Stroke Management in the Intensive Care Unit: Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke Care
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Multidisciplinary ICU Care and Team Approach
3. Hemodynamic and Physiological Management
3.1. Airway, Oxygenation, and Ventilation
3.2. Blood Pressure
3.2.1. Ischemic Stroke (AIS)
3.2.2. Hemorrhagic Stroke (HS)
3.3. Temperature and Glycemic Control
3.4. Other Physiological Considerations
3.5. Management of Comorbid Conditions
4. Neurological Monitoring and Intracranial Pressure Management
5. Seizure Prevention and Management
6. Prevention and Management of ICU Complications
7. Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis
8. Other Medical Complications and General Care
9. Prognostication, Palliative Care, and Ethical Considerations
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feigin, V.L.; Brainin, M.; Norrving, B.; Martins, S.O.; Pandian, J.; Lindsay, P.; Grupper, M.F.; Rautalin, I. World Stroke Organization: Global Stroke Fact Sheet 2025. Int. J. Stroke 2025, 20, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Y.; Kong, X.M.; Yang, C.H.; Cheng, Z.F.; Lv, J.J.; Guo, H.; Liu, X.H. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Ischemic Stroke, 1990–2021: An Analysis of Data from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. EClinicalMedicine 2024, 75, 102758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, A.; Zhao, Z.; Ren, B.; Gao, Z.; Fang, D.; Hei, B.; Sun, J.; Bao, X.; Ma, L.; et al. Epidemiology and Future Trend Predictions of Ischemic Stroke Based on the Global Burden of Disease Study 1990–2021. Commun. Med. 2025, 5, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.; Maillie, L.; Dhamoon, M.S. Patterns and Outcomes of Intensive Care on Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients in the US. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2023, 16, e008961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, D.-I.; Buleu, F.; Iancu, A.; Tudor, A.; Williams, C.G.; Militaru, M.; Levai, C.M.; Buleu, T.; Ciolac, L.; Militaru, A.G.; et al. Long COVID and Acute Stroke in the Emergency Department: An Analysis of Presentation, Reperfusion Treatment, and Early Outcomes. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhorne, P.; Ramachandra, S.; Stroke Unit Trialists’ Collaboration. Organised inpatient (stroke unit) care for stroke: Network meta-analysis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 4, CD000197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroke Unit Trialists’ Collaboration. Organised Inpatient (Stroke Unit) Care for Stroke. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 2013, CD000197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobeissi, H.; Ghozy, S.; Turfe, B.; Bilgin, C.; Kadirvel, R.; Kallmes, D.F.; Brinjikji, W.; Rabinstein, A.A. Tenecteplase vs. alteplase for treatment of acute ischemic stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1102463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, W.J.; Rabinstein, A.A.; Ackerson, T.; Adeoye, O.M.; Bambakidis, N.C.; Becker, K.; Biller, J.; Brown, M.; Demaerschalk, B.M.; Hoh, B.; et al. Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: 2019 Update to the 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2019, 50, e344–e418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: 2019 Update to the 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Summary for Healthcare Professionals; American Heart Association: Dallas, TX, USA, 2019; Available online: https://www.stroke.org/-/media/Stroke-Files/Ischemic-Stroke-Professional-Materials/AIS-Toolkit/Guidelines-for-Mangaging-Patients-with-AIS-2019-Update-to-2018-Guidelines.pdf (accessed on 17 August 2025).
- Meng, X.; Li, S.; Dai, H.; Lu, G.; Wang, W.; Che, F.; Geng, Y.; Sun, M.; Li, X.; Li, H.; et al. Tenecteplase vs. Alteplase for Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: The ORIGINAL Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2024, 332, 1437–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoh, B.L.; Ko, N.U.; Amin-Hanjani, S.; Chou, S.H.-Y.; Cruz-Flores, S.; Dangayach, N.S.; Derdeyn, C.P.; Du, R.; Hänggi, D.; Hetts, S.W.; et al. 2023 Guideline for the Management of Patients with Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: A Guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2023, 54, e314–e370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaiodimou, L.; Katsanos, A.H.; Turc, G.; Asimakopoulos, A.G.; Mavridis, D.; Schellinger, P.D.; Theodorou, A.; Lemmens, R.; Sacco, S.; Safouris, A.; et al. Tenecteplase vs. Alteplase in Acute Ischemic Stroke within 4.5 Hours: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials. Neurology 2024, 103, e209903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bevers, M.B.; Kimberly, W.T. Critical Care Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Curr. Treat. Options Cardiovasc. Med. 2017, 19, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Paulus, D.; Eyssen, M.; Maervoet, J.; Saka, O. A systematic review and meta-analysis of acute stroke unit care: What’s beyond the statistical significance? BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2013, 13, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.H.; Bang, J.; Jeong, W.; Yum, K.; Chang, J.; Hong, J.H.; Lee, K.; Han, M.K. A Dedicated Neurological Intensive Care Unit Offers Improved Outcomes for Patients with Brain and Spine Injuries. J. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 34, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diringer, M.N.; Edwards, D.F. Admission to a Neurologic/Neurosurgical Intensive Care Unit Is Associated with Reduced Mortality Rate after Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 29, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herpich, F.; Rincon, F. Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 48, 1654–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, H.; Price, C. Stroke Unit Care, Inpatient Rehabilitation and Early Supported Discharge. Clin. Med. 2017, 17, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; He, Y.; Wang, D.; Rezaei, M.J. Stroke Rehabilitation: From Diagnosis to Therapy. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1402729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.J.; Lee, J.S.; Yoon, J.S.; Oh, M.S.; Kim, J.W.; Jung, K.H.; Yu, K.H.; Lee, B.C.; Ko, S.B.; Yoon, B.W.; et al. Impact of the Dedicated Neurointensivists on the Outcome in Patients with Ischemic Stroke Based on the Linked Big Data for Stroke in Korea. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2020, 35, e135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robba, C.; Bonatti, G.; Battaglini, D.; Rocco, P.R.; Pelosi, P. Mechanical Ventilation in Patients with Acute Ischaemic Stroke: From Pathophysiology to Clinical Practice. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orso, D.; Vetrugno, L.; Federici, N.; D’Andrea, N.; Bove, T. Endotracheal Intubation to Reduce Aspiration Events in Acutely Comatose Patients: A Systematic Review. Scand. J. Trauma Resusc. Emerg. Med. 2020, 28, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Driscoll, B.R.; Howard, L.S.; Earis, J.; Mak, V. British Thoracic Society Guideline for Oxygen Use in Adults in Healthcare and Emergency Settings. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2017, 4, e000170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scudellari, A.; Dudek, P.; Marino, L.; Badenes, R.; Bilotta, F. Ventilation Targets for Patients Undergoing Mechanical Thrombectomy for Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, D.W.; Brasher, P.M.; Eng, J.J.; Harris, D.; Hoens, A.M.; Khazei, A.; Yao, J.K.; Abu-Laban, R.B. Hyperbaric Oxygen Post Established Stroke. Cureus 2024, 16, e63395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, M.; Young, P.J.; Laffey, J.G.; Asfar, P.; Taccone, F.S.; Skrifvars, M.B.; Meyhoff, C.S.; Radermacher, P. Dangers of Hyperoxia. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, S.; McDonagh, M.; Russman, B.; Helfand, M. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for Stroke: A Systematic Review of the Evidence. Clin. Rehabil. 2005, 19, 819–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asehnoune, K.; Rooze, P.; Robba, C.; Bouras, M.; Mascia, L.; Cinotti, R.; Pelosi, P.; Roquilly, A. Mechanical Ventilation in Patients with Acute Brain Injury: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, Q.; Wang, E. Hyperventilation in Neurological Patients: From Physiology to Outcome Evidence. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2019, 32, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neurocritical Care Society. Emergency Neurological Life Support (ENLS) 5.0 Protocol: Airway, Ventilation, and Sedation (AVS); Neurocritical Care Society: Chicago, IL, USA, 2023; Available online: https://www.neurocriticalcare.org/Portals/0/ENLS%205.0/ENLS%205.0%20Protocol%20-%20AVS.pdf (accessed on 8 September 2025).
- Lozada-Martínez, I.D.; Rodríguez-Gutiérrez, M.M.; Ospina-Rios, J.; Ortega-Sierra, M.G.; González-Herazo, M.A.; Ortiz-Roncallo, L.M.; Martínez-Imbett, R.; Llamas-Nieves, A.E.; Janjua, T.; Moscote-Salazar, L.R. Neurogenic Pulmonary Edema in Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Relevant Clinical Concepts. Egypt. J. Neurosurg. 2021, 36, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunino, G.; Battaglini, D.; Godoy, D.A. Effects of Positive End-Expiratory Pressure on Intracranial Pressure, Cerebral Perfusion Pressure, and Brain Oxygenation in Acute Brain Injury: Friend or Foe? A Scoping Review. J. Intensive Med. 2023, 4, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bösel, J.; Niesen, W.D.; Salih, F.; Morris, N.A.; Ragland, J.T.; Gough, B.; Schneider, H.; Neumann, J.O.; Hwang, D.Y.; Kantamneni, P.; et al. Effect of Early vs. Standard Approach to Tracheostomy on Functional Outcome at 6 Months among Patients with Severe Stroke Receiving Mechanical Ventilation: The SETPOINT2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2022, 327, 1899–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premraj, L.; Camarda, C.; White, N.; Godoy, D.A.; Cuthbertson, B.H.; Rocco, P.R.; Pelosi, P.; Robba, C.; Suarez, J.I.; Cho, S.M.; et al. Tracheostomy Timing and Outcome in Critically Ill Patients with Stroke: A Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güngen, A.C.; Aydemir, Y.; Güngen, B.D.; Yazar, E.E.; Yağız, O.; Aras, Y.G.; Gümüş, H.; Erkorkmaz, Ü. Effects of Aspiration Pneumonia on the Intensive Care Requirements and In-Hospital Mortality of Hospitalised Patients with Acute Cerebrovascular Disease. Arch. Med. Sci. 2017, 13, 1062–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.H.; Liu, C.H.; Wang, J.G. Blood Pressure Goals in Acute Stroke. Am. J. Hypertens. 2022, 35, 483–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, R.C.; Beishon, L.; Bor-Seng-Shu, E.; Panerai, R.B.; Robinson, T.G. Cerebral Autoregulation in Ischemic Stroke: From Pathophysiology to Clinical Concepts. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: 2019 Update to the 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke; Slide Deck; American Heart Association: Dallas, TX, USA, 2019; Available online: https://www.heart.org/-/media/Files/Professional/Quality-Improvement/Get-With-the-Guidelines/Get-With-The-Guidelines-Stroke/2019UpdateAHAASAAISGuidelineSlideDeckrevisedADL12919.pdf (accessed on 17 August 2025).
