Punch Incision versus Elliptical Excision for Epidermal Inclusion Cysts: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Type of Studies
2.2. Type of Outcomes
2.3. Search Method
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Data Extraction
2.6. Analysis
3. Results
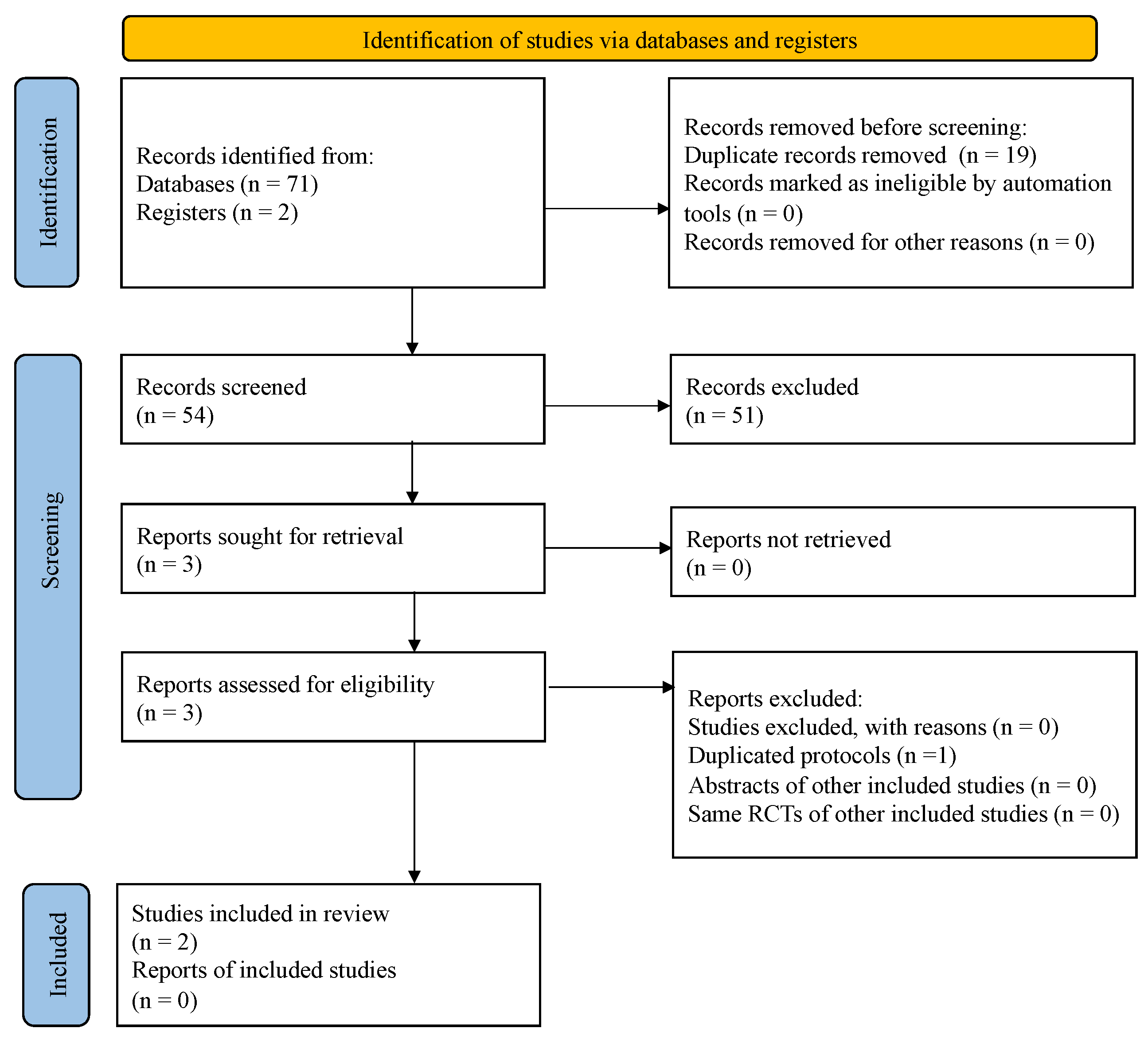
3.1. Search Results
3.2. Meta-Analysis
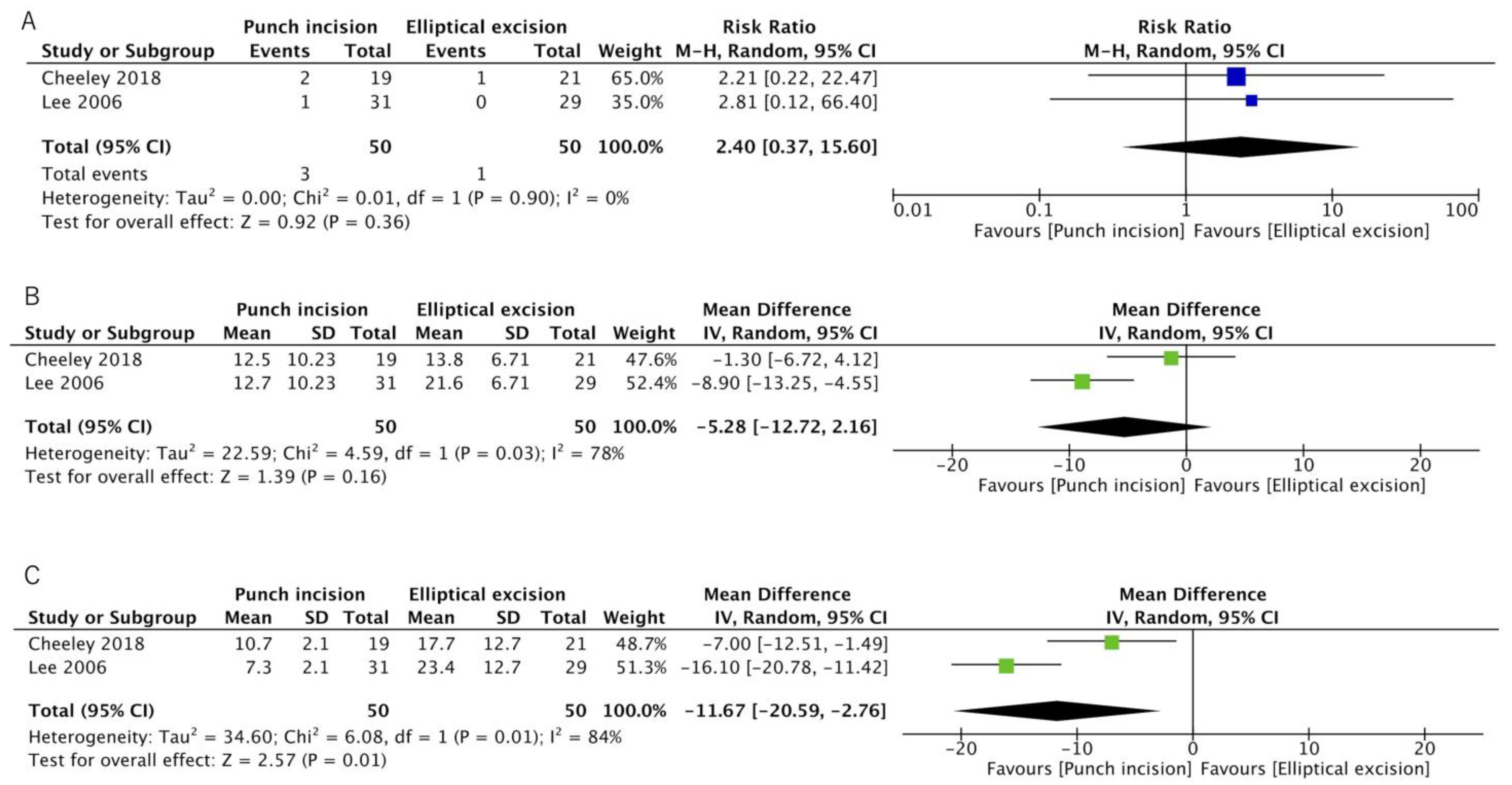
3.2.1. Recurrence Rate
3.2.2. Mean Operative Time
3.2.3. Mean Postoperative Wound Length
3.2.4. All Adverse Events
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. PRISMA 2020 Abstract Checklist
| Section and Topic | Item | Checklist Item | Reported (Yes/No) |
| TITLE | |||
| Title | 1 | Identify the report as a systematic review. | Yes |
| BACKGROUND | |||
| Objectives | 2 | Provide an explicit statement of the main objective(s) or question(s) the review addresses. | Yes |
| METHODS | |||
| Eligibility criteria | 3 | Specify the inclusion and exclusion criteria for the review. | Yes |
| Information sources | 4 | Specify the information sources (e.g., databases, registers) used to identify studies and the date when each was last searched. | No written in main text |
| Risk of bias | 5 | Specify the methods used to assess risk of bias in the included studies. | Yes |
| Synthesis of results | 6 | Specify the methods used to present and synthesise results. | Yes |
| RESULTS | |||
| Included studies | 7 | Give the total number of included studies and participants and summarise relevant characteristics of studies. | Yes |
| Synthesis of results | 8 | Present results for main outcomes, preferably indicating the number of included studies and participants for each. If meta-analysis was done, report the summary estimate and confidence/credible interval. If comparing groups, indicate the direction of the effect (i.e., which group is favoured). | Yes |
| DISCUSSION | |||
| Limitations of evidence | 9 | Provide a brief summary of the limitations of the evidence included in the review (e.g., study risk of bias, inconsistency and imprecision). | Yes |
| Interpretation | 10 | Provide a general interpretation of the results and important implications. | Yes |
| OTHER | |||
| Funding | 11 | Specify the primary source of funding for the review. | No written in main text |
| Registration | 12 | Provide the register name and registration number. | No written in main text |
Appendix B. PRISMA2020 Main Checklist
| Topic | No. | Item | Location Where Item Is Reported |
| TITLE | |||
| Title | 1 | Identify the report as a systematic review. | Line 1–3 |
| ABSTRACT | |||
| Abstract | 2 | See the PRISMA 2020 for Abstracts checklist | |
| INTRODUCTION | |||
| Rationale | 3 | Describe the rationale for the review in the context of existing knowledge. | Line 37–39 |
| Objectives | 4 | Provide an explicit statement of the objective(s) or question(s) the review addresses. | Line 40–41 |
| METHODS | |||
| Eligibility criteria | 5 | Specify the inclusion and exclusion criteria for the review and how studies were grouped for the syntheses. | Line 49–61 |
