Rainwater Harvesting as Sustainable Solution to Cope with Drinking Water Scarcity and Urban Flooding: A Case Study of Public Institutions in Lahore, Pakistan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
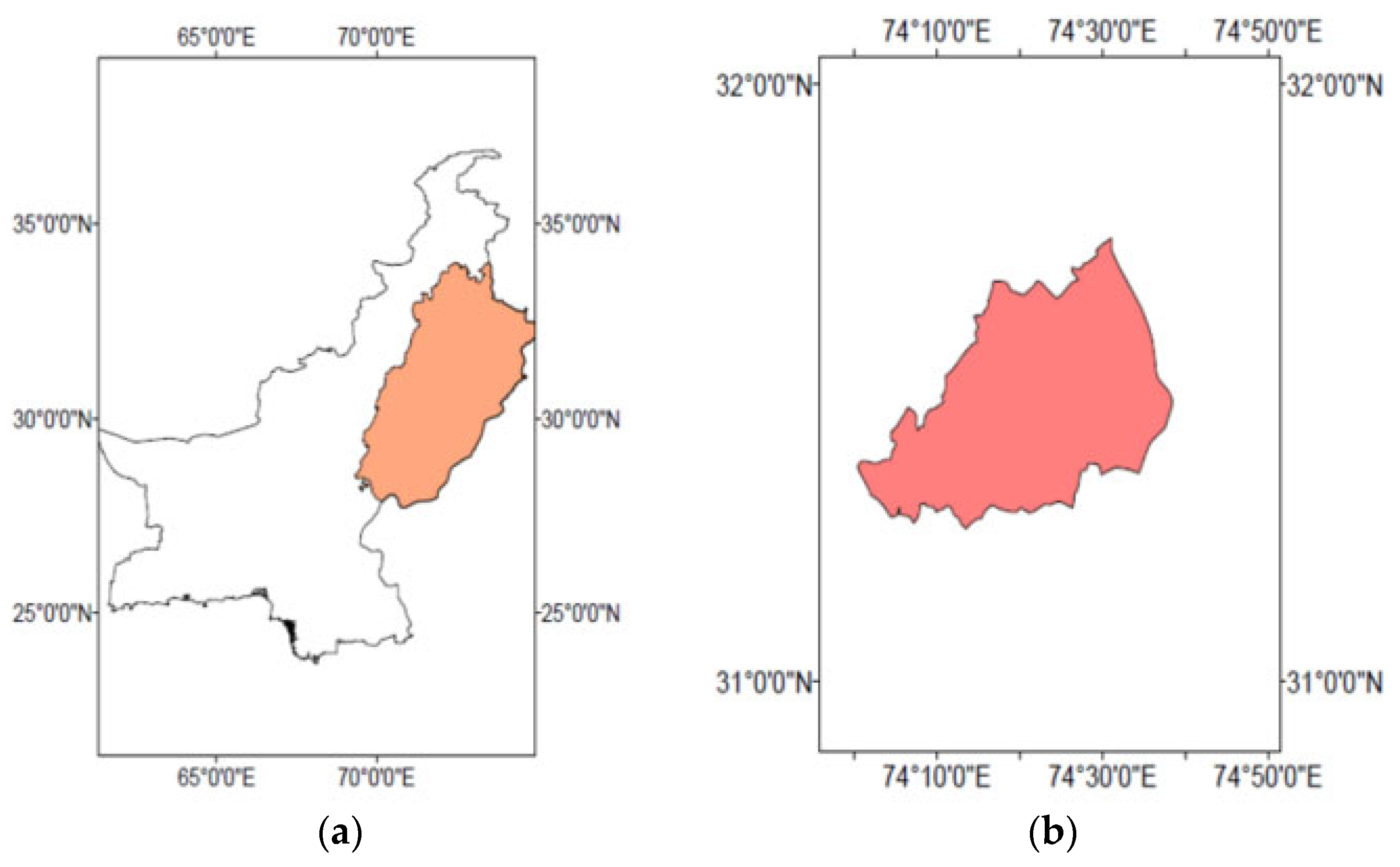
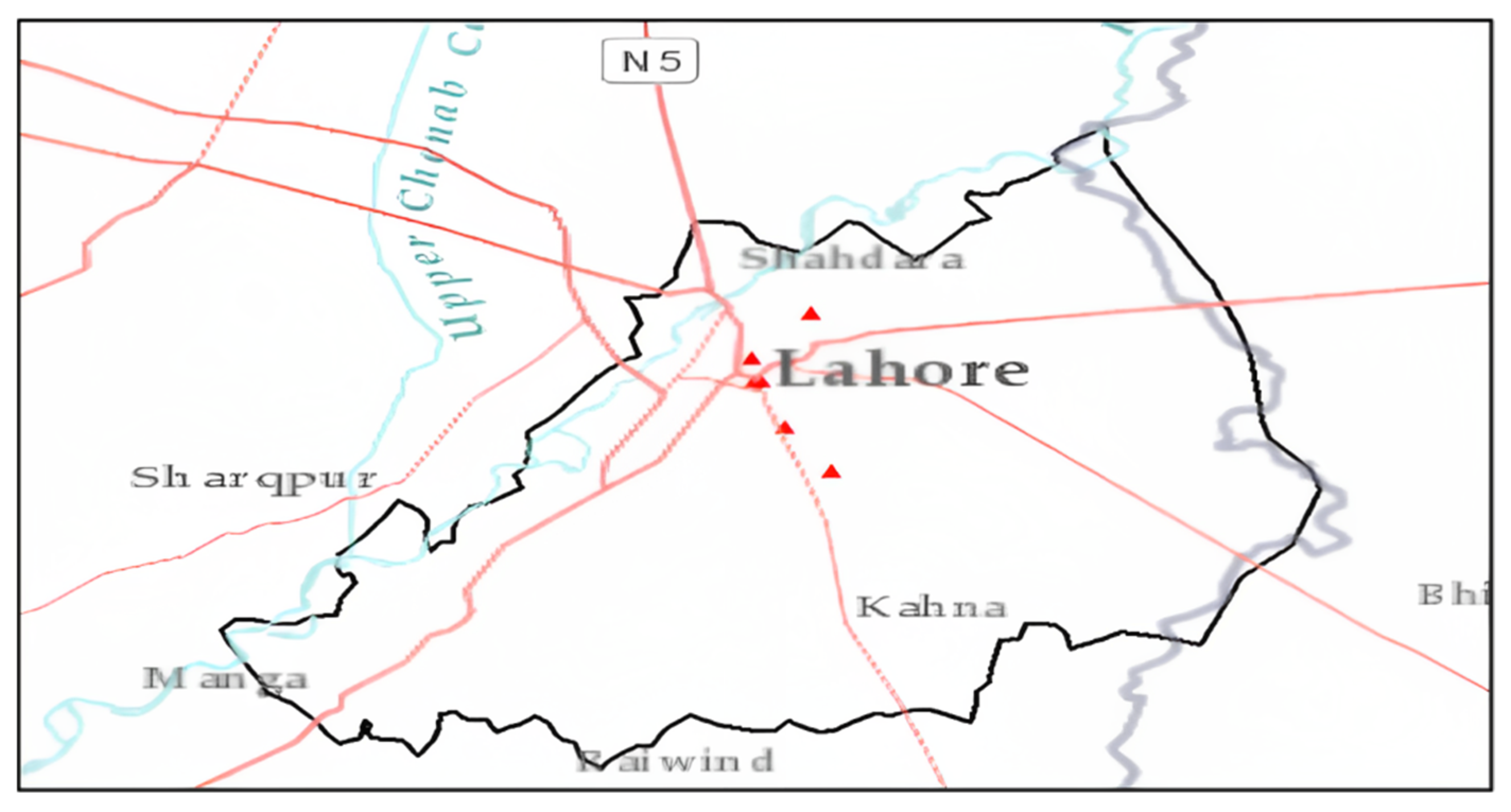
2.1. Study Area
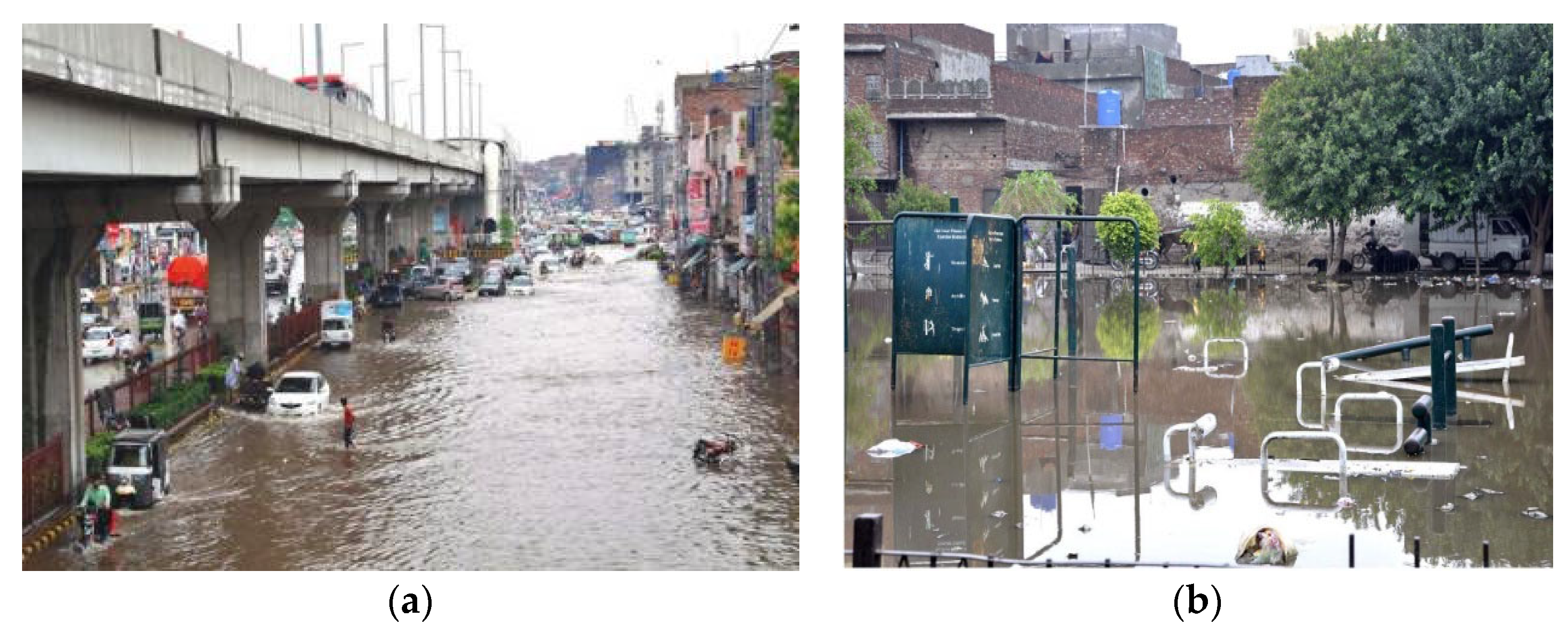
2.2. Current Situation of Water Sanitation in Lahore
2.3. Data Collection
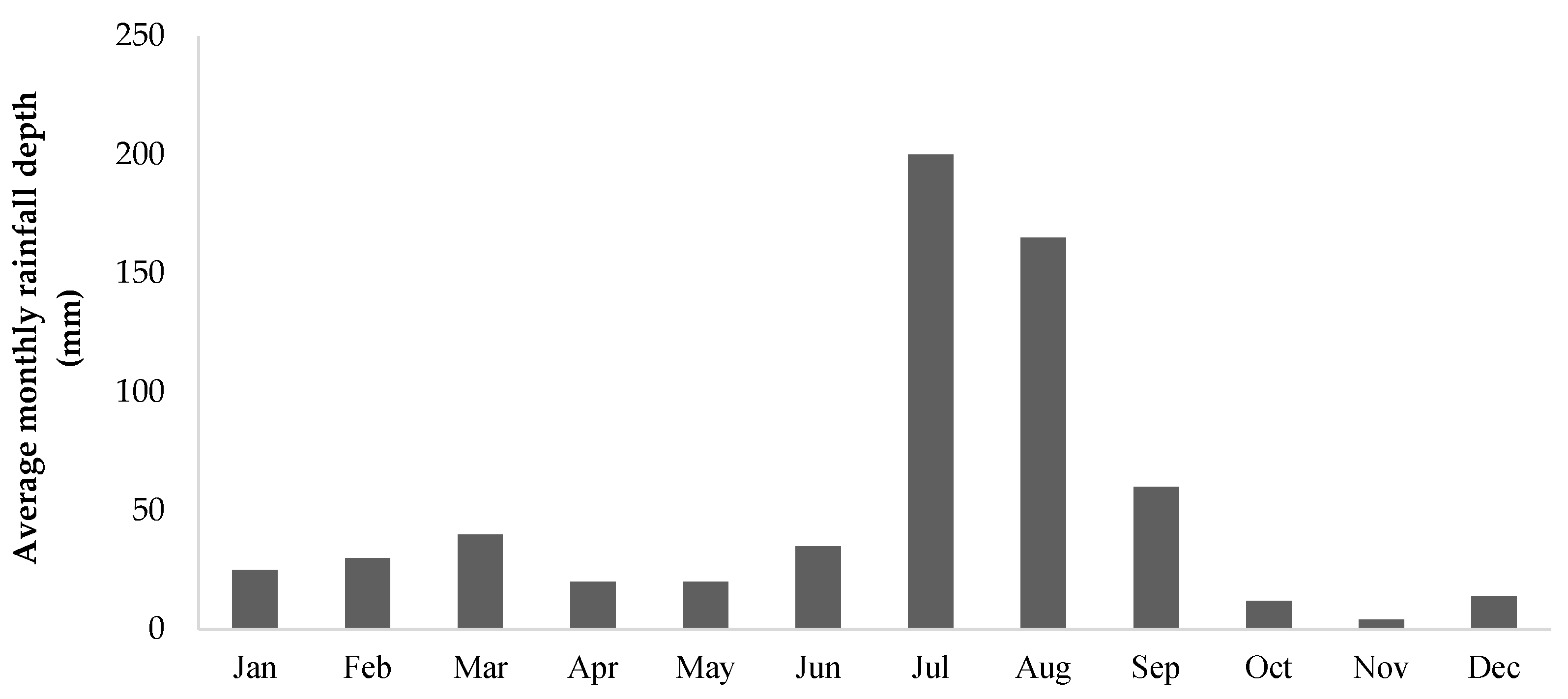
2.3.1. Rainfall Data
2.3.2. Construction of Surface Water Natural Drainage with ArcGIS
2.3.3. Water Consumption Data
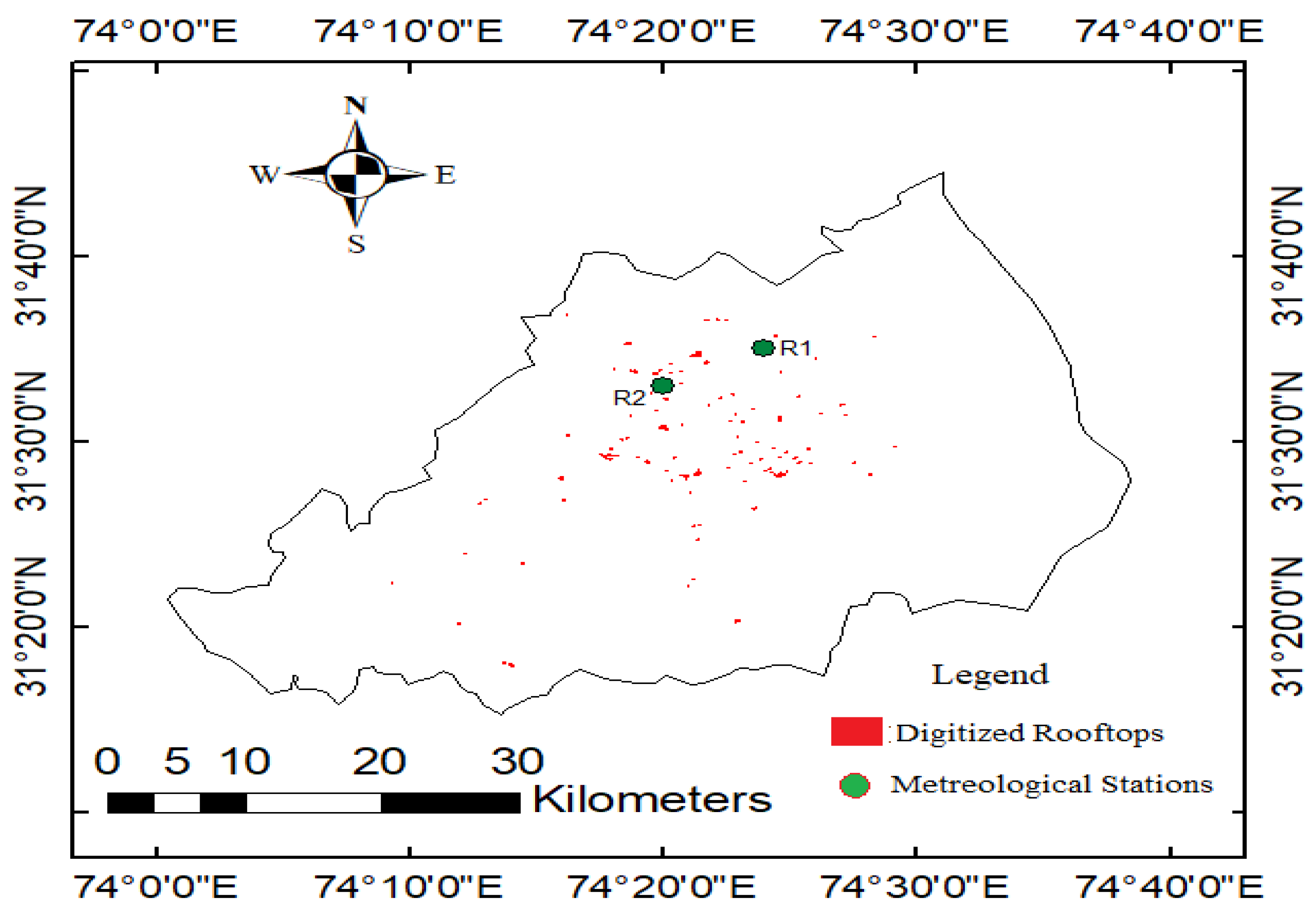
2.4. Rooftop Rainwater Potential and Identification of Ponding Sites
3. Results
3.1. Potential Volume of Monthly Rooftop RWH
3.2. Efficiency from Consumption and Supply
3.3. Location of Underground Storage Tanks/Recharge Wells
3.4. A Recommended RWH Model for Institutions and Households
3.5. Treatment of Stormwater
3.5.1. Mechanical Pre-Tank Filters
3.5.2. Microscopic Filtration
3.5.3. Disinfection
3.5.4. Ultraviolet Light
3.5.5. Chlorination
3.5.6. Distillation
3.5.7. Ozonation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Sr No. | Type of Data | Description | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DEM | SRTM DEM GL1 with spatial resolution of 30 m | Open Topography [72] |