- PracticalNeurology.com. In-Hospital Blood Pressure Control After Acute Ischemic Stroke. Practical Neurology, January 2022. Available online: https://practicalneurology.com/diseases-diagnoses/stroke/in-hospital-blood-pressure-control-after-acute-ischemic-stroke/31860/ (accessed on 14 September 2025).
- Turc, G.; Berge, E.; Whiteley, W.; Audebert, H.; De Marchis, G.M.; Fonseca, A.C.; Padiglioni, C.; Pérez de la Ossa, N.; Strbian, D.; Tsivgoulis, G.; et al. European Stroke Organisation (ESO) Guidelines on Intravenous Thrombolysis for Acute Ischaemic Stroke. Eur. Stroke J. 2021, 6, 1–63. Available online: https://files.magicapp.org/guideline/cff45da7-c509-4794-a6a9-3f3d0e69d653/published_guideline_5290-1_0.pdf (accessed on 14 September 2025). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Song, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, L.; Wan, Y.; Billot, L.; Li, Q.; et al. Intensive Blood Pressure Control after Endovascular Thrombectomy for Acute Ischaemic Stroke (ENCHANTED2/MT): A Multicentre, Open-Label, Blinded-Endpoint, Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet 2022, 400, 1585–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.C.; Lee, T.H.; Huang, Y.C.; Tsai, Y.H.; Yang, J.T.; Yang, L.Y.; Pan, Y.B.; Lee, M.; Chen, K.F.; Hung, Y.C.; et al. Enhanced versus standard hydration in acute ischemic stroke: REVIVE—A randomized clinical trial. Int. J. Stroke 2024, 19, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.; Moloney, J.A.; Elagamy, N.; Tuttle, J.; Tirgari, S.; Calo, S.; Thompson, R.; Nahab, B.; Lewandowski, C.; Levy, P. Cerebral Blood Flow Change with Fluid Resuscitation in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Brain Circ. 2024, 10, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strømsnes, T.A.; Kaugerud Hagen, T.J.; Ouyang, M.; Wang, X.; Chen, C.; Rygg, S.E.; Hewson, D.; Lenthall, R.; McConachie, N.; Izzath, W.; et al. Pressor Therapy in Acute Ischaemic Stroke: An Updated Systematic Review. Eur. Stroke J. 2022, 7, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arima, H. Three Rules for Blood Pressure Management in Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Fast, Intense and Stable. Hypertens. Res. 2023, 46, 264–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Woo, H.G.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, B.J. Blood Pressure Management in Stroke Patients. J. Neurocrit. Care 2020, 13, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, W.D.; Chang, W.W. ED BP Management for Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2022, 24, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neugebauer, H.; Kollmar, R.; Niesen, W.D.; Bösel, J.; Schneider, H.; Hobohm, C.; Zweckberger, K.; Heuschmann, P.U.; Schellinger, P.D.; Jüttler, E.; et al. DEcompressive Surgery Plus HypoTHermia for Space-Occupying Stroke (DEPTH-SOS): A Protocol of a Multicenter Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial and a Literature Review. Int. J. Stroke 2013, 8, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wästfelt, M.; Cao, Y.; Ström, J.O. Predictors of Post-Stroke Fever and Infections: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Neurol. 2018, 18, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, J.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Yenari, M.A. Therapeutic Hypothermia for Stroke: Unique Challenges at the Bedside. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 951586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, K.C.; Bruno, A.; Pauls, Q.; Hall, C.E.; Barrett, K.M.; Barsan, W.; Fansler, A.; Van de Bruinhorst, K.; Janis, S.; Durkalski-Mauldin, V.L.; et al. Intensive vs. Standard Treatment of Hyperglycemia and Functional Outcome in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: The SHINE Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2019, 322, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finfer, S.; Blair, D.; Bellomo, R.; McArthur, C.; Mitchell, I.; Myburgh, J.; Norton, R.; Potter, J.; Chittock, D.; Dhingra, V.; et al. Intensive versus Conventional Glucose Control in Critically Ill Patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1283–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, A.H.; Roberts, D.J.; Zygun, D.A. Optimal glycemic control in neurocritical care patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2012, 16, R203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, W.A.; Thorell, W. Cerebral Salt Wasting Syndrome; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534855 (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Gál, J.; Fülesdi, B.; Varga, D.; Fodor, B.; Varga, E.; Siró, P.; Bereczki, D.; Szabó, S.; Molnár, C. Assessment of two prophylactic fluid strategies in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A randomized trial. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 300060520927526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labib, H.; Tjerkstra, M.A.; Coert, B.A.; Post, R.; Vandertop, W.P.; Verbaan, D.; Müller, M.C.A. Sodium and Its Impact on Outcome after Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Patients with and without Delayed Cerebral Ischemia. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 52, 752–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwanwela, N.C.; Chutinet, A.; Mayotarn, S.; Thanapiyachaikul, R.; Chaisinanunkul, N.; Asawavichienjinda, T.; Muengtaweepongsa, S.; Nilanont, Y.; Samajarn, J.; Watcharasaksilp, K.; et al. A randomized controlled study of intravenous fluid in acute ischemic stroke. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2017, 161, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiser, T.H. Pharmacologic Options for Prevention and Management of Cerebral Vasospasm in Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Hosp. Pharm. 2013, 48 (Suppl. S5), S2–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.S.; Kim, D.W.; Kang, S.D. Endovascular Treatment of Symptomatic Vasospasm after Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: A Three-Year Experience. J. Cerebrovasc. Endovasc. Neurosurg. 2017, 19, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, M.S.; Lewis, S.C.; Warlow, C.; FOOD Trial Collaboration. Effect of Timing and Method of Enteral Tube Feeding for Dysphagic Stroke Patients (FOOD): A Multicentre Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet 2005, 365, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serón-Arbeloa, C.; Zamora-Elson, M.; Labarta-Monzón, L.; Mallor-Bonet, T. Enteral Nutrition in Critical Care. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2013, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, D.; Nie, L.; Xiang, X.; Guo, X.; Qin, M.; Wang, S.; Chen, J.; Feng, Y.; Huang, M.; Mao, L. Effects of Enteral Nutrition in Stroke: An Updated Review. Front. Nutr. 2025, 12, 1510111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Liu, S.; Yin, A.; Siddiqi, J. Risks and Benefits of Stress Ulcer Prophylaxis in Adult Neurocritical Care Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.; Bass, S.; Chaisson, N.F. Which ICU Patients Need Stress Ulcer Prophylaxis? Cleve Clin. J. Med. 2022, 89, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhash, S.; Rabbani, H.H.; Raina, R. Comparative Outcomes and Risk Analysis of Stroke Incidence in Adult Patients on Dialysis: FR-PO406. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2024, 35 (Suppl. S10), 10–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, N.; Mohammed, A.; Seddiq, M.; Kidwai, S.; Shahzad, D.; Mahmoud, M.M. The Effect of the Charlson Comorbidity Index on In-Hospital Complications, Hospital Length of Stay, Mortality, and Readmissions among Patients Hospitalized for Acute Stroke. Cureus 2024, 16, e60112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Critical Care Services Ontario; Neurosurgery Education and Outreach Network; Provincial Neurosurgery Advisory Committee (PNAC). Guidelines for Basic Adult Neurological Observation; Version 2.0; Critical Care Services Ontario: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2018; Available online: https://criticalcareontario.ca/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/BNO-Adult-Guidelines-Revised-FINAL-20190507.pdf (accessed on 18 September 2025).
- Sharma, R.; Tsikvadze, M.; Peel, J.; Howard, L.; Kapoor, N.; Freeman, W.D. Multimodal Monitoring: Practical Recommendations (Dos and Don’ts) in Challenging Situations and Uncertainty. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1135406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertuccio, A.; Marasco, S.; Longhitano, Y.; Romenskaya, T.; Elia, A.; Mezzini, G.; Vitali, M.; Zanza, C.; Barbanera, A. External Ventricular Drainage: A Practical Guide for Neuro-Anesthesiologists. Clin. Pract. 2023, 13, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, D.S.; Sahu, S.; Swain, A.; Kant, S. Intracranial Pressure Monitoring: Gold Standard and Recent Innovations. World J. Clin. Cases 2019, 7, 1535–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svedung Wettervik, T.; Hånell, A.; Howells, T.; Nilsson, P.; Enblad, P. Intracranial Pressure- and Cerebral Perfusion Pressure Threshold-Insults in Relation to Cerebral Energy Metabolism in Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir. 2022, 164, 1001–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mount, C.A.; Das, J.M. Cerebral Perfusion Pressure; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537271/ (accessed on 6 November 2025).
- Rossetti, A.O.; Schindler, K.; Sutter, R.; Rüegg, S.; Zubler, F.; Novy, J.; Oddo, M.; Warpelin-Decrausaz, L.; Alvarez, V. Continuous vs. Routine Electroencephalogram in Critically Ill Adults with Altered Consciousness and No Recent Seizure: A Multicenter Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, S.M.; Ziai, W.C.; Cordonnier, C.; Dowlatshahi, D.; Francis, B.; Goldstein, J.N.; Hemphill, J.C., 3rd; Johnson, R.; Keigher, K.M.; Mack, W.J.; et al. 2022 Guideline for the Management of Patients with Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage: A Guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2022, 53, e282–e361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A.; Ravikant; Bairwa, M.; Jithesh, G.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, N. Efficacy of Intravenous 20% Mannitol vs. 3% Hypertonic Saline in Reducing Intracranial Pressure in Nontraumatic Brain Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 28, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jüttler, E.; Bösel, J.; Amiri, H.; Schiller, P.; Limprecht, R.; Hacke, W.; Unterberg, A.; DESTINY II Study Group. DESTINY II: DEcompressive Surgery for the Treatment of Malignant INfarction of the Middle Cerebral ArterY II. Int. J. Stroke 2011, 6, 79–86. Available online: https://criticalcare.cooperhealth.org/fellows/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2019/07/DESTINY-II-TRIAL.pdf (accessed on 9 September 2025). [CrossRef]