| Information sources | 6 | Specify all databases, registers, websites, organisations, reference lists and other sources searched or consulted to identify studies. Specify the date when each source was last searched or consulted. | Line 71–81 |
| Search strategy | 7 | Present the full search strategies for all databases, registers and websites, including any filters and limits used. | Appendix C and Appendix D |
| Selection process | 8 | Specify the methods used to decide whether a study met the inclusion criteria of the review, including how many reviewers screened each record and each report retrieved, whether they worked independently, and if applicable, details of automation tools used in the process. | Line 82–87 |
| Data collection process | 9 | Specify the methods used to collect data from reports, including how many reviewers collected data from each report, whether they worked independently, any processes for obtaining or confirming data from study investigators, and if applicable, details of automation tools used in the process. | Line 88–96 |
| Data items | 10a | List and define all outcomes for which data were sought. Specify whether all results that were compatible with each outcome domain in each study were sought (e.g., for all measures, time points, analyses), and if not, the methods used to decide which results to collect. | Line 62–70 |
| 10b | List and define all other variables for which data were sought (e.g., participant and intervention characteristics, funding sources). Describe any assumptions made about any missing or unclear information. | Line 88–96 Table 1 | |
| Study risk of bias assessment | 11 | Specify the methods used to assess risk of bias in the included studies, including details of the tool(s) used, how many reviewers assessed each study and whether they worked independently, and if applicable, details of automation tools used in the process. | Line 97–104 |
| Effect measures | 12 | Specify for each outcome the effect measure(s) (e.g., risk ratio, mean difference) used in the synthesis or presentation of results. | Line 105–110 |
| Synthesis methods | 13a | Describe the processes used to decide which studies were eligible for each synthesis (e.g., tabulating the study intervention characteristics and comparing against the planned groups for each synthesis (item 5)). | Table 1 |
| 13b | Describe any methods required to prepare the data for presentation or synthesis, such as handling of missing summary statistics, or data conversions. | Line 94–96 | |
| 13c | Describe any methods used to tabulate or visually display results of individual studies and syntheses. | Line 128–130 | |
| 13d | Describe any methods used to synthesize results and provide a rationale for the choice(s). If meta-analysis was performed, describe the model(s), method(s) to identify the presence and extent of statistical heterogeneity, and software package(s) used. | Line 121–127 | |