| 2 | Rainfall data | Nearest meteorological stations | Pakistan meteorological department [73] |
| 3 | Water consumption | Water consumed in each category | Water and Sanitation Agency of Lahore [12] |
References
- Gardner-Outlaw, T.; Engelman, R. Sustaining Water Easing Scarcity: A Second Update; Population Action International, Population and Environment Program: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Cao, X.; Tian, L.; Sun, S.; Wu, P. A comprehensive analysis of blue water scarcity from the production, consumption, and water transfer perspectives. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 72, 870–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleick, P.H. Basic water requirements for human activities: Meeting basic needs. Water Int. 1996, 21, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grey, D.; Sadoff, C.W. Sink or Swim? Water security for growth and development. Water Policy 2007, 9, 545–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Engelenburg, J.; Van Slobbe, E.; Hellegers, P. Towards sustainable drinking water abstraction: An integrated sustainability assessment framework to support local adaptation planning. J. Integr. Environ. Sci. 2019, 16, 89–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.F.; Sheikh, A.A.; Shah, S.U.S.; Khan, M.A.; Afzal, M.A. Rainwater harvesting Scenarios and its prospective in Pakistan. Meteorol. Hydrol. Water Manag. 2019, 8, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Guan, Y.; Khan, F.; Khan, Z. A comprehensive index for measuring water security in an Urbanizing World: The case of Pakistan’s capital. Water 2020, 12, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, O.; Awan, F.M.; Ullah, Z.; Hassan, I. Rainwater harvesting, a measure to meet domestic water requirement; A case study Islamabad, Pakistan. IOP Conf. Series Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 414, 012018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, A.A. Technological gaps and innovation endeavours relating safe and sustainable water in developing countries. Asia-Pac. Tech Monit. 2017, 34, 14–22. [Google Scholar]
- Wada, Y.; Van Beek, L.P.H.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Nonsustainable groundwater sustaining irrigation: A global assessment. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, F.; Wu, R.-S.; Abbas, T. Rainwater harvesting potential and utilization for artificial recharge of groundwater using recharge wells. Processes 2019, 7, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WASA. Head Office of Water and Sanitation Authority, t31-B Zahoor Elahi Rd, Block B Gulberg 2, Lahore, Punjab 54660. Available online: https://wasa.punjab.gov.pk/ (accessed on 4 July 2022).
- WWF. A Special Report: Pakistans Waters at Risk, Water and Health Related Issues in Pakistan and Key Recommendations, Major Water Sectors in Pakistan; WWF: Ferozepur Road Lahore, Pakistan, 2015; pp. 5–6. [Google Scholar]
- Gade, A.D. Agricultural Transformation in India since Independence; Ashok Yakkaldevi: Maharashtra, India, 2017; p. 190. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.; Zhang, S.; Yue, T. Environmental and economic assessment of rainwater harvesting systems under five climatic conditions of Pakistan. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 259, 120829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.H. The limitations of roofwater harvesting in developing countries. Waterlines 2014, 33, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, D.N.; Gupta, A.K.; Anderson, D.M. Rainwater harvesting as an adaptation to climate change. Curr. Sci. 2003, 85, 46–59. [Google Scholar]
- Varma, K.H. Tiwari Current Status and Prospects of Rain Water Harvesting; (Scientific contribution No. 1995 INCOH/SAR-95/3); Indian National Committee on Hydrology (INCOH), National Institute of Hydrology: Roorkee, India, 1995.
