Venous Malformation of the Maxilla: A Systematic Review and a Report of an Unusual Case
Abstract
1. Introduction
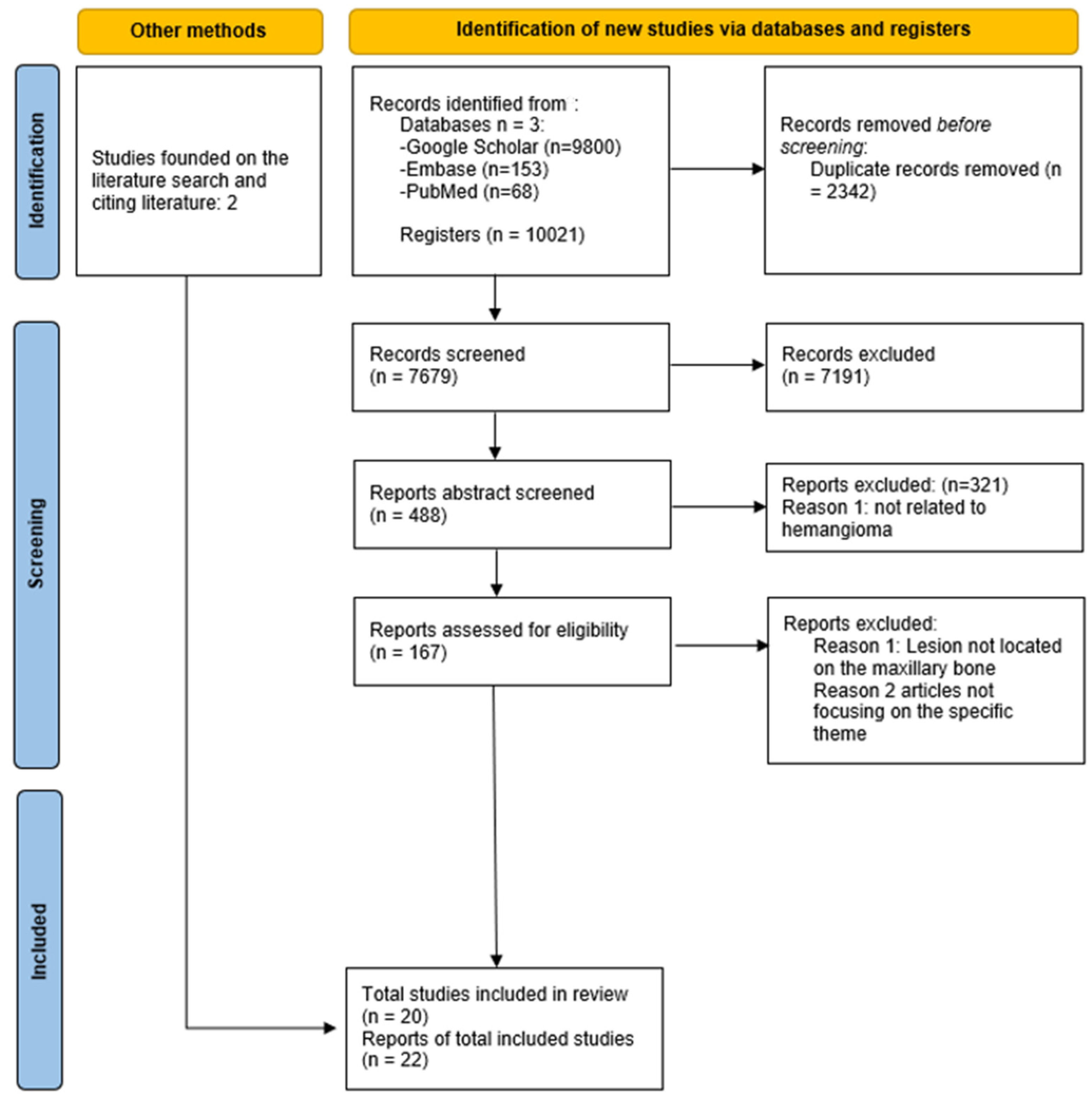
2. Methods
2.1. The Identifying Question
2.2. A Search Strategy
2.3. Inclusion Criteria
2.4. Exclusion Criteria
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis
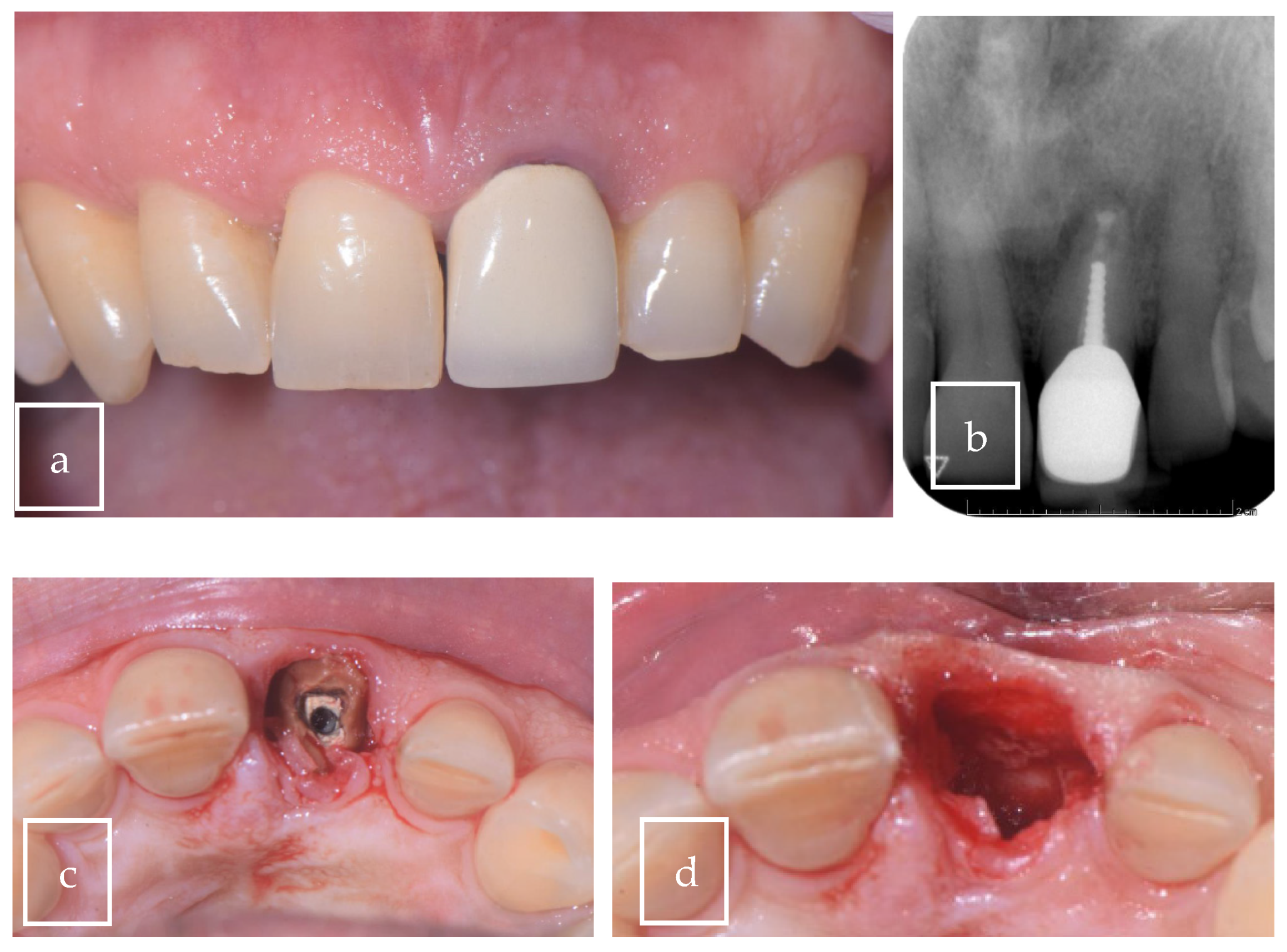
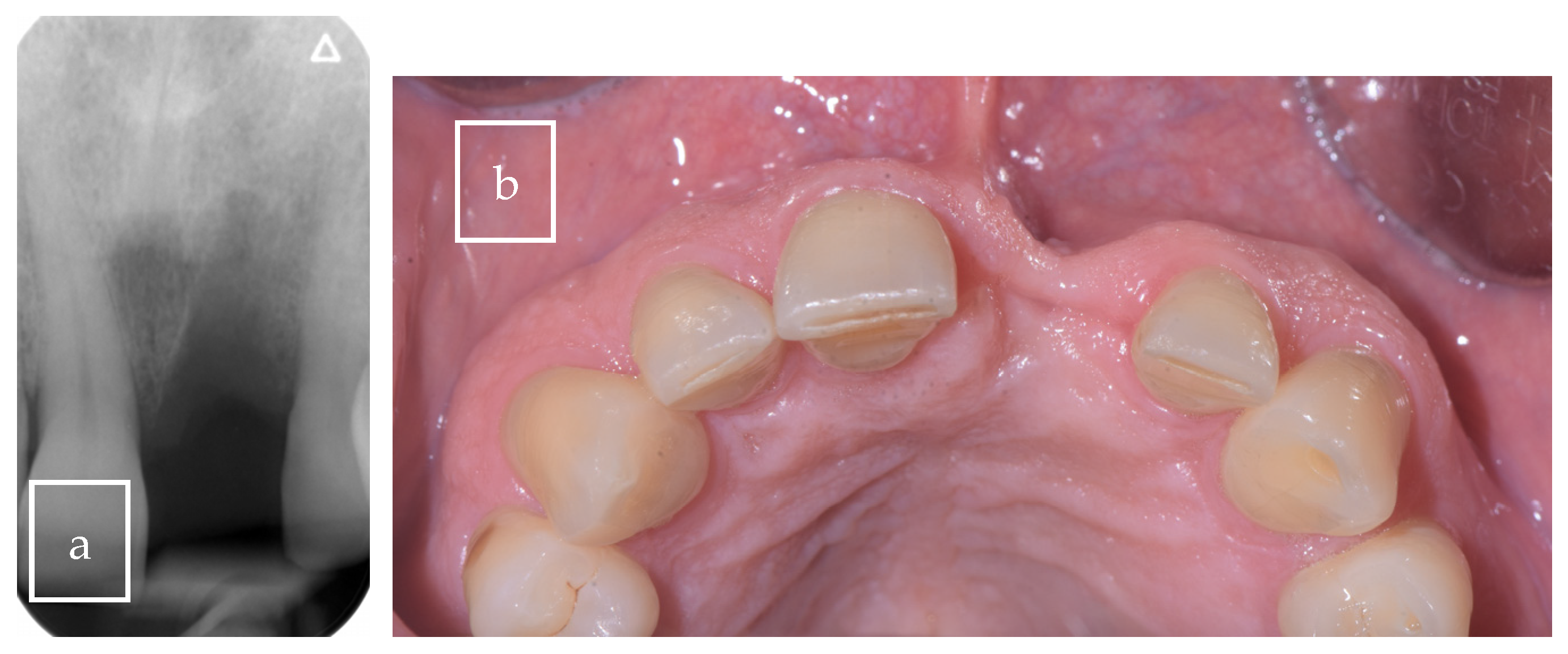
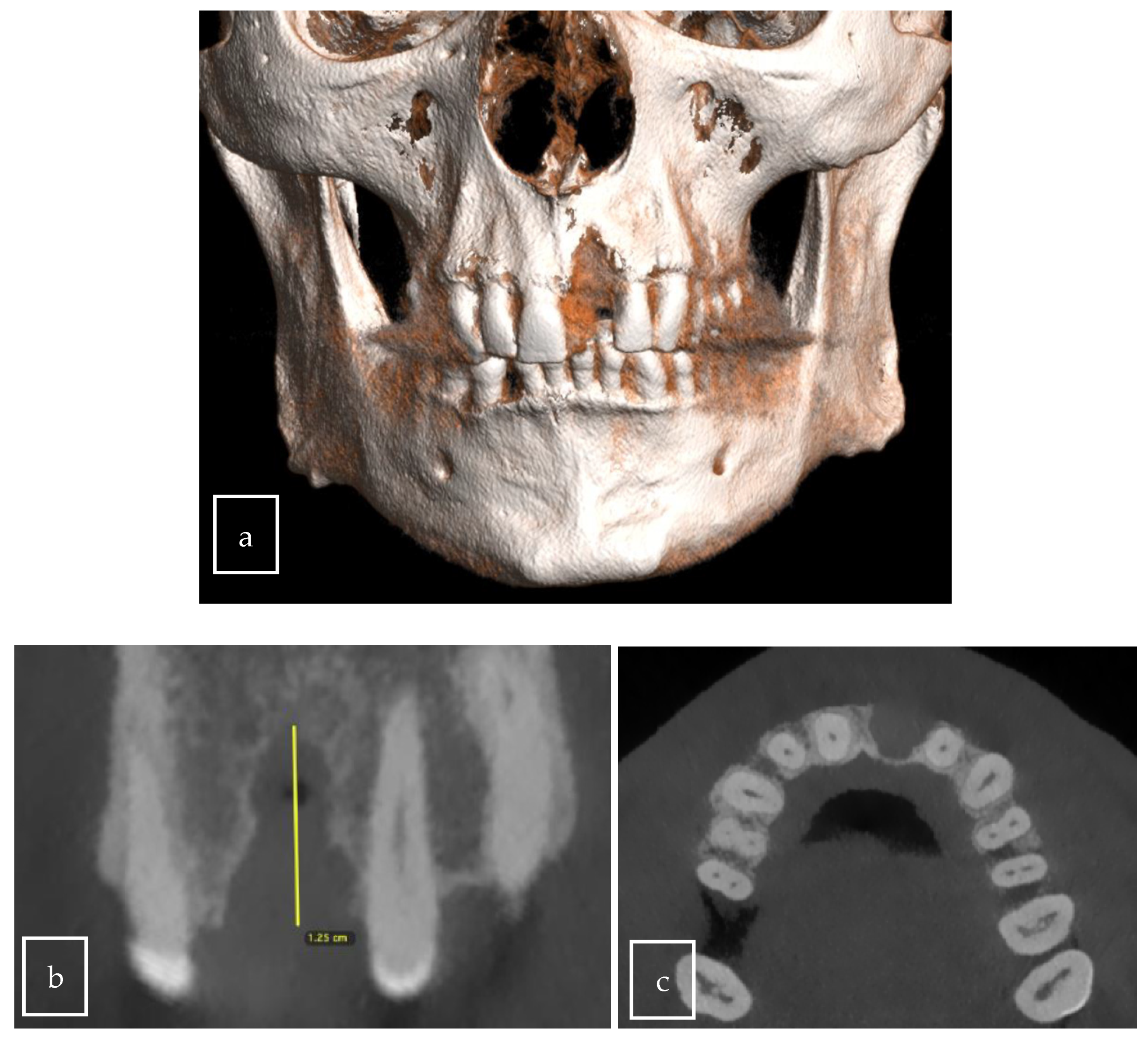
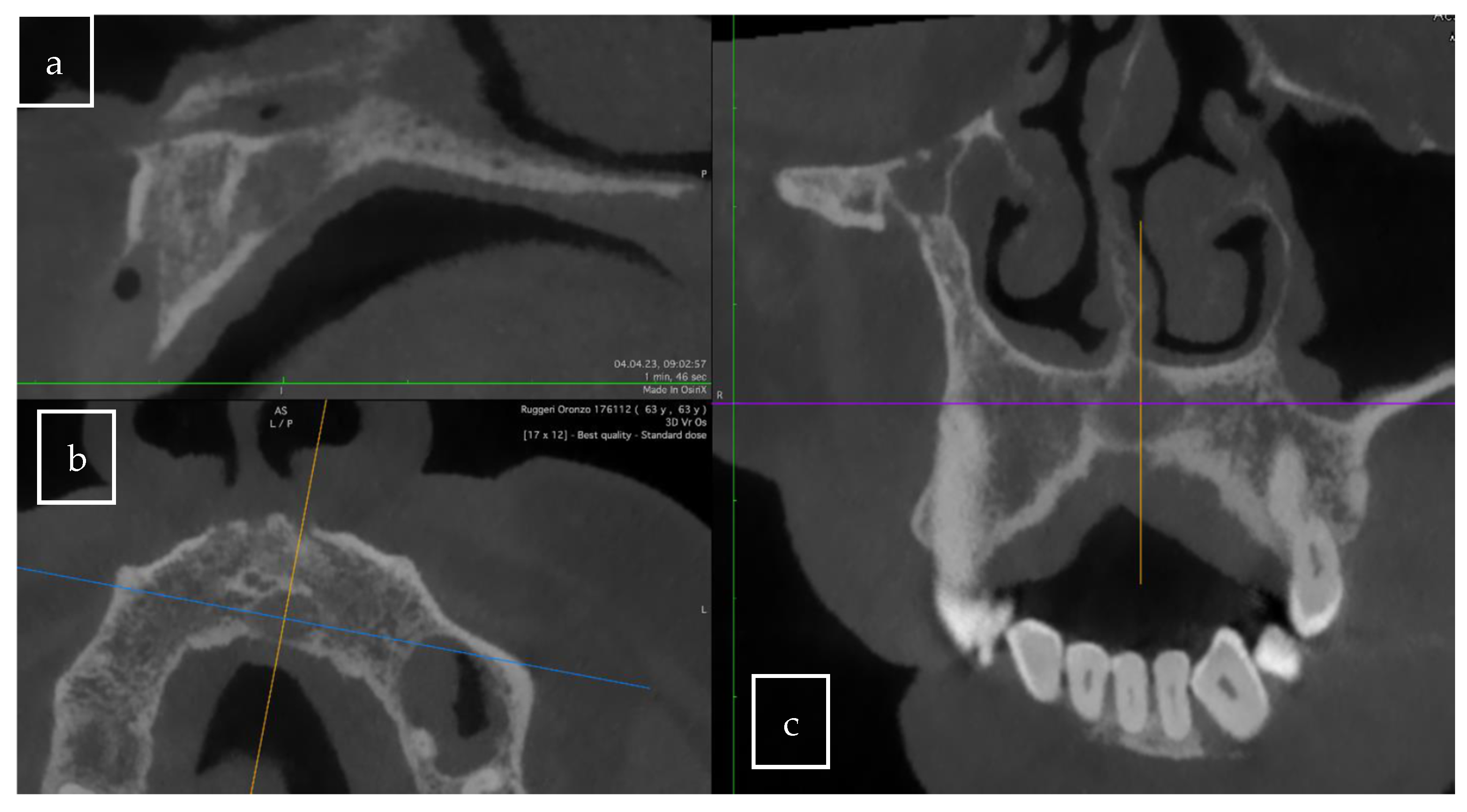