| 13e | Describe any methods used to explore possible causes of heterogeneity among study results (e.g., subgroup analysis, meta-regression). | Line 123 | |
| 13f | Describe any sensitivity analyses conducted to assess robustness of the synthesized results. | Line 123 | |
| Reporting bias assessment | 14 | Describe any methods used to assess risk of bias due to missing results in a synthesis (arising from reporting biases). | Line 97–103 |
| Certainty assessment | 15 | Describe any methods used to assess certainty (or confidence) in the body of evidence for an outcome. | Line 130–132 |
| RESULTS | |||
| Study selection | 16a | Describe the results of the search and selection process, from the number of records identified in the search to the number of studies included in the review, ideally using a flow diagram. | Line 138–141 |
| 16b | Cite studies that might appear to meet the inclusion criteria, but which were excluded, and explain why they were excluded. | Figure 1 | |
| Study characteristics | 17 | Cite each included study and present its characteristics. | Line 141–144 Table 1 |
| Risk of bias in studies | 18 | Present assessments of risk of bias for each included study. | Line 143–144 Table 2, Appendix E |
| Results of individual studies | 19 | For all outcomes, present, for each study: (a) summary statistics for each group (where appropriate) and (b) an effect estimate and its precision (e.g., confidence/credible interval), ideally using structured tables or plots. | Line 154–180 Figure 2 |
| Results of syntheses | 20a | For each synthesis, briefly summarise the characteristics and risk of bias among contributing studies. | Line 139–144 Table 1 and Table 2 Appendix E |
| 20b | Present results of all statistical syntheses conducted. If meta-analysis was done, present for each the summary estimate and its precision (e.g., confidence/credible interval) and measures of statistical heterogeneity. If comparing groups, describe the direction of the effect. | Line 154–180 Table 3 Figure 2 | |
| 20c | Present results of all investigations of possible causes of heterogeneity among study results. | Line 111–117 | |
| 20d | Present results of all sensitivity analyses conducted to assess the robustness of the synthesized results. | Line 123 | |
| Reporting biases | 21 | Present assessments of risk of bias due to missing results (arising from reporting biases) for each synthesis assessed. | Line 148–149 Table 2 Appendix E |
| Certainty of evidence | 22 | Present assessments of certainty (or confidence) in the body of evidence for each outcome assessed. | Table 3 |
| DISCUSSION | |||
| Discussion | 23a | Provide a general interpretation of the results in the context of other evidence. | Line 198–203 |
| 23b | Discuss any limitations of the evidence included in the review. | Line 234–235 | |
| 23c | Discuss any limitations of the review processes used. | Line 231–234 | |
| 23d | Discuss implications of the results for practice, policy, and future research. | Line 235–236 | |
| OTHER INFORMATION | |||
