Recurrence Rates of Pilonidal Sinus Disease Are High in Children and Recurrences Occur Exceedingly Early
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. High Recurrence Rates in Children and Adolescents
3. Recurrences in Children and Adolescents Occur Very Early Compared to Adults
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
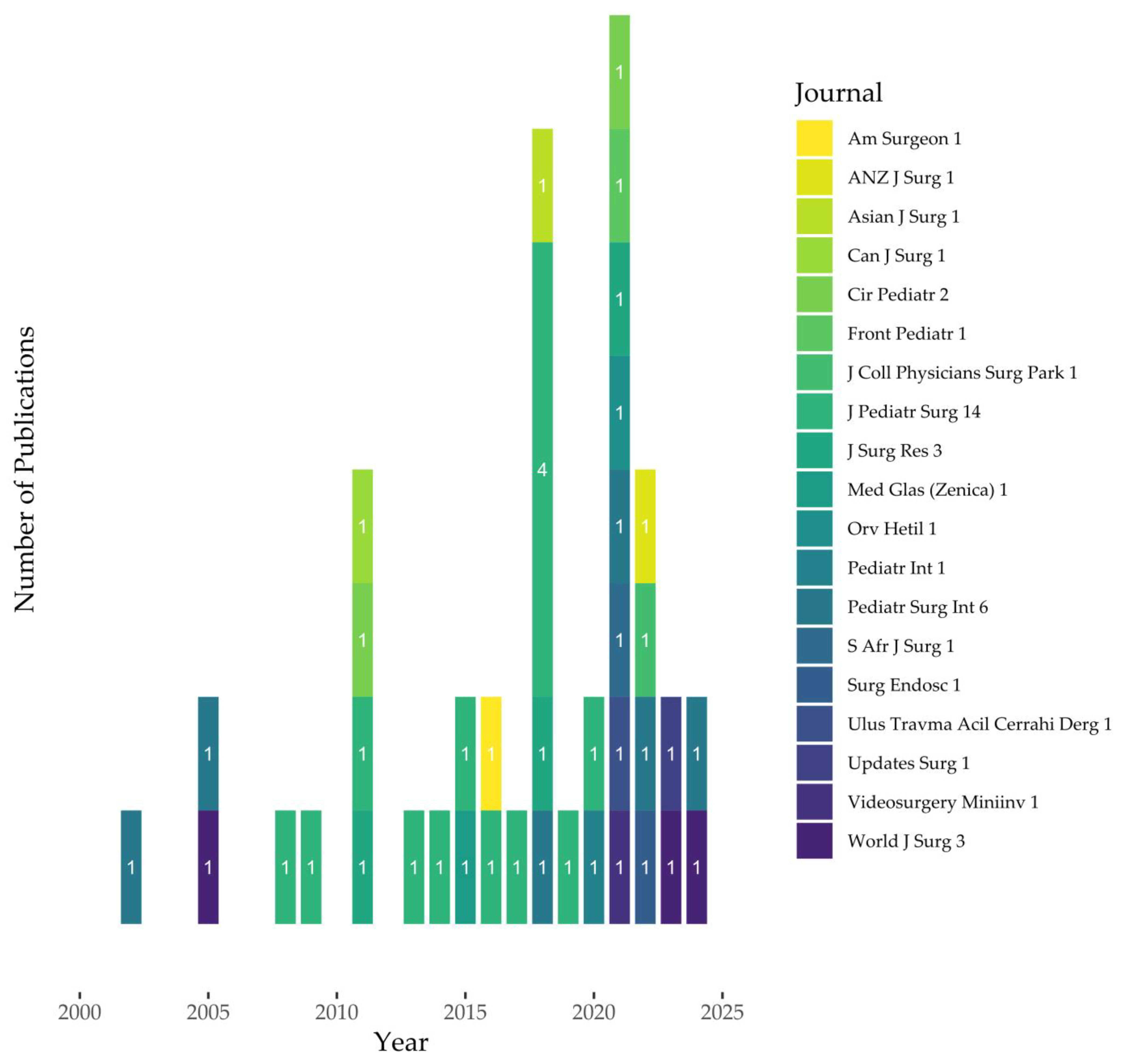
References
- Nasr, A.; Ein, S.H. A Pediatric Surgeon’s 35-Year Experience with Pilonidal Disease in a Canadian Children’s Hospital. Can. J. Surg. 2011, 54, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davage, O.N. The Origin of Sacrococcygeal Pilonidal Sinuses Based on an Analysis of Four Hundred Sixty-Three Cases. Am. J. Pathol. 1954, 30, 1191–1205. [Google Scholar]
- Engels, M.N.; Lüken-Darius, B.; Oetzmann von Sochaczewski, C.; Heydweiller, A.C. The Effects of Intraoperative Use of Blue Dyes in Paediatric Pilonidal Sinus Disease—A Retrospective Exploratory Cohort Study. Egypt Pediatric Association Gaz. 2024, 72, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karahan, O.; Eryilmaz, M.A.; Torun, V.; Sevinc, B.; Koksal, H.; Aksoy, F.; Ay, S. Is the Increase in the Number of Pilonidal Sinus Surgery Normal? Turkish J. Surg. 2010, 26, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evers, T.; Doll, D.; Matevossian, E.; Noe, S.; Neumann, K.; Li, H.; Hüser, N.; Lüdde, R.; Hoffmann, S.; Krapohl, B.D. Trends in incidence and long-term recurrence rate of pilonidal sinus disease and analysis of associated influencing factors. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi 2011, 49, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Doll, D.; Luedi, M.M.; Wieferich, K.; van der Zypen, D.; Maak, M.; Glanemann, M. Stop Insulting the Patient: Neither Incidence nor Recurrence of Pilonidal Sinus Disease Is Linked to Personal Hygiene. Pilonidal Sinus J. 2015, 1, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Oetzmann von Sochaczewski, C.; Gödeke, J. Pilonidal Sinus Disease on the Rise: A One-Third Incidence Increase in Inpatients in 13 Years with Substantial Regional Variation in Germany. Int. J. Colorectal. Dis. 2021, 36, 2135–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, D.; Orlik, A.; Maier, K.; Kauf, P.; Schmid, M.; Diekmann, M.; Vogt, A.P.; Stauffer, V.K.; Luedi, M.M. Impact of Geography and Surgical Approach on Recurrence in Global Pilonidal Sinus Disease. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, D.; Stauffer, V.; Diekann, M.; Van Wyk, P.; Luedi, M.M. Turkey Is Leading in the 21st Century Pilonidal Sinus Disease Research. Turk. J. Surg. 2020, 36, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Søndenaa, K.; Andersen, E.; Nesvik, I.; Søreide, J.A. Patient Characteristics and Symptoms in Chronic Pilonidal Sinus Disease. Int. J. Colorect. Dis. 1995, 10, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimi-Jazi, F.; Abrajano, C.; Garza, D.; Rafeeqi, T.; Yousefi, R.; Hartman, E.; Hah, K.; Wilcox, M.; Diyaolu, M.; Chao, S.; et al. Burden of Pilonidal Disease and Improvement in Quality of Life after Treatment in Adolescents. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2022, 38, 1453–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fike, F.B.; Mortellaro, V.E.; Juang, D.; Ostlie, D.J.; St. Peter, S.D. Experience with Pilonidal Disease in Children. J. Surg. Res. 2011, 170, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braungart, S.; Powis, M.; Sutcliffe, J.R.; Sugarman, I.D. Improving Outcomes in Pilonidal Sinus Disease. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2016, 51, 282–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halleran, D.R.; Lopez, J.J.; Lawrence, A.E.; Sebastião, Y.V.; Fischer, B.A.; Cooper, J.N.; Deans, K.J.; Minneci, P.C. Recurrence of Pilonidal Disease: Our Best Is Not Good Enough. J. Surg. Res. 2018, 232, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto, J.M.; Checchi, K.D.; Kling, K.M.; Ignacio, R.C.; Bickler, S.W.; Saenz, N.C.; Fairbanks, T.J.; Nicholson, S.I.; Lazar, D.A. Trephination versus Wide Excision for the Treatment of Pediatric Pilonidal Disease. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2020, 55, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, S.; Soares-Aquino, C.; Teixeira, I.; Monteiro, J.M.; Campos, M. Minimally Invasive Treatment of Pilonidal Sinus Disease in a Paediatric Population: Comparison of Two Techniques. ANZ J. Surg. 2022, 92, 3288–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Check, N.M.; Wynne, N.K.; Mooney, D.P. Resolution of Mild Pilonidal Disease in Adolescents Without Resection. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2022, 235, 773–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stauffer, V.K.; Luedi, M.M.; Kauf, P.; Schmid, M.; Diekmann, M.; Wieferich, K.; Schnüriger, B.; Doll, D. Common Surgical Procedures in Pilonidal Sinus Disease: A Meta-Analysis, Merged Data Analysis, and Comprehensive Study on Recurrence. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baur, T.; Stauffer, V.K.; Vogt, A.P.; Kauf, P.; Schmid, M.; Luedi, M.M.; Doll, D. Recurrence Rates after Uncommon Surgical Procedures for Pilonidal Sinus Disease: A Merged Data Analysis. Coloproctology 2019, 41, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonelli, C.M.; Lorenzo, I.; Bunn, C.; Kulshrestha, S.; Abdelsattar, Z.M.; Cohn, T.; Luchette, F.A.; Baker, M.S. Contemporary Matched-Cohort Comparison of Surgical Approach to Inguinal Hernia Repair: Are Minimally Invasive Approaches Associated with Higher Rates of Recurrence? J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2022, 235, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maasewerd, S.K.M.; Stefanescu, M.-C.; König, T.T.; Engels, M.N.; Rohleder, S.; Schwind, M.; Heydweiller, A.C.; Oetzmann Von Sochaczewski, C. Paediatric Pilonidal Sinus Disease: Early Recurrences Irrespective of the Treatment Approaches in a Retrospective Multi-Centric Analysis. World J. Surg. 2023, 47, 2296–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, E.J.O.; Herrod, P.J.; Doleman, B.; Phillips, H.G.; Ranat, R.; Lund, J.N. Surgical Interventions for the Treatment of Sacrococcygeal Pilonidal Sinus Disease in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2019, 54, 2222–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowski, J.; Oyetunji, T.A.; Goldin, A.B.; Baird, R.; Gosain, A.; Lal, D.R.; Kawaguchi, A.; Downard, C.; Sola, J.E.; Arthur, L.G.; et al. The Management of Pilonidal Disease: A Systematic Review. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2019, 54, 2210–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfammatter, M.; Erlanger, T.E.; Mayr, J. Primary Transverse Closure Compared to Open Wound Treatment for Primary Pilonidal Sinus Disease in Children. Children 2020, 7, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roldón Golet, M.; Siles Hinojosa, A.; González Ruiz, Y.; Escartín Villacampa, R.; Goded Broto, I.; Bragagnini Rodríguez, P. Pilonidal Sinus in Adolescence: Is There an Ideal Surgical Approach? Cir. Pediatr. 2021, 34, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sabapaty, A.; Salimi-Jazi, F.; Abrajano, C.; Yousefi, R.; Garza, D.; Dalusag, K.S.; Hui, T.; Su, W.; Mueller, C.; Fuchs, J.; et al. Comorbidities Are Not Associated with Pain Symptom or Recurrence in Patients with Pilonidal Disease. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2024, 40, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giles, W.; Murthi, G.; Lindley, R. Pit Excision with Fibrin Glue Closure versus Lateralizing Flap Procedures in the Management of Pilonidal Sinus Disease in Adolescents: A 14-Year Cohort Study. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2024, 40, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreznik, Y.; Sher, C.; Baazuv, A.; Yekutiel, G.; Kravarusic, D. Recurrence Rates of Pilonidal Sinus Disease in the Pediatric Population Following Trephine Surgery. World J. Surg. 2024, 48, 1261–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.G.; Short, C.; Zhong, A.; Vojvodic, V.; Sundin, A.; Spurrier, R.G.; Wang, K.S.; Pelayo, J.C. Outcomes of Pediatric Pilonidal Disease Treatment: Excision with off-Midline Flap Reconstruction versus Endoscopic Pilonidal Sinus Treatment. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2024, 40, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, C.; Leva, E.; Gamba, P.; Sgrò, A.; Ferrentino, U.; Papparella, A.; Chiarenza, F.; Bleve, C.; Mendoza-Sagaon, M.; Montaruli, E.; et al. Pediatric Endoscopic Pilonidal Sinus Treatment (PEPSiT): Report of a Multicentric National Study on 294 Patients. Updates Surg. 2023, 75, 1625–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erculiani, M.; Mottadelli, G.; Carlini, C.; Barbetta, V.; Dusio, M.P.; Pini Prato, A. Long-Term Results of EPSiT in Children and Adolescents: Still the Right Way to Go. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2022, 38, 1257–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozukucuk, A.; Cakiroglu, B.; Yapici, S.; Cesur, I.B.; Ozcelik, Z.; Kilic, H.H. Comparing Crystallized Phenol and Surgical Excision Treatments in Pilonidal Sinus Disease. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2022, 32, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baxter, J.; Espinosa, J.A.; Leinwand, M.J. The EPIC Procedure (Endoscopic-Assisted Pilonidal Irrigation and Cleaning): A Simple and Effective Treatment for Pilonidal Disease. Surg. Endosc. 2022, 36, 1380–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzger, G.A.; Apfeld, J.C.; Nishimura, L.; Beyene, T.J.; Lutz, C.; Deans, K.J.; Minneci, P.C. Room for Improvement: The Trephination Procedure for Pediatric Patients with Pilonidal Disease. J. Surg. Res. 2021, 267, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madenci, H.; Uysal, M. Risk Factors for Recurrence after Pilonidal Sinus Surgery in Children and Adolescents. S. Afr. J. Surg. 2021, 59, 62–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Bertólez, S.; Martín-Solé, O.; Moraleda, I.; Cuesta, M.; Massaguer, C.; Palazón, P.; Tarrado, X. Advantages of Endoscopic Pilonidal Sinus Treatment. Cir. Pediatr. 2021, 34, 191–199. [Google Scholar]
- Gökbuget, Z.M.; Özcan, R.; Karagöz, A.; Tütüncü, A.C.; Tekant, G.T. Endoscopic Pilonidal Sinus Treatment (EPSiT) in the Pediatric Age Group: Short-Term Results. Ulus. Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2021, 27, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotlacil, V.; Rygl, M.; Frybova, B. Initial Experience with Minimally Invasive Treatment of Pilonidal Sinus in Children. Videosurgery Miniinv. 2021, 16, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorth, D.; Königs, I.; Elrod, J.; Ghadban, T.; Reinshagen, K.; Boettcher, M. Combination of Side-Swing Flap with Negative-Pressure Wound Therapy Is Superior to Open Excision or Flap Alone in Children with Pilonidal Sinus—But at What Cost? Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 595684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslan, S.; Okur, M.H.; Basuguy, E.; Aydogdu, B.; Zeytun, H.; Cal, S.; Tegin, S.; Azizoglu, M. Crystallized Phenol for Treatment of Pilonidal Sinus Disease in Children: A Comparative Clinical Study. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2021, 37, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadgyas, B.; Langer, M.; Ringwald, Z. Sinus Pilonidalis Fisztuloszkópos Kezelése Gyermekekben. Orv. Hetil. 2021, 162, 1740–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gezer, H.Ö.; Ezer, S.S.; İnce, E.; Temiz, A. Treatment of Young Patients with Pilonidal Sinus Disease with the Original (Unmodified) Limberg Flap Standardized for the First Time. Pediatr. Int. 2020, 62, 1171–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, E.; Herrod, P.; Sian, T.; Boyd-Carson, H.; Blackwell, J.; Lund, J.; Quarmby, J. Fibrin Glue Obliteration Is Safe, Effective and Minimally Invasive as First Line Treatment for Pilonidal Sinus Disease in Children. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2019, 54, 1668–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sequeira, J.B.; Coelho, A.; Marinho, A.S.; Bonet, B.; Carvalho, F.; Moreira-Pinto, J. Endoscopic Pilonidal Sinus Treatment versus Total Excision with Primary Closure for Sacrococcygeal Pilonidal Sinus Disease in the Pediatric Population. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2018, 53, 2003–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozcan, R.; Hüseynov, M.; Bakır, A.C.; Emre, S.; Tütüncü, C.; Celayir, S.; Tekant, G.T. Which Treatment Modality for Pediatric Pilonidal Sinus: Primary Repair or Secondary Healing? Asian J. Surg. 2018, 41, 506–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pini Prato, A.; Mazzola, C.; Mattioli, G.; Escolino, M.; Esposito, C.; D’Alessio, A.; Abati, L.C.; Leonelli, L.; Carlini, C.; Rotundi, F.; et al. Preliminary Report on Endoscopic Pilonidal Sinus Treatment in Children: Results of a Multicentric Series. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2018, 34, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ates, U.; Ergun, E.; Gollu, G.; Sozduyar, S.; Kologlu, M.; Cakmak, M.; Dindar, H.; Yagmurlu, A. Pilonidal Sinus Disease Surgery in Children: The First Study to Compare Crystallized Phenol Application to Primary Excision and Closure. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2018, 53, 452–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umesh, V.; Sussman, R.H.; Smith, J.; Whyte, C. Long Term Outcome of the Bascom Cleft Lift Procedure for Adolescent Pilonidal Sinus. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2018, 53, 295–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutus, H.M.; Aksu, B.; Uzun, E.; Gulcin, N.; Gercel, G.; Ozatman, E.; Durakbasa, C.U.; Okur, H. Long-Term Analysis of Surgical Treatment Outcomes in Chronic Pilonidal Sinus Disease. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2018, 53, 293–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speter, C.; Zmora, O.; Nadler, R.; Shinhar, D.; Bilik, R. Minimal Incision as a Promising Technique for Resection of Pilonidal Sinus in Children. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2017, 52, 1484–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagory, J.A.; Golden, J.; Holoyda, K.; Demeter, N.; Nguyen, N.X. Excision and Primary Closure May Be the Better Option in the Surgical Management of Pilonidal Disease in the Pediatric Population. Am. Surgeon 2016, 82, 964–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.M.; Jones, A.; Dass, D.; Murthi, G.; Lindley, R. Early Experience of the Use of Fibrin Sealant in the Management of Children with Pilonidal Sinus Disease. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2015, 50, 320–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekmenli, T.; Ciftci, I. Surgical Therapy for Pilonidal Sinus in Adolescents: A Retrospective Study. Med. Glas. 2015, 12, 57–60. [Google Scholar]
- Yildiz, T.; Ilce, Z.; Kücük, A. Modified Limberg Flap Technique in the Treatment of Pilonidal Sinus Disease in Teenagers. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2014, 49, 1610–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afşarlar, Ç.E.; Yılmaz, E.; Karaman, A.; Karaman, İ.; Özgüner, İ.F.; Erdoğan, D.; Çavuşoğlu, Y.H.; Maden, H.A. Treatment of Adolescent Pilonidal Disease with a New Modification to the Limberg Flap: Symmetrically Rotated Rhomboid Excision and Lateralization of the Limberg Flap Technique. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2013, 48, 1744–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Temprano, N.; Sánchez-Vázquez, M.; Ayuso-González, L.; Pisón-Chacón, J.; Pérez-Martínez, A. ¿Estamos tratando bien la enfermedad pilonidal en los niños? Objetivos terapéuticos más allá de prevenir la recidiva. Cir. Pediatr. 2011, 24, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gendy, A.S.; Glick, R.D.; Hong, A.R.; Dolgin, S.E.; Soffer, S.Z.; Landers, H.; Herrforth, M.; Rosen, N.G. A Comparison of the Cleft Lift Procedure vs Wide Excision and Packing for the Treatment of Pilonidal Disease in Adolescents. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2011, 46, 1256–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamout, S.Z.; Caty, M.G.; Lee, Y.-H.; Lau, S.T.; Escobar, M.A.; Glick, P.L. Early Experience with the Use of Rhomboid Excision and Limberg Flap in 16 Adolescents with Pilonidal Disease. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2009, 44, 1586–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.L.; Tejirian, T.; Abbas, M.A. Current Management of Adolescent Pilonidal Disease. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2008, 43, 1124–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morden, P.; Drongowski, R.A.; Geiger, J.D.; Hirschl, R.B.; Teitelbaum, D.H. Comparison of Karydakis versus Midline Excision for Treatment of Pilonidal Sinus Disease. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2005, 21, 793–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arda, İ.S.; Güney, L.H.; Sevmiş, Ş.; Hiçsönmez, A. High Body Mass Index as a Possible Risk Factor for Pilonidal Sinus Disease in Adolescents. World J. Surg. 2005, 29, 469–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serour, F.; Somekh, E.; Krutman, B.; Gorenstein, A. Excision with Primary Closure and Suction Drainage for Pilonidal Sinus in Adolescent Patients. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2002, 18, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diéguez, I.; Costa, A.; Miró, I.; March Villalba, J.A.; del Peral, M.; Marco Macián, A.; Vila, J.J. En Bloc Resection vs. Dips Procedure in Pilonidal Sinus Surgery. Cir. Pediatr. 2022, 35, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, A.I.; Barroso, C.; Osório, A.; Correia-Pinto, J. Minimally Invasive Surgical Treatment of Pilonidal Disease: Mid-Term Retrospective Analysis of a Single Center. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doody, D.P. Pilonidal Cyst Disease. In Fundamentals of Pediatric Surgery; Mattei, P., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 467–474. ISBN 978-1-4419-6642-1. [Google Scholar]
- Collings, A.T.; Rymeski, B. Updates on the Management of Pilonidal Disease. Adv. Pediatr. 2022, 69, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froehlich, M.; Wagner, J.P.; Lee, S.L. Pilonidal Disease Surgery in the Pediatric Patient: Less Is More! Semin. Colon. Rectal. Surg. 2022, 33, 100911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, C.V.; Springall, R. ‘D’ Excision for Sacrococcygeal Pilonidal Sinus Disease. J. R. Soc. Med. 1987, 80, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattei, P. Pilonidal Disease. In Fundamentals of Pediatric Surgery; Mattei, P., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 403–406. ISBN 978-3-031-07523-0. [Google Scholar]
- Minneci, P.C.; Halleran, D.R.; Lawrence, A.E.; Fischer, B.A.; Cooper, J.N.; Deans, K.J. Laser Hair Depilation for the Prevention of Disease Recurrence in Adolescents and Young Adults with Pilonidal Disease: Study Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial. Trials 2018, 19, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minneci, P.C.; Gil, L.A.; Cooper, J.N.; Asti, L.; Nishimura, L.; Lutz, C.M.; Deans, K.J. Laser Epilation as an Adjunct to Standard Care in Reducing Pilonidal Disease Recurrence in Adolescents and Young Adults: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Surg. 2023, 159, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martina, A. Über kongenitale sacrococcygeale Fisteln. Dtsch. Z Chir. 1905, 80, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gage, M. Pilonidal Sinus: An Explanation of Its Embryologic Development. Arch. Surg. 1935, 31, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kark, W. Pilonidal Sinus. S. Afr. Med. J. 1946, 20, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lewin, R.A. Pilonidal Sinus in Infancy. Pediatrics 