- Al-Adamat, R.; Al-Ayyash, S.; Al-Amoush, H.; Al-Meshan, O.; Rawajfih, Z.; Shdeifat, A.; Al-Harahsheh, A.; Al-Farajat, M. The combination of indigenous knowledge and geo-informatics for water harvesting siting in the Jordanian Badia. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2012, 4, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, A.N.; Katibeh, H.; Farhadian, H. Numerical analysis of steady-state groundwater inflow into Tabriz line 2 metro tunnel, northwestern Iran, with special consideration of model dimensions. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2015, 75, 1617–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, A.N.; Farhadian, H.; Katibeh, H. A comparative study on evaluation of steady-state groundwater inflow into a circular shallow tunnel. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2018, 73, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit-Boix, A.; Devkota, J.; Phillips, R.; Vargas-Parra, M.V.; Josa, A.; Gabarrell, X.; Rieradevall, J.; Apul, D. Life cycle and hydrologic modeling of rainwater harvesting in urban neighborhoods: Implications of urban form and water demand patterns in the US and Spain. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 621, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, S.; Elangovan, K. Delineation of groundwater recharge potential zones in Namakkal District, Tamilnadu, India using remote sensing and GIS. J. Indian Soc. Remote. Sens. 2015, 43, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terêncio, D.P.S.; Sanches Fernandes, L.F.; Cortes, R.M.V.; Moura, J.P.; Pacheco, F.A.L. Rainwater harvesting in catchments for agro-forestry uses: A study focused on the balance between sustainability values and storage capacity. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613–614, 1079–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Winnaar, G.; Jewitt, G.P.W.; Horan, M. A GIS-based approach for identifying potential runoff harvesting sites in the Thukela River basin, South Africa. Phys. Chem. Earth 2007, 32, 1058–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahinda, J.M.; Lillie, E.; Taigbenu, A.; Taute, M.; Boroto, R. Developing suitability maps for rainwater harvesting in South Africa. Phys. Chem. Earth 2008, 33, 788–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campisano, A.; Butler, D.; Ward, S.; Burns, M.J.; Friedler, E.; DeBusk, K.; Fisher-Jeffes, L.N.; Ghisi, E.; Rahman, A.; Furumai, H.; et al. Urban rainwater harvesting systems: Research, implementation and future perspectives. Water Res. 2017, 115, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musayev, S.; Burgess, E.; Mellor, J. A global performance assessment of rainwater harvesting under climate change. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 132, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, J.; Qiang, Z.; Yuanhong, L.J.W. Using every last drop: Rainwater harvesting and utilization in Gansu Province, China. Waterlines 2014, 33, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.M.; Rahman, A.; Samali, B. Evaluation of climate change impacts on rainwater harvesting. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 137, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, S.; Memon, F.A.; Butler, D. Performance of a large building rainwater harvesting system. Water Res. 2012, 46, 5127–5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teston, A.; Geraldi, M.S.; Colasio, B.M.; Ghisi, E. Rainwater harvesting in buildings in Brazil: A literature review. Water 2018, 10, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazakli, E.; Alexopoulos, A.; Leotsinidis, M. Rainwater harvesting, quality assessment and utilization in Kefalonia Island, Greece. Water Res. 2007, 41, 2039–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chubaka, C.E.; Whiley, H.; Edwards, J.W.; Ross, K.E. A review of roof harvested rainwater in Australia. J. Environ. Public Health 2018, 2018, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, C.B.; Klenzendorf, J.B.; Afshar, B.R.; Simmons, M.T.; Barrett, M.E.; Kinney, K.A.; Kirisits, M.J. The effect of roofing material on the quality of harvested rainwater. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2049–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample, D.J.; Liu, J. Optimizing rainwater harvesting systems for the dual purposes of water supply and runoff capture. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 75, 174–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.C.; Xu, D.M.; Chau, K.W.; Lei, G.J. Assessment of river water quality based on theory of variable fuzzy sets and fuzzy binary comparison method. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 4183–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulla, F.A.; Al-Shareef, A.W. Assessment of Rainwater Roof Harvesting Systems for Household Water Supply in Jordan, in Integrated Urban Water Resources Management; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 291–300. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, S.; Sudhakar, S.; Desai, V.R. Remote sensing and geographic information system based approach for watershed conservation. J. Surv. Eng. 2002, 128, 108–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S. Satellite remote sensing and GIS application in agricultural meteorology. In Proceedings of the Training Workshop, Dehra Dun, India, 7–11 July 2003; pp. 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Burrough, P.A. Principles of Geographical Information Systems for Land Resources Assessments; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Krois, J.; Schulte, A. GIS-based multi-criteria evaluation to identify potential sites for soil and water conservation techniques in the Ronquillo watershed, northern Peru. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 51, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melville-Shreeve, P.; Ward, S.; Butler, D. Rainwater harvesting typologies for UK houses: A multi criteria analysis of system configurations. Water 2016, 8, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jozaghi, A.; Alizadeh, B.; Hatami, M.; Flood, I.; Khorrami, M.; Khodaei, N. A Comparative Study of the AHP and TOPSIS Techniques for Dam Site Selection Using GIS: A Case Study of Sistan and Baluchestan Province, Iran. Geosciences 2018, 8, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorrami, M.; Alizadeh, B.; Ghasemi Tousi, E.; Shakerian, M.; Maghsoudi, Y.; Rahgozar, P. How Groundwater Level Fluctuations and Geotechnical Properties Lead to Asymmetric Subsidence: A PSInSAR Analysis of Land Deformation over a Transit Corridor in the Los Angeles Metropolitan Area. Remote. Sens. 2019, 11, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Madrigal, V.M.; Muñiz-Jáuregui, J.A.; Garduño-Monroy, V.H.; Flores-Lázaro, N.; Figueroa-Miranda, S. Depreciation factor equation to evaluate the economic losses from ground failure due to subsidence related to groundwater withdrawal. Nat. Sci. 2014, 6, 43232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-shabeeb, A.R. The use of AHP within GIS in selecting potential sites for water harvesting sites in the Azraq Basin—Jordan. J. Geogr. Inf. Sys. 2016, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, A.; Riksen, M.; Ouessar, M.; Ritsema, C. Identification of suitable sites for rainwater harvesting structures in arid and semi-arid regions: A review. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2016, 4, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerasinghe, H.; Schneider, U.; Loew, A. Water harvest-and storage-location assessment model using GIS and remote sensing. Hydrol. Earth Sys. Sci. Discuss. 2011, 8, 3353–3381. [Google Scholar]
- Adham, A.; Riksen, M.; Ouessar, M.; Ritsema, C.J. A methodology to assess and evaluate rainwater harvesting techniques in (semi-) arid regions. Water 2016, 8, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adham, A.; Wesseling, J.G.; Riksen, M.; Ouessar, M.; Ritsema, C.J. A water harvesting model for optimizing rainwater harvesting in the wadi Oum Zessar watershed, Tunisia. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 176, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warraich, F.A. Urban Flooding Sweeps Away Official Claims. Available online: https://www.nation.com.pk/09-Aug-2016/urban-flooding-sweeps-away-official-claims (accessed on 12 February 2023).