| Registration and protocol | 24a | Provide registration information for the review, including register name and registration number, or state that the review was not registered. | Line 44–45 |
| 24b | Indicate where the review protocol can be accessed, or state that a protocol was not prepared. | Line 44–45 | |
| 24c | Describe and explain any amendments to information provided at registration or in the protocol. | Line 45–46 | |
| Support | 25 | Describe sources of financial or non-financial support for the review, and the role of the funders or sponsors in the review. | Line 46–47 |
| Competing interests | 26 | Declare any competing interests of review authors. | Line 47–48 |
| Availability of data, code and other materials | 27 | Report which of the following are publicly available and where they can be found: template data collection forms; data extracted from included studies; data used for all analyses; analytic code; any other materials used in the review. | Line 72–79 Appendix C and Appendix D |
Appendix C. The Electronic Database Search Strategy
Appendix D. The Trial Registry Search Strategy
Appendix E. Quality Scores for the Eligibility Studies for Others than Recurrence Rate
| Authors | Risk of Bias 2 Tool Assessment | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bias Arising from the Randomization Process | Bias Due to Deviations from Intended Interventions | Bias Due to Missing Outcome Data | Bias in Measurement of the Outcome | Bias in Selection of the Reported Results | Overall Risk of Bias | |
| [Ref Number] | ||||||
| [7] | Some concerns | Low | Low | Low | Some concerns | Some concerns |
| [4] | High | Low | Low | Low | Some concerns | High |
| Authors | Risk of Bias 2 Tool Assessment | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bias Arising from the Randomization Process | Bias Due to Deviations from Intended Interventions | Bias Due to Missing Outcome Data | Bias in Measurement of the Outcome | Bias in Selection of the Reported Results | Overall Risk of Bias | |
| [Ref Number] | ||||||
| [7] | Some concerns | Low | Low | Low | Some concerns | Some concerns |
| [4] | High | Low | Low | Low | Some concerns | High |
| Authors | Risk of Bias 2 Tool Assessment | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bias Arising from the Randomization Process | Bias Due to Deviations from Intended Interventions | Bias Due to Missing Outcome Data | Bias in Measurement of the Outcome | Bias in Selection of the Reported Results | Overall Risk of Bias | |
| [Ref Number] | ||||||
| [7] | Some concerns | Low | Low | Low | Some concerns | Some concerns |
| [4] | High | Low | Low | Low | Some concerns | High |
References