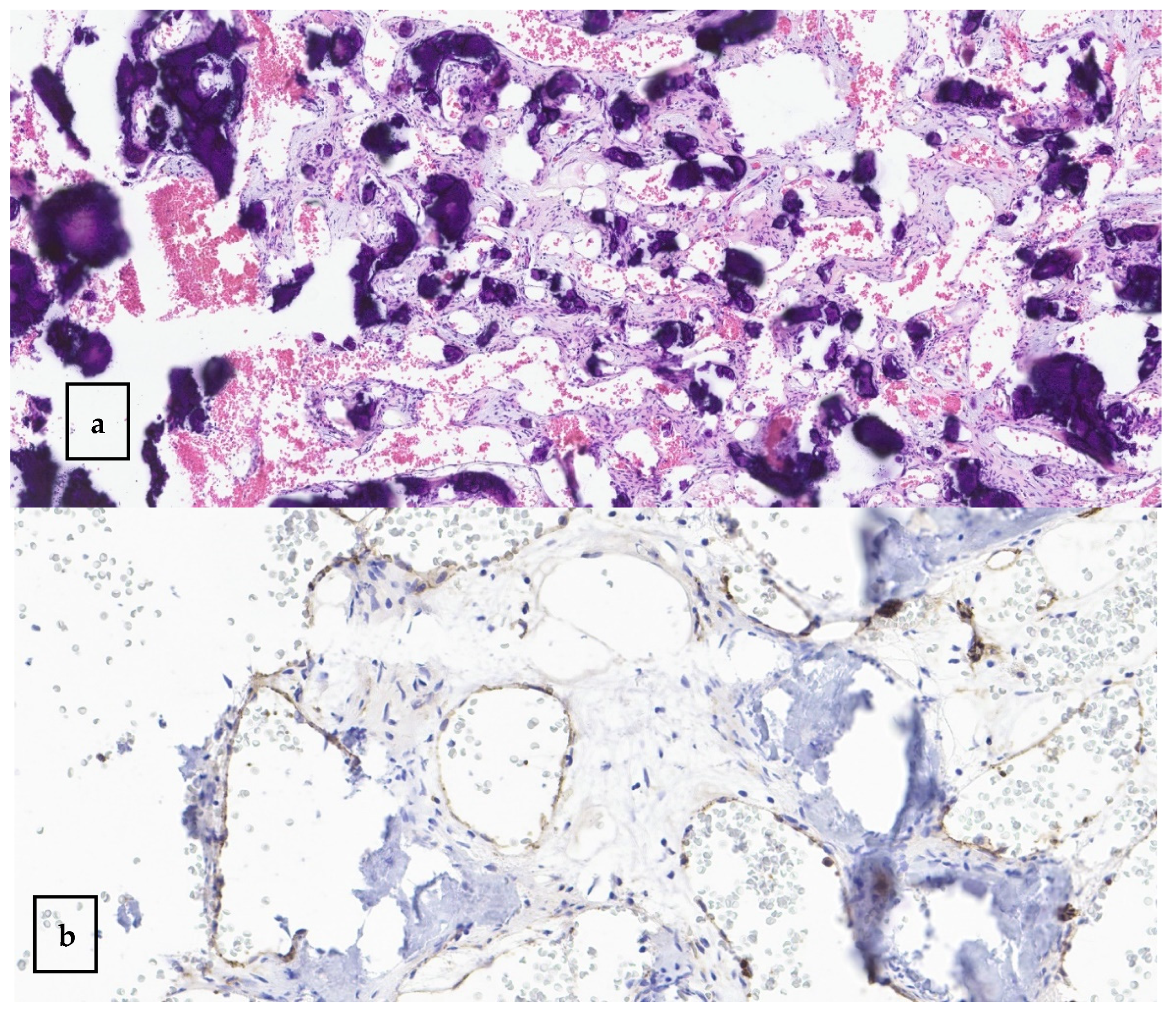
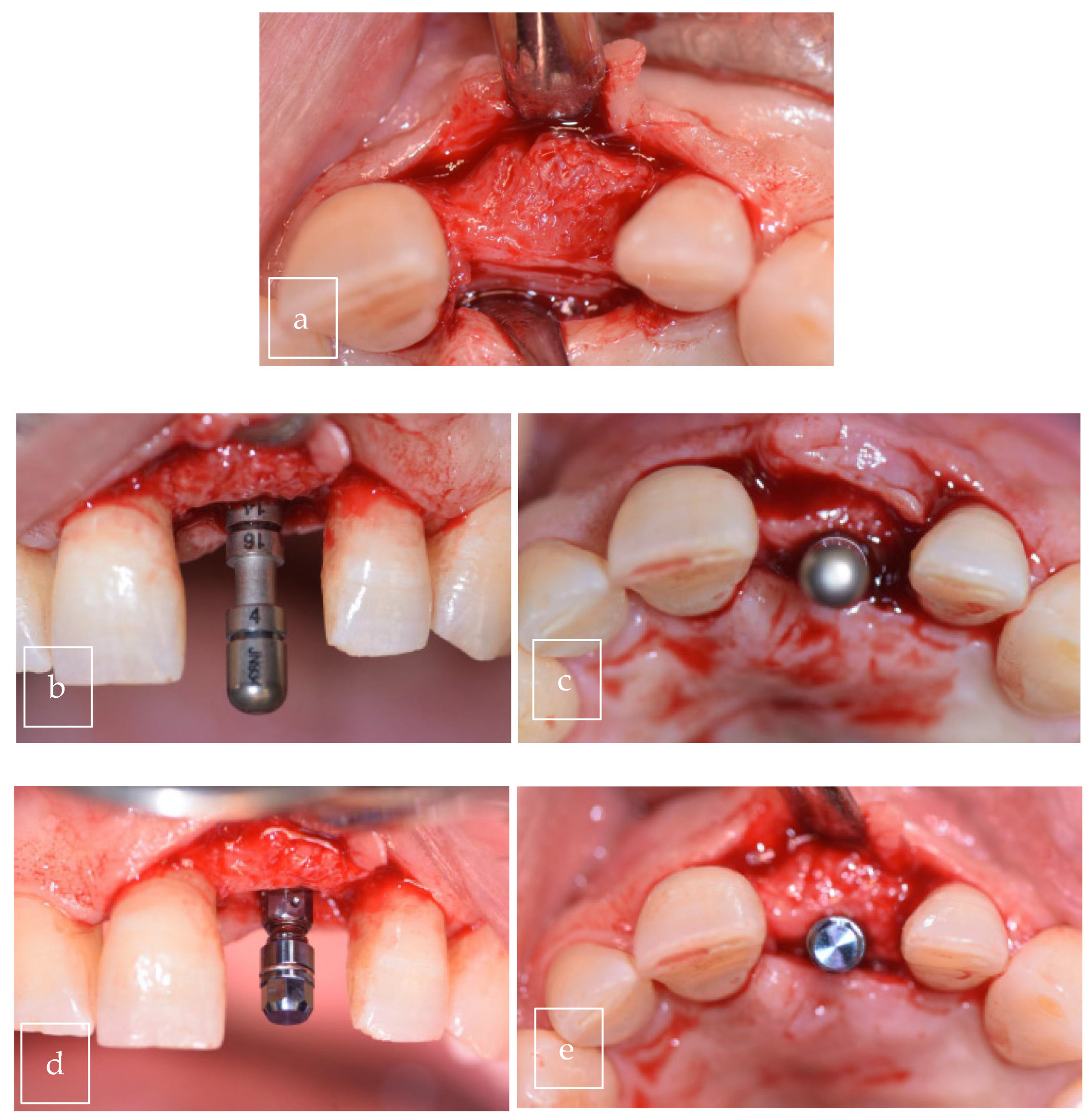
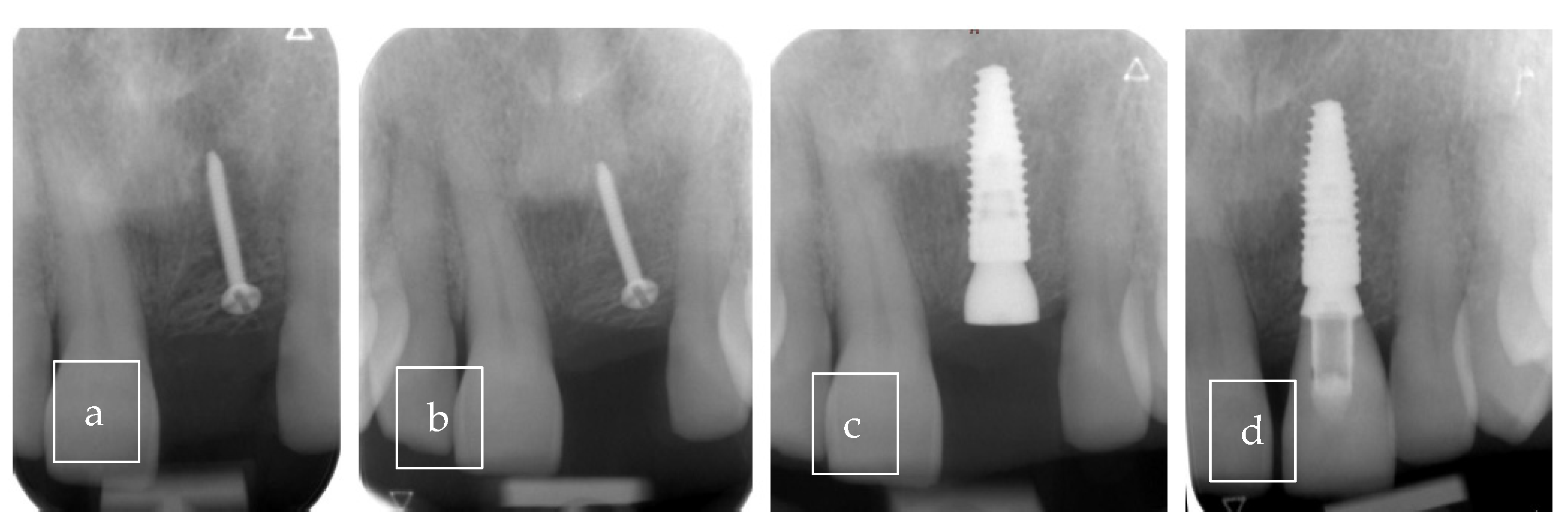
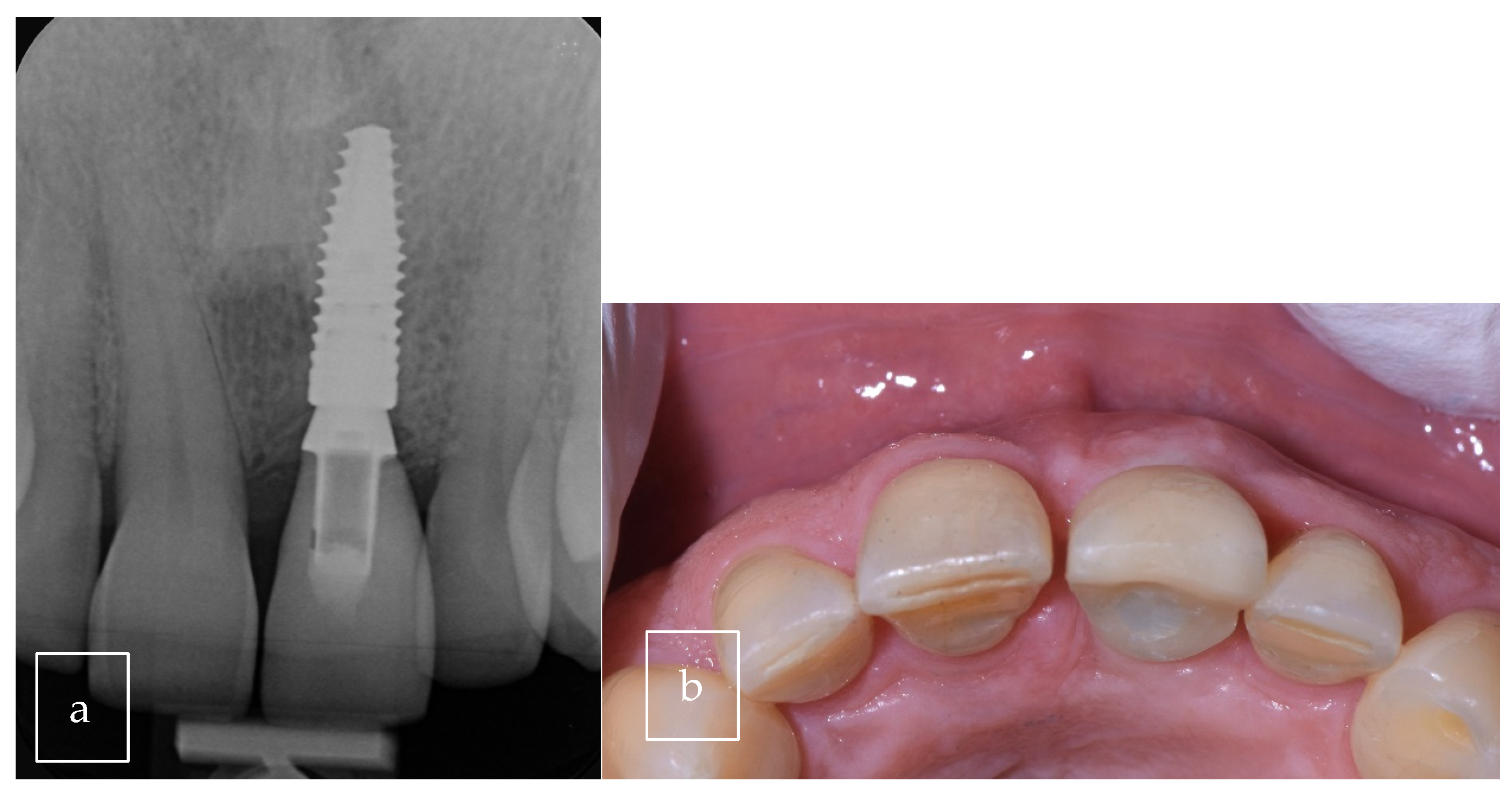
3.2. Case Presentation
4. Discussion
4.1. Radiological Criteria
- Small (<1 cm): These lesions are generally well-encapsulated and localized, with little tendency to expand;
- Medium (1–3 cm): These lesions may exhibit capillary or early cavernous features;
- Large (>3 cm): These lesions are more invasive due to the presence of large vascular spaces and are associated with faster growth;