- Pakistanviews. Life in Ruins: Hazardous Living around a Drain. Available online: https://english.pakistanviews.org/pakistan-news/punjab-news-2/life-in-ruins-hazardous-living-around-a-drain/ (accessed on 13 February 2023).
- Oliveira, M.C.; Iten, M.; Matos, H.A.; Michels, J. Water–Energy Nexus in Typical Industrial Water Circuits. Water 2019, 11, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaied, R.A. Water use and time analysis in ablution from taps. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 2329–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolnews. How Many People Attended Matches in Karachi? Available online: https://www.bolnews.com/sports/2022/09/how-many-people-attended-matches-in-karachi/ (accessed on 18 February 2023).
- Graana. Top 6 Shopping Malls in Lahore. Available online: https://www.graana.com/blog/shopping-malls-in-lahore/ (accessed on 18 February 2023).
- Davodi, H. Hotel Water Consumption Statistics & Conservation. Available online: https://purebluesustainability.com/hotel-water-consumption-statistics-conservation/#:~:text=Daily-Water-Usage-Per-Room,ranges-from-100-400-gallons (accessed on 18 February 2023).
- Mack. Club Management. Available online: https://www.referenceforbusiness.com/business-plans/Business-Plans-Volume-07/Nightclub.html (accessed on 19 February 2023).
- Carsroute. How Many Seats Are in A Cinema. Available online: https://carsroute.com.ar/auto/how-many-seats-are-in-a-cinema.html (accessed on 19 February 2023).
- Ijcp. Judicial Statistics Pakistan. Available online: http://ljcp.gov.pk/nljcp/assets/dist/Publication/JSP2020.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Mun, J.S.; Han, M.Y. Design and operational parameters of a rooftop rainwater harvesting system: Definition, sensitivity and verification. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 93, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, Y.S.; Ong, K.S.; Tan, Y.K.; Ghadimi, A. The Enhancement of Pre-Storage Filtration Efficiency for the Rainwater Harvesting System in Malaysia. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 152, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crișan, H.G. Microscopic Testing and Analysis of Drinking Water Filters after the Final Life Cycle, Using an Experimental Stand. Available online: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1757-899X/724/1/012036/pdf (accessed on 21 February 2023).
- Boyce, J.M. Modern technologies for improving cleaning and disinfection of environmental surfaces in hospitals. Antimicrob Resist. Infect Control. 2016, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, T.; Tatsuno, I.; Hasegawa, T. Instantaneous water purification by deep ultraviolet light in water waveguide: Escherichia coli bacteria disinfection. Water 2019, 11, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, A.; Garcia, L.; Silva, K.; Sabogal-Paz, L.; Hincapié, M.; Montoya, L.; Galeano, L.; Galdos-Balzategui, A.; Reygadas, F.; Herrera, C.; et al. Chlorination for low-cost household water disinfection–A critical review and status in three Latin American countries. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2022, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulett, G.A. Purification of Water by Distillation. J. Phys. Chem. 1896, 1, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manasfi, T. Chapter Four-Ozonation in drinking water treatment: An overview of general and practical aspects, mechanisms, kinetics, and byproduct formation. Compr. Anal. Chem. 2021, 92, 85–116. [Google Scholar]
- Freni, G.; Liuzzo, L. Effectiveness of Rainwater Harvesting Systems for Flood Reduction in Residential Urban Areas. Water 2019, 11, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stormsaver. Advantages of Rainwater Harvesting. Available online: https://www.stormsaver.com/Advantages-of-Rainwater-Harvesting (accessed on 18 February 2023).
- OpenTopography-Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM GL1) Global 30 m. Available online: https://portal.opentopography.org/raster?opentopoID=OTSRTM.082015.4326.1 (accessed on 27 April 2023).
- Pakistan Meteorogical Department. Available online: http://www.pmd.gov.pk/cdpc/home.htm (accessed on 27 April 2023).




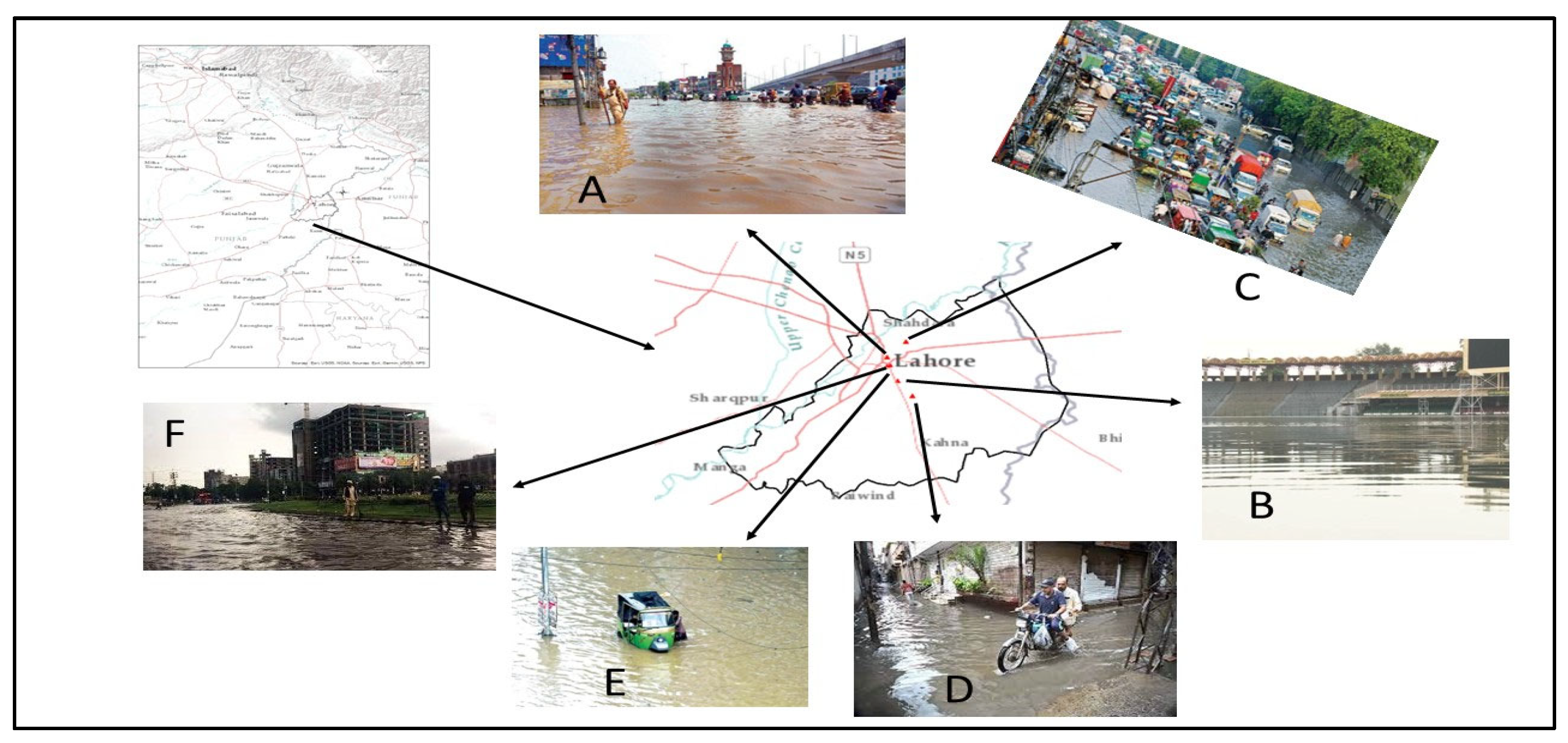
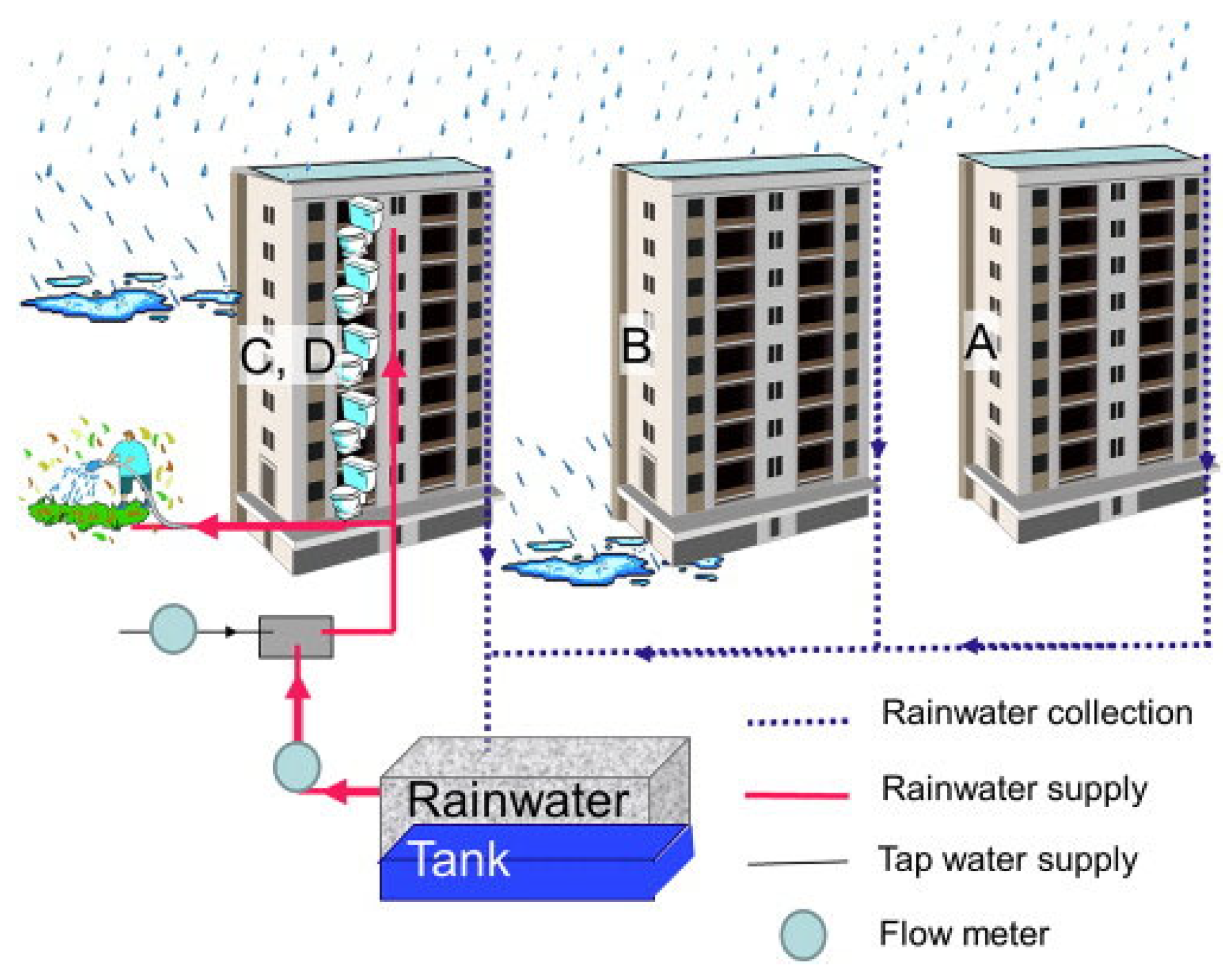

| Large Public Institutions | Consumption (m3) |
|---|---|
| Major industries | 292,708 |
| Large mosques/shrines | 1992 |
| Schools/colleges | 53,630 |
| Stadiums | 122,341 |
| Malls | 119,920 |
| Hotels (five stars) | 22,068 |
| Clubs | 3740 |
| Cinemas | 6120 |
| Airports | 9845 |
| Hospitals | 18,987 |
| Universities | 10,740 |
| Judicial courts | 4692 |
| Materials | Surface Runoff Coefficient |
|---|---|
| Concrete | 0.6–0.8 |
| Paving | 0.5–0.6 |
| PVC geomembrane | 0.85–0.9 |
| Roof tiles | 0.8–0.9 |
| Corrugated metal | 0.7–0.9 |
| Categories | Rooftop Areas (m2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sr. No | Large Public Institution Categories | No. of Digitized Buildings | Average Area of Digitized Buildings | Total Existing | Total Estimated Area |
| 1 | Major industries | 28 | 8175 | 300 | 2,452,500 |
| 2 | Large mosques/shrines | 10 | 3271 | 24 | 78,504 |
| 3 | Schools/colleges | 42 | 4535 | 500 | 2,267,500 |
| 4 | Stadiums | 4 | 12,067 | 19 | 229,273 |
| 5 | Malls | 3 | 26,780 | 10 | 267,800 |
| 6 | Hotels (five stars) | 4 | 6668 | 18 | 120,024 |
| 7 | Clubs | 3 | 11,340 | 11 | 124,740 |
| 8 | Cinemas | 7 | 1476 | 15 | 22,140 |
| 9 | Airports | 1 | 30,381 | 1 | 30,381 |
| 10 | Hospitals | 26 | 3606 | 47 | 169,482 |
| 11 | Universities | 7 | 20,262 | 28 | 567,336 |
| 12 | Judicial courts | 3 | 7344 | 23 | 168,912 |
| Total | 138 | 996 | 6,498,592 | ||
| Categories | January | February | March | April | May | June | July | August | September | October | November | December |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 36,481 | 43,777 | 58,370 | 29,185 | 29,185 | 51,073 | 291,848 | 240,774 | 87,554 | 17,511 | 5837 | 20,429 |