- Vahedi, K.; Hofmeijer, J.; Juettler, E.; Vicaut, E.; George, B.; Algra, A.; Amelink, G.J.; Schmiedeck, P.; Schwab, S.; Rothwell, P.M.; et al. Early Decompressive Surgery in Malignant Infarction of the Middle Cerebral Artery: A Pooled Analysis of Three Randomised Controlled Trials. Lancet Neurol. 2007, 6, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanley, D.F.; Thompson, R.E.; Rosenblum, M.; Yenokyan, G.; Lane, K.; McBee, N.; Mayo, S.W.; Bistran-Hall, A.J.; Gandhi, D.; Mould, W.A.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Minimally Invasive Surgery with Thrombolysis in Intracerebral Haemorrhage Evacuation (MISTIE III): A Randomised, Controlled, Open-Label, Blinded Endpoint Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 1021–1032, Erratum in Lancet 2019, 393, 1596. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30859-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viarasilpa, T. Managing Intracranial Pressure Crisis. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2024, 25, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, S.; Ahmad, S.R. Raised Intracranial Pressure Syndrome: A Stepwise Approach. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 23 (Suppl. 2), S129–S135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, W.D. Management of Intracranial Pressure. Continuum Lifelong Learn. Neurol. 2015, 21, 1299–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandan, A.; Zhou, Y.M.; Demoe, L.; Waheed, A.; Jain, P.; Widjaja, E. Incidence and risk factors of post-stroke seizures and epilepsy: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Int. Med. Res. 2023, 51, 3000605231213231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savalia, K.; Sekar, P.; Moomaw, C.J.; Koch, S.; Sheth, K.N.; Woo, D.; Mayson, D.; ERICH Investigators. Effect of Primary Prophylactic Antiseizure Medication for Seizure Prevention Following Intracerebral Hemorrhage in the ERICH Study. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2022, 31, 106143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, F.J.; Sanches, P.R.; Smith, J.R.; Zafar, S.F.; Hernandez-Diaz, S.; Blacker, D.; Hsu, J.; Schwamm, L.H.; Westover, M.B.; Moura, L.M. Anticonvulsant Primary and Secondary Prophylaxis for Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients: A Decision Analysis. Stroke 2021, 52, 2782–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaad, F.; Alkeneetir, N.; Almatroudi, M.; Alatawi, A.; Alotaibi, A.; Aldibasi, O.; Khatri, I.A. Early Seizures in Stroke—Frequency, Risk Factors, and Effect on Patient Outcomes in a Tertiary Center in Saudi Arabia. Neurosciences (Riyadh) 2022, 27, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, Z.K.; England, T.J.; Mistri, A.K.; Woodhouse, L.J.; Cala, L.; Dineen, R.; Ozturk, S.; Beridze, M.; Collins, R.; Bath, P.M.; et al. Incidence and Predictors of Early Seizures in Intracerebral Haemorrhage and the Effect of Tranexamic Acid. Eur. Stroke J. 2020, 5, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derex, L.; Rheims, S.; Peter-Derex, L. Seizures and Epilepsy after Intracerebral Hemorrhage: An Update. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 2605–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freiman, S.; Hauser, W.A.; Rider, F.; Yaroslavskaya, S.; Sazina, O.; Vladimirova, E.; Kaimovsky, I.; Shpak, A.; Gulyaeva, N.; Guekht, A. Post-stroke seizures, epilepsy, and mortality in a prospective hospital-based study. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1273270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, L.; Jia, D.; Faramand, A.; Chong, W.; Fang, Y.; Ma, L.; Fang, F. Levetiracetam versus phenytoin for the treatment of established status epilepticus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Seizure 2020, 78, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalziel, S.R.; Borland, M.L.; Furyk, J.; Bonisch, M.; Neutze, J.; Donath, S.; Francis, K.L.; Sharpe, C.; Harvey, A.S.; Davidson, A.; et al. Levetiracetam versus phenytoin for second-line treatment of convulsive status epilepticus in children (ConSEPT): An open-label, multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 2135–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigo, F.; Bragazzi, N.; Nardone, R.; Trinka, E. Direct and indirect comparison meta-analysis of levetiracetam versus phenytoin or valproate for convulsive status epilepticus. Epilepsy Behav. 2016, 64 Pt A, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoelhof, B.; Sanchez-Bautista, J.; Zorrilla-Vaca, A.; Kaplan, P.W.; Farrokh, S.; Mirski, M.; Freund, B.; Rivera-Lara, L. Impact of Antiepileptic Drugs for Seizure Prophylaxis on Short- and Long-Term Functional Outcomes in Patients with Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Seizure 2019, 69, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitar, R.; Khan, U.M.; Rosenthal, E.S. Utility and Rationale for Continuous EEG Monitoring: A Primer for the General Intensivist. Crit. Care 2024, 28, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, S.T.; Abend, N.S.; Bleck, T.P.; Chapman, K.E.; Drislane, F.W.; Emerson, R.G.; Gerard, E.E.; Hahn, C.D.; Husain, A.M.; Kaplan, P.W.; et al. Consensus Statement on Continuous EEG in Critically Ill Adults and Children, Part I: Indications. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 32, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, S.M.; Tran, A.; Cheng, W.; Sadeghirad, B.; Arabi, Y.M.; Cook, D.J.; Møller, M.H.; Mehta, S.; Fowler, R.A.; Burns, K.E.A.; et al. VTE prophylaxis in critically ill adults: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Chest 2022, 161, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Fan, Q.; Liu, X.; Sun, D. Patient’s care bundle benefits to prevent stroke-associated pneumonia: A meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 950662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banda, K.J.; Chu, H.; Kang, X.L.; Liu, D.; Pien, L.C.; Jen, H.J.; Hsiao, S.T.S.; Chou, K.R. Prevalence of Dysphagia and Risk of Pneumonia and Mortality in Acute Stroke Patients: A Meta-Analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2022, 22, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.C.; Choo, Y.J.; Seo, K.C.; Yang, S. The Relationship between Dysphagia and Pneumonia in Acute Stroke Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 834240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quyet, D.; Hien, N.M.; Khan, M.X.; Dai, P.D.; Thuan, D.D.; Duc, D.M.; Hai, N.D.; Nam, B.V.; Huy, P.Q.; Ton, M.D.; et al. Risk Factors for Stroke Associated Pneumonia. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 7, 4416–4419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Choo, Y.J.; Chang, M.C. The Preventive Effect of Dysphagia Screening on Pneumonia in Acute Stroke Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Healthcare 2021, 9, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.L.; Fu, S.Y.; Wang, W.H.; Ma, Y.C. Validity and Reliability of Swallowing Screening Tools Used by Nurses for Dysphagia: A Systematic Review. Tzu Chi Med. J. 2016, 28, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preiser, J.C.; Arabi, Y.M.; Berger, M.M.; Casaer, M.; McClave, S.; Montejo-González, J.C.; Peake, S.; Reintam Blaser, A.; Van den Berghe, G.; van Zanten, A.; et al. A Guide to Enteral Nutrition in Intensive Care Units: 10 Expert Tips for the Daily Practice. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metheny, N.A.; Davis-Jackson, J.; Stewart, B.J. Effectiveness of an Aspiration Risk-Reduction Protocol. Nurs. Res. 2010, 59, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollmeier, B.R.; Keenaghan, M.; Doerr, C. Aspiration Risk (Nursing); StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK568750 (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Westendorp, W.F.; Vermeij, J.D.; Zock, E.; Hooijenga, I.J.; Kruyt, N.D.; Bosboom, H.J.; Kwa, V.I.; Weisfelt, M.; Remmers, M.J.; ten Houten, R.; et al. The Preventive Antibiotics in Stroke Study (PASS): A Pragmatic Randomised Open-Label Masked Endpoint Clinical Trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 1519–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragan, V.; Wei, Y.; Elligsen, M.; Kiss, A.; Walker, S.A.N.; Leis, J.A. Prophylactic Antimicrobial Therapy for Acute Aspiration Pneumonitis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 67, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmeijer, A.A.; Nasa, P.; Ntoumenopoulos, G.; Battaglini, D.; Juneja, D.; Ball, L.; Ehrmann, S.; Schultz, M.J.; Paulus, F.; Stilma, W. Consensus Statements on Airway Clearance Interventions in Intubated Critically Ill Patients—Protocol for a Delphi Study. Life 2025, 15, 1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, L.; Irshad, S.; Hodsoll, J.; Simpson, M.; Gulliford, M.; Smithard, D.; Patel, A.; Rebollo-Mesa, I.; STROKE-INF Investigators. Prophylactic Antibiotics after Acute Stroke for Reducing Pneumonia in Patients with Dysphagia (STROKE-INF): A Prospective, Cluster-Randomised, Open-Label, Masked Endpoint, Controlled Clinical Trial. Lancet 2015, 386, 1835–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevention of Venous Thromboembolic Disease in Acutely Ill Hospitalized Medical Adults. UpToDate. 18 July 2025. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/prevention-of-venous-thromboembolic-disease-in-acutely-ill-hospitalized-medical-adults (accessed on 19 September 2025).
- Dennis, M.; Caso, V.; Kappelle, L.J.; Pavlovic, A.; Sandercock, P.; European Stroke Organisation. European Stroke Organisation (ESO) Guidelines for Prophylaxis for Venous Thromboembolism in Immobile Patients with Acute Ischaemic Stroke. Eur. Stroke J. 2016, 1, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Yang, J.M.; Qian, W.Y.; Xu, X.P.; Tung, T.H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, F. Risk Factors for Lower Extremity Deep Vein Thrombosis in Acute Stroke Patients Following Endovascular Thrombectomy: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1249365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLOTS Trials Collaboration; Dennis, M.; Sandercock, P.; Reid, J.; Graham, C.; Murray, G.; Venables, G.; Rudd, A.; Bowler, G. The Effect of Graduated Compression Stockings on Long-Term Outcomes after Stroke: The CLOTS Trials 1 and 2. Stroke 2013, 44, 1075–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, M.; Sandercock, P.; Graham, C.; Forbes, J.; CLOTS (Clots in Legs Or sTockings after Stroke) Trials Collaboration; Smith, J. The Clots in Legs Or sTockings after Stroke (CLOTS) 3 Trial: A Randomised Controlled Trial to Determine Whether or Not Intermittent Pneumatic Compression Reduces the Risk of Post-Stroke Deep Vein Thrombosis and to Estimate Its Cost-Effectiveness. Health Technol. Assess. 2015, 19, 1–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlisle, C.L.; Stuchiner, T.; Lesko, A.; Zurasky, J. Retrospective Study Supports That Pharmacologic Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis after Intracerebral Hemorrhage Is Safe, Underused. Neurohospitalist 2025, 16, 19418744251358092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendel, R.; Abdelhameed, N.; Salman, R.A.; Cohen, H.; Dowlatshahi, D.; Freemantle, N.; Paciaroni, M.; Parry-Jones, A.; Price, C.; Sprigg, N.; et al. Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism in Acute Spontaneous Intracerebral Haemorrhage: A Survey of Opinion. J. Neurol. Sci. 2023, 454, 120855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldemund, D. Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) in Stroke Patients. Stroke Manual. Available online: https://www.stroke-manual.com/prevention-venous-thromboembolism-vte (accessed on 19 September 2025).