- Computed tomography: Maxillary hemangiomas often appear as radiolucent lesions on CT, with well- or poorly defined margins. Images often show thin bony septa, giving a honeycomb or soap bubble appearance. The presence of calcified honeycomb structures is a suggestive although nonspecific sign. Contrast enhancement after injection highlights the vascular appearance of the lesion [36,37,38];
- MRI is the gold standard for characterizing the vascular nature of hemangiomas. On T1-weighted images, hemangiomas often appear hypointense or isointense compared to muscle. On T2-weighted images, they are typically hyperintense due to blood stasis in the dilated vascular spaces. After gadolinium injection, heterogeneous enhancement is observed, indicative of abundant vascularization of the lesion. This characteristic is essential for differentiating hemangiomas from other maxillary lesions [37,38,39];
- Angiography: This approach can be used to assess the vascularization of maxillary hemangiomas, confirming their vascular nature and aiding in planning of possible preoperative embolization, should surgery be necessary. However, this approach is generally reserved for complex cases due to its invasive nature [40,41,42].
4.2. Histological Criteria
- Capillary hemangioma: Consists of small, thin-walled vessels, often closely spaced. The capillaries are lined with endothelial cells without atypia. This type is more common in soft tissues but can also occur in maxillary bones;
- Cavernous hemangioma: Characterized by large vascular spaces, filled with blood and, in some cases, organized thrombi, separated by thin connective tissue walls. This cavernous structure is more common in bone hemangiomas, which explains their characteristic radiological appearance;
- Mixed hemangioma: Characterized by a combination of capillary and cavernous structures. This type is less common but presents with varied histological appearances within the same lesion [4].
