | 0.26 | 1.49 | 8.76 | 13.93 | [45] | |||||
| Red mud | 18.19 | 17.54 | 8.03 | 0.40 | 0.90 | 44.64 | 1.34 | 0.26 | 3.21 | 4.81 | [34] |
| Materials | Cost/Tons | Binder Course | Wearing Course | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSP | BLA | QD | SSP | BLA | QD | ||
| Fine Aggregates/tons | #6500 ($14.1) | 23,510.50 ($51) | 23,510.50 ($51) | 23,510.50 ($51) | 24,596 ($53.35) | 24,596 ($53.35) | 24,596 ($53.35) |
| Coarse Aggregates/tons | #8000 ($17.4) | 50,576.00 ($109.71) | 50,576.00 ($109.71) | 50,576.00 ($109.71) | 20,896 ($45.33) | 20,896 ($45.33) | 20,896 ($45.33) |
| Quarry Dust (Control)/tons | #5800 ($12.6) | 0 | 0 | 3550 ($7.70) | 0 | 0 | 3271 ($7.10) |
| Bitumen/tons | #40,000 ($86.8) | 23,160.00 ($50.24) | 23,160.00 ($50.24) | 23,160.00 ($50.24) | 18,400 ($39.91) | 18,400 ($39.91) | 18,400 ($39.91) |
| SSP | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| BLA/tons | #0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.5% Processing (Naira/dollar per ton) | 500 (1.08) | 350 ($0.76) | 0 | 500 $(1.08) | 350 ($0.76) | 0 | |
| Cost (Naira/Dollar) per ton | 97,247 ($210.95) | 97,247 ($210.95) | 100,796.10 ($218.65) | 63,892 ($138.59 | 63,892 ($138.59) | 67,163 ($145.69) | |
| Total Cost (Naira/Dollar) per ton | 97,747 ($212.03) | 97,597 ($211.71) | 100,796.10 ($218.65) | 64,392 ($139.68) | 64,242 ($139.35) | 67,163 ($145.69) | |
| Cost savings (%) | 3.03 | 3.17 | 0 | 4.13 | 4.35 | 0 | |
| Test | SD | LD | GP | CD | BD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asphalt coverage (%) | 97 | 95 | 55 | 95 | 90 |
| Mixing time (seconds), at 160 ± 5 °C | 94 | 101 | 154 | 107 | 110 |
| Indirect tensile strength (kPa), at 25 °C | 3124 | 3668 | 3452 | 3506 | 2876 |
| Fatigue life (cycles), at 25 °C | 6036 | 7022 | 6432 | 6746 | 6221 |
| Tensile strength ratio (%) | 89.26 | 86.85 | 17.65 | 85.27 | 81.47 |
| Permanent deformation (mm), at 35 °C | 0.075 | 0.045 | 0.056 | 0.049 | 0.065 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jwaida, Z.; Al Quraishy, Q.A.; Almuhanna, R.R.A.; Dulaimi, A.; Bernardo, L.F.A.; Andrade, J.M.d.A. The Use of Waste Fillers in Asphalt Mixtures: A Comprehensive Review. CivilEng 2024, 5, 801-826. https://doi.org/10.3390/civileng5040042
Jwaida Z, Al Quraishy QA, Almuhanna RRA, Dulaimi A, Bernardo LFA, Andrade JMdA. The Use of Waste Fillers in Asphalt Mixtures: A Comprehensive Review. CivilEng. 2024; 5(4):801-826. https://doi.org/10.3390/civileng5040042
Chicago/Turabian StyleJwaida, Zahraa, Qassim Ali Al Quraishy, Raid R. A. Almuhanna, Anmar Dulaimi, Luís Filipe Almeida Bernardo, and Jorge Miguel de Almeida Andrade. 2024. "The Use of Waste Fillers in Asphalt Mixtures: A Comprehensive Review" CivilEng 5, no. 4: 801-826. https://doi.org/10.3390/civileng5040042
APA StyleJwaida, Z., Al Quraishy, Q. A., Almuhanna, R. R. A., Dulaimi, A., Bernardo, L. F. A., & Andrade, J. M. d. A. (2024). The Use of Waste Fillers in Asphalt Mixtures: A Comprehensive Review. CivilEng, 5(4), 801-826. https://doi.org/10.3390/civileng5040042