| 2 | 1168 | 1401 | 1868 | 934 | 934 | 1635 | 9342 | 7707 | 2803 | 561 | 187 | 654 |
| 3 | 33,729 | 40,475 | 53,967 | 26,983 | 26,983 | 47,221 | 269,833 | 222,612 | 80,950 | 16,190 | 5397 | 18,888 |
| 4 | 3410 | 4093 | 5457 | 2728 | 2728 | 4775 | 27,283 | 22,509 | 8185 | 1637 | 546 | 1910 |
| 5 | 3984 | 4780 | 6374 | 3187 | 3187 | 5577 | 31,868 | 26,291 | 9560 | 1912 | 637 | 2231 |
| 6 | 1785 | 2142 | 2857 | 1428 | 1428 | 2499 | 14,283 | 11,783 | 4285 | 857 | 286 | 1000 |
| 7 | 1856 | 2227 | 2969 | 1484 | 1484 | 2598 | 14,844 | 12,246 | 4453 | 891 | 297 | 1039 |
| 8 | 329 | 395 | 527 | 263 | 263 | 461 | 2635 | 2174 | 790 | 158 | 53 | 184 |
| 9 | 452 | 542 | 723 | 362 | 362 | 633 | 3615 | 2983 | 1085 | 217 | 72 | 253 |
| 10 | 2521 | 3025 | 4034 | 2017 | 2017 | 3529 | 20,168 | 16,639 | 6051 | 1210 | 403 | 1412 |
| 11 | 8439 | 10,127 | 13,503 | 6751 | 6751 | 11,815 | 67,513 | 55,698 | 20,254 | 4051 | 1350 | 4726 |
| 12 | 2513 | 3015 | 4020 | 2010 | 2010 | 3518 | 20,101 | 16,583 | 6030 | 1206 | 402 | 1407 |
| Total | 96,667 | 116,000 | 154,666 | 77,333 | 77,333 | 135,333 | 773,332 | 637,999 | 232,000 | 46,400 | 15,467 | 54,133 |
| Large Public Institutions | Consumption (m3) | Supply (m3) | % of Water Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Major industries | 292,708 | 76,002 | 26 |
| Large mosques/shrines | 1992 | 2432 | 100 |
| Schools/colleges | 53,630 | 70,269 | 100 |
| Stadiums | 122,341 | 7105 | 5.8 |
| Malls | 119,920 | 8299 | 6.9 |
| Hotels (five stars) | 22,068 | 3719 | 16.8 |
| Clubs | 3740 | 3865 | 100 |
| Cinemas | 6120 | 686 | 11.2 |
| Airports | 9845 | 941 | 9.5 |
| Hospitals | 18,987 | 5252 | 27.6 |
| Universities | 10,740 | 17,581 | 100 |
| Judicial courts | 4692 | 5234 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Waseem, M.; Mutahir Ullah Ghazi, S.; Ahmed, N.; Ayaan, M.; Kebede Leta, M. Rainwater Harvesting as Sustainable Solution to Cope with Drinking Water Scarcity and Urban Flooding: A Case Study of Public Institutions in Lahore, Pakistan. CivilEng 2023, 4, 638-656. https://doi.org/10.3390/civileng4020037
Waseem M, Mutahir Ullah Ghazi S, Ahmed N, Ayaan M, Kebede Leta M. Rainwater Harvesting as Sustainable Solution to Cope with Drinking Water Scarcity and Urban Flooding: A Case Study of Public Institutions in Lahore, Pakistan. CivilEng. 2023; 4(2):638-656. https://doi.org/10.3390/civileng4020037
Chicago/Turabian StyleWaseem, Muhammad, Syed Mutahir Ullah Ghazi, Nameer Ahmed, Muhammad Ayaan, and Megersa Kebede Leta. 2023. "Rainwater Harvesting as Sustainable Solution to Cope with Drinking Water Scarcity and Urban Flooding: A Case Study of Public Institutions in Lahore, Pakistan" CivilEng 4, no. 2: 638-656. https://doi.org/10.3390/civileng4020037
APA StyleWaseem, M., Mutahir Ullah Ghazi, S., Ahmed, N., Ayaan, M., & Kebede Leta, M. (2023). Rainwater Harvesting as Sustainable Solution to Cope with Drinking Water Scarcity and Urban Flooding: A Case Study of Public Institutions in Lahore, Pakistan. CivilEng, 4(2), 638-656. https://doi.org/10.3390/civileng4020037