- Cai, Q.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H. Patients with Venous Thromboembolism after Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage: A Review. Thromb. J. 2021, 19, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, H.; Khan, S.U.; Nasir, F.; Hammad, T.; Meyer, M.A.; Kaluski, E. Optimal Duration of Aspirin Plus Clopidogrel After Ischemic Stroke or Transient Ischemic Attack. Stroke 2019, 50, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balu, A.; Ching Hui, S.; Yong-Qiang Tan, B.; Lip, G.Y.H. Timing of Oral Anticoagulation in Acute Ischaemic Stroke and Non-Valvular Atrial Fibrillation: Early, ‘Timely’ or Late? Open Heart 2024, 11, e002885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucà, F.; Colivicchi, F.; Oliva, F.; Abrignani, M.; Caretta, G.; Di Fusco, S.A.; Giubilato, S.; Cornara, S.; Di Nora, C.; Pozzi, A.; et al. Management of Oral Anticoagulant Therapy after Intracranial Hemorrhage in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1061618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RESTART Collaboration. Effects of Antiplatelet Therapy after Stroke Due to Intracerebral Haemorrhage (RESTART): A Randomised, Open-Label Trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 2613–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westendorp, W.F.; Nederkoorn, P.J.; Vermeij, J.D.; Dijkgraaf, M.G.; van de Beek, D. Post-stroke infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Neurol. 2011, 11, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ippolito, M.; Cortegiani, A.; Biancofiore, G.; Caiffa, S.; Corcione, A.; Giusti, G.D.; Iozzo, P.; Lucchini, A.; Pelosi, P.; Tomasoni, G.; et al. The Prevention of Pressure Injuries in the Positioning and Mobilization of Patients in the ICU: A Good Clinical Practice Document by the Italian Society of Anesthesia, Analgesia, Resuscitation and Intensive Care (SIAARTI). J. Anesth. Analg. Crit. Care 2022, 2, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Cascella, M. ICU Delirium; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559280 (accessed on 19 September 2025).
- Holloway, R.G. Palliative and End-of-Life Care in Stroke. Stroke 2014, 45, 1887–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.; Ebert, A.D.; Dörr, D.; Buchheidt, D.; Hennerici, M.G.; Szabo, K. End-of-Life Decisions in Acute Stroke Patients: An Observational Cohort Study. BMC Palliat. Care 2016, 15, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.Y.; Kim, K.S.; Muehlschlegel, S.; Wartenberg, K.E.; Rajajee, V.; Alexander, S.A.; Busl, K.M.; Creutzfeldt, C.J.; Fontaine, G.V.; Hocker, S.E.; et al. Guidelines for Neuroprognostication in Critically Ill Adults with Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Neurocrit. Care 2024, 40, 395–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witsch, J.; Siegerink, B.; Nolte, C.H.; Sprügel, M.; Steiner, T.; Endres, M.; Huttner, H.B. Prognostication after Intracerebral Hemorrhage: A Review. Neurol. Res. Pract. 2021, 3, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Davies, C.; Stokes, D.; O’Donnell, D. Shared Decision-Making for Patients with Stroke in Neurocritical Care: A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis. Neurocrit. Care 2025, 42, 644–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhachroum, A.; Zhou, L.; Asdaghi, N.; Gardener, H.; Ying, H.; Gutierrez, C.M.; Manolovitz, B.M.; Samano, D.; Bass, D.; Foster, D.; et al. Predictors and Temporal Trends of Withdrawal of Life-Sustaining Therapy after Acute Stroke in the Florida Stroke Registry. Crit. Care Explor. 2023, 5, e0934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamy, M.; Dewar, B.; Fedyk, M. Ethical Evaluation in Acute Stroke Decision-Making. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 2024, 30, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