4.3. Differential Diagnosis
4.4. Management and Treatment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eliot, C.A.; Castle, J.T. Intraosseous hemangioma of the anterior mandible. Head Neck Pathol. 2010, 4, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrêa, P.H.; Nunes, L.C.; Johann, A.C.; Aguiar, M.C.; Gomez, R.S.; Mesquita, R.A. Prevalence of oral hemangioma, vascular malformation and varix in a Brazilian population. Braz. Oral Res. 2007, 21, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunel, K.; Pederson, S.S.; Diws, A. A central hemangioma of the mandible. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 1993, 75, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies. Available online: https://www.issva.org/classification (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janahi, L.A.; Abuzaid, M.; Atallah, A. Cavernous hemangioma of the maxilla (case report). Saudi J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2002, 4, 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, I.L.H.; Vasconcelos, M.; Panjwani, C.M.B.R.G.; Silva, H.L.M.A.; da Hora Sales, P.H.; de Andrade, C.S. Surgical Treatment of Aggressive Intraosseous Cavernous Hemangioma in Maxilla Through Surgical Resection. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2020, 31, e445–e448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-M.; Lee, J.-H. Recurrence of intraosseous cavernous hemangioma in the maxilla: A case report. OMFS Cases 2020, 6, 100147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, J.; Mehrparvar, G. Cavernous Hemangioma Involving the Maxilla: A Case Report. ORLFPS 2019, 5, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumawat, R.; Sarika, D. Central cavernous hemangioma of the maxilla a case report. Libyan Dent J. 2012, 2, 21751. [Google Scholar]
- Kai, Y.J.; Jun, C.; Ritsuo, T.; Rei, T.; Takafumi, H.; Takashi, S. Central hemangioma of the maxilla: Report of a case with an exophytic growth. Oral Oncol. Extra 2004, 40, 88–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, B.; Işılgan, S.E.; Cerkez, C.; Otrakçı, V.; Serel, S. Intraosseous cavernous hemangioma: A rare presentation in maxilla. Eplasty 2014, 14, e35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, M.; Noguchi, T.; Jinbu, Y.; Mori, Y. Hemangioma of the Maxilla. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2020, 31, 501–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aditya, A.P.; Patil, S.A.; Kore, A.A.; Sawant, V.S. Cavernous Hemangioma of Maxilla: Report of a Rare Case. J. Indian Acad. Oral. Med. Radiol. 2023, 35, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastanduono, E.; Namazi, F.; Liang, H.; Nair, M.; Woo, V.; Patel, P.; Tahmasbi, A.M. Central hemangioma of the maxilla: Variance in clinical and radiographic features. Proc. Bayl. Univ. Med. Cent. 2024, 37, 979–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gupta, D.; Singh, I.; Goyal, K.; Sobti, P. Infantile Intraosseous Maxillary Hemangioma. Indian Pediatr. 2016, 53, 1103–1104. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Piastro, K.; Chen, T.; Khatiwala, R.V.; Pinheiro-Neto, C.D. Endoscopic endonasal resection of cavernous hemangioma of the palate. Otolaryngol. Case Rep. 2017, 10, e3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.R.; Chen, E.; Cousin, T.; Oda, D. A case series of intraosseous hemangioma of the jaws: Various presentations of a rare entity. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2017, 9, e1366–e1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, A.; Sheik, S.; Vinod, V.; Garg, P. Images: Central hemangioma of the maxilla. Indian J. Radiol. 2007, 17, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.; Karni, R.; Ho, T. Osteofascial Radial Forearm Free Flap Reconstruction of Midface Defect After Resection of Intraosseous Hemangioma. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2018, 29, 754–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Hirsch, D.L. Resection of a large, central hemangioma with reconstruction using a radial forearm flap combined with zygomatic and pterygoid implants. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009, 67, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, N.; Jones, M.; Sandison, A.; Clarke, P.M. Maxillary haemangioma. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2006, 120, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Yu, J.J.; Tian, H.; Shan, Z.F.; Liu, X.Y.; Jia, J. Intraosseous venous malformation of the maxilla after enucleation of a hemophilic pseudotumor: A case report. World J. Clin. Cases 2020, 8, 4644–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Persky, M.S.; Yoo, H.J.; Berenstein, A. Management of vascular malformations of the mandible and maxilla. Laryngoscope 2003, 113, 1885–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.N.; Mishra, C.; Mehta, S.; Preet, E.; Dua, G. A case of venous malformation of maxillary alveolar ridge managed with polydocanal injections and Er:Yag laser: A case report. Int. J. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2023, 9, 765–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douami, A.; Marsafi, O.; Belgadir, H.; Merzem, A.; Nashi, L.; Amriss, O.; Moussali, N.; Elbenna, N. Maxillary intraosseous hemangioma: Case report. Pan. Afr. Med. J. 2024, 48, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colletti, G.; Frigerio, A.; Giovanditto, F.; Biglioli, F.; Chiapasco, M.; Fredri, I.J. Surgical Treatment of Vascular Malformations of the Facial Bones. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 72, e1–e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strauss, S.B.; Steinklein, J.M.; Phillips, C.D.; Shatzkes, D.R. Intraosseous Venous Malformations of the Head and Neck. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2022, 8, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djemi, E.M. Tumeurs benignes des maxillaires: Aspects epidémiologiques, diagnostiques et thérapeutiques. Dakar Med. 2024, 67, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beziat, J.L.; Marcelino, J.P.; Bascoulergue, Y.; Vitrey, D. Central Vascular Malformation of the Mandible: A case report. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1997, 55, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neville, B.W.; Damm, D.D.; Chi, A.C.; Allen, C.M. Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology, 4th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Marchuk, D.A. Pathogenesis of hemangioma. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 665–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamala, K.A.; Ashok, L.; Sujatha, G.P. Cavernous hemangioma of the tongue: A rare case report. Contemp. Clin. Dent. 2014, 5, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberger, S.; Bischoff, J. Pathogenesis of infantile haemangioma. Br. J. Dermatol. 2013, 169, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, A.; Mani, V.; Noufal, A. Update on the classification of hemangioma. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 2014, 18, S117–S120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulliken, J.B.; Glowacki, J. Hemangiomas and vascular malformations in infants and children: A classification based on endothelial characteristics. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1982, 69, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, S.C.; Pharoah, M.J. Oral Radiology: Principles and Interpretation. In Mosby, 7th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lund, B.A.; Dahlin, D.C. Hemangiomas of the mandible and maxilla. J. Oral Surg. Anesth. Hosp. Dent. Serv. 1964, 22, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wyke, B.D. Primary hemangioma of the skull; a rare cranial tumor; review of the literature and report of a case, with special reference to the roentgenographic appearances. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1949, 61, 302–316. [Google Scholar]