1965, 35, 795–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, J.W.; Vawter, G.F. The Congenital Origin of Pilonidal Sinus. J. Pediatr. Surg. 1974, 9, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karydakis, G.E. Easy and Successful Treatment of Pilonidal Sinus After Explanation of Its Causative Process. ANZ J. Surg. 1992, 62, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özkan, Z.; Aksoy, N.; Emir, S.; Kanat, B.H.; Gönen, A.N.; Yazar, F.M.; Çimen, A.R. Investigation of the Relationship between Serum Hormones and Pilonidal Sinus Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study. Colorectal. Dis. 2014, 16, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjei, N.N.; Yung, N.; Towers, G.; Caty, M.; Solomon, D.; Vash-Margita, A. Establishing an Association between Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome and Pilonidal Disease in Adolescent Females. J. Pediatr. Adolesc. Gynecol. 2023, 36, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurbanov, A.; Ergün, E.; Göllü, G.; Ateş, U. Management of Sacrococcygeal Pilonidal Sinus Disease in Children: A Survey Study in Turkey. Turk. J. Surg. 2021, 37, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riis, P.T.; Saunte, D.M.; Sigsgaard, V.; Villani, A.P.; Guillem, P.; Pascual, J.C.; Kappe, N.N.; Vanlaerhoven, A.M.J.D.; Van Der Zee, H.H.; Prens, E.P.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Pediatric Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A Cross-Sectional Multicenter Study of 140 Patients. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2020, 312, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcovich, S.; Fania, L.; Caposiena, D.; Giovanardi, G.; Chiricozzi, A.; De Simone, C.; Tartaglia, C.; Ciccone, D.; Bianchi, L.; Abeni, D.; et al. Pediatric Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A Cross-Sectional Study on Clinical Features and Treatment Approaches. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2022, 26, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ureña-Paniego, C.; Gamissans-Cañada, M.; Molina-Leyva, A.; Romaní, J. Pilonidal Sinus Disease Is Associated with Severe Hidradenitis Suppurativa in a Spanish Cohort. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2023, 103, adv6569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safadi, M.F.; Dettmer, M.; Berger, M.; Degiannis, K.; Wilhelm, D.; Doll, D. Demographic Overview of Pilonidal Sinus Carcinoma: Updated Insights into the Incidence. Int. J. Colorectal. Dis. 2023, 38, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safadi, M.F.; Degiannis, K.; Doll, D. Pilonidal Sinus Disease Carcinoma: Survival and Recurrence Analysis. J. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 128, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safadi, M.F.; Ghareb, K.; Daher, A.; Dettmer, M.; Shamma, H.; Doll, D. Eight Patients with Pilonidal Carcinoma in One Decade—Is the Incidence Rising? Cureus 2022, 14, e27054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.J.; Strong, E.B.; Lund, J.; Hind, D.; Brown, S.R.; the PITSTOP Management Group. A Survey of Treatment Preferences of UK Surgeons in the Treatment of Pilonidal Sinus Disease. Colorectal. Dis. 2023, 25, 2010–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamdark, T.; Vuille-dit-Bille, R.N.; Bielicki, I.N.; Guglielmetti, L.C.; Choudhury, R.A.; Peters, N.; Doll, D.; Luedi, M.M.; Adamina, M. Treatment Strategies for Pilonidal Sinus Disease in Switzerland and Austria. Medicina 2020, 56, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolsøe, A.; Andresen, K.; Rosenberg, J. Repair of Recurrent Hernia Is Often Performed at a Different Clinic. Hernia 2016, 20, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kati, Ö.; Kandur, Y.; Kaya, M.; Güler, A.G.; Dalkiran, T. A Comparative Study between Adolescent and Adult Patients with Pilonidal Sinus Disease. Anatolian Curr. Med. J. 2021, 3, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iesalnieks, I.; Ommer, A.; Herold, A.; Doll, D. German National Guideline on the Management of Pilonidal Disease: Update 2020. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2021, 406, 2569–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.K.; Vogel, J.D.; Cowan, M.L.; Feingold, D.L.; Steele, S.R. The American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons’ Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Pilonidal Disease. Dis. Colon Rectum 2019, 62, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milone, M.; Basso, L.; Manigrasso, M.; Pietroletti, R.; Bondurri, A.; La Torre, M.; Milito, G.; Pozzo, M.; Segre, D.; Perinotti, R.; et al. Consensus Statement of the Italian Society of Colorectal Surgery (SICCR): Management and Treatment of Pilonidal Disease. Tech. Coloproctol. 2021, 25, 1269–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, C.; Lepore, B.; Cerulo, M.; Borgogni, R.; Del Conte, F.; Coppola, V.; Di Mento, C.; Carulli, R.; Cardone, R.; Cortese, G.; et al. Quality of Life of Pediatric Patients Operated for Pilonidal Sinus Disease. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2023, 182, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop-Jordanova, N. Chronic Diseases in Children as a Challenge for Parenting. Prilozi 2023, 44, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohan, J.M.; Winter, M.A. Ethical Considerations in Pediatric Chronic Illness: The Relationship between Psychological Factors, Treatment Adherence, and Health Outcomes. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2021, 39, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delshad, H.R.; Henry, O.; Mooney, D.P. Improving Resource Utilization and Outcomes Using a Minimally Invasive Pilonidal Protocol. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2020, 55, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, O.S.; Farr, B.J.; Check, N.M.; Mooney, D.P. A Minimally Invasive Pilonidal Protocol Improves Quality of Life in Adolescents. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2021, 56, 1861–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafeeqi, T.; Abrajano, C.; Salimi-Jazi, F.; Garza, D.; Hartman, E.; Hah, K.; Wilcox, M.; Diyaolu, M.; Chao, S.; Su, W.; et al. Adoption of a Standardized Treatment Protocol for Pilonidal Disease Leads to Low Recurrence. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2023, 58, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, L.A.; Deans, K.J.; Minneci, P.C. Management of Pilonidal Disease: A Review. JAMA Surg. 2023, 158, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igler, E.C.; Austin, J.E.; Sejkora, E.K.D.; Davies, W.H. Friends’ Perspective: Young Adults’ Reaction to Disclosure of Chronic Illness. J. Clin. Psychol. Med. Settings 2024, 31, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taddeo, D.; Egedy, M.; Frappier, J.-Y. Adherence to Treatment in Adolescents. Paediatr. Child Health 2008, 13, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, C.; Adams, M.; Abrajano, C.; Yousefi, R.; Dalusag, K.S.; Hui, T.; Su, W.; Fuchs, J.; Chiu, B. A Standardized Treatment Protocol for Pilonidal Disease Can Influence the Health Mindset of Adolescents. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2024, 409, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, R.E.K. Challenges in Long-Term Health Care for Children. Ambul. Pediatr. 2001, 1, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, L.A.; Huddleston-Casas, C.; Morgan, K.; Feldman, D. Mixed Methods Study of Management of Health Conditions in Rural Low-Income Families: Implications for Health Care Policy in the USA. Rural. Remote Health 2012, 12, 1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wende, D.; Karmann, A.; Weinhold, I. Deprivation as a Fundamental Cause of Morbidity and Reduced Life Expectancy: An Observational Study Using German Statutory Health Insurance Data. Int. J. Health Econ. Manag. 2024, 24, 257–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