- Vanhoenacker, A.S.; Seynaeve, P.; Vanrietvelde, F.; Alaerts, H.; Verstraete, K. Subsynovial epidermal inclusion cyst of the knee. Skelet. Radiol. 2020, 49, 317–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamyab, K.; Kianfar, N.; Dasdar, S.; Salehpour, Z.; Nasimi, M. Cutaneous cysts: A clinicopathologic analysis of 2,438 cases. Int. J. Dermatol. 2020, 59, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suliman, M.T. Excision of epidermoid (sebaceous) cyst: Description of the operative technique. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2005, 116, 2042–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.E.; Yang, C.H.; Chen, C.H.; Hong, H.S.; Kuan, Y.Z. Comparison of the surgical outcomes of punch incision and elliptical excision in treating epidermal inclusion cysts: A prospective, randomized study. Dermatol. Surg. 2006, 32, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, D.L.; Bisno, A.L.; Chambers, H.F.; Dellinger, E.P.; Goldstein, E.J.; Gorbach, S.L.; Hirschmann, J.V.; Kaplan, S.L.; Montoya, J.G.; Wade, J.C. Practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of skin and soft tissue infections: 2014 update by the infectious diseases society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 59, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheeley, J.; Delong Aspey, L.; MacKelfresh, J.; Pennie, M.; Chen, S. Comparison of elliptical excision versus punch incision for the treatment of epidermal inclusion cysts: A prospective, randomized study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 79, 360–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Furukawa, T.A.; Barbui, C.; Cipriani, A.; Brambilla, P.; Watanabe, N. Imputing missing standard deviations in meta-analyses can provide accurate results. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2006, 59, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Welch, V.A. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.1; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrabi, D.; Leonhardt, J.M.; Brodell, R.T. Removal of keratinous and pilar cysts with the punch incision technique: Analysis of surgical outcomes. Dermatol. Surg. 2002, 28, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, K.H.; Yuk, J.S.; Ji, H.Y.; Lee, J.H. Skin closure methods after single port laparoscopic surgery: A randomized clinical trial. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2015, 189, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vercelli, S.; Ferriero, G.; Sartorio, F.; Stissi, V.; Franchignoni, F. How to assess postsurgical scars: A review of outcome measures. Disabil. Rehabil. 2009, 31, 2055–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangl, O.; Hofer, W.; Tomaselli, F.; Sautner, T.; Fugger, R. Single incision laparoscopic cholecystectomy (SILC) versus laparoscopic cholecystectomy (LC)-a matched pair analysis. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2011, 396, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christenson, L.J.; Phillips, P.K.; Weaver, A.L.; Otley, C.C. Primary closure vs second-intention treatment of skin punch biopsy sites: A randomized trial. Arch. Dermatol. 2005, 141, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nischal, U.; Nischal, K.; Khopkar, U. Techniques of skin biopsy and practical considerations. J. Cutan. Aesthet. Surg. 2008, 1, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abhishek, K.; Khunger, N. Complications of skin biopsy. J. Cutan. Aesthet. Surg. 2015, 8, 239–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Authors | Year | Subject Number | Age | Procedure | Female | Follow-Up | Cyst Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [Ref Number] | (Years) | (%) | (Months) | (mm) | |||