- Afshin, H.; Sharmin, R. Hemangioma involving the maxillary sinus. Oral. Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1974, 38, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magliocca, K.R.; Helman, J.I. Diagnostic Pathology: Head and Neck; Amirsys: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Marwah, N.; Agnihotri, A.; Dutta, S. Central Hemangioma: An overview and case report. Pediatr. Dent. 2006, 28, 460–466. [Google Scholar]



| Author | Type of Study | Cases (n) | Gender | Age (y) | Symptoms | Localization | Treatment | Size | X-Ray |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Janahi et al. [6] | Case report | 1 | M | 16 | Swelling | Palate (anterior part) | Embolization, radiotherapy, and excision | 1 × 2 cm | Radiodense |
| Ribeiro et al. [7] | Case report | 1 | M | 20 | Swelling | Right maxillary region | Surgical resection | Radiolucent | |
| Park et al. [8] | Case report | 1 | F | 12 | Asymptomatic | Right maxilla | Complete excision and curettage, with sodium tetradecyl sulfate injection | 3 × 2.9 × 2.7 | Radiolucent |
| Ghorbani et al. [9] | Case report | 1 | F | 45 | Swelling | Right maxilla (extending into the middle meatal) | Excision with 3 mm of margin | Mixed | |
| Kumawat et al. [10] | Case report | 1 | F | 16 | Swelling | Left maxillary bone, in region 23 to 26 | Surgical excision and curettage | 3 cm × 2 cm (extraoral) | Mixed |
| Kai Yu Jen [11] | Case report | 1 | F | 74 | Conspicuous swelling around her nasal vestibule | From the maxillary anterior to premolars region | Surgical excision (hemi maxillectomy) | 20 mm × 38 mm × 58 mm | Radiolucent |
| Kaya et al. [12]. | Case report | 1 | F | 42 | Asymptomatic | Left maxilla in close proximity to the zygomatic | Surgical excision | 16 mm diameter | MRI |
| Yamashita et al. [13] | Case report | 1 | F | 64 | Asymptomatic | Base of the left maxilla | Surgical excision and curettage, with tetracycline hydrochloride ointment gauze applied | Radio-opaque | |
| Aditya et al. [14] | Case report | 1 | M | 16 | Swelling | Maxillary left anterior region | Sclerotherapy: 3% Setrol (sodium tetradecyl sulfate) intralesional injection at multiple sites each 2–3 weeks of interval and follow-up. Surgery only if necessary | 31 × 26 × 49 mm | Mixed |
| Mastanduono et al. [15] | Case series | 2 | 1: F 2: M | 1: 62 2: 14 | Swelling | 1: 13–14–15 region 2: 11–24 region | Not specified | 1 Radiolucent 2: Mixed | |
| Gupta et al. [16] | Case report | 1 | M | 1 month old | Progressive swelling and alveolar fullness | Right maxilla | Oral steroids (2 mg/kg/day) for two months, followed by gradual fortnightly tapering | / | Mixed |
| Piastro et al. [17] | Case report | 1 | F | 56 | Left nasal epistaxis and discomfort | Palate | Surgical excision | / | Radiolucent |
| Chandra et al. [18] | Case report | 1 | M | 46 | Teeth pushed apart | Between teeth 12 and 13 | Surgical excision | / | Radiolucent |
| Mittal et al. [19] | Case report | 1 | F | 21 | Slow and gradually increasing swelling; exfoliation of one of the upper right teeth | Right maxilla | Not specified | / | Mixed |
| Johnson et al. [20] | Case report | 1 | M | 47 | Enlarging, painless mass | Right maxilla | Surgical resection | / | Radio-opaque |
| Panagos et al. [21] | Case report | 1 | M | 77 | Sinus congestion and frequent epistaxis, which required hospitalization and transfusion | Left palate and maxilla | Selective embolization of the feeding vessels, followed by surgical resection | 6 × 4 cm | Radio-opaque |
| Goyal et al. [22] | Case report | 1 | F | Unspecified (young patient) | Asymptomatic | Left maxilla | Surgical excision | 2.1 × 1.5 × 1.5 cm | Mixed |
| Cai X et al. [23] | Case report | 1 | M | 11 | Swelling | Right maxilla and right maxillary sinus | Surgical resection | 3 cm × 2.5 cm × 2.5 cm | Radiolucent |
| Persky MS et al. [24] | Case series | 3 cases | 1: F 2: M 3: M | 1: 10 2: 4 3: 23 | Asymptomatic | Not specified | Not specified | ||
| Kumar N. A. et al. [25] | Case report | 1 | F | 65 | Asymptomatic | Left maxillary alveolar ridge | Polidocanol injections and Excision | Soft swelling of approximately 0.8 × 1 cm | Not specified |
| Douami A. [26] | Case report | 1 | F | 71 | Asymptomatic | Left maxillary bone | Surgical excision | 1.5 × 1 cm approximately | Radio-opaque |
| Colletti et al. [27] | Case series | 1, 3 not specified | F, 3 not specified | 16 n3 not specified | Swelling, palatal mass 3 not specified | Right maxillary bone 3 not specified | Surgical excision and curettage 3 not specified | Not specified | Radiolucent lesion 3 not specified |
| Our case | Case report | 1 | M | 63 | Asymptomatic | Right palate | Surgical excision | 9 × 8 × 12.5 mm | Radiolucent |
| Vascular Tumors | Vascular Malformation |
|---|---|
| Benign Infantile hemangioma rapidly involuting (RICH) Non-involuting (NICH) Partially involuting (PICH) Tufted angioma Spindle-cell hemangioma Pyogenic granuloma Others | Capillary malformations Lymphatic malformations Venous malformation Arteriovenous malformations Arteriovenous fistula |
| Locally aggressive or borderline
Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma Retiform hemangioendothelioma Papilary lintralymphatic angioendothelioma Dabska tumor Composite hemangioendothelioma Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma not otherwise specified Kaposi sarcoma Others | |
| Malignant Angiosarcoma Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma Others |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perez, A.; Pierantozzi, E.; Cancela, A.J.; Cimini, V.; Lombardi, T. Venous Malformation of the Maxilla: A Systematic Review and a Report of an Unusual Case. Surgeries 2025, 6, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/surgeries6030056
Perez A, Pierantozzi E, Cancela AJ, Cimini V, Lombardi T. Venous Malformation of the Maxilla: A Systematic Review and a Report of an Unusual Case. Surgeries. 2025; 6(3):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/surgeries6030056
Chicago/Turabian StylePerez, Alexandre, Elena Pierantozzi, Anaël Jose Cancela, Valerio Cimini, and Tommaso Lombardi. 2025. "Venous Malformation of the Maxilla: A Systematic Review and a Report of an Unusual Case" Surgeries 6, no. 3: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/surgeries6030056
APA StylePerez, A., Pierantozzi, E., Cancela, A. J., Cimini, V., & Lombardi, T. (2025). Venous Malformation of the Maxilla: A Systematic Review and a Report of an Unusual Case. Surgeries, 6(3), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/surgeries6030056