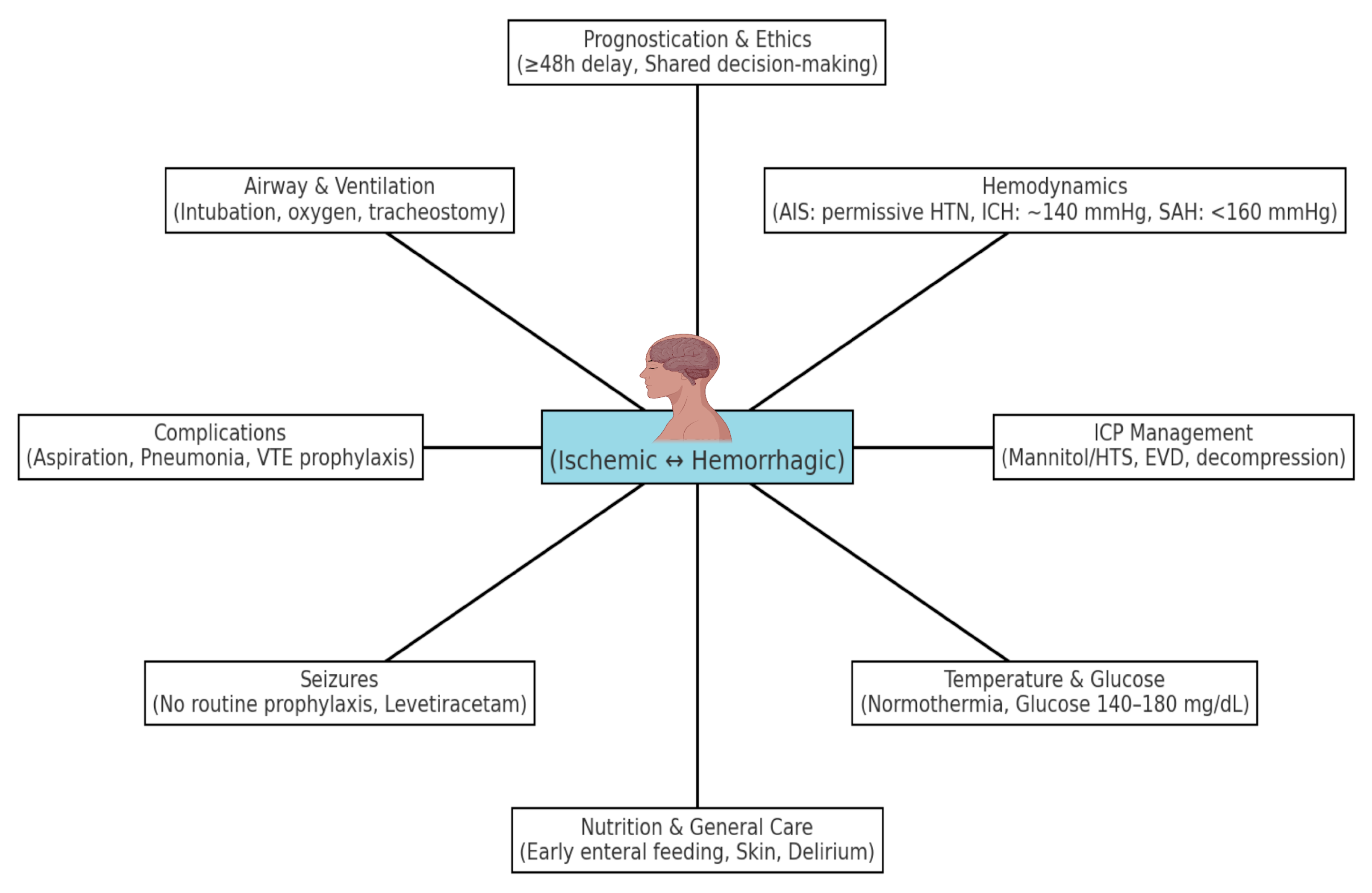
| Domain | Dos (Recommended) | Don’ts (Avoid) | Cautions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blood Pressure Management | Maintain SBP ≤ 220/120 mmHg in AIS patients not receiving reperfusion therapy, or ≤185/110 mmHg before and ≤180/105 mmHg after thrombolysis; maintain SBP ≈ 140 mmHg in ICH patients; use titratable IV agents (e.g., nicardipine, labetalol) | Rapid BP drops <120 mmHg | Individualize targets based on perfusion status and stroke subtype |
| Glycemic Control | Keep glucose 140–180 mg/dL; treat persistent hyperglycemia with insulin | Intensive insulin protocols (80–110 mg/dL) | Prevent hypoglycemia, especially in sedated or enterally fed patients |
| Temperature Management | Maintain normothermia; treat fever >37.5 °C with antipyretics or cooling | Unnecessary therapeutic hypothermia | Monitor for shivering and metabolic stress |
| Seizure Management | Use EEG for unexplained decline in consciousness or neurological status; treat only confirmed seizures or status epilepticus | Routine prophylaxis in ischemic stroke | Consider prophylaxis short-term in ICH with cortical involvement |
| Antithrombotic Therapy | Start antiplatelet (aspirin) 24–48 h after excluding bleeding; time anticoagulant restart based on imaging and infarct size | Early full-dose anticoagulation post-ICH | Multidisciplinary assessment of bleeding vs. thrombotic risk |
| Intracranial Pressure and Fluids | Maintain ICP < 20–22 mmHg and CPP > 60 mmHg; use osmotherapy if elevated | Hypotonic fluids | Ensure CPP > 60 mmHg; monitor sodium closely |
| Nutrition and General Care | Start enteral feeding within 48 h; use protein-rich formulas | Prolonged fasting or overfeeding | Balance caloric intake with glucose control |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sič, A.; Tseriotis, V.-S.; Belanović, B.; Nemet, M.; Baralić, M. Stroke Management in the Intensive Care Unit: Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke Care. NeuroSci 2025, 6, 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6040121
Sič A, Tseriotis V-S, Belanović B, Nemet M, Baralić M. Stroke Management in the Intensive Care Unit: Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke Care. NeuroSci. 2025; 6(4):121. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6040121
Chicago/Turabian StyleSič, Aleksandar, Vasilis-Spyridon Tseriotis, Božidar Belanović, Marko Nemet, and Marko Baralić. 2025. "Stroke Management in the Intensive Care Unit: Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke Care" NeuroSci 6, no. 4: 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6040121
APA StyleSič, A., Tseriotis, V.-S., Belanović, B., Nemet, M., & Baralić, M. (2025). Stroke Management in the Intensive Care Unit: Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke Care. NeuroSci, 6(4), 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6040121