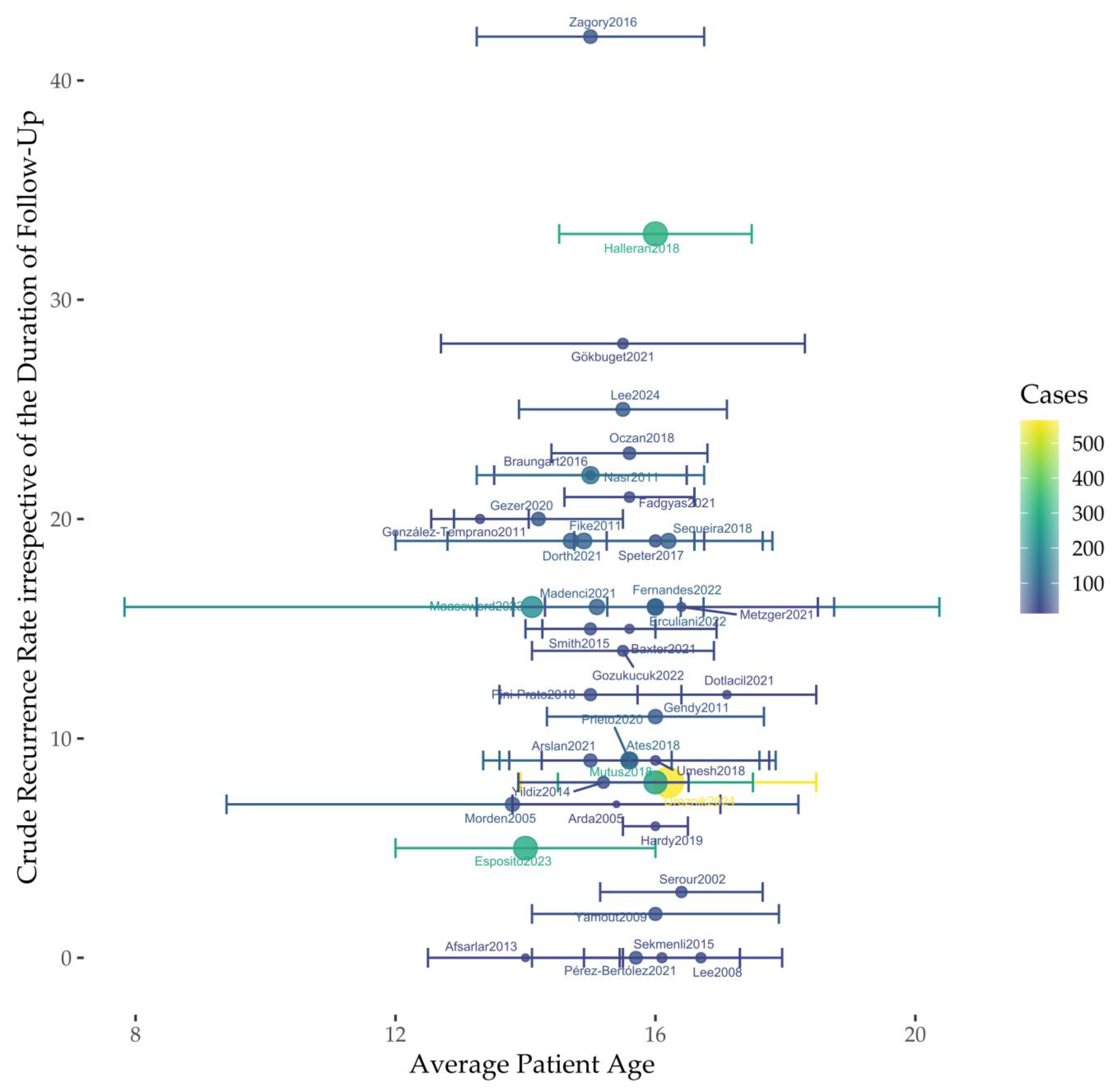
| Study | Year | Cases | Crude Recurrence Rate | Age | Measure of Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [28] | 2024 | 565 | 8% (n = 46) | 16.2 * | 8.9–18 ~ |
| [29] | 2024 | 63 | 25% (n = 16) | 15.5 # | 1.6 § (12–18) ~ |
| [21] | 2023 | 213 | 16% (n = 34) | 14.1 * | 3.7–15.6 $ |
| [30] | 2023 | 294 | 5% (n = 14) | 14 * | 10–18 ~ |
| [16] | 2022 | 106 | 16% (n = 17) | 16 * | 15–16 $ |
| [31] | 2022 | 99 | 14% (n = 16) | 16 * | 8–19 ~ |
| [32] | 2022 | 319 | 6% (n = 19) | 15.5 # | 1.4 § |
| [33] | 2022 | 20 | 15% (n = 3) | 15.6 # | 1.64 § |
| [34] | 2021 | 19 | 16% (n = 3) | 16.4 # | 2.1 § (12.5–19.9) ~ |
| [35] | 2021 | 86 | 16% (n = 14) | 15.1 # | 1.29 § |
| [36] | 2021 | 49 | 0% | 15.7 # | 1.6 § (14.7–16.7) $ |
| [37] | 2021 | 29 | 28% (n = 8) | 15.5 # | 2.8 § |
| [38] | 2021 | 17 | 12% (n = 2) | 17.1 * | 12.5–18 ~ |
| [39] | 2021 | 85 | 19% (n = 16) | 14.7 # | 1.9 § |
| [40] | 2021 | 54 | 9% (n = 5) | 15 # | 12–17 ~ |
| [41] | 2021 | 28 | 21% (n = 6) | 15.6 # | 13–17 ~ |
| [15] | 2020 | 105 | 9% (n = 9) | 15.6 # | 10–19 ~ |
| [42] | 2020 | 60 | 20% (n = 12) | 14.2 # | 1.3 § (9–17) ~ |
| [43] | 2019 | 18 | 6% (n = 1) | 16 * | 15–17 ~ |
| [14] | 2018 | 307 | 33% (n = 102) | 16 * | 15–17 $ |
| [44] | 2018 | 84 | 18% (n = 15) | 16.2 * | 12.1–17.9 ~ |
| [45] | 2018 | 47 | 23% (n = 11) | 15.6 # | 1.2 § |
| [46] | 2018 | 43 | 12% (n = 5) | 15 # | 1.4 § |
| [47] | 2018 | 117 | 9% (n = 11) | 15.6 # | 12–20 ~ |
| [48] | 2018 | 22 | 9% (n = 2) | 16 * | 11–18 ~ |
| [49] | 2018 | 268 | 8% (n = 21) | 16 * | 12–18 ~ |
| [50] | 2017 | 43 | 19% (n = 8) | 16 * | 14–17 $ |
| [51] | 2016 | 60 | 42% (n = 25) | 15 # | 13–20 ~ |
| [13] | 2016 | 19 | 21% (n = 4) | 15 * | 13.8–15.8 $ |
| [52] | 2015 | 41 | 15% (n = 6) | 15 * | 12–16 ~ |
| [53] | 2015 | 25 | 0% | 16.1 # | 1.2 § |
| [54] | 2014 | 40 | 8% (n = 3) | 15.2 # | 1.3 § (12–17) ~ |
| [55] | 2013 | 15 | 0% | 14 * | 12–18 ~ |
| [12] | 2011 | 120 | 22% (n = 26) | 14.9 # | 2.9 § |
| [1] | 2011 | 121 | 20% (n = 24) | 15 # | 12–19 ~ |
| [56] | 2011 | 20 | 20% (n = 4) | 13.3 # | 12–15 ~ |
| [57] | 2011 | 70 | 11% (n = 8) | 16 # | 1.7 § |
| [58] | 2009 | 54 | 2% (n = 1) | 16 # | 1.9 § (13–19) ~ |
| [59] | 2008 | 26 | 0% | 16.7 # | 14–19 ~ |
| [60] | 2005 | 68 | 7% (n = 5) | 13.8 # | 4.4 § |
| [61] | 2005 | 14 | 7% (n = 1) | 15.4 § | 1.6 § (13–18) ~ |
| [62] | 2002 | 34 | 3% (n = 1) | 16.4 § | 13–18 ~ |
| Study | Cases | Crude Recurrence Rate | Time to Recurrence | Measure of Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [28] | 565 | 8% (n = 46) | 9.3 * months | 1–41 ~ months |
| [29] | 63 | 25% (n = 16) | 4.1 * months | 1–45 ~ months |
| [21] | 213 | 16% (n = 34) | 5.8 * months | 4–10 & months |
| [31] | 99 | 14% (n = 16) | 14 # months | 10 § months |
| [37] | 29 | 28% (n = 8) | 5.8 # months | 2.8 § months |
| [49] | 268 | 8% (n = 21) | 5 * months | 2–28 ~ months |
| [51] | 60 | 42% (n = 25) | 8 # months | 1–36 ~ months |
| [1] | 121 | 22% (n = 24) | 6.5 # months | 1–13 ~ months |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oetzmann von Sochaczewski, C.; Doll, D. Recurrence Rates of Pilonidal Sinus Disease Are High in Children and Recurrences Occur Exceedingly Early. Surgeries 2024, 5, 726-737. https://doi.org/10.3390/surgeries5030057
Oetzmann von Sochaczewski C, Doll D. Recurrence Rates of Pilonidal Sinus Disease Are High in Children and Recurrences Occur Exceedingly Early. Surgeries. 2024; 5(3):726-737. https://doi.org/10.3390/surgeries5030057
Chicago/Turabian StyleOetzmann von Sochaczewski, Christina, and Dietrich Doll. 2024. "Recurrence Rates of Pilonidal Sinus Disease Are High in Children and Recurrences Occur Exceedingly Early" Surgeries 5, no. 3: 726-737. https://doi.org/10.3390/surgeries5030057
APA StyleOetzmann von Sochaczewski, C., & Doll, D. (2024). Recurrence Rates of Pilonidal Sinus Disease Are High in Children and Recurrences Occur Exceedingly Early. Surgeries, 5(3), 726-737. https://doi.org/10.3390/surgeries5030057