| [7] | 2018 | 40 | 59.6 | Punch incision | 1 | 16 | 19.1 |
| Elliptical excision | 10 | 15.5 | |||||
| [4] | 2006 | 60 | 37.5 | Punch Technique | 32 | 14–29 | 1.14 |
| Excision Technique | 45 | 1.06 |
| Authors | Risk of Bias 2 Tool Assessment | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [Ref Number] | Bias Arising from the Randomization Process | Bias Due to Deviations from Intended Interventions | Bias Due to Missing Outcome Data | Bias in Measurement of the Outcome | Bias in Selection of the Reported Results | Overall Risk of Bias |
| [7] | Some concerns | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [4] | High | Low | Low | Low | Some concerns | High |
| Outcomes | Anticipated Absolute Effects (95% CI) * | Relative Effect (95% CI) | Patient Number (Studies) | Certainty | Comments | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risk with Elliptical Excision | Risk with Punch Incision | |||||
| Recurrence rate | 2% | 5% | RR 2.46 | 100 | LOW a | Punch incision may make little to no difference in recurrence rate. |
| (0.7 to 27.2) | (0.35 to 13.59) | (2 RCTs) | ||||
| Mean operative time | - | MD 5.28 min lower | - | 100 | LOW a,b | Punch incision may result in a slight reduction in operative time. |
| [−12.72 to 2.16] | (2 RCTs) | |||||
| Mean length of the postoperative wound | - | MD 11.67 mm lower | - | 100 | MODERATE a | Punch incision likely has a shorter operative time. |
| [−20.59 to −2.76] | (2 RCTs) | |||||
| All adverse events | Just one study reported the adverse events. | 100 | MODERATE a | Both had one or two of Dehiscence, Infection, Bleeding, Tenderness, and Drainage. Punch incision had Bleeding and Drainage. Elliptical excision had a hematoma. | ||
| (2 RCTs) | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mukuda, K.; Watanabe, J. Punch Incision versus Elliptical Excision for Epidermal Inclusion Cysts: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Surgeries 2021, 2, 335-346. https://doi.org/10.3390/surgeries2030033
Mukuda K, Watanabe J. Punch Incision versus Elliptical Excision for Epidermal Inclusion Cysts: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Surgeries. 2021; 2(3):335-346. https://doi.org/10.3390/surgeries2030033
Chicago/Turabian StyleMukuda, Kengo, and Jun Watanabe. 2021. "Punch Incision versus Elliptical Excision for Epidermal Inclusion Cysts: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Surgeries 2, no. 3: 335-346. https://doi.org/10.3390/surgeries2030033
APA StyleMukuda, K., & Watanabe, J. (2021). Punch Incision versus Elliptical Excision for Epidermal Inclusion Cysts: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Surgeries, 2(3), 335-346. https://doi.org/10.3390/surgeries2030033






